f2e4d1edb004c0f53f86eb82cc8302f1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION The overwhelming need of organizations and their workers is for connectivity, integration & ease of access to information. The technology that is bringing all these together & making it possible is NETWORKING !
INTRODUCTION The overwhelming need of organizations and their workers is for connectivity, integration & ease of access to information. The technology that is bringing all these together & making it possible is NETWORKING !
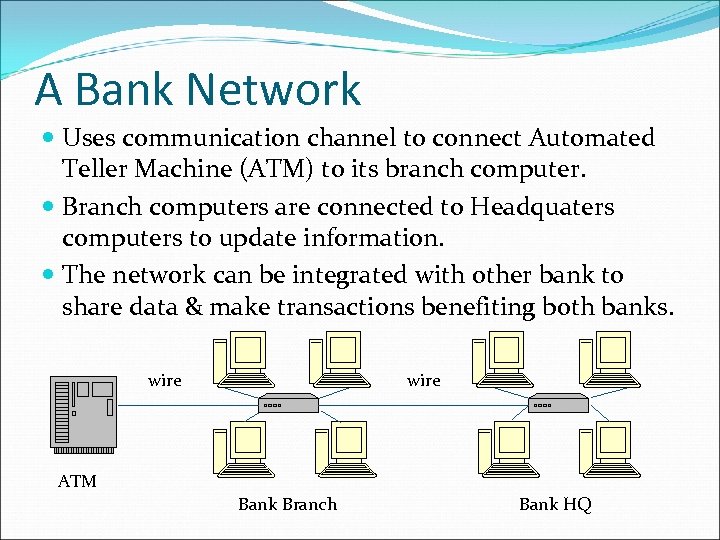 A Bank Network Uses communication channel to connect Automated Teller Machine (ATM) to its branch computer. Branch computers are connected to Headquaters computers to update information. The network can be integrated with other bank to share data & make transactions benefiting both banks. wire ATM Bank Branch Bank HQ
A Bank Network Uses communication channel to connect Automated Teller Machine (ATM) to its branch computer. Branch computers are connected to Headquaters computers to update information. The network can be integrated with other bank to share data & make transactions benefiting both banks. wire ATM Bank Branch Bank HQ
 Definition Information Is the result of processing, manipulating & organizing data in a many way that adds to the knowledge of a person receiving it. Ex: of information is a picture, news, population of a country. Data Information stored on the computer system used by applications to accomplish tasks. Ex : numbers & characters.
Definition Information Is the result of processing, manipulating & organizing data in a many way that adds to the knowledge of a person receiving it. Ex: of information is a picture, news, population of a country. Data Information stored on the computer system used by applications to accomplish tasks. Ex : numbers & characters.
 Need of Today’s Organization compared with Bank Network Easy storage, protection & retrieval of data Ex: bank account holder data is protected & coded inside the chip of ATM/Smart card. The data is easily retrievable by trusted bank ATM. Data sharing among its users & departments Ex: the data (account holder information & bank information) can be shared among bank employees from all over the branches.
Need of Today’s Organization compared with Bank Network Easy storage, protection & retrieval of data Ex: bank account holder data is protected & coded inside the chip of ATM/Smart card. The data is easily retrievable by trusted bank ATM. Data sharing among its users & departments Ex: the data (account holder information & bank information) can be shared among bank employees from all over the branches.
 Need of Today’s Organization compared with Bank Network Faster & safer flow of data Ex: whole banking network system work fast & safe allowing KL customer to withdraw in any ATM in Kedah. Management of huge volumes of data & across long distance. Ex: banking system holds account information, profile data & transactions of millions of its customer in Malaysia.
Need of Today’s Organization compared with Bank Network Faster & safer flow of data Ex: whole banking network system work fast & safe allowing KL customer to withdraw in any ATM in Kedah. Management of huge volumes of data & across long distance. Ex: banking system holds account information, profile data & transactions of millions of its customer in Malaysia.
 Need of Today’s Organization compared with Bank Network Interconnectivity with other existing technologies & inter exchange of data. One bank network is connected to other bank network allowing Maybank customer to with draw money from HSBC ATM. Ease of use & easy to learn ATM is user friendly and has multiple language option.
