26ddc63d07e6a95006c1c55c86083651.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 CHAIMS January 1999 CHAIMS 1
CHAIMS January 1999 CHAIMS 1
 CHAIMS: Compiling High-level Access Interfaces for Multi-site Software CHAIMS Stanford University Objective: Investigate new approaches to large-scale software composition. Approach: Develop and validate a composition-only language, a protocol for large, distributed, heterogeneous and autonomous megamodules, and a supporting system. January 1999 CHAIMS 2
CHAIMS: Compiling High-level Access Interfaces for Multi-site Software CHAIMS Stanford University Objective: Investigate new approaches to large-scale software composition. Approach: Develop and validate a composition-only language, a protocol for large, distributed, heterogeneous and autonomous megamodules, and a supporting system. January 1999 CHAIMS 2
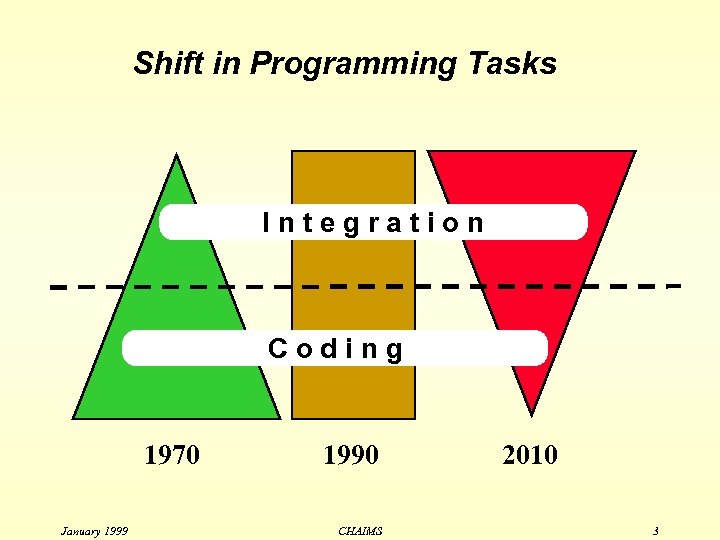 Shift in Programming Tasks Integration Coding 1970 January 1999 1990 CHAIMS 2010 3
Shift in Programming Tasks Integration Coding 1970 January 1999 1990 CHAIMS 2010 3
 Typical Scenario - Logistics A general has to ship troops and/or various material from L. A. to Chicago: – – different kind of material, not every airport equally suited congestion, prices, weather constraints exact due or ready dates different transport service providers Today: ·calling different companies, looking up information on the web, reservations by hand ·hand coded systems Future: fast system development by tools supporting automated composition January 1999 CHAIMS 4
Typical Scenario - Logistics A general has to ship troops and/or various material from L. A. to Chicago: – – different kind of material, not every airport equally suited congestion, prices, weather constraints exact due or ready dates different transport service providers Today: ·calling different companies, looking up information on the web, reservations by hand ·hand coded systems Future: fast system development by tools supporting automated composition January 1999 CHAIMS 4
 What CHAIMS does: Composition of megamodules by a composition only language (CLAM) that also provides run-time cost estimation and allows automatic run-time invocation scheduling. Composition is automated by using the protocol CPAM on top of several distribution systems by hiding protocol details in CLAM, and by providing a compiler for CLAM. January 1999 CHAIMS 5
What CHAIMS does: Composition of megamodules by a composition only language (CLAM) that also provides run-time cost estimation and allows automatic run-time invocation scheduling. Composition is automated by using the protocol CPAM on top of several distribution systems by hiding protocol details in CLAM, and by providing a compiler for CLAM. January 1999 CHAIMS 5
