87ca5c4e380b2c36c4ce1f93de7b4002.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand The Law of Demand § The Law of Demand: There is an inverse relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded in a defined time period, ceteris paribus. P QD 1
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand The Law of Demand § The Law of Demand: There is an inverse relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded in a defined time period, ceteris paribus. P QD 1
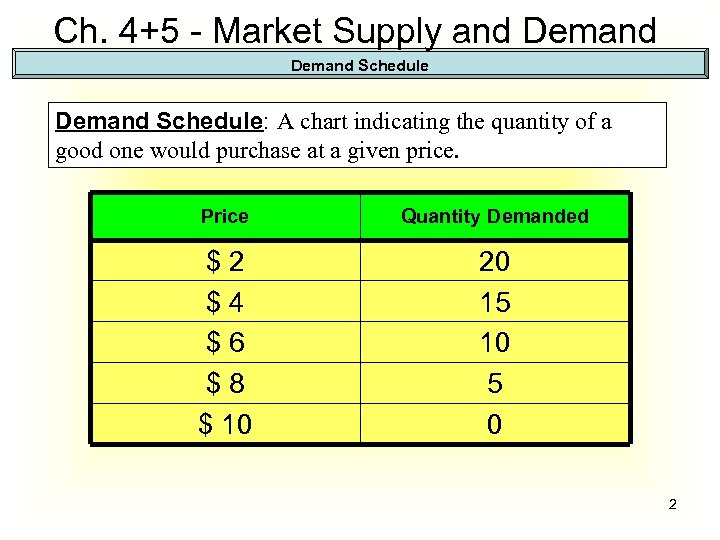 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Schedule: A chart indicating the quantity of a good one would purchase at a given price. Price Quantity Demanded $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 20 15 10 5 0 2
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Schedule: A chart indicating the quantity of a good one would purchase at a given price. Price Quantity Demanded $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 20 15 10 5 0 2
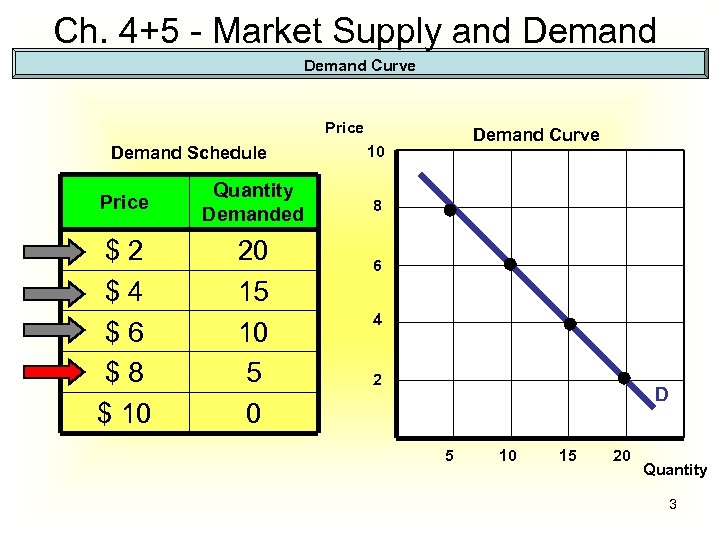 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Curve Price Demand Schedule Price Quantity Demanded $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 20 15 10 5 0 Demand Curve 10 8 6 4 2 D 5 10 15 20 Quantity 3
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Curve Price Demand Schedule Price Quantity Demanded $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 20 15 10 5 0 Demand Curve 10 8 6 4 2 D 5 10 15 20 Quantity 3
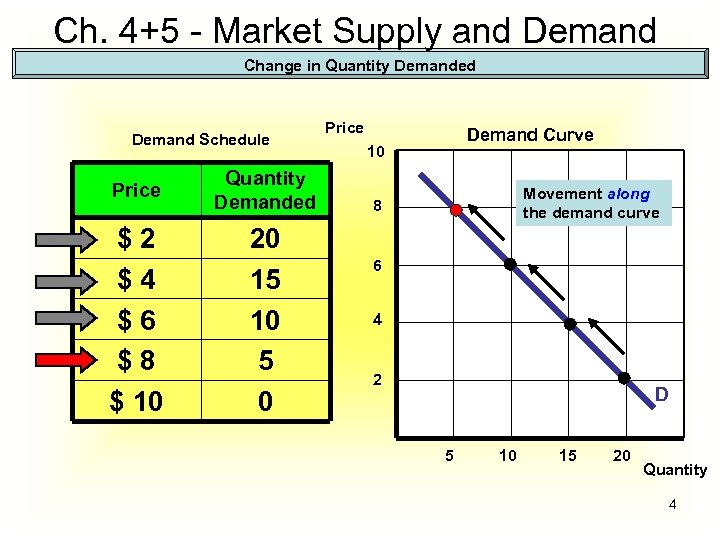 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Quantity Demanded Demand Schedule Price Quantity Demanded $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 20 15 10 5 0 Price Demand Curve 10 Movement along the demand curve 8 6 4 2 D 5 10 15 20 Quantity 4
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Quantity Demanded Demand Schedule Price Quantity Demanded $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 20 15 10 5 0 Price Demand Curve 10 Movement along the demand curve 8 6 4 2 D 5 10 15 20 Quantity 4
