13453d9f59068efd07cb5cf578cbe5eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 CHAPTER 1 Taking Risks and Making Profits within the Dynamic Business Environment Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2015 by the Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
CHAPTER 1 Taking Risks and Making Profits within the Dynamic Business Environment Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2015 by the Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Why Study Business? • Find a successful career (what do you want to be when you grow up? ) • Be a successful owner • Be a better employee • Become a smarter consumer and investor
Why Study Business? • Find a successful career (what do you want to be when you grow up? ) • Be a successful owner • Be a better employee • Become a smarter consumer and investor
 BUSINESS and ENTREPRENEURSHIP • Business -- Any activity that seeks to provide goods and services to others while operating at a profit. • Entrepreneur -- A person who risks time and money to start and manage a business. • LO 1 -1 Success in business is often based on the strategy of finding a need and filling it. A profit is earned when a company’s revenue (the money a business brings in) is greater than its expenses (the money a business pays out). Nick Woodman, Founder/CEO, Go. Pro Nonprofit organizations focus on causes not profit 1 -3
BUSINESS and ENTREPRENEURSHIP • Business -- Any activity that seeks to provide goods and services to others while operating at a profit. • Entrepreneur -- A person who risks time and money to start and manage a business. • LO 1 -1 Success in business is often based on the strategy of finding a need and filling it. A profit is earned when a company’s revenue (the money a business brings in) is greater than its expenses (the money a business pays out). Nick Woodman, Founder/CEO, Go. Pro Nonprofit organizations focus on causes not profit 1 -3
 What is a Business? • (my definition)…the organized effort of individuals to produce and sell, for a profit, the goods and services that satisfy society’s needs. • Important Components of Business • Organized Effort of Individuals (Buyers, Sellers, and Resources) • Product Elements • Profit Motivation • Customer Satisfaction • Stakeholders • Changing Business Environment 1 -4
What is a Business? • (my definition)…the organized effort of individuals to produce and sell, for a profit, the goods and services that satisfy society’s needs. • Important Components of Business • Organized Effort of Individuals (Buyers, Sellers, and Resources) • Product Elements • Profit Motivation • Customer Satisfaction • Stakeholders • Changing Business Environment 1 -4
 Organized Effort of Individuals Buyers • Consumers (people who buy products for personal consumption) • Business (organizations who buy products for to resell to others, use as part of their product, or help in the operation of their business) • Government (organizations that purchase products for societal purposes, i. e. military, roads, park maintenance, etc. ) • Other (non-profit institutions, churches, libraries, etc. ) Sellers • Manufacturers (businesses that assemble and make products, i. e. Apple, Kodak, Stone Container) • Resellers (businesses that resell tangible products to customers or to the other businesses, i. e. Wal-Mart, Target, Lowes, Home Depot) • Service Providers (businesses that provide intangible products or perform useful labor on behalf of their customers, i. e. insurance, banking, haircuts, cleaning service) • Combination Resources • Human/Labor (physical labor and knowledge) • Land or Natural Materials (raw/natural materials) • Entrepreneurship (Willingness to start business) • Capital (Financial, Realphysical facilities, machines, computers) • Knowledge/Intellectual (information technology, business information, patents, copyrights, trademarks) 1 -5
