9b86d32d3784acfdee60136411b63c97.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 Chapter 1 Introduction Kanchala Sudtachat Introduction AMS 1
Chapter 1 Introduction Kanchala Sudtachat Introduction AMS 1
 Contents l l Production System Facilities Manufacturing Support System Automation in Production System Automation Principles and Strategies Introduction AMS 2
Contents l l Production System Facilities Manufacturing Support System Automation in Production System Automation Principles and Strategies Introduction AMS 2
 Production system l คอ ระบบ ซงรวม คน, เครองมอ เครองจกร และขนตอนการจดการ เพอใหบรษทสามารถดำเนนการผล ตได แบงออกไดเปน 2 สวนงาน 1. Facilities 2. Manufacturing Support System Introduction AMS 3
Production system l คอ ระบบ ซงรวม คน, เครองมอ เครองจกร และขนตอนการจดการ เพอใหบรษทสามารถดำเนนการผล ตได แบงออกไดเปน 2 สวนงาน 1. Facilities 2. Manufacturing Support System Introduction AMS 3
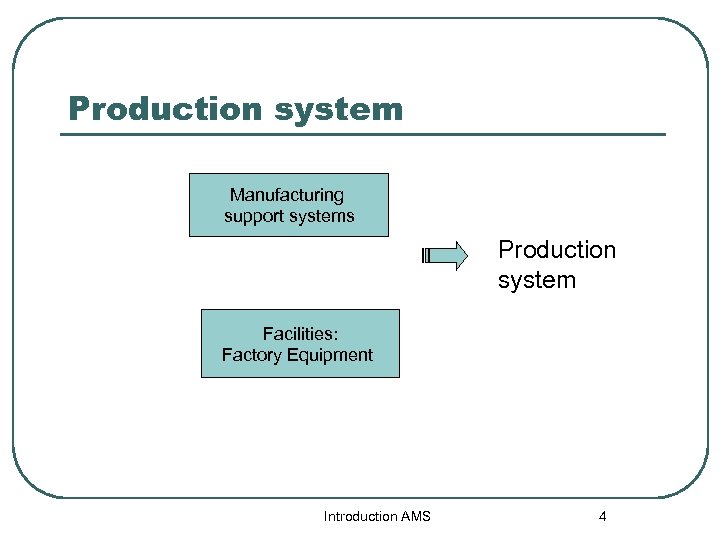 Production system Manufacturing support systems Production system Facilities: Factory Equipment Introduction AMS 4
Production system Manufacturing support systems Production system Facilities: Factory Equipment Introduction AMS 4
 Production System Facilities l • Facilities สงสนบสนนระบบการผลต ประกอบดวย factory, equipment ตางๆ ในโรงงานและแนวทางในการจดการกบส งเหลาน Manufacturing Support System หมายถง set ของขนตอนตางๆ ทใชเพอจดการการผลต ผลตภณฑ รวมทงเพอแกปญหาทางเทคนค 5 Introduction AMS ตางๆ
Production System Facilities l • Facilities สงสนบสนนระบบการผลต ประกอบดวย factory, equipment ตางๆ ในโรงงานและแนวทางในการจดการกบส งเหลาน Manufacturing Support System หมายถง set ของขนตอนตางๆ ทใชเพอจดการการผลต ผลตภณฑ รวมทงเพอแกปญหาทางเทคนค 5 Introduction AMS ตางๆ
 Facilities l l หมายถง factory, equipment, tooling, Material Handling, Inspection และระบบ Computer ทควบคมอปกรณเหลาน นอกจากนยงรวม Plant Layout หมายถง เครองมอ เครองจกรและการจดเรยงของเครองจ กร มคนงานเปนผดำเนนการในสายการผล ต Introduction AMS 6
Facilities l l หมายถง factory, equipment, tooling, Material Handling, Inspection และระบบ Computer ทควบคมอปกรณเหลาน นอกจากนยงรวม Plant Layout หมายถง เครองมอ เครองจกรและการจดเรยงของเครองจ กร มคนงานเปนผดำเนนการในสายการผล ต Introduction AMS 6
 Manufacturing System l l l Manufacturing System refer to these equipment and the workers who operate them Manufacturing can be individual work cells. Manufacturing system as groups of machines and worker, for ex. A production line. Introduction AMS 7
Manufacturing System l l l Manufacturing System refer to these equipment and the workers who operate them Manufacturing can be individual work cells. Manufacturing system as groups of machines and worker, for ex. A production line. Introduction AMS 7
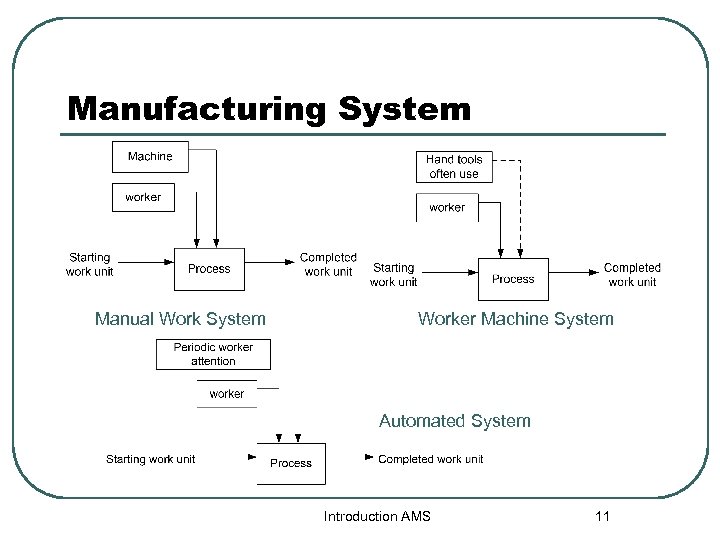
 Manufacturing System l l l Manufacturing system touch the product. The quantity produced by a factory has a very significant and the way manufacturing is organized. โดยมมมองของ คนททำงานในสายการผลตสามารถแยกออกเป นประเภทตางๆ ได 3 ประเภท • Manual work system • Worker-machine system • Automated system Introduction AMS 8
