c46ba472da7440edd46802e8c3de041e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Services Marketing Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 1
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Services Marketing Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 1
 Overview of Chapter 1 = Why study services? = Powerful forces that are transforming service Markets = What are services? = Four broad categories of services = Challenges posed by services = Expanded marketing mix for services = Framework for effective services marketing strategies Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 2
Overview of Chapter 1 = Why study services? = Powerful forces that are transforming service Markets = What are services? = Four broad categories of services = Challenges posed by services = Expanded marketing mix for services = Framework for effective services marketing strategies Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 2
 Why Study Services? Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 3
Why Study Services? Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 3
 Why Study Services? = Services Dominate Economy in Most Nations = Most New Jobs are Generated by Services è Fastest Growth Expected in Knowledge-Based Industries è Many New Jobs are Well-Paid Positions Requiring Good Educational Qualifications = Many manufacturing firms moved to marketing stand- alone services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 4
Why Study Services? = Services Dominate Economy in Most Nations = Most New Jobs are Generated by Services è Fastest Growth Expected in Knowledge-Based Industries è Many New Jobs are Well-Paid Positions Requiring Good Educational Qualifications = Many manufacturing firms moved to marketing stand- alone services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 4
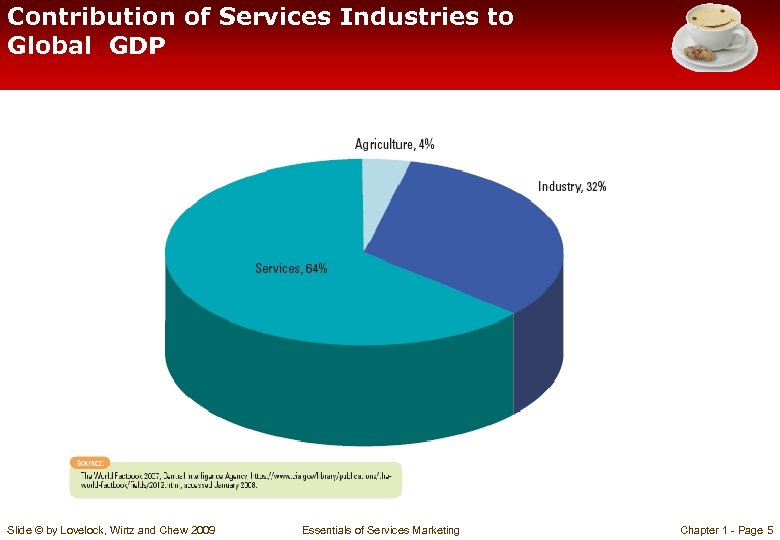 Contribution of Services Industries to Global GDP Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 5
Contribution of Services Industries to Global GDP Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 5
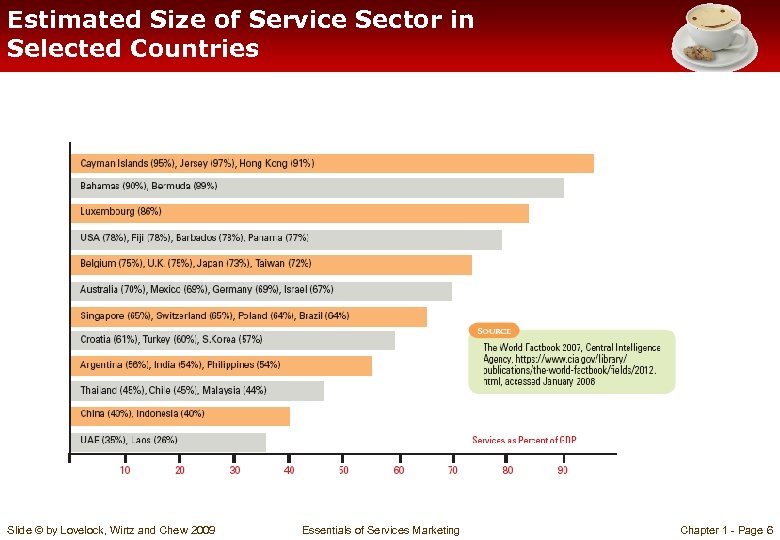 Estimated Size of Service Sector in Selected Countries Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 6
Estimated Size of Service Sector in Selected Countries Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 6
 Powerful Forces Are Transforming Service Markets Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 7
Powerful Forces Are Transforming Service Markets Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 7
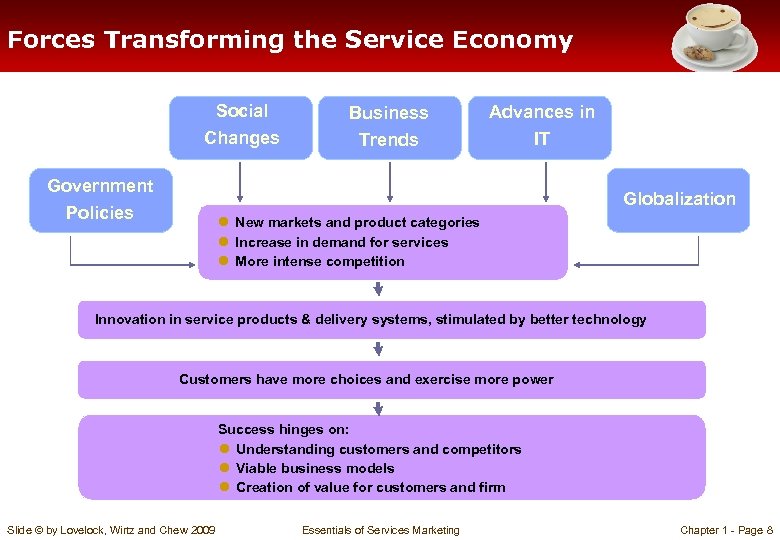 Forces Transforming the Service Economy Social Changes Government Policies Business Trends Advances in IT ● New markets and product categories ● Increase in demand for services ● More intense competition Globalization Innovation in service products & delivery systems, stimulated by better technology Customers have more choices and exercise more power Success hinges on: ● Understanding customers and competitors ● Viable business models ● Creation of value for customers and firm Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 8
Forces Transforming the Service Economy Social Changes Government Policies Business Trends Advances in IT ● New markets and product categories ● Increase in demand for services ● More intense competition Globalization Innovation in service products & delivery systems, stimulated by better technology Customers have more choices and exercise more power Success hinges on: ● Understanding customers and competitors ● Viable business models ● Creation of value for customers and firm Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 8
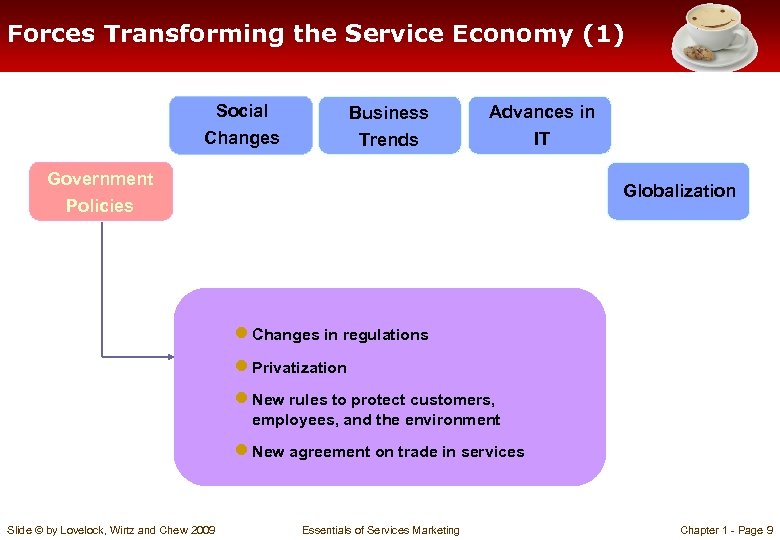 Forces Transforming the Service Economy (1) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● Changes in regulations ● Privatization ● New rules to protect customers, employees, and the environment ● New agreement on trade in services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 9
Forces Transforming the Service Economy (1) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● Changes in regulations ● Privatization ● New rules to protect customers, employees, and the environment ● New agreement on trade in services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 9
