098a5f9c15873dc3b3ca8e00873ac056.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 CH. 2 - MEASUREMENT Section 2 -2 I II III Units of Measurement
CH. 2 - MEASUREMENT Section 2 -2 I II III Units of Measurement
 A. Number vs. Quantity Ø Quantity – is something that has magnitude, size, or amount; number + unit UNITS MATTER!!
A. Number vs. Quantity Ø Quantity – is something that has magnitude, size, or amount; number + unit UNITS MATTER!!
 B. SI Units Ø SI units of measurement is the system that all scientists around the world have agreed upon as the single measurement system. Ø SI units are defined in terms of standards of measurement. Ø The standards are objects or natural phenomena that are of constant value, easy to preserve and reproduce, and practical in size.
B. SI Units Ø SI units of measurement is the system that all scientists around the world have agreed upon as the single measurement system. Ø SI units are defined in terms of standards of measurement. Ø The standards are objects or natural phenomena that are of constant value, easy to preserve and reproduce, and practical in size.
 C. SI Base Units Quantity Symb Base Unit Abbre ol v. l Length meter m Mass m kilogram kg Time t second s Temp T kelvin K Amount n mole mol
C. SI Base Units Quantity Symb Base Unit Abbre ol v. l Length meter m Mass m kilogram kg Time t second s Temp T kelvin K Amount n mole mol
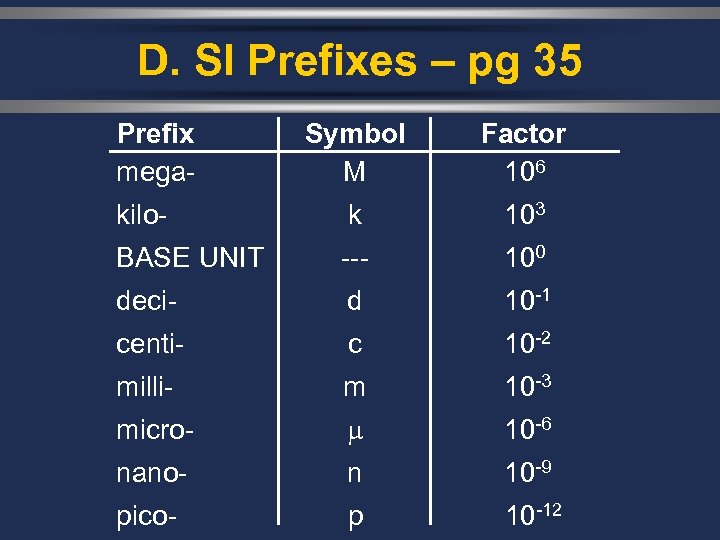 D. SI Prefixes – pg 35 Prefix mega- Symbol M Factor 106 kilo- k 103 BASE UNIT --- 100 deci- d 10 -1 centi- c 10 -2 milli- m 10 -3 micro- 10 -6 nano- n 10 -9 pico- p 10 -12
D. SI Prefixes – pg 35 Prefix mega- Symbol M Factor 106 kilo- k 103 BASE UNIT --- 100 deci- d 10 -1 centi- c 10 -2 milli- m 10 -3 micro- 10 -6 nano- n 10 -9 pico- p 10 -12
 E. SI Prefix Conversions Ø A conversion factor is a ratio derived from the equality between two different units that can be used to convert from one unit to the other. 1. Find the difference between the exponents of the two prefixes. 2. Move the decimal that many places. To the left or right?
E. SI Prefix Conversions Ø A conversion factor is a ratio derived from the equality between two different units that can be used to convert from one unit to the other. 1. Find the difference between the exponents of the two prefixes. 2. Move the decimal that many places. To the left or right?