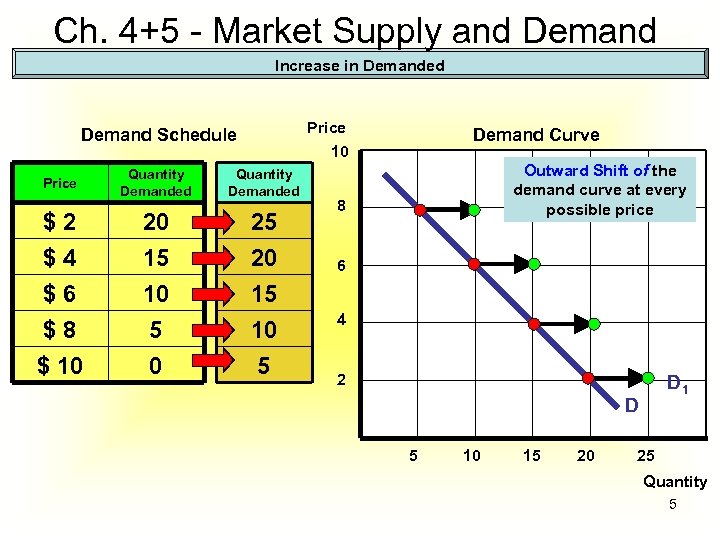 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Increase in Demanded Price Demand Schedule Price $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 Demand Curve 10 Quantity Demanded 20 15 10 5 0 25 20 15 10 5 Outward Shift of the demand curve at every possible price 8 6 4 2 D 1 D 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity 5
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Increase in Demanded Price Demand Schedule Price $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 Demand Curve 10 Quantity Demanded 20 15 10 5 0 25 20 15 10 5 Outward Shift of the demand curve at every possible price 8 6 4 2 D 1 D 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity 5
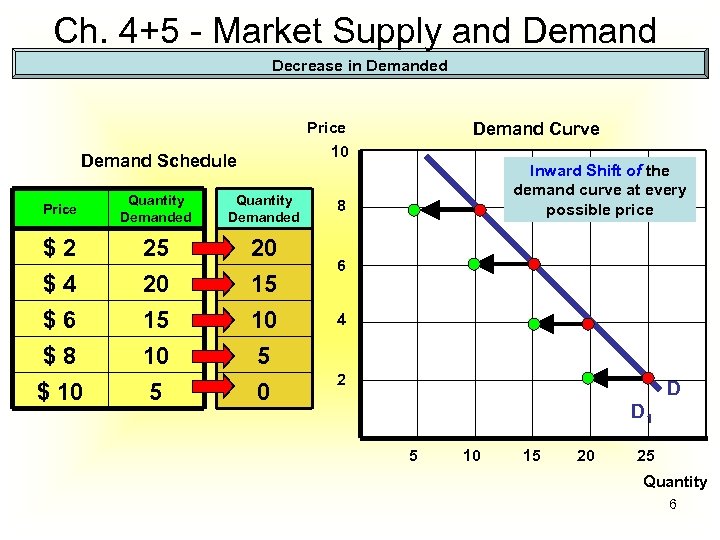 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Decrease in Demanded Price Demand Curve 10 Demand Schedule Price Quantity Demanded $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 25 20 15 10 5 0 Inward Shift of the demand curve at every possible price 8 6 4 2 D D 1 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity 6
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Decrease in Demanded Price Demand Curve 10 Demand Schedule Price Quantity Demanded $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 25 20 15 10 5 0 Inward Shift of the demand curve at every possible price 8 6 4 2 D D 1 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity 6
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded Nonprice Determinants of Demand §Number of Buyers • More buyers leads to increase in demand 7
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded Nonprice Determinants of Demand §Number of Buyers • More buyers leads to increase in demand 7
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded §Tastes and Preferences • Fashion, Fads, Endorsements, Styles, etc. lead to changes in demand 8
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded §Tastes and Preferences • Fashion, Fads, Endorsements, Styles, etc. lead to changes in demand 8
