8cf34a9400bd3e98540bbbb2be60a267.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Chapter 1 Managing in the Digital World 1 -1 “If we'd given customers what they said they wanted, we'd have built a computer they'd have been happy with a year after we spoke to them—not something they'd want now…” Steve Jobs, Apple Computer IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Chapter 1 Managing in the Digital World 1 -1 “If we'd given customers what they said they wanted, we'd have built a computer they'd have been happy with a year after we spoke to them—not something they'd want now…” Steve Jobs, Apple Computer IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 1 -2 1. Explain what an information system is, contrasting its data, technology, people, and organizational components. 2. Describe types of jobs and career opportunities in information systems and in related fields. 3. Describe the dual nature of information systems in the success and failure of modern organizations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 1 -2 1. Explain what an information system is, contrasting its data, technology, people, and organizational components. 2. Describe types of jobs and career opportunities in information systems and in related fields. 3. Describe the dual nature of information systems in the success and failure of modern organizations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 1 -3 1. Explain what an information system is, contrasting its data, technology, people, and organizational components. 2. Describe types of jobs and career opportunities in information systems and in related fields. 3. Describe the dual nature of information systems in the success and failure of modern organizations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 1 -3 1. Explain what an information system is, contrasting its data, technology, people, and organizational components. 2. Describe types of jobs and career opportunities in information systems and in related fields. 3. Describe the dual nature of information systems in the success and failure of modern organizations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Information Systems Today 1 -4 The Knowledge Worker Term coined by Peter Drucker in 1959 An individual who is relatively well educated and who creates, modifies, and/or synthesizes knowledge as a fundamental part of a job Knowledge Society New Economy/Digital World Digital Divide IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Information Systems Today 1 -4 The Knowledge Worker Term coined by Peter Drucker in 1959 An individual who is relatively well educated and who creates, modifies, and/or synthesizes knowledge as a fundamental part of a job Knowledge Society New Economy/Digital World Digital Divide IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
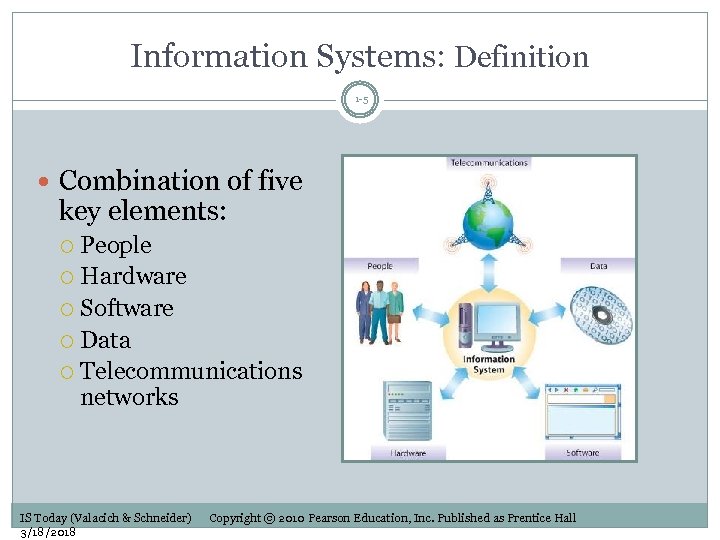 Information Systems: Definition 1 -5 Combination of five key elements: People Hardware Software Data Telecommunications networks IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Information Systems: Definition 1 -5 Combination of five key elements: People Hardware Software Data Telecommunications networks IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
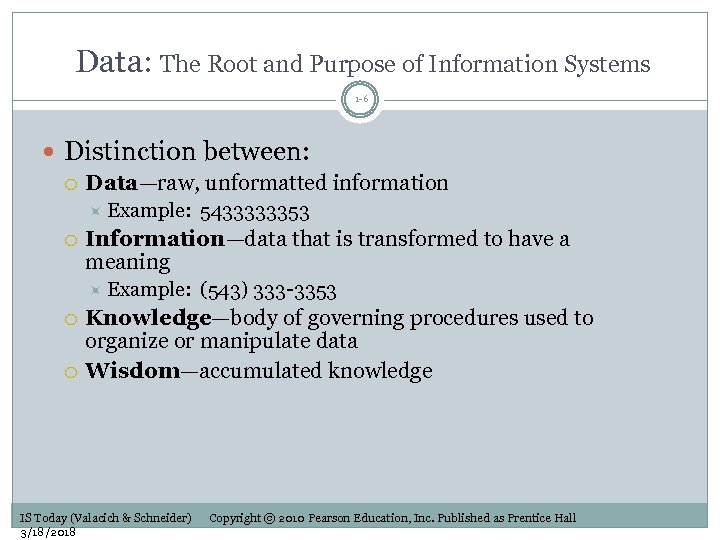 Data: The Root and Purpose of Information Systems 1 -6 Distinction between: Data—raw, unformatted information Example: Information—data that is transformed to have a meaning Example: 5433333353 (543) 333 -3353 Knowledge—body of governing procedures used to organize or manipulate data Wisdom—accumulated knowledge IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Data: The Root and Purpose of Information Systems 1 -6 Distinction between: Data—raw, unformatted information Example: Information—data that is transformed to have a meaning Example: 5433333353 (543) 333 -3353 Knowledge—body of governing procedures used to organize or manipulate data Wisdom—accumulated knowledge IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
