79bd8b6455744d8f7b950091b281144d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Challenges of the public sector Maria Eugenia Luengo, EFQM Bilbao, 15 th November 2007

Content ú EFQM in brief ú A look into the public sector ú How can EFQM help? 2

Content ú EFQM in brief ú A look into the public sector ú How can EFQM help? 3

Who are we? ú ú Not for Profit Membership Foundation Independent Central team in Brussels 4

We are also our members ú Over 600 members in 56 countries ú ú ú Germany = 128 Switzerland = 48 Spain = 40 France = 37 UK = 35 ú Botswana, Brazil, China, Egypt, India, Iran, Israel, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Philippines, Qatar, Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Taiwan, Trinidad & Tobago, UAE, Zambia 5

Public sector members ú 17% public sector members: Government: – European Investment Bank – Library of the European Parliament – The Cabinet Office, UK – Ministry of Flemish region, Belgium – Tax office, DK – Ministry of Finance, Slovak Republic – Civil Service Commission, Israel – Comune di Mantova, Italy – Forem, Belgium – Federal Police, Belgium 6

Public sector members Education: – University of Versailles, France – University of Piraeus, Greece – University of Rome ‘Sapienza’, Italy – London Metropolitan University, UK – Sabanci University, Turkey – Basel University, Switzerland – Technical University of Ostrava, Czech Republic 7

Public sector members Spain: – Clinica Tambre – Comarca Gipuzkoa Ekialde - Osakidetza – Esade Business School – Euskal Irrati Telebista – Fundacion Novia Salcedo – Instituto de Empresa – Lauaxeta Ikastola – Universitat Oberta de Catalunya – Universidad Comercial de Deusto – Universidad Politecnica de Valencia – Universidad Politecnica de Cataluña – Town hall of Esplugues de Llobregat 8
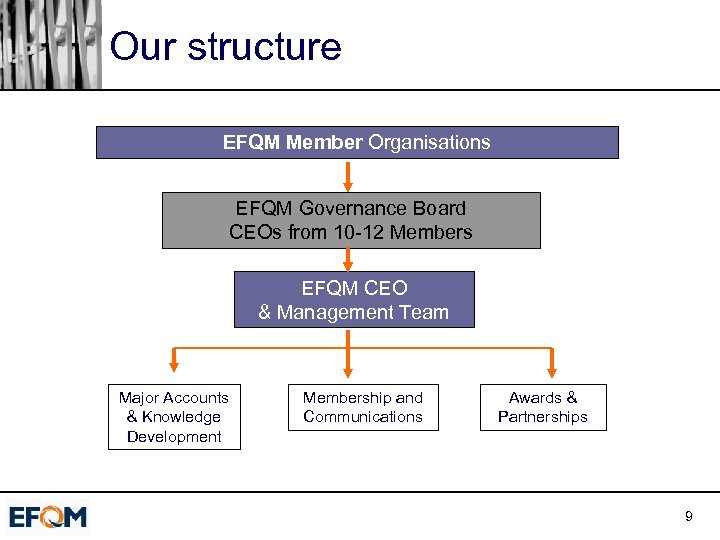
Our structure EFQM Member Organisations EFQM Governance Board CEOs from 10 -12 Members EFQM CEO & Management Team Major Accounts & Knowledge Development Membership and Communications Awards & Partnerships 9

Our vision = back to basics ú Active membership = 1, 000 members ú Leadership group as role model = Pact projects ú More visible and upgraded recognition = integrated EEA 10

EFQM Value proposition Share what works between organisations through mutual assessment …to implement strategies 11

