523cec73a6abe5619dc86a4420c1b726.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Changes in the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing & Implications for Healthcare Organizations AHIA Northwest Regional Seminar May 7, 2010 Exaltant TM Grant Baumgartner Chief Consulting Officer Phone: 206 -999 -3663 grant. baumgartner@exaltant. com Protiviti. TM Keith Kawashima Managing Director Phone: 408 -808 -3222 keith. kawashima@protiviti. com
Changes in the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing & Implications for Healthcare Organizations AHIA Northwest Regional Seminar May 7, 2010 Exaltant TM Grant Baumgartner Chief Consulting Officer Phone: 206 -999 -3663 grant. baumgartner@exaltant. com Protiviti. TM Keith Kawashima Managing Director Phone: 408 -808 -3222 keith. kawashima@protiviti. com
 Summary of Changes • Effective January 1, 2009, the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) made changes to the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing (Standards): Ø Changed from “should” to “must” throughout most of the Standards Ø Added six new Standards Ø Added new verbiage to existing Standards Ø Interpretations added that were previously part of the Practice Advisories 1
Summary of Changes • Effective January 1, 2009, the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) made changes to the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing (Standards): Ø Changed from “should” to “must” throughout most of the Standards Ø Added six new Standards Ø Added new verbiage to existing Standards Ø Interpretations added that were previously part of the Practice Advisories 1
 Summary of Changes • Areas Affected: – IT Governance – Fraud Risk Management – Communication with the Board – Ethics Programs – Technology Based Audit and Other Data Analysis Techniques – Limitation and Adequacy of Resources – Records Retention – Quality Assurance Reviews – Modifications to the IA Charter – Prohibition on Managing Risk – Conducted in Conformance with The Standards 2
Summary of Changes • Areas Affected: – IT Governance – Fraud Risk Management – Communication with the Board – Ethics Programs – Technology Based Audit and Other Data Analysis Techniques – Limitation and Adequacy of Resources – Records Retention – Quality Assurance Reviews – Modifications to the IA Charter – Prohibition on Managing Risk – Conducted in Conformance with The Standards 2
 Actions Required by Internal Audit Leadership • Discuss changes with Management and Audit Committees • Develop gap analysis • Disclose incremental required actions to be taken 3
Actions Required by Internal Audit Leadership • Discuss changes with Management and Audit Committees • Develop gap analysis • Disclose incremental required actions to be taken 3