Need of Today’s Organization compared with Bank Network Interconnectivity with other existing technologies & inter exchange of data. One bank network is connected to other bank network allowing Maybank customer to with draw money from HSBC ATM. Ease of use & easy to learn ATM is user friendly and has multiple language option.
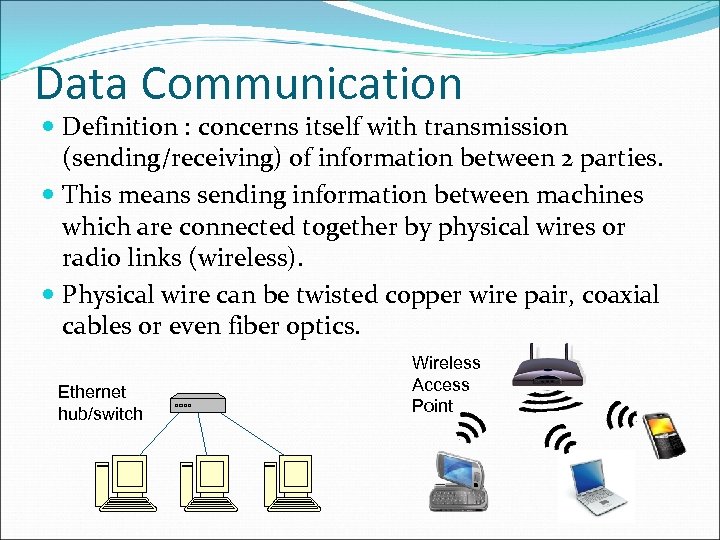 Data Communication Definition : concerns itself with transmission (sending/receiving) of information between 2 parties. This means sending information between machines which are connected together by physical wires or radio links (wireless). Physical wire can be twisted copper wire pair, coaxial cables or even fiber optics. Ethernet hub/switch Wireless Access Point
Data Communication Definition : concerns itself with transmission (sending/receiving) of information between 2 parties. This means sending information between machines which are connected together by physical wires or radio links (wireless). Physical wire can be twisted copper wire pair, coaxial cables or even fiber optics. Ethernet hub/switch Wireless Access Point
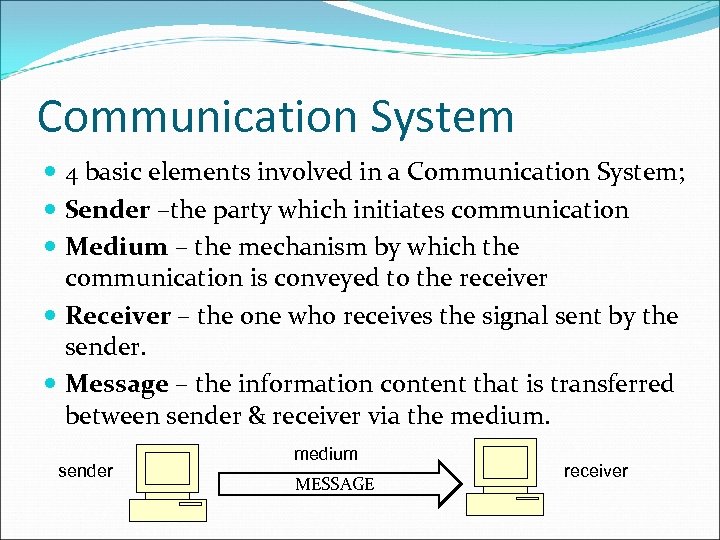 Communication System 4 basic elements involved in a Communication System; Sender –the party which initiates communication Medium – the mechanism by which the communication is conveyed to the receiver Receiver – the one who receives the signal sent by the sender. Message – the information content that is transferred between sender & receiver via the medium. sender medium MESSAGE receiver
Communication System 4 basic elements involved in a Communication System; Sender –the party which initiates communication Medium – the mechanism by which the communication is conveyed to the receiver Receiver – the one who receives the signal sent by the sender. Message – the information content that is transferred between sender & receiver via the medium. sender medium MESSAGE receiver
 Networks Definition : a group of stations (computers, telephone & other devices) connected by communication facilities for exchanging information. A network can be connected to another network, thus making a bigger network. A network can be part of other networks & it is known as sub-network.
