 Chaos, Communication and Consciousness Module PH 19510 Lecture 4 The Dawn of the Electric Age
Chaos, Communication and Consciousness Module PH 19510 Lecture 4 The Dawn of the Electric Age
 Review of Lecture #2 n Pre-electronic Communication Ø Pictographs Ø Development of the alphabet Ø Number systems Ø Printing n Transfer of Information Ø Navigation Ø Signalling
Review of Lecture #2 n Pre-electronic Communication Ø Pictographs Ø Development of the alphabet Ø Number systems Ø Printing n Transfer of Information Ø Navigation Ø Signalling
 Communication The dawn of the electric age The Electric Pioneers n First messages by wire n Development of telegraphy n Samuel Morse and his code n
Communication The dawn of the electric age The Electric Pioneers n First messages by wire n Development of telegraphy n Samuel Morse and his code n
 Highly Recommended Electric Universe n n n David Bodanis £ 7. 99 ISBN Ø n n 0 -349 -11766 -7 Aventis prize for popular science How Electrons hold the universe together
Highly Recommended Electric Universe n n n David Bodanis £ 7. 99 ISBN Ø n n 0 -349 -11766 -7 Aventis prize for popular science How Electrons hold the universe together
 Electricity in antiquity n n n Lightning Ancient Greece Thales (600 BC) Rubbed Amber with fur picked up feathers Static electricity “Resinous” vs “Vitreous”
Electricity in antiquity n n n Lightning Ancient Greece Thales (600 BC) Rubbed Amber with fur picked up feathers Static electricity “Resinous” vs “Vitreous”
 Benjamin Franklin (1706 -1790) n n Printer, scientist, writer, inventor, activist, statesman Static electricity +ve and –ve charge 1752 Proved storm clouds are charged
Benjamin Franklin (1706 -1790) n n Printer, scientist, writer, inventor, activist, statesman Static electricity +ve and –ve charge 1752 Proved storm clouds are charged
 Luigi Galvani (1737 -1798) n n 1780 Frogs leg Dissimilar metals Static Bioelectricity
Luigi Galvani (1737 -1798) n n 1780 Frogs leg Dissimilar metals Static Bioelectricity
 Alessandro Volta (1745 -1827) n n Lombary, Italy 1800 Voltaic pile Ø Battery Ø n n n Zinc/Silver Brine/Cardboard Steady current
Alessandro Volta (1745 -1827) n n Lombary, Italy 1800 Voltaic pile Ø Battery Ø n n n Zinc/Silver Brine/Cardboard Steady current
 The Zinc/Silver Cell n n n Zinc Anode Silver Cathode Zn(s) Zn 2+(aq) + 2 e 2 H+(aq)+2 e- H 2 (g) ≈0. 75 volts/element +ve Ag Cardboard + Brine -ve Zn
The Zinc/Silver Cell n n n Zinc Anode Silver Cathode Zn(s) Zn 2+(aq) + 2 e 2 H+(aq)+2 e- H 2 (g) ≈0. 75 volts/element +ve Ag Cardboard + Brine -ve Zn
 1820 – A key year n Link between Electricity & Magnetism Ø HC Ørsted (Denmark) Ø Compass needle n Galvanometer ØJ Schweigger Ø Wind wire around compass Ø Increased sensitivity
1820 – A key year n Link between Electricity & Magnetism Ø HC Ørsted (Denmark) Ø Compass needle n Galvanometer ØJ Schweigger Ø Wind wire around compass Ø Increased sensitivity