Manufacturing System l l l Manufacturing system touch the product. The quantity produced by a factory has a very significant and the way manufacturing is organized. โดยมมมองของ คนททำงานในสายการผลตสามารถแยกออกเป นประเภทตางๆ ได 3 ประเภท • Manual work system • Worker-machine system • Automated system Introduction AMS 8
 Manual Work System l l ประกอบดวยพนงงานใชมอในการผลต ในสายการผลตประกอบดวยคนงาน หนงหรอมากกวาหนงคน ผลตงานโดยไมอาศยพลงงานจากเครองจกร เครองขนถายวสด อตโนมตใดๆ ตองใช hand tool ซงเปนเครองมอพนฐานขนาดเลก ตวอยาง • คนงานควบคมเครองกลงเพลา ใหไดขนาด • คนงานทำหนาทตรวจสอบคณภาพ โดยใช micrometer Introduction AMS 9
Manual Work System l l ประกอบดวยพนงงานใชมอในการผลต ในสายการผลตประกอบดวยคนงาน หนงหรอมากกวาหนงคน ผลตงานโดยไมอาศยพลงงานจากเครองจกร เครองขนถายวสด อตโนมตใดๆ ตองใช hand tool ซงเปนเครองมอพนฐานขนาดเลก ตวอยาง • คนงานควบคมเครองกลงเพลา ใหไดขนาด • คนงานทำหนาทตรวจสอบคณภาพ โดยใช micrometer Introduction AMS 9
 Worker Machine System l ใชคนงานควบคมเครองจกรอตโนมต เพอความไดเปรยบในเครองของความส ามารถในการผลต ตวอยางระบบน • คนงานควบคมกระบวนการกลงเพลาของเครอง • • • CNC Robot ททำหนาท Arc-welding คนงานควบคมเครอง hot steel slabs ใหเปน flat plate สานการผลตทขนถายวสดดวยสายพานลำเ ลยง Introduction AMS 10
Worker Machine System l ใชคนงานควบคมเครองจกรอตโนมต เพอความไดเปรยบในเครองของความส ามารถในการผลต ตวอยางระบบน • คนงานควบคมกระบวนการกลงเพลาของเครอง • • • CNC Robot ททำหนาท Arc-welding คนงานควบคมเครอง hot steel slabs ใหเปน flat plate สานการผลตทขนถายวสดดวยสายพานลำเ ลยง Introduction AMS 10
 Manufacturing System Manual Work System Worker Machine System Automated System Introduction AMS 11
Manufacturing System Manual Work System Worker Machine System Automated System Introduction AMS 11
 Automated System l l เปนกระบวนการผลตทดำเนนการโดยเค รองจกรโดยปราศจากแรงงานทางตรงทำงา นรวมในสายการผลต มกใชโปรแกรมคำสง รวมกบระบบควบคม ซงทำงานตามคำสง แบงออกเปน 2 ระดบ • Semi-Automated ในแตละ • work cycle ในแรงงานคนในการ load-unload งานกบเครองจกร Fully Automated ในแตละ work cycle Introduction AMS 12
Automated System l l เปนกระบวนการผลตทดำเนนการโดยเค รองจกรโดยปราศจากแรงงานทางตรงทำงา นรวมในสายการผลต มกใชโปรแกรมคำสง รวมกบระบบควบคม ซงทำงานตามคำสง แบงออกเปน 2 ระดบ • Semi-Automated ในแตละ • work cycle ในแรงงานคนในการ load-unload งานกบเครองจกร Fully Automated ในแตละ work cycle Introduction AMS 12
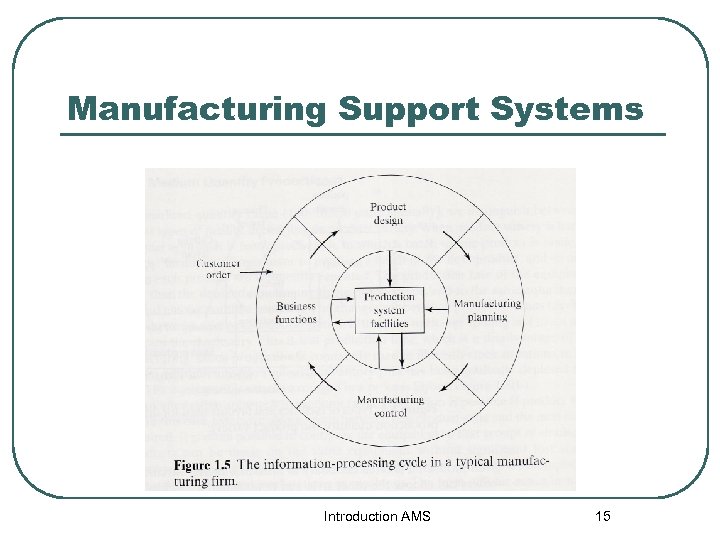
 Manufacturing Support System l l l เปนสวนทมหนาทเพอใหเกดก ารดำเนนการทมประสทธภาพมากท สด บรษทตองจดแผนกเพอ ออกแบบกระบวนการผลต กำหนดเครองมอ เครองจกร , งานวางแผนและควบคมการสงผลต และคณภาพของผลตภณฑทตองการ ระบบนมกจะไมสมผสโดยตรงกบผล ตภณฑ 13 Introduction AMS แตจะใชในการวางแผนและควบคมการดำเ
Manufacturing Support System l l l เปนสวนทมหนาทเพอใหเกดก ารดำเนนการทมประสทธภาพมากท สด บรษทตองจดแผนกเพอ ออกแบบกระบวนการผลต กำหนดเครองมอ เครองจกร , งานวางแผนและควบคมการสงผลต และคณภาพของผลตภณฑทตองการ ระบบนมกจะไมสมผสโดยตรงกบผล ตภณฑ 13 Introduction AMS แตจะใชในการวางแผนและควบคมการดำเ
 Manufacturing Support System l Business Functions เปนสวนทมหนาทหลกทตองสอ สารกบลกคา • l l l เรอง การขายการตลาดการคาดการณความตองการ คำสงซอของลกคา บญชตนทน และบลเกบเงน Product Design ทำการวจยและพฒนาผลตภณฑ ออกแบบทางวศวกรรม และทำ prototype Manufacturing Planning วางแผนการผลต ประกอบดวย process, ตารางการผลตหลก , วางแผนพสดคงคลง Introduction AMS Manufacturing control 14
