5ca05ca8c2c4690690e183d28f250009.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Chapter 1. 3 Computer Networks
Chapter 1. 3 Computer Networks
 Client-Server systems • The question : Within a large organization, what is the optimal localization of – Processing power – Data storage • The possibilities : – In a global computer center – In local computer centers – With the user – Any combination of the three previous solutions
Client-Server systems • The question : Within a large organization, what is the optimal localization of – Processing power – Data storage • The possibilities : – In a global computer center – In local computer centers – With the user – Any combination of the three previous solutions
 Client-Server systems • The question : What is the optimal localization of – Processing power – Data storage • The possibilities : – In a global computer center – In local computer centers – With the user – Any combination of the three previous solutions
Client-Server systems • The question : What is the optimal localization of – Processing power – Data storage • The possibilities : – In a global computer center – In local computer centers – With the user – Any combination of the three previous solutions
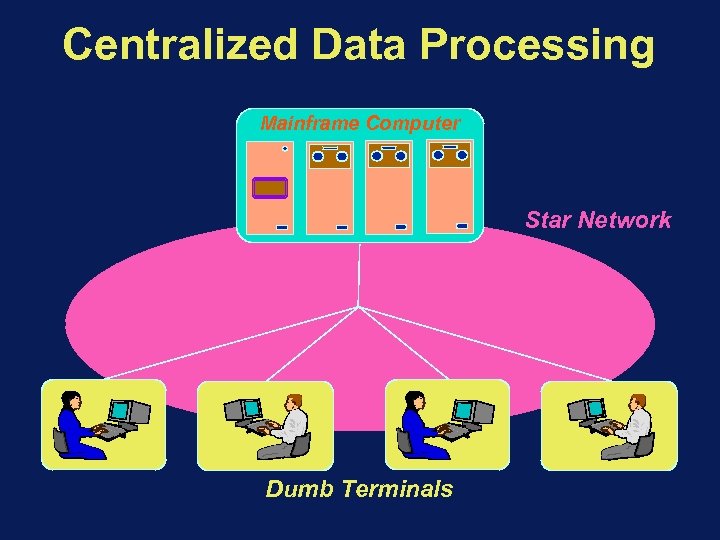 Centralized Data Processing Mainframe Computer Star Network Dumb Terminals
Centralized Data Processing Mainframe Computer Star Network Dumb Terminals
 Benefits : Simple Access to Common Data Professional Data Management Enforceable Security Well Defined Cost Full control by EDP people
Benefits : Simple Access to Common Data Professional Data Management Enforceable Security Well Defined Cost Full control by EDP people
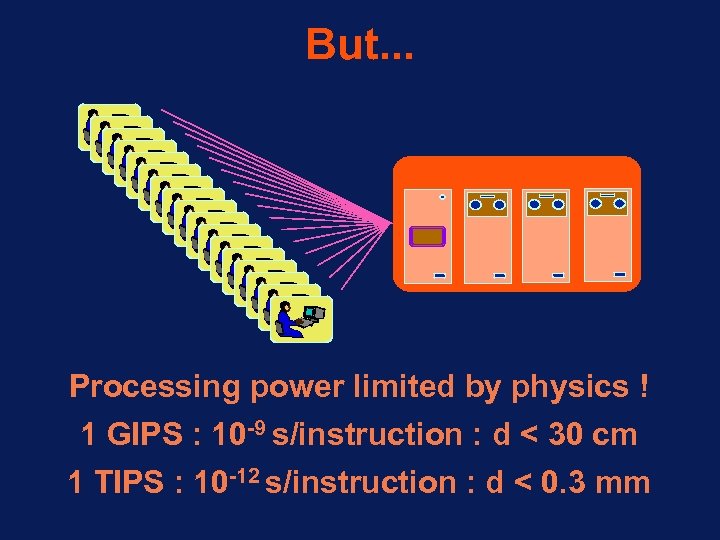 But. . . Mainframe Computer Processing power limited by physics ! 1 GIPS : 10 -9 s/instruction : d < 30 cm 1 TIPS : 10 -12 s/instruction : d < 0. 3 mm
But. . . Mainframe Computer Processing power limited by physics ! 1 GIPS : 10 -9 s/instruction : d < 30 cm 1 TIPS : 10 -12 s/instruction : d < 0. 3 mm
 Technical arguments against Central Computers Processing Power of a single CPU can not grow indefinitely Transmission capacity needed between processor and terminal has become enormous
Technical arguments against Central Computers Processing Power of a single CPU can not grow indefinitely Transmission capacity needed between processor and terminal has become enormous
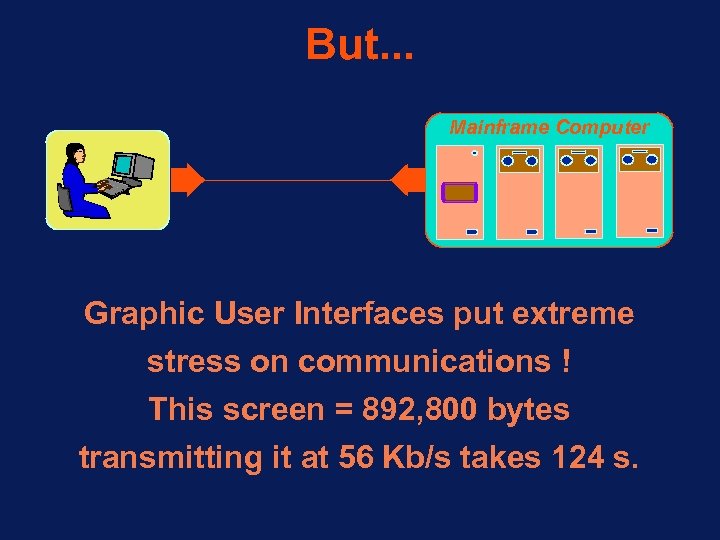 But. . . Mainframe Computer Graphic User Interfaces put extreme stress on communications ! This screen = 892, 800 bytes transmitting it at 56 Kb/s takes 124 s.
