5227b06f2c33b8229a20d8f80237ea79.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 8
 Challenges for the Computational Discovery of Scientific Knowledge Pat Langley School of Computing and Informatics Arizona State University Tempe, Arizona Institute for the Study of Learning and Expertise Palo Alto, California Thanks to K. Arrigo, D. Billman, M. Bravo, S. Borrett, W. Bridewell, S. Dzeroski, and L. Todorovski for their contributions to this research, which is funded by a grant from the National Science Foundation.
Challenges for the Computational Discovery of Scientific Knowledge Pat Langley School of Computing and Informatics Arizona State University Tempe, Arizona Institute for the Study of Learning and Expertise Palo Alto, California Thanks to K. Arrigo, D. Billman, M. Bravo, S. Borrett, W. Bridewell, S. Dzeroski, and L. Todorovski for their contributions to this research, which is funded by a grant from the National Science Foundation.
 Drawbacks of Scientific Data Mining Because it borrows from work on commercial applications, most work on scientific data mining: · generates models in forms inappropriate to most sciences · makes incorrect assumptions about the available inputs · focuses on convenient algorithmic issues, not scientists’ needs We need to redirect attention toward a broader range of discovery tasks that actually arise in scientific fields. Data-mining researchers would benefit from looking at the older literature on computational scientific discovery.
Drawbacks of Scientific Data Mining Because it borrows from work on commercial applications, most work on scientific data mining: · generates models in forms inappropriate to most sciences · makes incorrect assumptions about the available inputs · focuses on convenient algorithmic issues, not scientists’ needs We need to redirect attention toward a broader range of discovery tasks that actually arise in scientific fields. Data-mining researchers would benefit from looking at the older literature on computational scientific discovery.
