CHANGE MANAGEMENT Introductory elements. Barcelona, October, 2015 Francesc














introductory_elements_of_change_management.pptx
- Размер: 541.9 Кб
- Автор:
- Количество слайдов: 14
Описание презентации CHANGE MANAGEMENT Introductory elements. Barcelona, October, 2015 Francesc по слайдам
 CHANGE MANAGEMENT Introductory elements. Barcelona, October, 2015 Francesc Cots Professor of Change Management
CHANGE MANAGEMENT Introductory elements. Barcelona, October, 2015 Francesc Cots Professor of Change Management
 Definition What is change management? Parts of an organisaton: Processes Systems Organization structure Job roles While the notion of ‘becoming more competitive’ or ‘becoming closer to the customer’ or ‘becoming more efficient’ can be the motivation to change, at some point these goals must be transformed into thespecific impactson processes, systems, organization structures or job roles. This is the process of defining ‘the change’.
Definition What is change management? Parts of an organisaton: Processes Systems Organization structure Job roles While the notion of ‘becoming more competitive’ or ‘becoming closer to the customer’ or ‘becoming more efficient’ can be the motivation to change, at some point these goals must be transformed into thespecific impactson processes, systems, organization structures or job roles. This is the process of defining ‘the change’.
 Organisation as a system It is not only the sum of the parts In fact, the organisation intelligence may be superior, inferior or the same than the sum of its members. If the team learns evolution will be faster with better results that separately. The essence of team learning is personal domain and shared vision. It is a permanent process. creating change within an organization takes hard work and structure around what must actually take place to make thechangehappen
Organisation as a system It is not only the sum of the parts In fact, the organisation intelligence may be superior, inferior or the same than the sum of its members. If the team learns evolution will be faster with better results that separately. The essence of team learning is personal domain and shared vision. It is a permanent process. creating change within an organization takes hard work and structure around what must actually take place to make thechangehappen
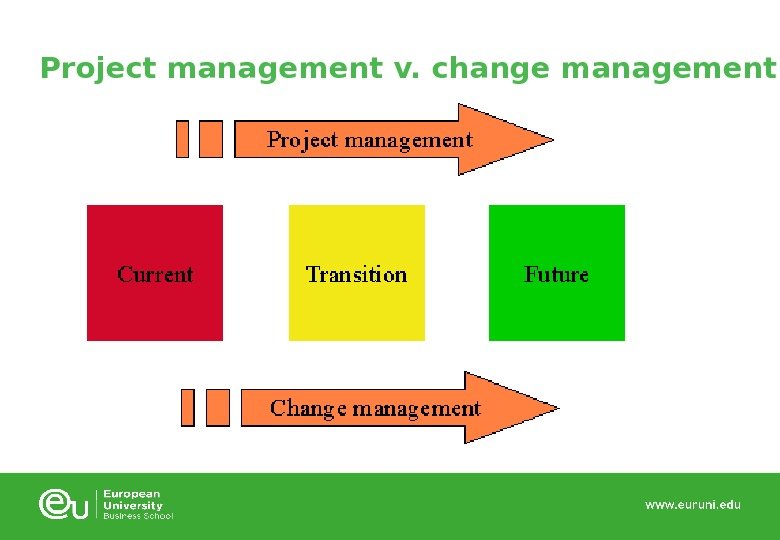
 Project management v. change management Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques toproject activitiesto meet project requirements. Application and integration of the project management processes of initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing. Change management is the process, tools and techniques to manage thepeople-sideof change to achieve the required business outcome. Change management incorporates the organizational tools that can be utilized to help individuals make successful personal transitions resulting in the adoption and realization of change. Project management focuses on thetasksto achieve the project requirements. Change management focuses on thepeopleimpacted by the change.
Project management v. change management Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques toproject activitiesto meet project requirements. Application and integration of the project management processes of initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing. Change management is the process, tools and techniques to manage thepeople-sideof change to achieve the required business outcome. Change management incorporates the organizational tools that can be utilized to help individuals make successful personal transitions resulting in the adoption and realization of change. Project management focuses on thetasksto achieve the project requirements. Change management focuses on thepeopleimpacted by the change.
