 CH. 6 DEMAND I. A. • • What is Demand? Demand is the quantities of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given period of time. ****Quantity Demanded – how much you are willing to buy at a given price ****PRICE IS THE ONLY THING THAT CAN CHANGE QUANTITY DEMANDED!
CH. 6 DEMAND I. A. • • What is Demand? Demand is the quantities of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given period of time. ****Quantity Demanded – how much you are willing to buy at a given price ****PRICE IS THE ONLY THING THAT CAN CHANGE QUANTITY DEMANDED!
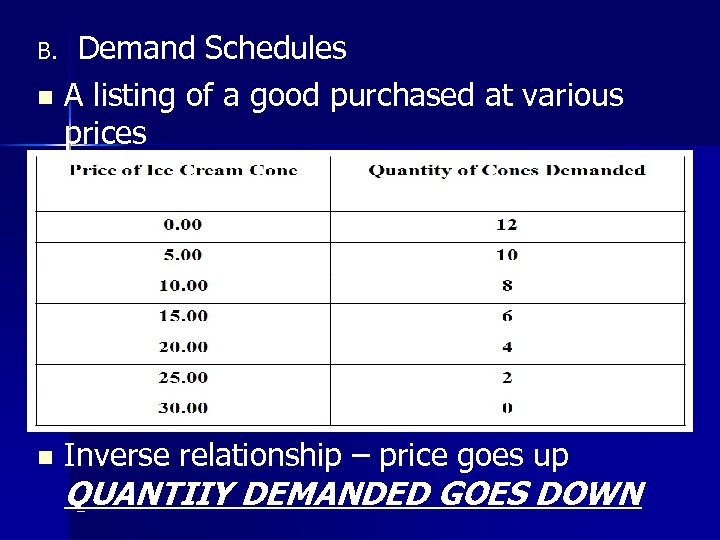 Demand Schedules n A listing of a good purchased at various prices B. n Inverse relationship – price goes up QUANTIIY DEMANDED GOES DOWN
Demand Schedules n A listing of a good purchased at various prices B. n Inverse relationship – price goes up QUANTIIY DEMANDED GOES DOWN
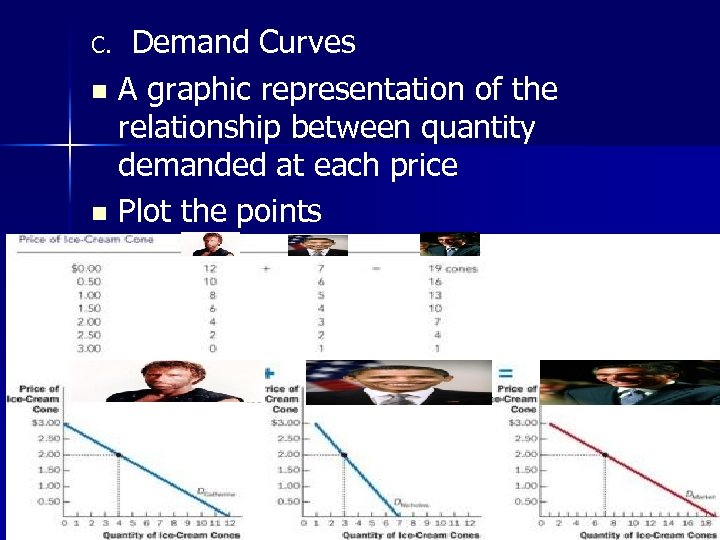 Demand Curves n A graphic representation of the relationship between quantity demanded at each price n Plot the points C. CK
Demand Curves n A graphic representation of the relationship between quantity demanded at each price n Plot the points C. CK
 You to can be an Ichabod!
You to can be an Ichabod!
 Various economic factors affect demand curves n Buyers respond to price changes in various ways n Responsiveness to price changes refers to the degree to which a price change affects quantity demanded n This is also known as elasticity of demand D.
Various economic factors affect demand curves n Buyers respond to price changes in various ways n Responsiveness to price changes refers to the degree to which a price change affects quantity demanded n This is also known as elasticity of demand D.