Organized Effort of Individuals Buyers • Consumers (people who buy products for personal consumption) • Business (organizations who buy products for to resell to others, use as part of their product, or help in the operation of their business) • Government (organizations that purchase products for societal purposes, i. e. military, roads, park maintenance, etc. ) • Other (non-profit institutions, churches, libraries, etc. ) Sellers • Manufacturers (businesses that assemble and make products, i. e. Apple, Kodak, Stone Container) • Resellers (businesses that resell tangible products to customers or to the other businesses, i. e. Wal-Mart, Target, Lowes, Home Depot) • Service Providers (businesses that provide intangible products or perform useful labor on behalf of their customers, i. e. insurance, banking, haircuts, cleaning service) • Combination Resources • Human/Labor (physical labor and knowledge) • Land or Natural Materials (raw/natural materials) • Entrepreneurship (Willingness to start business) • Capital (Financial, Realphysical facilities, machines, computers) • Knowledge/Intellectual (information technology, business information, patents, copyrights, trademarks) 1 -5
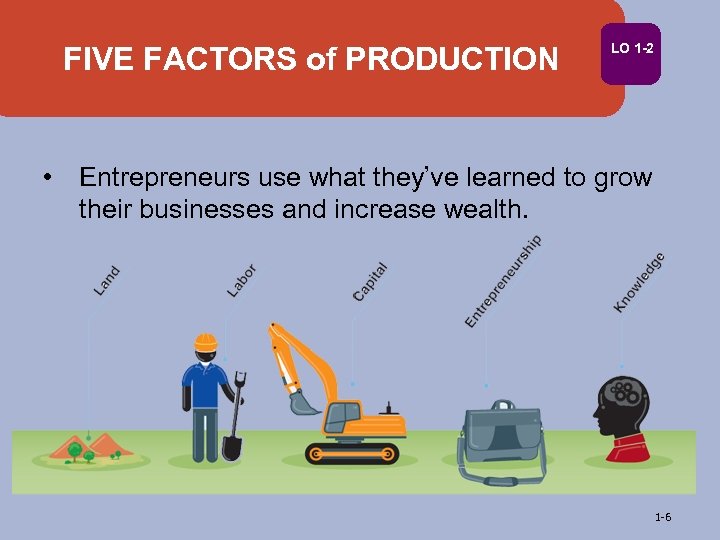 FIVE FACTORS of PRODUCTION LO 1 -2 • Entrepreneurs use what they’ve learned to grow their businesses and increase wealth. 1 -6
FIVE FACTORS of PRODUCTION LO 1 -2 • Entrepreneurs use what they’ve learned to grow their businesses and increase wealth. 1 -6
 Product Elements: Understanding GOODS and SERVICES • Goods -- Tangible products such as computers, food, clothing, cars and appliances. • Services -- Intangible products (that can’t be held in your hand) like education, healthcare, insurance, recreation and travel. • LO 1 -1 PRODUCTS CAN CONSIST OF BOTH GOOD AND SERVICE ELEMENTS! 1 -7
Product Elements: Understanding GOODS and SERVICES • Goods -- Tangible products such as computers, food, clothing, cars and appliances. • Services -- Intangible products (that can’t be held in your hand) like education, healthcare, insurance, recreation and travel. • LO 1 -1 PRODUCTS CAN CONSIST OF BOTH GOOD AND SERVICE ELEMENTS! 1 -7
 Profit Motivation: Understanding Revenue, Profit & Loss • • • Profit is what remains after all business expenses have been deducted from sales revenue. Revenue – Expenses = Profit Sales Revenue = the money a business receive from selling its products (product price * number of products sold) Expenses = the money a business spends trying to sell its products and operate A loss (negative profit) results when a firm’s expenses are greater than its revenues. LO 1 -1 What do you have when? • Revenue > Expenses • Expenses > Revenue Sales Revenue - Business Expenses Profit (Loss)* *Profit becomes property of its owners 1 -8
Profit Motivation: Understanding Revenue, Profit & Loss • • • Profit is what remains after all business expenses have been deducted from sales revenue. Revenue – Expenses = Profit Sales Revenue = the money a business receive from selling its products (product price * number of products sold) Expenses = the money a business spends trying to sell its products and operate A loss (negative profit) results when a firm’s expenses are greater than its revenues. LO 1 -1 What do you have when? • Revenue > Expenses • Expenses > Revenue Sales Revenue - Business Expenses Profit (Loss)* *Profit becomes property of its owners 1 -8