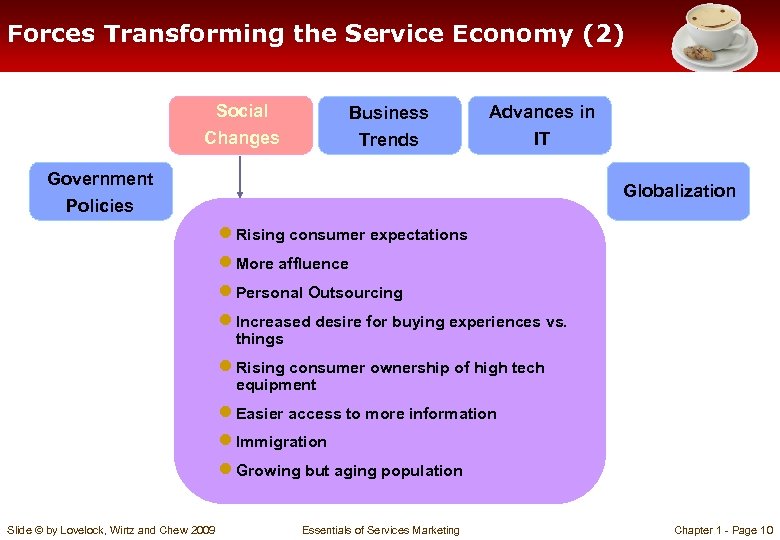 Forces Transforming the Service Economy (2) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● Rising consumer expectations ● More affluence ● Personal Outsourcing ● Increased desire for buying experiences vs. things ● Rising consumer ownership of high tech equipment ● Easier access to more information ● Immigration ● Growing but aging population Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 10
Forces Transforming the Service Economy (2) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● Rising consumer expectations ● More affluence ● Personal Outsourcing ● Increased desire for buying experiences vs. things ● Rising consumer ownership of high tech equipment ● Easier access to more information ● Immigration ● Growing but aging population Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 10
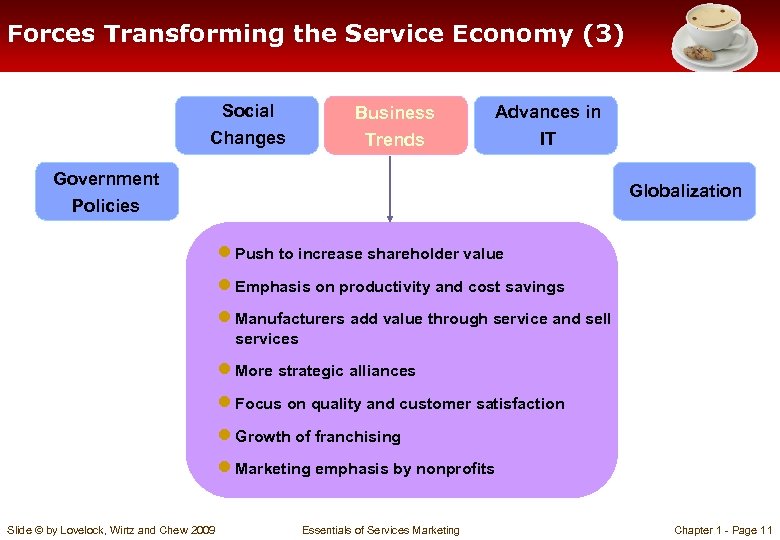 Forces Transforming the Service Economy (3) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● Push to increase shareholder value ● Emphasis on productivity and cost savings ● Manufacturers add value through service and sell services ● More strategic alliances ● Focus on quality and customer satisfaction ● Growth of franchising ● Marketing emphasis by nonprofits Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 11
Forces Transforming the Service Economy (3) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● Push to increase shareholder value ● Emphasis on productivity and cost savings ● Manufacturers add value through service and sell services ● More strategic alliances ● Focus on quality and customer satisfaction ● Growth of franchising ● Marketing emphasis by nonprofits Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 11
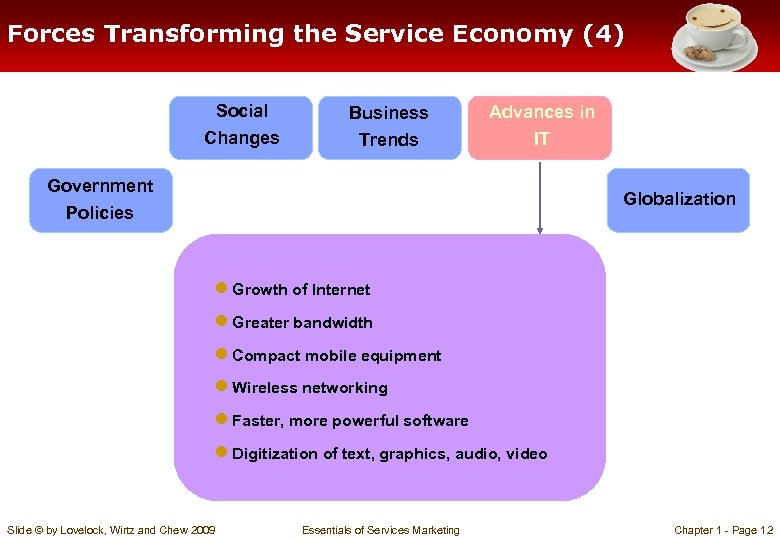 Forces Transforming the Service Economy (4) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● Growth of Internet ● Greater bandwidth ● Compact mobile equipment ● Wireless networking ● Faster, more powerful software ● Digitization of text, graphics, audio, video Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 12
Forces Transforming the Service Economy (4) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● Growth of Internet ● Greater bandwidth ● Compact mobile equipment ● Wireless networking ● Faster, more powerful software ● Digitization of text, graphics, audio, video Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 12
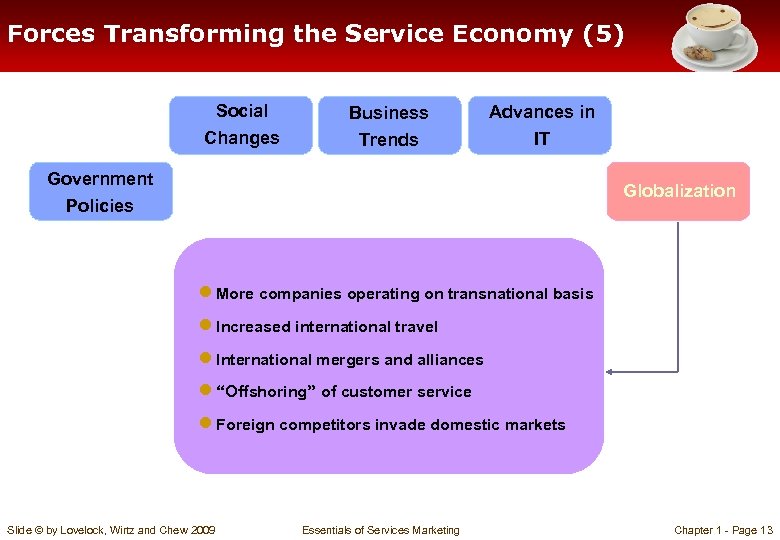 Forces Transforming the Service Economy (5) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● More companies operating on transnational basis ● Increased international travel ● International mergers and alliances ● “Offshoring” of customer service ● Foreign competitors invade domestic markets Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 13
Forces Transforming the Service Economy (5) Social Changes Business Trends Advances in IT Government Policies Globalization ● More companies operating on transnational basis ● Increased international travel ● International mergers and alliances ● “Offshoring” of customer service ● Foreign competitors invade domestic markets Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 13
 What Are Services? Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 14
What Are Services? Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 14
 What are Services? (1) = Services involve a form of rental, offering benefits without transfer of ownership èInclude rental of goods èMarketing tasks for services differ from those involved in selling goods and transferring ownership Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 15
What are Services? (1) = Services involve a form of rental, offering benefits without transfer of ownership èInclude rental of goods èMarketing tasks for services differ from those involved in selling goods and transferring ownership Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 15
 What are Services? (2) = Five broad categories within non-ownership framework: 1. Rented goods services 2. Defined space and place rentals 3. Labor and expertise rentals 4. Access to shared physical environments 5. Systems and networks: access and usage Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 16
