4c5b579803315d4ddec909884ac3e660.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Ch 3: 2 -D motion & vectors Use arrows to show the direction and magnitude of vectors Scalar: just magnitude Vector: magnitude (length of vector) and direction tail head
Ch 3: 2 -D motion & vectors Use arrows to show the direction and magnitude of vectors Scalar: just magnitude Vector: magnitude (length of vector) and direction tail head
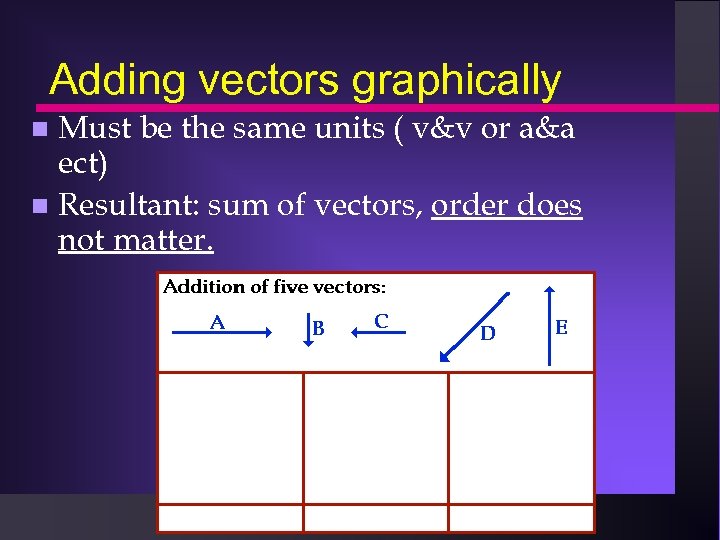 Adding vectors graphically Must be the same units ( v&v or a&a ect) Resultant: sum of vectors, order does not matter.
Adding vectors graphically Must be the same units ( v&v or a&a ect) Resultant: sum of vectors, order does not matter.
 Steps determine 0 o north and list know vectors est. scale ( 1 cm = 200 m ect. ) est. starting pt. , place tail of 1 st vector there with correct mag. & direction connect tail of 2 nd to head of 1 st ( correct mag. & direction) continue until all vectors added connect tail 1 st to head last ( resultant) use scale to determine mag. and protractor to measure . cw rotation, add to 1 st vector direction. ccw rotation, subtract from 1 st vector direction.
Steps determine 0 o north and list know vectors est. scale ( 1 cm = 200 m ect. ) est. starting pt. , place tail of 1 st vector there with correct mag. & direction connect tail of 2 nd to head of 1 st ( correct mag. & direction) continue until all vectors added connect tail 1 st to head last ( resultant) use scale to determine mag. and protractor to measure . cw rotation, add to 1 st vector direction. ccw rotation, subtract from 1 st vector direction.
 Board work A boy walks 5. 0 km north to a friends house and has lunch then walks 3. 0 km west to the hardware store to pick up a rake. What is his total distance and displacement? 8. 0 km, 5. 8 km at 31 owest of north(329 o) Two concurrent forces of 80. 0 Nsouth and 50. 0 Neast act on a body. What is the resultant force? 94. 3 N at 320 east of south(148 o)
Board work A boy walks 5. 0 km north to a friends house and has lunch then walks 3. 0 km west to the hardware store to pick up a rake. What is his total distance and displacement? 8. 0 km, 5. 8 km at 31 owest of north(329 o) Two concurrent forces of 80. 0 Nsouth and 50. 0 Neast act on a body. What is the resultant force? 94. 3 N at 320 east of south(148 o)
