3df66eb550a5d490730cce64eff10b6a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Chapter 1: Introduction Chemistry 1020: Interpretive chemistry Andy Aspaas, Instructor
Chapter 1: Introduction Chemistry 1020: Interpretive chemistry Andy Aspaas, Instructor
 What is chemistry? • “The science that deals with the materials of the universe and the changes that these materials undergo. ” • Chemistry in relation to other sciences
What is chemistry? • “The science that deals with the materials of the universe and the changes that these materials undergo. ” • Chemistry in relation to other sciences
 Chemistry around us • Advances from chemistry – Medicine – Agriculture – Energy – Plastics • Problems from chemistry?
Chemistry around us • Advances from chemistry – Medicine – Agriculture – Energy – Plastics • Problems from chemistry?
 Scientific problem solving • The scientific method: process behind all scientific inquiry • Flexible, changes when new information is learned • Start with a question, problem or observation • Hypothesis: possible explanation • Experimentation: controlled process of gathering new information • Observations, do they support the hypothesis? • Theory: a tested hypothesis, can still be revised
Scientific problem solving • The scientific method: process behind all scientific inquiry • Flexible, changes when new information is learned • Start with a question, problem or observation • Hypothesis: possible explanation • Experimentation: controlled process of gathering new information • Observations, do they support the hypothesis? • Theory: a tested hypothesis, can still be revised
 Law vs. theory • Natural law: generally observed behavior, result of measurements • Theory: our attempt to explain why certain behaviors happen • Scientific method is still limited by human imperfection
Law vs. theory • Natural law: generally observed behavior, result of measurements • Theory: our attempt to explain why certain behaviors happen • Scientific method is still limited by human imperfection
 How to learn chemistry • Reading, vocabulary, memorization are only a start – Should be considered a minor part of your learning process in chemistry • Problem solving skills are even more important! – Why practice homework problems are assigned – Struggle with them, use answers carefully – Mistakes can be valuable
How to learn chemistry • Reading, vocabulary, memorization are only a start – Should be considered a minor part of your learning process in chemistry • Problem solving skills are even more important! – Why practice homework problems are assigned – Struggle with them, use answers carefully – Mistakes can be valuable
 Chapter 2: Scientific Notation Chemistry 1020: Interpretive chemistry Andy Aspaas, Instructor
Chapter 2: Scientific Notation Chemistry 1020: Interpretive chemistry Andy Aspaas, Instructor
 Types of observations • Observations are a key part of any type of scientific research • Qualitative: a description (a white solid was formed) • Quantitative: a specific measurement (the product weighs 1. 43 grams)
Types of observations • Observations are a key part of any type of scientific research • Qualitative: a description (a white solid was formed) • Quantitative: a specific measurement (the product weighs 1. 43 grams)
 Measurements and numbers • Measurements must contain both a number and a unit - without both, the measurement is meaningless • Many numbers in measurements are very large or very small – Distance from earth to sun: 93, 000 miles – Width of an oxygen atom: 0. 0000013 meters • Is there an easier way to deal with such ungainly numbers?
Measurements and numbers • Measurements must contain both a number and a unit - without both, the measurement is meaningless • Many numbers in measurements are very large or very small – Distance from earth to sun: 93, 000 miles – Width of an oxygen atom: 0. 0000013 meters • Is there an easier way to deal with such ungainly numbers?
 Scientific notation • Used to make very large or very small numbers more manageable • Multiply a number between 1 and 10 by any power of 10 • 200 in scientific notation? • For even larger numbers, count the number of places the decimal point must move, and make that the power of 10 • 230, 000, 000 in scientific notation?
Scientific notation • Used to make very large or very small numbers more manageable • Multiply a number between 1 and 10 by any power of 10 • 200 in scientific notation? • For even larger numbers, count the number of places the decimal point must move, and make that the power of 10 • 230, 000, 000 in scientific notation?