What does EFQM mean? EXCELLENCE 12

Excellence What is Excellence? ú What characterises Excellent organisations ? 13

Excellence It’s a journey, a state of mind It evokes words like “superior”, “best” and “unique” It means improvement and innovation, enabling sustainable performance It’s about fulfilling and, why not, exceeding the needs and expectations of the stakeholders by mobilising the whole organisation 14
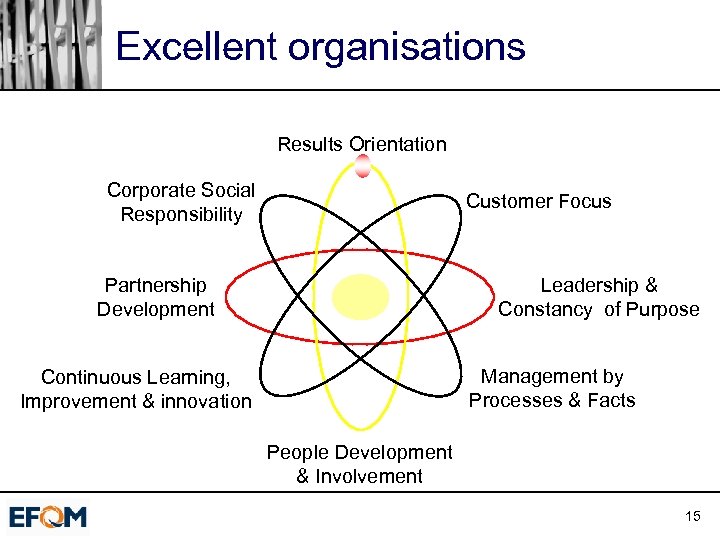
Excellent organisations Results Orientation Corporate Social Responsibility Customer Focus Partnership Development Leadership & Constancy of Purpose Management by Processes & Facts Continuous Learning, Improvement & innovation People Development & Involvement 15
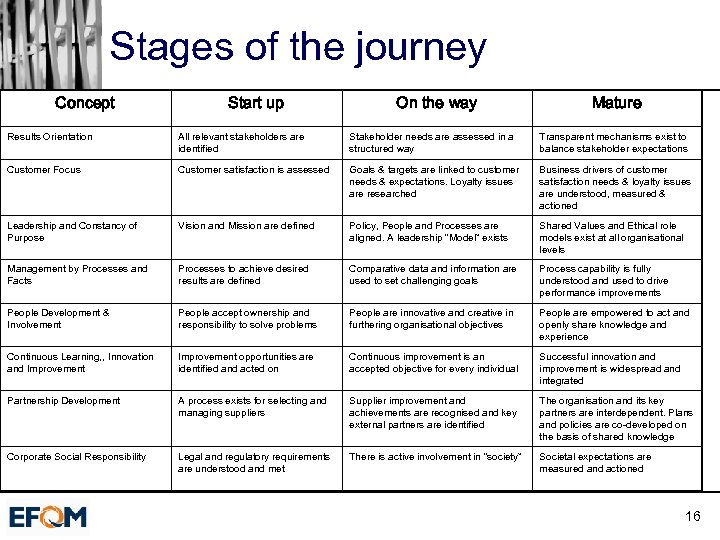
Stages of the journey Concept Start up On the way Mature Results Orientation All relevant stakeholders are identified Stakeholder needs are assessed in a structured way Transparent mechanisms exist to balance stakeholder expectations Customer Focus Customer satisfaction is assessed Goals & targets are linked to customer needs & expectations. Loyalty issues are researched Business drivers of customer satisfaction needs & loyalty issues are understood, measured & actioned Leadership and Constancy of Purpose Vision and Mission are defined Policy, People and Processes are aligned. A leadership “Model” exists Shared Values and Ethical role models exist at all organisational levels Management by Processes and Facts Processes to achieve desired results are defined Comparative data and information are used to set challenging goals Process capability is fully understood and used to drive performance improvements People Development & Involvement People accept ownership and responsibility to solve problems People are innovative and creative in furthering organisational objectives People are empowered to act and openly share knowledge and experience Continuous Learning, , Innovation and Improvement opportunities are identified and acted on Continuous improvement is an accepted objective for every individual Successful innovation and improvement is widespread and integrated Partnership Development A process exists for selecting and managing suppliers Supplier improvement and achievements are recognised and key external partners are identified The organisation and its key partners are interdependent. Plans and policies are co-developed on the basis of shared knowledge Corporate Social Responsibility Legal and regulatory requirements are understood and met There is active involvement in “society” Societal expectations are measured and actioned 16

