524b2e86f7f06a851b891c88c2645d18.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Challenges and Opportunities in the Adoption of CAP Checklists in Electronic Format Perspectives and Experience of RPP 2 Participant Laboratories NAACCR 2009 Conference Lewis A. Hassell, MD
Challenges and Opportunities in the Adoption of CAP Checklists in Electronic Format Perspectives and Experience of RPP 2 Participant Laboratories NAACCR 2009 Conference Lewis A. Hassell, MD
 RPP 2 - Participants ¡ ¡ Pathology Laboratories -City of Hope -UPMC -DCPA -Nor. Dx (MMC) State and Hospital Registries CA, PA, ME ¡ ¡ LIS and Registry vendors -Cerner -IMPAC -CNex. T Others -CDC NPCR -CAP- SNOMED CT
RPP 2 - Participants ¡ ¡ Pathology Laboratories -City of Hope -UPMC -DCPA -Nor. Dx (MMC) State and Hospital Registries CA, PA, ME ¡ ¡ LIS and Registry vendors -Cerner -IMPAC -CNex. T Others -CDC NPCR -CAP- SNOMED CT
 Project endpoint goals ¡ Participant pathology groups report CAP Checklist data in synoptic format for breast, prostate and melanoma ¡ Synoptic electronically encoded data captured from report ¡ Checklist data transmitted electronically to registry and entered into database
Project endpoint goals ¡ Participant pathology groups report CAP Checklist data in synoptic format for breast, prostate and melanoma ¡ Synoptic electronically encoded data captured from report ¡ Checklist data transmitted electronically to registry and entered into database
 Pathology-Specific Project Queries Will Pathologists use the CAP Checklists as a routine part of reporting? ¡ What barriers exist for registries and laboratories in implementing the CAP Cancer Checklists in electronic format? ¡ What unique opportunities might exist for users of electronic checklists? ¡
Pathology-Specific Project Queries Will Pathologists use the CAP Checklists as a routine part of reporting? ¡ What barriers exist for registries and laboratories in implementing the CAP Cancer Checklists in electronic format? ¡ What unique opportunities might exist for users of electronic checklists? ¡
 Baseline State- Pathology labs City of Hope– Text only reports ¡ UPMC- Text diagnoses, Synoptic (text) in a separate section of report for many tumor types ¡ DCPA- Text and synoptic (text, locally developed) in diagnosis section of report ¡ Nor. Dx- Text and synoptic (local) in diagnosis section of report ¡
Baseline State- Pathology labs City of Hope– Text only reports ¡ UPMC- Text diagnoses, Synoptic (text) in a separate section of report for many tumor types ¡ DCPA- Text and synoptic (text, locally developed) in diagnosis section of report ¡ Nor. Dx- Text and synoptic (local) in diagnosis section of report ¡