What are Services? (2) = Five broad categories within non-ownership framework: 1. Rented goods services 2. Defined space and place rentals 3. Labor and expertise rentals 4. Access to shared physical environments 5. Systems and networks: access and usage Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 16
 What are Services? (3) = Implications of Renting Versus Owning (Service Insights 1. 1) è Markets exist for renting durable goods rather than selling them è Renting portions of larger physical entity (e. g. , office space, apartment) can form basis for service è Customers more closely engaged with service suppliers è Time plays central role in most services è Customer choice criteria may differ between rentals and outright purchases è Services offer opportunities for resource sharing Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 17
What are Services? (3) = Implications of Renting Versus Owning (Service Insights 1. 1) è Markets exist for renting durable goods rather than selling them è Renting portions of larger physical entity (e. g. , office space, apartment) can form basis for service è Customers more closely engaged with service suppliers è Time plays central role in most services è Customer choice criteria may differ between rentals and outright purchases è Services offer opportunities for resource sharing Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 17
 Four Broad Categories of Services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 18
Four Broad Categories of Services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 18
 Four Broad Categories of Services = Based on differences in nature of service act (tangible/intangible) and who or what is direct recipient of service (people/possessions), there are four categories of services: èPeople processing èPossession processing èMental stimulus processing èInformation processing Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 19
Four Broad Categories of Services = Based on differences in nature of service act (tangible/intangible) and who or what is direct recipient of service (people/possessions), there are four categories of services: èPeople processing èPossession processing èMental stimulus processing èInformation processing Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 19
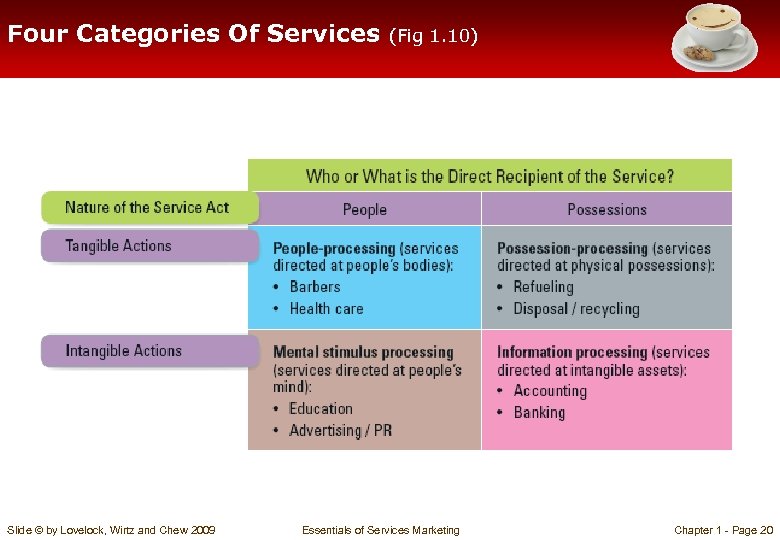 Four Categories Of Services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 (Fig 1. 10) Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 20
Four Categories Of Services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 (Fig 1. 10) Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 20
 Four Categories Of Services = People Processing = Customers must: è physically enter the service factory è co-operate actively with the service operation = Managers should think about process and output from customer’s perspective è to identify benefits created and non-financial costs: - Time, mental, physical effort Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 21
Four Categories Of Services = People Processing = Customers must: è physically enter the service factory è co-operate actively with the service operation = Managers should think about process and output from customer’s perspective è to identify benefits created and non-financial costs: - Time, mental, physical effort Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 21
 Possession Processing §Customers are less physically involved compared to people processing services §Involvement is limited §Production and consumption are separable Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 22
Possession Processing §Customers are less physically involved compared to people processing services §Involvement is limited §Production and consumption are separable Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 22
 Mental Stimulus Processing ● Ethical standards required when customers who depend on such services can potentially be manipulated by suppliers ● Physical presence of recipients not required ● Core content of services is information-based èCan be ‘inventoried’ Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 23
Mental Stimulus Processing ● Ethical standards required when customers who depend on such services can potentially be manipulated by suppliers ● Physical presence of recipients not required ● Core content of services is information-based èCan be ‘inventoried’ Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 23
