ccd6f261322c980203871e1bc0f31821.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Ch. 4
Ch. 4
 Sec. 1: Colonial Government
Sec. 1: Colonial Government
 Magna Carta • 1215: “Great Charter” signed by Eng King John • Placed restrictions on pwr of ruler – Needed nobles’ permission to levy taxes – Protected right to own private property – Right to trial by jury
Magna Carta • 1215: “Great Charter” signed by Eng King John • Placed restrictions on pwr of ruler – Needed nobles’ permission to levy taxes – Protected right to own private property – Right to trial by jury
 Parliament • Br legislature (law-making body) • 2 houses (bicameral): House of Lords (by title) & House of Commons (elected) • Right to approve taxes – “pwr of the purse” • Other 2 -house legislatures: – Congress: Senate, House of Reps – NY State Leg: State Senate, Assembly
Parliament • Br legislature (law-making body) • 2 houses (bicameral): House of Lords (by title) & House of Commons (elected) • Right to approve taxes – “pwr of the purse” • Other 2 -house legislatures: – Congress: Senate, House of Reps – NY State Leg: State Senate, Assembly
 English Bill of Rights • Glorious Revolution (1688): King James was removed from power & replaced by William & Mary • Bill of rights: written list of freedoms gov’t promises to protect – trial by jury – Habeas corpus: to be held in prison, must be charged w/ crime – Free elections – Freedom of speech & debate in Parliament
English Bill of Rights • Glorious Revolution (1688): King James was removed from power & replaced by William & Mary • Bill of rights: written list of freedoms gov’t promises to protect – trial by jury – Habeas corpus: to be held in prison, must be charged w/ crime – Free elections – Freedom of speech & debate in Parliament
 Colonial Legislatures • 1619: House of Burgesses est in VA • Made laws for Jamestown (& eventually all of VA) • 1629: General Court (MA legislature) • 1701: General Assembly (PA legislature)
Colonial Legislatures • 1619: House of Burgesses est in VA • Made laws for Jamestown (& eventually all of VA) • 1629: General Court (MA legislature) • 1701: General Assembly (PA legislature)
 Right to Vote in Colonies • 50 -75 % white males could vote • In some col had to own property &/or belong to specific church • Women, Nat Am, Afr Am couldn’t vote
Right to Vote in Colonies • 50 -75 % white males could vote • In some col had to own property &/or belong to specific church • Women, Nat Am, Afr Am couldn’t vote
 Freedom of the Press • 1735: Zenger Trial • John Peter Zenger— newspaper publisher in NY • Printed articles criticizing gov • Charged w/ libel (publishing of statements that damage a person’s reputation)
Freedom of the Press • 1735: Zenger Trial • John Peter Zenger— newspaper publisher in NY • Printed articles criticizing gov • Charged w/ libel (publishing of statements that damage a person’s reputation)
 • Slander—spoken false statements • Zenger’s lawyer—Andrew Hamilton— argued that Zenger didn’t commit libel if the statements were true • Jury agreed • Showed col valued freedom of the press (right of journalists to publish the truth w/o restriction or penalty)
• Slander—spoken false statements • Zenger’s lawyer—Andrew Hamilton— argued that Zenger didn’t commit libel if the statements were true • Jury agreed • Showed col valued freedom of the press (right of journalists to publish the truth w/o restriction or penalty)
 Regulating Trade • Mercantilism: colonies exist to serve the econ needs of their parent country • 1651: Navigation Acts – Shipments from Eur to col had to go through Eng 1 st – Had to use Br ships – Col could sell key products only to Eng • Created jobs for Eng workers
Regulating Trade • Mercantilism: colonies exist to serve the econ needs of their parent country • 1651: Navigation Acts – Shipments from Eur to col had to go through Eng 1 st – Had to use Br ships – Col could sell key products only to Eng • Created jobs for Eng workers
