ae455be66213ca10b591900eba3b10f3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Challenges in Creating and Curating Plant PGDBs: Lessons Learned from Ara. Cyc and Poplar. Cyc Peifen Zhang Carnegie Institution For Science Department of Plant Biology Stanford, CA

Who We Are PMN: - Sue Rhee (PI) - Kate Dreher (curator) - A. Karthik (curator, previous) - Lee Chae (Postdoc) - Anjo Chi (programmer) - Cynthia Lee (TAIR tech team) - Larry Ploetz (TAIR tech team) - Shanker Singh (TAIR tech team) - Bob Muller (TAIR tech team) http: //plantcyc. org Key Collaborators: - Peter Karp (Meta. Cyc, SRI) - Ron Caspi (Meta. CYc, SRI) - Lukas Mueller (SGN) - Anuradha Pujar (SGN)

Introduction • Background and rationale – Plants (food, feed, forest, medicine, biofuel…) – An ocean of sequences • More than 60 species in genome sequencing projects, hundreds in EST projects – Putting individual genes onto a network of metabolic reactions and pathways • Annotating, visualizing and analyzing at system level – Ara. Cyc (Arabidopsis thaliana, TAIR/PMN) • predicted by using the Pathway Tools software, followed by manual curation

Introduction (cont) • Background and rationale – Plants (food, feed, forest, medicine, biofuel…) – An ocean of sequences • More than 60 species in genome sequencing projects, hundreds in EST projects – Putting individual genes onto a network of metabolic reactions and pathways • Annotating, visualizing and analyzing at system level – Ara. Cyc (Arabidopsis thaliana, TAIR/PMN) • predicted by using the Pathway Tools software, followed by manual curation – Other plant pathway databases predicted by using the Pathway Tools • Rice. Cyc (Oryza sativa, Gramene) • Medic. Cyc (Medicago truncatula, Noble Foundation) • Lyco. Cyc (Solanum lycopersicum, SGN), …

Limitations • Creating pathway databases includes three major components, and is resource-intensive – Sequence annotation – Reference pathway database – Pathway prediction, validation, refinement • Heterogeneous sequence annotation protocols and varying levels of pathway validation impact quality and hinder meaningful cross-species comparison • Using a non-plant reference database causes many false-positive and false-negative pathway predictions

Introducing the PMN • Scope – A platform for plant metabolic pathway database creation – A community for data curation • Curators, editorial board, ally in other databases, researchers • Major goals – Create a plant-specific reference pathway database (Plant. Cyc) – Create an enzyme sequence annotation pipeline – Enhance pathway prediction by using Plant. Cyc, and including an automated initial validation step – Create metabolic pathway databases for plant species – e. g. Poplar. Cyc (Populus trichocarpa), Soy. Cyc (soybean)

Plant. Cyc Creation • Nature of Plant. Cyc – Multiple-species, plants-only – curator-reviewed pathways, predicted, hypothetical, empirical – primary and secondary metabolism • Major Source – All Ara. Cyc pathways and enzymes – Plant pathways and enzymes from Meta. Cyc – Additional pathways and enzymes manually curated and added – Enzymes from Rice. Cyc, Lyco. Cyc and Medic. Cyc
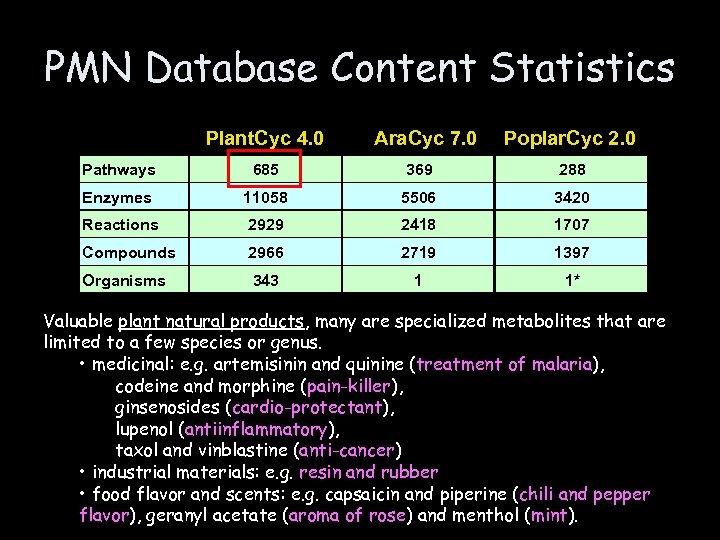
PMN Database Content Statistics Plant. Cyc 4. 0 Ara. Cyc 7. 0 Poplar. Cyc 2. 0 Pathways 685 369 288 Enzymes 11058 5506 3420 Reactions 2929 2418 1707 Compounds 2966 2719 1397 Organisms 343 1 1* Valuable plant natural products, many are specialized metabolites that are limited to a few species or genus. • medicinal: e. g. artemisinin and quinine (treatment of malaria), codeine and morphine (pain-killer), ginsenosides (cardio-protectant), lupenol (antiinflammatory), taxol and vinblastine (anti-cancer) • industrial materials: e. g. resin and rubber • food flavor and scents: e. g. capsaicin and piperine (chili and pepper flavor), geranyl acetate (aroma of rose) and menthol (mint).

