6121cefc2099afe8203b6dd097c5a4f5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Ch 18 Cold War Conflicts
Ch 18 Cold War Conflicts
 Main Ideas • The Cold War and danger of nuclear war define international affairs, especially after the Korean War. • Fear of Communism in the U. S. leads to accusations against innocent citizens.
Main Ideas • The Cold War and danger of nuclear war define international affairs, especially after the Korean War. • Fear of Communism in the U. S. leads to accusations against innocent citizens.
 Origins of the Cold War • The U. S. and Soviet Union emerge from WWII as two “superpowers” with very different political and economic systems. United states • capitalist • democracy soviet union • Communist • totalitarian
Origins of the Cold War • The U. S. and Soviet Union emerge from WWII as two “superpowers” with very different political and economic systems. United states • capitalist • democracy soviet union • Communist • totalitarian
 U. S. Soviet Relations • U. S. suspicious of Stalin because he had been Hitler’s ally but switched sides in the war. • Stalin resents the U. S. delayed attacking Germany and hid knowledge of the atom bomb.
U. S. Soviet Relations • U. S. suspicious of Stalin because he had been Hitler’s ally but switched sides in the war. • Stalin resents the U. S. delayed attacking Germany and hid knowledge of the atom bomb.
 United Nations • 1945 UN established as new peacekeeping body • UN. Becomes the arena where U. S. and U. S. S. R. compete. • Truman was not included in policy decisions as vice-president. He did not know about the Manhattan Project until he became President.
United Nations • 1945 UN established as new peacekeeping body • UN. Becomes the arena where U. S. and U. S. S. R. compete. • Truman was not included in policy decisions as vice-president. He did not know about the Manhattan Project until he became President.
 The Potsdam Conference • July 1945 conference between U. S. , Great Britain, and Soviet Union. • Stalin does not allow free, multiparty elections in Poland. Bans democratic parties. Churchill, Truman, and Stalin at Potsdam • U. S. wants Eastern European raw materials Becomes apparent at Potsdam that and markets. U. S. and Soviet interests conflict.
The Potsdam Conference • July 1945 conference between U. S. , Great Britain, and Soviet Union. • Stalin does not allow free, multiparty elections in Poland. Bans democratic parties. Churchill, Truman, and Stalin at Potsdam • U. S. wants Eastern European raw materials Becomes apparent at Potsdam that and markets. U. S. and Soviet interests conflict.
 Soviets tighten grip in E. Europe • Soviet Union also a superpower. • Suffered heavy devastation on own soil. • Installs Communist rule in satellite nations and countries it dominates. • 1946 Stalin announces war between Communism and Capitalism inevitable. Joseph Stalin
Soviets tighten grip in E. Europe • Soviet Union also a superpower. • Suffered heavy devastation on own soil. • Installs Communist rule in satellite nations and countries it dominates. • 1946 Stalin announces war between Communism and Capitalism inevitable. Joseph Stalin
 Containment • U. S. policy to prevent spread of Communism. • Churchill describes the division of Europe between Capitalist and Communist the “iron curtain”