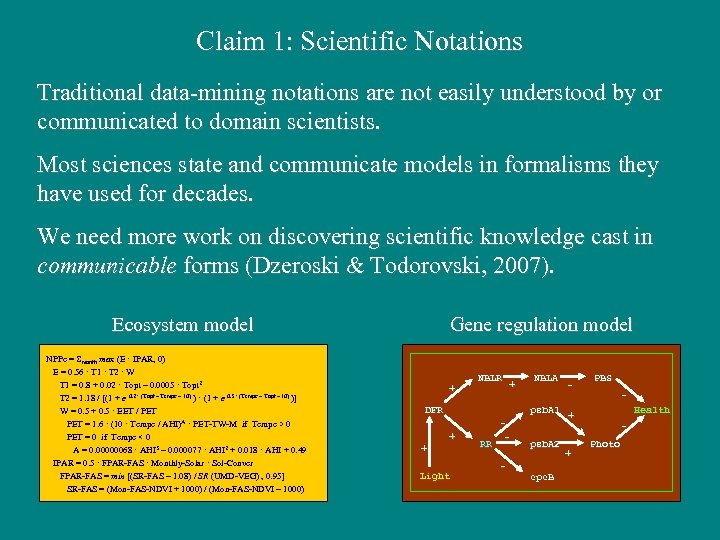 Claim 1: Scientific Notations Traditional data-mining notations are not easily understood by or communicated to domain scientists. Most sciences state and communicate models in formalisms they have used for decades. We need more work on discovering scientific knowledge cast in communicable forms (Dzeroski & Todorovski, 2007). Ecosystem model NPPc = Smonth max (E · IPAR, 0) E = 0. 56 · T 1 · T 2 · W T 1 = 0. 8 + 0. 02 · Topt – 0. 0005 · Topt 2 T 2 = 1. 18 / [(1 + e 0. 2 · (Topt – Tempc – 10) ) · (1 + e 0. 3 · (Tempc – Topt – 10) )] W = 0. 5 + 0. 5 · EET / PET = 1. 6 · (10 · Tempc / AHI)A · PET-TW-M if Tempc > 0 PET = 0 if Tempc < 0 A = 0. 00000068 · AHI 3 – 0. 000077 · AHI 2 + 0. 018 · AHI + 0. 49 IPAR = 0. 5 · FPAR-FAS · Monthly-Solar · Sol-Conver FPAR-FAS = min [(SR-FAS – 1. 08) / SR (UMD-VEG) , 0. 95] SR-FAS = (Mon-FAS-NDVI + 1000) / (Mon-FAS-NDVI – 1000) Gene regulation model + NBLR + DFR NBLA psb. A 1 + + Light RR - psb. A 2 cpc. B - PBS Health + + Photo
Claim 1: Scientific Notations Traditional data-mining notations are not easily understood by or communicated to domain scientists. Most sciences state and communicate models in formalisms they have used for decades. We need more work on discovering scientific knowledge cast in communicable forms (Dzeroski & Todorovski, 2007). Ecosystem model NPPc = Smonth max (E · IPAR, 0) E = 0. 56 · T 1 · T 2 · W T 1 = 0. 8 + 0. 02 · Topt – 0. 0005 · Topt 2 T 2 = 1. 18 / [(1 + e 0. 2 · (Topt – Tempc – 10) ) · (1 + e 0. 3 · (Tempc – Topt – 10) )] W = 0. 5 + 0. 5 · EET / PET = 1. 6 · (10 · Tempc / AHI)A · PET-TW-M if Tempc > 0 PET = 0 if Tempc < 0 A = 0. 00000068 · AHI 3 – 0. 000077 · AHI 2 + 0. 018 · AHI + 0. 49 IPAR = 0. 5 · FPAR-FAS · Monthly-Solar · Sol-Conver FPAR-FAS = min [(SR-FAS – 1. 08) / SR (UMD-VEG) , 0. 95] SR-FAS = (Mon-FAS-NDVI + 1000) / (Mon-FAS-NDVI – 1000) Gene regulation model + NBLR + DFR NBLA psb. A 1 + + Light RR - psb. A 2 cpc. B - PBS Health + + Photo