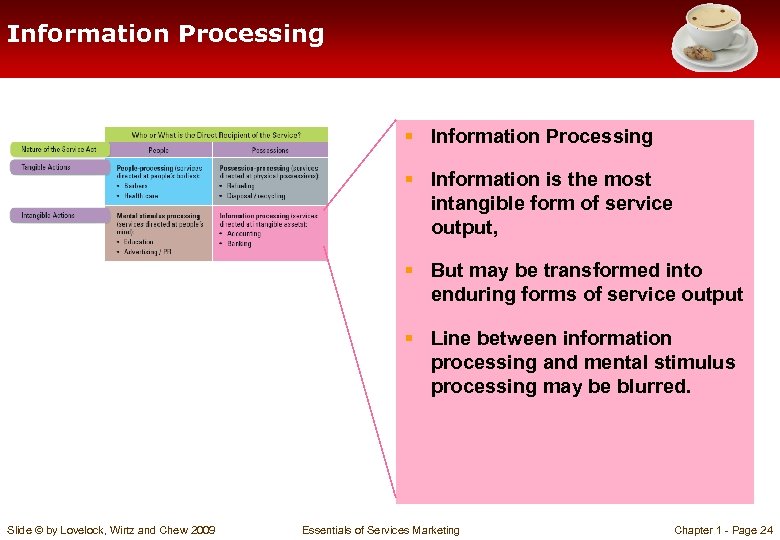 Information Processing § Information is the most intangible form of service output, § But may be transformed into enduring forms of service output § Line between information processing and mental stimulus processing may be blurred. Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 24
Information Processing § Information is the most intangible form of service output, § But may be transformed into enduring forms of service output § Line between information processing and mental stimulus processing may be blurred. Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 24
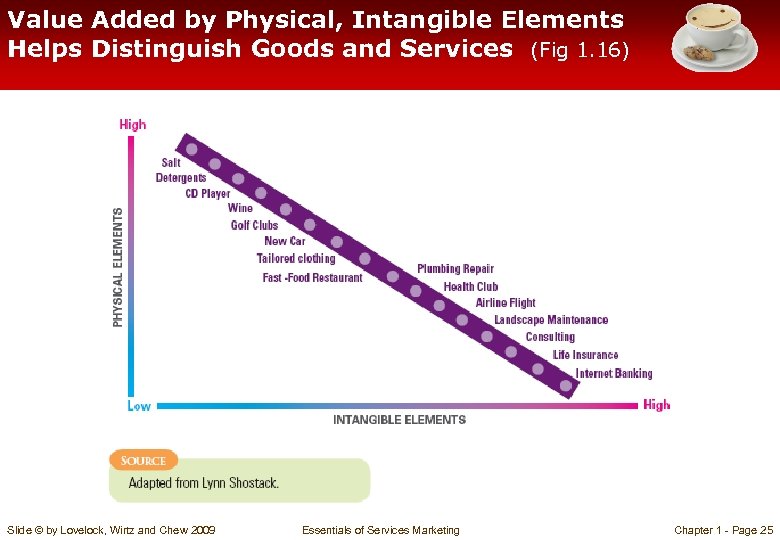 Value Added by Physical, Intangible Elements Helps Distinguish Goods and Services (Fig 1. 16) Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 25
Value Added by Physical, Intangible Elements Helps Distinguish Goods and Services (Fig 1. 16) Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 25
 Defining Services = Services è Are economic activities offered by one party to another è Most commonly employ time-based performances to bring about desired results in: - Recipients themselves - Objects or other assets for which purchasers have responsibility = In exchange for their money, time, and effort, service customers expect to obtain value from è Access to goods, labor, facilities, environments, professional skills, networks, and systems; è But they do not normally take ownership of any of the physical elements involved. Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 26
Defining Services = Services è Are economic activities offered by one party to another è Most commonly employ time-based performances to bring about desired results in: - Recipients themselves - Objects or other assets for which purchasers have responsibility = In exchange for their money, time, and effort, service customers expect to obtain value from è Access to goods, labor, facilities, environments, professional skills, networks, and systems; è But they do not normally take ownership of any of the physical elements involved. Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 26
 Challenges Posed by Services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 27
Challenges Posed by Services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 27
 Services Pose Distinctive Marketing Challenges = Marketing management tasks in the service sector differ from those in the manufacturing sector. = The eight common differences are: è Most service products cannot be inventoried è Intangible elements usually dominate value creation è Services are often difficult to visualize and understand è Customers may be involved in co-production è People may be part of the service experience è Operational inputs and outputs tend to vary more widely è The time factor often assumes great importance è Distribution may take place through nonphysical channels Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 28
Services Pose Distinctive Marketing Challenges = Marketing management tasks in the service sector differ from those in the manufacturing sector. = The eight common differences are: è Most service products cannot be inventoried è Intangible elements usually dominate value creation è Services are often difficult to visualize and understand è Customers may be involved in co-production è People may be part of the service experience è Operational inputs and outputs tend to vary more widely è The time factor often assumes great importance è Distribution may take place through nonphysical channels Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 28
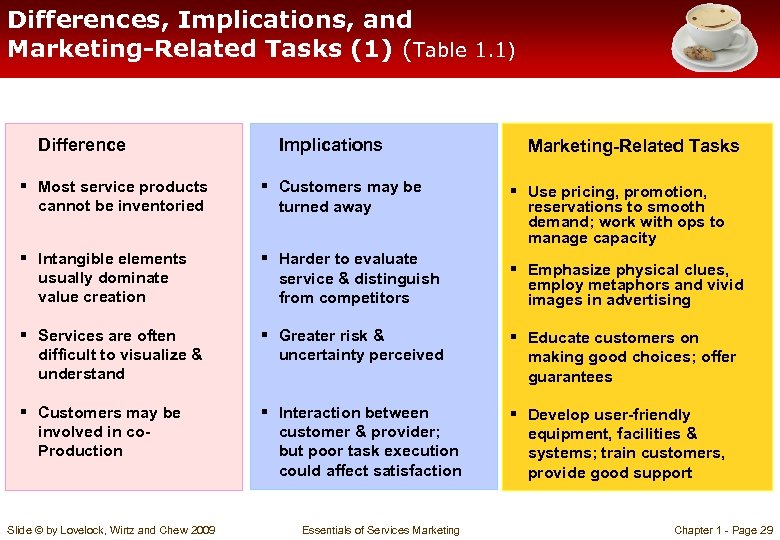 Differences, Implications, and Marketing-Related Tasks (1) (Table 1. 1) Difference Implications Marketing-Related Tasks § Most service products cannot be inventoried § Customers may be turned away § Intangible elements usually dominate value creation § Harder to evaluate service & distinguish from competitors § Services are often difficult to visualize & understand § Greater risk & uncertainty perceived § Educate customers on making good choices; offer guarantees § Customers may be involved in co. Production § Interaction between customer & provider; but poor task execution could affect satisfaction § Develop user-friendly equipment, facilities & systems; train customers, provide good support Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing § Use pricing, promotion, reservations to smooth demand; work with ops to manage capacity § Emphasize physical clues, employ metaphors and vivid images in advertising Chapter 1 - Page 29