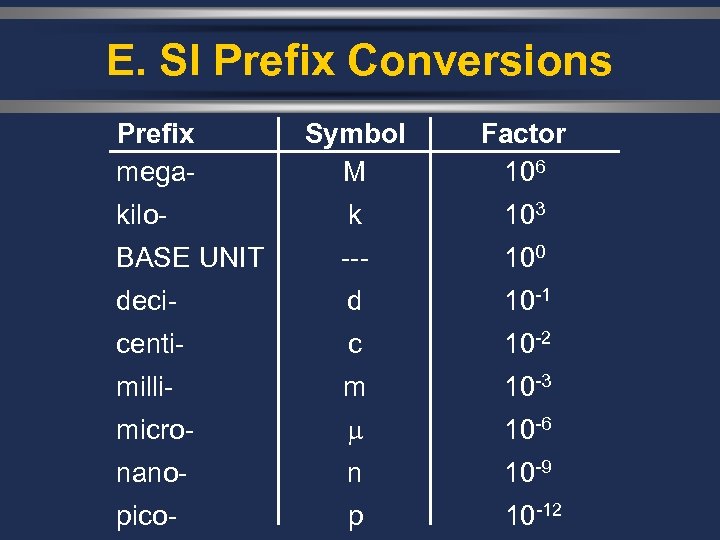 E. SI Prefix Conversions Prefix mega- Symbol M Factor 106 kilo- k 103 BASE UNIT --- 100 deci- d 10 -1 centi- c 10 -2 milli- m 10 -3 micro- 10 -6 nano- n 10 -9 pico- p 10 -12
E. SI Prefix Conversions Prefix mega- Symbol M Factor 106 kilo- k 103 BASE UNIT --- 100 deci- d 10 -1 centi- c 10 -2 milli- m 10 -3 micro- 10 -6 nano- n 10 -9 pico- p 10 -12
 E. SI Prefix Conversions Ø Large unit being converted to a smaller unit: w Move the decimal place to the right the specified number of places Ø Small unit being converted to a larger unit: w Move the decimal place to the left the specified number of places
E. SI Prefix Conversions Ø Large unit being converted to a smaller unit: w Move the decimal place to the right the specified number of places Ø Small unit being converted to a larger unit: w Move the decimal place to the left the specified number of places
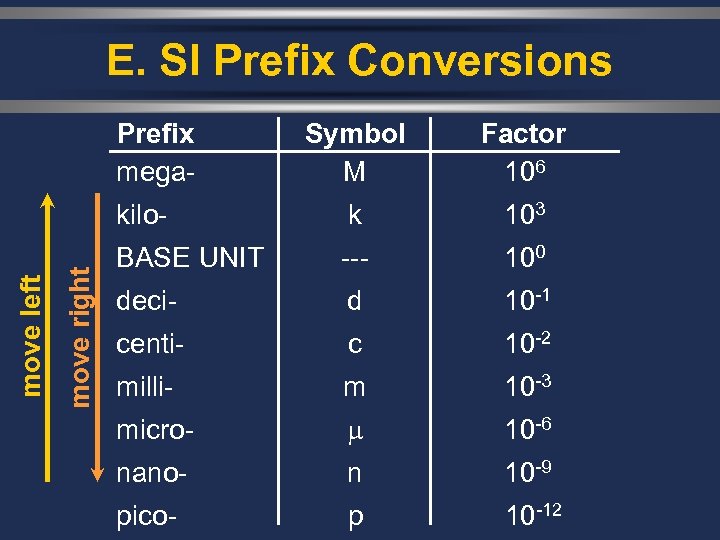 E. SI Prefix Conversions move right Symbol M Factor 106 kilomove left Prefix mega- k 103 BASE UNIT --- 100 deci- d 10 -1 centi- c 10 -2 milli- m 10 -3 micro- 10 -6 nano- n 10 -9 pico- p 10 -12
E. SI Prefix Conversions move right Symbol M Factor 106 kilomove left Prefix mega- k 103 BASE UNIT --- 100 deci- d 10 -1 centi- c 10 -2 milli- m 10 -3 micro- 10 -6 nano- n 10 -9 pico- p 10 -12
 E. SI Prefix Conversions 532 m NUMBER UNIT 0. 532 = _______ km = NUMBER UNIT
E. SI Prefix Conversions 532 m NUMBER UNIT 0. 532 = _______ km = NUMBER UNIT