 Scientific notation • Works with small numbers too • For small numbers, move the decimal point to the right, and use that as the negative power of 10 • Left is positive, “LIP” • Using a calculator – The E or EE button on your scientific calculator
Scientific notation • Works with small numbers too • For small numbers, move the decimal point to the right, and use that as the negative power of 10 • Left is positive, “LIP” • Using a calculator – The E or EE button on your scientific calculator
 Units of measurement • Unit: which scale or standard is used for a particular measurement • English system: US residents are most familiar with • Metric system: used in most of the rest of the world • SI, or International System, used in scientific work – Based on metric system – Agreed upon by scientists worldwide
Units of measurement • Unit: which scale or standard is used for a particular measurement • English system: US residents are most familiar with • Metric system: used in most of the rest of the world • SI, or International System, used in scientific work – Based on metric system – Agreed upon by scientists worldwide
 Some fundamental SI units Quantity mass length time temperature Name of unit kilogram meter second kelvin Abbreviation kg m s K • Most other SI units can be derived from these
Some fundamental SI units Quantity mass length time temperature Name of unit kilogram meter second kelvin Abbreviation kg m s K • Most other SI units can be derived from these
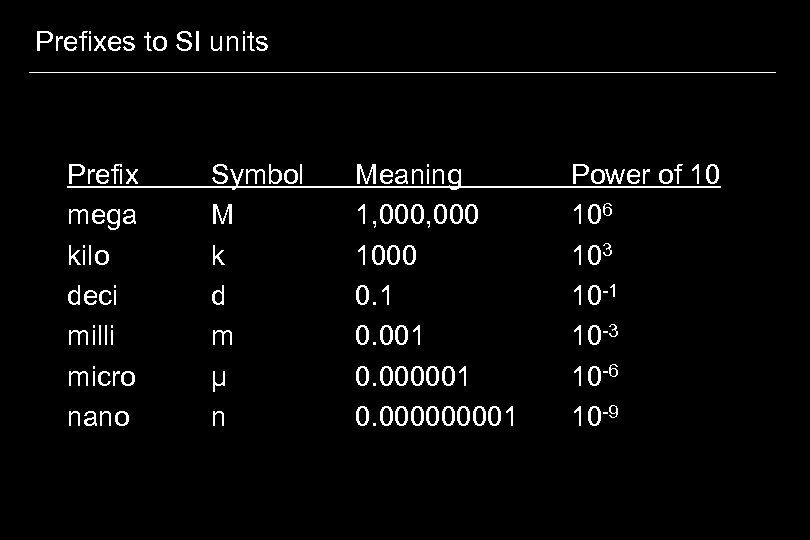 Prefixes to SI units Prefix mega kilo deci milli micro nano Symbol M k d m µ n Meaning 1, 000 1000 0. 1 0. 000001 0. 00001 Power of 10 106 103 10 -1 10 -3 10 -6 10 -9
Prefixes to SI units Prefix mega kilo deci milli micro nano Symbol M k d m µ n Meaning 1, 000 1000 0. 1 0. 000001 0. 00001 Power of 10 106 103 10 -1 10 -3 10 -6 10 -9
 Length • Fundamental SI unit for length: meter – A little longer than a yard • Using prefixes as the power of 10 – 1 mm = 10 -3 m = 0. 001 m • 1 inch = 2. 54 cm • Measured with a ruler or caliper
Length • Fundamental SI unit for length: meter – A little longer than a yard • Using prefixes as the power of 10 – 1 mm = 10 -3 m = 0. 001 m • 1 inch = 2. 54 cm • Measured with a ruler or caliper
 Volume • Amount of 3 -dimensional space occupied by an object • Unit: liter (L) • 1 L = 1 dm 3 (cubic decimeter) • 1 millileter (m. L) = 1 cm 3 – Commonly used volume unit in chemistry • Volume measurements: – Graduated cylinder – Syringe – Buret
Volume • Amount of 3 -dimensional space occupied by an object • Unit: liter (L) • 1 L = 1 dm 3 (cubic decimeter) • 1 millileter (m. L) = 1 cm 3 – Commonly used volume unit in chemistry • Volume measurements: – Graduated cylinder – Syringe – Buret
 Mass • The specific amount of matter present in an object – Measured on a balance • Not to be confused with weight – (Force of gravity acting on the mass of an object) – Dependent on the strength of gravity – Earth vs. moon? – Measured on a scale • Mass used much more commonly in chemistry • SI fundamental unit: kilogram
Mass • The specific amount of matter present in an object – Measured on a balance • Not to be confused with weight – (Force of gravity acting on the mass of an object) – Dependent on the strength of gravity – Earth vs. moon? – Measured on a scale • Mass used much more commonly in chemistry • SI fundamental unit: kilogram
 Uncertainty in measurement • Analog measurements - measured mechanically against some type of physical scale – Estimate required for last digit of measurement – Last digit = the uncertain digit – Can be expressed as ± amount of the uncertain digit (4. 542 ± 0. 001) • Digital measurements - read from a display – Last digit still uncertain even though you don’t do an estimation
Uncertainty in measurement • Analog measurements - measured mechanically against some type of physical scale – Estimate required for last digit of measurement – Last digit = the uncertain digit – Can be expressed as ± amount of the uncertain digit (4. 542 ± 0. 001) • Digital measurements - read from a display – Last digit still uncertain even though you don’t do an estimation
 Accuracy vs. Precision • Accuracy: how close a single measurement or set of measurements are to their true value • Precision: how similar a number of measurements are • Dartboard example • Beaker of water example