 Synoptic Reporting: Implementation Factors ¡ Data element (DE) structure ¡ Data content & maintenance ¡ Synoptic design to facilitate data entry ¡ Workflow integration ¡ Synoptic data in reporting- where? ¡ Monitoring pathologist compliance (!!) ¡ Continuous process and quality improvement From Winters and Parwani, APIII 2007
Synoptic Reporting: Implementation Factors ¡ Data element (DE) structure ¡ Data content & maintenance ¡ Synoptic design to facilitate data entry ¡ Workflow integration ¡ Synoptic data in reporting- where? ¡ Monitoring pathologist compliance (!!) ¡ Continuous process and quality improvement From Winters and Parwani, APIII 2007
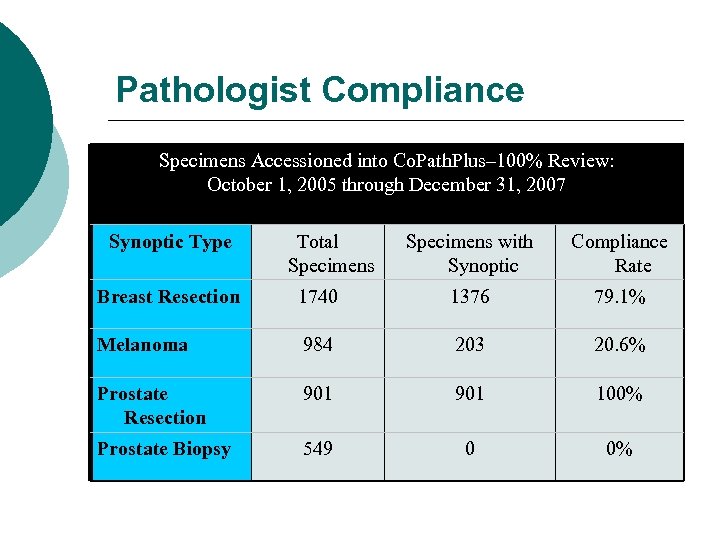 Pathologist Compliance Specimens Accessioned into Co. Path. Plus– 100% Review: October 1, 2005 through December 31, 2007 Synoptic Type Total Specimens with Synoptic Compliance Rate Breast Resection 1740 1376 79. 1% Melanoma 984 203 20. 6% Prostate Resection 901 100% Prostate Biopsy 549 0 0%
Pathologist Compliance Specimens Accessioned into Co. Path. Plus– 100% Review: October 1, 2005 through December 31, 2007 Synoptic Type Total Specimens with Synoptic Compliance Rate Breast Resection 1740 1376 79. 1% Melanoma 984 203 20. 6% Prostate Resection 901 100% Prostate Biopsy 549 0 0%
 Pathologist Compliance Usage highest in sections or practices with “mandate” ¡ Resistance encountered in complex situations such as multiple tumors, unusual histology, recurrences ¡
Pathologist Compliance Usage highest in sections or practices with “mandate” ¡ Resistance encountered in complex situations such as multiple tumors, unusual histology, recurrences ¡
 Synoptic Reporting Barriers. Pathologist Data-entry interface and workflow ¡ Traditional view of report ownership ¡ l l l Ignorance of expanded audience Resistance to externally imposed standards from authoritative organizations– JCAHO, CAP, ASC-Co. C and others Dislike of the rigid, sterile style of synoptic information
Synoptic Reporting Barriers. Pathologist Data-entry interface and workflow ¡ Traditional view of report ownership ¡ l l l Ignorance of expanded audience Resistance to externally imposed standards from authoritative organizations– JCAHO, CAP, ASC-Co. C and others Dislike of the rigid, sterile style of synoptic information
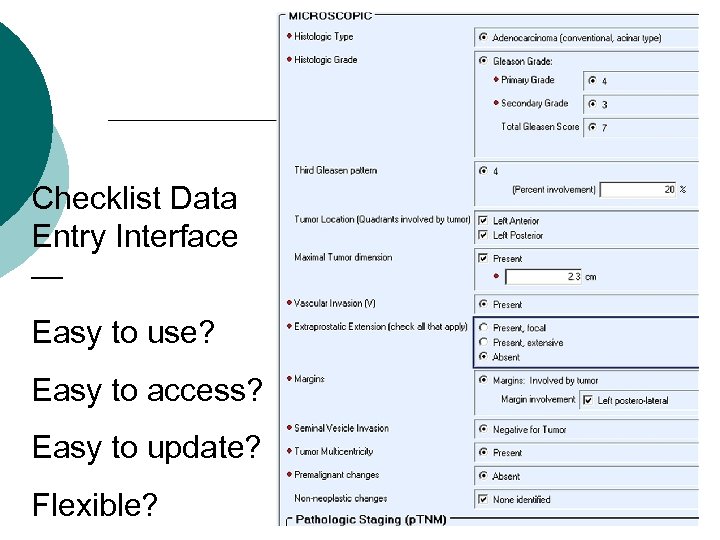 Checklist Data Entry Interface — Easy to use? Easy to access? Easy to update? Flexible?
Checklist Data Entry Interface — Easy to use? Easy to access? Easy to update? Flexible?