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded §Income • Higher income = Increase in Demand Normal Good: Buy more when income increases Inferior Good: Buy less when income increases 9
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded §Income • Higher income = Increase in Demand Normal Good: Buy more when income increases Inferior Good: Buy less when income increases 9
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded §Future Expectation of Buyers • Expect Price to increase = Increase in demand today Buy before price goes up • Expect Price to decrease = Decrease in demand today Wait to buy until price goes down 10
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded §Future Expectation of Buyers • Expect Price to increase = Increase in demand today Buy before price goes up • Expect Price to decrease = Decrease in demand today Wait to buy until price goes down 10
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded §Price of Related Goods • Increase in price of substitute = Increase in demand for good • Increase in price of compliment = Decrease in demand for good 11
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Demanded §Price of Related Goods • Increase in price of substitute = Increase in demand for good • Increase in price of compliment = Decrease in demand for good 11
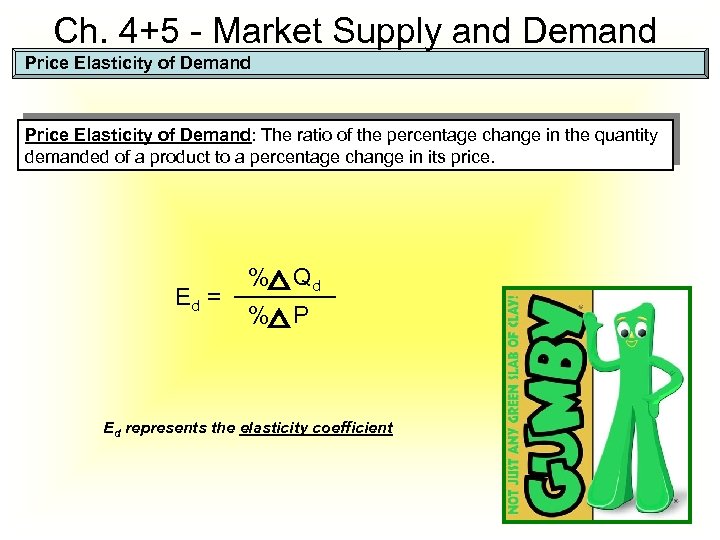 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Price Elasticity of Demand: The ratio of the percentage change in the quantity demanded of a product to a percentage change in its price. Ed = % Qd % P Ed represents the elasticity coefficient 12
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Price Elasticity of Demand: The ratio of the percentage change in the quantity demanded of a product to a percentage change in its price. Ed = % Qd % P Ed represents the elasticity coefficient 12