Enzyme Sequence Annotation (version 1. 0) • Reference sequences, enzymes with known functions – 14, 187 enzyme sequences compiled from GOAUni. Prot, Brenda, Meta. Cyc, and TAIR – 3805 functional identifiers (full EC number, Meta. Cyc reaction id, GO id) • Annotation methods – BLASTP • Cut-off – unique e-value threshold for each functional identifier
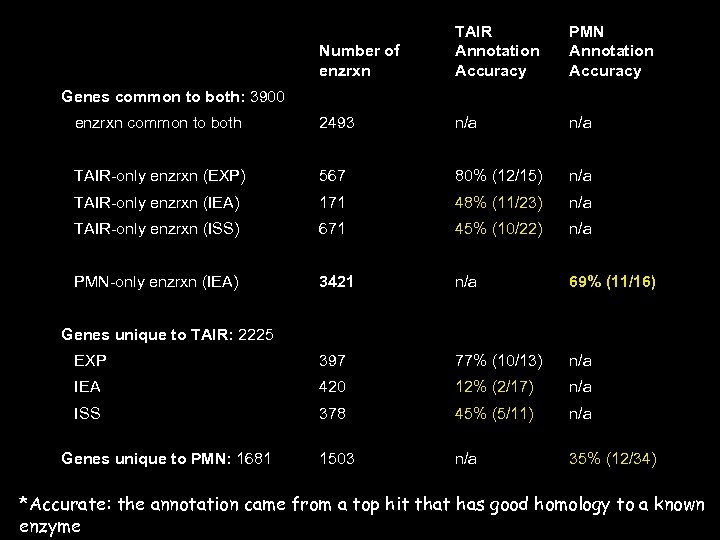
Number of enzrxn TAIR Annotation Accuracy PMN Annotation Accuracy enzrxn common to both 2493 n/a TAIR-only enzrxn (EXP) 567 80% (12/15) n/a TAIR-only enzrxn (IEA) 171 48% (11/23) n/a TAIR-only enzrxn (ISS) 671 45% (10/22) n/a PMN-only enzrxn (IEA) 3421 n/a 69% (11/16) EXP 397 77% (10/13) n/a IEA 420 12% (2/17) n/a ISS 378 45% (5/11) n/a 1503 n/a 35% (12/34) Genes common to both: 3900 Genes unique to TAIR: 2225 Genes unique to PMN: 1681 *Accurate: the annotation came from a top hit that has good homology to a known enzyme

Conclusion • Increased performance with potentially true enzymes • Over-prediction for non-enzyme proteins