 Continue Vectors add and act independently A boat traveling 5. 0 m/s west is moving through a river with a current of 1. 5 m/s south and is 100. 0 m wide. What is the boat’s resultant velocity? How long does it take to cross and how far down stream does the boat land? 5. 2 m/s at 17 osouth of west(253 o) t= 20. s d= 30 m
Continue Vectors add and act independently A boat traveling 5. 0 m/s west is moving through a river with a current of 1. 5 m/s south and is 100. 0 m wide. What is the boat’s resultant velocity? How long does it take to cross and how far down stream does the boat land? 5. 2 m/s at 17 osouth of west(253 o) t= 20. s d= 30 m
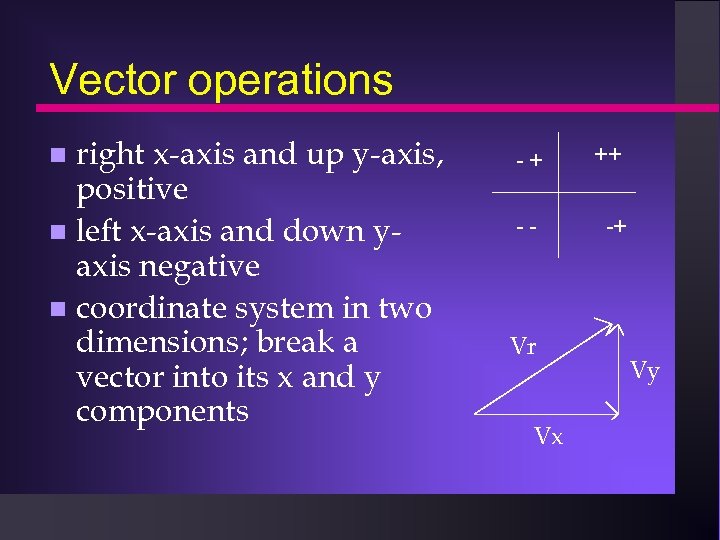 Vector operations right x-axis and up y-axis, positive left x-axis and down yaxis negative coordinate system in two dimensions; break a vector into its x and y components -+ ++ -- -+ Vr Vx Vy
Vector operations right x-axis and up y-axis, positive left x-axis and down yaxis negative coordinate system in two dimensions; break a vector into its x and y components -+ ++ -- -+ Vr Vx Vy
 Determine resultant vector 2 perpendicular vectors: cal. using Pythagorean theorem and tangent function Board work: A plane travels from Houston, Tx to Washington D. C. which is 1540 km E and 1160 km N of Houston. What is the planes total displacement? 1930 km 37. 0 onorth of east ( 53. 0 o)
Determine resultant vector 2 perpendicular vectors: cal. using Pythagorean theorem and tangent function Board work: A plane travels from Houston, Tx to Washington D. C. which is 1540 km E and 1160 km N of Houston. What is the planes total displacement? 1930 km 37. 0 onorth of east ( 53. 0 o)
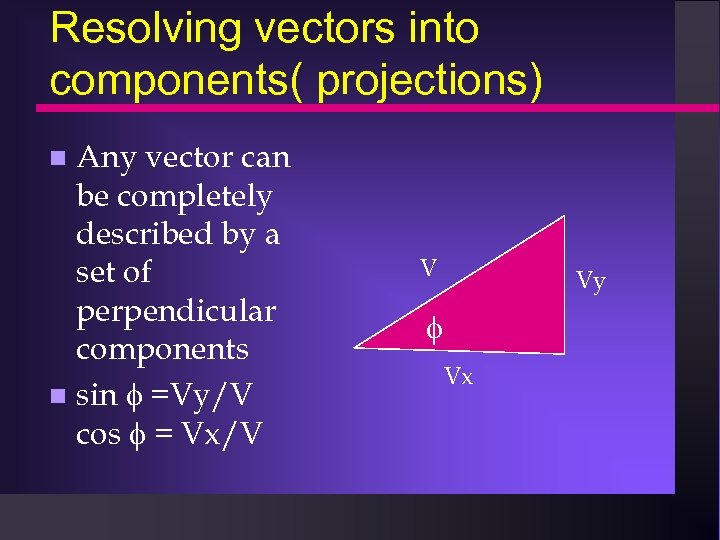 Resolving vectors into components( projections) Any vector can be completely described by a set of perpendicular components sin =Vy/V cos = Vx/V V Vy Vx
Resolving vectors into components( projections) Any vector can be completely described by a set of perpendicular components sin =Vy/V cos = Vx/V V Vy Vx
 Board work An arrow is shot from a bow at an angle of 25 o above the horizontal with a velocity of 45 m/s. determine the hor. (Vx) and vert (Vy) components of the arrows initial velocity. vh=41 m/s and vv=19 m/s vh>vv?
Board work An arrow is shot from a bow at an angle of 25 o above the horizontal with a velocity of 45 m/s. determine the hor. (Vx) and vert (Vy) components of the arrows initial velocity. vh=41 m/s and vv=19 m/s vh>vv?
