802fc4f99b82753deb14e6c2cb571447.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 97

Chapter 1 Introduction to Public Relations

Definition BIPR n. PR is the planned and sustained effort to establish and maintain goodwill and mutual understanding between an organization and its publics
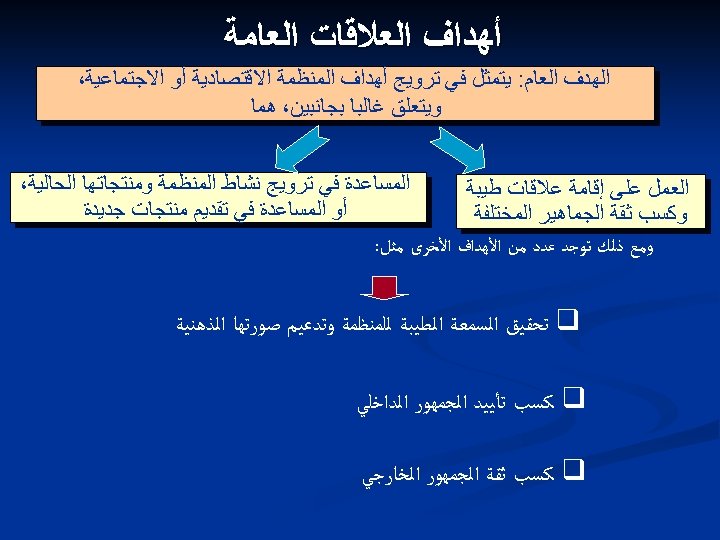
ﺃﻬﺪﺍﻑ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻡ: ﻳﺘﻤﺜﻞ ﻓﻲ ﺗﺮﻭﻳﺞ ﺃﻬﺪﺍﻑ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻻﻗﺘﺼﺎﺩﻳﺔ ﺃﻮ ﺍﻻﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻴﺔ، ﻭﻳﺘﻌﻠﻖ ﻏﺎﻟﺒﺎ ﺑﺠﺎﻧﺒﻴﻦ، ﻫﻤﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻓﻲ ﺗﺮﻭﻳﺞ ﻧﺸﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﻣﻨﺘﺠﺎﺗﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ، ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻞ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺇﻗﺎﻣﺔ ﻋﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﻃﻴﺒﺔ ﺃﻮ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻓﻲ ﺗﻘﺪﻳﻢ ﻣﻨﺘﺠﺎﺕ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ ﻭﻛﺴﺐ ﺛﻘﺔ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﺎﻫﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ ﻭﻣﻊ ﺫﻟﻚ ﺗﻮﺟﺪ ﻋﺪﺩ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻬﺪﺍﻑ ﺍﻷﺨﺮﻯ ﻣﺜﻞ: q ﺗﺤﻘﻴﻖ ﺍﻟﺴﻤﻌﺔ ﺍﻟﻄﻴﺒﺔ ﻟﻠﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﺗﺪﻋﻴﻢ ﺻﻮﺭﺗﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺬﻫﻨﻴﺔ q ﻛﺴﺐ ﺗﺄﻴﻴﺪ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻬﻮﺭ ﺍﻟﺪﺍﺧﻠﻲ q ﻛﺴﺐ ﺛﻘﺔ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻬﻮﺭ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺭﺟﻲ
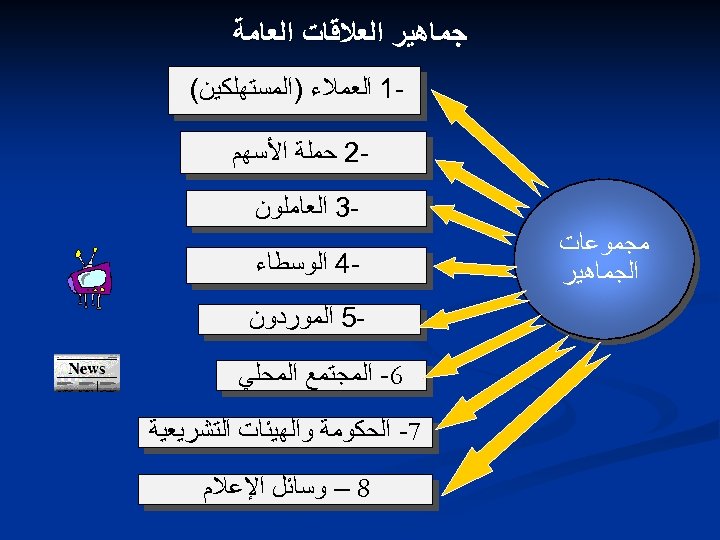
ﺟﻤﺎﻫﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻣﺔ 1 ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼﺀ )ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻬﻠﻜﻴﻦ( 2 ﺣﻤﻠﺔ ﺍﻷﺴﻬﻢ 3 ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻣﻠﻮﻥ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﺎﻫﻴﺮ 4 ﺍﻟﻮﺳﻄﺎﺀ 5 ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺭﺩﻭﻥ 6 - ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺘﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﻠﻲ 7 - ﺍﻟﺤﻜﻮﻣﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻬﻴﺌﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﺮﻳﻌﻴﺔ 8 – ﻭﺳﺎﺋﻞ ﺍﻹﻋﻼﻡ