 Andrè-Marie Ampere (1775 -1836) n n 1820 Formalised EM Theory 1821 Proposed Telegraphy with galvanometers 1 wire per galvanometer 200 ft (60 -70 m)
Andrè-Marie Ampere (1775 -1836) n n 1820 Formalised EM Theory 1821 Proposed Telegraphy with galvanometers 1 wire per galvanometer 200 ft (60 -70 m)
 Early systems based on galvanometers n n n Schilling 1832 Gauss & Weber 1833 Wheatstone & Cooke 5 Needle Telegraph 1837 Ø Commercial system 1839 Ø
Early systems based on galvanometers n n n Schilling 1832 Gauss & Weber 1833 Wheatstone & Cooke 5 Needle Telegraph 1837 Ø Commercial system 1839 Ø
 William Sturgeon invents the Electromagnet 1825 n n b. 1783 1825 Electromagnet Coil of wire on iron Ø Uninsulated wire Ø
William Sturgeon invents the Electromagnet 1825 n n b. 1783 1825 Electromagnet Coil of wire on iron Ø Uninsulated wire Ø
 Joseph Henry (1797 -1878) – Electrical signalling at a distance n 1827 Improves electromagnet Ø n 1830 First signalling Ø n Many turns of insulated wire Ring bell >1 mile of cable 1837 Electromechanical Relay
Joseph Henry (1797 -1878) – Electrical signalling at a distance n 1827 Improves electromagnet Ø n 1830 First signalling Ø n Many turns of insulated wire Ring bell >1 mile of cable 1837 Electromechanical Relay
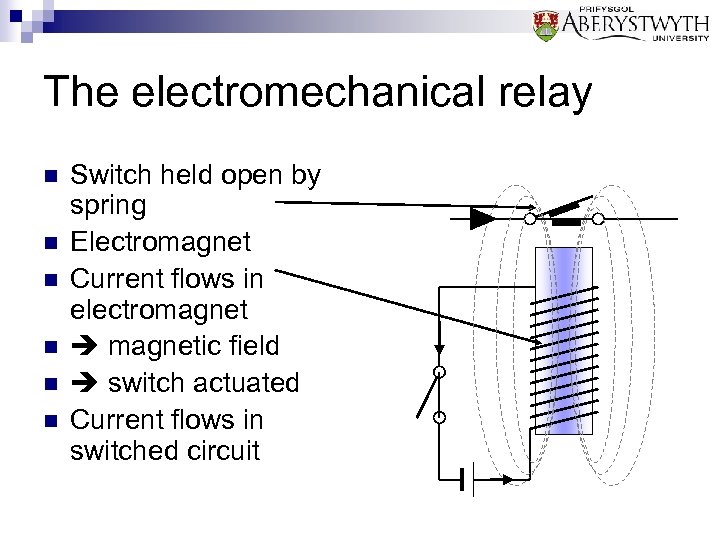 The electromechanical relay n n n Switch held open by spring Electromagnet Current flows in electromagnet magnetic field switch actuated Current flows in switched circuit
The electromechanical relay n n n Switch held open by spring Electromagnet Current flows in electromagnet magnetic field switch actuated Current flows in switched circuit
 Samuel Morse & Alfred Vail n n 1838 – First system test Vail developed signalling code 1843 – U. S. congress funds $30, 000 for line from Washington to Baltimore – 40 miles (65 km) 1844 Line operational Ø “What hath God wrought”
Samuel Morse & Alfred Vail n n 1838 – First system test Vail developed signalling code 1843 – U. S. congress funds $30, 000 for line from Washington to Baltimore – 40 miles (65 km) 1844 Line operational Ø “What hath God wrought”
 Morse’s apparatus n n n Paper tape moved by clockwork Electromagnet pulls ‘pendulum’ Marks embossed on paper tape
Morse’s apparatus n n n Paper tape moved by clockwork Electromagnet pulls ‘pendulum’ Marks embossed on paper tape
 Paper Tape Output
Paper Tape Output
 Morse Code n n Evolved from Vail’s original Letters & Numbers Punctuation 2 symbols Dot Ø Dash Ø n Variable length Ø Frequent letters, shortest codes
Morse Code n n Evolved from Vail’s original Letters & Numbers Punctuation 2 symbols Dot Ø Dash Ø n Variable length Ø Frequent letters, shortest codes
 Review of Lecture #3 Dawn of the electric age n Key technologies n Ø Cells & Batteries Ø Electromagnet Ø Relay n Use of standardised code
Review of Lecture #3 Dawn of the electric age n Key technologies n Ø Cells & Batteries Ø Electromagnet Ø Relay n Use of standardised code