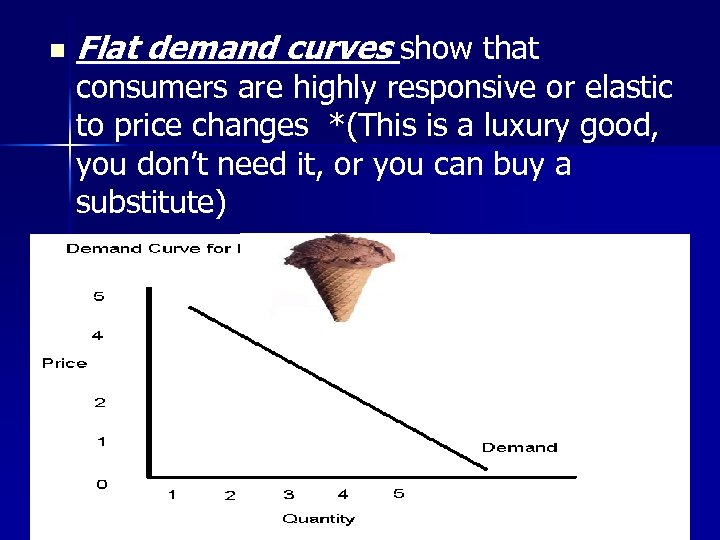 n Flat demand curves show that consumers are highly responsive or elastic to price changes *(This is a luxury good, you don’t need it, or you can buy a substitute)
n Flat demand curves show that consumers are highly responsive or elastic to price changes *(This is a luxury good, you don’t need it, or you can buy a substitute)
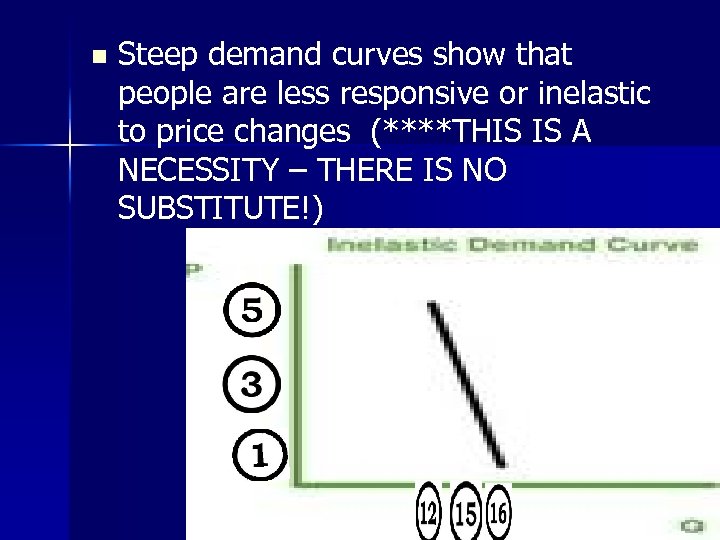 n Steep demand curves show that people are less responsive or inelastic to price changes (****THIS IS A NECESSITY – THERE IS NO SUBSTITUTE!) GAS
n Steep demand curves show that people are less responsive or inelastic to price changes (****THIS IS A NECESSITY – THERE IS NO SUBSTITUTE!) GAS
 Ch. 6 continued What will shift the Demand (change) Curve? n The following DETERMINANTS will shift the demand curve either right (up) or left (down) creating a new curve E.
Ch. 6 continued What will shift the Demand (change) Curve? n The following DETERMINANTS will shift the demand curve either right (up) or left (down) creating a new curve E.
 n n a. b. ****Change in consumer tastes (fads) ****Change in income (unemployment rate) ****Change in the number of consumers (population) example: the main business in a town shuts down – and people move Change in the price of: ****substitutes (replacement if one good is priced to high) example: If a Mercedes price is to high, you buy a BMW ****complements (price of a good is essential to the good that is being purchased) example: gas prices to SUVS
n n a. b. ****Change in consumer tastes (fads) ****Change in income (unemployment rate) ****Change in the number of consumers (population) example: the main business in a town shuts down – and people move Change in the price of: ****substitutes (replacement if one good is priced to high) example: If a Mercedes price is to high, you buy a BMW ****complements (price of a good is essential to the good that is being purchased) example: gas prices to SUVS
 ****Change in income (unemployment rate) n ****Taxation (govt. – lowers or raises taxes giving you more/less $ to spend on g/s) n
****Change in income (unemployment rate) n ****Taxation (govt. – lowers or raises taxes giving you more/less $ to spend on g/s) n
 Never criticize a woman’s choice in fashion!
Never criticize a woman’s choice in fashion!
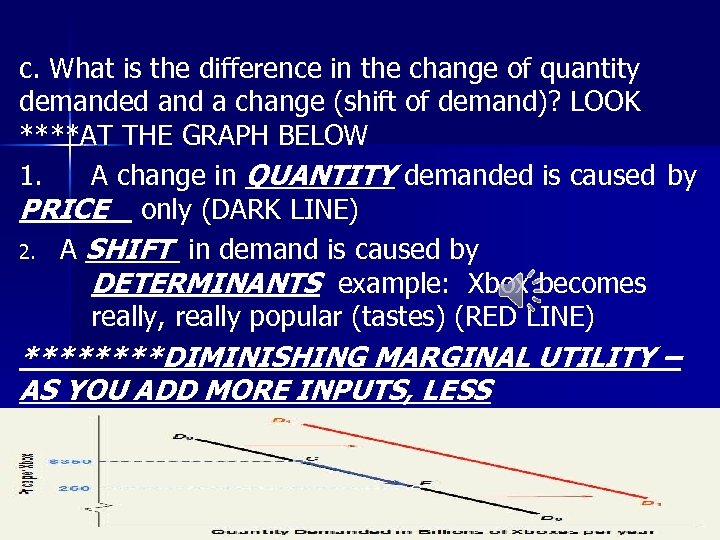 c. What is the difference in the change of quantity demanded and a change (shift of demand)? LOOK ****AT THE GRAPH BELOW 1. A change in QUANTITY demanded is caused by PRICE only (DARK LINE) 2. A SHIFT in demand is caused by DETERMINANTS example: Xbox becomes really, really popular (tastes) (RED LINE) ****DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY – AS YOU ADD MORE INPUTS, LESS SATISFACTION!
c. What is the difference in the change of quantity demanded and a change (shift of demand)? LOOK ****AT THE GRAPH BELOW 1. A change in QUANTITY demanded is caused by PRICE only (DARK LINE) 2. A SHIFT in demand is caused by DETERMINANTS example: Xbox becomes really, really popular (tastes) (RED LINE) ****DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY – AS YOU ADD MORE INPUTS, LESS SATISFACTION!