But. . . Mainframe Computer Graphic User Interfaces put extreme stress on communications ! This screen = 892, 800 bytes transmitting it at 56 Kb/s takes 124 s.
 Technical arguments against Central Computers Processing Power of a single CPU can not grow indefinitely Transmission capacity needed between processor and terminal has become enormous
Technical arguments against Central Computers Processing Power of a single CPU can not grow indefinitely Transmission capacity needed between processor and terminal has become enormous
 Client-Server systems • The question : What is the optimal localization of – Processing power – Data storage • The possibilities : – In a global computer center – In local computer centers – With the user – Any combination of the three previous solutions
Client-Server systems • The question : What is the optimal localization of – Processing power – Data storage • The possibilities : – In a global computer center – In local computer centers – With the user – Any combination of the three previous solutions
 The Reaction : Independent Personal Computers
The Reaction : Independent Personal Computers
 But. . . Access to common data ? ? ? Risk of loss of data ! Software Maintenance ! Cost of some peripheral equipment Limited processing power And many other hidden costs !
But. . . Access to common data ? ? ? Risk of loss of data ! Software Maintenance ! Cost of some peripheral equipment Limited processing power And many other hidden costs !
 Client-Server systems • The question : What is the optimal localization of – Processing power – Data storage • The possibilities : – In a global computer center – In local computer centers – With the user – Any combination of the three previous solutions
Client-Server systems • The question : What is the optimal localization of – Processing power – Data storage • The possibilities : – In a global computer center – In local computer centers – With the user – Any combination of the three previous solutions
 Client - Server Systems Many computers with characteristics matching their specific usage interconnected by means of a network
Client - Server Systems Many computers with characteristics matching their specific usage interconnected by means of a network
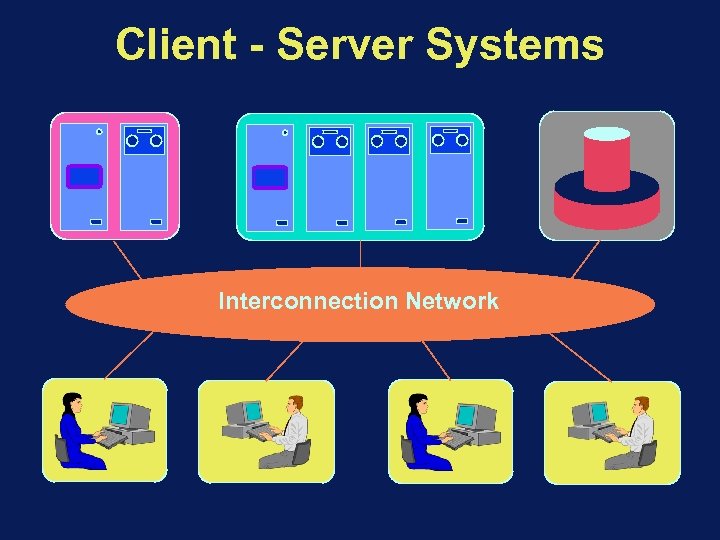 Client - Server Systems Interconnection Network
Client - Server Systems Interconnection Network
 Networked Computers Benefits Sharing of disk space (= access to common data & programs) (= centralized disk back-up facilities) Sharing of expensive peripherals (Spooling required) Sharing of processing power
Networked Computers Benefits Sharing of disk space (= access to common data & programs) (= centralized disk back-up facilities) Sharing of expensive peripherals (Spooling required) Sharing of processing power
 Client Server Systems Minimal integration: “Terminal Emulation” Very User Unfriendly Full Integration: “Virtual Mainframe” The user has the feeling all resources of all networked computers are part of her/his personal computer
Client Server Systems Minimal integration: “Terminal Emulation” Very User Unfriendly Full Integration: “Virtual Mainframe” The user has the feeling all resources of all networked computers are part of her/his personal computer
 Terminal Emulation = sub-minimal Client-server system • The personal workstations are used – as stand alone computers – as terminals connected to other computers • The user has to mentally switch between widely different user interfaces and operating systems. • Transferring data between local and remote applications is far from trivial • Terminal emulation is very user unfriendly !!!