ﺍﻟﺪﻭﺭ ﺍﻟﺤﺪﻳﺚ ﻟﻠﻌﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌـﺎﻣﺔ ﺍﻟـﺪﻭﺭ ﺍﻻﺳﺘـﺮﺍﺗﻴـﺠــﻰ q ﺻﻴﺎﻏﺔ ﺭﺳﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﺭﺅﻴﺘﻬﺎ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺔ. q ﺩﺭﺍﺳﺔ ﻋﻮﺍﻣﻞ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺌﺔ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺭﺟﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺆﺜﺮﺓ ﻋﻠﻲ ﻧﺸﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﺍﻟﻔﺮﺹ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻬﺪﻳﺪﺍﺕ. q ﺩﺭﺍﺳﺔ ﻋﻮﺍﻣﻞ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺌﺔ ﺍﻟﺪﺍﺧﻠﻴﺔ ﻭﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﻧﻘﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﻀﻌﻒ ﺩﺍﺧﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ. q ﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﺍﻟﺒﺪﺍﺋﻞ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﺎﺣﺔ ﻟﻠﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﻣﺪﻱ ﺗﻤﺸﻴﻬﺎ ﻣﻊ ﺭﺳﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﺻﻮﺭﺗﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺬﻫﻨﻴﺔ. q ﻭﺿﻊ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺪﻋﻢ ﻣﻦ ﺍﺳﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﺗﺴﻬﻢ ﻓﻲ ﺗﺤﻘﻴﻖ ﻣﺮﻛﺰ ﺗﻨﺎﻓﺴﻲ ﻣﻤﻴﺰ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺴﻮﻕ.

ﺍﻟــﺪﻭﺭ ﺍﻟﺒﻴـﺌــﻰ q ﺩﺭﺍﺳﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺿﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﺫﺍﺕ ﺍﻻﻫﺘﻤﺎﻡ ﻣﻦ ﺟﺎﻧﺐ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺪﻭﻟﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻷﻬﻠﻴﺔ ﻭﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﺃﻮﻟﻮﻳﺎﺗﻬﺎ ﻭﻣﺪﻱ ﺗﻤﺸﻲ ﺳﻴﺎﺳﺎﺕ ﻭﺍﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻣﻊ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﺘﻮﺟﻬﺎﺕ. q ﺍﻗﺘﺮﺍﺡ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻤﻜﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﻔﺎﻅ ﻋﻠﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺍﺭﺩ ﺑﺸﻜﻞ ﺃﻔﻀﻞ ﻭﺗﺤﺴﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺌﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻌﻤﻞ ﻓﻴﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ. q ﺍﻗﺘﺮﺍﺡ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻦ ﺗﺸﺎﺭﻙ ﻓﻴﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﺗﻌﺘﺒﺮ ﺩﻋﻤ ﻟﻠﻤﺠﺘﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﻠﻲ ﻭﺍﻟﺮﺃﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻡ. q ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﺭﻛﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺮﺍﺟﻌﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﺘﺠﺎﺕ )ﺍﻟﺴﻠﻊ ﻭﺍﻟﺨﺪﻣﺎﺕ( ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻘﺪﻣﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺄﻜﻴﺪ ﻋﻠﻲ ﺗﻘﺪﻳﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﺘﺠﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺼﺪﻳﻘﺔ ﻟﻠﺒﻴﺌﺔ.