Differences, Implications, and Marketing-Related Tasks (1) (Table 1. 1) Difference Implications Marketing-Related Tasks § Most service products cannot be inventoried § Customers may be turned away § Intangible elements usually dominate value creation § Harder to evaluate service & distinguish from competitors § Services are often difficult to visualize & understand § Greater risk & uncertainty perceived § Educate customers on making good choices; offer guarantees § Customers may be involved in co. Production § Interaction between customer & provider; but poor task execution could affect satisfaction § Develop user-friendly equipment, facilities & systems; train customers, provide good support Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing § Use pricing, promotion, reservations to smooth demand; work with ops to manage capacity § Emphasize physical clues, employ metaphors and vivid images in advertising Chapter 1 - Page 29
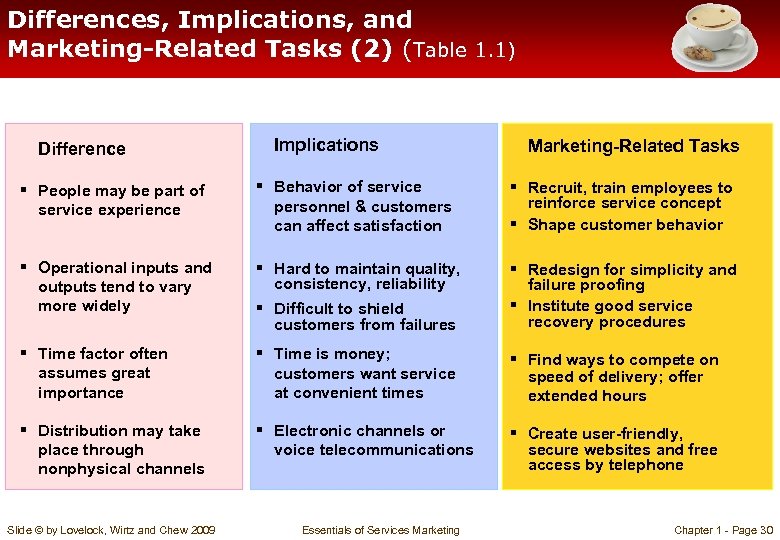 Differences, Implications, and Marketing-Related Tasks (2) (Table 1. 1) Difference Implications Marketing-Related Tasks § People may be part of service experience § Behavior of service personnel & customers can affect satisfaction § Recruit, train employees to reinforce service concept § Shape customer behavior § Operational inputs and outputs tend to vary more widely § Hard to maintain quality, consistency, reliability § Difficult to shield customers from failures § Redesign for simplicity and failure proofing § Institute good service recovery procedures § Time factor often assumes great importance § Time is money; customers want service at convenient times § Find ways to compete on speed of delivery; offer extended hours § Distribution may take place through nonphysical channels § Electronic channels or voice telecommunications § Create user-friendly, secure websites and free access by telephone Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 30
Differences, Implications, and Marketing-Related Tasks (2) (Table 1. 1) Difference Implications Marketing-Related Tasks § People may be part of service experience § Behavior of service personnel & customers can affect satisfaction § Recruit, train employees to reinforce service concept § Shape customer behavior § Operational inputs and outputs tend to vary more widely § Hard to maintain quality, consistency, reliability § Difficult to shield customers from failures § Redesign for simplicity and failure proofing § Institute good service recovery procedures § Time factor often assumes great importance § Time is money; customers want service at convenient times § Find ways to compete on speed of delivery; offer extended hours § Distribution may take place through nonphysical channels § Electronic channels or voice telecommunications § Create user-friendly, secure websites and free access by telephone Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 30
 Expanded Marketing Mix for Services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 31
Expanded Marketing Mix for Services Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 31
 Services Require An Expanded Marketing Mix ● Marketing can be viewed as: è A strategic and competitive thrust pursued by top management è A set of functional activities performed by line managers è A customer-driven orientation for the entire organization ● Marketing is only function to bring operating revenues into a business; all other functions are cost centers. ● The “ 7 Ps” of services marketing are needed to create viable strategies for meeting customer needs profitably in a competitive marketplace Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 32
Services Require An Expanded Marketing Mix ● Marketing can be viewed as: è A strategic and competitive thrust pursued by top management è A set of functional activities performed by line managers è A customer-driven orientation for the entire organization ● Marketing is only function to bring operating revenues into a business; all other functions are cost centers. ● The “ 7 Ps” of services marketing are needed to create viable strategies for meeting customer needs profitably in a competitive marketplace Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 32
