17a63cebab376ec046ec39c9d826c966.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Change Models: Managing the Evolving Role of the Budget Office Presenter: William A. Flexner & Associates, Chapel Hill, NC NC Local Government Budget Association Summer Conference July 18, 2007
Change Models: Managing the Evolving Role of the Budget Office Presenter: William A. Flexner & Associates, Chapel Hill, NC NC Local Government Budget Association Summer Conference July 18, 2007
 Creating Reality • First we shape our structures, then they shape us – Winston Churchill • The best way to predict the future is to invent it – Alan Kay • The best thing about reality is you get to make it up – Kimbal Wheatley • If you don’t know where you’re going, you’re going to get there anyway – Anonymous • If you don’t change directions, you’re going to get where you are going -- Anonymous
Creating Reality • First we shape our structures, then they shape us – Winston Churchill • The best way to predict the future is to invent it – Alan Kay • The best thing about reality is you get to make it up – Kimbal Wheatley • If you don’t know where you’re going, you’re going to get there anyway – Anonymous • If you don’t change directions, you’re going to get where you are going -- Anonymous
 Have you ever used an anonymous opinion gathering device such as this? 1. No 2. Yes
Have you ever used an anonymous opinion gathering device such as this? 1. No 2. Yes
 Have you ever driven more than 30 MPH over the speed limit? 1. No 2. Yes
Have you ever driven more than 30 MPH over the speed limit? 1. No 2. Yes
 Did you ever lie to Mom? 1. No 2. Well, it wasn’t exactly a lie 3. Yes
Did you ever lie to Mom? 1. No 2. Well, it wasn’t exactly a lie 3. Yes
 What is the role of the Budget Office? The non-budget person might say… “The budget office translates an organization’s plans and policies into financial terms” Starting with this definition… How has the role of the Budget Office evolved over the past 10 years?