 Megamodules - Definition Megamodules are large, autonomous, distributed, heterogeneous services or processes. • from different providers: several services from different providers available for similar tasks • autonomous: maintenance of megamodule and control over resources remains with provider • heterogeneous: accessible by various distribution protocols like RMI, DCE, CORBA • distributed: to be used by more than one client • large: computation intensive, data intensive, ongoing processes January 1999 CHAIMS 6
Megamodules - Definition Megamodules are large, autonomous, distributed, heterogeneous services or processes. • from different providers: several services from different providers available for similar tasks • autonomous: maintenance of megamodule and control over resources remains with provider • heterogeneous: accessible by various distribution protocols like RMI, DCE, CORBA • distributed: to be used by more than one client • large: computation intensive, data intensive, ongoing processes January 1999 CHAIMS 6
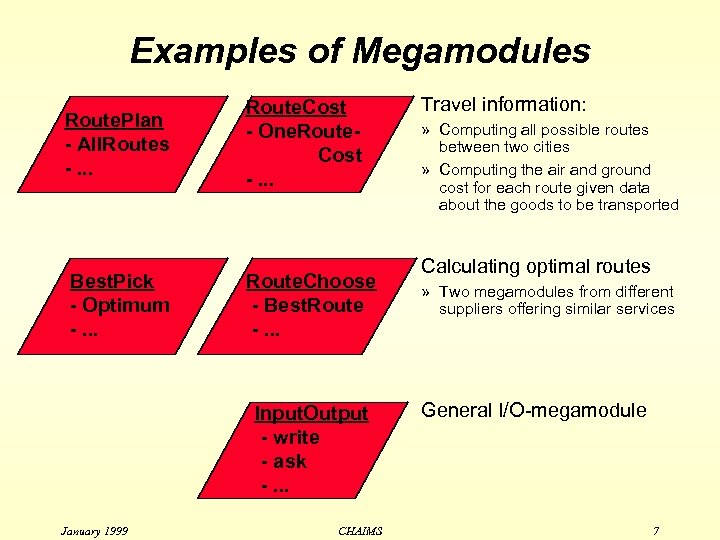 Examples of Megamodules Route. Plan - All. Routes -. . . Best. Pick - Optimum -. . . Route. Cost - One. Route. Cost -. . . Route. Choose - Best. Route -. . . Input. Output - write - ask -. . . January 1999 CHAIMS Travel information: » Computing all possible routes between two cities » Computing the air and ground cost for each route given data about the goods to be transported Calculating optimal routes » Two megamodules from different suppliers offering similar services General I/O-megamodule 7
Examples of Megamodules Route. Plan - All. Routes -. . . Best. Pick - Optimum -. . . Route. Cost - One. Route. Cost -. . . Route. Choose - Best. Route -. . . Input. Output - write - ask -. . . January 1999 CHAIMS Travel information: » Computing all possible routes between two cities » Computing the air and ground cost for each route given data about the goods to be transported Calculating optimal routes » Two megamodules from different suppliers offering similar services General I/O-megamodule 7
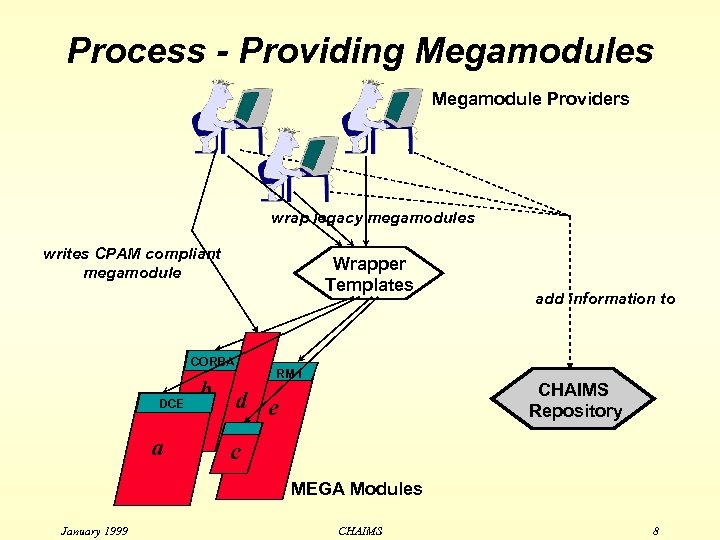 Process - Providing Megamodules Megamodule Providers wrap legacy megamodules writes CPAM compliant megamodule Wrapper Templates CORBA DCE a RM I b d e add information to CHAIMS Repository c MEGA Modules January 1999 CHAIMS 8
Process - Providing Megamodules Megamodule Providers wrap legacy megamodules writes CPAM compliant megamodule Wrapper Templates CORBA DCE a RM I b d e add information to CHAIMS Repository c MEGA Modules January 1999 CHAIMS 8