Accuracy vs. Precision • Accuracy: how close a single measurement or set of measurements are to their true value • Precision: how similar a number of measurements are • Dartboard example • Beaker of water example
 Significant figures • Sum of all certain numbers in a measurement plus the first uncertain number • Indicates the amount of precision with which a measurement can be made • Since each measurement contains uncertainty, that uncertainty must be tracked when manipulating the measurements
Significant figures • Sum of all certain numbers in a measurement plus the first uncertain number • Indicates the amount of precision with which a measurement can be made • Since each measurement contains uncertainty, that uncertainty must be tracked when manipulating the measurements
 How many sig figs does a measurement have? • • Nonzero integers are always significant (1 thru 9) Leading zeroes (on the left) are never significant Captive zeroes are always significant Trailing zeroes (at the end) are only significant if there’s a decimal point • Exact numbers (obtained by counting) have an infinite number of sig figs
How many sig figs does a measurement have? • • Nonzero integers are always significant (1 thru 9) Leading zeroes (on the left) are never significant Captive zeroes are always significant Trailing zeroes (at the end) are only significant if there’s a decimal point • Exact numbers (obtained by counting) have an infinite number of sig figs
 Rounding off • Calculators don’t understand sig figs • Will return as many digits to you as possible • You must round the answer to the correct number of sig figs • Look at the digit to the right of the last sig fig – 0 -4, just drop it and everything to the right – 5 -9, increase last sig fig by one, drop rest – Look only at the one digit to the right of the last sig fig, ignore all others!
Rounding off • Calculators don’t understand sig figs • Will return as many digits to you as possible • You must round the answer to the correct number of sig figs • Look at the digit to the right of the last sig fig – 0 -4, just drop it and everything to the right – 5 -9, increase last sig fig by one, drop rest – Look only at the one digit to the right of the last sig fig, ignore all others!
 Determining sig figs in calculations • When multiplying or dividing, find the measurement with the smallest number of sig figs – Answer must be rounded to that many sig figs • When adding or subtracting, find the measurement with the smallest number of decimal places – Answer must be rounded to that many decimal places • Practice!
Determining sig figs in calculations • When multiplying or dividing, find the measurement with the smallest number of sig figs – Answer must be rounded to that many sig figs • When adding or subtracting, find the measurement with the smallest number of decimal places – Answer must be rounded to that many decimal places • Practice!
 Dimensional analysis introduction • We do this all the time without even thinking about it • Example: planning a party – 15 guests – 3 drinks per guest – How many drinks should you buy? • Conversion factor: a ratio of two measurements with different units that are equal to each other • Expressed as a fraction, two possible orders!
Dimensional analysis introduction • We do this all the time without even thinking about it • Example: planning a party – 15 guests – 3 drinks per guest – How many drinks should you buy? • Conversion factor: a ratio of two measurements with different units that are equal to each other • Expressed as a fraction, two possible orders!
 Dimensional analysis calculations • Set up an equation like this Known quantity x conversion factor = unknown quantity • Orient conversion factor so units of known quantity are cancelled • Multiply the known by the conversion factor • The only remaining unit should be the one you’re solving for • Correct for sig figs • Does the answer make sense? • Practice, practice, practice!
Dimensional analysis calculations • Set up an equation like this Known quantity x conversion factor = unknown quantity • Orient conversion factor so units of known quantity are cancelled • Multiply the known by the conversion factor • The only remaining unit should be the one you’re solving for • Correct for sig figs • Does the answer make sense? • Practice, practice, practice!