Containment • U. S. policy to prevent spread of Communism. • Churchill describes the division of Europe between Capitalist and Communist the “iron curtain”
 The Truman Doctrine (Containment) • 1945 -1991 era known as Cold War between U. S. and U. S. S. R. • Neither nation directly fights on battlefield. • Truman Doctrine-U. S. policy of send aid to any nation trying to prevent a Communist takeover. – The U. S. replaces British aid to Greece and Turkey to reduce Communist threat in those nations. President Harry Truman
The Truman Doctrine (Containment) • 1945 -1991 era known as Cold War between U. S. and U. S. S. R. • Neither nation directly fights on battlefield. • Truman Doctrine-U. S. policy of send aid to any nation trying to prevent a Communist takeover. – The U. S. replaces British aid to Greece and Turkey to reduce Communist threat in those nations. President Harry Truman
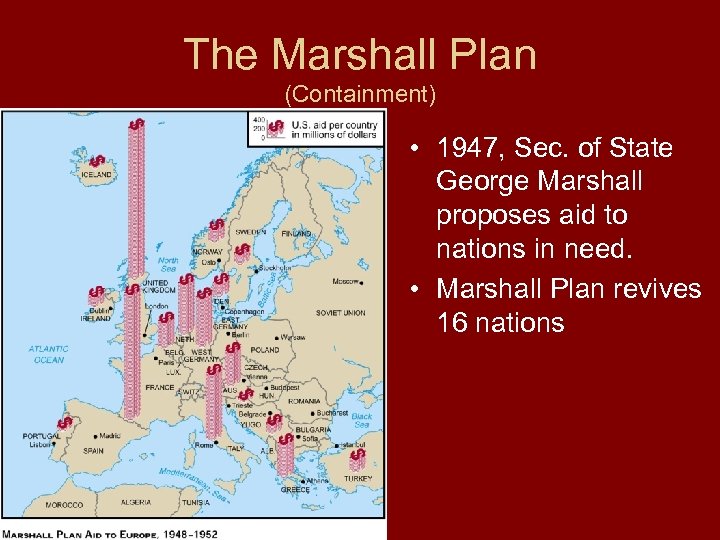 The Marshall Plan (Containment) • 1947, Sec. of State George Marshall proposes aid to nations in need. • Marshall Plan revives 16 nations
The Marshall Plan (Containment) • 1947, Sec. of State George Marshall proposes aid to nations in need. • Marshall Plan revives 16 nations
 Berlin Airlift • 1948 Stalin closes highway and rail routes into West Berlin. • Berlin Airlift-Britain, U. S. fly food and supplies into West Berlin. • 1949 Stalin lifts blockade • Federal Republic of Germany, German Democratic Republic form West Berlin
Berlin Airlift • 1948 Stalin closes highway and rail routes into West Berlin. • Berlin Airlift-Britain, U. S. fly food and supplies into West Berlin. • 1949 Stalin lifts blockade • Federal Republic of Germany, German Democratic Republic form West Berlin
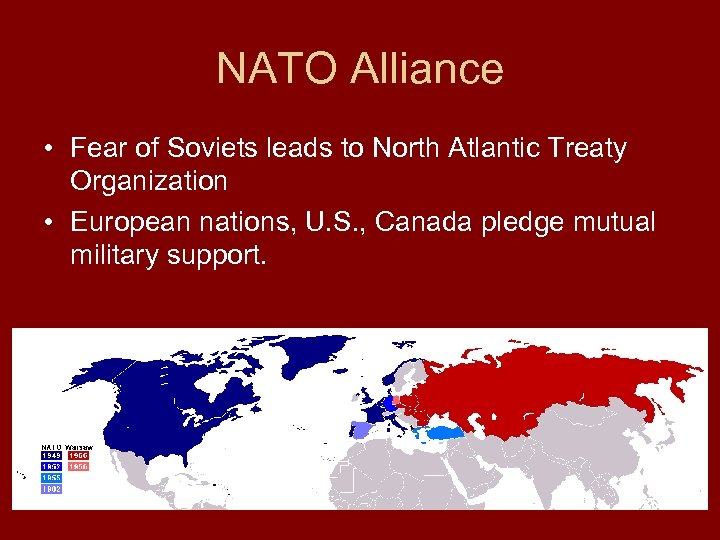 NATO Alliance • Fear of Soviets leads to North Atlantic Treaty Organization • European nations, U. S. , Canada pledge mutual military support.
NATO Alliance • Fear of Soviets leads to North Atlantic Treaty Organization • European nations, U. S. , Canada pledge mutual military support.
 Section 2: The Cold War heats up • After WWII, China becomes a Communist nation and Korea is split into a Communist north and a Democratic south. Communist China’s Mao Zedong
Section 2: The Cold War heats up • After WWII, China becomes a Communist nation and Korea is split into a Communist north and a Democratic south. Communist China’s Mao Zedong
 China: Nationalists vs. Communists • Nationalist government led by Chiang Kai-shek battle against Communists led by Mao Zedong. • Communists get peasant and Soviet support. Nationalists get U. S. monetary aid. • Communists control north China 1945 and all of China by 1949. • Communists establish People’s Republic of China. • The U. S. government does not recognize new Chinese government. Nationalist leader Chiang Kai-shek fled to Taiwan with his party in 1949.
China: Nationalists vs. Communists • Nationalist government led by Chiang Kai-shek battle against Communists led by Mao Zedong. • Communists get peasant and Soviet support. Nationalists get U. S. monetary aid. • Communists control north China 1945 and all of China by 1949. • Communists establish People’s Republic of China. • The U. S. government does not recognize new Chinese government. Nationalist leader Chiang Kai-shek fled to Taiwan with his party in 1949.