 Benefits of Navigation Acts • Col had a guaranteed market for their goods • Helped develop shipbuilding industry in New England Disadvantages • Felt laws favored Br. merchants • Col couldn’t sell directly to foreign markets • Led to smuggling (illegal trading)
Benefits of Navigation Acts • Col had a guaranteed market for their goods • Helped develop shipbuilding industry in New England Disadvantages • Felt laws favored Br. merchants • Col couldn’t sell directly to foreign markets • Led to smuggling (illegal trading)
 Sec 2: Colonial Society
Sec 2: Colonial Society
 Colonial Farm • Where most col lived • Having a large family was an advantage— needed many hands to do work • Self-sufficient • Raise crops, tend animals, maintenance • Farmhouses made of wood, had few rms • Fireplace—only source of heat • In towns, single ppl expected to live w/ a family as a servant or boarder
Colonial Farm • Where most col lived • Having a large family was an advantage— needed many hands to do work • Self-sufficient • Raise crops, tend animals, maintenance • Farmhouses made of wood, had few rms • Fireplace—only source of heat • In towns, single ppl expected to live w/ a family as a servant or boarder
 Men • Carpenters, wheelwrights, coopers, butchers, tanners, shoemakers, chandlers • Ctrled income & property • Held authority in families • Voters, officeholders • Represented family in public
Men • Carpenters, wheelwrights, coopers, butchers, tanners, shoemakers, chandlers • Ctrled income & property • Held authority in families • Voters, officeholders • Represented family in public
 Women • Couldn’t choose husband—families arranged marriages • Cooked, did laundry, made cloth, tended garden & animals, churned butter, preserved food, cared for children, etc • Little or no role in public life • Couldn’t own property • Could teach in dame schools
Women • Couldn’t choose husband—families arranged marriages • Cooked, did laundry, made cloth, tended garden & animals, churned butter, preserved food, cared for children, etc • Little or no role in public life • Couldn’t own property • Could teach in dame schools
 Children • • Beg work @ 7 yrs Did household or farm chores Fetched water & wood Helped in kitchen Boys worked in fields Girls helped mothers Apprentice: someone who learns a trade by working for someone in that trade for a period of X
Children • • Beg work @ 7 yrs Did household or farm chores Fetched water & wood Helped in kitchen Boys worked in fields Girls helped mothers Apprentice: someone who learns a trade by working for someone in that trade for a period of X
 Social Classes • Eur—land was measure of wealth • America offered immigrants chance to own land • Eur—prospects determined by birth • Amer-more social equality • Gentry – Upper class – Wealthy planters, merchants, ministers, royal officials – Most powerful – Public office (only ones who could afford to)
Social Classes • Eur—land was measure of wealth • America offered immigrants chance to own land • Eur—prospects determined by birth • Amer-more social equality • Gentry – Upper class – Wealthy planters, merchants, ministers, royal officials – Most powerful – Public office (only ones who could afford to)
 • Middle Class – Majority of col – Sm planters, artisans, independent farmers – Could vote but few held office – Mostly white, 1 % Afr Am – Opportunity to move up social scale • Indentured Servants – Signed contract to work 4 – 10 yrs in exchange for passage to America – Had few rights – @ end of service, received clothes, tools, land
• Middle Class – Majority of col – Sm planters, artisans, independent farmers – Could vote but few held office – Mostly white, 1 % Afr Am – Opportunity to move up social scale • Indentured Servants – Signed contract to work 4 – 10 yrs in exchange for passage to America – Had few rights – @ end of service, received clothes, tools, land
 • Free Afr Amer – Allowed to own property – Some actually purchased slaves who were relatives & set them free – Couldn’t vote or sit on juries