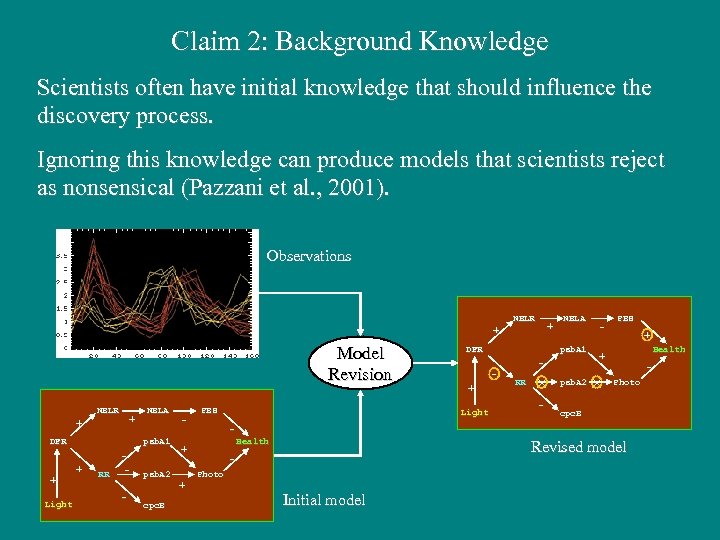 Claim 2: Background Knowledge Scientists often have initial knowledge that should influence the discovery process. Ignoring this knowledge can produce models that scientists reject as nonsensical (Pazzani et al. , 2001). Observations NBLR + + Model Revision NBLR + + DFR + Light NBLA psb. A 1 + RR - psb. A 2 cpc. B - PBS psb. A 1 + Light - RR × - psb. A 2 - PBS + Health + × Photo cpc. B Health + + DFR NBLA Revised model Photo Initial model
Claim 2: Background Knowledge Scientists often have initial knowledge that should influence the discovery process. Ignoring this knowledge can produce models that scientists reject as nonsensical (Pazzani et al. , 2001). Observations NBLR + + Model Revision NBLR + + DFR + Light NBLA psb. A 1 + RR - psb. A 2 cpc. B - PBS psb. A 1 + Light - RR × - psb. A 2 - PBS + Health + × Photo cpc. B Health + + DFR NBLA Revised model Photo Initial model
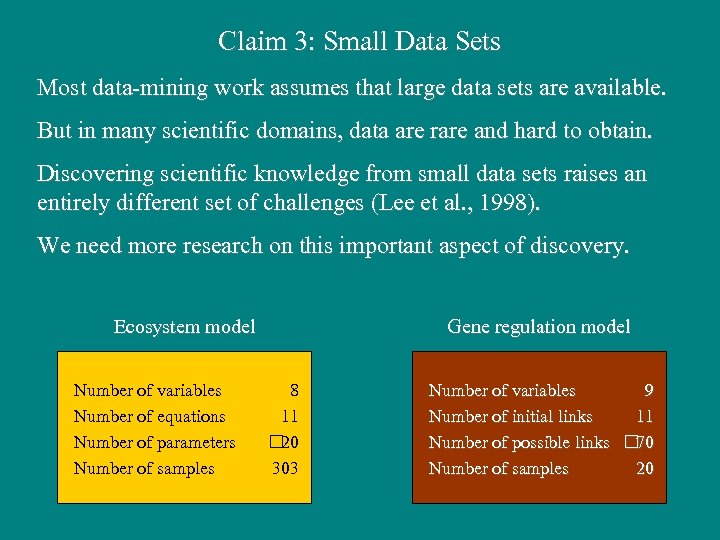 Claim 3: Small Data Sets Most data-mining work assumes that large data sets are available. But in many scientific domains, data are rare and hard to obtain. Discovering scientific knowledge from small data sets raises an entirely different set of challenges (Lee et al. , 1998). We need more research on this important aspect of discovery. Ecosystem model Number of variables Number of equations Number of parameters Number of samples Gene regulation model 8 11 20 303 9 Number of variables 11 Number of initial links 70 Number of possible links 20 Number of samples
Claim 3: Small Data Sets Most data-mining work assumes that large data sets are available. But in many scientific domains, data are rare and hard to obtain. Discovering scientific knowledge from small data sets raises an entirely different set of challenges (Lee et al. , 1998). We need more research on this important aspect of discovery. Ecosystem model Number of variables Number of equations Number of parameters Number of samples Gene regulation model 8 11 20 303 9 Number of variables 11 Number of initial links 70 Number of possible links 20 Number of samples