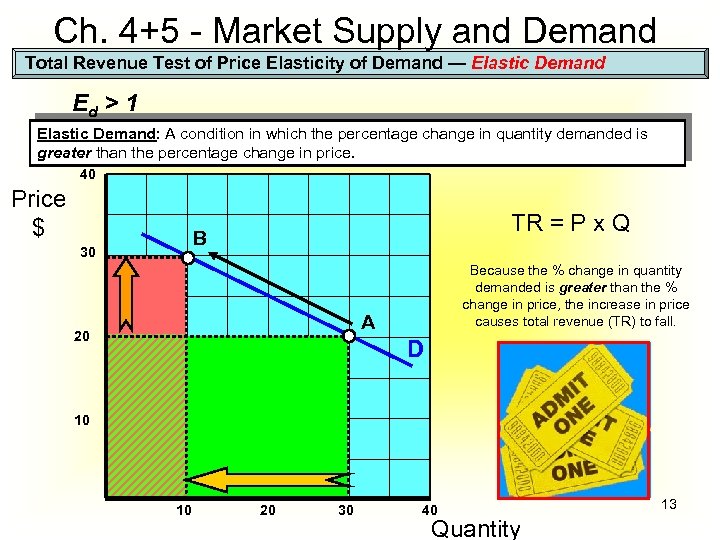 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Total Revenue Test of Price Elasticity of Demand — Elastic Demand Ed > 1 Elastic Demand: A condition in which the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price. 40 Price $ TR = P x Q B 30 Because the % change in quantity demanded is greater than the % change in price, the increase in price causes total revenue (TR) to fall. A 20 D 10 10 20 30 40 Quantity 13
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Total Revenue Test of Price Elasticity of Demand — Elastic Demand Ed > 1 Elastic Demand: A condition in which the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price. 40 Price $ TR = P x Q B 30 Because the % change in quantity demanded is greater than the % change in price, the increase in price causes total revenue (TR) to fall. A 20 D 10 10 20 30 40 Quantity 13
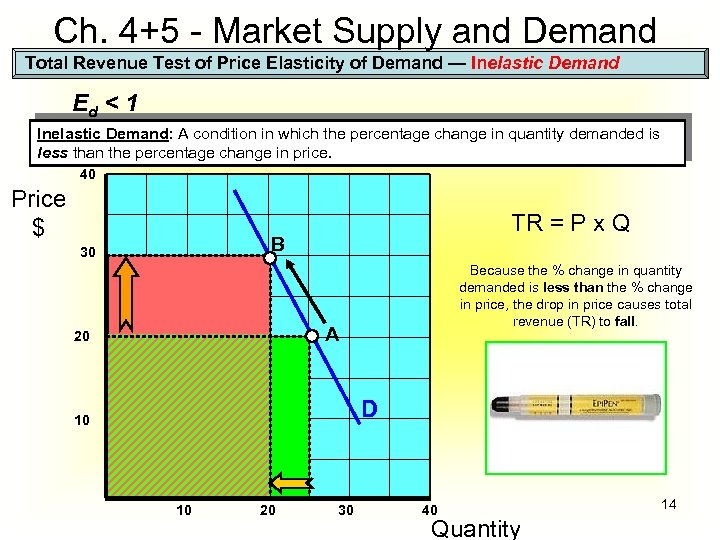 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Total Revenue Test of Price Elasticity of Demand — Inelastic Demand Ed < 1 Inelastic Demand: A condition in which the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price. 40 Price $ TR = P x Q B 30 Because the % change in quantity demanded is less than the % change in price, the drop in price causes total revenue (TR) to fall. A 20 D 10 10 20 30 40 Quantity 14
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Total Revenue Test of Price Elasticity of Demand — Inelastic Demand Ed < 1 Inelastic Demand: A condition in which the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price. 40 Price $ TR = P x Q B 30 Because the % change in quantity demanded is less than the % change in price, the drop in price causes total revenue (TR) to fall. A 20 D 10 10 20 30 40 Quantity 14
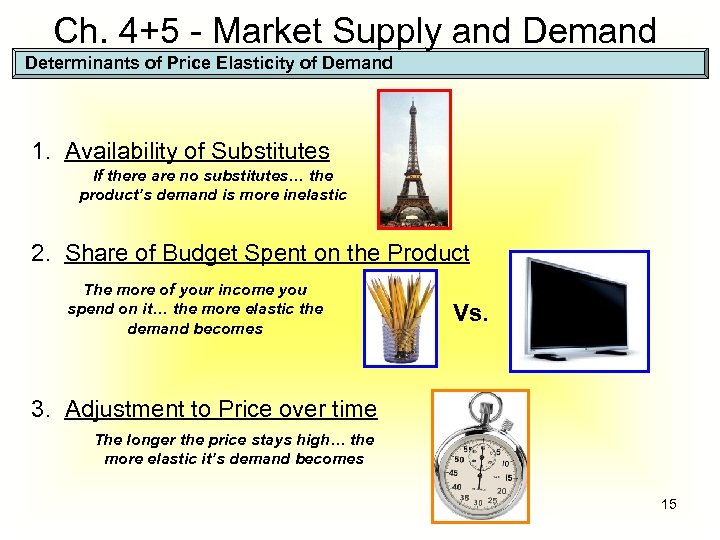 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand 1. Availability of Substitutes If there are no substitutes… the product’s demand is more inelastic 2. Share of Budget Spent on the Product The more of your income you spend on it… the more elastic the demand becomes Vs. 3. Adjustment to Price over time The longer the price stays high… the more elastic it’s demand becomes 15