What is the role of the Budget Office? The non-budget person might say… “The budget office translates an organization’s plans and policies into financial terms” Starting with this definition… How has the role of the Budget Office evolved over the past 10 years?
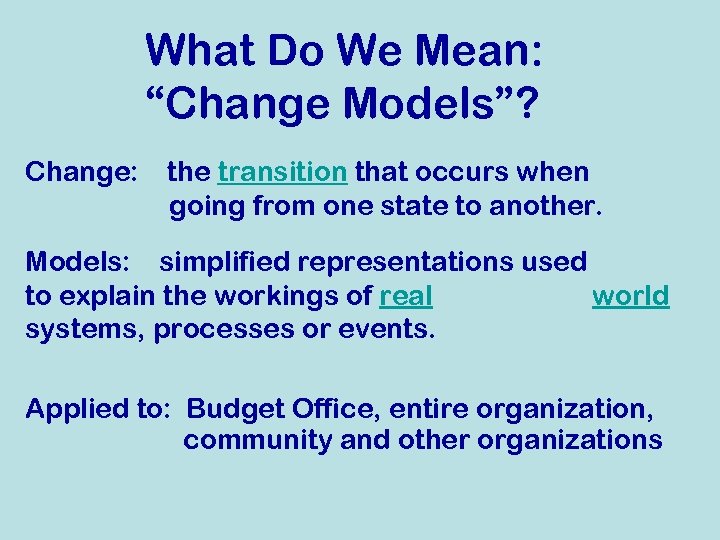 What Do We Mean: “Change Models”? Change: the transition that occurs when going from one state to another. Models: simplified representations used to explain the workings of real world systems, processes or events. Applied to: Budget Office, entire organization, community and other organizations
What Do We Mean: “Change Models”? Change: the transition that occurs when going from one state to another. Models: simplified representations used to explain the workings of real world systems, processes or events. Applied to: Budget Office, entire organization, community and other organizations
 Change Model # 1 “Pull Change”
Change Model # 1 “Pull Change”
 In order to solve the Social Security System crisis, President Bush proposed the shifting up to 25% of retirement funds into Personal Savings Accounts. Can you support this solution? 1. No 2. Yes
In order to solve the Social Security System crisis, President Bush proposed the shifting up to 25% of retirement funds into Personal Savings Accounts. Can you support this solution? 1. No 2. Yes
 In order to absorb 8, 000 to 10, 000 new students a year, the Wake County School Board is proposing to move a significant number of its schools to 12 month calendars. Can you support this solution? 1. No 2. Yes
In order to absorb 8, 000 to 10, 000 new students a year, the Wake County School Board is proposing to move a significant number of its schools to 12 month calendars. Can you support this solution? 1. No 2. Yes
 Scholars at the “Phoenix Institute for Public Management” have proposed that Local Government Budget Offices stick with the knitting and focus only on budget preparation and not on any expanded roles. Can you support this solution? 1. No 2. Yes