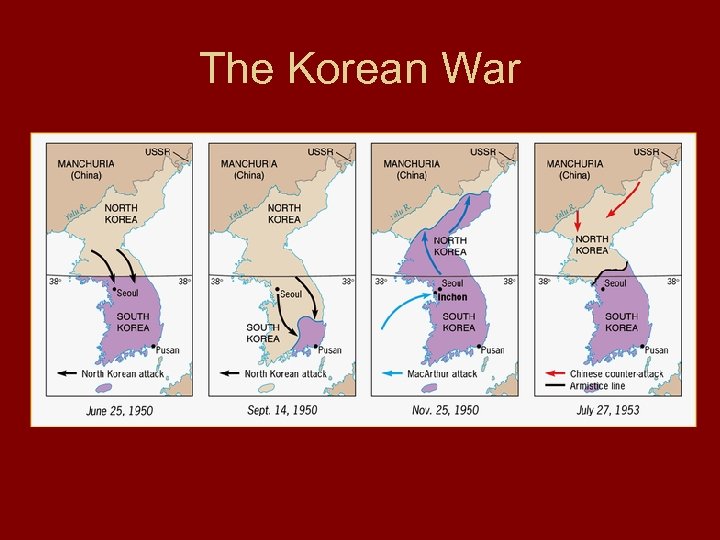
 The Korean War • 38 th parallel (38 N latitude) divides Korea after Japanese surrender of WWII. – North surrendered to U. S. S. R. , the South to U. S. • 1950 North Korea invades South Korea: begins the Korean War. • South Korea asks UN to stop invasion and Security Council approves. • Mac. Arthur put in command of South Korean, U. S. , and other forces.
The Korean War • 38 th parallel (38 N latitude) divides Korea after Japanese surrender of WWII. – North surrendered to U. S. S. R. , the South to U. S. • 1950 North Korea invades South Korea: begins the Korean War. • South Korea asks UN to stop invasion and Security Council approves. • Mac. Arthur put in command of South Korean, U. S. , and other forces.
 The Korean War
The Korean War
 The U. S. in Korea • Mac. Arthur recommends war with China-Truman denies request. • The U. S. and U. N. forces fought back to the 38 th parallel. • Truman fires Mac. Arthur after repeated pushes to invade China. • Public outraged over firing of war hero. • Truman’s decision upheld by Congressional committee. General Douglas Mac. Arthur President Harry Truman
The U. S. in Korea • Mac. Arthur recommends war with China-Truman denies request. • The U. S. and U. N. forces fought back to the 38 th parallel. • Truman fires Mac. Arthur after repeated pushes to invade China. • Public outraged over firing of war hero. • Truman’s decision upheld by Congressional committee. General Douglas Mac. Arthur President Harry Truman
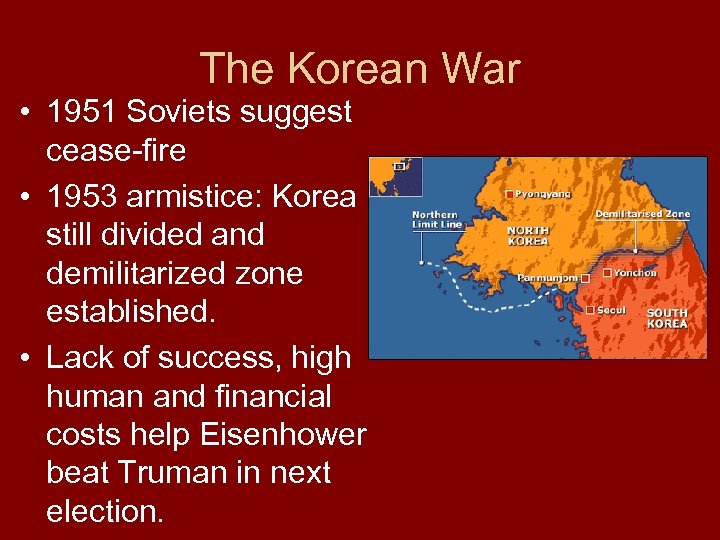 The Korean War • 1951 Soviets suggest cease-fire • 1953 armistice: Korea still divided and demilitarized zone established. • Lack of success, high human and financial costs help Eisenhower beat Truman in next election.
The Korean War • 1951 Soviets suggest cease-fire • 1953 armistice: Korea still divided and demilitarized zone established. • Lack of success, high human and financial costs help Eisenhower beat Truman in next election.
