fd6d3fcb10a600c1c372f66055991e01.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Changing Agribusiness and Agriculture Organization: Implications for Reforms in Karnataka Gopal Naik Professor Indian Institute of Management Bangalore

Changing Market Environment • Globalization and integrated markets • By 2050 the world food demand is expected to double – Asia is the major source of demand increase • Population increase • Income increase

Dynamics of Food Demand • Upto $2 per day (Rs 3000/month) – demand for staple food – cereals and pulses • Between $2 and $9 per day ( Rs 3000 to Rs 5000/month) people eat more – animal protein, fruits, vegetables & edible oils, causing rapid growth in raw ag commodity demand • After $10 per day (Rs 5000/month) people buy more – Processed and packaged food, variety • ( Source: Thompson, 2005)
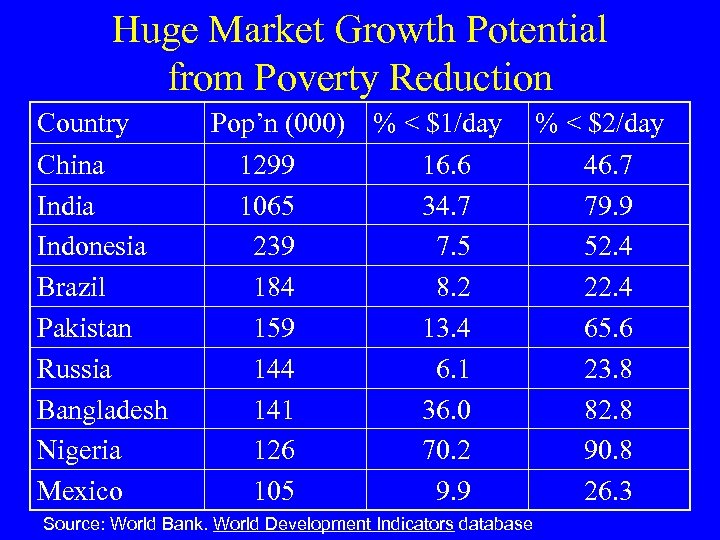
Huge Market Growth Potential from Poverty Reduction Country China India Indonesia Brazil Pakistan Russia Bangladesh Nigeria Mexico Pop’n (000) % < $1/day 1299 16. 6 1065 34. 7 239 7. 5 184 8. 2 159 13. 4 144 6. 1 141 36. 0 126 70. 2 105 9. 9 Source: World Bank. World Development Indicators database % < $2/day 46. 7 79. 9 52. 4 22. 4 65. 6 23. 8 82. 8 90. 8 26. 3

Structure of Indian Agriculture Sector • Large number of small/marginal farmers • Poor market orientation in agriculture production • Increasing risk in farming business • Inadequate facility to address farm risk • Need to evolve appropriate business models
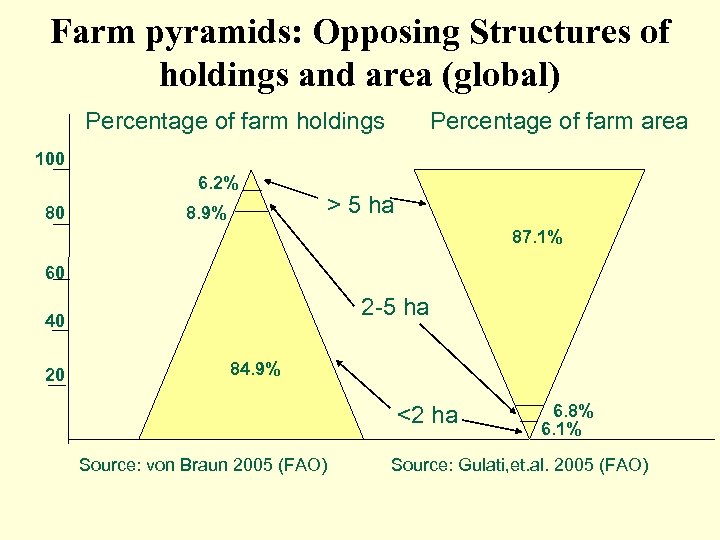
Farm pyramids: Opposing Structures of holdings and area (global) Percentage of farm holdings Percentage of farm area 100 6. 2% 80 8. 9% > 5 ha 87. 1% 60 2 -5 ha 40 20 84. 9% <2 ha Source: von Braun 2005 (FAO) 6. 8% 6. 1% Source: Gulati, et. al. 2005 (FAO)

Implications of Globalization • Gear up the sector to compete effectively in the market – Market oriented production • Quality of the produce • Right quantity – Improve quality to address SPS concerns and compete in the international markets • Production, Procurement, grading, transportation, storage and processing – Increase productivity • • Research and Technology Development Technology adoption Infrastructure – production, marketing and services Macro production management