 21 st Century View of the Pathology Report ¡ ¡ ¡ Part of the medical record, often an EMR Read by many– patient, surgeon, oncologist, coders, insurers, public health personnel Diagnosis only one part of total picture of disease, stage, and clinical setting Prescriptive of specific therapy Must meet quality standards for completeness and consistency Electronically encoded discrete data?
21 st Century View of the Pathology Report ¡ ¡ ¡ Part of the medical record, often an EMR Read by many– patient, surgeon, oncologist, coders, insurers, public health personnel Diagnosis only one part of total picture of disease, stage, and clinical setting Prescriptive of specific therapy Must meet quality standards for completeness and consistency Electronically encoded discrete data?
 Barriers to Adoption Coded database system complexity -Adaptations require adjustments in IT, registry, LIS vendor, workflow ¡ Unevenly distributed costs and benefits between lab, registry, others ¡ Institutional boundaries and control ¡ Rigidity of the status quo ¡
Barriers to Adoption Coded database system complexity -Adaptations require adjustments in IT, registry, LIS vendor, workflow ¡ Unevenly distributed costs and benefits between lab, registry, others ¡ Institutional boundaries and control ¡ Rigidity of the status quo ¡
 Opportunities Streamlined workflow ¡ Effort/cost savings ¡ Rules-based quality checks ¡ Data mining ¡ Data sharing with tissue banks, etc. ¡ Compliance ¡
Opportunities Streamlined workflow ¡ Effort/cost savings ¡ Rules-based quality checks ¡ Data mining ¡ Data sharing with tissue banks, etc. ¡ Compliance ¡
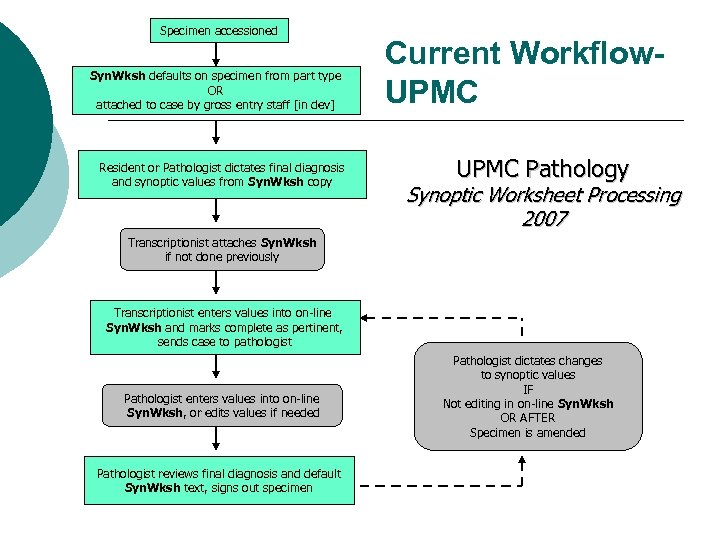 Specimen accessioned Syn. Wksh defaults on specimen from part type OR attached to case by gross entry staff [in dev] Resident or Pathologist dictates final diagnosis and synoptic values from Syn. Wksh copy Current Workflow. UPMC Pathology Synoptic Worksheet Processing 2007 Transcriptionist attaches Syn. Wksh if not done previously Transcriptionist enters values into on-line Syn. Wksh and marks complete as pertinent, sends case to pathologist Pathologist enters values into on-line Syn. Wksh, or edits values if needed Pathologist reviews final diagnosis and default Syn. Wksh text, signs out specimen Pathologist dictates changes to synoptic values IF Not editing in on-line Syn. Wksh OR AFTER Specimen is amended