Content ú EFQM in brief ú A look into the public sector ú How can EFQM help? 17

Why the need for a performance management system? ú They are organisations ú Modernisation/Reform = transformation of the old model in a new one 18

What does this imply? ú Change in the culture, in the mentality ú From bureaucracy to management ú Performance management tools 19

What tools do they use? ú Balanced Scorecard ú Juran Project Methodologies ú Six Sigma ú Diversiry Model ú ISO ú Business Process Reengineering ú CAF ú EFQM Excellence Model 20
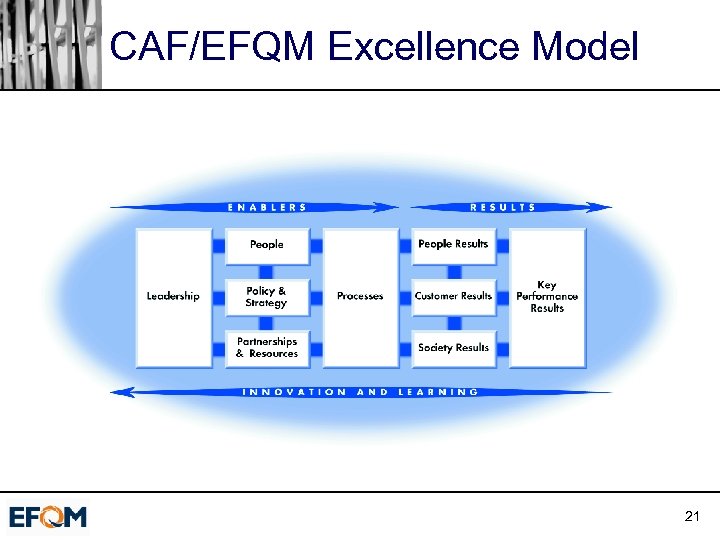
CAF/EFQM Excellence Model 21
Similarities ú Same structure ú Self-Assessment ú Measure performance ú Benchmarking ú Recognition 22
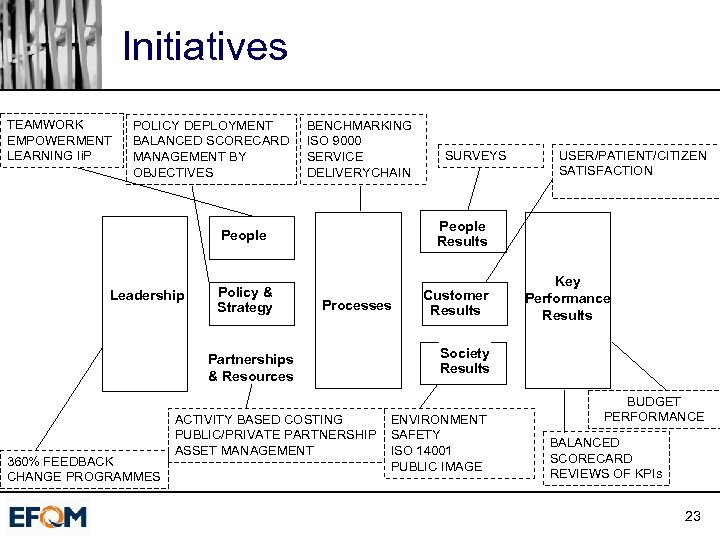
Initiatives TEAMWORK EMPOWERMENT LEARNING Ii. P POLICY DEPLOYMENT BALANCED SCORECARD MANAGEMENT BY OBJECTIVES BENCHMARKING ISO 9000 SERVICE DELIVERYCHAIN Leadership Processes Partnerships & Resources 360% FEEDBACK CHANGE PROGRAMMES USER/PATIENT/CITIZEN SATISFACTION People Results People Policy & Strategy SURVEYS ACTIVITY BASED COSTING PUBLIC/PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP ASSET MANAGEMENT Customer Results Key Performance Results Society Results ENVIRONMENT SAFETY ISO 14001 PUBLIC IMAGE BUDGET PERFORMANCE BALANCED SCORECARD REVIEWS OF KPIs 23