 Section 3: The Cold War at home • Americans fear Communist takeover in Eastern Europe and China. Spreads fear. • 100, 000 people in U. S. Communist Party, fear some may be loyal to U. S. S. R.
Section 3: The Cold War at home • Americans fear Communist takeover in Eastern Europe and China. Spreads fear. • 100, 000 people in U. S. Communist Party, fear some may be loyal to U. S. S. R.
 Loyalty Review Board • Truman accused of being soft on Communism. • Sets up Federal Employee Loyalty Program to investigate employees. • 1947 -1951 loyalty boards investigate 3. 2 million, dismiss 212.
Loyalty Review Board • Truman accused of being soft on Communism. • Sets up Federal Employee Loyalty Program to investigate employees. • 1947 -1951 loyalty boards investigate 3. 2 million, dismiss 212.
 House Un-American Activities Committee • Investigates Communist ties, especially in movie industry. • Hollywood ten refuse to testify, are sent to prison. • Hollywood blacklist— people with Communist ties, cannot get work.
House Un-American Activities Committee • Investigates Communist ties, especially in movie industry. • Hollywood ten refuse to testify, are sent to prison. • Hollywood blacklist— people with Communist ties, cannot get work.
 Spy Cases in the U. S. • Alger Hiss-Accused of spying for Soviet Union. Convicted of perjury (lying in court). • Rosenburgs: – Soviet union explodes atomic bomb sooner than expected in 1949. – Physicist Klaus Fuchs admits giving information about U. S. bomb. – Ethel, Julius Rosenberg (minor Communist party activists) implicated and convicted. Sentenced to death. The Rosenbergs
Spy Cases in the U. S. • Alger Hiss-Accused of spying for Soviet Union. Convicted of perjury (lying in court). • Rosenburgs: – Soviet union explodes atomic bomb sooner than expected in 1949. – Physicist Klaus Fuchs admits giving information about U. S. bomb. – Ethel, Julius Rosenberg (minor Communist party activists) implicated and convicted. Sentenced to death. The Rosenbergs
 Mc. Carthyism • Senator Joseph Mc. Carthy strong anti-Communist activist. • Needs successful issue to win reelection. • Mc. Carthyism—attacking suspected Communists without evidence. • Mc. Carthy accuses members of state department and U. S. Army. • Televised hearings show him bullying witnesses. • Loses public support.
Mc. Carthyism • Senator Joseph Mc. Carthy strong anti-Communist activist. • Needs successful issue to win reelection. • Mc. Carthyism—attacking suspected Communists without evidence. • Mc. Carthy accuses members of state department and U. S. Army. • Televised hearings show him bullying witnesses. • Loses public support.
 Anti-Communist Measures • States and towns forbid speech favoring violent overthrow of government. • Millions forced to take loyalty oaths and are investigated. • People become afraid to speak out on public issues.
Anti-Communist Measures • States and towns forbid speech favoring violent overthrow of government. • Millions forced to take loyalty oaths and are investigated. • People become afraid to speak out on public issues.
 Section 4: Two Nations Live on the Edge • During the 1950 s, the U. S. and Soviet Union come to the brink of nuclear war. • Race for the H-bomb: – Hydrogen bomb: nuclear weapon more powerful than the atomic bomb. – 1952 U. S. explodes first H-bomb. 1953 Soviets explode one.
Section 4: Two Nations Live on the Edge • During the 1950 s, the U. S. and Soviet Union come to the brink of nuclear war. • Race for the H-bomb: – Hydrogen bomb: nuclear weapon more powerful than the atomic bomb. – 1952 U. S. explodes first H-bomb. 1953 Soviets explode one.