Specimen accessioned Syn. Wksh defaults on specimen from part type OR attached to case by gross entry staff [in dev] Resident or Pathologist dictates final diagnosis and synoptic values from Syn. Wksh copy Current Workflow. UPMC Pathology Synoptic Worksheet Processing 2007 Transcriptionist attaches Syn. Wksh if not done previously Transcriptionist enters values into on-line Syn. Wksh and marks complete as pertinent, sends case to pathologist Pathologist enters values into on-line Syn. Wksh, or edits values if needed Pathologist reviews final diagnosis and default Syn. Wksh text, signs out specimen Pathologist dictates changes to synoptic values IF Not editing in on-line Syn. Wksh OR AFTER Specimen is amended
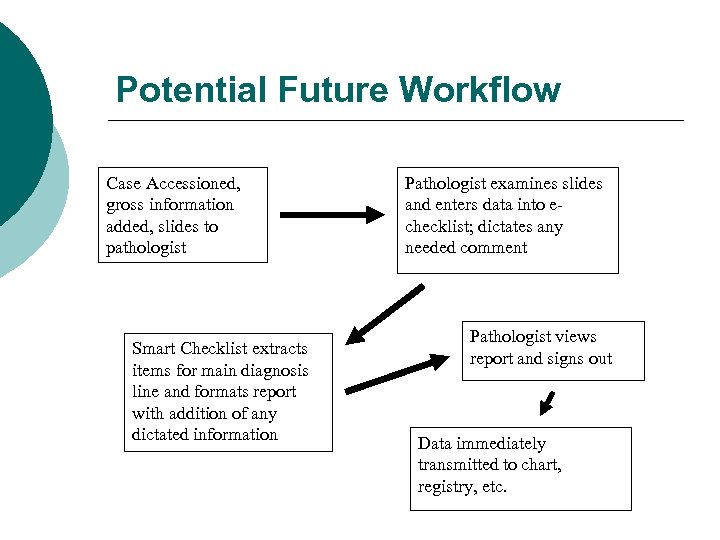 Potential Future Workflow Case Accessioned, gross information added, slides to pathologist Smart Checklist extracts items for main diagnosis line and formats report with addition of any dictated information Pathologist examines slides and enters data into echecklist; dictates any needed comment Pathologist views report and signs out Data immediately transmitted to chart, registry, etc.
Potential Future Workflow Case Accessioned, gross information added, slides to pathologist Smart Checklist extracts items for main diagnosis line and formats report with addition of any dictated information Pathologist examines slides and enters data into echecklist; dictates any needed comment Pathologist views report and signs out Data immediately transmitted to chart, registry, etc.
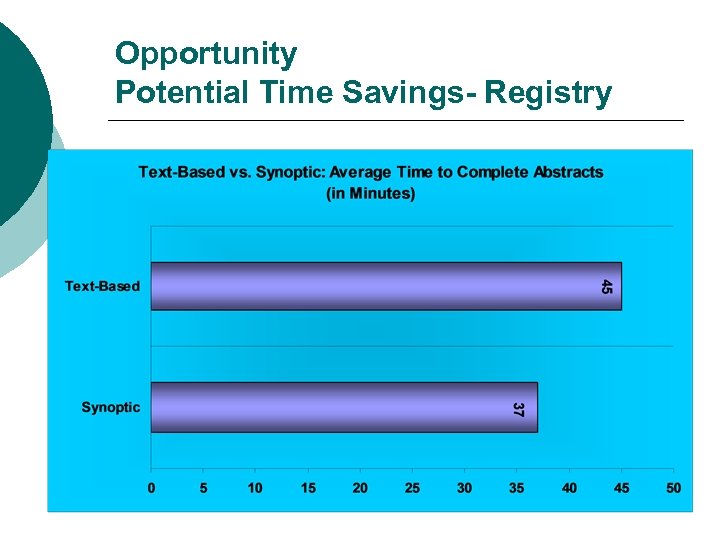 Opportunity Potential Time Savings- Registry
Opportunity Potential Time Savings- Registry
 Opportunity. Rules application for consistency
Opportunity. Rules application for consistency
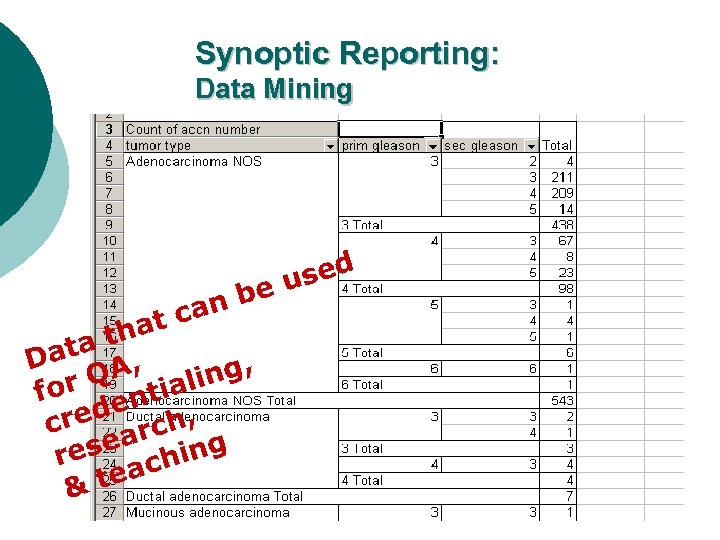 Synoptic Reporting: Data Mining sed eu b an at c a th Dat A, ng, Q for entiali red rch, c sea hing re ac & te
Synoptic Reporting: Data Mining sed eu b an at c a th Dat A, ng, Q for entiali red rch, c sea hing re ac & te
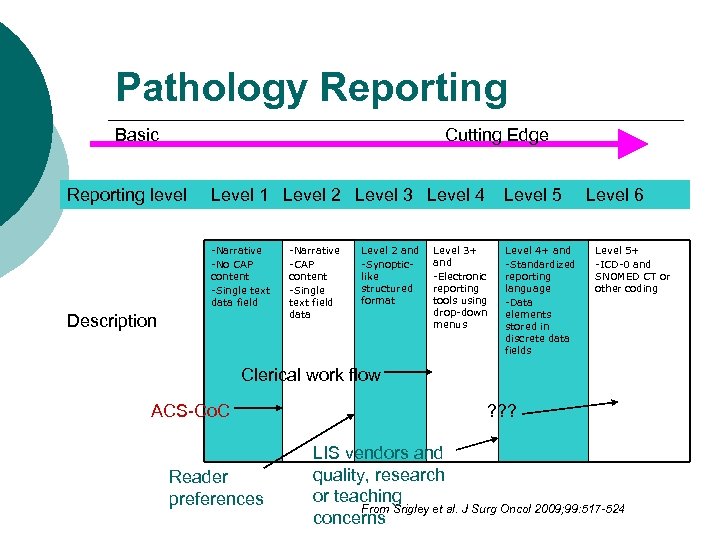 Pathology Reporting Basic Cutting Edge Reporting level Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 -Narrative -No CAP content -Single text data field Level 4+ and -Standardized reporting language -Data elements stored in discrete data fields Description -Narrative -CAP content -Single text field data Level 2 and -Synopticlike structured format Level 3+ and -Electronic reporting tools using drop-down menus Level 6 Level 5+ -ICD-0 and SNOMED CT or other coding Clerical work flow ACS-Co. C Reader preferences ? ? ? LIS vendors and quality, research or teaching From Srigley et al. J Surg Oncol 2009; 99: 517 -524 concerns