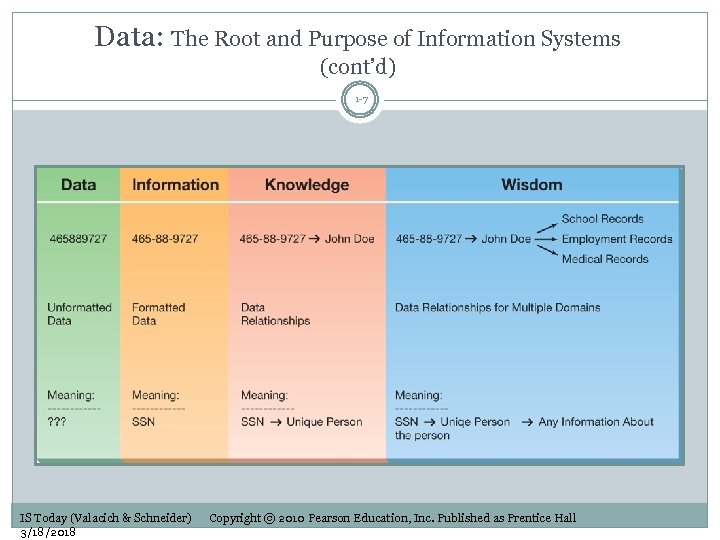 Data: The Root and Purpose of Information Systems (cont’d) 1 -7 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Data: The Root and Purpose of Information Systems (cont’d) 1 -7 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
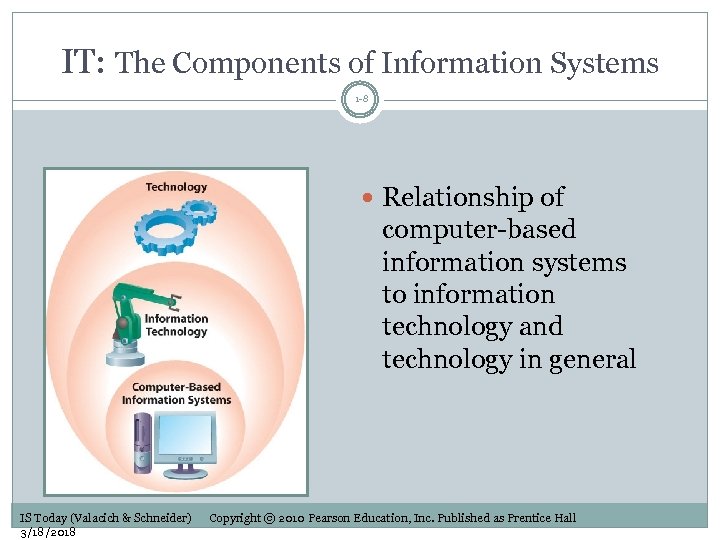 IT: The Components of Information Systems 1 -8 Relationship of computer-based information systems to information technology and technology in general IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
IT: The Components of Information Systems 1 -8 Relationship of computer-based information systems to information technology and technology in general IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 IT: The Components of Information Systems—Technology 1 -9 Any machine that can supplement or replace human manual work Examples: Heating system Surgical laser IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
IT: The Components of Information Systems—Technology 1 -9 Any machine that can supplement or replace human manual work Examples: Heating system Surgical laser IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
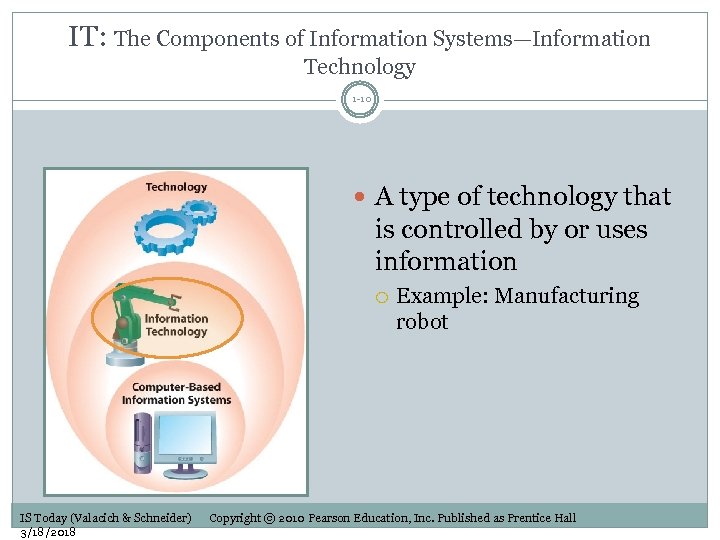 IT: The Components of Information Systems—Information Technology 1 -10 A type of technology that is controlled by or uses information IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Example: Manufacturing robot Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
IT: The Components of Information Systems—Information Technology 1 -10 A type of technology that is controlled by or uses information IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Example: Manufacturing robot Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
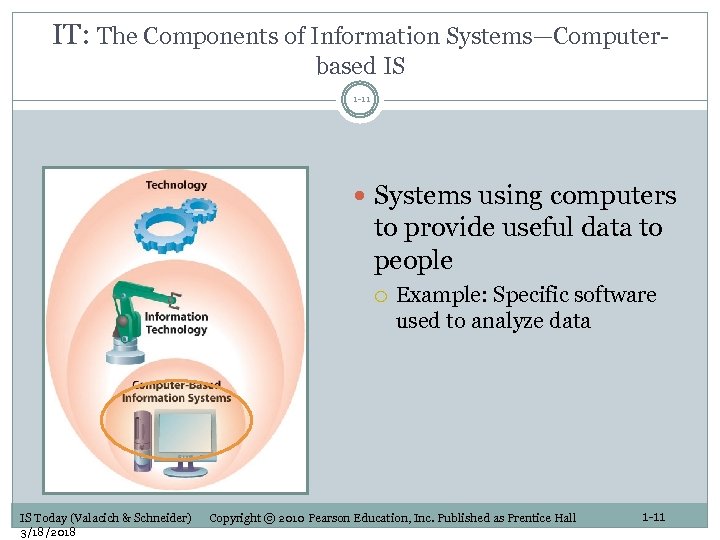 IT: The Components of Information Systems—Computerbased IS 1 -11 Systems using computers to provide useful data to people IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Example: Specific software used to analyze data Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall 1 -11
IT: The Components of Information Systems—Computerbased IS 1 -11 Systems using computers to provide useful data to people IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Example: Specific software used to analyze data Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall 1 -11
 Learning Objectives 1 -12 1. Explain what an information system is, contrasting its data, technology, people, and organizational components. 2. Describe types of jobs and career opportunities in information systems and in related fields. 3. Describe the dual nature of information systems in the success and failure of modern organizations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 1 -12 1. Explain what an information system is, contrasting its data, technology, people, and organizational components. 2. Describe types of jobs and career opportunities in information systems and in related fields. 3. Describe the dual nature of information systems in the success and failure of modern organizations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
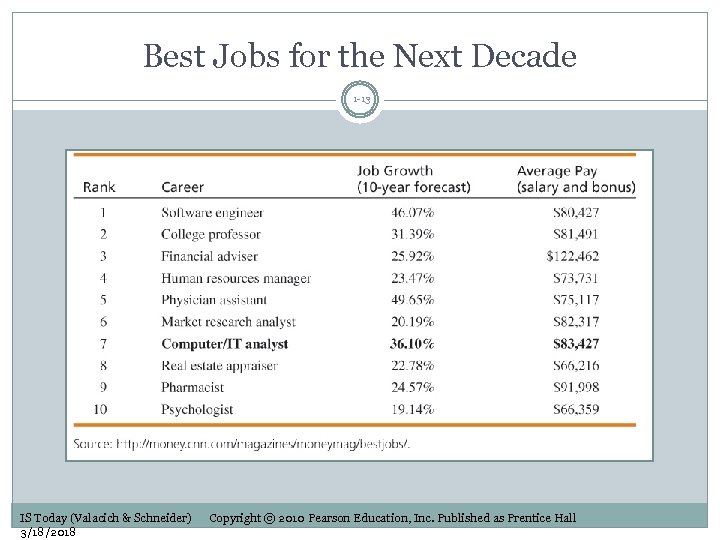 Best Jobs for the Next Decade 1 -13 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Best Jobs for the Next Decade 1 -13 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
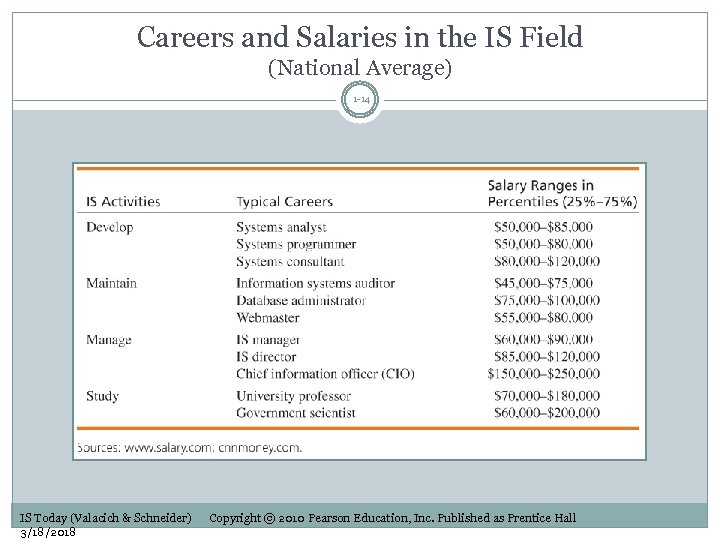 Careers and Salaries in the IS Field (National Average) 1 -14 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Careers and Salaries in the IS Field (National Average) 1 -14 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 What Makes IS Personnel Valuable? 1 -15 Integrated knowledge and skills in three areas: Technical Competency—skills in hardware, software, networking, and security Business Competency—understanding of the nature of the business; this is key in addition to technical competency Systems Competency—understanding of how to build and integrate large scale systems IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