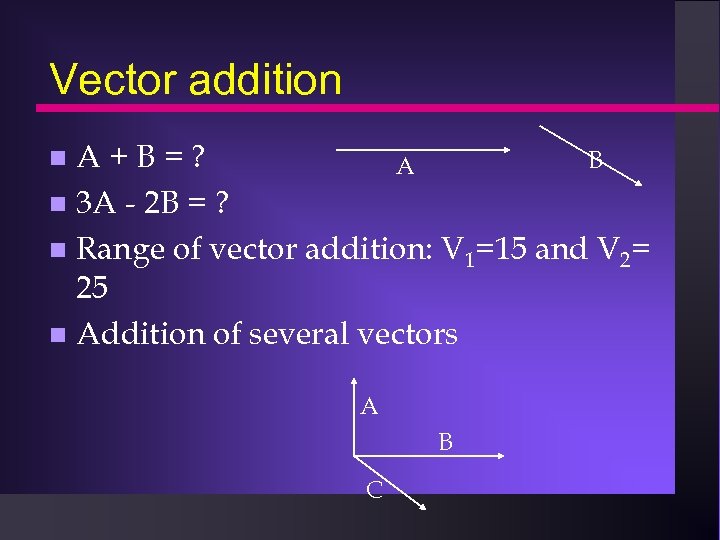 Vector addition A+B=? B A 3 A - 2 B = ? Range of vector addition: V 1=15 and V 2= 25 Addition of several vectors A B C
Vector addition A+B=? B A 3 A - 2 B = ? Range of vector addition: V 1=15 and V 2= 25 Addition of several vectors A B C
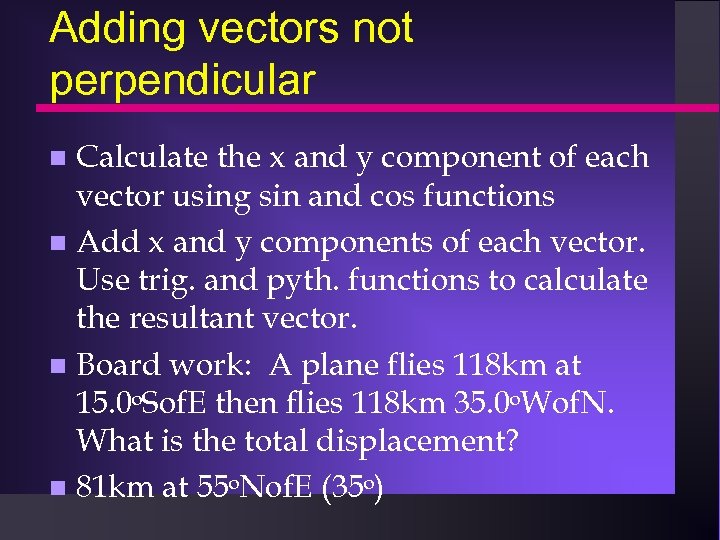 Adding vectors not perpendicular Calculate the x and y component of each vector using sin and cos functions Add x and y components of each vector. Use trig. and pyth. functions to calculate the resultant vector. Board work: A plane flies 118 km at 15. 0 o. Sof. E then flies 118 km 35. 0 o. Wof. N. What is the total displacement? 81 km at 55 o. Nof. E (35 o)
Adding vectors not perpendicular Calculate the x and y component of each vector using sin and cos functions Add x and y components of each vector. Use trig. and pyth. functions to calculate the resultant vector. Board work: A plane flies 118 km at 15. 0 o. Sof. E then flies 118 km 35. 0 o. Wof. N. What is the total displacement? 81 km at 55 o. Nof. E (35 o)
 Projectile motion Motion of objects moving in two dimensions under the influence of gravity Paths followed is a parabolic trajectories Will always have a horizontal velocity component of flight that is constant. ( neglect air resistance, no force in Vx direction) Projectile motion is free fall motion with an initial constant horizontal velocity and Vyi = 0 that is constantly changing.
Projectile motion Motion of objects moving in two dimensions under the influence of gravity Paths followed is a parabolic trajectories Will always have a horizontal velocity component of flight that is constant. ( neglect air resistance, no force in Vx direction) Projectile motion is free fall motion with an initial constant horizontal velocity and Vyi = 0 that is constantly changing.