 The 7 Ps of Services Marketing ● Product elements (Chapter 4) ● Place and time (Chapter 5) ● Price and other user outlays (Chapter 6) ● Promotion and education (Chapter 7) ● Process (Chapter 8) ● Physical environment (Chapter 10) ● People (Chapter 11) Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 33
The 7 Ps of Services Marketing ● Product elements (Chapter 4) ● Place and time (Chapter 5) ● Price and other user outlays (Chapter 6) ● Promotion and education (Chapter 7) ● Process (Chapter 8) ● Physical environment (Chapter 10) ● People (Chapter 11) Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 33
 Traditional 4 Ps Applied to Services (1) = Product elements è Service products are at the heart of services marketing strategy è Marketing mix begins with creating service concept that offers value è Service product consists of core and supplementary elements - Core products meet primary needs - Supplementary elements are value-added enhancements Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 34
Traditional 4 Ps Applied to Services (1) = Product elements è Service products are at the heart of services marketing strategy è Marketing mix begins with creating service concept that offers value è Service product consists of core and supplementary elements - Core products meet primary needs - Supplementary elements are value-added enhancements Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 34
 Traditional 4 Ps Applied to Services (2) = Place and time è Service distribution can take place through physical and nonphysical channels è Some firms can use electronic channels to deliver all (or at least some) of their service elements è Information-based services can be delivered almost instantaneously electronically è Delivery Decisions: Where, When, How è Time is of great importance as customers are physically present è Convenience of place and time become important determinants of effective service delivery Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 35
Traditional 4 Ps Applied to Services (2) = Place and time è Service distribution can take place through physical and nonphysical channels è Some firms can use electronic channels to deliver all (or at least some) of their service elements è Information-based services can be delivered almost instantaneously electronically è Delivery Decisions: Where, When, How è Time is of great importance as customers are physically present è Convenience of place and time become important determinants of effective service delivery Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 35
 Traditional 4 Ps Applied to Services (3) = Price and other user outlays è From the firm’s perspective, pricing generates income and creates profits è From the customer’s perspective, pricing is key part of costs to obtained wanted benefits è Marketers must recognize that customer costs involve more than price paid to seller è Identify and minimize non-monetary costs incurred by users: - Additional monetary costs associated with service usage (e. g. , travel to service location, parking, phone, babysitting, etc. ) - Time expenditures, especially waiting - Unwanted mental and physical effort - Negative sensory experiences è Revenue management is an important part of pricing Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 36
Traditional 4 Ps Applied to Services (3) = Price and other user outlays è From the firm’s perspective, pricing generates income and creates profits è From the customer’s perspective, pricing is key part of costs to obtained wanted benefits è Marketers must recognize that customer costs involve more than price paid to seller è Identify and minimize non-monetary costs incurred by users: - Additional monetary costs associated with service usage (e. g. , travel to service location, parking, phone, babysitting, etc. ) - Time expenditures, especially waiting - Unwanted mental and physical effort - Negative sensory experiences è Revenue management is an important part of pricing Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 36