Terminal Emulation = sub-minimal Client-server system • The personal workstations are used – as stand alone computers – as terminals connected to other computers • The user has to mentally switch between widely different user interfaces and operating systems. • Transferring data between local and remote applications is far from trivial • Terminal emulation is very user unfriendly !!!
 Client Server Systems Minimal integration: “Terminal Emulation” Very User Unfriendly Full Integration: “Virtual Mainframe” The user has the feeling all resources of all networked computers are part of her/his personal computer
Client Server Systems Minimal integration: “Terminal Emulation” Very User Unfriendly Full Integration: “Virtual Mainframe” The user has the feeling all resources of all networked computers are part of her/his personal computer
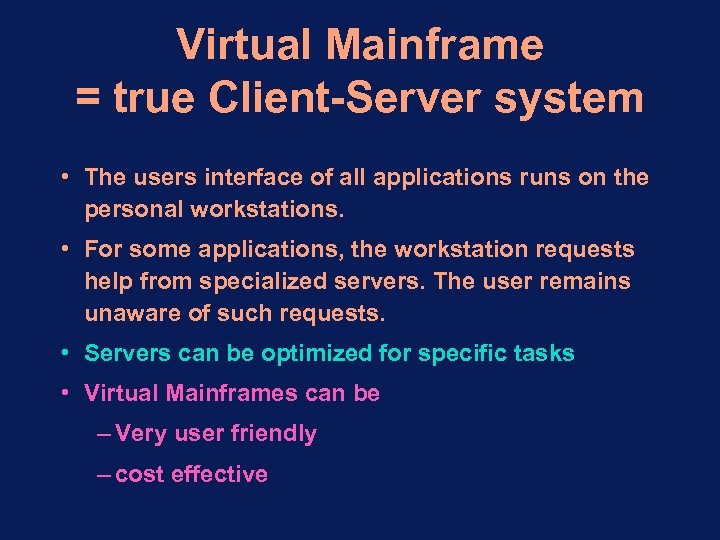 Virtual Mainframe = true Client-Server system • The users interface of all applications runs on the personal workstations. • For some applications, the workstation requests help from specialized servers. The user remains unaware of such requests. • Servers can be optimized for specific tasks • Virtual Mainframes can be – Very user friendly – cost effective
Virtual Mainframe = true Client-Server system • The users interface of all applications runs on the personal workstations. • For some applications, the workstation requests help from specialized servers. The user remains unaware of such requests. • Servers can be optimized for specific tasks • Virtual Mainframes can be – Very user friendly – cost effective