Manufacturing Support System l Business Functions เปนสวนทมหนาทหลกทตองสอ สารกบลกคา • l l l เรอง การขายการตลาดการคาดการณความตองการ คำสงซอของลกคา บญชตนทน และบลเกบเงน Product Design ทำการวจยและพฒนาผลตภณฑ ออกแบบทางวศวกรรม และทำ prototype Manufacturing Planning วางแผนการผลต ประกอบดวย process, ตารางการผลตหลก , วางแผนพสดคงคลง Introduction AMS Manufacturing control 14
 Manufacturing Support Systems Introduction AMS 15
Manufacturing Support Systems Introduction AMS 15
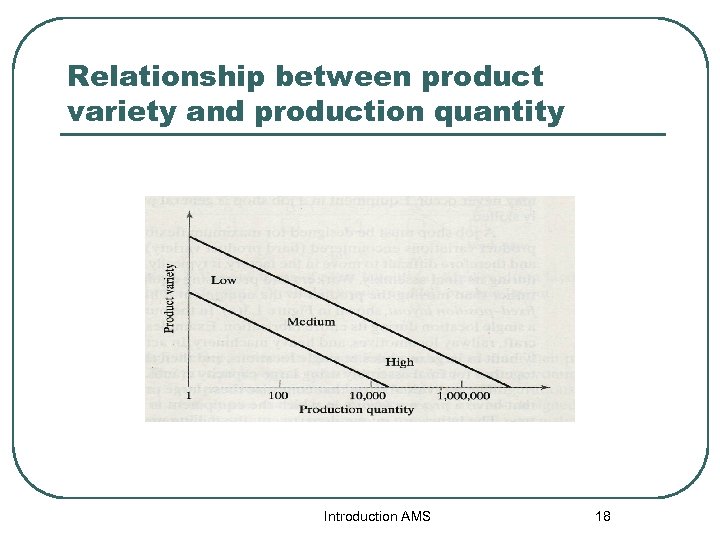
 Classified quantities production 1. Low production: range of 1 to 100 units/year 2. Medium production: range of 100 to 10, 000 units/year 3. High production: 10, 000 to millions of units Introduction AMS 16
Classified quantities production 1. Low production: range of 1 to 100 units/year 2. Medium production: range of 100 to 10, 000 units/year 3. High production: 10, 000 to millions of units Introduction AMS 16
 Product variety l l l Refer to the different product designs or types that are produced in a plant. Different product have different shapes and sizes and styles. When the number of product types made in a factory is high, this indicates high product variety. Introduction AMS 17
Product variety l l l Refer to the different product designs or types that are produced in a plant. Different product have different shapes and sizes and styles. When the number of product types made in a factory is high, this indicates high product variety. Introduction AMS 17
 Relationship between product variety and production quantity Introduction AMS 18
Relationship between product variety and production quantity Introduction AMS 18
 Product variety l l Hard product variety is when the product differ substantially, is characterized by a low proportion common parts among the products. Such as the differences between car and truck. Soft product variety is when there are only small differences between product. Such as differences between car models made on the same production line. Introduction AMS 19
Product variety l l Hard product variety is when the product differ substantially, is characterized by a low proportion common parts among the products. Such as the differences between car and truck. Soft product variety is when there are only small differences between product. Such as differences between car models made on the same production line. Introduction AMS 19
 Low Quantity Production l l l is the “job shop production”. The product are typically complex. Customer orders are often special, and repeat orders may never occur. Equipment is general purpose and the labor force is highly skilled. A job shop must be designed for maximum flexibility for hard product variety. Introduction AMS 20
Low Quantity Production l l l is the “job shop production”. The product are typically complex. Customer orders are often special, and repeat orders may never occur. Equipment is general purpose and the labor force is highly skilled. A job shop must be designed for maximum flexibility for hard product variety. Introduction AMS 20