Scholars at the “Phoenix Institute for Public Management” have proposed that Local Government Budget Offices stick with the knitting and focus only on budget preparation and not on any expanded roles. Can you support this solution? 1. No 2. Yes
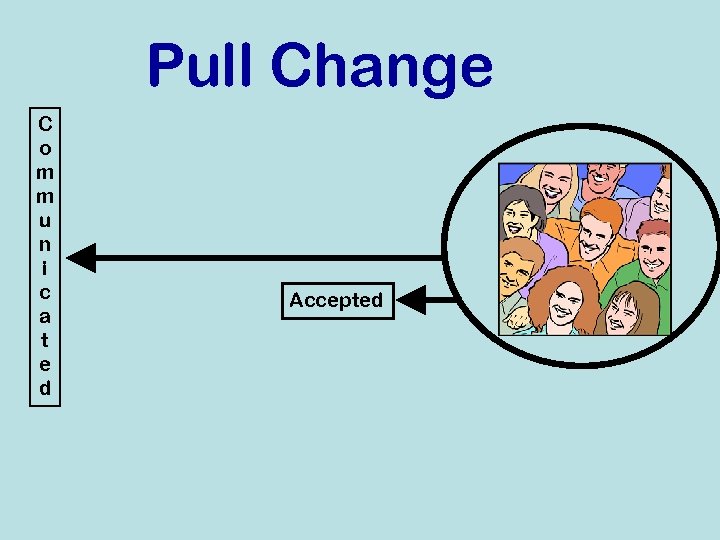 Pull Change C o m m u n i c a t e d Accepted
Pull Change C o m m u n i c a t e d Accepted
 Change Model # 2 “Starting Change”
Change Model # 2 “Starting Change”
 Have you ever had a really messy office, garage or closet? 1. No 2. It wasn’t really messy 3. Yes
Have you ever had a really messy office, garage or closet? 1. No 2. It wasn’t really messy 3. Yes
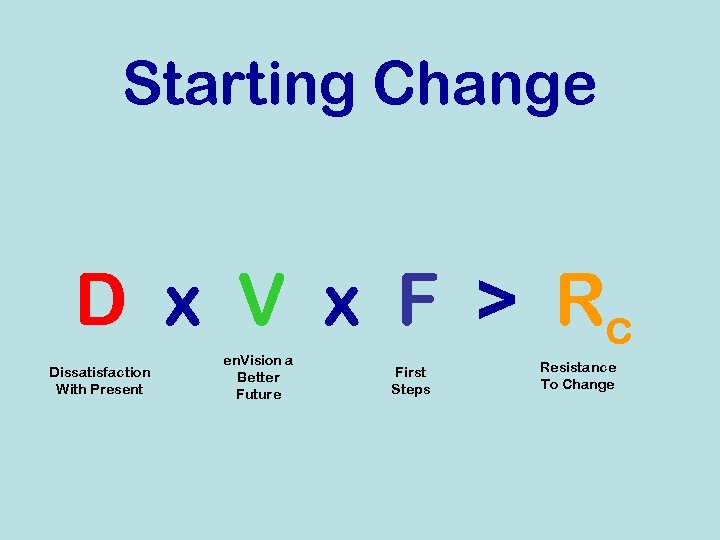 Starting Change D x V x F > Rc Dissatisfaction With Present en. Vision a Better Future First Steps Resistance To Change
Starting Change D x V x F > Rc Dissatisfaction With Present en. Vision a Better Future First Steps Resistance To Change
 Change Model # 3 “Adoption of Innovation”
Change Model # 3 “Adoption of Innovation”
 Which of the following best describes you and an Apple IPod? 1. One of the first to buy it 2. Bought one early on, but only after talking with someone who already had one 3. Bought one, but waited until the technology and access to songs were proven 4. Am still investigating buying one, but not ready yet 5. Really have no interest
Which of the following best describes you and an Apple IPod? 1. One of the first to buy it 2. Bought one early on, but only after talking with someone who already had one 3. Bought one, but waited until the technology and access to songs were proven 4. Am still investigating buying one, but not ready yet 5. Really have no interest
 “Budget AI” is a new software product combining artificial intelligence software with a national “local gov’t” budgeting database to reduce the time to produce a first draft of a city or county budget by 50%. Which of the following best describes your reaction? 1. Sign me up for the Beta version. I want it now 2. It sounds great but let me talk with someone who has it up and running 3. Show me that it really works in the real world and I’ll consider it 4. Not interested now, but send me updated information periodically 5. Really have no interest