 Network Technology Local Area Networks In a room, a building, a campus High throughput, low delays, low cost VUBNET: 10 -100 Mbit/s in buildings Twisted pairs / coaxial cables 1 Gbit/s between buildings Optical Fibers
Network Technology Local Area Networks In a room, a building, a campus High throughput, low delays, low cost VUBNET: 10 -100 Mbit/s in buildings Twisted pairs / coaxial cables 1 Gbit/s between buildings Optical Fibers
 Network Technology Wide Area Networks All over the world Low throughput, high delays, high cost Leased lines: From Brussels to 64 Kb/s 2 Mb/s Antwerp Paris New York 400 1. 600 5 000 20. 000 2. 500 30. 000 (Indicative prices in Euro per month)
Network Technology Wide Area Networks All over the world Low throughput, high delays, high cost Leased lines: From Brussels to 64 Kb/s 2 Mb/s Antwerp Paris New York 400 1. 600 5 000 20. 000 2. 500 30. 000 (Indicative prices in Euro per month)
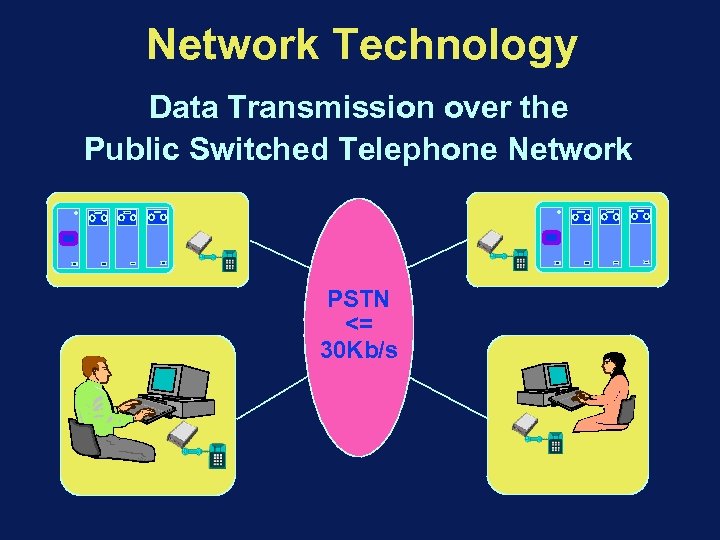 Network Technology Data Transmission over the Public Switched Telephone Network PSTN <= 30 Kb/s
Network Technology Data Transmission over the Public Switched Telephone Network PSTN <= 30 Kb/s
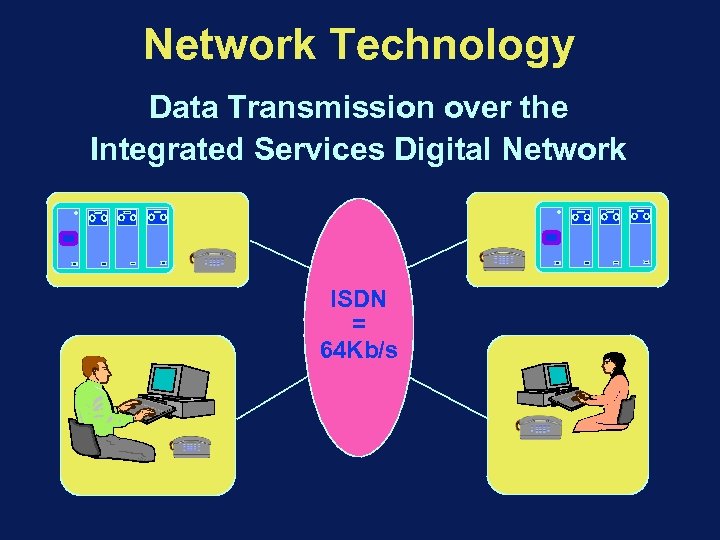 Network Technology Data Transmission over the Integrated Services Digital Network ISDN = 64 Kb/s
Network Technology Data Transmission over the Integrated Services Digital Network ISDN = 64 Kb/s
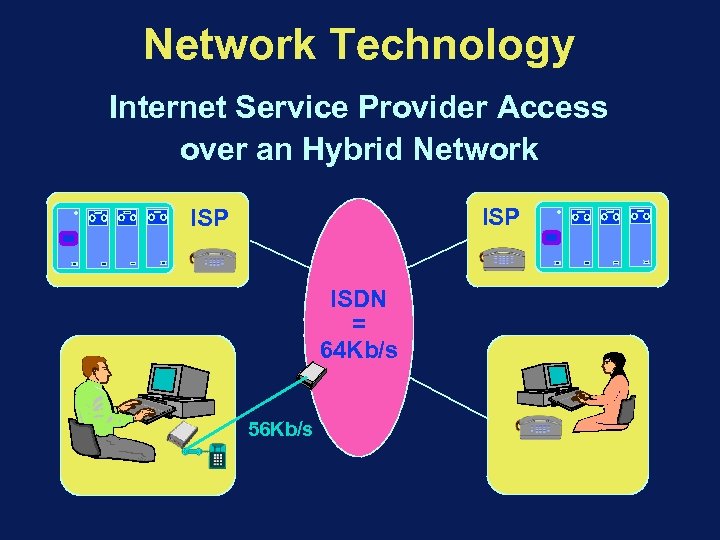 Network Technology Internet Service Provider Access over an Hybrid Network ISP ISDN = 64 Kb/s 56 Kb/s
Network Technology Internet Service Provider Access over an Hybrid Network ISP ISDN = 64 Kb/s 56 Kb/s
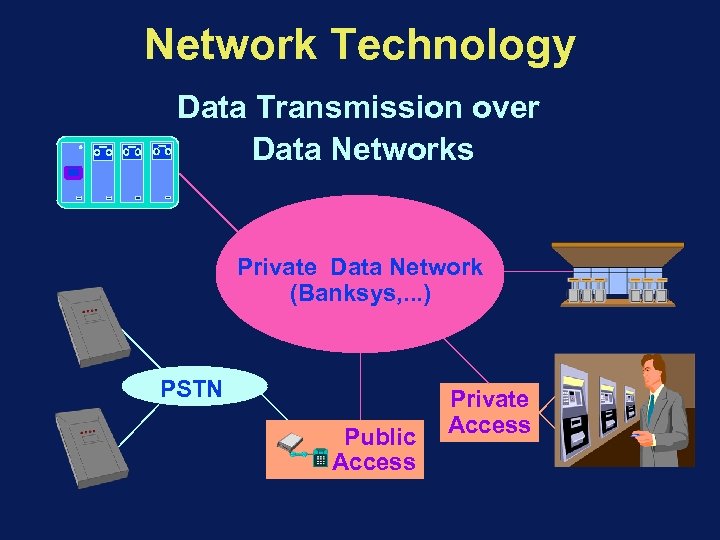 Network Technology Data Transmission over Data Networks Private Data Network (Banksys, . . . ) PSTN Public Access Private Access