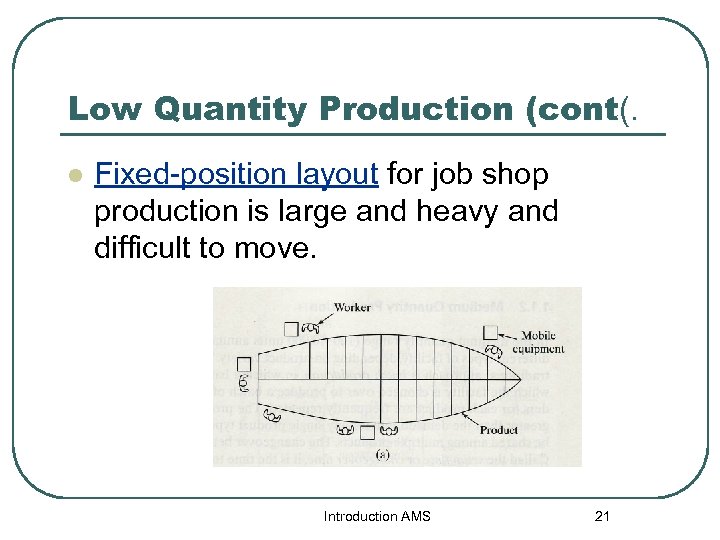 Low Quantity Production (cont(. l Fixed-position layout for job shop production is large and heavy and difficult to move. Introduction AMS 21
Low Quantity Production (cont(. l Fixed-position layout for job shop production is large and heavy and difficult to move. Introduction AMS 21
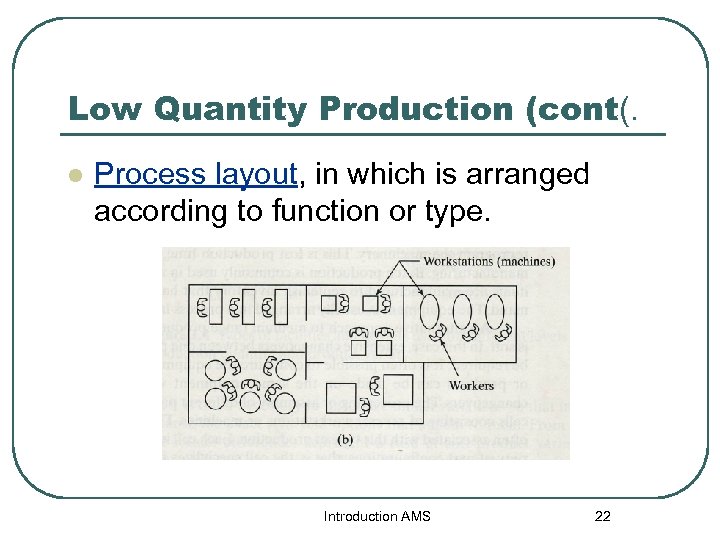 Low Quantity Production (cont(. l Process layout, in which is arranged according to function or type. Introduction AMS 22
Low Quantity Production (cont(. l Process layout, in which is arranged according to function or type. Introduction AMS 22
 Low Quantity Production (cont(. l l Process layout is produced different parts, each requiring a different operation sequence. are routed through the departments in the particular order needed for their processing, usually in batches. Machinery and methods to produce a part are not designed for high efficiency. In-Process inventory can be high. Introduction AMS 23
Low Quantity Production (cont(. l l Process layout is produced different parts, each requiring a different operation sequence. are routed through the departments in the particular order needed for their processing, usually in batches. Machinery and methods to produce a part are not designed for high efficiency. In-Process inventory can be high. Introduction AMS 23
 Medium Quantity Production l l has two different types of facility. Batch production • When product variety is hard, the traditional approach is “batch production”. • The changeover between production runs takes time that called the setup time or changeover time Introduction AMS 24
Medium Quantity Production l l has two different types of facility. Batch production • When product variety is hard, the traditional approach is “batch production”. • The changeover between production runs takes time that called the setup time or changeover time Introduction AMS 24
 Medium Quantity Production (cont(. • Batch production is commonly used in make -to-stock situation. • The equipment is usually arranged in a process layout Introduction AMS 25
Medium Quantity Production (cont(. • Batch production is commonly used in make -to-stock situation. • The equipment is usually arranged in a process layout Introduction AMS 25
 Medium Quantity Production (cont(. l Cellular manufacturing • Product variety is soft. • Product can be made on the same equipment without significant lost time for changeover. • Cells consisting of several workstations or machines. • The layout is called a cellular layout. Introduction AMS 26
Medium Quantity Production (cont(. l Cellular manufacturing • Product variety is soft. • Product can be made on the same equipment without significant lost time for changeover. • Cells consisting of several workstations or machines. • The layout is called a cellular layout. Introduction AMS 26
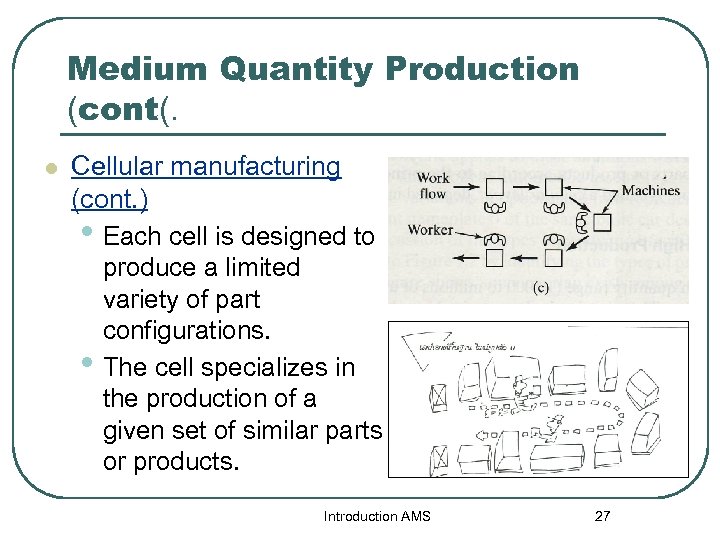 Medium Quantity Production (cont(. l Cellular manufacturing (cont. ) • Each cell is designed to produce a limited variety of part configurations. • The cell specializes in the production of a given set of similar parts or products. Introduction AMS 27