ﺍﻟــﺪﻭﺭ ﺍﻟﺘﺴﻮﻳﻘﻰ q ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻲ ﺍﺣﺘﻴﺎﺟﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼﺀ ﻭﺭﻏﺒﺎﺗﻬﻢ. q ﺗﺼﻤﻴﻢ ﺫﻟﻚ ﺍﻟﻤﺰﻳﺞ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﺘﺠﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺬﻱ ﻳﻔﻲ ﺑﻬﺬﻩ ﺍﻻﺣﺘﻴﺎﺟﺎﺕ. q ﺍﻟﻘﻴﺎﻡ ﺑﺎﻟﺪﻭﺭ ﺍﻟﺘﺮﻭﻳﺠﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻄﻠﻮﺏ ﻓﻲ ﻫﺬﺍ ﺍﻟﺨﺼﻮﺹ. q ﻗﻴﺎﺱ ﺭﺿﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼﺀ ﻭﺍﻗﺘﺮﺍﺣﺎﺗﻬﻢ ﻭﺷﻜﻮﺍﻫﻢ.

ﺍﻟــﺪﻭﺭ ﺍﻹﻋـﻼﻣﻰ q ﺍﻹﻋﻼﻡ ﻋﻦ ﺃﻬﺪﺍﻑ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻭﺃﻮﺟﻪ ﻧﺸﺎﻃﻬﺎ ﻭﻣﺤﺎﺭﺑﺔ ﺃﻲ ﺷﺎﺋﻌﺎﺕ ﺿﺎﺭﺓ ﺑﻬﺎ. q ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻞ ﻋﻠﻲ ﻛﺴﺐ ﺗﺄﻴﻴﺪ ﻭﺛﻘﺔ ﺍﻟﺮﺃﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻡ ﻋﻦ ﻃﺮﻳﻖ ﺇﻣﺪﺍﺩﻩ ﺑﺎﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺼﺤﻴﺤﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺤﻘﺎﺋﻖ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺸﺮﻭﻋﺎﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺨﺪﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺆﺪﻳﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ. q ﻧﺸﺮ ﺍﻟﻮﻋﻲ ﻓﻴﻤﺎ ﻳﺘﻌﻠﻖ ﺑﺪﻭﺭ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺧﺪﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺘﻤﻊ. q ﺧﻠﻖ ﺻﻮﺭﺓ ﺫﻫﻨﻴﺔ ﻭﻣﺮﻛﺰ ﻣﻤﺘﺎﺯ ﻟﻠﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺃﻌﻴﻦ ﺟﻤﺎﻫﻴﺮﻫﺎ. q ﻣﺪ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻣﻠﻴﻦ ﺑﺎﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﺑﻜﺎﻓﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻄﻮﺭﺍﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺠﺪﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺆﺜﺮﺓ ﻋﻠﻲ ﻧﺸﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ. q ﺷﺮﺡ ﺳﻴﺎﺳﺔ ﺍﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﻟﻠﻌﺎﻣﻠﻴﻦ.

ﺍﻟــﺪﻭﺭ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺎﻋﻠـﻰ q ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺎﻋﻞ ﺍﻟﺸﺨﺼﻲ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺃﺨﺼﺎﺋﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻣﺔ ﻭﺍﻹﻋﻼﻡ ﻭﺟﻤﺎﻫﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺪﺍﺧﻠﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺨﺎﺭﺟﻴﺔ. q ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺎﻋﻞ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﺸﺨﺼﻲ ﻋﺒﺮ ﻭﺳﺎﺋﻞ ﺍﻻﺗﺼﺎﻝ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﺎﻫﻴﺮﻱ. q ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺎﻋﻞ ﺍﻻﻟﻜﺘﺮﻭﻧﻲ ﻋﺒﺮ ﺍﻻﻧﺘﺮﻧﺖ ﻭﺍﻻﻧﺘﺮﺍﻧﺖ ﻭﺍﻻﻛﺴﺘﺮﺍﻧﺖ.

Example: Corporate identity n Aim: to distinguish and establish visual recognition by means of physical, visible identification n L og o n Typography n Color n Livery n Clothing

Application of corporate identity n All print & advertising n Decoration of vehicles n Uniforms n Tableware n Serviettes n Mats n Coaster n Give aways n Business cards n Office stationary How about slogans?

Example: Crisis Management n Handling calamities especially regarding media relations (SAT TV) n. Lauda Air, strikes, fires, takeovers, new legislation, scandals, deaths, resignation, recession.

Examples of Crises n Accidents n Food poisoning n Contamination of products at retail stores n Recall of a faulty product n Tampering, malfunction, design error. Procedure Media advertising – News releases – Display material.