Networks Definition : a group of stations (computers, telephone & other devices) connected by communication facilities for exchanging information. A network can be connected to another network, thus making a bigger network. A network can be part of other networks & it is known as sub-network.
 Computer Network Definition : a data communication system which interconnects computer systems at various locations with the help of communication devices like hubs, router, cables & NICs. Networking is done to facilitate data flow, implement security, share applications, resources & hardware. Common computer networks are; Local Area Network (LAN), Wide Area Network (WAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), Virtual Private Network (VPN), Intranet & Internet.
Computer Network Definition : a data communication system which interconnects computer systems at various locations with the help of communication devices like hubs, router, cables & NICs. Networking is done to facilitate data flow, implement security, share applications, resources & hardware. Common computer networks are; Local Area Network (LAN), Wide Area Network (WAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), Virtual Private Network (VPN), Intranet & Internet.
 Why use a computer networks? Resource sharing Ex: sharing of information, sharing hardware, sharing software & application Centralizing administration & support Communication Ex : Email, IRC, Voice/Video conferencing, Internet phone/Vo. IP)
Why use a computer networks? Resource sharing Ex: sharing of information, sharing hardware, sharing software & application Centralizing administration & support Communication Ex : Email, IRC, Voice/Video conferencing, Internet phone/Vo. IP)
 Types of networks Depending on the size & coverage area of the network, it can be classified into following groups. Local Area Network - LAN Def: Connects a group of computers in a small geographical area such as in a building or office. Also known as high speed networks that connects PC, printers & other network devices together in an organization. Usually controlled by a single administrator due to its size.
Types of networks Depending on the size & coverage area of the network, it can be classified into following groups. Local Area Network - LAN Def: Connects a group of computers in a small geographical area such as in a building or office. Also known as high speed networks that connects PC, printers & other network devices together in an organization. Usually controlled by a single administrator due to its size.
 Types of networks Metropolitan Area Network – MAN Def : a backbone network that connects LANs in a metropolitan area such as a city or town. It handles many communication activities or traffic. Storage Area Network (SAN) – network designed to attach computer storage devices such as disk array controllers & tape libraries to servers.
Types of networks Metropolitan Area Network – MAN Def : a backbone network that connects LANs in a metropolitan area such as a city or town. It handles many communication activities or traffic. Storage Area Network (SAN) – network designed to attach computer storage devices such as disk array controllers & tape libraries to servers.
 Types of networks Wide Area Network – WAN Def : a computer network covering broad geographical areas such as state or country. Data & information delivery is made via telephone lines, microwaves or satellites. WAN is used to connect LANs & also MANs. The largest & well known WAN is Internet.
Types of networks Wide Area Network – WAN Def : a computer network covering broad geographical areas such as state or country. Data & information delivery is made via telephone lines, microwaves or satellites. WAN is used to connect LANs & also MANs. The largest & well known WAN is Internet.
 Types of networks Virtual Private Network – VPN Def : private data networks that makes use of the public telecommunication infrastructures. It is also a WAN but it is private & only that particular company people have access to it. It maintains data privacy through the use of security procedures. To give the company the capabilities of full access at much lower cost by using the shared public infrastructure like public telephone lines or internet rather than their own.
Types of networks Virtual Private Network – VPN Def : private data networks that makes use of the public telecommunication infrastructures. It is also a WAN but it is private & only that particular company people have access to it. It maintains data privacy through the use of security procedures. To give the company the capabilities of full access at much lower cost by using the shared public infrastructure like public telephone lines or internet rather than their own.
 Types of networks Intranet Def : private network of any organization which is only accessed by allowed users from the organization itself. Main aim : to share part of the organization’s information & computer resources among its employees geographically dispersed. Also used to monitor workgroup or teleconferencing within the organization. External users can not access the company data. Ex : leave management system, human resource system
Types of networks Intranet Def : private network of any organization which is only accessed by allowed users from the organization itself. Main aim : to share part of the organization’s information & computer resources among its employees geographically dispersed. Also used to monitor workgroup or teleconferencing within the organization. External users can not access the company data. Ex : leave management system, human resource system
 Types of networks Extranet Def : private network of an organization that allows trusted external partners or clients such as suppliers, customer or business partners to access the network. An intranet extended to trusted external parties becomes extranet ! External parties would have limited access as compared to internal employee.