 IT Governance 2110. A 2 – The internal audit activity must assess whether the information technology governance of the organization sustains and supports the organization’s strategies and objectives. v Assess IT governance and determine appropriate reporting v Potentially increase IT auditing to adequately report on IT Governance v Perform enhanced IT risk assessment v Use IT Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) or outside resources as needed and re-evaluate capability of existing resources v Consider adopting the ITGI Five Elements of IT Governance to review the IT organization’s governance framework 4 NEW Standard
IT Governance 2110. A 2 – The internal audit activity must assess whether the information technology governance of the organization sustains and supports the organization’s strategies and objectives. v Assess IT governance and determine appropriate reporting v Potentially increase IT auditing to adequately report on IT Governance v Perform enhanced IT risk assessment v Use IT Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) or outside resources as needed and re-evaluate capability of existing resources v Consider adopting the ITGI Five Elements of IT Governance to review the IT organization’s governance framework 4 NEW Standard
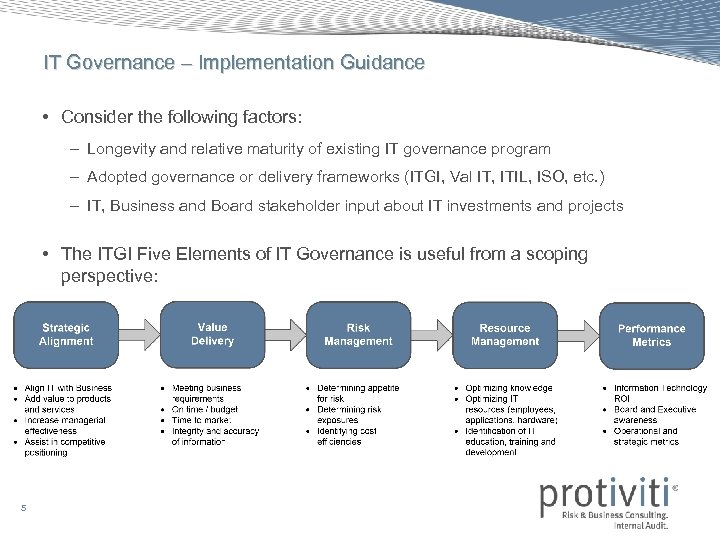 IT Governance – Implementation Guidance • Consider the following factors: – Longevity and relative maturity of existing IT governance program – Adopted governance or delivery frameworks (ITGI, Val IT, ITIL, ISO, etc. ) – IT, Business and Board stakeholder input about IT investments and projects • The ITGI Five Elements of IT Governance is useful from a scoping perspective: 5
IT Governance – Implementation Guidance • Consider the following factors: – Longevity and relative maturity of existing IT governance program – Adopted governance or delivery frameworks (ITGI, Val IT, ITIL, ISO, etc. ) – IT, Business and Board stakeholder input about IT investments and projects • The ITGI Five Elements of IT Governance is useful from a scoping perspective: 5
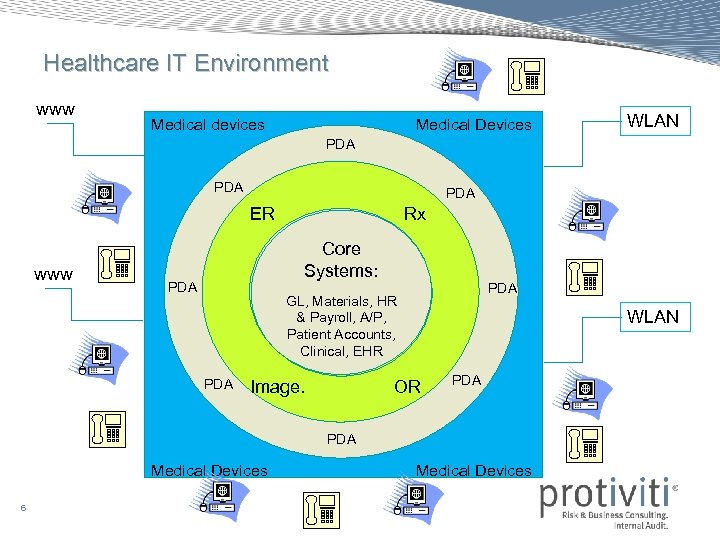 Healthcare IT Environment www Medical devices Medical Devices WLAN PDA PDA ER www Rx Core Systems: PDA GL, Materials, HR & Payroll, A/P, Patient Accounts, Clinical, EHR PDA Image. OR WLAN PDA Medical Devices 6 Medical Devices
Healthcare IT Environment www Medical devices Medical Devices WLAN PDA PDA ER www Rx Core Systems: PDA GL, Materials, HR & Payroll, A/P, Patient Accounts, Clinical, EHR PDA Image. OR WLAN PDA Medical Devices 6 Medical Devices
 Healthcare IT Environment • Must support the organization’s strategies and objectives – Accountable Care Organizations – Medical Homes – Co-ops – Insurance Exchanges – Capitation – Claims – Other Contracting and Reporting 7
Healthcare IT Environment • Must support the organization’s strategies and objectives – Accountable Care Organizations – Medical Homes – Co-ops – Insurance Exchanges – Capitation – Claims – Other Contracting and Reporting 7
 Discussion Questions IT Governance Ø Ø How did you approach this effort? Ø 8 Has your organization performed an IT Governance assessment? If not, how do you intend to comply with the Standard?
Discussion Questions IT Governance Ø Ø How did you approach this effort? Ø 8 Has your organization performed an IT Governance assessment? If not, how do you intend to comply with the Standard?
