20 ВАРИАНТ.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Chapter 1 Lecture Outlines Today’s Managers and Entrepreneurs Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Chapter 1 Lecture Outlines Today’s Managers and Entrepreneurs Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Objectives 1. Define the term management and explain the managerial significance of the terms effectiveness and efficiency. 2. Identify and summarize five major sources of change for today’s managers. 3. Identify and briefly explain the eight managerial functions. 4. Explain how managers learn to manage. 5. Challenge two myths about small business and describe entrepreneurs. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2
Chapter Objectives 1. Define the term management and explain the managerial significance of the terms effectiveness and efficiency. 2. Identify and summarize five major sources of change for today’s managers. 3. Identify and briefly explain the eight managerial functions. 4. Explain how managers learn to manage. 5. Challenge two myths about small business and describe entrepreneurs. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2
 Four Realities of Managing Today 1. The only certainty today is change. 2. Speed, teamwork, and flexibility are the orders of the day. 3. Managers at all levels need to stay close to the customer. 4. Without continuous improvement and lifelong learning, there can be no true economic progress. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 3
Four Realities of Managing Today 1. The only certainty today is change. 2. Speed, teamwork, and flexibility are the orders of the day. 3. Managers at all levels need to stay close to the customer. 4. Without continuous improvement and lifelong learning, there can be no true economic progress. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 3
 Management Defined • Management – The process of working with and through others to achieve organizational objectives in a changing environment. – Management entails the effective and efficient use of limited resources. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 4
Management Defined • Management – The process of working with and through others to achieve organizational objectives in a changing environment. – Management entails the effective and efficient use of limited resources. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 4
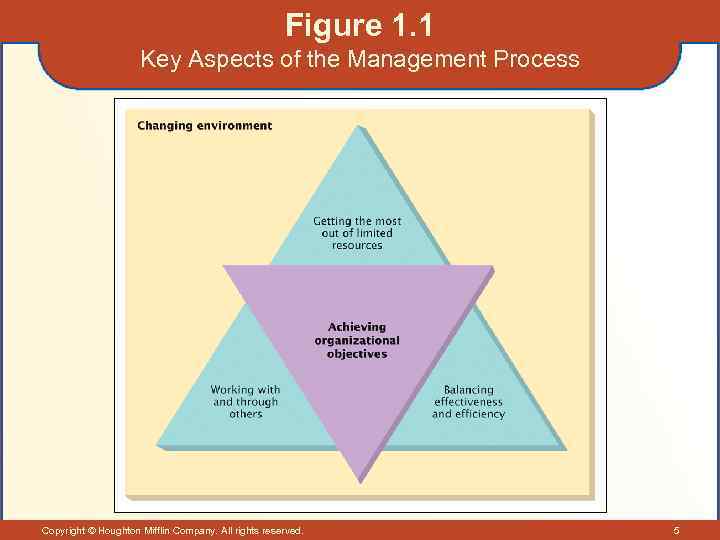 Figure 1. 1 Key Aspects of the Management Process Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 5
Figure 1. 1 Key Aspects of the Management Process Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 5
 Working with and Through Others • Management is a social process in which managers get things done by working with and through others. • Shortcomings of “derailed” managers – Problems with interpersonal relationships – Failure to meet business objectives – Failure to build and lead a team – Inability to change and adapt during a transition Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 6
Working with and Through Others • Management is a social process in which managers get things done by working with and through others. • Shortcomings of “derailed” managers – Problems with interpersonal relationships – Failure to meet business objectives – Failure to build and lead a team – Inability to change and adapt during a transition Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 6
 Achieving Organizational Objectives • An objective is a target to be strived for and attained. – Challenging yet achievable objectives provide guidance for effective and efficient actions by individuals and organizations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7
Achieving Organizational Objectives • An objective is a target to be strived for and attained. – Challenging yet achievable objectives provide guidance for effective and efficient actions by individuals and organizations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7
 Balancing Effectiveness and Efficiency • Effectiveness – Entails promptly achieving a stated organizational objective. – Managers are held responsible for attaining objectives. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. • Efficiency – Entails balancing the amount of resources used to achieve an objective against what was actually accomplished. – Managers must not waste scarce and costly resources. 8
Balancing Effectiveness and Efficiency • Effectiveness – Entails promptly achieving a stated organizational objective. – Managers are held responsible for attaining objectives. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. • Efficiency – Entails balancing the amount of resources used to achieve an objective against what was actually accomplished. – Managers must not waste scarce and costly resources. 8
 Making the Most of Limited Resources • We live in a world of scarcity. • There is a lopsided use of resources. • Our planet is becoming increasingly crowded. • Over 80% of the world’s population lives in poor and less-developed countries. • Managers are responsible for the efficient and effective use of the basic factors of production— land, labor, and capital. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 9
Making the Most of Limited Resources • We live in a world of scarcity. • There is a lopsided use of resources. • Our planet is becoming increasingly crowded. • Over 80% of the world’s population lives in poor and less-developed countries. • Managers are responsible for the efficient and effective use of the basic factors of production— land, labor, and capital. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 9
 Coping with a Changing Environment • Five Major Sources of Change for Today’s Managers – Globalization – Environmentalism – An ethical reawakening – The Internet and the e-business revolution – The evolution of product quality Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 10
Coping with a Changing Environment • Five Major Sources of Change for Today’s Managers – Globalization – Environmentalism – An ethical reawakening – The Internet and the e-business revolution – The evolution of product quality Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 10
 The Evolution Of Product Quality • The fix-it-in approach – Rework defective products after they are produced. • The inspect-it-in approach – Sample work-in-process and adjust machines to avoid substandard output • The build-it-in approach – Identify and eliminate the causes of defects • The design-it-in approach – Continuous improvement eliminates defects Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11
The Evolution Of Product Quality • The fix-it-in approach – Rework defective products after they are produced. • The inspect-it-in approach – Sample work-in-process and adjust machines to avoid substandard output • The build-it-in approach – Identify and eliminate the causes of defects • The design-it-in approach – Continuous improvement eliminates defects Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11
 Ethical Problems in the Workplace • Lying to supervisors • Lying on reports or falsifying records • Stealing and theft • Sexual harassment • Abusing drugs or alcohol • Conflict of interest Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 12