• Free Afr Amer – Allowed to own property – Some actually purchased slaves who were relatives & set them free – Couldn’t vote or sit on juries
 Sec 3: Slavery in Colonies
Sec 3: Slavery in Colonies
 Atlantic Slave Trade • Posts set up along coast of Africa • Africans sold other Africans to Eur • 10 million+ transported to America
Atlantic Slave Trade • Posts set up along coast of Africa • Africans sold other Africans to Eur • 10 million+ transported to America
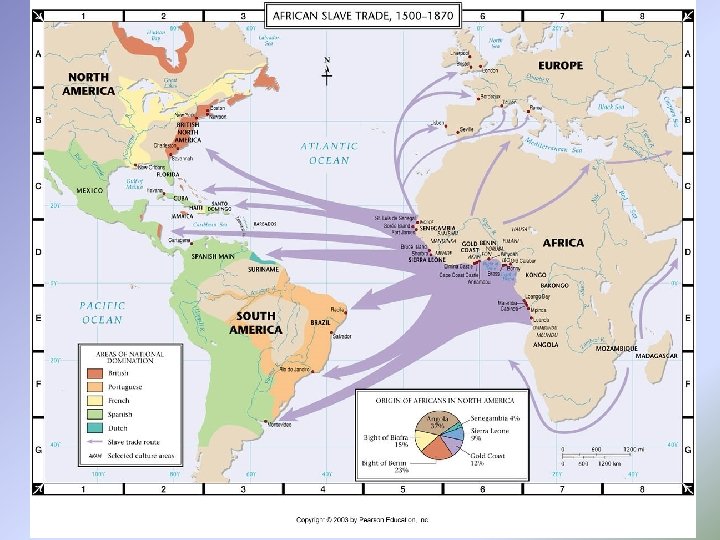
 Middle Passage • Captives traded for guns & goods • Loaded on slave ships & transported across Atlantic on brutal voyage known as Middle Passage • Cramped onto boats, no light or air • Olaudah Equiano-slave who desc conditions • 15 -20% died or committed suicide along way • Auctioned upon arrival in America • Families separated
Middle Passage • Captives traded for guns & goods • Loaded on slave ships & transported across Atlantic on brutal voyage known as Middle Passage • Cramped onto boats, no light or air • Olaudah Equiano-slave who desc conditions • 15 -20% died or committed suicide along way • Auctioned upon arrival in America • Families separated
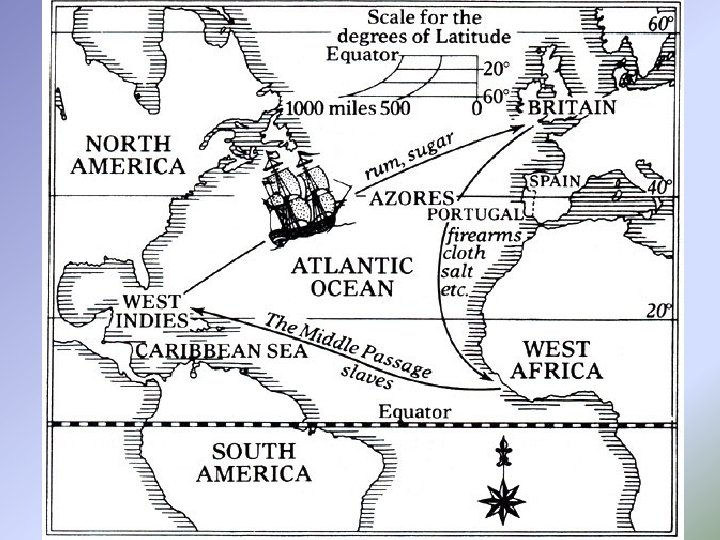
 Triangular Trade • 3 -way trade between colonies, Caribbean (West Indies), & Africa • New Eng sent fish, lumber, & goods to Caribbean for sugar & molasses (for rum) • New Eng sent goods to Afr in exchange for slaves (which were sent to W. Indies) • Africa sent slaves to W Indies for $ & molasses
Triangular Trade • 3 -way trade between colonies, Caribbean (West Indies), & Africa • New Eng sent fish, lumber, & goods to Caribbean for sugar & molasses (for rum) • New Eng sent goods to Afr in exchange for slaves (which were sent to W. Indies) • Africa sent slaves to W Indies for $ & molasses
 Slavery in Colonies • • • Dev b/c of plantation system Needed workers Preferable to servants (slavery permanent) S. econ depended on it Children of slaves were also slaves Linked to racism b/c only Afr were slaves in America • Racism: belief that 1 race is superior to others
Slavery in Colonies • • • Dev b/c of plantation system Needed workers Preferable to servants (slavery permanent) S. econ depended on it Children of slaves were also slaves Linked to racism b/c only Afr were slaves in America • Racism: belief that 1 race is superior to others
 Resistance • Wrote slave codes to prevent rebellions • Slave codes – laws that restricted rights & activities of slaves – Slaves can’t meet in large #s – Illegal to tch slave to rd or write – Masters who killed slaves couldn’t be tried for murder
Resistance • Wrote slave codes to prevent rebellions • Slave codes – laws that restricted rights & activities of slaves – Slaves can’t meet in large #s – Illegal to tch slave to rd or write – Masters who killed slaves couldn’t be tried for murder
 African Cultural Influences • Spoke Gullah (combined lang of W Afr w/ S dialect) • crafts—ie woven baskets • Music—ie banjo • Folk tales
African Cultural Influences • Spoke Gullah (combined lang of W Afr w/ S dialect) • crafts—ie woven baskets • Music—ie banjo • Folk tales
 Sec 4: Spread of New Ideas
Sec 4: Spread of New Ideas
 Puritans • Laws said children & servants had to be taught to rd • Towns w/ 50 families had to have an elem school • 100 families had to have grammar school (like H. S. ) • Public school: school supported by taxes
Puritans • Laws said children & servants had to be taught to rd • Towns w/ 50 families had to have an elem school • 100 families had to have grammar school (like H. S. ) • Public school: school supported by taxes
 Colonial Schools • • Taught rel, rd, writing, math S had private tutors Plantations too far apart Dame schools: young women taught very young children to rd & write • Most schools not open to Afr Am • Some ppl taught slaves in secret
Colonial Schools • • Taught rel, rd, writing, math S had private tutors Plantations too far apart Dame schools: young women taught very young children to rd & write • Most schools not open to Afr Am • Some ppl taught slaves in secret