Increasing activity ú Europe and beyond ú No longer limited to UK and Scandinavia ú Recognition ú Good practices conferences 24
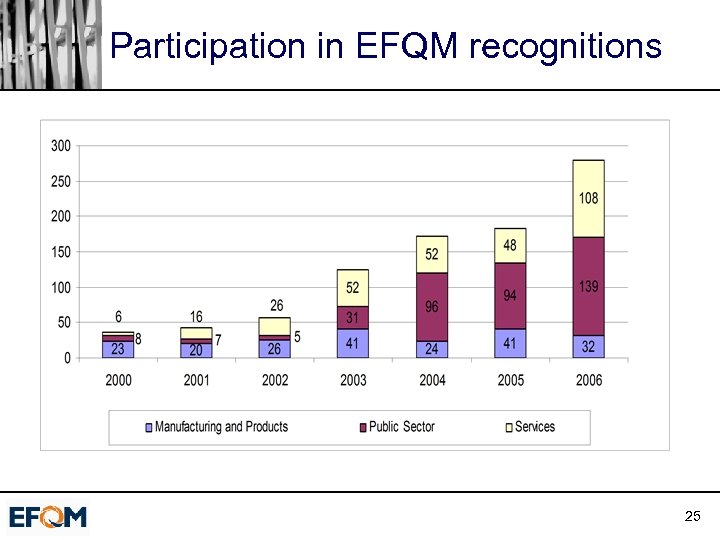
Participation in EFQM recognitions 25
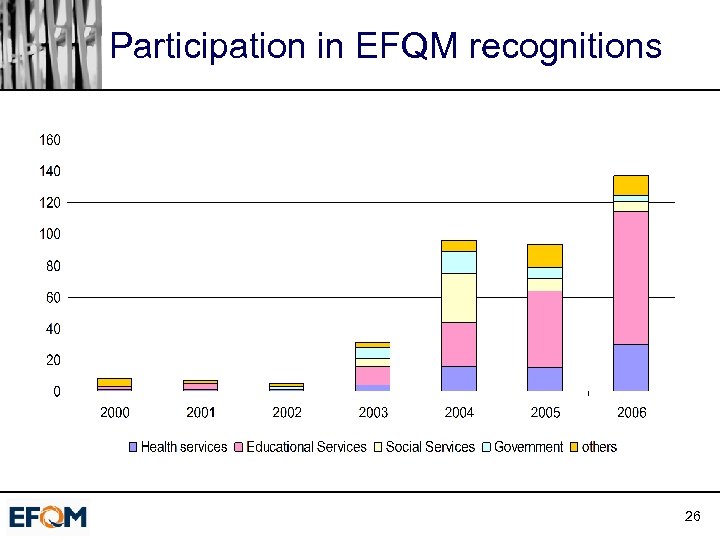
Participation in EFQM recognitions 26

Implementation issues ú Concentrate on completing assessments rather than the results ú Little quantification of the benefits of improvement activities ú No specific tracking of perfomance over time 27

Results ú Reduced number of complaints ú Reduction in customer response time ú Service performance against budget ú Prompt payment of invoices ú Fall in absenteism rates ú Increased levels of staff responsiveness, courtesy and accessibility 28

How has the Model helped? ú Influenced the degree of scrutiny of the organisation ú Influenced the degree of structure and integration ú Encouraged external recognition ú Helped identify role model orgnisations ú Encourage sharing good practice 29

Content ú EFQM in brief ú A look into the public sector ú How can EFQM help? 30

How can EFQM help? ú Customised training ú Support with starting the journey ú Facilitate the exchange and the learning (COPs, benchmarking, good practice visits) ú Facilitate networking ú Recognition = Levels of Excellence ú EUPAN/IPSG ú EU funded projects 31

THANK YOU! 32
79bd8b6455744d8f7b950091b281144d.ppt