Types of networks Extranet Def : private network of an organization that allows trusted external partners or clients such as suppliers, customer or business partners to access the network. An intranet extended to trusted external parties becomes extranet ! External parties would have limited access as compared to internal employee.
 Network topology Def : the method used to do the physical configuration of cables, computer & network devices. Choice of topology is dependent upon: Type & number of equipment being used. Planned applications & rate of data transfer. Required response times. Cost Ex of network topologies : linear bus, star, ring, mesh, hybrid, tree.
Network topology Def : the method used to do the physical configuration of cables, computer & network devices. Choice of topology is dependent upon: Type & number of equipment being used. Planned applications & rate of data transfer. Required response times. Cost Ex of network topologies : linear bus, star, ring, mesh, hybrid, tree.
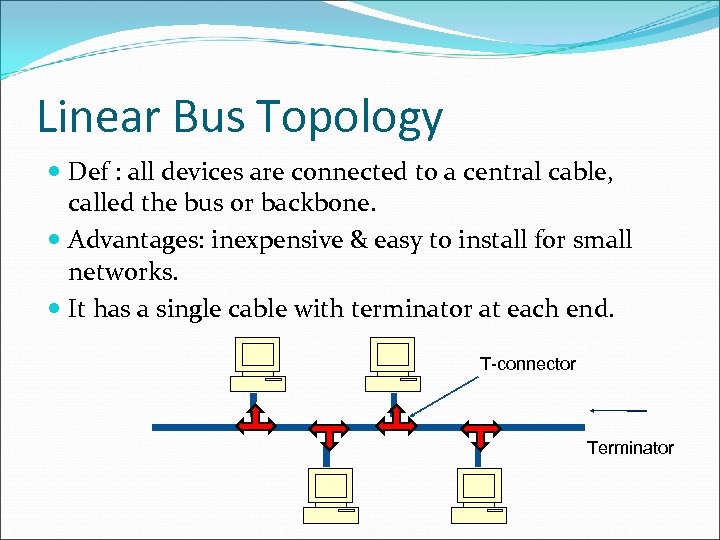 Linear Bus Topology Def : all devices are connected to a central cable, called the bus or backbone. Advantages: inexpensive & easy to install for small networks. It has a single cable with terminator at each end. T-connector Terminator
Linear Bus Topology Def : all devices are connected to a central cable, called the bus or backbone. Advantages: inexpensive & easy to install for small networks. It has a single cable with terminator at each end. T-connector Terminator
 Linear Bus topology Features: Requires less cable length than star topology Easy to connect a computer / peripheral to a linear bus Entire network shuts down if there a break in the main cable. Difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shuts down. Not meant to be used as a stand alone solution in a large building.
Linear Bus topology Features: Requires less cable length than star topology Easy to connect a computer / peripheral to a linear bus Entire network shuts down if there a break in the main cable. Difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shuts down. Not meant to be used as a stand alone solution in a large building.
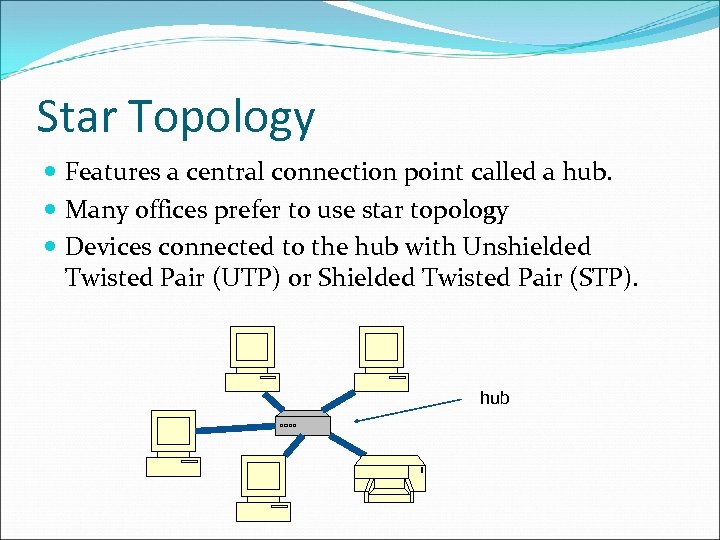 Star Topology Features a central connection point called a hub. Many offices prefer to use star topology Devices connected to the hub with Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) or Shielded Twisted Pair (STP). hub
Star Topology Features a central connection point called a hub. Many offices prefer to use star topology Devices connected to the hub with Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) or Shielded Twisted Pair (STP). hub
 Star Topology Features ; All devices revolve around a central hub / switch. Switch / hub controls the network communications & can communicate with other hubs. Easy to install. No disruptions to the network when connecting / removing devices. Requires more cable length than bus topology. A failure in any network cable will only take down one computer’s network access & not entire LAN. If hub fails = entire LAN fails !