Pathology Reporting Basic Cutting Edge Reporting level Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 -Narrative -No CAP content -Single text data field Level 4+ and -Standardized reporting language -Data elements stored in discrete data fields Description -Narrative -CAP content -Single text field data Level 2 and -Synopticlike structured format Level 3+ and -Electronic reporting tools using drop-down menus Level 6 Level 5+ -ICD-0 and SNOMED CT or other coding Clerical work flow ACS-Co. C Reader preferences ? ? ? LIS vendors and quality, research or teaching From Srigley et al. J Surg Oncol 2009; 99: 517 -524 concerns
 Motivators to get closer to Level 6 Regulatory/Accrediting ¡ Careful workflow planning and implementation of lean, low cost work methods integrated with ereporting (LIS vendors, etc. ) ¡ Catalytic, creative collaboration ¡ Political will (EMR-like incentives) or legislative fiat ¡
Motivators to get closer to Level 6 Regulatory/Accrediting ¡ Careful workflow planning and implementation of lean, low cost work methods integrated with ereporting (LIS vendors, etc. ) ¡ Catalytic, creative collaboration ¡ Political will (EMR-like incentives) or legislative fiat ¡
 Acknowledgements Pathology colleagues at UPMC, COH, MMC and DCPA Anil Parwani, MD Lawrence Weiss, MD Michael Jones, MD Jay Ye, MD Registry Collaborators Molly Schwenn, MD Wendy Aldinger Sharon Winters Castine Verrill Cheryl Moody CDC NPCR Colleagues Ken Gerlach, MPH, CTR Missy Jameson Vendors Cerner IMPAC Other members of the Evaluation Workgroup of RPP 2
Acknowledgements Pathology colleagues at UPMC, COH, MMC and DCPA Anil Parwani, MD Lawrence Weiss, MD Michael Jones, MD Jay Ye, MD Registry Collaborators Molly Schwenn, MD Wendy Aldinger Sharon Winters Castine Verrill Cheryl Moody CDC NPCR Colleagues Ken Gerlach, MPH, CTR Missy Jameson Vendors Cerner IMPAC Other members of the Evaluation Workgroup of RPP 2
 Outline of presentation Historical Backdrop of Reporting Pathology Protocols Projects ¡ Specific Pathology-related queries ¡ Accomplishments ¡ Barriers to further implementation ¡ Opportunities or strategies ¡
Outline of presentation Historical Backdrop of Reporting Pathology Protocols Projects ¡ Specific Pathology-related queries ¡ Accomplishments ¡ Barriers to further implementation ¡ Opportunities or strategies ¡