 Profit Motivation: Matching RISK with Profit • Risk -- The chance an entrepreneur takes of losing time and money on a business that may not prove profitable • Not all businesses make the same amount of profit. • Businesses take risks, but with great risks could come great profit. • The purposes of profit – To reward business owners for producing goods and services consumers want – Profit compensates for RISK • Non-Payment Risk • Business Failure Risk LO 1 -1 1 -9
Profit Motivation: Matching RISK with Profit • Risk -- The chance an entrepreneur takes of losing time and money on a business that may not prove profitable • Not all businesses make the same amount of profit. • Businesses take risks, but with great risks could come great profit. • The purposes of profit – To reward business owners for producing goods and services consumers want – Profit compensates for RISK • Non-Payment Risk • Business Failure Risk LO 1 -1 1 -9
 Profit Motivation: Taxes Come From Profit LO 1 -1 Taxes are used to provide: • Hospitals • Schools • Libraries • Playgrounds • Roads • Fire Protection • Police Protection • Environmental Programs • Support for People in Need 1 -10
Profit Motivation: Taxes Come From Profit LO 1 -1 Taxes are used to provide: • Hospitals • Schools • Libraries • Playgrounds • Roads • Fire Protection • Police Protection • Environmental Programs • Support for People in Need 1 -10
 Profit Motivation: Profit enhance society • Standard of Living -- The amount of goods and services people can buy with the money they have. • The U. S. has one of the highest standards of living in the world. • Workers in other countries may make more money, but prices for products are higher. • Quality of Life -- The general well-being of a society in terms of its political freedom, natural environment, education, healthcare, safety, amount of leisure and rewards that add to personal satisfaction. LO 1 -1 Photo Credit: Walmart Stores 1 -11
Profit Motivation: Profit enhance society • Standard of Living -- The amount of goods and services people can buy with the money they have. • The U. S. has one of the highest standards of living in the world. • Workers in other countries may make more money, but prices for products are higher. • Quality of Life -- The general well-being of a society in terms of its political freedom, natural environment, education, healthcare, safety, amount of leisure and rewards that add to personal satisfaction. LO 1 -1 Photo Credit: Walmart Stores 1 -11
 Customer Satisfaction: The Ultimate Objective of Every Business …to satisfy the needs of its customers. • People buy products not just to own them, but to satisfy particular needs • Goal of businesses are to produce products that people need and want at a price they are willing to pay • Businesses that understand customer needs, and work to satisfy those needs, are usually successful • Has a business ever failed or succeeded in satisfying your needs?
Customer Satisfaction: The Ultimate Objective of Every Business …to satisfy the needs of its customers. • People buy products not just to own them, but to satisfy particular needs • Goal of businesses are to produce products that people need and want at a price they are willing to pay • Businesses that understand customer needs, and work to satisfy those needs, are usually successful • Has a business ever failed or succeeded in satisfying your needs?