 Traditional 4 Ps Applied to Services (4) = Promotion and Education èPlays three vital roles: - Provide information and advice - Persuades the target customers of merit of service product or brand - Encourages customer to take action at specific time èCustomers may be involved in co-production so: - Teach customer how to move effectively through the service process - Shape customers’ roles and manage their behavior Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 37
Traditional 4 Ps Applied to Services (4) = Promotion and Education èPlays three vital roles: - Provide information and advice - Persuades the target customers of merit of service product or brand - Encourages customer to take action at specific time èCustomers may be involved in co-production so: - Teach customer how to move effectively through the service process - Shape customers’ roles and manage their behavior Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 37
 Extended Mix for Managing the Customer Interface (1) = Process è How firm does things may be as important as what it does è Customers often actively involved in processes, especially when acting as coproducers of service è Operational inputs and outputs vary more widely - Quality and content varies among employees, between employees - Variations can be with different customers - Variations from time of the day è Variability can be reduced by: - Standardized procedures - Implementing rigorous management of service quality - Training employees more carefully - Automating tasks - Train employees in service recovery procedures è Manage process design and “flow of customers Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 38
Extended Mix for Managing the Customer Interface (1) = Process è How firm does things may be as important as what it does è Customers often actively involved in processes, especially when acting as coproducers of service è Operational inputs and outputs vary more widely - Quality and content varies among employees, between employees - Variations can be with different customers - Variations from time of the day è Variability can be reduced by: - Standardized procedures - Implementing rigorous management of service quality - Training employees more carefully - Automating tasks - Train employees in service recovery procedures è Manage process design and “flow of customers Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 38
 Extended Mix for Managing the Customer Interface (2) = Physical environment è Design servicescape and provide tangible evidence of service performances è Create and maintain physical appearances - Buildings/landscaping - Interior design/furnishings - Vehicles/equipment - Staff grooming/clothing - Sounds and smells - Other tangibles è Manage physical cues carefully— can have profound impact on customer impressions Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 39
Extended Mix for Managing the Customer Interface (2) = Physical environment è Design servicescape and provide tangible evidence of service performances è Create and maintain physical appearances - Buildings/landscaping - Interior design/furnishings - Vehicles/equipment - Staff grooming/clothing - Sounds and smells - Other tangibles è Manage physical cues carefully— can have profound impact on customer impressions Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 39
 Extended Mix for Managing the Customer Interface (3) = People è Interactions between customers and contact personnel strongly influence customer perceptions of service quality è Well-managed firms devote special care to selecting, training and motivating service employees è Other customers can also affect one’s satisfaction with a service Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 40
Extended Mix for Managing the Customer Interface (3) = People è Interactions between customers and contact personnel strongly influence customer perceptions of service quality è Well-managed firms devote special care to selecting, training and motivating service employees è Other customers can also affect one’s satisfaction with a service Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 40
 Framework for Effective Service Marketing Strategies Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 41
Framework for Effective Service Marketing Strategies Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 41