Responding to a Crisis n n n Develop a plan and checklist for dealing with a crisis. Deploy members of public relations staff as quickly as possible. Return calls to media immediately. Quickly gather the information you will need to communicate to the media. Designate one person to be a spokesperson to the media. Communicate with all employees immediately. Provide updates on a regular basis. Be available 24 hours a day to the media. Confess when the organization has made an error. Convey the steps the organization is taking to correct the crisis. Empathize with any victims of the crisis. Keep all publics informed of the progress. 14

Chapter 2 Public Relations vs Marketing & Advertising

PR VS Advertising n Advertising’s emphasis is on selling n PR emphasis is on informing, educating, and creating understanding through knowledge

But…Sometimes Advertising doesn’t sell n Consumer protests and government scrutiny n Advertisers were asked how their products answered social needs and civil responsibilities n Rumors about particular companies spread like wildfire n General image problems were fanned by a continuous blaze of media criticism
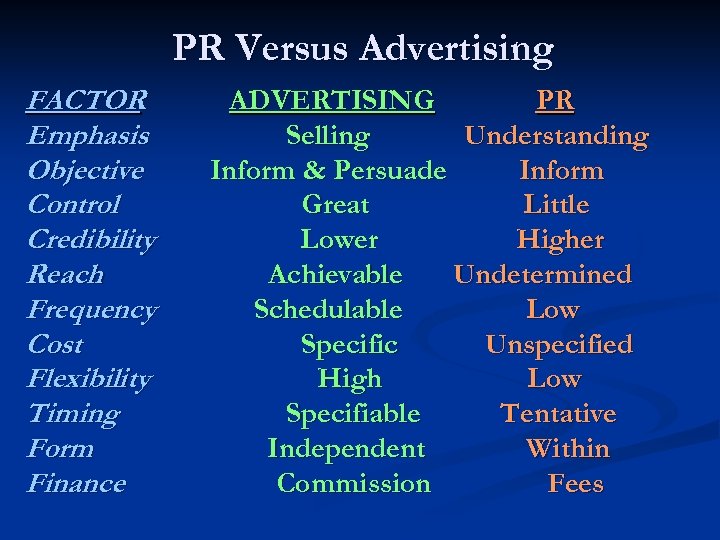
PR Versus Advertising FACTOR Emphasis Objective Control Credibility Reach Frequency Cost Flexibility Timing Form Finance ADVERTISING PR Selling Understanding Inform & Persuade Inform Great Little Lower Higher Achievable Undetermined Schedulable Low Specific Unspecified High Low Specifiable Tentative Independent Within Commission Fees

PR VS Marketing is the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably PR’s role in the marketing mix

Marketing vs. PR n Sells service or product through pricing, promoting, & distributing n Creates & maintains a market for products & services n Sells the organization n Creates & maintains a hospitable environment for the organization Marketing versus Public Relations

Propaganda n The means of gaining support for an opinion or belief. These are emotional, intellectual and spiritual topics Publicity n Publicity results from information being known. n It is uncontrollable; might be good or bad. n It yields an image


Chapter 3 Public Relations Department Organization

PR Departments 1. Need for an Internal department n Ad agency vs. PR consultancy n Skill in planning & buying space and air time n Creative skills n PR people speak on behalf of the company

2. Size of PR Department n Size of the organization n The value placed on PR by management n Type of company / product

3. PR Staff n Manager / Director n Press Officer n House journal Officer n Print Designer n Photographer

4. n n n Title of a PR Manager Director of Public Affairs Communication’s Manager Advertising and PR Manager

5. Responsibilities of a PR Manager n To set objectives n To estimate budgets (activities, payroll & expenses) n Devising action plans to reach the objectives
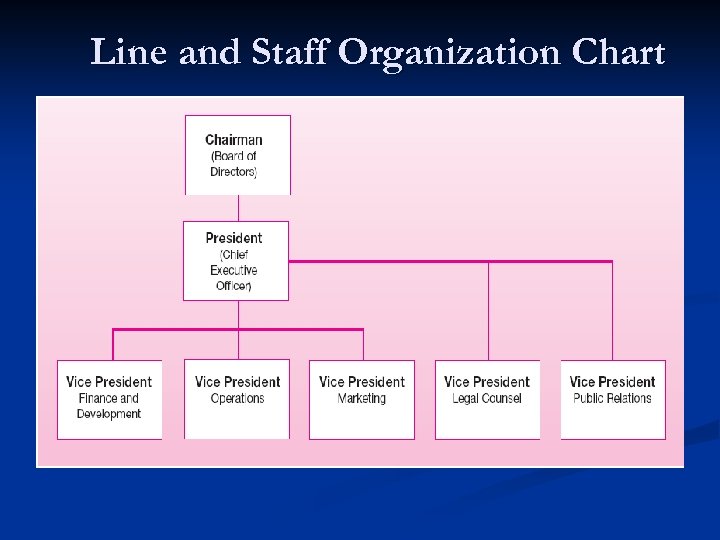
Line and Staff Organization Chart