 STAKEHOLDERS LO 1 -1 • Stakeholders -- All the people who stand to gain or lose by the policies and activities of a business and whose concerns the businesses need to address. • Who are Stakeholders? - Owners Customers Employees Suppliers Dealers - Community Media Elected Officials Bankers Environmentalists 1 -13
STAKEHOLDERS LO 1 -1 • Stakeholders -- All the people who stand to gain or lose by the policies and activities of a business and whose concerns the businesses need to address. • Who are Stakeholders? - Owners Customers Employees Suppliers Dealers - Community Media Elected Officials Bankers Environmentalists 1 -13
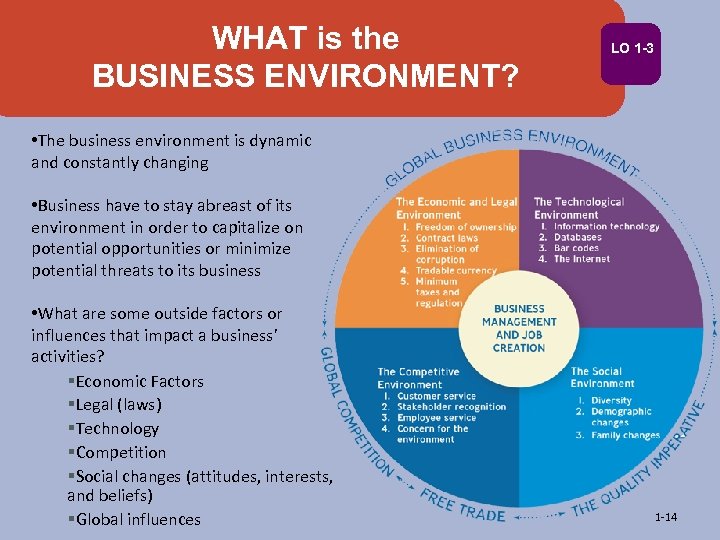 WHAT is the BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT? LO 1 -3 • The business environment is dynamic and constantly changing • Business have to stay abreast of its environment in order to capitalize on potential opportunities or minimize potential threats to its business • What are some outside factors or influences that impact a business’ activities? §Economic Factors §Legal (laws) §Technology §Competition §Social changes (attitudes, interests, and beliefs) §Global influences 1 -14
WHAT is the BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT? LO 1 -3 • The business environment is dynamic and constantly changing • Business have to stay abreast of its environment in order to capitalize on potential opportunities or minimize potential threats to its business • What are some outside factors or influences that impact a business’ activities? §Economic Factors §Legal (laws) §Technology §Competition §Social changes (attitudes, interests, and beliefs) §Global influences 1 -14
 GOVERNMENT’S ROLE in BUSINESS LO 1 -3 Government can promote business by… 1. Minimizing spending and keeping taxes and regulations to a minimum. 2. Allowing private ownership of businesses. 3. Minimizing interference with the free exchange of goods and services. 4. Passing laws that enable businesspeople to write enforceable contracts. 5. Establishing a currency that’s tradable in world markets. 6. Minimizing corruption. 1 -15
GOVERNMENT’S ROLE in BUSINESS LO 1 -3 Government can promote business by… 1. Minimizing spending and keeping taxes and regulations to a minimum. 2. Allowing private ownership of businesses. 3. Minimizing interference with the free exchange of goods and services. 4. Passing laws that enable businesspeople to write enforceable contracts. 5. Establishing a currency that’s tradable in world markets. 6. Minimizing corruption. 1 -15
 ETHICS BEGINS with YOU The number of employees calling in sick has reached a five-year high. 3/5 of all callers were not even sick. Others conduct personal business at work, play video games and check their Facebook pages while at work. What is the problem with this situation? What are the alternatives? What are the consequences of each alternative? What path would you choose? Is it ethical? 1 -16
ETHICS BEGINS with YOU The number of employees calling in sick has reached a five-year high. 3/5 of all callers were not even sick. Others conduct personal business at work, play video games and check their Facebook pages while at work. What is the problem with this situation? What are the alternatives? What are the consequences of each alternative? What path would you choose? Is it ethical? 1 -16