What Makes IS Personnel Valuable? 1 -15 Integrated knowledge and skills in three areas: Technical Competency—skills in hardware, software, networking, and security Business Competency—understanding of the nature of the business; this is key in addition to technical competency Systems Competency—understanding of how to build and integrate large scale systems IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Hot Skills for 2010 and Beyond 1 -16 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Hot Skills for 2010 and Beyond 1 -16 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 1 -17 1. Explain what an information system is, contrasting its data, technology, people, and organizational components. 2. Describe types of jobs and career opportunities in information systems and in related fields. 3. Describe the dual nature of information systems in the success and failure of modern organizations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 1 -17 1. Explain what an information system is, contrasting its data, technology, people, and organizational components. 2. Describe types of jobs and career opportunities in information systems and in related fields. 3. Describe the dual nature of information systems in the success and failure of modern organizations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 The Dual Nature of IS 1 -18 IS can make you or break you London Heathrow—The failure Baggage handling system: original cost of $500 million Disaster on opening day, costing $ 50 million due to over 28, 000 bags being misrouted Fed. Ex—The success $ 38 billion family of companies—largest express transportation company “Information hub for business where managing information is the business” IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
The Dual Nature of IS 1 -18 IS can make you or break you London Heathrow—The failure Baggage handling system: original cost of $500 million Disaster on opening day, costing $ 50 million due to over 28, 000 bags being misrouted Fed. Ex—The success $ 38 billion family of companies—largest express transportation company “Information hub for business where managing information is the business” IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 IS for Competitive Advantage 1 -19 Both Fed. Ex and London Heathrow were developing strategic information systems Only strategic information systems can help sustain competitive advantage IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
IS for Competitive Advantage 1 -19 Both Fed. Ex and London Heathrow were developing strategic information systems Only strategic information systems can help sustain competitive advantage IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Why Information Systems Matter 1 -20 Nicholas Carr article—“IT Doesn’t Matter” IT no longer a source of advantage on the firm level Companies should focus IT on cost reduction and risk mitigation Many experts disagree with his arguments Abbie Lundberg—Interview with Carr Don Tapscott—“The Engine That Drives Success: The Best Companies Have the Best Business Models Because They Have the Best IT Strategies” Many successful companies use IT to support a unique business strategy IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Why Information Systems Matter 1 -20 Nicholas Carr article—“IT Doesn’t Matter” IT no longer a source of advantage on the firm level Companies should focus IT on cost reduction and risk mitigation Many experts disagree with his arguments Abbie Lundberg—Interview with Carr Don Tapscott—“The Engine That Drives Success: The Best Companies Have the Best Business Models Because They Have the Best IT Strategies” Many successful companies use IT to support a unique business strategy IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