– Alternative marketing formats • • • Meet customer requirements Reduce transaction cost Enhance quality Expand market – Domestic and International Improve value addition Improve realization – Professional Management • Plan, coordinate and execute market oriented production
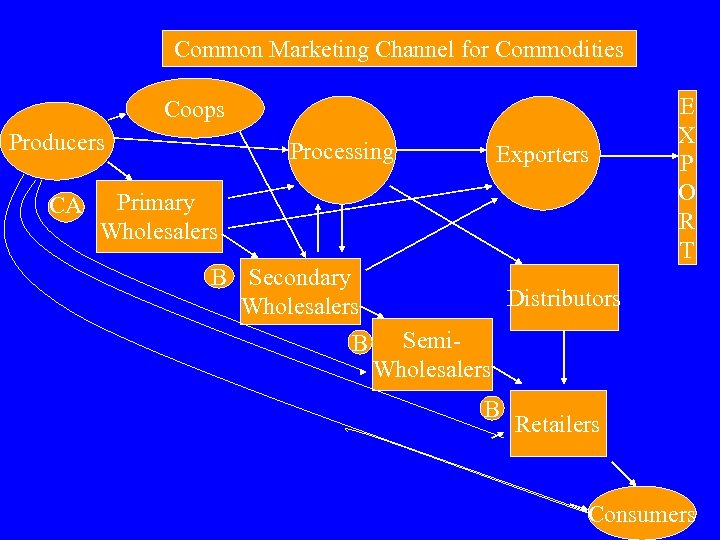
Common Marketing Channel for Commodities Coops Producers CA Processing Exporters Primary Wholesalers B Secondary Wholesalers B E X P O R T Distributors Semi. Wholesalers B Retailers Consumers

Problems in the current value chain • High cost • Quality loss is high – Anonymity of buyers and seller – Absence of grading – Number of times packing, unpacking and handling done is high – Handled by unskilled people – Quality orientation is low • Time requirement is high • Wastage is high • Inadequate information

Overcoming constraints • Reduce transaction cost – Group financing (SHG mode) • Joint liability group • Farmers club – Credit rating • Incentive schemes – KCC – Increase credit limit – Reduce interest rate – Encourage financing through contract farming – Bundle services • Form - input supplies/output marketing • Time/space – loan melas

Reduce risk • Institutional support - facilitating structured commodity financing – Legal/policy support • Contract farming – Grades and standards • Appropriateness • Institutional mechanism – Infrastructural support • Network of warehouses • Grading system – Warehouse receipt system • Tradable warehousing system – Futures contract
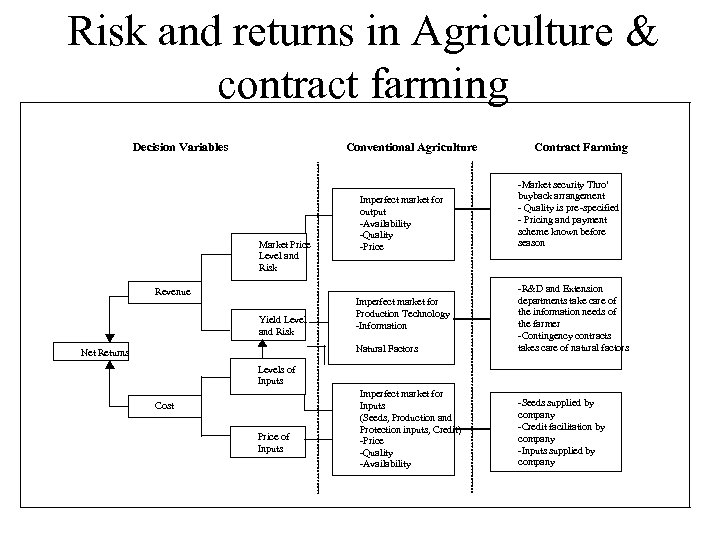
Risk and returns in Agriculture & contract farming Decision Variables Conventional Agriculture Market Price Level and Risk Revenue Yield Level and Risk Imperfect market for output -Availability -Quality -Price Imperfect market for Production Technology -Information Natural Factors Net Returns Contract Farming -Market security Thro’ buyback arrangement - Quality is pre -specified - Pricing and payment scheme known before season -R&D and Extension departments take care of the information needs of the farmer -Contingency contracts takes care of natural factors Levels of Inputs Cost Price of Inputs Imperfect market for Inputs (Seeds, Production and Protection inputs, Credit) -Price -Quality -Availability -Seeds supplied by company -Credit facilitation by company -Inputs supplied by company

Key Requirements for facilitating agribusiness • • Macro commodity sector management Integrated but efficient services to farmers Improve Agricultural marketing facilities Opportunity to high value realization

Macro commodity sector management – Matching estimated supply and demand • Track of production commitment within and outside the state through a market intelligence service – – Input supply tracking Computerize information Weekly commodity meeting Forecast prices and make it available to farmers • Action: Start a pilot for tomato and sugarcane on a PPP basis

Integrated Efficient Services to farmers • Production • • Technology Inputs Credit Knowledge • Marketing • Market selection • Prices • Channel selection Action: Allow contract farming Set up Farm integrated services at APMC level on a PPP basis
Modernizing APMC • Modernize Regulated Markets (Safal) – – – Electronic transaction Grade based transaction Infrastructure for grading and handling Process simplification Information on prices in different markets and different forms of product – Facilitate forward contracting and futures trading – Facilitate value addition – Facilitate market oriented production

Create Opportunity for high value realization • Grade based transaction • Value added product transaction : baled cotton – Packed product - mango • Certification and certified product transaction: organic product

• Partnering with Farmers
fd6d3fcb10a600c1c372f66055991e01.ppt