 Brinkmanship • John Foster Dulles (Eisenhower’s secretary of state) proposes brinkmanship: – Willingness to risk nuclear war to prevent the spread of communism. • The nation prepares for the threat of nuclear war. • Millions can die in nuclear war occurs. Soviet Premier Nikita Kruschev and President John F. Kennedy
Brinkmanship • John Foster Dulles (Eisenhower’s secretary of state) proposes brinkmanship: – Willingness to risk nuclear war to prevent the spread of communism. • The nation prepares for the threat of nuclear war. • Millions can die in nuclear war occurs. Soviet Premier Nikita Kruschev and President John F. Kennedy
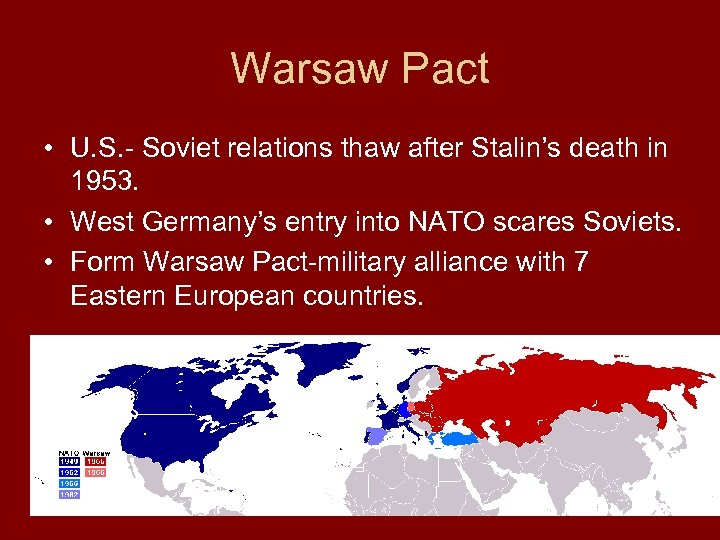 Warsaw Pact • U. S. - Soviet relations thaw after Stalin’s death in 1953. • West Germany’s entry into NATO scares Soviets. • Form Warsaw Pact-military alliance with 7 Eastern European countries.
Warsaw Pact • U. S. - Soviet relations thaw after Stalin’s death in 1953. • West Germany’s entry into NATO scares Soviets. • Form Warsaw Pact-military alliance with 7 Eastern European countries.
 Summit in Geneva • Eisenhower meets Soviets in Geneva, proposes “open sky” policy. • Soviets reject proposal • “Spirit of Geneva” seen as a step toward peace. Eisenhower Doctrine • Doctrine that the U. S. will defend Middle East against Communists. President Dwight “Ike” Eisenhower
Summit in Geneva • Eisenhower meets Soviets in Geneva, proposes “open sky” policy. • Soviets reject proposal • “Spirit of Geneva” seen as a step toward peace. Eisenhower Doctrine • Doctrine that the U. S. will defend Middle East against Communists. President Dwight “Ike” Eisenhower
 Hungarian Uprising • 1956 Hungarians revolt. Want a democratic government. • Imre Nagy, Communist leader, forms government, promises elections. • Soviet army fights Hungarians in the streets and overthrows Nagy. • U. S. does not help Hungary, Soviet Union vetos any action by the U. N.
Hungarian Uprising • 1956 Hungarians revolt. Want a democratic government. • Imre Nagy, Communist leader, forms government, promises elections. • Soviet army fights Hungarians in the streets and overthrows Nagy. • U. S. does not help Hungary, Soviet Union vetos any action by the U. N.
 Nikita Krushchev • Emerges as new Soviet leader. • Favors peaceful coexistence and economic, scientific competition
Nikita Krushchev • Emerges as new Soviet leader. • Favors peaceful coexistence and economic, scientific competition
 Space Race • 1957 Soviets launch Sputnik, the first artificial satellite. • Shocked Americans pour money into the space program. Sputnik
Space Race • 1957 Soviets launch Sputnik, the first artificial satellite. • Shocked Americans pour money into the space program. Sputnik
 U-2 Spy Plane Shot Down • CIA makes secret high-altitude flights to spy on Soviets. • Eisenhower wants flights discontinued before summit with Krushchev. • Francis Gary Powers Shot down on last flight over Soviet territory.
U-2 Spy Plane Shot Down • CIA makes secret high-altitude flights to spy on Soviets. • Eisenhower wants flights discontinued before summit with Krushchev. • Francis Gary Powers Shot down on last flight over Soviet territory.
 Renewed Confrontation • Eisenhower first denies, then concedes the U-2 was spying. • Agrees to stop flights, but refuses to apologize as Krushchev demands • U-2 incident renews tension between U. S. and Soviet Union. • Summit with Krushchev cancelled. Back to this again
Renewed Confrontation • Eisenhower first denies, then concedes the U-2 was spying. • Agrees to stop flights, but refuses to apologize as Krushchev demands • U-2 incident renews tension between U. S. and Soviet Union. • Summit with Krushchev cancelled. Back to this again