“Budget AI” is a new software product combining artificial intelligence software with a national “local gov’t” budgeting database to reduce the time to produce a first draft of a city or county budget by 50%. Which of the following best describes your reaction? 1. Sign me up for the Beta version. I want it now 2. It sounds great but let me talk with someone who has it up and running 3. Show me that it really works in the real world and I’ll consider it 4. Not interested now, but send me updated information periodically 5. Really have no interest
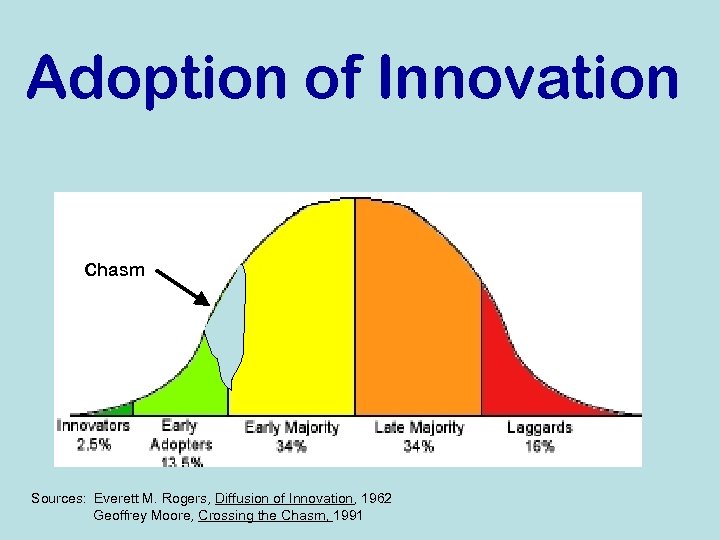 Adoption of Innovation Chasm Sources: Everett M. Rogers, Diffusion of Innovation, 1962 Geoffrey Moore, Crossing the Chasm, 1991
Adoption of Innovation Chasm Sources: Everett M. Rogers, Diffusion of Innovation, 1962 Geoffrey Moore, Crossing the Chasm, 1991
 Change Model # 4 “Grow or Die”
Change Model # 4 “Grow or Die”
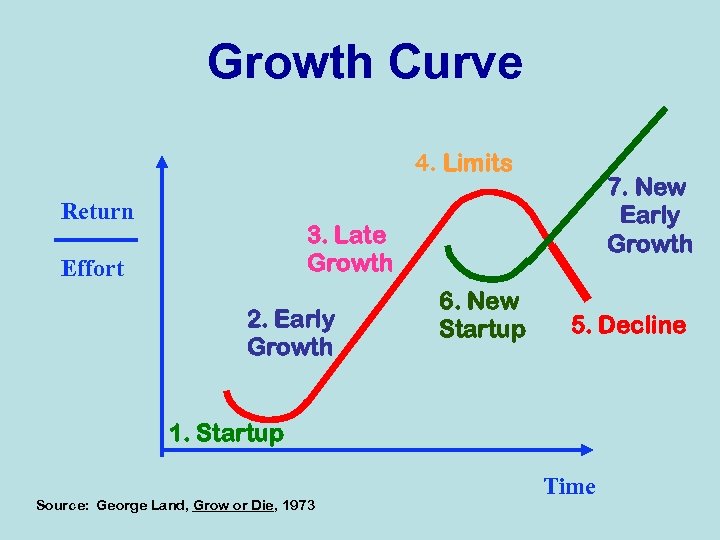 Growth Curve 4. Limits Return 7. New Early Growth 3. Late Growth Effort 2. Early Growth 6. New Startup 5. Decline 1. Startup Source: George Land, Grow or Die, 1973 Time
Growth Curve 4. Limits Return 7. New Early Growth 3. Late Growth Effort 2. Early Growth 6. New Startup 5. Decline 1. Startup Source: George Land, Grow or Die, 1973 Time
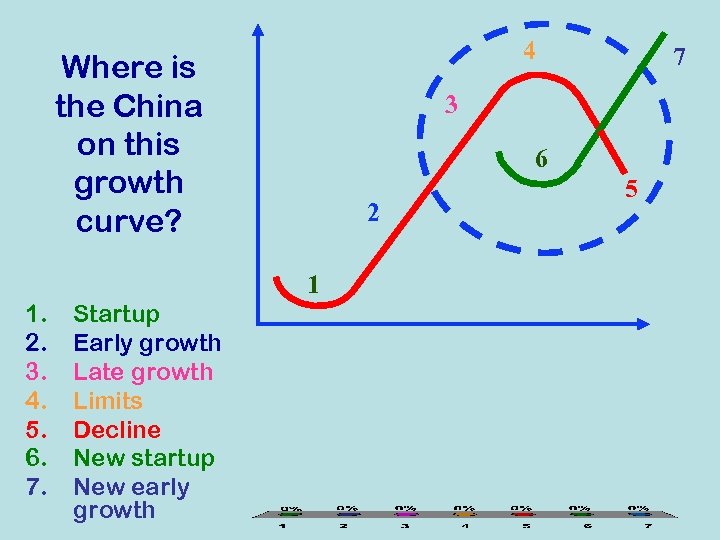 4 Where is the China on this growth curve? 3 6 2 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Startup Early growth Late growth Limits Decline New startup New early growth 7 5
4 Where is the China on this growth curve? 3 6 2 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Startup Early growth Late growth Limits Decline New startup New early growth 7 5