 Fraud Risk Management 2120. A 2 – The internal audit activity must evaluate the potential for the occurrence of fraud and how the organization manages fraud risk. NEW Standard v Perform a fraud risk assessment and evaluate fraud risk management program by: § Assisting management in performing one § Leveraging an existing assessment performed as part of SOX or § Performing an independent assessment v Utilize outside resources as needed v Utilize data analysis and continuous auditing and monitoring to enhance detection v Determine style and scope of reporting v Coordinate with legal counsel as appropriate 9
Fraud Risk Management 2120. A 2 – The internal audit activity must evaluate the potential for the occurrence of fraud and how the organization manages fraud risk. NEW Standard v Perform a fraud risk assessment and evaluate fraud risk management program by: § Assisting management in performing one § Leveraging an existing assessment performed as part of SOX or § Performing an independent assessment v Utilize outside resources as needed v Utilize data analysis and continuous auditing and monitoring to enhance detection v Determine style and scope of reporting v Coordinate with legal counsel as appropriate 9
 Healthcare Fraud Risk Management • Coding • Charging • Procurement • Expense reporting • Time keeping • Cash locations • Credit card locations • Self-funded insurance • Electronic transactions • Financial, utilization and clinic outcomes reporting 10
Healthcare Fraud Risk Management • Coding • Charging • Procurement • Expense reporting • Time keeping • Cash locations • Credit card locations • Self-funded insurance • Electronic transactions • Financial, utilization and clinic outcomes reporting 10
 Discussion Questions Fraud Risk Management Ø Has your IA function conducted a Fraud Risk Assessment? - Examples § Discrete Fraud Risk Assessment project § Identification of fraud-related risks/controls during audit projects § Other - Who was involved in the effort? - Lessons learned Ø What have been your challenges in conducting fraud risk assessments? Ø How do you support fraud prevention and detection activities with training and awareness programs for Management and employees? 11
Discussion Questions Fraud Risk Management Ø Has your IA function conducted a Fraud Risk Assessment? - Examples § Discrete Fraud Risk Assessment project § Identification of fraud-related risks/controls during audit projects § Other - Who was involved in the effort? - Lessons learned Ø What have been your challenges in conducting fraud risk assessments? Ø How do you support fraud prevention and detection activities with training and awareness programs for Management and employees? 11
 Discussion Questions Fraud Risk Management • Whose responsibility is it to monitor fraud risk within your operations on a daily, on-going basis (i. e. , “continuous monitoring”)? • How are “computer-assisted audit techniques” or electronic data analysis used to help identify potential fraud risk within financial or operational processes? • What is the role of your Board of Directors in fraud risk governance? 12
Discussion Questions Fraud Risk Management • Whose responsibility is it to monitor fraud risk within your operations on a daily, on-going basis (i. e. , “continuous monitoring”)? • How are “computer-assisted audit techniques” or electronic data analysis used to help identify potential fraud risk within financial or operational processes? • What is the role of your Board of Directors in fraud risk governance? 12
 Communication with the Board 1111 – Direct Interaction with the Board The chief audit executive must communicate and interact directly with the board. • Increasing the Chief Audit Executive’s visibility with the Board NEW Standard • Implement the Standards communications requirements with the Board • Evaluate if reporting style and approach should be revised and enhanced • Coordinate with legal counsel on reporting guidelines 13
Communication with the Board 1111 – Direct Interaction with the Board The chief audit executive must communicate and interact directly with the board. • Increasing the Chief Audit Executive’s visibility with the Board NEW Standard • Implement the Standards communications requirements with the Board • Evaluate if reporting style and approach should be revised and enhanced • Coordinate with legal counsel on reporting guidelines 13
 Discussion Questions Communication with the Board • Does your IA function have any plans to change their current level of interaction with the Board or AC? • In the current economic climate, have there been changes in requests from the Board? – Frequency? – Level of information? • Does your IA function plan to change the type of reporting? 14
Discussion Questions Communication with the Board • Does your IA function have any plans to change their current level of interaction with the Board or AC? • In the current economic climate, have there been changes in requests from the Board? – Frequency? – Level of information? • Does your IA function plan to change the type of reporting? 14
 15 © 2010 Protiviti Inc. An Equal Opportunity Employer.
15 © 2010 Protiviti Inc. An Equal Opportunity Employer.