Medium Quantity Production (cont(. l Cellular manufacturing (cont. ) • Each cell is designed to produce a limited variety of part configurations. • The cell specializes in the production of a given set of similar parts or products. Introduction AMS 27
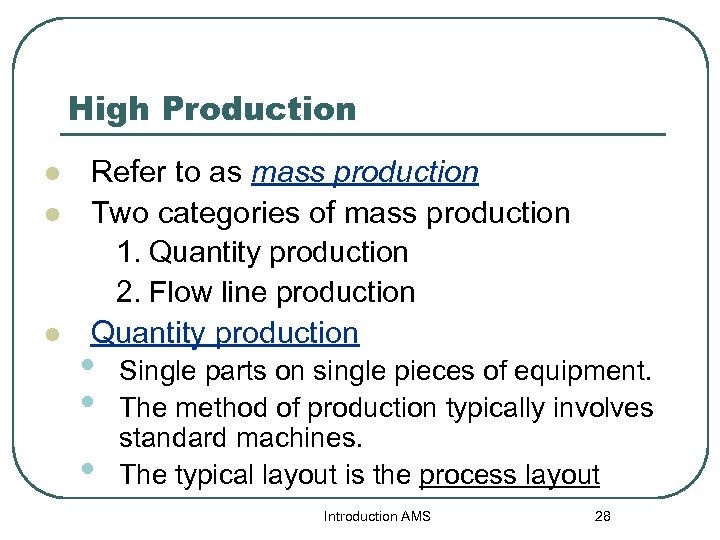 High Production l l l Refer to as mass production Two categories of mass production 1. Quantity production 2. Flow line production Quantity production • • • Single parts on single pieces of equipment. The method of production typically involves standard machines. The typical layout is the process layout Introduction AMS 28
High Production l l l Refer to as mass production Two categories of mass production 1. Quantity production 2. Flow line production Quantity production • • • Single parts on single pieces of equipment. The method of production typically involves standard machines. The typical layout is the process layout Introduction AMS 28
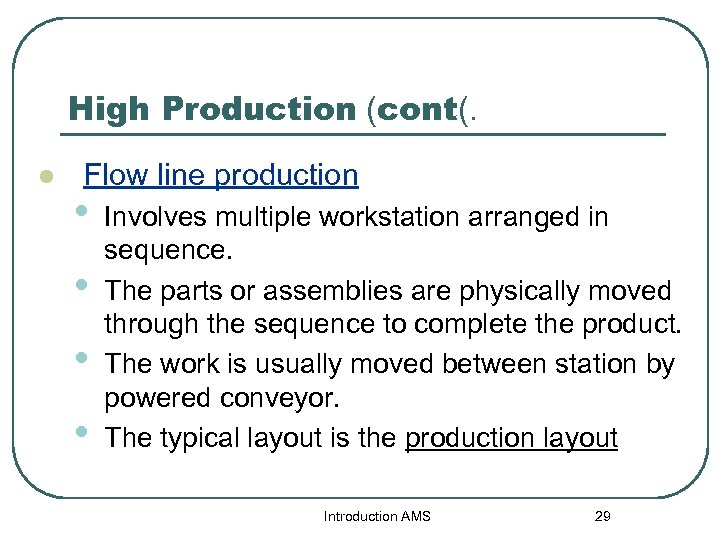 High Production (cont(. l Flow line production • • Involves multiple workstation arranged in sequence. The parts or assemblies are physically moved through the sequence to complete the product. The work is usually moved between station by powered conveyor. The typical layout is the production layout Introduction AMS 29
High Production (cont(. l Flow line production • • Involves multiple workstation arranged in sequence. The parts or assemblies are physically moved through the sequence to complete the product. The work is usually moved between station by powered conveyor. The typical layout is the production layout Introduction AMS 29
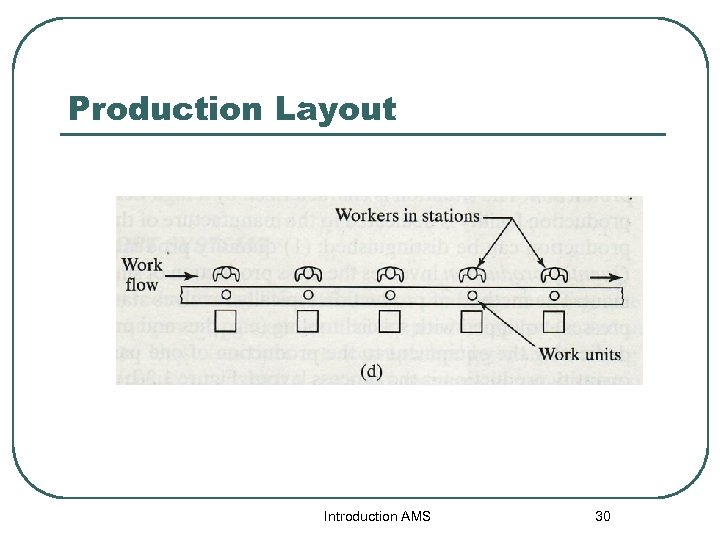 Production Layout Introduction AMS 30
Production Layout Introduction AMS 30
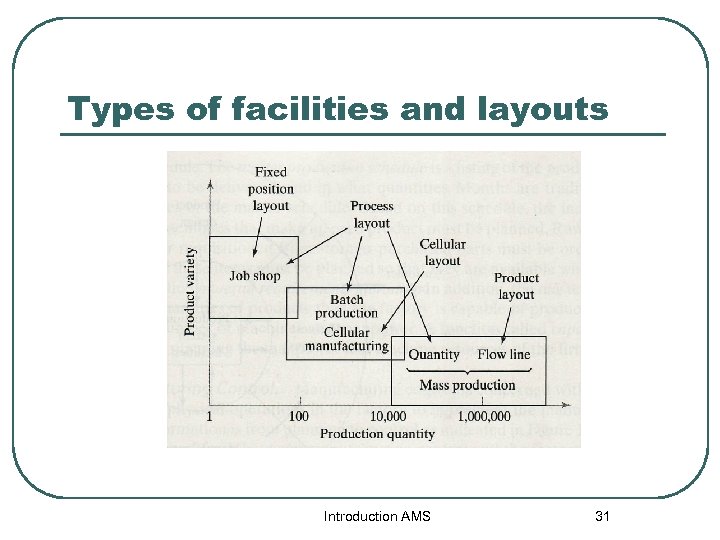 Types of facilities and layouts Introduction AMS 31
Types of facilities and layouts Introduction AMS 31
 High Production (cont(. l l Flow line production is where there is no variation in the products made on the line, called a single model production line. Mixed-model production line applies to a case of soft product variety in the products made on the line. Introduction AMS 32
High Production (cont(. l l Flow line production is where there is no variation in the products made on the line, called a single model production line. Mixed-model production line applies to a case of soft product variety in the products made on the line. Introduction AMS 32
 Automation in Production Systems l l Automation can be defined as a technology concerned with the application of mechanical, electronic, and com-base systems to operate and control production. Separated into 2 categories: 1. Automated of the Manufacturing system in factory 2. Computerization of the manufacturing support systems. Introduction AMS 33
Automation in Production Systems l l Automation can be defined as a technology concerned with the application of mechanical, electronic, and com-base systems to operate and control production. Separated into 2 categories: 1. Automated of the Manufacturing system in factory 2. Computerization of the manufacturing support systems. Introduction AMS 33