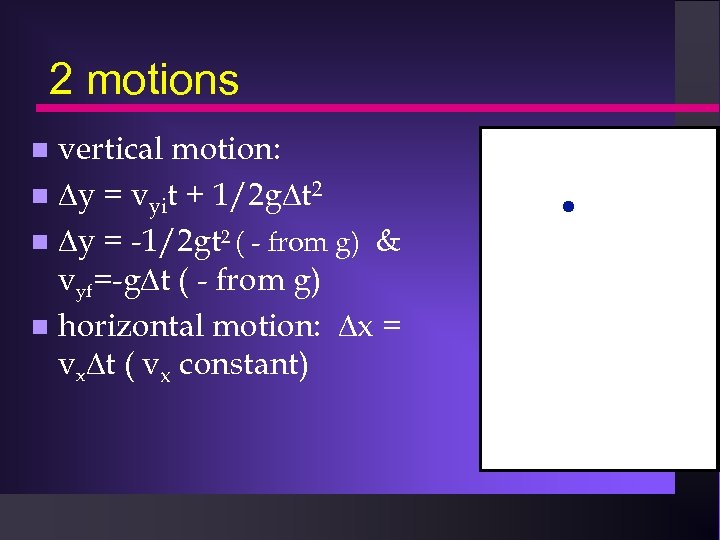 2 motions vertical motion: y = vyit + 1/2 g t 2 y = -1/2 gt 2 ( - from g) & vyf=-g t ( - from g) horizontal motion: x = vx t ( vx constant)
2 motions vertical motion: y = vyit + 1/2 g t 2 y = -1/2 gt 2 ( - from g) & vyf=-g t ( - from g) horizontal motion: x = vx t ( vx constant)
 Board work People in movies often jump from buildings into pools. If a person jumps from the 10 th floor(30. 0 m) to a pool that is 5. 0 m away from the building. What is the initial horizontal velocity the person must jump with? 2. 0 m/s
Board work People in movies often jump from buildings into pools. If a person jumps from the 10 th floor(30. 0 m) to a pool that is 5. 0 m away from the building. What is the initial horizontal velocity the person must jump with? 2. 0 m/s
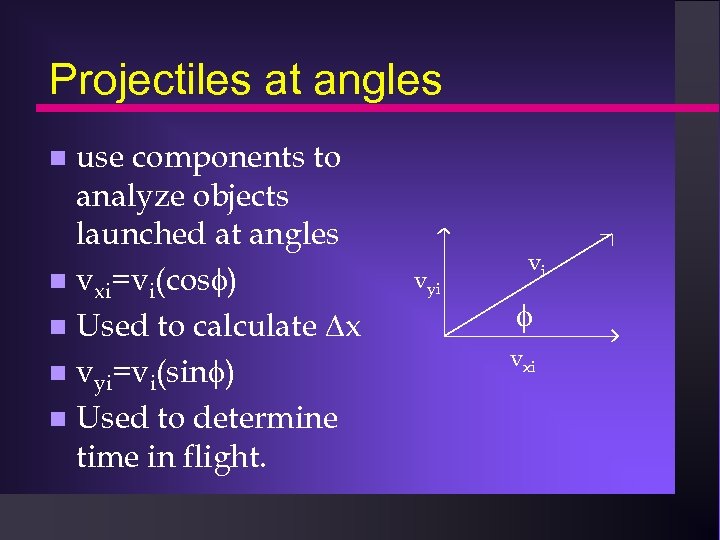 Projectiles at angles use components to analyze objects launched at angles vxi=vi(cos ) Used to calculate x vyi=vi(sin ) Used to determine time in flight. vyi vi vxi
Projectiles at angles use components to analyze objects launched at angles vxi=vi(cos ) Used to calculate x vyi=vi(sin ) Used to determine time in flight. vyi vi vxi
 Cont. equations x = vi(cos ) t : x=vx t : vx const. y=vi(sin ) t - 1/2 g t 2 vyf=vi(sin ) - g t vyf 2=vi 2(sin )2 - 2 g y Derived: Vi = g x/2 sin cos
Cont. equations x = vi(cos ) t : x=vx t : vx const. y=vi(sin ) t - 1/2 g t 2 vyf=vi(sin ) - g t vyf 2=vi 2(sin )2 - 2 g y Derived: Vi = g x/2 sin cos
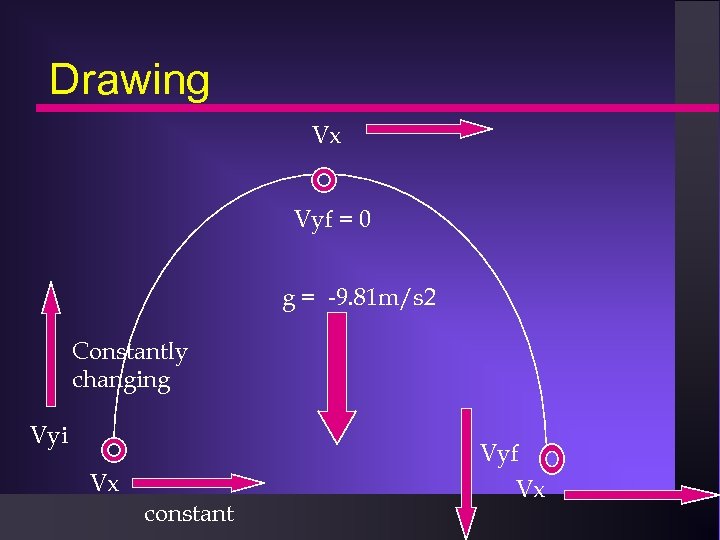 Drawing Vx Vyf = 0 g = -9. 81 m/s 2 Constantly changing Vyi Vx constant Vyf Vx
Drawing Vx Vyf = 0 g = -9. 81 m/s 2 Constantly changing Vyi Vx constant Vyf Vx
 Continue A football is kicked at an initial velocity of 20. 0 m/s at an angle of 35 o. How high and how far does the ball travel? x = 38. 4 m y = 6. 7 m A batter hits a softball 100. 0 m at an angle of 40. 0 o. What was the initial velocity of the softball? 31. 6 m/s