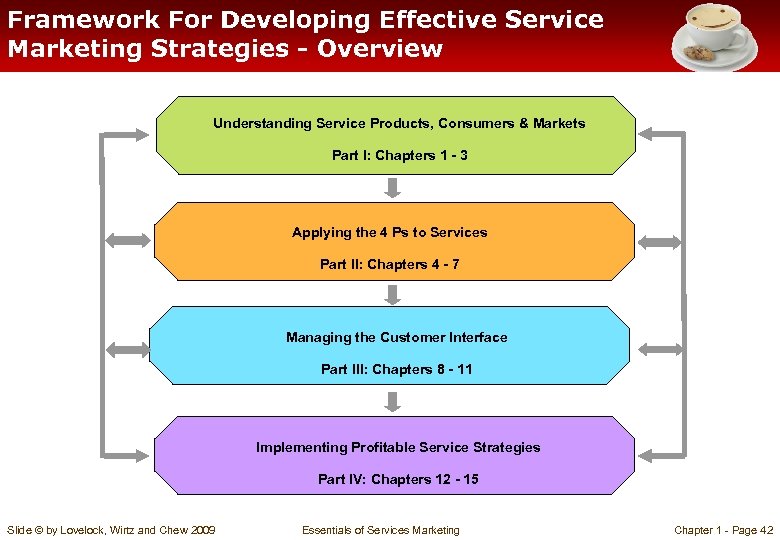 Framework For Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies - Overview Understanding Service Products, Consumers & Markets Part I: Chapters 1 - 3 Applying the 4 Ps to Services Part II: Chapters 4 - 7 Managing the Customer Interface Part III: Chapters 8 - 11 Implementing Profitable Service Strategies Part IV: Chapters 12 - 15 Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 42
Framework For Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies - Overview Understanding Service Products, Consumers & Markets Part I: Chapters 1 - 3 Applying the 4 Ps to Services Part II: Chapters 4 - 7 Managing the Customer Interface Part III: Chapters 8 - 11 Implementing Profitable Service Strategies Part IV: Chapters 12 - 15 Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 42
 Framework for Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies- Part I Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 43
Framework for Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies- Part I Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 43
 Framework for Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies – Part II Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 44
Framework for Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies – Part II Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 44
 Framework for Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies – Part III Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 45
Framework for Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies – Part III Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 45
 Framework for Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies – Part IV Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 46
Framework for Developing Effective Service Marketing Strategies – Part IV Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 46
 Chapter 1 Summary: Introduction to Services Marketing (1) = Reasons for studying services è Service sector dominates economy in most nations è Most new jobs are generated by services è Powerful forces—government policies, social changes, business trends, IT advances, and globalization—are transforming service markets = The service concept and its definition: è Services offer benefits without transfer of ownership è Four broad categories of services – people processing, possession processing, mental stimulus processing and information processing è Customers expect value from access to goods, facilities, labor, professional skills, environments, networks & systems in return for money, time, effort Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 47
Chapter 1 Summary: Introduction to Services Marketing (1) = Reasons for studying services è Service sector dominates economy in most nations è Most new jobs are generated by services è Powerful forces—government policies, social changes, business trends, IT advances, and globalization—are transforming service markets = The service concept and its definition: è Services offer benefits without transfer of ownership è Four broad categories of services – people processing, possession processing, mental stimulus processing and information processing è Customers expect value from access to goods, facilities, labor, professional skills, environments, networks & systems in return for money, time, effort Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 47
 Chapter 1 Summary: Introduction to Services Marketing (2) = Services present distinctive marketing challenges relative to goods, requiring: è Expanded marketing mix comprising 7 Ps instead of traditional 4 Ps = Framework for developing effective services marketing strategies: è Understanding service products, consumers & markets è Applying the 4 Ps to services è Managing the customer interface è Implementing profitable service strategies Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 48
Chapter 1 Summary: Introduction to Services Marketing (2) = Services present distinctive marketing challenges relative to goods, requiring: è Expanded marketing mix comprising 7 Ps instead of traditional 4 Ps = Framework for developing effective services marketing strategies: è Understanding service products, consumers & markets è Applying the 4 Ps to services è Managing the customer interface è Implementing profitable service strategies Slide © by Lovelock, Wirtz and Chew 2009 Essentials of Services Marketing Chapter 1 - Page 48