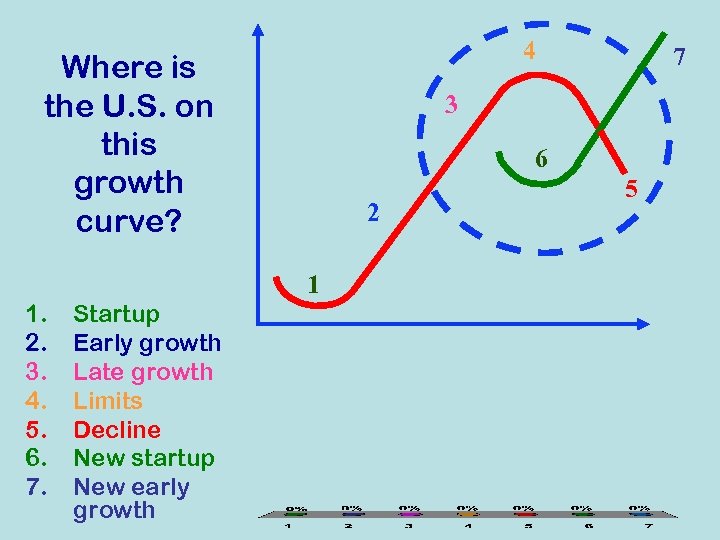 4 Where is the U. S. on this growth curve? 3 6 2 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Startup Early growth Late growth Limits Decline New startup New early growth 7 5
4 Where is the U. S. on this growth curve? 3 6 2 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Startup Early growth Late growth Limits Decline New startup New early growth 7 5
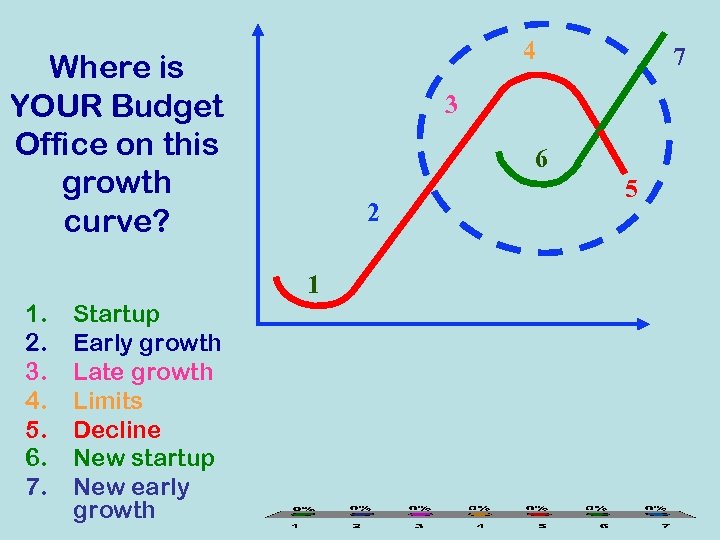 4 Where is YOUR Budget Office on this growth curve? 3 6 2 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Startup Early growth Late growth Limits Decline New startup New early growth 7 5
4 Where is YOUR Budget Office on this growth curve? 3 6 2 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Startup Early growth Late growth Limits Decline New startup New early growth 7 5
 Change Model # 5 “Linking Strategy to Action”
Change Model # 5 “Linking Strategy to Action”
 Change: Linking Strategy to Action WW What Where now/Where future WH Who/When How WW
Change: Linking Strategy to Action WW What Where now/Where future WH Who/When How WW
 Change Model #6 “Setting Priorities”
Change Model #6 “Setting Priorities”
 Focus on the “Whats” Let’s say you have developed a list of Critical Success Factors (CSFs)…the “Whats” that will help you get to “Where” you are going A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. Aaaaa aa aaaaa aa Bbbbbbb Ccc ccc ccc Dddddd d E eeeeeee Fffffff ff fff Ggggg ggg gggg Hhh hhhhhh h hhh Iiiiiiii iiiiiii Jjjjjjjjjjj How do you assess which ones are more important; how do you determine “what” to focus on?
Focus on the “Whats” Let’s say you have developed a list of Critical Success Factors (CSFs)…the “Whats” that will help you get to “Where” you are going A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. Aaaaa aa aaaaa aa Bbbbbbb Ccc ccc ccc Dddddd d E eeeeeee Fffffff ff fff Ggggg ggg gggg Hhh hhhhhh h hhh Iiiiiiii iiiiiii Jjjjjjjjjjj How do you assess which ones are more important; how do you determine “what” to focus on?