 Temperature scales • Fahrenheit scale: used in the US • Celsius scale: used in most rest of world, and by most scientists • Kelvin scale: SI base unit of temperature – 0 K is lowest possible theoretical temperature
Temperature scales • Fahrenheit scale: used in the US • Celsius scale: used in most rest of world, and by most scientists • Kelvin scale: SI base unit of temperature – 0 K is lowest possible theoretical temperature
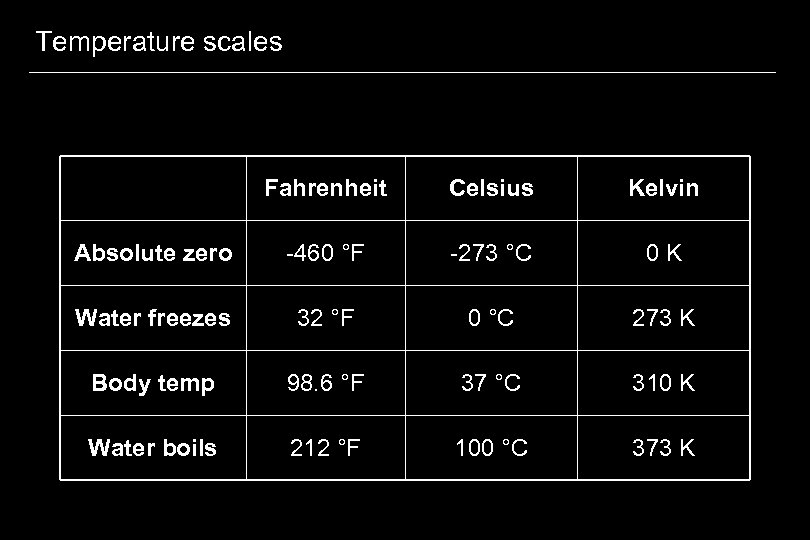 Temperature scales Fahrenheit Celsius Kelvin Absolute zero -460 °F -273 °C 0 K Water freezes 32 °F 0 °C 273 K Body temp 98. 6 °F 37 °C 310 K Water boils 212 °F 100 °C 373 K
Temperature scales Fahrenheit Celsius Kelvin Absolute zero -460 °F -273 °C 0 K Water freezes 32 °F 0 °C 273 K Body temp 98. 6 °F 37 °C 310 K Water boils 212 °F 100 °C 373 K
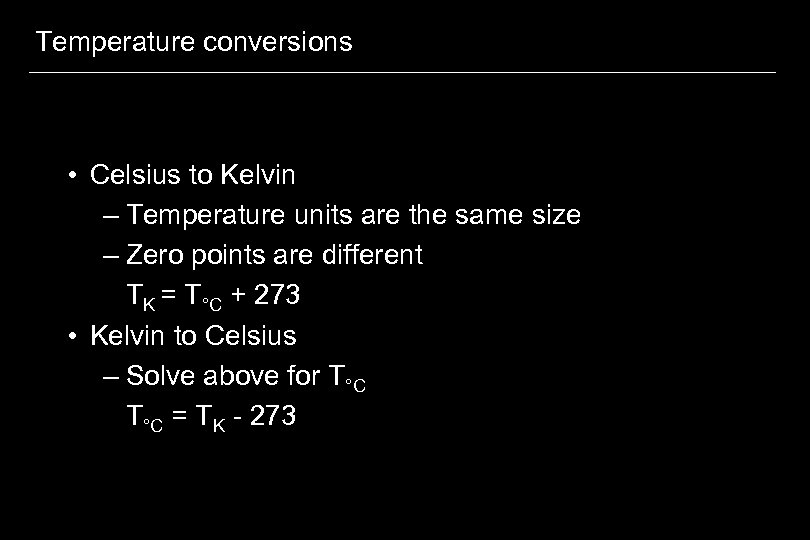 Temperature conversions • Celsius to Kelvin – Temperature units are the same size – Zero points are different TK = T°C + 273 • Kelvin to Celsius – Solve above for T°C = TK - 273
Temperature conversions • Celsius to Kelvin – Temperature units are the same size – Zero points are different TK = T°C + 273 • Kelvin to Celsius – Solve above for T°C = TK - 273
 Fahrenheit and Celsius • Different degree units and zero points T°F = 1. 80(T°C) + 32 T°C = (T°F - 32) / 1. 80
Fahrenheit and Celsius • Different degree units and zero points T°F = 1. 80(T°C) + 32 T°C = (T°F - 32) / 1. 80
 Density • Density: amount of matter present in a given volume of substance Density = mass / volume – Units could be kg/L, g/cm 3, g/m. L, etc.
Density • Density: amount of matter present in a given volume of substance Density = mass / volume – Units could be kg/L, g/cm 3, g/m. L, etc.