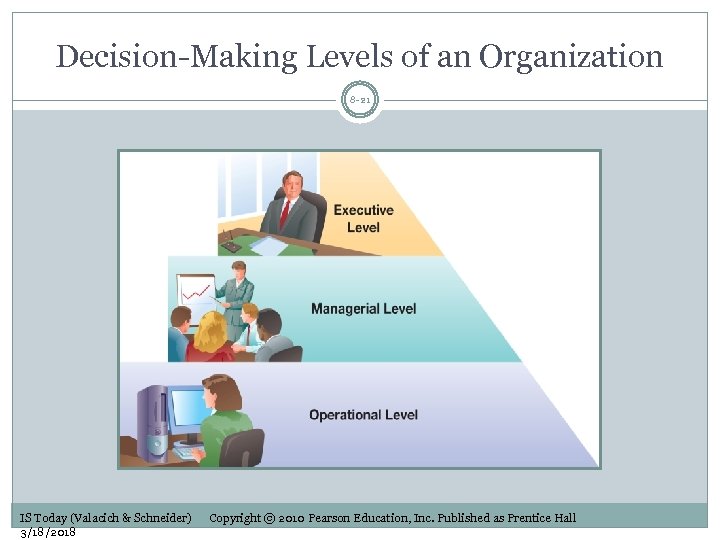 Decision-Making Levels of an Organization 8 -21 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Decision-Making Levels of an Organization 8 -21 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Operational Level 8 -22 Day-to-day business processes Interactions with customers Decisions: Structured ( Procedures is specified). Recurring Can often be automated using IS( Inventory System). BI used to: Optimize processes Understand causes of performance problems IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Operational Level 8 -22 Day-to-day business processes Interactions with customers Decisions: Structured ( Procedures is specified). Recurring Can often be automated using IS( Inventory System). BI used to: Optimize processes Understand causes of performance problems IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Managerial Level 8 -23 Functional managers Monitor and control operational-level activities Focus: effectively utilizing and deploying resources Goal: achieving strategic objectives Managers’ decisions Semistructured Moderately complex Time horizon of few days to few months BI can help with: Performance analytics Forecasts Providing key performance indicators on dashboards IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Managerial Level 8 -23 Functional managers Monitor and control operational-level activities Focus: effectively utilizing and deploying resources Goal: achieving strategic objectives Managers’ decisions Semistructured Moderately complex Time horizon of few days to few months BI can help with: Performance analytics Forecasts Providing key performance indicators on dashboards IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
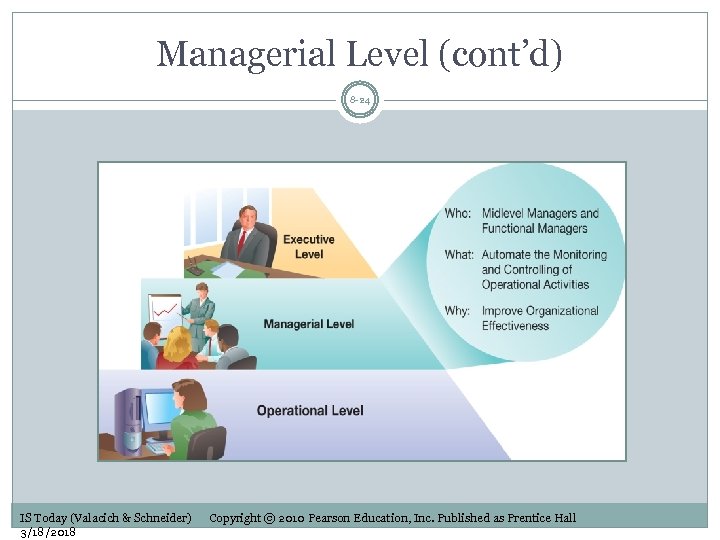 Managerial Level (cont’d) 8 -24 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Managerial Level (cont’d) 8 -24 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Executive Level 8 -25 The president, CEO, vice presidents, board of directors Decisions Unstructured Long-term strategic issues Complex and nonroutine problems with long-term ramifications BI is used to: Obtain aggregate summaries of trends and projections Provide KPIs across the organization IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Executive Level 8 -25 The president, CEO, vice presidents, board of directors Decisions Unstructured Long-term strategic issues Complex and nonroutine problems with long-term ramifications BI is used to: Obtain aggregate summaries of trends and projections Provide KPIs across the organization IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
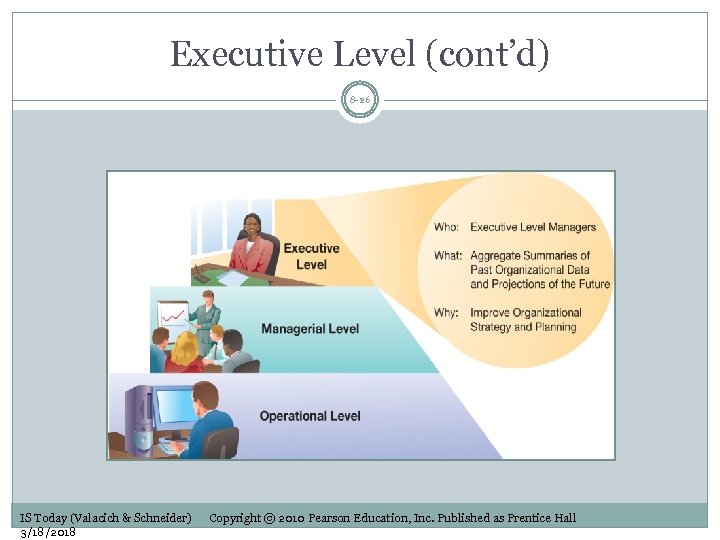 Executive Level (cont’d) 8 -26 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Executive Level (cont’d) 8 -26 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Providing Inputs into BI Applications 8 -27 Decisions made by different departments need to be based on the same underlying data “Single version of the truth” BI systems access multiple databases or data warehouses Data aggregated from operational systems E. g. , Transaction processing systems IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Providing Inputs into BI Applications 8 -27 Decisions made by different departments need to be based on the same underlying data “Single version of the truth” BI systems access multiple databases or data warehouses Data aggregated from operational systems E. g. , Transaction processing systems IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) 8 -28 Operational level Purpose: Processing of business events and transactions Increase efficiency Automation Lower costs Increased speed and accuracy Examples: Payroll processing Sales and order processing Inventory management Product purchasing, receiving, and shipping Accounts payable and receivable IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) 8 -28 Operational level Purpose: Processing of business events and transactions Increase efficiency Automation Lower costs Increased speed and accuracy Examples: Payroll processing Sales and order processing Inventory management Product purchasing, receiving, and shipping Accounts payable and receivable IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