Network Technology Data Transmission over Data Networks Private Data Network (Banksys, . . . ) PSTN Public Access Private Access
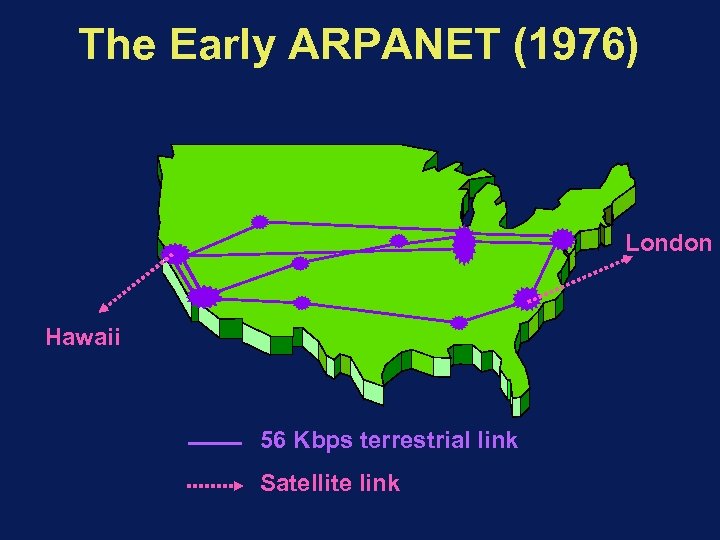 The Early ARPANET (1976) London Hawaii 56 Kbps terrestrial link Satellite link
The Early ARPANET (1976) London Hawaii 56 Kbps terrestrial link Satellite link
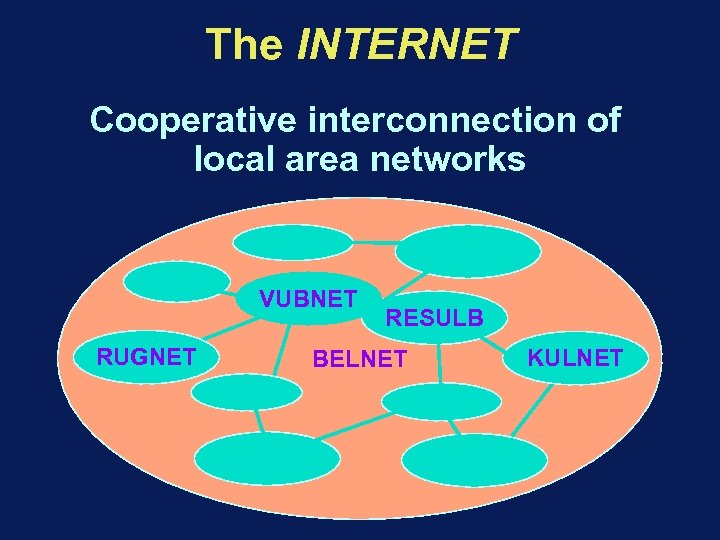 The INTERNET Cooperative interconnection of local area networks VUBNET RUGNET RESULB BELNET KULNET
The INTERNET Cooperative interconnection of local area networks VUBNET RUGNET RESULB BELNET KULNET
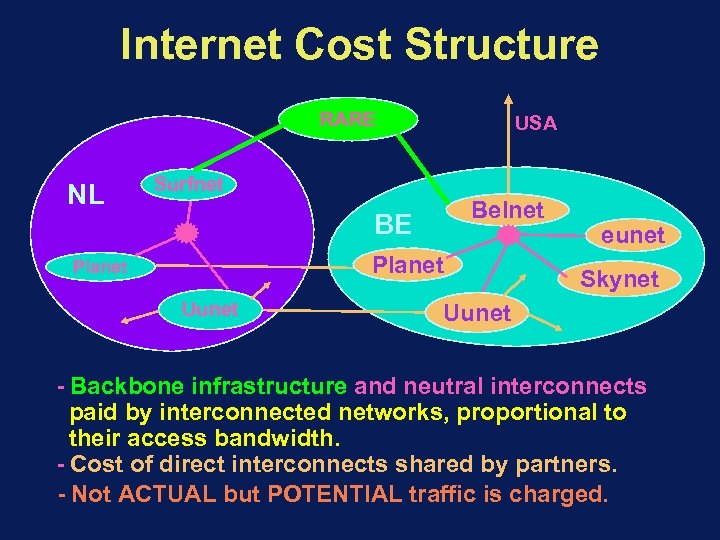 Internet Cost Structure RARE NL USA Surfnet Belnet BE Planet Uunet eunet Skynet Uunet - Backbone infrastructure and neutral interconnects paid by interconnected networks, proportional to their access bandwidth. - Cost of direct interconnects shared by partners. - Not ACTUAL but POTENTIAL traffic is charged.
Internet Cost Structure RARE NL USA Surfnet Belnet BE Planet Uunet eunet Skynet Uunet - Backbone infrastructure and neutral interconnects paid by interconnected networks, proportional to their access bandwidth. - Cost of direct interconnects shared by partners. - Not ACTUAL but POTENTIAL traffic is charged.
 Private Internet Access • Via Internet Service Provider • Main problem : local access line – Via PSTN or ISDN • Low throughput • time based charges • conflicting with phone and fax – Via ADSL or Cable TV • High throughput • Volume based charges • No Conflict with phone, fax or TV – Via Wireless link • GSM : slow & expensive • GPRS : much better but not yet widely used • UMTS : the wireless paradise ? ? ?