Work Assignments • • • Writing and editing Media relations and placement Research Counseling Speaking Producing communications

Job Description 1

Job Requirements

Qualities of a Good PR Practitioner Ability to get on with all kinds of people. n Ability to communicate n Ability to organize and plan n Personal integrity in professional and private lives. n Creativity. (designing journals, writing scripts, seeking solutions to problems. n Access to information n Ability to research and evaluate. n

6. Specialist Tasks of PR Manager To establish and maintain a correct image of the organization and of its policies, products, services and personnel n To monitor outside opinion and convey this intelligence to management n To advise management on communication problems, solutions and techniques n To inform publics about policies, activities, products, services and personnel so that maximum knowledge and understanding is won n

7. Cooperation between PR & Management A competent professional practitioner so as to gain respect n Set up internal lines of communications. Win the confidence of the staff n Create external lines of communications and be regarded as a reliable source of information n Must keep top management well briefed for interviews, speeches and public occasions n Management must keep PR fully informed of its actions n

8. PR Activities Writing and distributing news releases, photographs and feature articles to the press. n Organizing press conferences, receptions and facility visits. n Maintaining a media information service n Arranging press, radio and television interviews for management. n Briefing photographers and maintaining a picture library. n Editing & producing staff magazines & organizing other forms of internal communication. n

PR Activities Editing and producing external journals aimed at distributors and customers. n Producing educational literature, company histories, annual reports, induction literature for new staff. n Commissioning audio visual aids (presentations, videos. . etc. , ). (P&G). n Commissioning and maintaining forms of corporate identity such as logos, color schemes, typography, livery of vehicles, clothing. n Organizing site tours. n

PR Activities Attendance at appropriate meetings of the board, production, marketing and sales. n Attendance at sales and distributors conferences. n Representation of the company at trade association meetings. n Liaison with PR consultancy if one is employed. n Training PR staff. n Commissioning opinion surveys. n Liaison with advertising agency. n

PR Activities Official opening of new premises, arrangements for VIPs, guests and Press. n Liaison with politicians and civil servants. n Arranging visits by royalty, MPs, VIPs and foreign visitors. n Celebrating centenaries. n Organizing feed back by press cuttings, radio, and TV transcripts. n Analysis of feed back and evaluation of the results. n


Chapter 4 Planning PR Programs

Reasons for Planning n To set targets for PR operations against which results can be assessed n To estimate the required budget n To select priorities regarding the timing and number of operations n To decide the feasibility of carrying out the declared objectives (staff, equipment and budget)
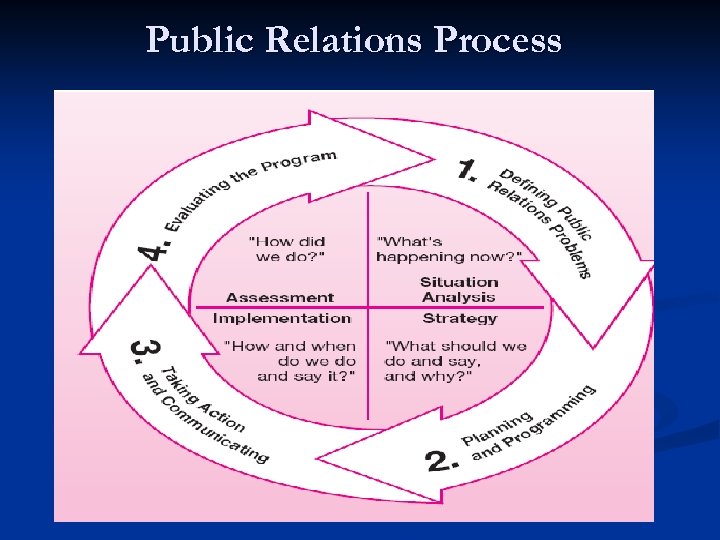
Public Relations Process

PR Planning Model 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Appreciation of the situation Definition of objectives Definition of publics Selection of media and techniques Planning of a budget Assessment of results

Appreciation of the situation n Logical planning: Where are we now? What image do our publics have? n The PR transfer process: n Hostility to sympathy n Prejudice to acceptance n Apathy to interest n Ignorance to knowledge

Appreciation of the situation n A necessary compromise: Can you be 100% successful? n Investigating the situation: through research (secondary and primary data) n Opinion polls: questionnaire, relevant sample, measure change in attitudes and degree of understanding n Problem solving: How to act to correct the situation