Ethical Problems in the Workplace • Lying to supervisors • Lying on reports or falsifying records • Stealing and theft • Sexual harassment • Abusing drugs or alcohol • Conflict of interest Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 12
 The Internet and E-Business Revolution • The Internet – A global network of integrated servers and computers – Began as a government project to allow researchers to share information – Became the World Wide Web (WWW) • E-business – A business using the Internet for greater efficiency in every respect of its operations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 13
The Internet and E-Business Revolution • The Internet – A global network of integrated servers and computers – Began as a government project to allow researchers to share information – Became the World Wide Web (WWW) • E-business – A business using the Internet for greater efficiency in every respect of its operations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 13
 Figure 1. 3 Identifiable Functions in the Management Process Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 14
Figure 1. 3 Identifiable Functions in the Management Process Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 14
 Managerial Functions • Planning – Formulating future courses of action. • Decision making – Choosing among the alternatives for action. • Organizing – Deciding on the HR structure of the organization. • Staffing – Recruiting, training, and developing people. • Communicating – Providing information, direction, and feedback. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 15
Managerial Functions • Planning – Formulating future courses of action. • Decision making – Choosing among the alternatives for action. • Organizing – Deciding on the HR structure of the organization. • Staffing – Recruiting, training, and developing people. • Communicating – Providing information, direction, and feedback. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 15
 Managerial Functions (cont’d) • Motivating – Providing meaningful work and valued rewards to individuals pursuing collective objectives. • Leading – Serving as role models and adapting management styles as the situation demands. • Controlling – Comparing desired results with actual results and taking corrective action as needed. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 16
Managerial Functions (cont’d) • Motivating – Providing meaningful work and valued rewards to individuals pursuing collective objectives. • Leading – Serving as role models and adapting management styles as the situation demands. • Controlling – Comparing desired results with actual results and taking corrective action as needed. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 16
 Managerial Facts of Life: What Managers Lose the Right to Do • Lose their temper. • Get even with adversaries. • Be one of the gang. • Play favorites. • Bring personal problems to work. • Put self-interests first. • Vent frustrations and express opinions at work. • Resist change. • Pass the buck on tough assignments. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. • Ask others to do what they wouldn’t do. • Expect to be immediately recognized and rewarded for doing a good job. 17
Managerial Facts of Life: What Managers Lose the Right to Do • Lose their temper. • Get even with adversaries. • Be one of the gang. • Play favorites. • Bring personal problems to work. • Put self-interests first. • Vent frustrations and express opinions at work. • Resist change. • Pass the buck on tough assignments. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. • Ask others to do what they wouldn’t do. • Expect to be immediately recognized and rewarded for doing a good job. 17
 Learning to Manage • How Do Managers Learn to Manage? – By attending the school of “hard knocks” – Making a big mistake. – Being overstretched by a difficult assignment. – Feeling threatened. – Being stuck in an impasse or dilemma. – Suffering an injustice at work. – Losing out to someone else. – Being personally attacked. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 18
Learning to Manage • How Do Managers Learn to Manage? – By attending the school of “hard knocks” – Making a big mistake. – Being overstretched by a difficult assignment. – Feeling threatened. – Being stuck in an impasse or dilemma. – Suffering an injustice at work. – Losing out to someone else. – Being personally attacked. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 18
 How Can Future Managers Learn to Manage? • Future managers can learn by – Integrating management theory (i. E. , Formal training and education) and managerial practice (e. G. , Workstudy and internships). – Observing role models. – Learning from experiences in the school of “hard knocks”. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 19
How Can Future Managers Learn to Manage? • Future managers can learn by – Integrating management theory (i. E. , Formal training and education) and managerial practice (e. G. , Workstudy and internships). – Observing role models. – Learning from experiences in the school of “hard knocks”. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 19
 Small-Business Management • What is a Small Business? – An independently owned and managed profit-seeking enterprise with fewer than 100 employees. • Exploding Myths About Small Businesses – The 80 -percent-failure-rate myth – Research shows a failure rate of only 18% for small businesses over an 8 -year period. – Low-wage-jobs myth – Rapidly growing small businesses (“gazelles”) accounted for 56% of new job growth and added to the majority of high paying jobs from 1980 to 1990. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 20
Small-Business Management • What is a Small Business? – An independently owned and managed profit-seeking enterprise with fewer than 100 employees. • Exploding Myths About Small Businesses – The 80 -percent-failure-rate myth – Research shows a failure rate of only 18% for small businesses over an 8 -year period. – Low-wage-jobs myth – Rapidly growing small businesses (“gazelles”) accounted for 56% of new job growth and added to the majority of high paying jobs from 1980 to 1990. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 20
 Entrepreneurship • Entrepreneurship – The process by which individuals–either on their own or inside organizations–pursue opportunities without regard to the resources they currently control. • Entrepreneur’s Dilemma – Either grow with the company or have the courage to step aside and turn control over to professional managers with the requisite administrative skills. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 21
Entrepreneurship • Entrepreneurship – The process by which individuals–either on their own or inside organizations–pursue opportunities without regard to the resources they currently control. • Entrepreneur’s Dilemma – Either grow with the company or have the courage to step aside and turn control over to professional managers with the requisite administrative skills. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 21