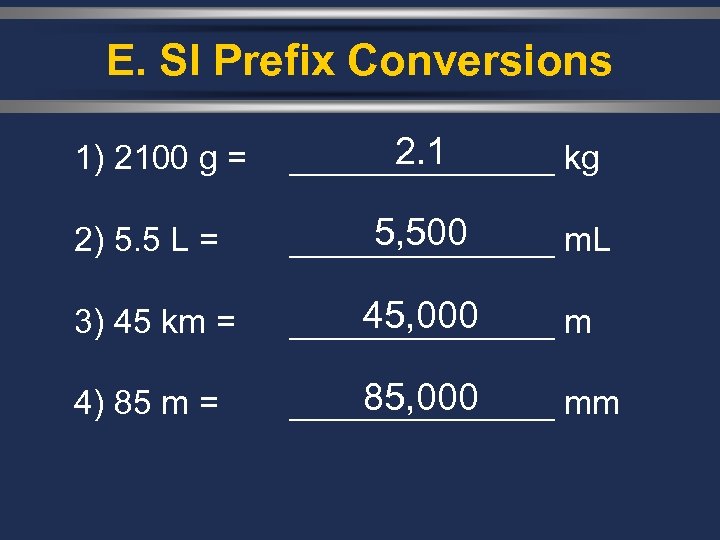 E. SI Prefix Conversions 1) 2100 g = 2. 1 _______ kg 2) 5. 5 L = 5, 500 _______ m. L 3) 45 km = 45, 000 _______ m 4) 85 m = 85, 000 _______ mm
E. SI Prefix Conversions 1) 2100 g = 2. 1 _______ kg 2) 5. 5 L = 5, 500 _______ m. L 3) 45 km = 45, 000 _______ m 4) 85 m = 85, 000 _______ mm
 F. Derived Units Ø Combination of base units. Ø Volume (m 3 or cm 3) – the 1 cm 3 = 1 m. L amount of space occupied by an object 1 dm 3 = 1 L w length Ø Density (kg/m 3 or g/cm 3) – the ratio of mass to volume w mass per volume M D= V
F. Derived Units Ø Combination of base units. Ø Volume (m 3 or cm 3) – the 1 cm 3 = 1 m. L amount of space occupied by an object 1 dm 3 = 1 L w length Ø Density (kg/m 3 or g/cm 3) – the ratio of mass to volume w mass per volume M D= V
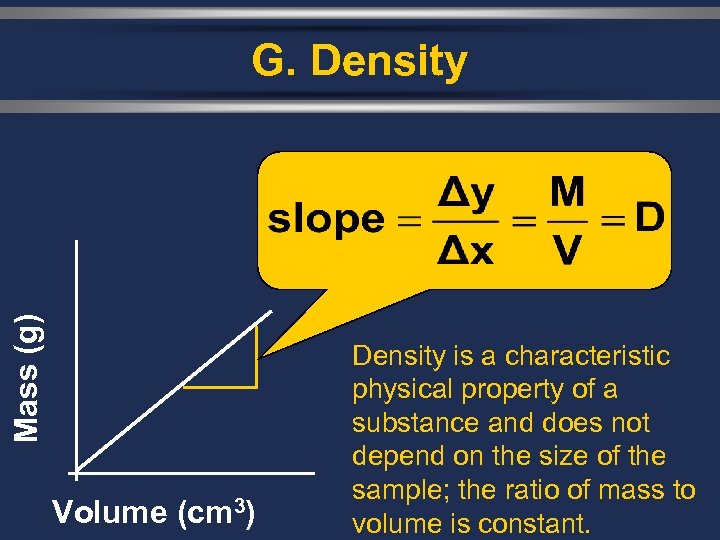 Mass (g) G. Density Volume (cm 3) Density is a characteristic physical property of a substance and does not depend on the size of the sample; the ratio of mass to volume is constant.
Mass (g) G. Density Volume (cm 3) Density is a characteristic physical property of a substance and does not depend on the size of the sample; the ratio of mass to volume is constant.
 G. Density Ø Density is dependent on temperature. Ø An increase in temperature usually causes a decrease in density for most substances.
G. Density Ø Density is dependent on temperature. Ø An increase in temperature usually causes a decrease in density for most substances.
 H. Problem-Solving Steps 1. Analyze 2. Plan 3. Compute 4. Evaluate
H. Problem-Solving Steps 1. Analyze 2. Plan 3. Compute 4. Evaluate
 I. Solving Density Problems Ø An object has a volume of 825 cm 3 and a density of 13. 6 g/cm 3. Find its mass. GIVEN: WORK: V = 825 cm 3 D = 13. 6 g/cm 3 M=? M = DV M = (13. 6 g/cm 3)(825 cm 3) M = 11, 200 g
I. Solving Density Problems Ø An object has a volume of 825 cm 3 and a density of 13. 6 g/cm 3. Find its mass. GIVEN: WORK: V = 825 cm 3 D = 13. 6 g/cm 3 M=? M = DV M = (13. 6 g/cm 3)(825 cm 3) M = 11, 200 g
 I. Solving Density Problems Ø A liquid has a density of 0. 87 g/m. L. What volume is occupied by 25 g of the liquid? GIVEN: WORK: D = 0. 87 g/m. L V=? M = 25 g V=M D V= 25 g 0. 87 g/m. L V = 29 m. L
I. Solving Density Problems Ø A liquid has a density of 0. 87 g/m. L. What volume is occupied by 25 g of the liquid? GIVEN: WORK: D = 0. 87 g/m. L V=? M = 25 g V=M D V= 25 g 0. 87 g/m. L V = 29 m. L
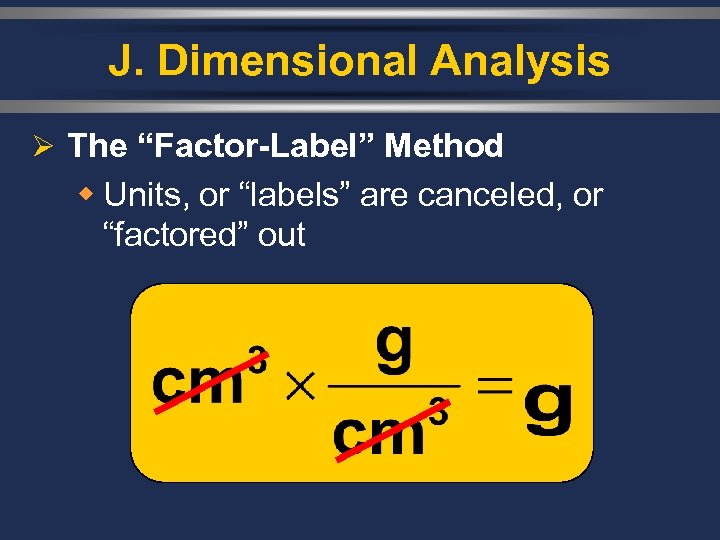 J. Dimensional Analysis Ø The “Factor-Label” Method w Units, or “labels” are canceled, or “factored” out
J. Dimensional Analysis Ø The “Factor-Label” Method w Units, or “labels” are canceled, or “factored” out
 J. Dimensional Analysis Ø Steps: 1. Identify starting & ending units. 2. Line up conversion factors so units cancel. 3. Multiply all top numbers & divide by each bottom number. 4. Check units & answer.
J. Dimensional Analysis Ø Steps: 1. Identify starting & ending units. 2. Line up conversion factors so units cancel. 3. Multiply all top numbers & divide by each bottom number. 4. Check units & answer.
 J. Dimensional Analysis Ø Your European hairdresser wants to cut your hair 8. 0 cm shorter. How many inches will he be cutting off? (Hint: 2. 54 cm = 1 inch) 8. 0 cm 1 in 2. 54 cm = 3. 2 in
J. Dimensional Analysis Ø Your European hairdresser wants to cut your hair 8. 0 cm shorter. How many inches will he be cutting off? (Hint: 2. 54 cm = 1 inch) 8. 0 cm 1 in 2. 54 cm = 3. 2 in
 J. Dimensional Analysis Ø How many milliliters are in 1. 00 quart of milk? (Hint: 1. 057 qt = 1 L) qt 1. 00 qt m. L 1 L 1000 m. L 1. 057 qt 1 L = 946 m. L
J. Dimensional Analysis Ø How many milliliters are in 1. 00 quart of milk? (Hint: 1. 057 qt = 1 L) qt 1. 00 qt m. L 1 L 1000 m. L 1. 057 qt 1 L = 946 m. L