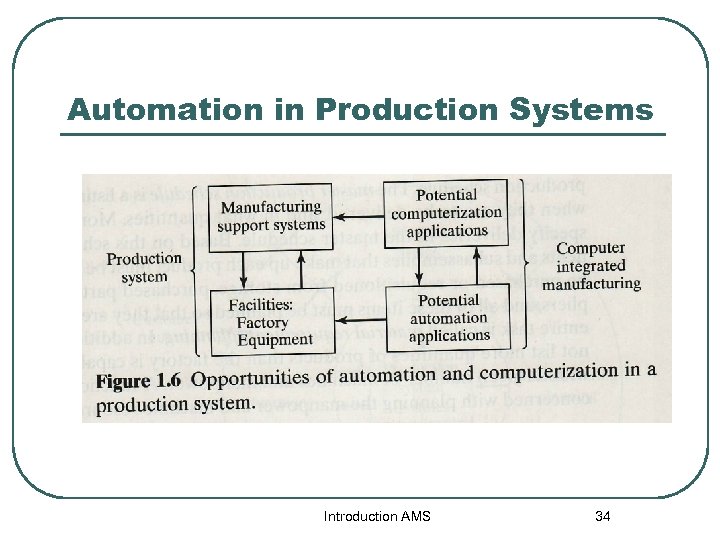 Automation in Production Systems Introduction AMS 34
Automation in Production Systems Introduction AMS 34
 Automated Manufacturing Systems l l l ในสวนน AMS เกยวของกบกระบวนการผลตอตโนมต ซงเกยวกบผลตภณฑโดยตรง ใชในการดำเนนการผลต processing, assembly, inspection, material handling ตวอยางระบบอตโนมต • • กระบวนการประกอบชนสวนรถยนตอตโนมต กระบวนการผลตทใชหนยนตอตสาหกรรมเพอ ผลตและประกอบ เครองจกร NC สำหรบผลตชนงาน Introduction AMS ระบบขนถาย จดเกบอตโนมต 35
Automated Manufacturing Systems l l l ในสวนน AMS เกยวของกบกระบวนการผลตอตโนมต ซงเกยวกบผลตภณฑโดยตรง ใชในการดำเนนการผลต processing, assembly, inspection, material handling ตวอยางระบบอตโนมต • • กระบวนการประกอบชนสวนรถยนตอตโนมต กระบวนการผลตทใชหนยนตอตสาหกรรมเพอ ผลตและประกอบ เครองจกร NC สำหรบผลตชนงาน Introduction AMS ระบบขนถาย จดเกบอตโนมต 35
 Automated Manufacturing Systems Classified into 3 basic types. 1. Fixed Automation : sequence of processing (or assembly) operations is fixed. Typical features of fixed automation are l • High initial investment • High production rate • Relative inflexible in accommodating product variety Introduction AMS 36
Automated Manufacturing Systems Classified into 3 basic types. 1. Fixed Automation : sequence of processing (or assembly) operations is fixed. Typical features of fixed automation are l • High initial investment • High production rate • Relative inflexible in accommodating product variety Introduction AMS 36
 Automated Manufacturing Systems l Fixed Automation : • Very large quantities and high production rate • High initial cost of the equipment can be spread over a very large number of units • Ex Machining transfer lines and Automated assembly machines. Introduction AMS 37
Automated Manufacturing Systems l Fixed Automation : • Very large quantities and high production rate • High initial cost of the equipment can be spread over a very large number of units • Ex Machining transfer lines and Automated assembly machines. Introduction AMS 37
 Automated Manufacturing Systems 2. Programmable Automation • The operation sequence is controlled by a program. • New programs can be prepared and entered into the equipment to produce new products. • Typical features of programmable automation are • High investment • Low production rate than fixed automation Introduction AMS 38
Automated Manufacturing Systems 2. Programmable Automation • The operation sequence is controlled by a program. • New programs can be prepared and entered into the equipment to produce new products. • Typical features of programmable automation are • High investment • Low production rate than fixed automation Introduction AMS 38
 Automated Manufacturing Systems • Compare with the features of fixed automation are • Flexibility to deal with variation and change in product configuration • Most suitable for batch production • Include numerically controlled (NC) machine tools, in industrial robots, and programmable logic controllers. Introduction AMS 39
Automated Manufacturing Systems • Compare with the features of fixed automation are • Flexibility to deal with variation and change in product configuration • Most suitable for batch production • Include numerically controlled (NC) machine tools, in industrial robots, and programmable logic controllers. Introduction AMS 39