 Traditional Pathologist’s view of the report Consultation for a patient ¡ Report is addressed to a clinician giving care, or obtaining the sample, or both ¡ Requires style– owned by pathologist ¡ Unique ¡ The “diagnosis” is the critical thing, the rest is secondary ¡
Traditional Pathologist’s view of the report Consultation for a patient ¡ Report is addressed to a clinician giving care, or obtaining the sample, or both ¡ Requires style– owned by pathologist ¡ Unique ¡ The “diagnosis” is the critical thing, the rest is secondary ¡
 Synoptic Reporting in Pathology. Background Pathology reports are data-intense ¡ Traditional methods- text only, individual styles numerous ¡ Variability of content, quality and consistency ¡ Significance of individual items sometimes unclear prospectively ¡ Retrospective research required rework ¡
Synoptic Reporting in Pathology. Background Pathology reports are data-intense ¡ Traditional methods- text only, individual styles numerous ¡ Variability of content, quality and consistency ¡ Significance of individual items sometimes unclear prospectively ¡ Retrospective research required rework ¡
 Synoptic Reporting in Pathology Background • The College of American Pathologist Cancer Protocols and Checklists goal is improving the quality and uniformity of reports. • Many LIS Systems do not support discrete data elements for synoptic data elements thus, the CAP checklists have been incorporated as unstructured text blocks which are embedded in the pathology reports. • Text block data presentation is cumbersome to search and transmit to data repositories
Synoptic Reporting in Pathology Background • The College of American Pathologist Cancer Protocols and Checklists goal is improving the quality and uniformity of reports. • Many LIS Systems do not support discrete data elements for synoptic data elements thus, the CAP checklists have been incorporated as unstructured text blocks which are embedded in the pathology reports. • Text block data presentation is cumbersome to search and transmit to data repositories
 Synoptic Reporting in Pathology Background Synoptic reporting schemes attempt to address key quality issues -Consistency -Completeness -Comprehensibility ¡ Efforts of ADASP and CAP led to consensus development of Cancer Protocols specific site and specimen type Checklists ¡
Synoptic Reporting in Pathology Background Synoptic reporting schemes attempt to address key quality issues -Consistency -Completeness -Comprehensibility ¡ Efforts of ADASP and CAP led to consensus development of Cancer Protocols specific site and specimen type Checklists ¡