Star Topology Features ; All devices revolve around a central hub / switch. Switch / hub controls the network communications & can communicate with other hubs. Easy to install. No disruptions to the network when connecting / removing devices. Requires more cable length than bus topology. A failure in any network cable will only take down one computer’s network access & not entire LAN. If hub fails = entire LAN fails !
 Ring topology Every device has exactly 2 neighbours for communication purposes. All messages travel through a ring in the same direction (clockwise / anti clockwise). A Data Token is used to grant permission for each computer to communicate. A failure in any cable or device breaks the loop & can take down the entire network. Commonly used in campuses, school, buildings.
Ring topology Every device has exactly 2 neighbours for communication purposes. All messages travel through a ring in the same direction (clockwise / anti clockwise). A Data Token is used to grant permission for each computer to communicate. A failure in any cable or device breaks the loop & can take down the entire network. Commonly used in campuses, school, buildings.
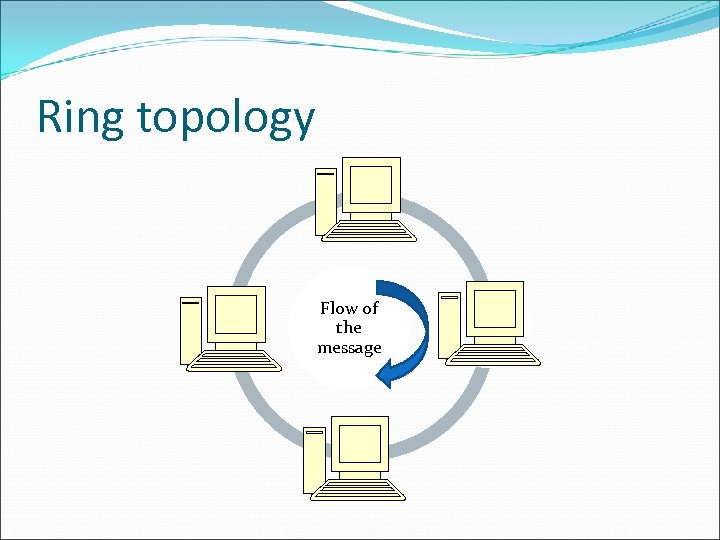 Ring topology Flow of the message
Ring topology Flow of the message
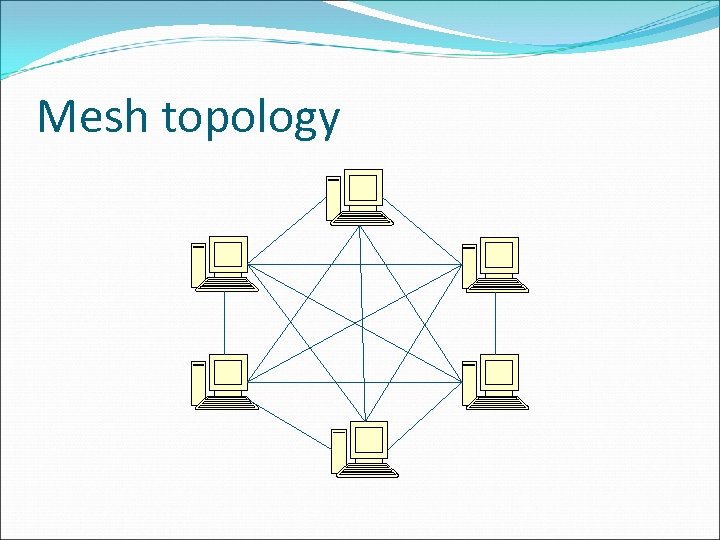