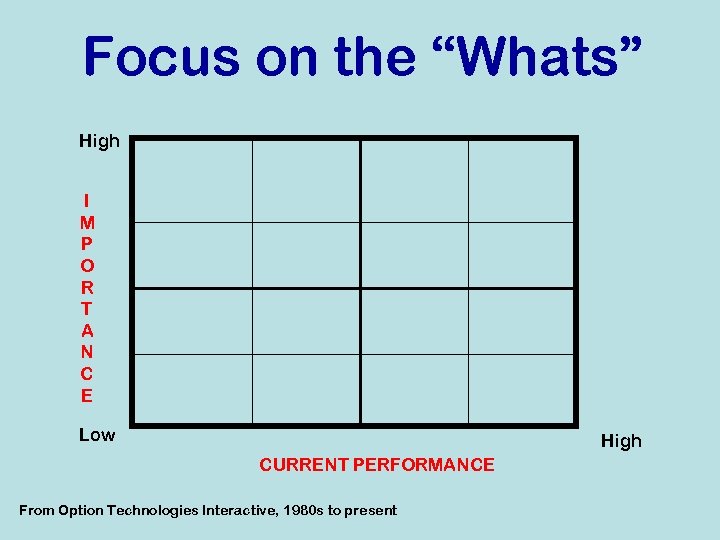 Focus on the “Whats” High I M P O R T A N C E Low High CURRENT PERFORMANCE From Option Technologies Interactive, 1980 s to present
Focus on the “Whats” High I M P O R T A N C E Low High CURRENT PERFORMANCE From Option Technologies Interactive, 1980 s to present
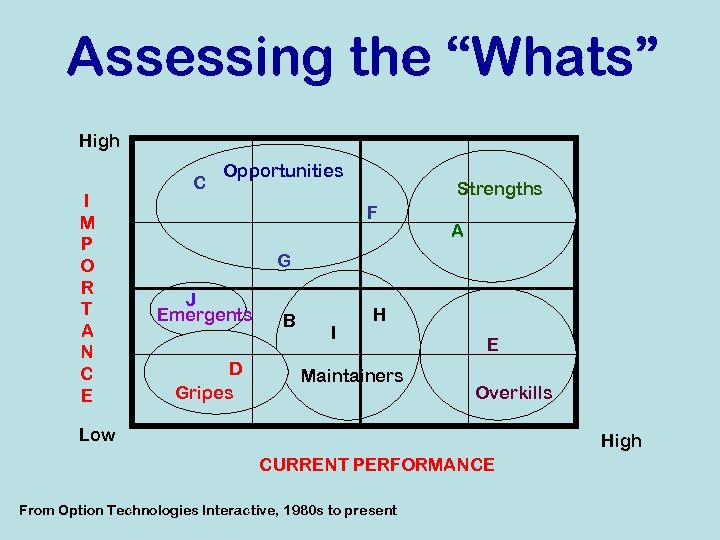 Assessing the “Whats” High I M P O R T A N C E C Opportunities Strengths F A G J Emergents D Gripes B I H Maintainers E Overkills Low High CURRENT PERFORMANCE From Option Technologies Interactive, 1980 s to present
Assessing the “Whats” High I M P O R T A N C E C Opportunities Strengths F A G J Emergents D Gripes B I H Maintainers E Overkills Low High CURRENT PERFORMANCE From Option Technologies Interactive, 1980 s to present
 Change Model #7 “Action Planning”
Change Model #7 “Action Planning”
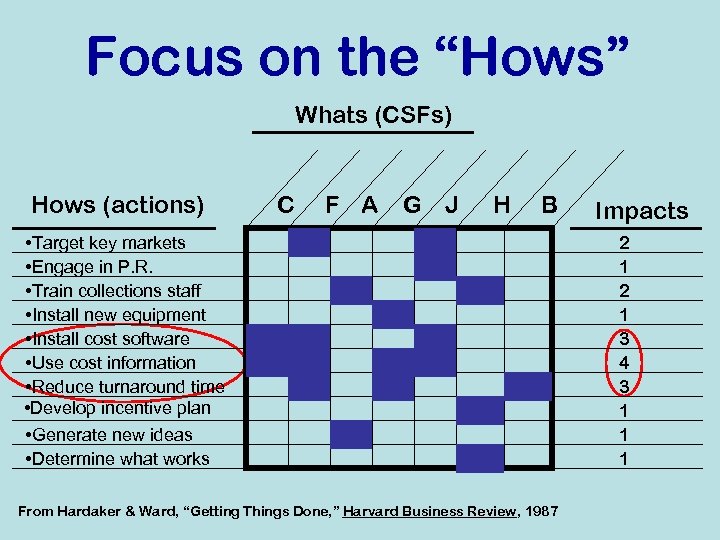 Focus on the “Hows” Whats (CSFs) Hows (actions) C F A G J H B • Target key markets • Engage in P. R. • Train collections staff • Install new equipment • Install cost software • Use cost information • Reduce turnaround time • Develop incentive plan • Generate new ideas • Determine what works From Hardaker & Ward, “Getting Things Done, ” Harvard Business Review, 1987 Impacts 2 1 3 4 3 1 1 1