Methods of Appreciating the Situation Opinion, attitude or image surveys n Press cuttings, monitored broadcast strips n Sales figure trends n State of competition n Share price, dividends and balance sheet n Industrial relations (strikes, wage settlements) n Customer complaints n Frontline feedback n Prices and effect of price changes n External market forces n Attitudes of opinion leaders n

Definitions of Objectives n To change the image n To improve the caliber of job applicants n To tell the little known story of the company n To introduce the company in new export markets n To prepare the stock market for a new share issue

Definitions of Objectives n To improve community relations following public criticism n To educate consumers about the product n To regain public confidence after a disaster n To strengthen the company against risk of a takeover n To establish a new corporate identity

Definitions of Objectives n To make known the chairperson’s participation in public life n To support a sponsorship scheme n To inform politicians about company’s activities n To make known the company’s research activities
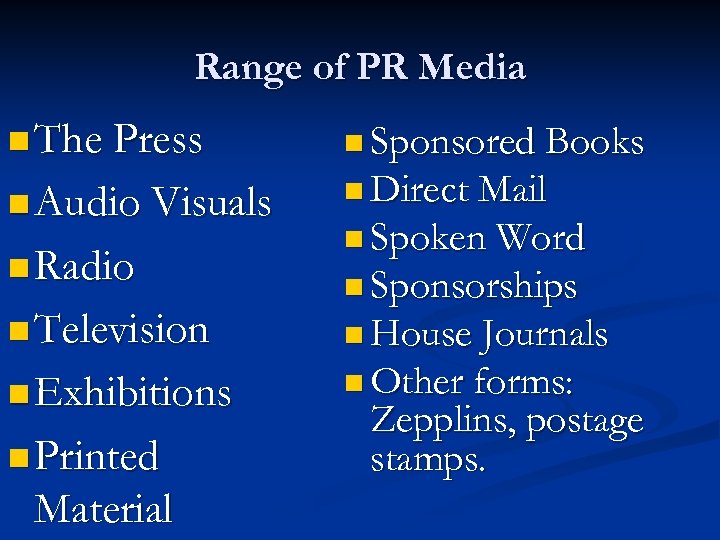
Range of PR Media n The Press n Sponsored Books n Audio Visuals n Direct Mail n Radio n Television n Exhibitions n Printed Material n Spoken Word n Sponsorships n House Journals n Other forms: Zepplins, postage stamps.

n News Releases: PR Vehicles n. Single-page news stories sent to media who might print or broadcast the content. n Feature Articles: n. Larger manuscripts composed and edited for a particular medium. n Captioned Photos: n. Photographs with content identified and explained below the picture. n Press Conferences: n. Meetings and presentations to invited reporters and editors. n Special Events: n. Sponsorship of events, teams, or programs of public value.

Chapter 5 Publics Of Public Relations

Publics Defined “Groups of people, internally and externally, with whom an organization communicates”. Activities are aimed at subdivisions of the “general public”. Unlike mass media advertising (do you agree with that? ).
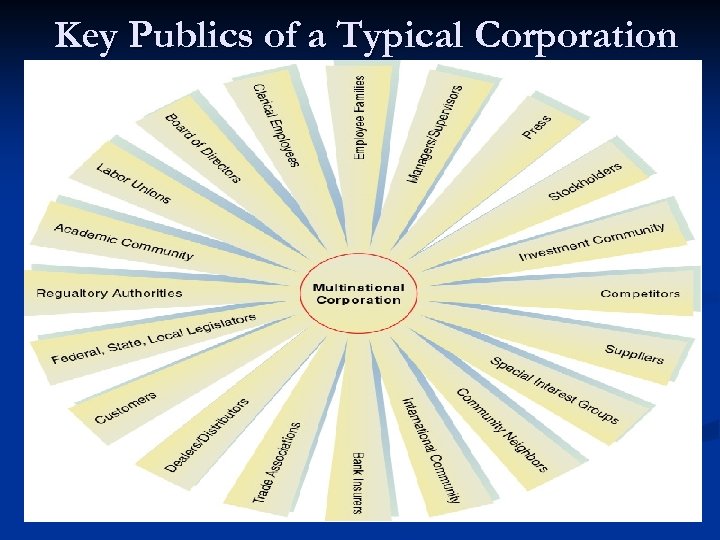
Key Publics of a Typical Corporation

Reasons for defining Publics 1. 2. 3. 4. To identify all groups of people relative to a PR program To establish priorities within the scope of the budget To select media and techniques To prepare the message in acceptable and effective form