 Automated Manufacturing Systems l Flexible Automation: • No time lost for changeovers from one part style to the next • Soft variety • Typical features of flexible automation are • High investment • Continuous production of variable mixtures of products Introduction AMS 40
Automated Manufacturing Systems l Flexible Automation: • No time lost for changeovers from one part style to the next • Soft variety • Typical features of flexible automation are • High investment • Continuous production of variable mixtures of products Introduction AMS 40
 Automated Manufacturing Systems l Typical features of flexible automation are • Medium production rate • Flexible to deal with product design variations Introduction AMS 41
Automated Manufacturing Systems l Typical features of flexible automation are • Medium production rate • Flexible to deal with product design variations Introduction AMS 41
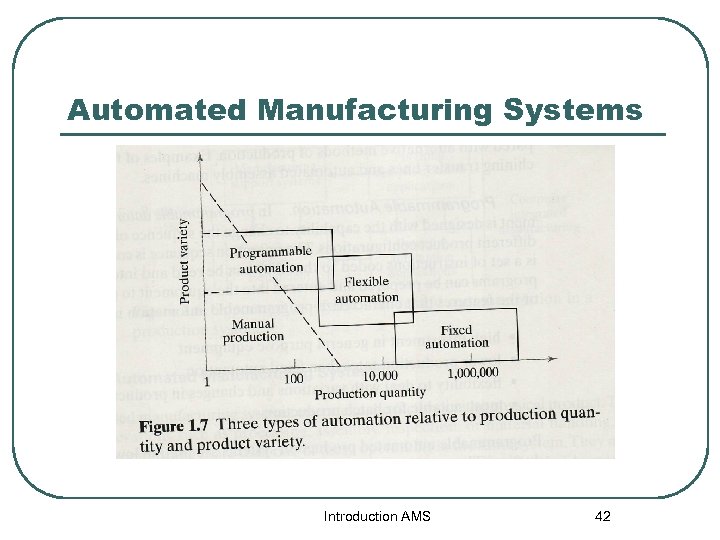 Automated Manufacturing Systems Introduction AMS 42
Automated Manufacturing Systems Introduction AMS 42
 Computerized Manufacturing Support System l เปนระบบคอมพวเตอรชวยในการออกแบบ ผลตภณฑ , การวางแผนและควบคมการผลต ไดแก • CIM ใชระบบคอมพวเตอร • • เพอออกแบบผลตภณฑ วางแผนการผลต และควบคมการดำเนนงานการผลต ขอมลทจำเปนตอการผลต CAD ใชระบบคอมพวเตอร สนบสนนฟงกชนในการออกแบบผลตภณฑ CAM ใชคอมพวเตอร 43 Introduction AMS เพอสรางฟงกชนทสมพนธกบกระบว
Computerized Manufacturing Support System l เปนระบบคอมพวเตอรชวยในการออกแบบ ผลตภณฑ , การวางแผนและควบคมการผลต ไดแก • CIM ใชระบบคอมพวเตอร • • เพอออกแบบผลตภณฑ วางแผนการผลต และควบคมการดำเนนงานการผลต ขอมลทจำเปนตอการผลต CAD ใชระบบคอมพวเตอร สนบสนนฟงกชนในการออกแบบผลตภณฑ CAM ใชคอมพวเตอร 43 Introduction AMS เพอสรางฟงกชนทสมพนธกบกระบว
 Reasons for Automation 1. 2. 3. 4. To increase labor productivity To reduce labor cost To mitigate the effect of labor shortage To reduce or eliminate routing manual and clerical tasks 5. To improve worker safety Introduction AMS 44
Reasons for Automation 1. 2. 3. 4. To increase labor productivity To reduce labor cost To mitigate the effect of labor shortage To reduce or eliminate routing manual and clerical tasks 5. To improve worker safety Introduction AMS 44
 Reasons for Automation 6. To improve product quantity 7. To reduce manufacturing lead time 8. To accomplish processes that cannot be done manually 9. To avoid the high cost of not automating Introduction AMS 45
Reasons for Automation 6. To improve product quantity 7. To reduce manufacturing lead time 8. To accomplish processes that cannot be done manually 9. To avoid the high cost of not automating Introduction AMS 45
 Automation Principles And Strategies l แนวทางของการทำ automation project 3 แนวทาง 1. The U. S. A principle 2. Ten Strategies for Automation and Process Improvement 3. An Automation Migration Strategy Introduction AMS 46
Automation Principles And Strategies l แนวทางของการทำ automation project 3 แนวทาง 1. The U. S. A principle 2. Ten Strategies for Automation and Process Improvement 3. An Automation Migration Strategy Introduction AMS 46