 BENEFITS of TECHNOLOGY LO 1 -4 • Technology -- Everything from phones to copiers and the various software programs that make businesses more effective, efficient and productive. • Effectiveness -- Producing the desired result. • Efficiency -- Producing goods and services using the least amount of resources. • Productivity -- The amount of output you generate given the amount of input (example: hours you work). 1 -17
BENEFITS of TECHNOLOGY LO 1 -4 • Technology -- Everything from phones to copiers and the various software programs that make businesses more effective, efficient and productive. • Effectiveness -- Producing the desired result. • Efficiency -- Producing goods and services using the least amount of resources. • Productivity -- The amount of output you generate given the amount of input (example: hours you work). 1 -17
 NONPROFIT ORGANIZATIONS LO 1 -1 • Nonprofit Organization -- An organization whose goals do not include making a personal profit for its owners or organizers. 1 -18
NONPROFIT ORGANIZATIONS LO 1 -1 • Nonprofit Organization -- An organization whose goals do not include making a personal profit for its owners or organizers. 1 -18
 WELL-KNOWN NONPROFITS in the UNITED STATES LO 1 -1 United Way American Heart Association Salvation Army American Cancer Society American Red Cross 1 -19
WELL-KNOWN NONPROFITS in the UNITED STATES LO 1 -1 United Way American Heart Association Salvation Army American Cancer Society American Red Cross 1 -19
 KEEPING STRONG EMPLOYEES at NONPROFITS LO 1 -1 1. Set ambitious, but realistic goals. 2. Allow all employees to work with the groups they are serving. 3. Give employees a break. Nonprofit work is draining. Source: Fast Company, accessed October 2014. 1 -20
KEEPING STRONG EMPLOYEES at NONPROFITS LO 1 -1 1. Set ambitious, but realistic goals. 2. Allow all employees to work with the groups they are serving. 3. Give employees a break. Nonprofit work is draining. Source: Fast Company, accessed October 2014. 1 -20
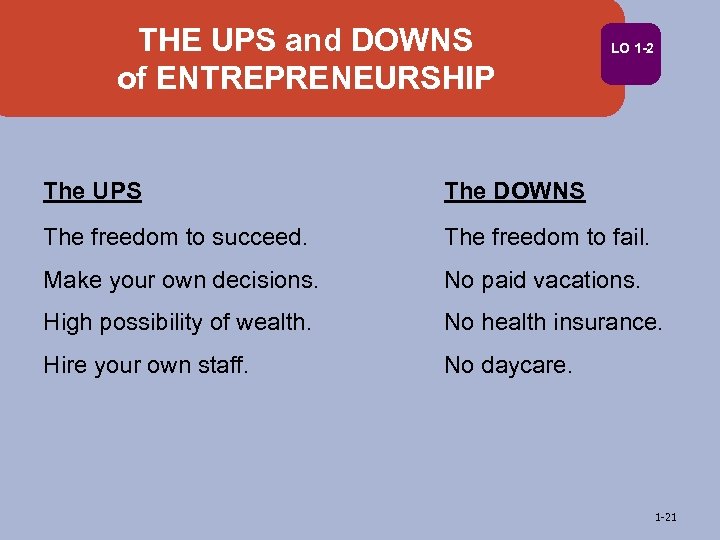 THE UPS and DOWNS of ENTREPRENEURSHIP LO 1 -2 The UPS The DOWNS The freedom to succeed. The freedom to fail. Make your own decisions. No paid vacations. High possibility of wealth. No health insurance. Hire your own staff. No daycare. 1 -21
THE UPS and DOWNS of ENTREPRENEURSHIP LO 1 -2 The UPS The DOWNS The freedom to succeed. The freedom to fail. Make your own decisions. No paid vacations. High possibility of wealth. No health insurance. Hire your own staff. No daycare. 1 -21
 HOW a FOOD TRUCK HELPED REBUILD a STORM-STRUCK COMMUNITY • After witnessing the destruction left behind after Hurricane Sandy, Mike Diamond started Rockaway Plate to serve free lunches. • Now the truck is a profitable business that helps local teens gain work experience. 1 -22
HOW a FOOD TRUCK HELPED REBUILD a STORM-STRUCK COMMUNITY • After witnessing the destruction left behind after Hurricane Sandy, Mike Diamond started Rockaway Plate to serve free lunches. • Now the truck is a profitable business that helps local teens gain work experience. 1 -22
 WHO TAKES the ENTREPRENEURIAL CHALLENGE? LO 1 -2 • Millions of people have started businesses and succeeded. • The number of Hispanicowned businesses in the U. S. has grown dramatically. • Women now own over onethird of all businesses. 1 -23
WHO TAKES the ENTREPRENEURIAL CHALLENGE? LO 1 -2 • Millions of people have started businesses and succeeded. • The number of Hispanicowned businesses in the U. S. has grown dramatically. • Women now own over onethird of all businesses. 1 -23