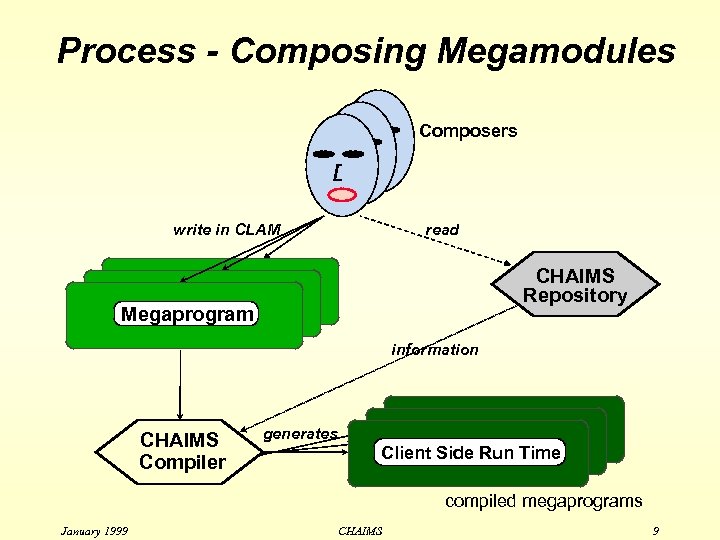 Process - Composing Megamodules Composers write in CLAM read CHAIMS Repository Megaprogram information CHAIMS Compiler generates Client Side Run Time compiled megaprograms January 1999 CHAIMS 9
Process - Composing Megamodules Composers write in CLAM read CHAIMS Repository Megaprogram information CHAIMS Compiler generates Client Side Run Time compiled megaprograms January 1999 CHAIMS 9
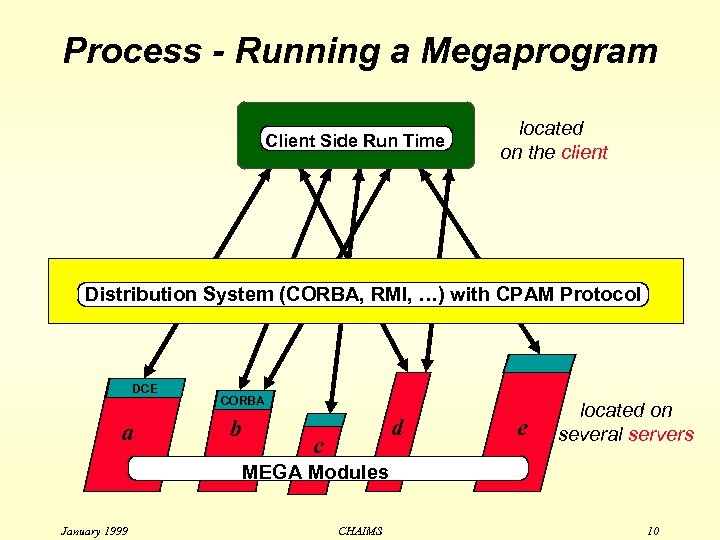 Process - Running a Megaprogram Client Side Run Time located on the client Distribution System (CORBA, RMI, …) with CPAM Protocol DCE a CORBA b d c e located on several servers MEGA Modules January 1999 CHAIMS 10
Process - Running a Megaprogram Client Side Run Time located on the client Distribution System (CORBA, RMI, …) with CPAM Protocol DCE a CORBA b d c e located on several servers MEGA Modules January 1999 CHAIMS 10
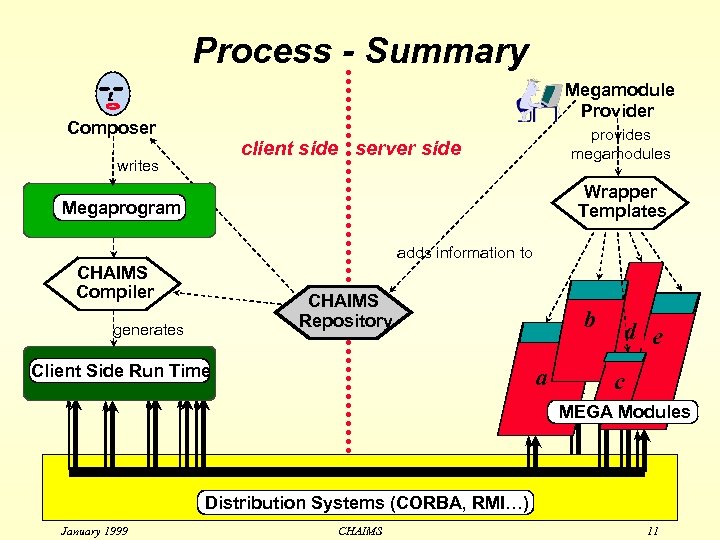 Process - Summary Megamodule Provider Composer provides megamodules client side server side writes Wrapper Templates Megaprogram adds information to CHAIMS Compiler CHAIMS Repository generates Client Side Run Time b a d e c MEGA Modules Distribution Systems (CORBA, RMI…) January 1999 CHAIMS 11
Process - Summary Megamodule Provider Composer provides megamodules client side server side writes Wrapper Templates Megaprogram adds information to CHAIMS Compiler CHAIMS Repository generates Client Side Run Time b a d e c MEGA Modules Distribution Systems (CORBA, RMI…) January 1999 CHAIMS 11
 CHAIMS - Special Features CHAIMS supports megamodule heterogeneity: • The CHAIMS compiler ensures that clients support the various megamodule distribution systems • The CHAIMS data encoding-rules facilitates heterogeneous data transmission between megamodules CHAIMS preserves megamodule autonomy: • The CHAIMS repository contains the information necessary to access megamodules • Run-time cost estimation allows to leave control over resources to providers CHAIMS enables optimized composition: • Parallelism, invocation monitoring, and cost estimation allow clients to optimize the invocation sequence to megamodules • Global pre-setting of parameters and partial extraction of results allow minimized data flow between megamodules January 1999 CHAIMS 12
CHAIMS - Special Features CHAIMS supports megamodule heterogeneity: • The CHAIMS compiler ensures that clients support the various megamodule distribution systems • The CHAIMS data encoding-rules facilitates heterogeneous data transmission between megamodules CHAIMS preserves megamodule autonomy: • The CHAIMS repository contains the information necessary to access megamodules • Run-time cost estimation allows to leave control over resources to providers CHAIMS enables optimized composition: • Parallelism, invocation monitoring, and cost estimation allow clients to optimize the invocation sequence to megamodules • Global pre-setting of parameters and partial extraction of results allow minimized data flow between megamodules January 1999 CHAIMS 12