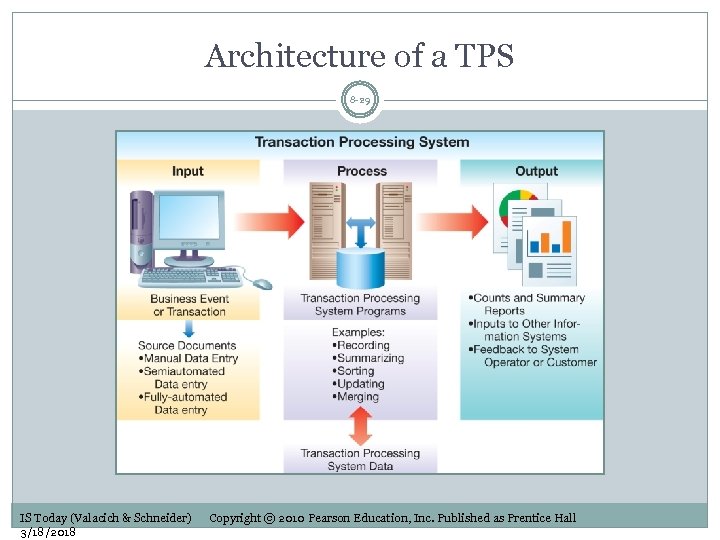 Architecture of a TPS 8 -29 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Architecture of a TPS 8 -29 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
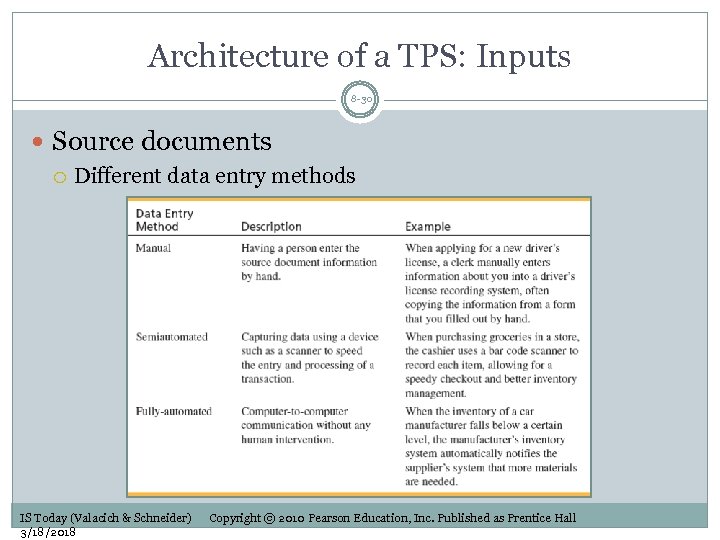 Architecture of a TPS: Inputs 8 -30 Source documents Different data entry methods IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Architecture of a TPS: Inputs 8 -30 Source documents Different data entry methods IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
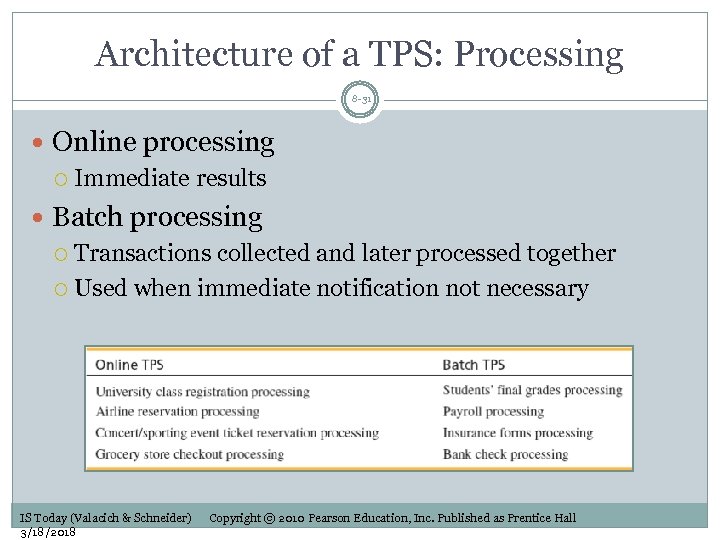 Architecture of a TPS: Processing 8 -31 Online processing Immediate results Batch processing Transactions collected and later processed together Used when immediate notification not necessary IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Architecture of a TPS: Processing 8 -31 Online processing Immediate results Batch processing Transactions collected and later processed together Used when immediate notification not necessary IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Architecture of a TPS: Outputs 8 -32 Counts, summary reports Inputs to other systems Feedback to systems operator IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Architecture of a TPS: Outputs 8 -32 Counts, summary reports Inputs to other systems Feedback to systems operator IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
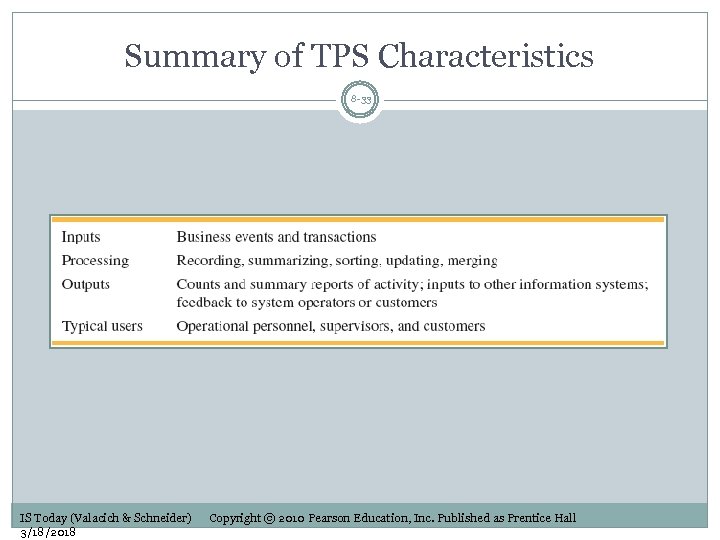 Summary of TPS Characteristics 8 -33 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Summary of TPS Characteristics 8 -33 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8 -34 Managerial level Purpose: Produce reports Support of midlevel managers’ decisions Examples: Sales forecasting Financial management and forecasting Manufacturing, planning and scheduling Inventory management and planning Advertising and product pricing IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8 -34 Managerial level Purpose: Produce reports Support of midlevel managers’ decisions Examples: Sales forecasting Financial management and forecasting Manufacturing, planning and scheduling Inventory management and planning Advertising and product pricing IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
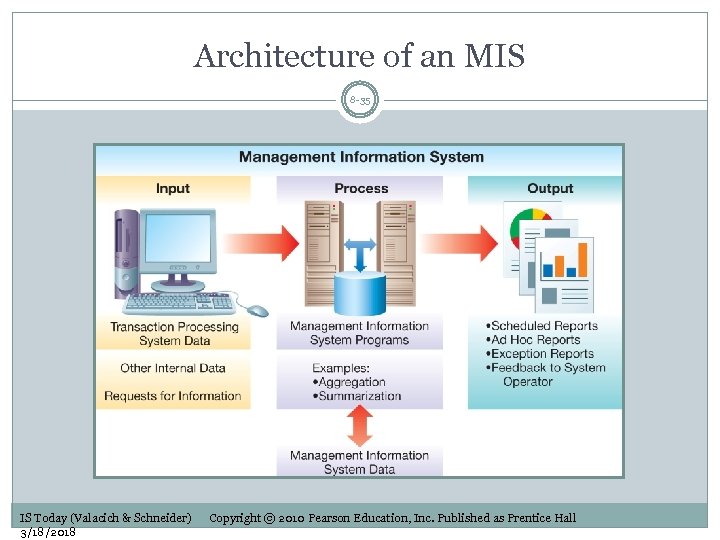 Architecture of an MIS 8 -35 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Architecture of an MIS 8 -35 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
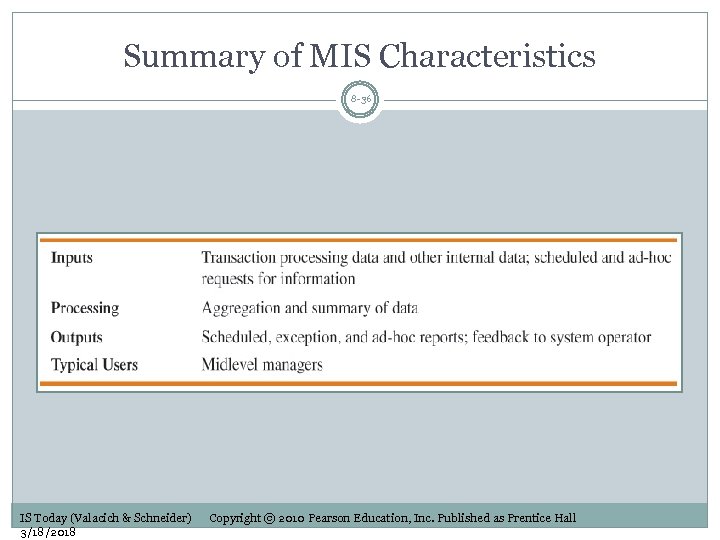 Summary of MIS Characteristics 8 -36 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Summary of MIS Characteristics 8 -36 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Decision Support Systems (DSS) 8 -37 Decision-making support for recurring problems Used mostly by managerial level employees Interactive decision aid What-if analyses Analyze results for hypothetical changes Example: Microsoft Excel IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Decision Support Systems (DSS) 8 -37 Decision-making support for recurring problems Used mostly by managerial level employees Interactive decision aid What-if analyses Analyze results for hypothetical changes Example: Microsoft Excel IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
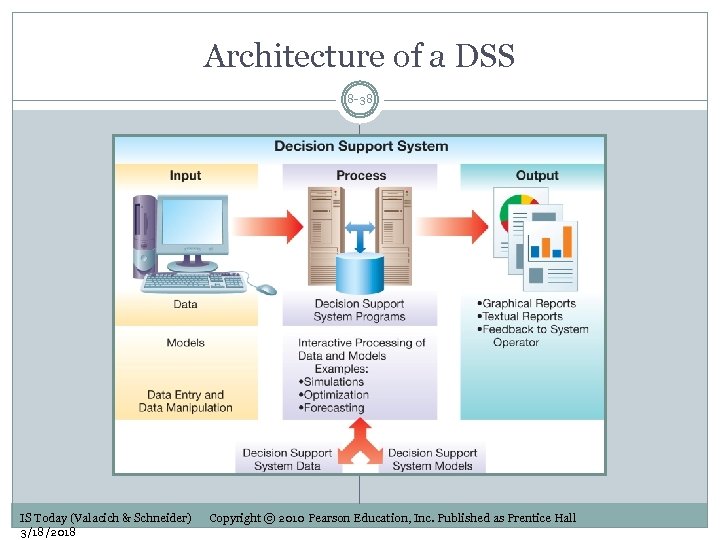 Architecture of a DSS 8 -38 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Architecture of a DSS 8 -38 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