Results of Not Defining Publics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Efforts and funds will be scattered indiscriminately in the attempt to reach too many publics The same message would be issued irrespective of its suitability to reach too many publics Work would not be timed to make the most cost effective use of working hours, material and equipment Objectives would not be achieved Dissatisfaction with the results

Publics of a National Tourist Board 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Government officials Distributors (travel agents, convention organizers) Transport operators Banks, credit cards & travelers’ cheques operators Hotel owners/operators (Chain or independent) Motoring organization Visitors Opinion leaders (travel writers – teachers) Media

Consider these behavioral possibiliti The public perceives big business to have concern primarily for investor and senior management stakeholders, though it should have more concern for other stakeholders.

Consider these behavioral possibilitie If employees are not part of the team, they can sabotage production, contribute to quality control problems, or conduct a negative word-of-mouth campaign against the firm.

If special-interest groups are not listened to and their concerns addressed, they can take legal action that stops production or expansion. If the media is not treated as a partner, then the first time the company has a product crisis the media will be more willing to look for irresponsible behavior rather than to explain the company's perspective.

1. The Community n. A good neighbor policy. n. Safety, dirt, noise, pollution, strikes, smells, car parking

2. Potential Employees n Exist in other organizations n Recruited from schools, colleges and universities or overseas. n. Helps them understand what is the nature of the organization n. Should regard it as a potentially good employer

3. Suppliers n. Services n. Raw materials, components, packaging and professional services

4. Financial Publics Banks n Lending institutions n Investors n Investment analysts n Insurance companies The financial community, investors, stockbrokers, and the financial press is another important audience for publicly -held companies. a) Financial relations experts must have a basic understanding of business law, economics, corporate finance, and investment practices. b) They must understand how corporate and external activities affect stock prices and changes in the company's bond rating. n

5. Distributors n Wholesalers (Tour operators) n Retailers (Travel agencies) n Airlines n Transporters (Transport companies) n Discount stores

6. Consumers n End users Consumers are a large external public. They are reached directly through advertising and sales and indirectly through media publicity. n Industrial/trade buyers

Consumers Why has dealing with consumers become so important for public relations? ing tis ” er e dv ois A N “ Knowledgeable Consumers Competition Sav Co vy nsu me rs

PR Customer Service n Investigate complaints made against the firm n Provide a central location for customers who seek redress n Monitor difficulties customers have with products n Influence organizations to improve service
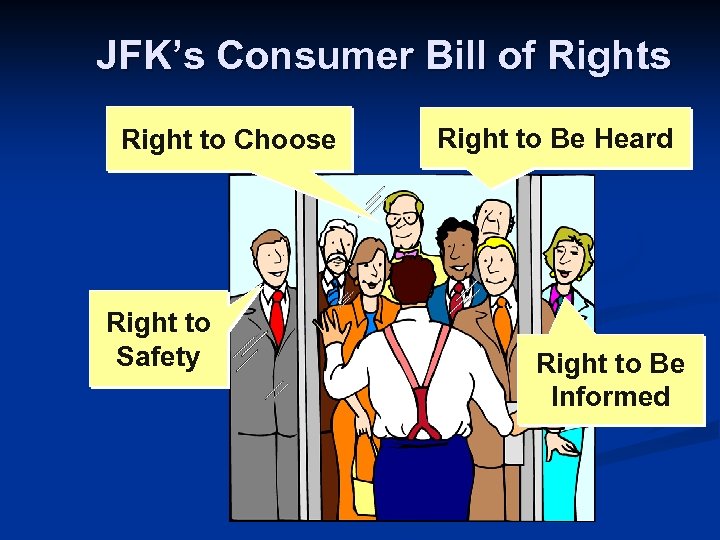
JFK’s Consumer Bill of Rights Right to Choose Right to Safety Right to Be Heard Right to Be Informed

Chrysler Corporation’s “Customer’s Bill of Rights” Every customer has the following rights: Quality Satisfactio n Grievance Opportuniti es Long-term Protection Service with a Smile Safe Vehicles

7. Opinion Leaders n People whose expressed opinions may harm or help the organization. n Parents n Politicians n Religious leaders

8. Trade Unions n. Exert a powerful influence on trade, commercial, industrial and political life.

9. The Media n The direct route to the public n It has control on what the public see and hear in their vehicles n Editors seek a good story; searching for news. In external relations the first concern is usually with the press because it can have tremendous influence over public opinion.

Ten Principles of Good Media Relations • Reporters are never “off • Become a trusted duty. ” • You ARE the organization. • Treat reporters as individuals. • Treat journalists professionally. • Don’t try to “buy” a journalist. • Become a trusted source. • Inform journalists even when you’re not “selling. ” • Don’t expect news viewpoint agreement. • Read the paper. • Never lie.
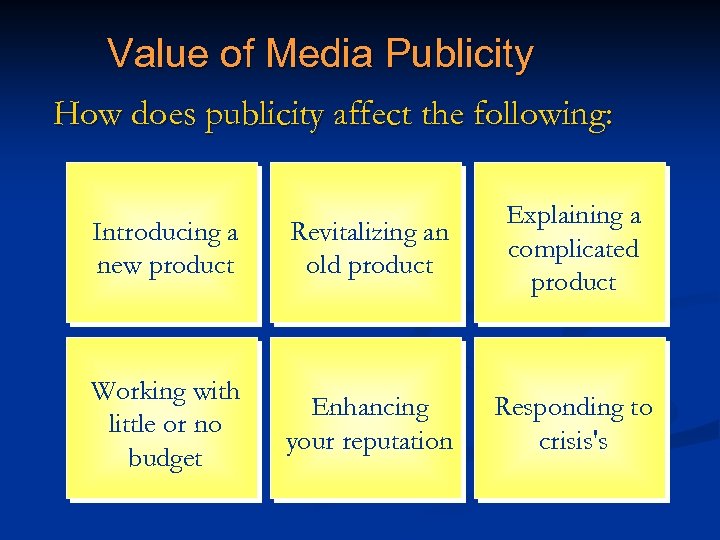
Value of Media Publicity How does publicity affect the following: Introducing a new product Revitalizing an old product Explaining a complicated product Working with little or no budget Enhancing your reputation Responding to crisis's

10. Employees The most important internal audience in internal communication is employees. Companies rely on a combination of downward, upward, and horizontal communication to foster employee relations. n Pride in their organization n High morale n Job security

Secrets of Effective Employee Relations 1. Security: How secure is the company and my job within it? 2. Respect: Am I recognized as a person who does something worth doing? 3. Participation: How much do I have to say about the processes of which I am a part? 4. Consideration: Is there an opportunity for me to express my ideas? 5. Recognition: What rewards are given for good and faithful service? 6. Opportunity: Is there a chance to advance?

Effectiveness of Internal PR n Candid Management n Recognition by management of the value and importance of employee communication n A skilled, experienced communication manager who is backed up by modern technical resources (budget, production)

Internal Techniques n House journals n Notice boards n Videotapes and closed circuit TV n Radio station n Phone in news service and ideas

Another Way of Communicating With Emp Make Them Catching Change Them Weekly Motivate People NEWS!

Internal Techniques n Ideas box n PA broadcasts n Shop floor talks n Works councils and committees n Video/slide presentations n Induction literature

Internal Techniques n Staff conferences and area meetings n Visits by management n Staff visits n Staff events n Exhibitions and displays n Clubs and societies

Explaining Company Policy n Level of job security n Prospects for advancement

Explaining the Annual Report and Accounts n Financial results n Cost configuration n Profit sharing n Dividends n Cost of labor

Integrating Staff Following an Acquisition n Who is better n Who is to stay and who is to go n A new mission statement n New job organization and assignment

Explaining New Technology n Automation, robotization, computerization n Redundancies n Advantages

Safety n Physical safety (special clothing, goggles, correct handling of materials) n Do we have to repeat these instructions? Why?

News About Staff n Retired n Best n Nominations n Left n Right n Birth, wedding…. . etc.

Management Structure n Organization charts n Reassignments

Shares n Stock market activities n Issuance of new stock n Why is a private company going public n Issuance of shares to employees n performance

Employee Benefits n Pensions n Christmas n Incentive schemes n Sales contests n Educational awards n Training

Legislation n Passing out of new laws by the government. n How do these affect the organization and its operations.

11. Investor Relations Timely and valuable communications that gain and maintain shareholder support Material Information: Any fact that would be important to an investor making an investment decision

Examples of Material Information: or acquisitions n Proposed mergers n Changed dividend policy n Determination of earnings n Acquisition or loss of significant business contract n Major management changes n Significant change in capital investment plans

Examples of Material Information: sale of a major asset n Purchase or n n Incurring a major debt or selling a significant amount of equity annuities Pending significant legislation A major discovery or innovation Marketing a new product

Investor Relations Activities Annual Reports: n Company description n Letter to shareholders n Financial review n Explanation/analysis n Management/marketing discussions n Graphics
802fc4f99b82753deb14e6c2cb571447.ppt