Private Internet Access • Via Internet Service Provider • Main problem : local access line – Via PSTN or ISDN • Low throughput • time based charges • conflicting with phone and fax – Via ADSL or Cable TV • High throughput • Volume based charges • No Conflict with phone, fax or TV – Via Wireless link • GSM : slow & expensive • GPRS : much better but not yet widely used • UMTS : the wireless paradise ? ? ?
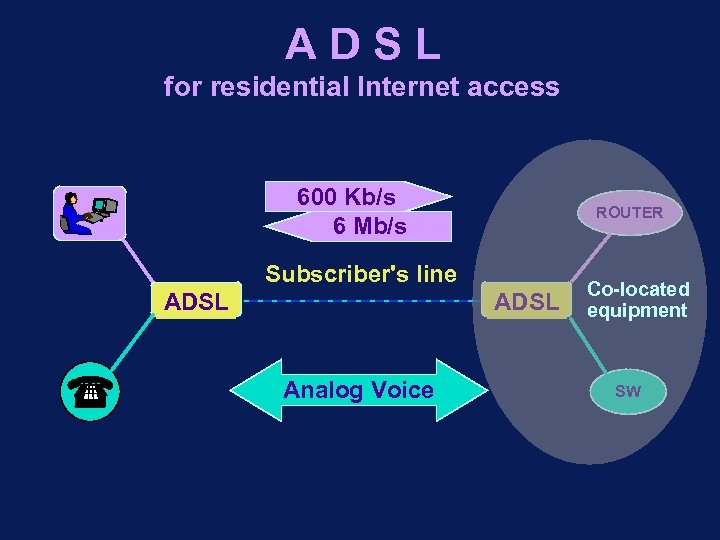 ADSL for residential Internet access 600 Kb/s 6 Mb/s ROUTER Subscriber's line ADSL Analog Voice Co-located equipment SW
ADSL for residential Internet access 600 Kb/s 6 Mb/s ROUTER Subscriber's line ADSL Analog Voice Co-located equipment SW
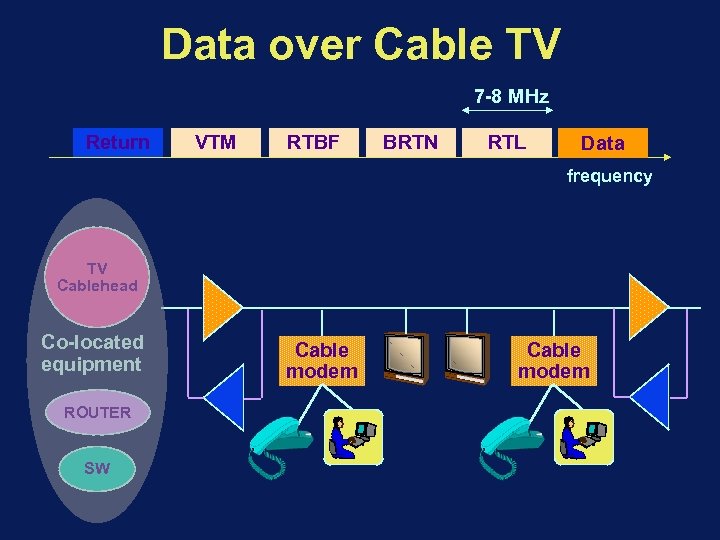 Data over Cable TV 7 -8 MHz Return VTM RTBF BRTN RTL Data frequency TV Cablehead Co-located equipment ROUTER SW Cable modem
Data over Cable TV 7 -8 MHz Return VTM RTBF BRTN RTL Data frequency TV Cablehead Co-located equipment ROUTER SW Cable modem
 Internet Usage Access to distributed multimedia databases (World Wide Web) Electronic Mail Internet Real-time Chat Remote Login (TELNET) File transfers (FTP) Internet Telephony Network File System
Internet Usage Access to distributed multimedia databases (World Wide Web) Electronic Mail Internet Real-time Chat Remote Login (TELNET) File transfers (FTP) Internet Telephony Network File System
 World Wide Web • Uniform hypertext based users friendly interface for distributed databases. • Inexpensive, high quality, browsers available for almost all computers. • Sophisticated and application specific users interactivity possible by downloading programs to be executed on client’s workstation (Java). • Already over 200, 000 pages available worldwide, mainly for public relations, publicity and, to some extent, electronic commerce. • Electronic commerce still restrained by security concerns.
World Wide Web • Uniform hypertext based users friendly interface for distributed databases. • Inexpensive, high quality, browsers available for almost all computers. • Sophisticated and application specific users interactivity possible by downloading programs to be executed on client’s workstation (Java). • Already over 200, 000 pages available worldwide, mainly for public relations, publicity and, to some extent, electronic commerce. • Electronic commerce still restrained by security concerns.