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand 1. Availability of Substitutes If there are no substitutes… the product’s demand is more inelastic 2. Share of Budget Spent on the Product The more of your income you spend on it… the more elastic the demand becomes Vs. 3. Adjustment to Price over time The longer the price stays high… the more elastic it’s demand becomes 15
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand The Law of Supply § The Law of Supply: There is a direct relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied in a defined time period, ceteris paribus. P QS 16
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand The Law of Supply § The Law of Supply: There is a direct relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied in a defined time period, ceteris paribus. P QS 16
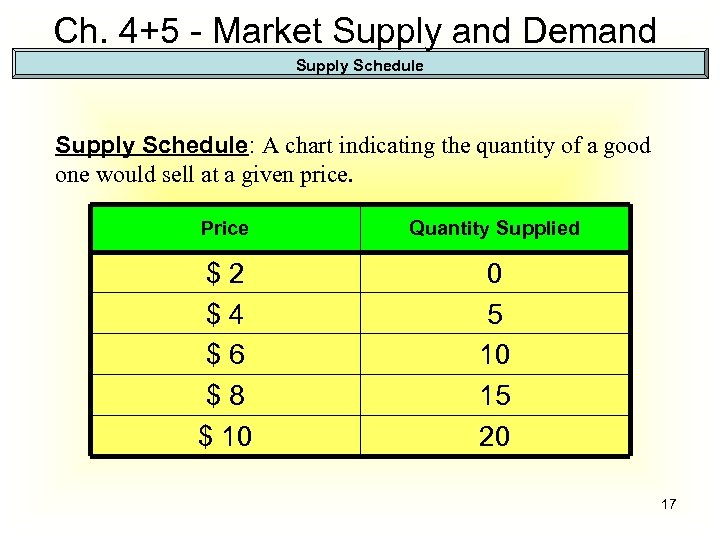 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Supply Schedule: A chart indicating the quantity of a good one would sell at a given price. Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 0 5 10 15 20 17
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Supply Schedule: A chart indicating the quantity of a good one would sell at a given price. Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 $ 10 0 5 10 15 20 17
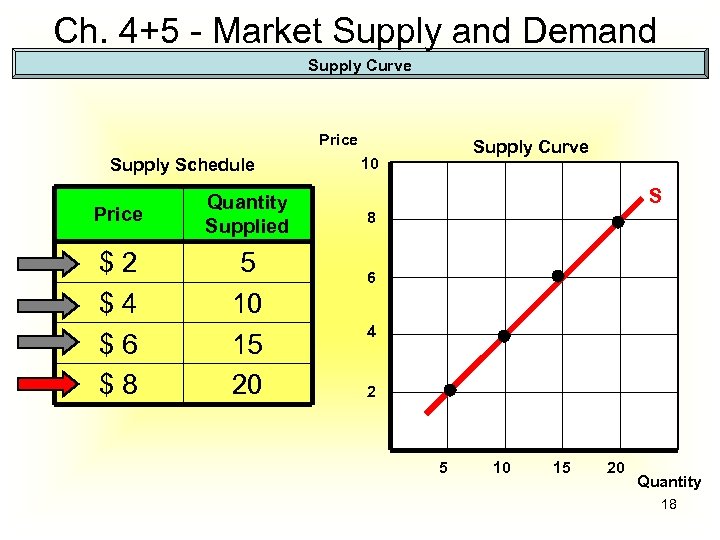 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Supply Curve Price Supply Schedule Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 5 10 15 20 Supply Curve 10 S 8 6 4 2 5 10 15 20 Quantity 18
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Supply Curve Price Supply Schedule Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 5 10 15 20 Supply Curve 10 S 8 6 4 2 5 10 15 20 Quantity 18
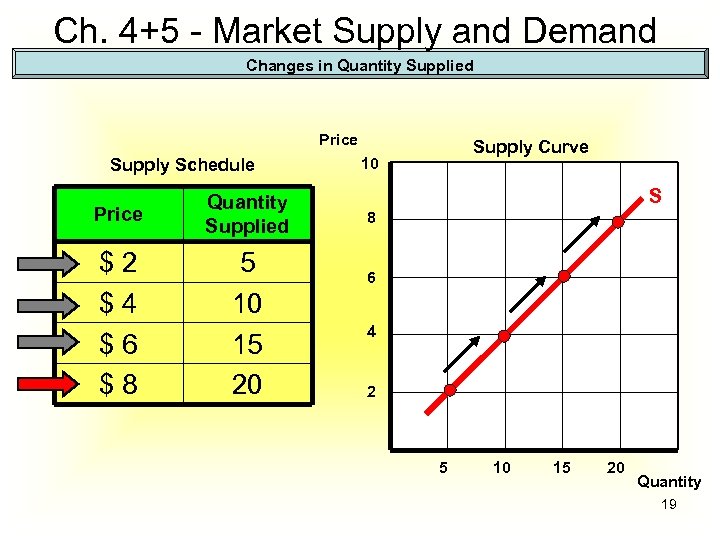 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Changes in Quantity Supplied Price Supply Schedule Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 5 10 15 20 Supply Curve 10 S 8 6 4 2 5 10 15 20 Quantity 19