Focus on the “Hows” Whats (CSFs) Hows (actions) C F A G J H B • Target key markets • Engage in P. R. • Train collections staff • Install new equipment • Install cost software • Use cost information • Reduce turnaround time • Develop incentive plan • Generate new ideas • Determine what works From Hardaker & Ward, “Getting Things Done, ” Harvard Business Review, 1987 Impacts 2 1 3 4 3 1 1 1
 Change Model # 8 “Creating an Adaptive Organization”
Change Model # 8 “Creating an Adaptive Organization”
 Which of the following would you prefer? Have someone… 1. Tell you what to do 2. Ask your opinion about what should be done
Which of the following would you prefer? Have someone… 1. Tell you what to do 2. Ask your opinion about what should be done
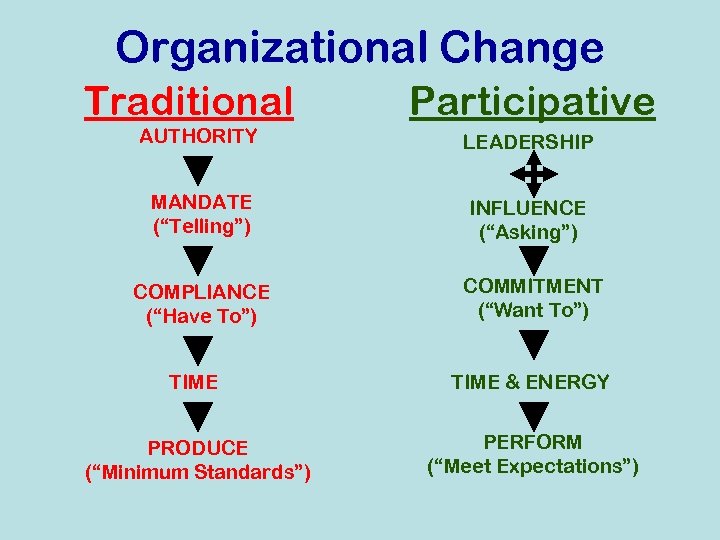 Organizational Change Traditional Participative AUTHORITY LEADERSHIP MANDATE (“Telling”) INFLUENCE (“Asking”) COMPLIANCE (“Have To”) COMMITMENT (“Want To”) TIME & ENERGY PRODUCE (“Minimum Standards”) PERFORM (“Meet Expectations”)
Organizational Change Traditional Participative AUTHORITY LEADERSHIP MANDATE (“Telling”) INFLUENCE (“Asking”) COMPLIANCE (“Have To”) COMMITMENT (“Want To”) TIME & ENERGY PRODUCE (“Minimum Standards”) PERFORM (“Meet Expectations”)
 Time Universal
Time Universal