Enzyme Sequence Annotation (version 2. 0, in progress) • Reference sequences, proteins with known functions (ERL) – Swiss. Prot • 117, 000 proteins, 26, 000 enzymes, 2, 400 full EC numbers – Additional enzymes from Brenda, Meta. Cyc, and TAIR – Functional identifiers: full EC number, Meta. Cyc reaction id, GO id, • Annotation methods – BLASTP – Priam (enzyme-specific, motif-based) – Cat. Fam (enzyme-specific, motif-based) • Function calling – Ensemble and voting
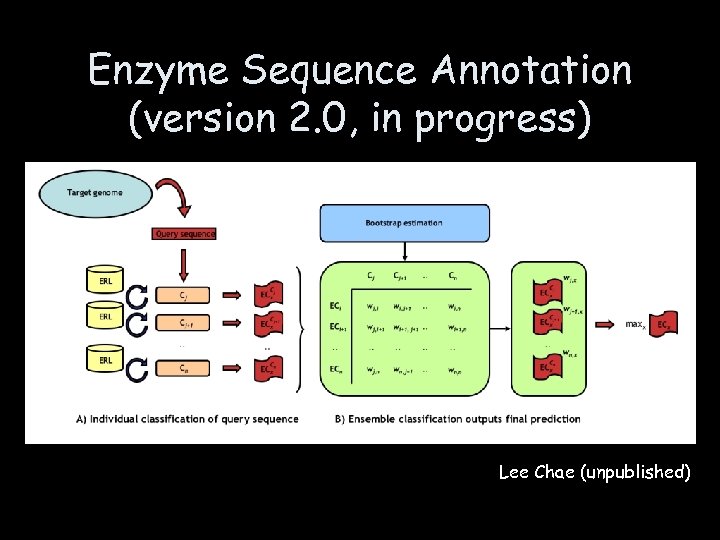
Enzyme Sequence Annotation (version 2. 0, in progress) Lee Chae (unpublished)
Application to the Poplar Genome • Sequence annotation version 1. 0 • Pathway Tools version 12. 5 • PGDB creation using Plant. Cyc vs Meta. Cyc
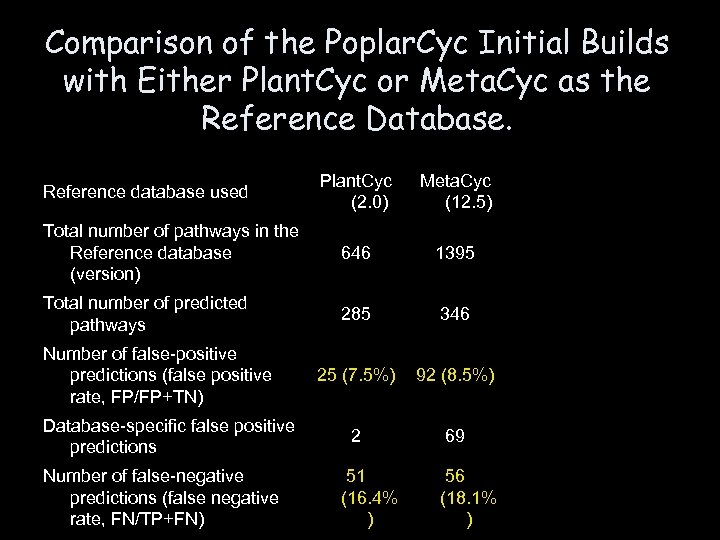
Comparison of the Poplar. Cyc Initial Builds with Either Plant. Cyc or Meta. Cyc as the Reference Database. Plant. Cyc (2. 0) Meta. Cyc (12. 5) Total number of pathways in the Reference database (version) 646 1395 Total number of predicted pathways 285 346 25 (7. 5%) 92 (8. 5%) 2 69 Reference database used Number of false-positive predictions (false positive rate, FP/FP+TN) Database-specific false positive predictions Number of false-negative predictions (false negative rate, FN/TP+FN) 51 (16. 4% ) 56 (18. 1% )