 Primitives in CHAIMS Pre-invocation: SETUP: set up a connection to a megamodule SET-, GETPARAM: preset / get parameters in a megamodule ESTIMATE: get cost estimation for optimization Invocation and result gathering: INVOKE: start a specific method EXAMINE: test status and progress of an invoked method EXTRACT: extract results from an invoked method Termination: TERMINATE: terminate a method invocation TERMINATEALL: terminate the connection to a megamodule January 1999 CHAIMS 13
Primitives in CHAIMS Pre-invocation: SETUP: set up a connection to a megamodule SET-, GETPARAM: preset / get parameters in a megamodule ESTIMATE: get cost estimation for optimization Invocation and result gathering: INVOKE: start a specific method EXAMINE: test status and progress of an invoked method EXTRACT: extract results from an invoked method Termination: TERMINATE: terminate a method invocation TERMINATEALL: terminate the connection to a megamodule January 1999 CHAIMS 13
 CHAIMS proves that. . . » We can do composition in a high-level language and hide technical details » Large-scale composition can be automated » Run-time cost estimation is essential for invocation scheduling optimization. January 1999 CHAIMS 14
CHAIMS proves that. . . » We can do composition in a high-level language and hide technical details » Large-scale composition can be automated » Run-time cost estimation is essential for invocation scheduling optimization. January 1999 CHAIMS 14
 Focus for Future • Applying CHAIMS to a larger real-life example. • Automated scheduling of invocations and extractions, automatic optimization of dataflows. • Automatic generation of direct dataflows between megamodules. • Flexible interaction with megamodules; extracting and handling overview results. • Enhancing CHAIMS language CLAM and complementing it by graphical front-end. January 1999 CHAIMS 15
Focus for Future • Applying CHAIMS to a larger real-life example. • Automated scheduling of invocations and extractions, automatic optimization of dataflows. • Automatic generation of direct dataflows between megamodules. • Flexible interaction with megamodules; extracting and handling overview results. • Enhancing CHAIMS language CLAM and complementing it by graphical front-end. January 1999 CHAIMS 15
 CHAIMS January 1999 CHAIMS 16
CHAIMS January 1999 CHAIMS 16