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Changes in Quantity Supplied Price Supply Schedule Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 5 10 15 20 Supply Curve 10 S 8 6 4 2 5 10 15 20 Quantity 19
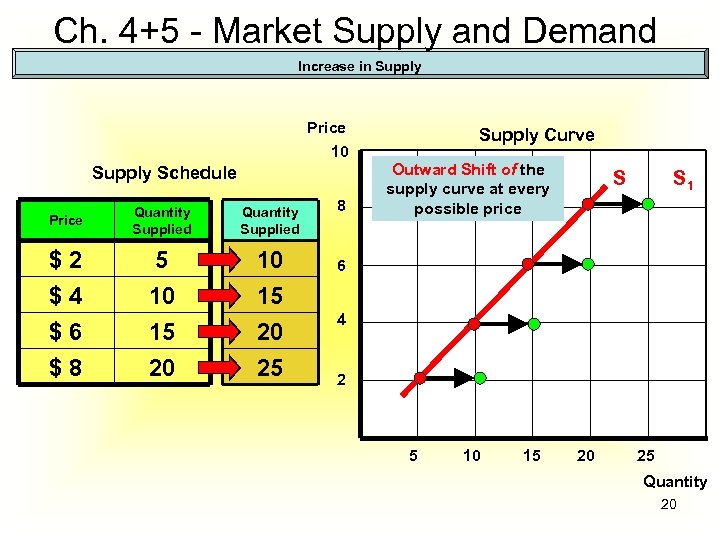 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Increase in Supply Price Supply Curve 10 Supply Schedule Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 5 10 15 20 25 8 Outward Shift of the supply curve at every possible price S S 1 6 4 2 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity 20
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Increase in Supply Price Supply Curve 10 Supply Schedule Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 5 10 15 20 25 8 Outward Shift of the supply curve at every possible price S S 1 6 4 2 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity 20
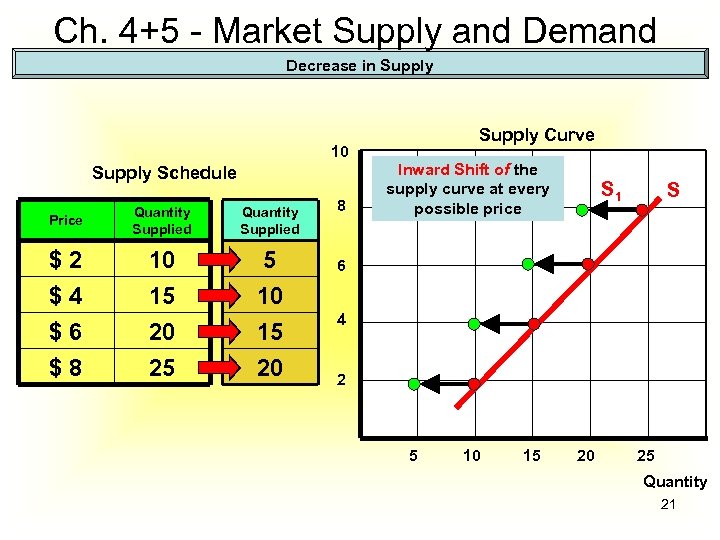 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Decrease in Supply Curve 10 Supply Schedule Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 10 15 20 25 5 10 15 20 8 Inward Shift of the supply curve at every possible price S 1 S 6 4 2 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity 21
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Decrease in Supply Curve 10 Supply Schedule Price Quantity Supplied $2 $4 $6 $8 10 15 20 25 5 10 15 20 8 Inward Shift of the supply curve at every possible price S 1 S 6 4 2 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity 21
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Supply Nonprice Determinants of Supply §Number of Sellers • More sellers leads to increase in supply 22
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Supply Nonprice Determinants of Supply §Number of Sellers • More sellers leads to increase in supply 22
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand §Technology • New technology reduces production costs and increases supply 23
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand §Technology • New technology reduces production costs and increases supply 23