 The U. S. A Principle 1. Understand the existing process l l l อะไรคอ input ของกระบวนการ อะไรคอ output ของกระบวนการ อะไรทเกดขนเมอ work unit อยระหวางกระบวนการผลต อะไรคอฟงกชนของกระบวนการผลต (ผลตเพออะไร ) เราจะเพมคณคา (value) ใหกบผลตภณฑไดอยางไร อะไรคอ upstream และ downstream Introduction AMS ของขนตอนการผลต 47
The U. S. A Principle 1. Understand the existing process l l l อะไรคอ input ของกระบวนการ อะไรคอ output ของกระบวนการ อะไรทเกดขนเมอ work unit อยระหวางกระบวนการผลต อะไรคอฟงกชนของกระบวนการผลต (ผลตเพออะไร ) เราจะเพมคณคา (value) ใหกบผลตภณฑไดอยางไร อะไรคอ upstream และ downstream Introduction AMS ของขนตอนการผลต 47
 The U. S. A Principle 2. Simplify the process คนหาวธทจะทำใหกระบวนการผลตสามา รถผลตไดอยางงายๆ โดยใชวธการตงคำถามกบกระบวนการผล ตปจจบน l อะไรเปนสงทตองการของขนตอนนห รอการขนสงวสดในสวนน l ขนตอนนเปนขนตอนทจำเปนหรอ ไม เราสามารถตดออกไดหรอไม แลวทำให work unit เปลยนแปลงไปหรอไม l ขนตอนนสามารถใชเทคโนโลยอะไรแทนจะเ 48 Introduction AMS l
The U. S. A Principle 2. Simplify the process คนหาวธทจะทำใหกระบวนการผลตสามา รถผลตไดอยางงายๆ โดยใชวธการตงคำถามกบกระบวนการผล ตปจจบน l อะไรเปนสงทตองการของขนตอนนห รอการขนสงวสดในสวนน l ขนตอนนเปนขนตอนทจำเปนหรอ ไม เราสามารถตดออกไดหรอไม แลวทำให work unit เปลยนแปลงไปหรอไม l ขนตอนนสามารถใชเทคโนโลยอะไรแทนจะเ 48 Introduction AMS l
 Ten Strategies for Automation and Process Improvement 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Specialization of operation Combined operation Simultaneous operation Integration of operation Increased flexibility Improved material handling and storage Introduction AMS 49
Ten Strategies for Automation and Process Improvement 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Specialization of operation Combined operation Simultaneous operation Integration of operation Increased flexibility Improved material handling and storage Introduction AMS 49
 Ten Strategies for Automation and Process Improvement 7. 8. 9. 10. On-line inspection Process control and Optimization Plant operation control Computer integrated manufacturing Introduction AMS 50
Ten Strategies for Automation and Process Improvement 7. 8. 9. 10. On-line inspection Process control and Optimization Plant operation control Computer integrated manufacturing Introduction AMS 50
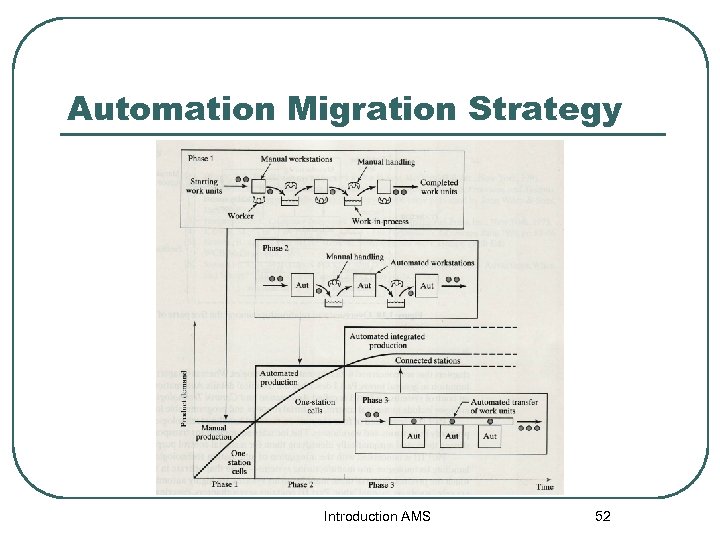
 Automation Migration Strategy l การปรบปรงกระบวนการผลตเปนรปแบบอตโนม ต แบงเปน 3 ชวง • Phase 1: Manual production • Phase 2: Automated production • • แตละสถานงานดำเนนการอสระแกกน ใชเพอใหสามารถนำผลตภณฑใหมเข าสตลาดเรวทสด • แตละสถานดำเนนงานอสระแกกน ใชแรงงานคนในการขนถายวสด unload งาน สวนอตโนมตอยทเครองจกรทผ ลต Introduction AMS Phase 3: Automated integrated production load- 51
Automation Migration Strategy l การปรบปรงกระบวนการผลตเปนรปแบบอตโนม ต แบงเปน 3 ชวง • Phase 1: Manual production • Phase 2: Automated production • • แตละสถานงานดำเนนการอสระแกกน ใชเพอใหสามารถนำผลตภณฑใหมเข าสตลาดเรวทสด • แตละสถานดำเนนงานอสระแกกน ใชแรงงานคนในการขนถายวสด unload งาน สวนอตโนมตอยทเครองจกรทผ ลต Introduction AMS Phase 3: Automated integrated production load- 51
 Automation Migration Strategy Introduction AMS 52
Automation Migration Strategy Introduction AMS 52