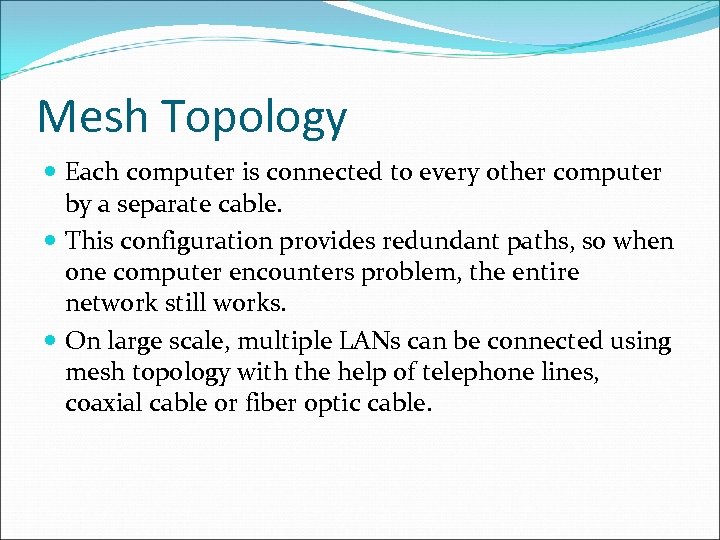 Mesh Topology Each computer is connected to every other computer by a separate cable. This configuration provides redundant paths, so when one computer encounters problem, the entire network still works. On large scale, multiple LANs can be connected using mesh topology with the help of telephone lines, coaxial cable or fiber optic cable.
Mesh Topology Each computer is connected to every other computer by a separate cable. This configuration provides redundant paths, so when one computer encounters problem, the entire network still works. On large scale, multiple LANs can be connected using mesh topology with the help of telephone lines, coaxial cable or fiber optic cable.
 Mesh topology
Mesh topology
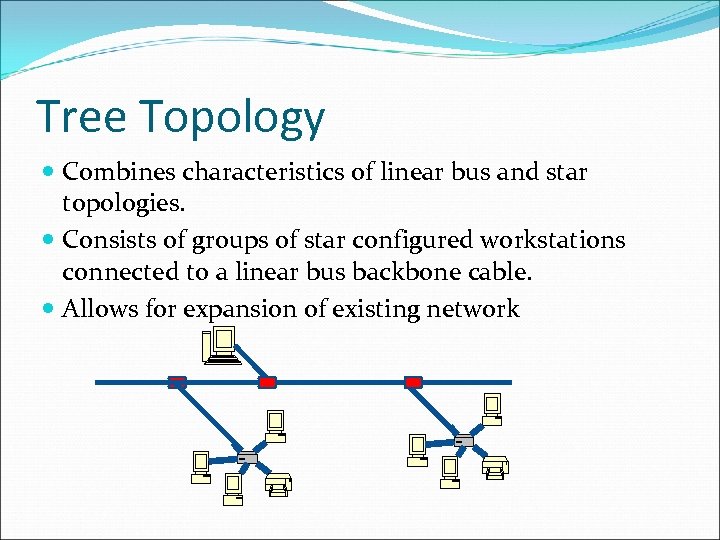 Tree Topology Combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies. Consists of groups of star configured workstations connected to a linear bus backbone cable. Allows for expansion of existing network
Tree Topology Combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies. Consists of groups of star configured workstations connected to a linear bus backbone cable. Allows for expansion of existing network
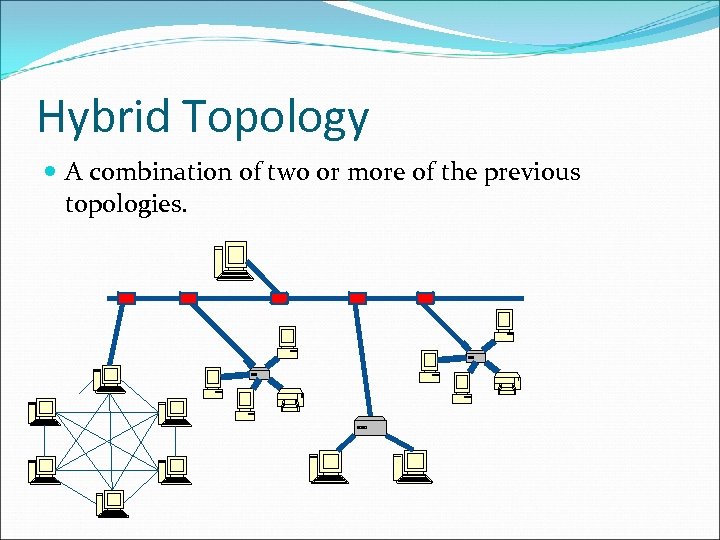 Hybrid Topology A combination of two or more of the previous topologies.