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand §Resource Prices • Increase in price of inputs decreases supply • Decrease in price of inputs increases supply 24
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand §Resource Prices • Increase in price of inputs decreases supply • Decrease in price of inputs increases supply 24
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Supply Nonprice Determinants of Supply §Government Action • Taxes decrease the supply • Subsidies increase the supply 25
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Change in Supply Nonprice Determinants of Supply §Government Action • Taxes decrease the supply • Subsidies increase the supply 25
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand §Future Expectations • If price is expected to rise, less will be supplied today • If price is expected to fall, more will be supplied today 26
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand §Future Expectations • If price is expected to rise, less will be supplied today • If price is expected to fall, more will be supplied today 26
 Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Decrease in Supply Production Costs Fixed Costs: Costs incurred that do not change as output increases Variable Costs: Costs incurred that increase as output increases Total Costs: Fixed Cost + Variable Cost Marginal Cost: The change in Total Cost from increasing output by 1 unit Increasing Returns Occur when hiring new workers causes marginal product to increas Diminishing Returns Occur when hiring new workers causes marginal product to decrease 27
Ch. 4+5 - Market Supply and Demand Decrease in Supply Production Costs Fixed Costs: Costs incurred that do not change as output increases Variable Costs: Costs incurred that increase as output increases Total Costs: Fixed Cost + Variable Cost Marginal Cost: The change in Total Cost from increasing output by 1 unit Increasing Returns Occur when hiring new workers causes marginal product to increas Diminishing Returns Occur when hiring new workers causes marginal product to decrease 27