 Upper Levels • Grammar schools taught Greek, Latin, geography, math, composition • Like prep schools • Universities incl Harvard, William & Mary
Upper Levels • Grammar schools taught Greek, Latin, geography, math, composition • Like prep schools • Universities incl Harvard, William & Mary
 American Colonial Poetry • Anne Bradstreet—wrote about joys & hardships of Puritan life • Phillis Wheatley—slave in Boston
American Colonial Poetry • Anne Bradstreet—wrote about joys & hardships of Puritan life • Phillis Wheatley—slave in Boston
 Ben Franklin • Own newspaper • Poor Richard’s Almanack • Businessman, leader, scientist, inventor, diplomat • Founded library & fire dept • Disc about electricity • Bifocals, stove • Founding Father
Ben Franklin • Own newspaper • Poor Richard’s Almanack • Businessman, leader, scientist, inventor, diplomat • Founded library & fire dept • Disc about electricity • Bifocals, stove • Founding Father
 Great Awakening • • 1730 s & 1740 s—religious revival in col Emotion-packed Christian movement Reaction to decline of rel zeal in col Led by preachers like Jonathan Edwards who called on ppl to examine lives & commit selves to God • Also warned sinners to change ways
Great Awakening • • 1730 s & 1740 s—religious revival in col Emotion-packed Christian movement Reaction to decline of rel zeal in col Led by preachers like Jonathan Edwards who called on ppl to examine lives & commit selves to God • Also warned sinners to change ways
 Impact of Great Awakening • Rise of new churches (Methodists, Baptists) • Split in other churches (Presbyterian, Dutch Reformed, Congregationalist) • More religious toleration • Reinforced democratic ideas
Impact of Great Awakening • Rise of new churches (Methodists, Baptists) • Split in other churches (Presbyterian, Dutch Reformed, Congregationalist) • More religious toleration • Reinforced democratic ideas
 Enlightenment • Change in way ppl thought—many no longer relied on faith to find answers to difficult questions • Believed all problems could be solved by human reason • “natural laws” governed society, religion, & politics
Enlightenment • Change in way ppl thought—many no longer relied on faith to find answers to difficult questions • Believed all problems could be solved by human reason • “natural laws” governed society, religion, & politics
 John Locke • Natural rights: rts that belong to every human from birth – Life, liberty, property – Rights inalienable (can’t be taken away) • Challenged idea of divine right (belief that monarchs get their authority to rule directly from God) • Natural rights come from God
John Locke • Natural rights: rts that belong to every human from birth – Life, liberty, property – Rights inalienable (can’t be taken away) • Challenged idea of divine right (belief that monarchs get their authority to rule directly from God) • Natural rights come from God
 Social Contract • Ppl set up gov’t to protect rights • Give up some individual freedoms to safeguard rights of community • Leader can only rule as long as ppl approve • If monarch violates rule, ppl can overthrow him
Social Contract • Ppl set up gov’t to protect rights • Give up some individual freedoms to safeguard rights of community • Leader can only rule as long as ppl approve • If monarch violates rule, ppl can overthrow him
 Montesquieu • Pwrs of gov’t should be clearly defined • Separation of powers: div of pwr of gov’t into separate branches • Keeps any one person from getting too much power • 3 branches – Legislative: law-making body – Executive: carries out laws – Judicial: interprets laws
Montesquieu • Pwrs of gov’t should be clearly defined • Separation of powers: div of pwr of gov’t into separate branches • Keeps any one person from getting too much power • 3 branches – Legislative: law-making body – Executive: carries out laws – Judicial: interprets laws