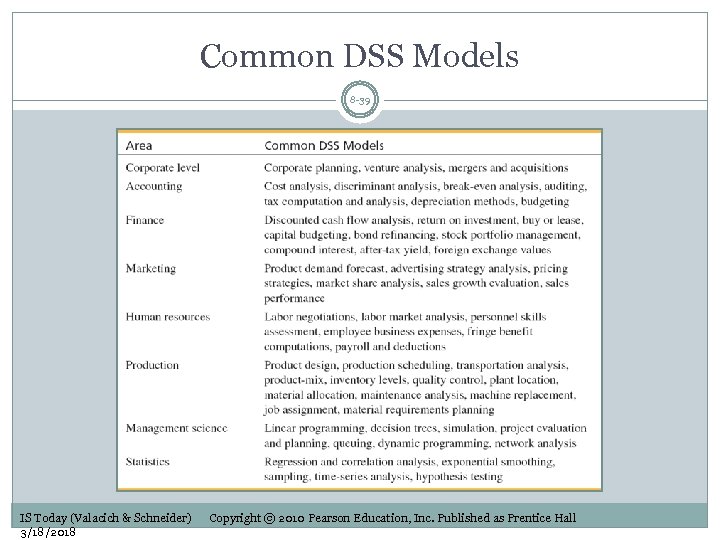 Common DSS Models 8 -39 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Common DSS Models 8 -39 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Executive Information Systems 8 -40 Aka Executive support system Executive level Purpose: Aid in executive decision making Provide information in highly aggregated form Examples: Executive-level decision making Long-range and strategic planning Monitoring of internal and external events and resources Crisis management Staffing and labor relations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Executive Information Systems 8 -40 Aka Executive support system Executive level Purpose: Aid in executive decision making Provide information in highly aggregated form Examples: Executive-level decision making Long-range and strategic planning Monitoring of internal and external events and resources Crisis management Staffing and labor relations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
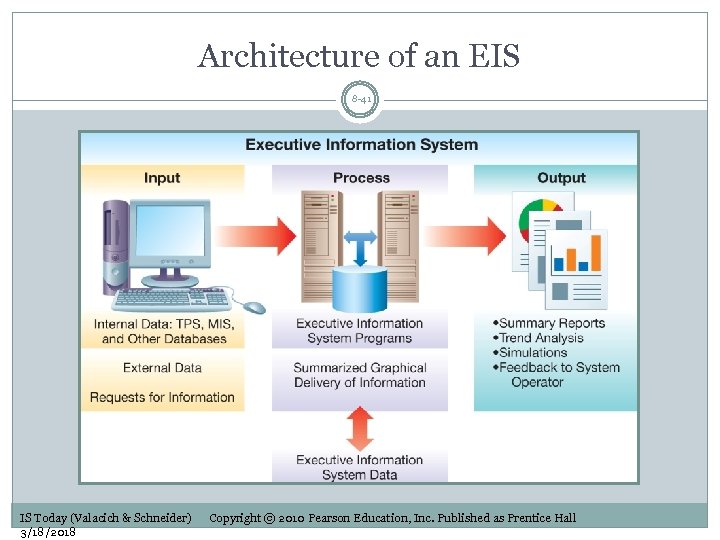 Architecture of an EIS 8 -41 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Architecture of an EIS 8 -41 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
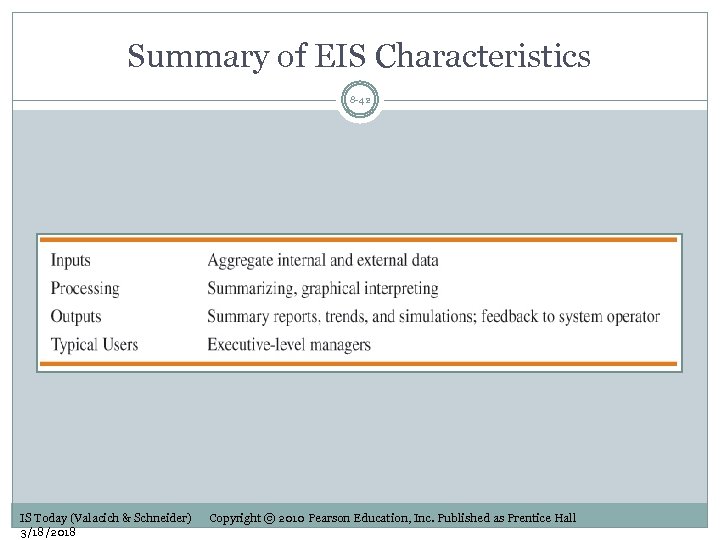 Summary of EIS Characteristics 8 -42 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Summary of EIS Characteristics 8 -42 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
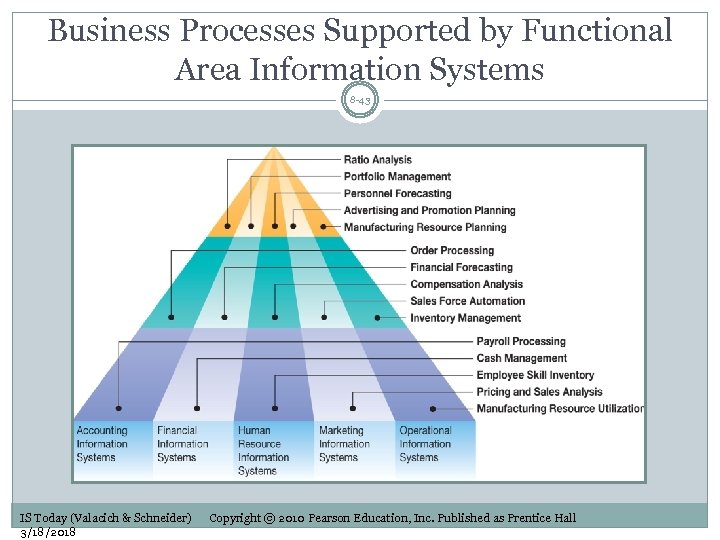 Business Processes Supported by Functional Area Information Systems 8 -43 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Business Processes Supported by Functional Area Information Systems 8 -43 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
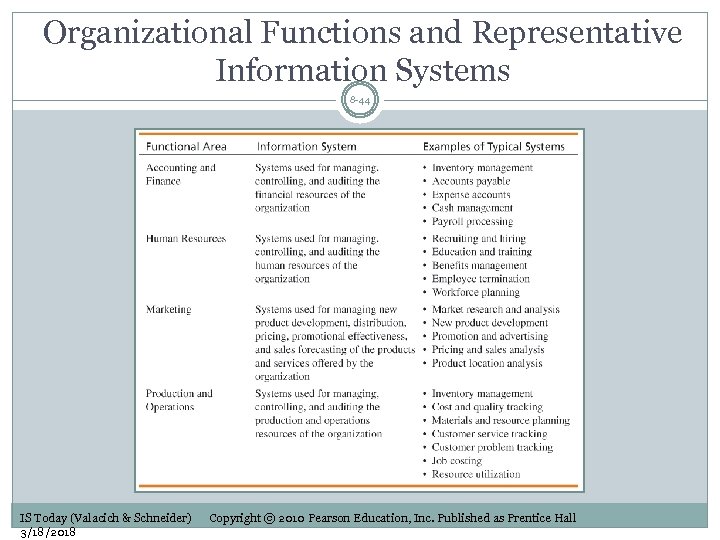 Organizational Functions and Representative Information Systems 8 -44 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Organizational Functions and Representative Information Systems 8 -44 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
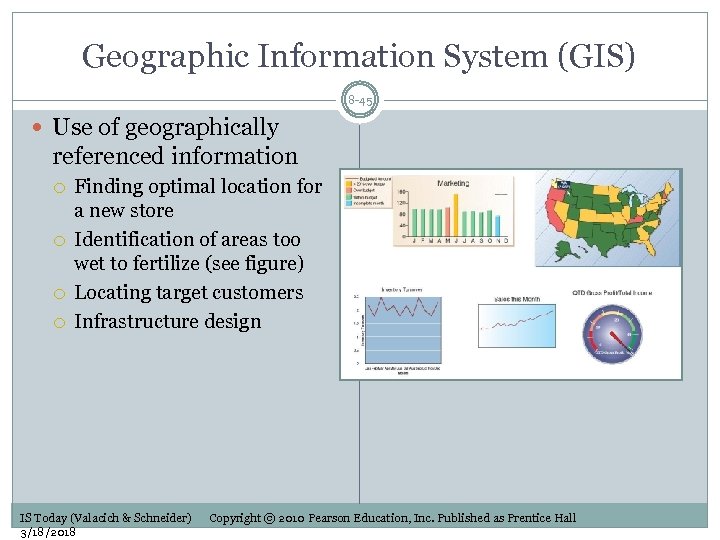 Geographic Information System (GIS) 8 -45 Use of geographically referenced information Finding optimal location for a new store Identification of areas too wet to fertilize (see figure) Locating target customers Infrastructure design IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Geographic Information System (GIS) 8 -45 Use of geographically referenced information Finding optimal location for a new store Identification of areas too wet to fertilize (see figure) Locating target customers Infrastructure design IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Health information technology 1 -46 (HIT) provides the umbrella framework to describe the comprehensive management of health information across computerized systems and its secure exchange between consumers, providers, government and quality entities, and insurers. Health information technology (HIT) is in general increasingly viewed as the most promising tool for improving the overall quality, safety and efficiency of the health delivery system (Chaudhry et al. , 2006). Broad and consistent utilization of HIT will: Improve health care quality; Prevent medical errors; Reduce health care costs; Increase administrative efficiencies Decrease paperwork; and Expand access to affordable care. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Health information technology 1 -46 (HIT) provides the umbrella framework to describe the comprehensive management of health information across computerized systems and its secure exchange between consumers, providers, government and quality entities, and insurers. Health information technology (HIT) is in general increasingly viewed as the most promising tool for improving the overall quality, safety and efficiency of the health delivery system (Chaudhry et al. , 2006). Broad and consistent utilization of HIT will: Improve health care quality; Prevent medical errors; Reduce health care costs; Increase administrative efficiencies Decrease paperwork; and Expand access to affordable care. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Health information technology… cont. 1 -47 Interoperable HIT will improve individual patient care, but it will also bring many public health benefits including: Early detection of infectious disease outbreaks around the country; Improved tracking of chronic disease management; and Evaluation of health care based on value enabled by the collection of de-identified price and quality information that can be compared IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Health information technology… cont. 1 -47 Interoperable HIT will improve individual patient care, but it will also bring many public health benefits including: Early detection of infectious disease outbreaks around the country; Improved tracking of chronic disease management; and Evaluation of health care based on value enabled by the collection of de-identified price and quality information that can be compared IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 End of Chapter Content 1 -48 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
End of Chapter Content 1 -48 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 8 -49 1. Describe the concept of business intelligence and how it is used at the operational, managerial, and executive levels of an organization. 2. Explain the three components of business intelligence: information and knowledge discovery, business analytics, and information visualization. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 8 -49 1. Describe the concept of business intelligence and how it is used at the operational, managerial, and executive levels of an organization. 2. Explain the three components of business intelligence: information and knowledge discovery, business analytics, and information visualization. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Opening Case—Managing in the Digital World: Apple Computer 1 -50 Apple changed the way in which everyday people use computers Long list of successful products Success of i. Pod: tight integration with i. Tunes and App. Store IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Opening Case—Managing in the Digital World: Apple Computer 1 -50 Apple changed the way in which everyday people use computers Long list of successful products Success of i. Pod: tight integration with i. Tunes and App. Store IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Apple Computers 1 -51 A company’s survival may depend upon those employees who fail over and over as they try new ideas (Consultant & author Tom Peters) Apple has had many failures: Mac TV, Power. Mac G 4 Cube, Lisa, Newton, etc. Apple’s overall success shows that a company without an interesting list of failures probably isn’t trying hard enough. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Apple Computers 1 -51 A company’s survival may depend upon those employees who fail over and over as they try new ideas (Consultant & author Tom Peters) Apple has had many failures: Mac TV, Power. Mac G 4 Cube, Lisa, Newton, etc. Apple’s overall success shows that a company without an interesting list of failures probably isn’t trying hard enough. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Bionic Contact Lens 1 -52 • Bionic eye implants for blind and partially • blind people are being developed Problems that must be solved first: Plastics for electronic must be biocompatible LED must be small enough to fit over the eye without causing discomfort, and yet must be functional Where will the power for the device come from? • • • IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Bionic Contact Lens 1 -52 • Bionic eye implants for blind and partially • blind people are being developed Problems that must be solved first: Plastics for electronic must be biocompatible LED must be small enough to fit over the eye without causing discomfort, and yet must be functional Where will the power for the device come from? • • • IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 The Two Steves—Jobs & Wozniak 1 -53 Knew each other in high school Started selling Apple computers in 1976 Both left Apple in 1985 In 1996 Jobs returned to become Apple’s CEO IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