Conclusion • The absolute number of false-positive pathways was reduced significantly by using Plant. Cyc as the reference • The number of false-negative pathways was comparable using either Plant. Cyc or Meta. Cyc as the reference, indicating the usefulness of both databases as references
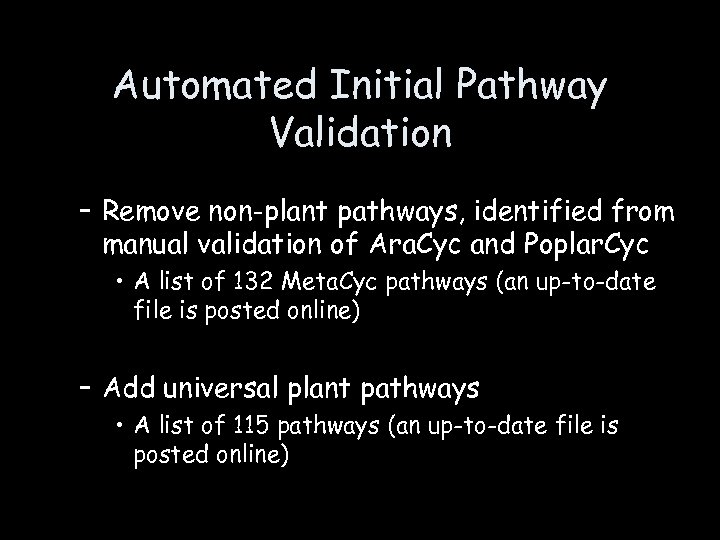
Automated Initial Pathway Validation – Remove non-plant pathways, identified from manual validation of Ara. Cyc and Poplar. Cyc • A list of 132 Meta. Cyc pathways (an up-to-date file is posted online) – Add universal plant pathways • A list of 115 pathways (an up-to-date file is posted online)
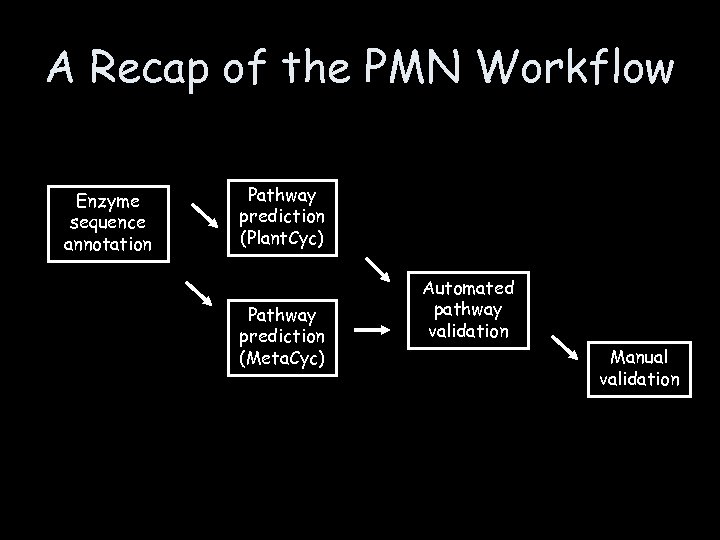
A Recap of the PMN Workflow Enzyme sequence annotation Pathway prediction (Plant. Cyc) Pathway prediction (Meta. Cyc) Automated pathway validation Manual validation

An Example of Practical Issues

Updating Ara. Cyc with TAIR Functional Annotations • Source and quality – Literature-based GO annotations – Catalytic activities – Experimental evidence (IDA, IMP, IGI, IPI, IEP)

Problem • TAIR: AT 5 G 13700 (polyamine oxidase, IDA, Pub. Med 16778015) • Polyamine oxidase reactions in Meta. Cyc/Plant. Cyc: • Which one of the reaction catalyzed by AT 5 G 13700 was supported in the paper?

Conclusion • Not to automatically propagate GO-exp annotations to enzrxns • Manually enter along with appropriate evidence

Future Work • Enhance pathway prediction and validation – Using additional evidence, such as presence of compounds, weighted confidence of enzyme annotations • Refine pathways, hole-filling – Including non-sequence homology based information in enzyme function prediction, such as phylogenetic profiles, coexpression, protein structure • Create new pathway databases – moss (P. patens), Selaginella, maize, cassava, wine grape … • Add new data types, critical for strategic planning of metabolic engineering – Rate-limiting step – Transcriptional regulator

Thank you for your attention!
ae455be66213ca10b591900eba3b10f3.ppt