Continue A football is kicked at an initial velocity of 20. 0 m/s at an angle of 35 o. How high and how far does the ball travel? x = 38. 4 m y = 6. 7 m A batter hits a softball 100. 0 m at an angle of 40. 0 o. What was the initial velocity of the softball? 31. 6 m/s
 Maximum hor. displacement
Maximum hor. displacement
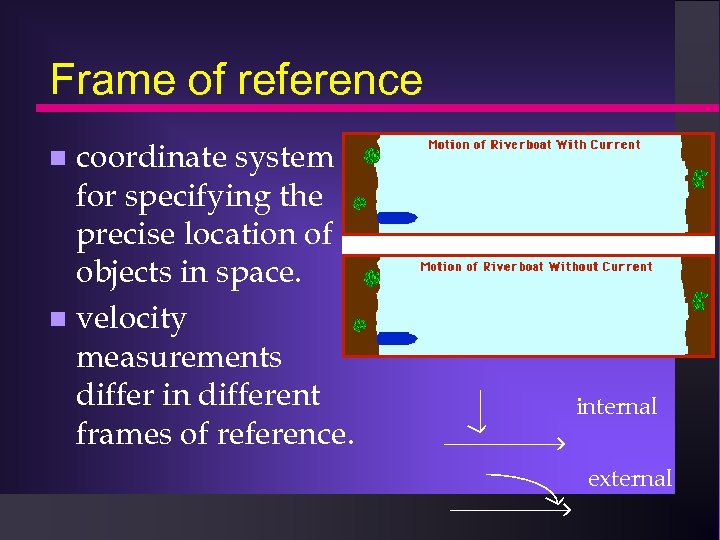 Frame of reference coordinate system for specifying the precise location of objects in space. velocity measurements differ in different frames of reference. internal external
Frame of reference coordinate system for specifying the precise location of objects in space. velocity measurements differ in different frames of reference. internal external
 F of R cont. A car is traveling 30 km/hr north with another car traveling 20 km/hr south behind the first car. What is the velocity of the second car relative to the first car? 50 km/hr south A boy on a bus is walking toward the back at 3. 0 km/h while the bus travels south at 15 km/h. The boys velocity to the road is 12 km/h south
F of R cont. A car is traveling 30 km/hr north with another car traveling 20 km/hr south behind the first car. What is the velocity of the second car relative to the first car? 50 km/hr south A boy on a bus is walking toward the back at 3. 0 km/h while the bus travels south at 15 km/h. The boys velocity to the road is 12 km/h south
 Board work A plane flies northeast at an airspeed of 563. 0 km/hr. A 48. 0 km/hr wind is blowing to southeast. What is the planes velocity relative to the ground? 565 km/hr at 40. 1 o. N of E( 49. 9 o)
Board work A plane flies northeast at an airspeed of 563. 0 km/hr. A 48. 0 km/hr wind is blowing to southeast. What is the planes velocity relative to the ground? 565 km/hr at 40. 1 o. N of E( 49. 9 o)