 HTML Hyper. Text Markup Language • Hypertext – Multimedia document » Normal text » Graphics and images (stored in separate files) » Sound (stored in separate files) » Executable programs (Java Applets) – References of other hypertext documents (“Anchors”) » “clickable” normal text or image (icon) » address (URL) where the corresponding document can be found
HTML Hyper. Text Markup Language • Hypertext – Multimedia document » Normal text » Graphics and images (stored in separate files) » Sound (stored in separate files) » Executable programs (Java Applets) – References of other hypertext documents (“Anchors”) » “clickable” normal text or image (icon) » address (URL) where the corresponding document can be found
 Search Engines • Finding information becomes more and more difficult due to the amount of information. • Automated indexing services, searching all available databases on the Internet and setting up keyword databases are very popular. • Good ranking of keywords can be purchased from indexing services. • Many sites use tricks to be favorably presented by search engines
Search Engines • Finding information becomes more and more difficult due to the amount of information. • Automated indexing services, searching all available databases on the Internet and setting up keyword databases are very popular. • Good ranking of keywords can be purchased from indexing services. • Many sites use tricks to be favorably presented by search engines
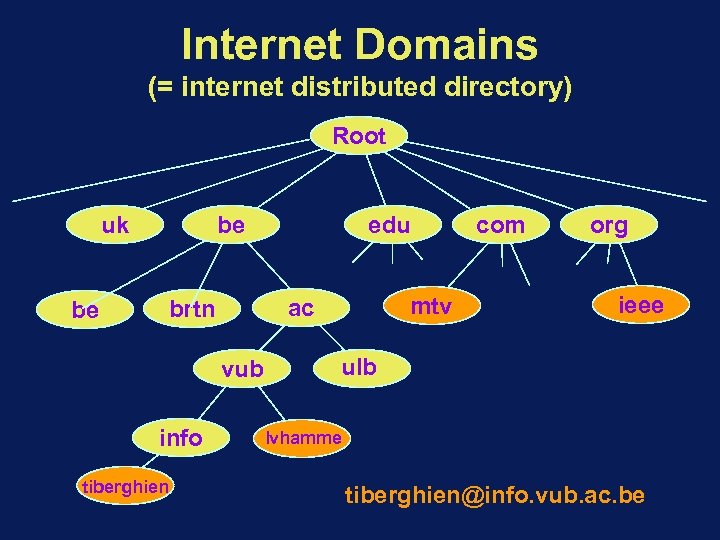 Internet Domains (= internet distributed directory) Root uk be be vub tiberghien mtv ac brtn info edu com org ieee ulb lvhamme tiberghien@info. vub. ac. be
Internet Domains (= internet distributed directory) Root uk be be vub tiberghien mtv ac brtn info edu com org ieee ulb lvhamme tiberghien@info. vub. ac. be
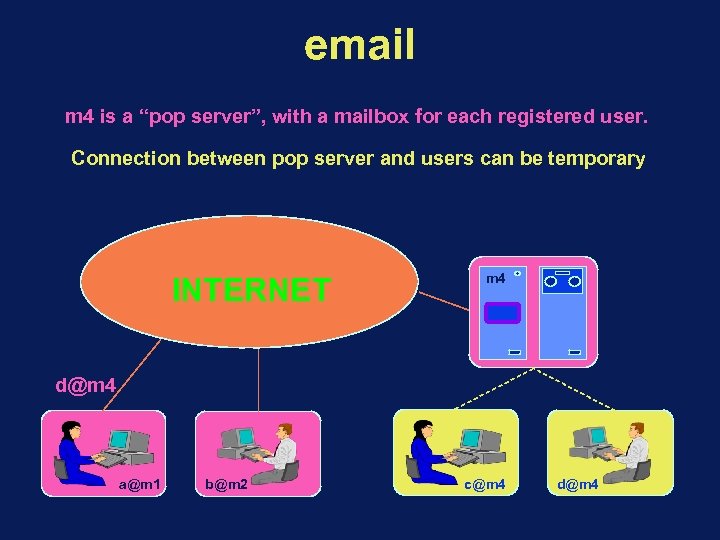 email m 4 is a “pop server”, with a mailbox for each registered user. Connection between pop server and users can be temporary INTERNET m 4 d@m 4 a@m 1 b@m 2 c@m 4 d@m 4
email m 4 is a “pop server”, with a mailbox for each registered user. Connection between pop server and users can be temporary INTERNET m 4 d@m 4 a@m 1 b@m 2 c@m 4 d@m 4
 IRC Internet
IRC Internet
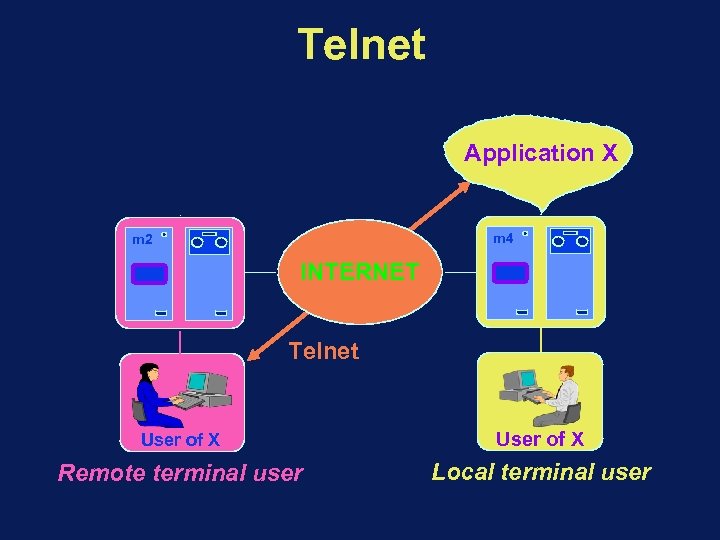 Telnet Application X m 4 m 2 INTERNET Telnet User of X Remote terminal user Local terminal user
Telnet Application X m 4 m 2 INTERNET Telnet User of X Remote terminal user Local terminal user
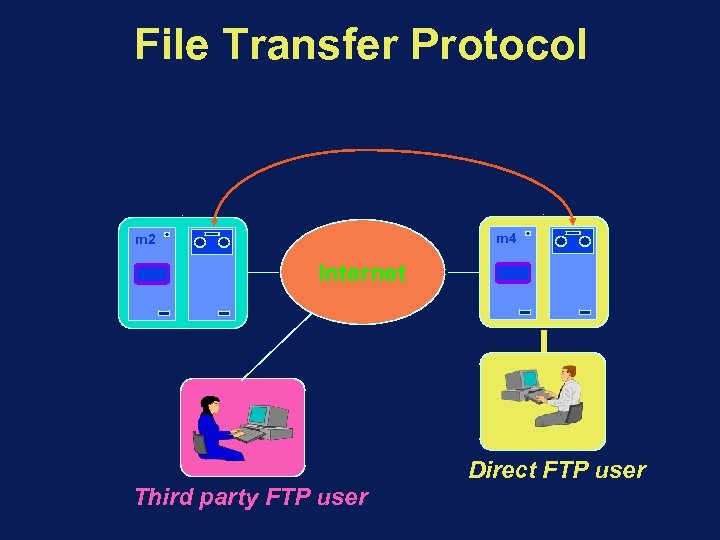 File Transfer Protocol m 4 m 2 Internet Direct FTP user Third party FTP user
File Transfer Protocol m 4 m 2 Internet Direct FTP user Third party FTP user
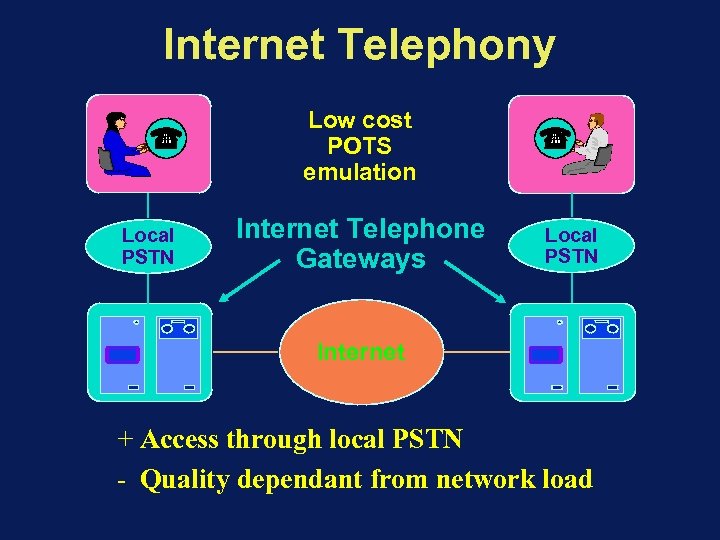 Internet Telephony Low cost POTS emulation Local PSTN Internet Telephone Gateways Local PSTN Internet + Access through local PSTN - Quality dependant from network load
Internet Telephony Low cost POTS emulation Local PSTN Internet Telephone Gateways Local PSTN Internet + Access through local PSTN - Quality dependant from network load
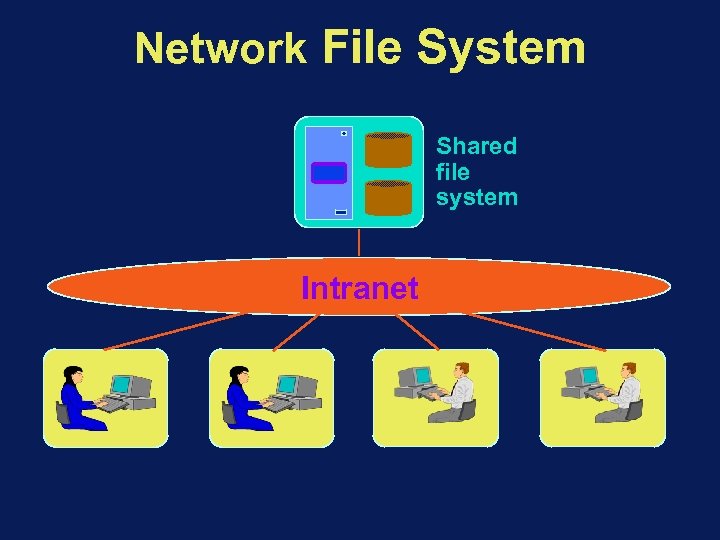 Network File System Shared file system Intranet
Network File System Shared file system Intranet