Hybrid Topology A combination of two or more of the previous topologies.
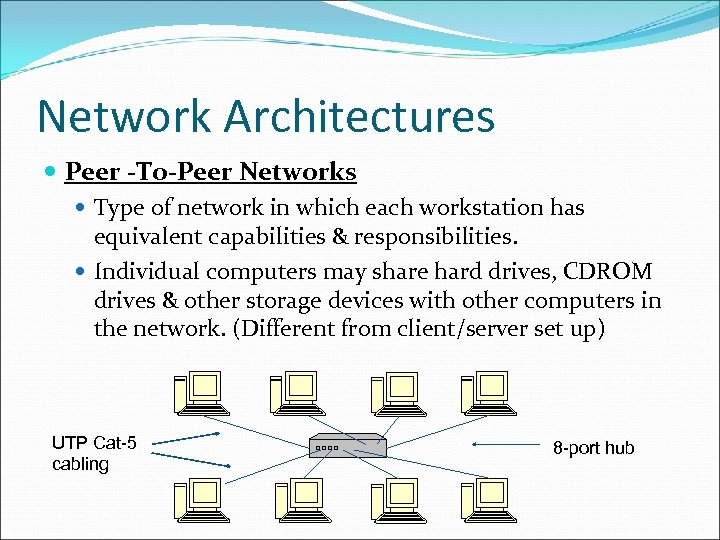 Network Architectures Peer -To-Peer Networks Type of network in which each workstation has equivalent capabilities & responsibilities. Individual computers may share hard drives, CDROM drives & other storage devices with other computers in the network. (Different from client/server set up) UTP Cat-5 cabling 8 -port hub
Network Architectures Peer -To-Peer Networks Type of network in which each workstation has equivalent capabilities & responsibilities. Individual computers may share hard drives, CDROM drives & other storage devices with other computers in the network. (Different from client/server set up) UTP Cat-5 cabling 8 -port hub
 Peer to Peer Networks Features : Peers acts as equals, merging the roles of clients & server There is no central server managing the network There is no central router Every computer can share the resources it has.
Peer to Peer Networks Features : Peers acts as equals, merging the roles of clients & server There is no central server managing the network There is no central router Every computer can share the resources it has.
 Network Architectures Client-Server Network A computer network where one or more computers are formed to be the server. Other computers (clients) can request resources from the server. Clients depends on the server for few resources such as files, devices, processing power & storage space. The server controls access towards devices & software in the network & offers storage capacity for program, data & information.
Network Architectures Client-Server Network A computer network where one or more computers are formed to be the server. Other computers (clients) can request resources from the server. Clients depends on the server for few resources such as files, devices, processing power & storage space. The server controls access towards devices & software in the network & offers storage capacity for program, data & information.
 Client-Server Networks Features: A well planned client/server system provides inexpensive networks. The servers are easier to secure & maintain from one location. Client/server computing uses a powerful server to store data. Data is more secure in a client/server environment. Server backups can be scheduled to occur automatically. A server based networks can support thousand of users. Servers can be physically isolated for additional security. Sensitive data can be secure from unauthorized users.
Client-Server Networks Features: A well planned client/server system provides inexpensive networks. The servers are easier to secure & maintain from one location. Client/server computing uses a powerful server to store data. Data is more secure in a client/server environment. Server backups can be scheduled to occur automatically. A server based networks can support thousand of users. Servers can be physically isolated for additional security. Sensitive data can be secure from unauthorized users.
 Network Devices Network Interface Cards Hub Assignment 1 : Switch Repeater Explain what each devices ! Bridge Router Brouter Gateway Cable
Network Devices Network Interface Cards Hub Assignment 1 : Switch Repeater Explain what each devices ! Bridge Router Brouter Gateway Cable