The Two Steves—Jobs & Wozniak 1 -53 Knew each other in high school Started selling Apple computers in 1976 Both left Apple in 1985 In 1996 Jobs returned to become Apple’s CEO IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
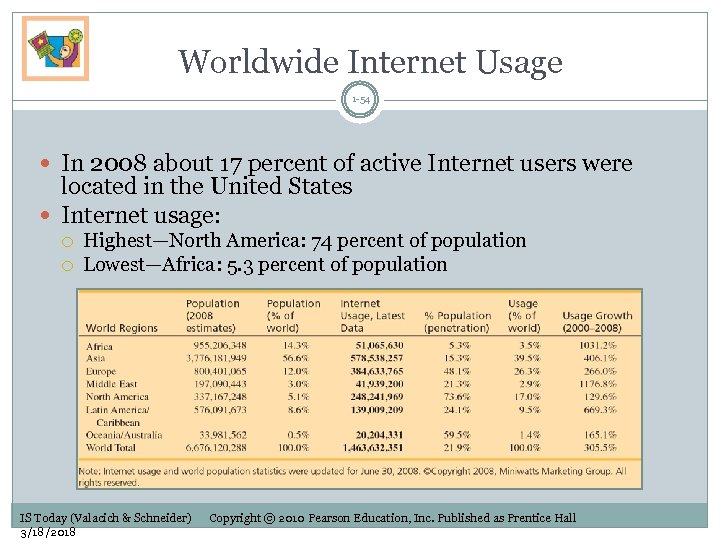 Worldwide Internet Usage 1 -54 In 2008 about 17 percent of active Internet users were located in the United States Internet usage: Highest—North America: 74 percent of population Lowest—Africa: 5. 3 percent of population IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Worldwide Internet Usage 1 -54 In 2008 about 17 percent of active Internet users were located in the United States Internet usage: Highest—North America: 74 percent of population Lowest—Africa: 5. 3 percent of population IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Online Rights Not Always Universal 1 -55 • Governments in some countries regulate • • access to information on the Web (e. g. , China) Reporters Without Borders call this behavior unethical What is the role of companies such as Microsoft in dealing with these governments? Who owns Web-posted data? Should the Internet create its own laws? IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Online Rights Not Always Universal 1 -55 • Governments in some countries regulate • • access to information on the Web (e. g. , China) Reporters Without Borders call this behavior unethical What is the role of companies such as Microsoft in dealing with these governments? Who owns Web-posted data? Should the Internet create its own laws? IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Guerilla Wi-Fi 1 -56 Digital divide is the “haves” and the “have-nots” in the IT world One Laptop Per Child (OLPC) attempted to overcome this. Meraki Network was founded to provide affordable Wi-Fi for these new computers $50 Mini (wireless routers about the size of two stacked i. Phones) can be piggy-backed so that one Mini connected to the Internet can relay the connection to other Minis, thus forming a large network IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Guerilla Wi-Fi 1 -56 Digital divide is the “haves” and the “have-nots” in the IT world One Laptop Per Child (OLPC) attempted to overcome this. Meraki Network was founded to provide affordable Wi-Fi for these new computers $50 Mini (wireless routers about the size of two stacked i. Phones) can be piggy-backed so that one Mini connected to the Internet can relay the connection to other Minis, thus forming a large network IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Business Career Outlook 1 -57 Globalization trend is increasing the need for “Global Skills”—What can you do? Gain international experience Learn more than one language Sensitize yourself to global cultural and political issues In Addition—Immerse yourself into the culture: Learn about local food Watch locally produced television Read books and newspapers IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Business Career Outlook 1 -57 Globalization trend is increasing the need for “Global Skills”—What can you do? Gain international experience Learn more than one language Sensitize yourself to global cultural and political issues In Addition—Immerse yourself into the culture: Learn about local food Watch locally produced television Read books and newspapers IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/18/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall


