ae7b16296d03d02f0327b82e518afcee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Chapter 1. Introduction q A case for mobility q Application q History of mobile communication q Market q Areas of research Adopted from Prof. Dr. -Ing. Jochen Schiller, http: //www. jochenschiller. de/
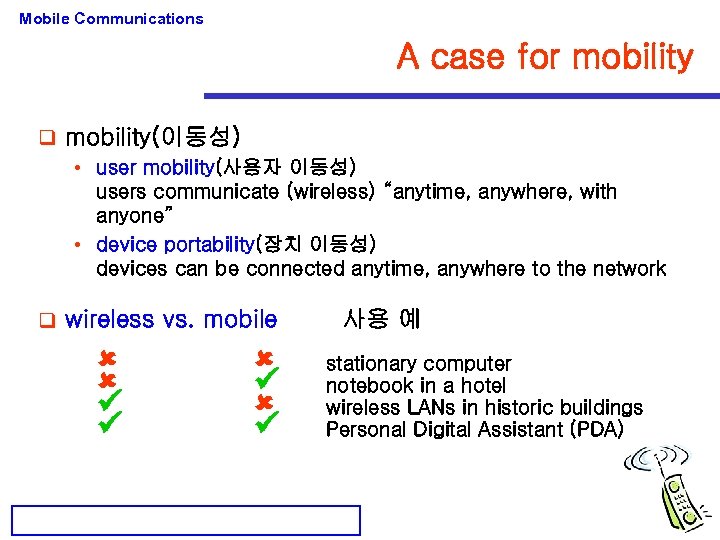
Mobile Communications A case for mobility q mobility(이동성) • user mobility(사용자 이동성) users communicate (wireless) “anytime, anywhere, with anyone” • device portability(장치 이동성) devices can be connected anytime, anywhere to the network q wireless vs. mobile 사용 예 stationary computer notebook in a hotel wireless LANs in historic buildings Personal Digital Assistant (PDA)

Mobile Communications wireless and fixed network q 무선 네트워크와 기존의 유선 네트워크의 통합 필요성 증대 • local area networks: IEEE 802. 11, ETSI (HIPERLAN) • Internet: 인터넷 프로토콜의 Mobile IP 확장 • wide area networks: GSM/CDMA와 ISDN 연동

Application Adopted from Prof. Dr. -Ing. Jochen Schiller, http: //www. jochenschiller. de/

Mobile Communications Applications I q 자동차(Vehicles) • 뉴스, 기상, 도로상황, DAB(digital audio broadcasting)을 통한 음악 등을 수신 • GSM/CDMA를 이용한 통한 모바일 폰 사용 • GPS(Global Positioning System)를 사용한 위치 추적 • 비상 시 빠른 정보교환이나 안전거리 유지를 위해 ad-hoc 네트워크를 구성 q 재난구조(Emergencies) • 환자의 상태 등을 병원에 긴급 전송 • 지진, 태풍, 화재 시 파손된 인프라 대체 • 전쟁, 비상상태 …. . 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 5
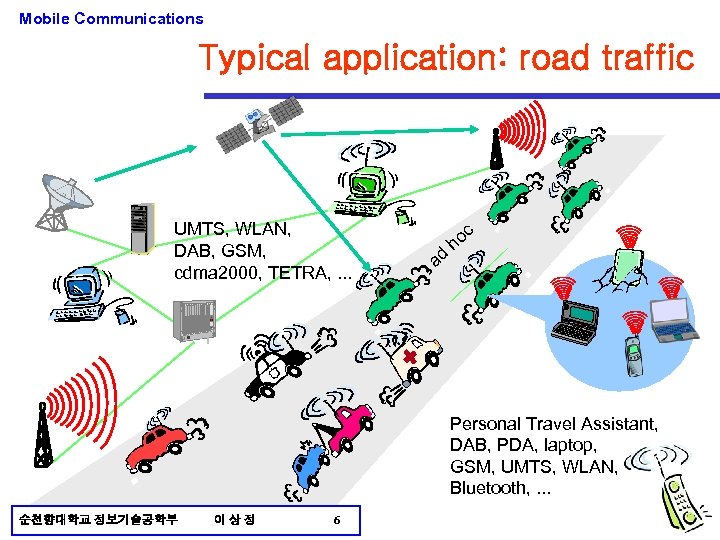
Mobile Communications Typical application: road traffic UMTS, WLAN, DAB, GSM, cdma 2000, TETRA, . . . c ad ho Personal Travel Assistant, DAB, PDA, laptop, GSM, UMTS, WLAN, Bluetooth, . . . 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 6
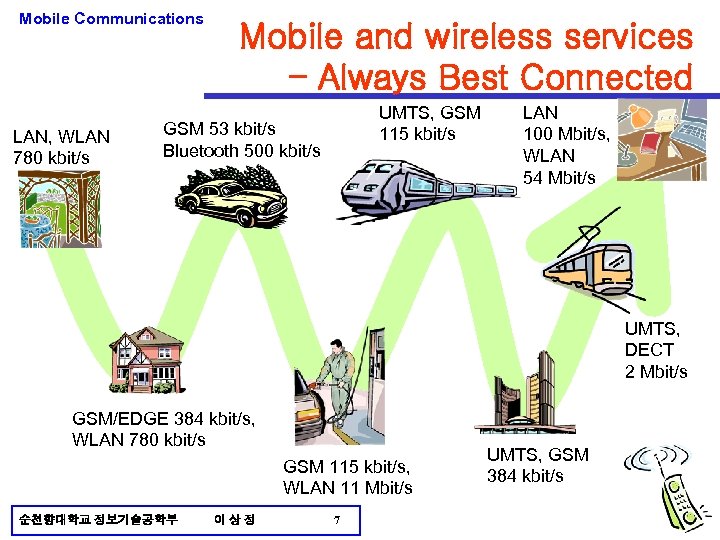
Mobile Communications LAN, WLAN 780 kbit/s Mobile and wireless services – Always Best Connected UMTS, GSM 115 kbit/s GSM 53 kbit/s Bluetooth 500 kbit/s LAN 100 Mbit/s, WLAN 54 Mbit/s UMTS, DECT 2 Mbit/s GSM/EDGE 384 kbit/s, WLAN 780 kbit/s GSM 115 kbit/s, WLAN 11 Mbit/s 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 7 UMTS, GSM 384 kbit/s
Mobile Communications Applications II q 여행 중인 세일즈맨 • 회사에 저장된 고객 파일을 직접 접근 • 모든 에이젼트에 대해 일관된 데이터베이스 • 모바일 사무실 q 고정된 유선 네트워크 대체 • 기상, 지구활동 관측용 원격 센서 • 박람회, 미술관, 박물관 q 오락, 연예, 교육, …. . • 야외에서의 인터넷 사용 • 위치기반 지능형 여행 안내 • 다자간 게임을 위한 ad-hoc networks 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 8 History Info

Mobile Communications Location dependent services q Location aware services • 인근 지역에서 printer, fax, phone, server 등의 서비스 검색 q Follow-on services • 메일/전화, 자료 등을 현재 사용자 위치로 자동전달 q Information services • push: e. g. , current special offers in the supermarket • pull: e. g. , where is the Black Forrest Cherry Cake? q Support services • 계산의 중간 결과, 상태 정보 혹은 캐쉬의 내용 등이 고정 네 트워크를 통해 모바일 장치에 전달 q Privacy • 자신의 현재 위치 등 개인 정보를 보호 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 9
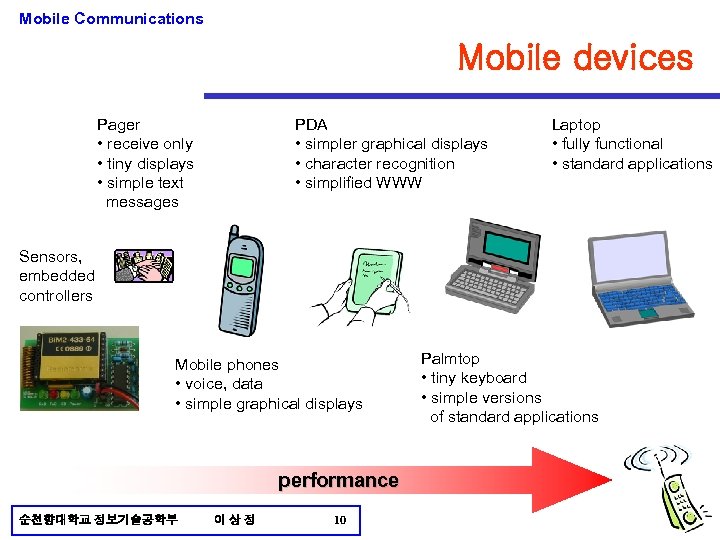
Mobile Communications Mobile devices PDA • simpler graphical displays • character recognition • simplified WWW Pager • receive only • tiny displays • simple text messages Laptop • fully functional • standard applications Sensors, embedded controllers Mobile phones • voice, data • simple graphical displays performance 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 10 Palmtop • tiny keyboard • simple versions of standard applications
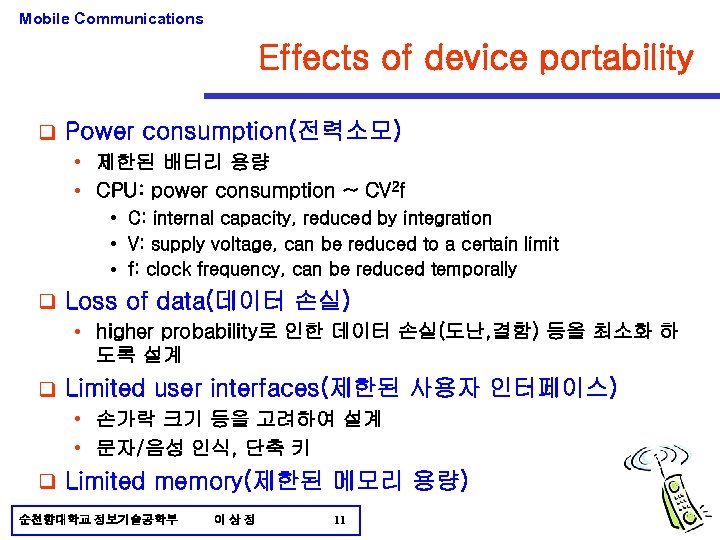
Mobile Communications Effects of device portability q Power consumption(전력소모) • 제한된 배터리 용량 • CPU: power consumption ~ CV 2 f • C: internal capacity, reduced by integration • V: supply voltage, can be reduced to a certain limit • f: clock frequency, can be reduced temporally q Loss of data(데이터 손실) • higher probability로 인한 데이터 손실(도난, 결함) 등을 최소화 하 도록 설계 q Limited user interfaces(제한된 사용자 인터페이스) • 손가락 크기 등을 고려하여 설계 • 문자/음성 인식, 단축 키 q Limited memory(제한된 메모리 용량) 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 11

Mobile Communications Wireless networks in comparison to fixed networks q 간섭으로 인한 높은 데이터 손실율 • 번개, 기계 잡음 등의 방출 등 q 주파수 사용 규제 • 대부분 가용한 주파수 대역의 국가, 국제기구 규제 및 점유 q 낮은 전송율(transmission rate) • local some Mbit/s, regional currently, e. g. , 9. 6 kbit/s with GSM q Higher delays, higher jitter • GSM 연결설정 수 초(second), 기타 무선장치 milliseconds q 취약한 보안(security) • 무선매체 공유 • 누구나 무선 접근 가능, 베이스스테이션 역할 모방하여 도청 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 12

History of mobile communication Adopted from Prof. Dr. -Ing. Jochen Schiller, http: //www. jochenschiller. de/

Mobile Communications Early history of wireless communication q 빛을 사용 • 반사경, 깃발. . . • 150 BC 연기 사용: Polybius, Greece q 전자파(electromagnetic wave) 등장 • 1831 Faraday • 전자기 유도(demonstrates electromagnetic induction) • J. Maxwell (1831 -79) • theory of electromagnetic Fields, wave equations (1864) • H. Hertz (1857 -94) • 공간 상의 무선전송 실험 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 14

Mobile Communications History of wireless communication I q 1895 Guglielmo Marconi • first demonstration of wireless telegraphy (digital!) • long wave transmission, high transmission power necessary (> 200 kw) q 1907 상업용 대서양 무선연결 • huge base stations (30개 100 m high antennas) q 1915 New York - San Francisco 간 무선 음성 전송 q 1920 Marconi 단파(short wave) 발견 • 전리층 반사(reflection at the ionosphere) • 진공관 발견으로 송수신기 소형화 (1906, Lee De. Forest and Robert von Lieben) 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 15

Mobile Communications History of wireless communication II q 1928 TV 방송 시범 서비스(across Atlantic, color TV, TV news) q 1933 주파수 변조(Frequency modulation) (E. H. Armstrong) q 1982 유럽 GSM 사양 정의 • goal: pan-European digital mobile phone system with roaming q 1983 미국 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System, analog) q 1984 CT-1 standard (Europe) for cordless telephones 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 16

Mobile Communications History of wireless communication III q 1991 DECT 사양 • Digital European Cordless Telephone (today: Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications) • 1880 -1900 MHz, ~100 -500 m range, 120 duplex channels, 1. 2 Mbit/s data transmission, voice encryption, authentication, up to several 10000 user/km 2, used in more than 50 countries q 1992 GSM 서비스 시작 • fully digital, 900 MHz, 124 channels • automatic location, hand-over, cellular • roaming in Europe - now worldwide in more than 170 countries • services: data with 9. 6 kbit/s, FAX, voice, . . . 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 17

Mobile Communications History of wireless communication IV q 1996 Hiper. LAN (High Performance Radio Local Area Network) • ETSI, standardization of type 1: 5. 15 - 5. 30 GHz, 23. 5 Mbit/s • recommendations for type 2 and 3 (both 5 GHz) and 4 (17 GHz) as wireless ATM-networks (up to 155 Mbit/s) q 1997 Wireless LAN - IEEE 802. 11 • IEEE standard, 2. 4 - 2. 5 GHz and infrared, 2 Mbit/s • already many (proprietary) products available in the beginning q 1998 Specification of GSM successors • for UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunication System) as European proposals for IMT-2000 q 1998 Iridium • 66 satellites (+6 spare), 1. 6 GHz to the mobile phone 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 18

Mobile Communications History of wireless communication V q 1999 Standardization of additional wireless LANs • IEEE standard 802. 11 b, 2. 4 -2. 5 GHz, 11 Mbit/s • Bluetooth for piconets, 2. 4 Ghz, <1 Mbit/s q 1999 Decision about IMT-2000 • Several “members” of a “family”: UMTS, cdma 2000, DECT, … q 1999 Start of WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) and i- mode • First step towards a unified Internet/mobile communication system • Access to many services via the mobile phone q 2001 Start of 3 G systems • Cdma 2000 in Korea, UMTS in Europe, Foma (almost UMTS) in Japan 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 19
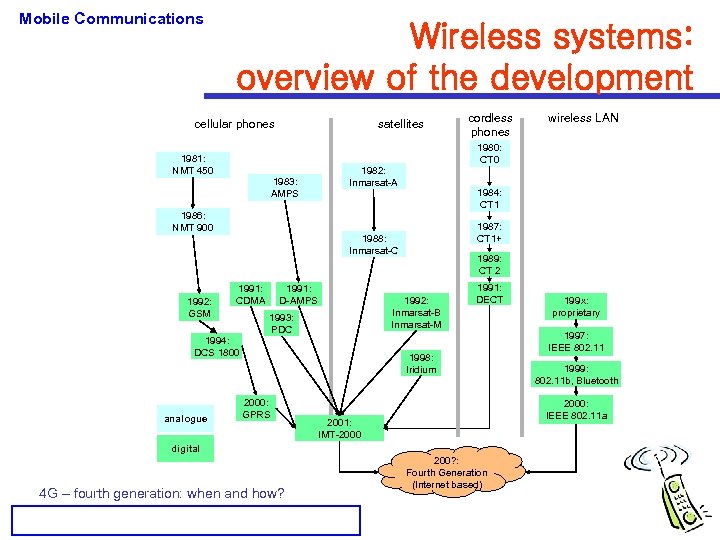
Mobile Communications Wireless systems: overview of the development cellular phones 1981: NMT 450 satellites 1983: AMPS 1986: NMT 900 1992: GSM 1994: DCS 1800 analogue 1982: Inmarsat-A 1991: D-AMPS 1984: CT 1 1987: CT 1+ 1989: CT 2 1992: Inmarsat-B Inmarsat-M 1993: PDC 1991: DECT 1998: Iridium 2000: GPRS 199 x: proprietary 1997: IEEE 802. 11 1999: 802. 11 b, Bluetooth 2000: IEEE 802. 11 a 2001: IMT-2000 digital 4 G – fourth generation: when and how? wireless LAN 1980: CT 0 1988: Inmarsat-C 1991: CDMA cordless phones 200? : Fourth Generation (Internet based)

Market Adopted from Prof. Dr. -Ing. Jochen Schiller, http: //www. jochenschiller. de/
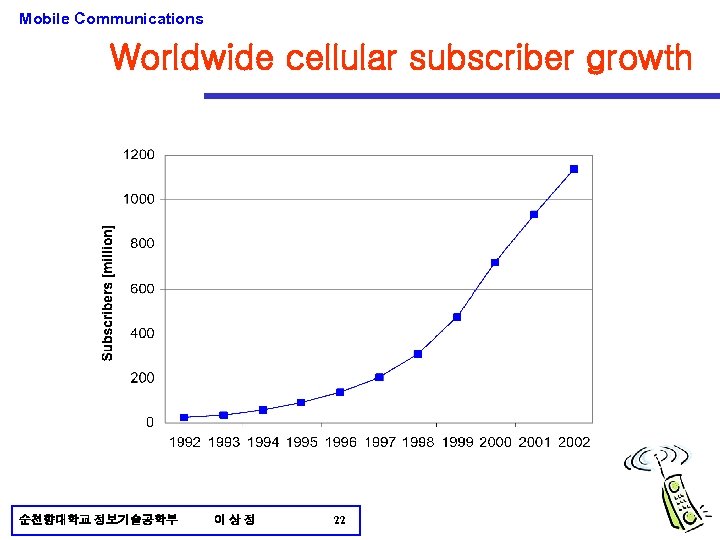
Mobile Communications Worldwide cellular subscriber growth 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 22
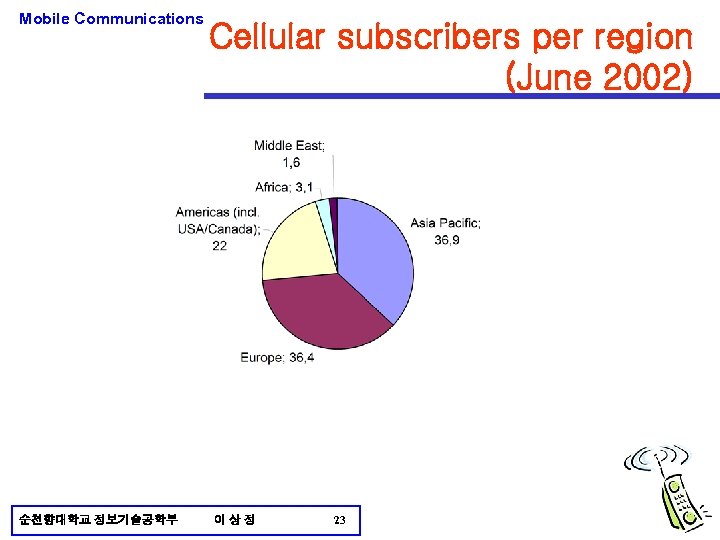
Mobile Communications 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 Cellular subscribers per region (June 2002) 이상정 23

Area of Research Adopted from Prof. Dr. -Ing. Jochen Schiller, http: //www. jochenschiller. de/

Mobile Communications Areas of research in mobile communication q Wireless Communication • transmission quality (bandwidth, error rate, delay) • modulation, coding, interference • media access, regulations • . . . q Mobility • location dependent services • location transparency • quality of service support (delay, jitter, security) • . . . q Portability • power consumption • limited computing power, sizes of display, . . . • usability • . . . 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 25
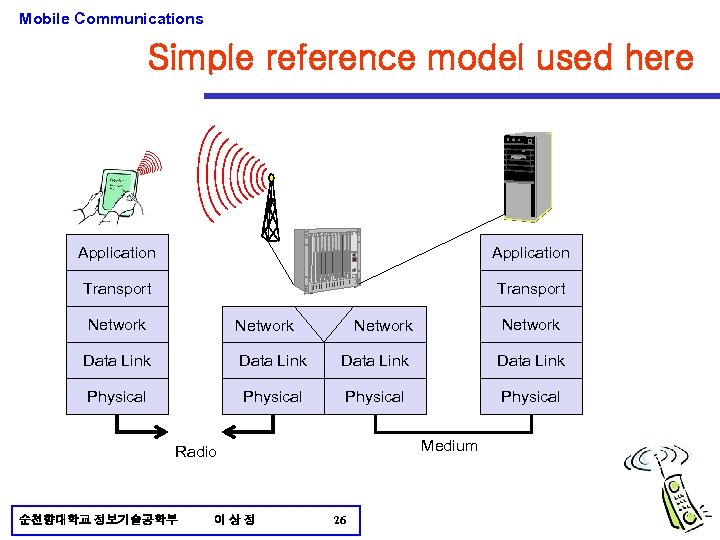
Mobile Communications Simple reference model used here Application Transport Network Data Link Physical Medium Radio 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 26
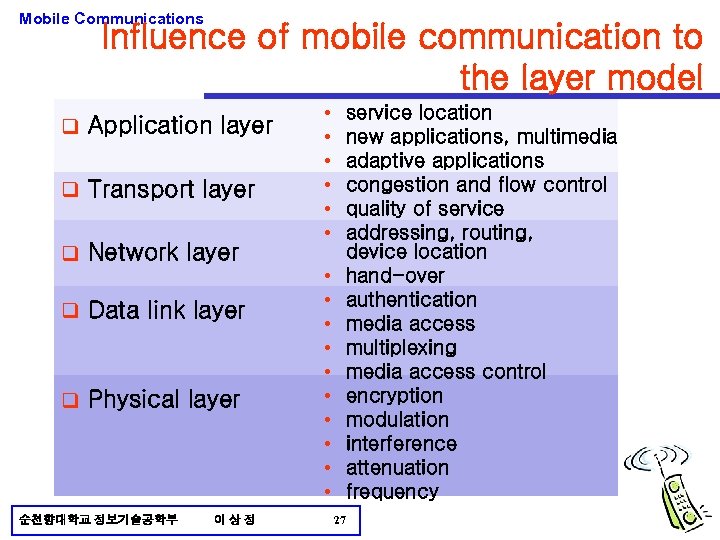
Mobile Communications Influence of mobile communication to the layer model q Application layer q Transport layer q Network layer q Data link layer q Physical layer 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 • • • service location new applications, multimedia adaptive applications congestion and flow control quality of service addressing, routing, device location hand-over authentication media access multiplexing media access control encryption modulation interference attenuation frequency • • • 27
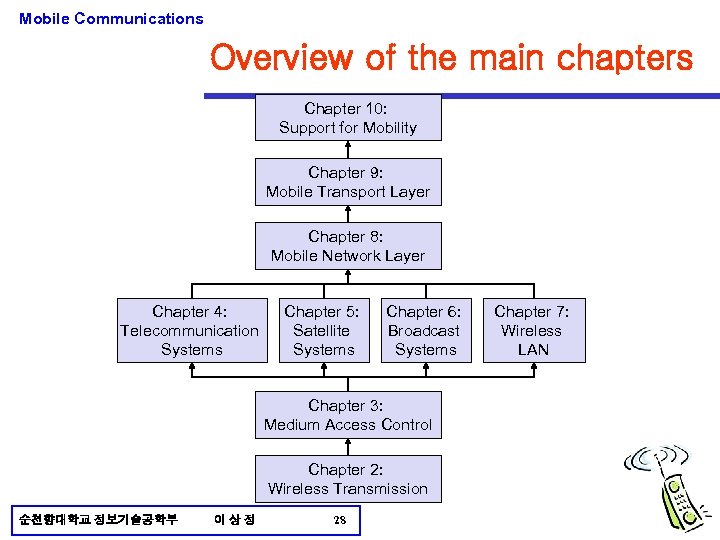
Mobile Communications Overview of the main chapters Chapter 10: Support for Mobility Chapter 9: Mobile Transport Layer Chapter 8: Mobile Network Layer Chapter 4: Telecommunication Systems Chapter 5: Satellite Systems Chapter 6: Broadcast Systems Chapter 3: Medium Access Control Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 28 Chapter 7: Wireless LAN
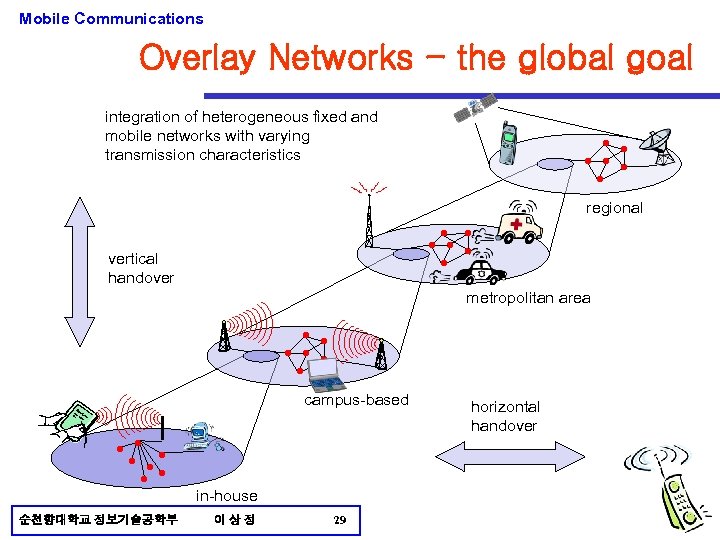
Mobile Communications Overlay Networks - the global goal integration of heterogeneous fixed and mobile networks with varying transmission characteristics regional vertical handover metropolitan area campus-based in-house 순천향대학교 정보기술공학부 이상정 29 horizontal handover
ae7b16296d03d02f0327b82e518afcee.ppt