 Project management v. change management
Project management v. change management
 Project management v. change management Element: Goal or objective: «The change» To improve the organization in some fashion — for instance reducing costs, improving revenues, solving problems, seizing opportunities, aligning work and strategy, streamlining information flow within the organization Project management To develop a set of specific plans and actions to achieve «the change» given time, cost and scope constraints and to utilize resources effectively (managing the ‘technical’ side of the change) Change management To apply a systematic approach to helping the individuals impacted by «the change» to be successful by building support, addressing resistance and developing the required knowledge and ability to implement the change (managing the ‘people’ side of the change)
Project management v. change management Element: Goal or objective: «The change» To improve the organization in some fashion — for instance reducing costs, improving revenues, solving problems, seizing opportunities, aligning work and strategy, streamlining information flow within the organization Project management To develop a set of specific plans and actions to achieve «the change» given time, cost and scope constraints and to utilize resources effectively (managing the ‘technical’ side of the change) Change management To apply a systematic approach to helping the individuals impacted by «the change» to be successful by building support, addressing resistance and developing the required knowledge and ability to implement the change (managing the ‘people’ side of the change)
 Activities for change management
Activities for change management
 Factors for change EXTERNAL New technologies Mergers and acquisitions, restructurings Cultural transformation Globalization E-business Consumer demands such as social and environmental issues
Factors for change EXTERNAL New technologies Mergers and acquisitions, restructurings Cultural transformation Globalization E-business Consumer demands such as social and environmental issues
 Factors for change INTERNAL Workers’ unsatisfaction Low productivity Change of mentality: Work as a realization platform instead of “I want time to live after work”. New strategies If you handle well these factors, you win. If not, it can cost a great deal of money and cause lot of pain
Factors for change INTERNAL Workers’ unsatisfaction Low productivity Change of mentality: Work as a realization platform instead of “I want time to live after work”. New strategies If you handle well these factors, you win. If not, it can cost a great deal of money and cause lot of pain
 Analytical v. emotional skills Central point: change people’s behaviour The heart of change is in the emotions, not in the thinking, analysis, etc. Frustration, fear, anger, resentment, ignoring how the world is changing…can be overcomed in the realm of feelings, not analysis Limitations of analysis You don’t need analysis to find big truths In a turbulent and uncertain world… It does not motivate people
Analytical v. emotional skills Central point: change people’s behaviour The heart of change is in the emotions, not in the thinking, analysis, etc. Frustration, fear, anger, resentment, ignoring how the world is changing…can be overcomed in the realm of feelings, not analysis Limitations of analysis You don’t need analysis to find big truths In a turbulent and uncertain world… It does not motivate people
 Analytical v. emotional skills We don’t fail at changes because we are not competent or not able… we fail because we haven’t sufficiently experienced highly successful change… we don’t even try… Core pattern: see/ feel / change Motivation https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=rrkrv. AUb. U 9 Y
Analytical v. emotional skills We don’t fail at changes because we are not competent or not able… we fail because we haven’t sufficiently experienced highly successful change… we don’t even try… Core pattern: see/ feel / change Motivation https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=rrkrv. AUb. U 9 Y
 Innovation Radical change in human behavior needed to face current challenges (economic, personal, environmental, organisational, etc) Innovation is one way Innovating at the concept stage, or developing new products and services capable of performing the same function than existing ones with significant less resources, or with significant greater satisfaction for the consumer Incremental v. radical It is an opportunity for business
Innovation Radical change in human behavior needed to face current challenges (economic, personal, environmental, organisational, etc) Innovation is one way Innovating at the concept stage, or developing new products and services capable of performing the same function than existing ones with significant less resources, or with significant greater satisfaction for the consumer Incremental v. radical It is an opportunity for business
 Innovation Example of the toothbrush Product o service redesign: making adjustments in raw materials, packaging, delivery, etc. Your toothbrush is still a toothbrush Innovation: need to question fundamental assumptions (specially treated chewing gum or benign food additive). Ability to project an image as a leader, innovator, etc. External innovation: product innovation, business model, system innovation Zipcar, power purchase agreement, ebook, etc. Innovation inside the organisation
Innovation Example of the toothbrush Product o service redesign: making adjustments in raw materials, packaging, delivery, etc. Your toothbrush is still a toothbrush Innovation: need to question fundamental assumptions (specially treated chewing gum or benign food additive). Ability to project an image as a leader, innovator, etc. External innovation: product innovation, business model, system innovation Zipcar, power purchase agreement, ebook, etc. Innovation inside the organisation
 THANK YOU!
THANK YOU!