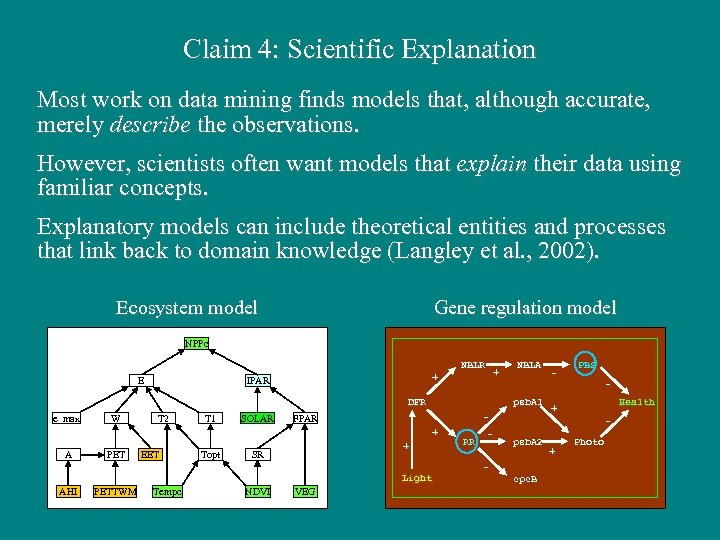 Claim 4: Scientific Explanation Most work on data mining finds models that, although accurate, merely describe the observations. However, scientists often want models that explain their data using familiar concepts. Explanatory models can include theoretical entities and processes that link back to domain knowledge (Langley et al. , 2002). Ecosystem model Gene regulation model NPPc NBLR E + + IPAR DFR e_max W T 2 T 1 SOLAR psb. A 1 - FPAR + A PET EET Topt + SR Light AHI PETTWM Tempc NDVI VEG NBLA RR - - PBS Health + - psb. A 2 cpc. B + Photo
Claim 4: Scientific Explanation Most work on data mining finds models that, although accurate, merely describe the observations. However, scientists often want models that explain their data using familiar concepts. Explanatory models can include theoretical entities and processes that link back to domain knowledge (Langley et al. , 2002). Ecosystem model Gene regulation model NPPc NBLR E + + IPAR DFR e_max W T 2 T 1 SOLAR psb. A 1 - FPAR + A PET EET Topt + SR Light AHI PETTWM Tempc NDVI VEG NBLA RR - - PBS Health + - psb. A 2 cpc. B + Photo
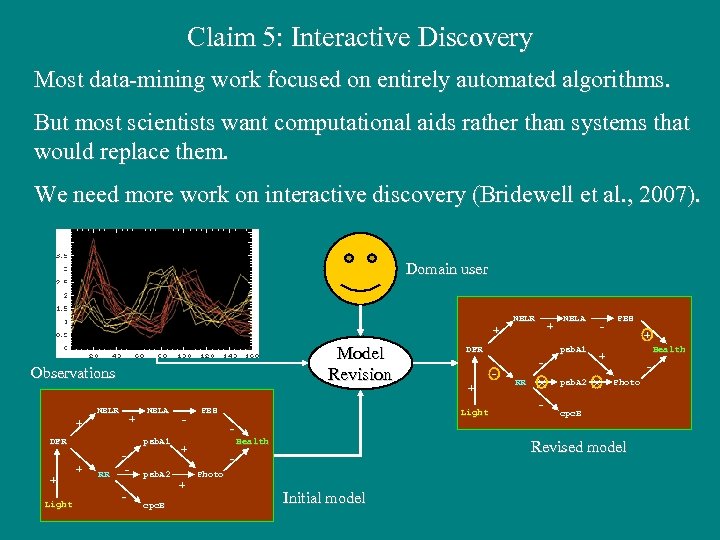 Claim 5: Interactive Discovery Most data-mining work focused on entirely automated algorithms. But most scientists want computational aids rather than systems that would replace them. We need more work on interactive discovery (Bridewell et al. , 2007). Domain user NBLR + + Model Revision Observations NBLR + + DFR + Light NBLA psb. A 1 + RR - psb. A 2 cpc. B - PBS psb. A 1 + Light - RR × - psb. A 2 - PBS + Health + × Photo cpc. B Health + + DFR NBLA Revised model Photo Initial model
Claim 5: Interactive Discovery Most data-mining work focused on entirely automated algorithms. But most scientists want computational aids rather than systems that would replace them. We need more work on interactive discovery (Bridewell et al. , 2007). Domain user NBLR + + Model Revision Observations NBLR + + DFR + Light NBLA psb. A 1 + RR - psb. A 2 cpc. B - PBS psb. A 1 + Light - RR × - psb. A 2 - PBS + Health + × Photo cpc. B Health + + DFR NBLA Revised model Photo Initial model
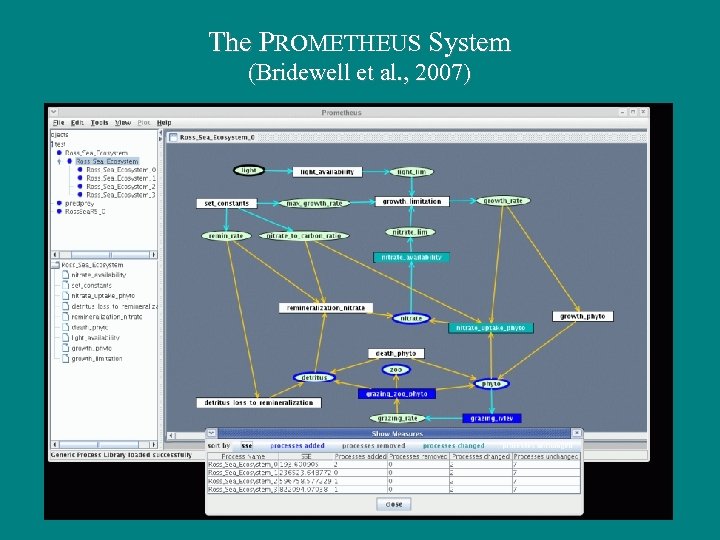 The PROMETHEUS System (Bridewell et al. , 2007)
The PROMETHEUS System (Bridewell et al. , 2007)


