af191cae8ca3d2e677baac54f05eb558.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 5
 Ch. 12 -----Ch. 15 Term 052
Ch. 12 -----Ch. 15 Term 052
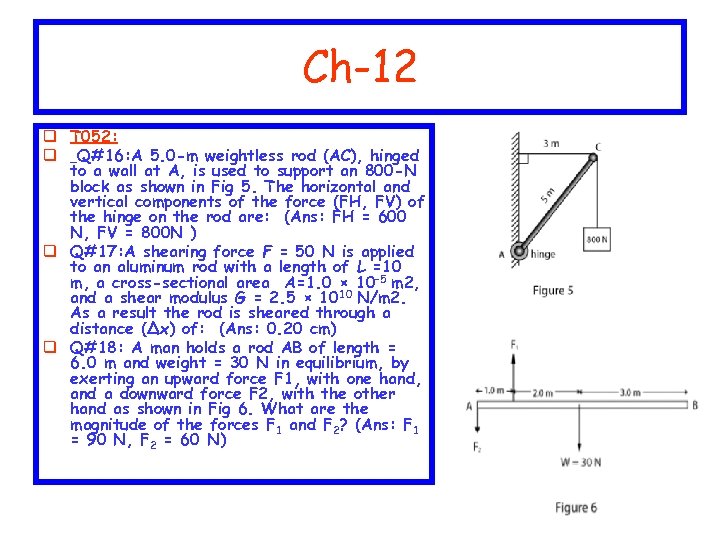 Ch-12 q T 052: q Q#16: A 5. 0 -m weightless rod (AC), hinged to a wall at A, is used to support an 800 -N block as shown in Fig 5. The horizontal and vertical components of the force (FH, FV) of the hinge on the rod are: (Ans: FH = 600 N, FV = 800 N ) q Q#17: A shearing force F = 50 N is applied to an aluminum rod with a length of L =10 m, a cross-sectional area A=1. 0 × 10– 5 m 2, and a shear modulus G = 2. 5 × 1010 N/m 2. As a result the rod is sheared through a distance (Δx) of: (Ans: 0. 20 cm) q Q#18: A man holds a rod AB of length = 6. 0 m and weight = 30 N in equilibrium, by exerting an upward force F 1, with one hand, and a downward force F 2, with the other hand as shown in Fig 6. What are the magnitude of the forces F 1 and F 2? (Ans: F 1 = 90 N, F 2 = 60 N)
Ch-12 q T 052: q Q#16: A 5. 0 -m weightless rod (AC), hinged to a wall at A, is used to support an 800 -N block as shown in Fig 5. The horizontal and vertical components of the force (FH, FV) of the hinge on the rod are: (Ans: FH = 600 N, FV = 800 N ) q Q#17: A shearing force F = 50 N is applied to an aluminum rod with a length of L =10 m, a cross-sectional area A=1. 0 × 10– 5 m 2, and a shear modulus G = 2. 5 × 1010 N/m 2. As a result the rod is sheared through a distance (Δx) of: (Ans: 0. 20 cm) q Q#18: A man holds a rod AB of length = 6. 0 m and weight = 30 N in equilibrium, by exerting an upward force F 1, with one hand, and a downward force F 2, with the other hand as shown in Fig 6. What are the magnitude of the forces F 1 and F 2? (Ans: F 1 = 90 N, F 2 = 60 N)
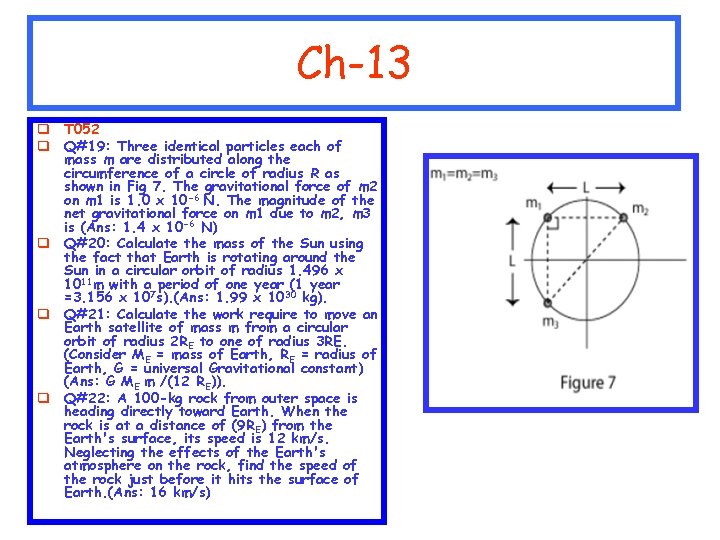 Ch-13 q T 052 q Q#19: Three identical particles each of mass m are distributed along the circumference of a circle of radius R as shown in Fig 7. The gravitational force of m 2 on m 1 is 1. 0 x 10 -6 N. The magnitude of the net gravitational force on m 1 due to m 2, m 3 is (Ans: 1. 4 x 10 -6 N) q Q#20: Calculate the mass of the Sun using the fact that Earth is rotating around the Sun in a circular orbit of radius 1. 496 x 1011 m with a period of one year (1 year =3. 156 x 107 s). (Ans: 1. 99 x 1030 kg). q Q#21: Calculate the work require to move an Earth satellite of mass m from a circular orbit of radius 2 RE to one of radius 3 RE. (Consider ME = mass of Earth, RE = radius of Earth, G = universal Gravitational constant) (Ans: G ME m /(12 RE)). q Q#22: A 100 -kg rock from outer space is heading directly toward Earth. When the rock is at a distance of (9 RE) from the Earth's surface, its speed is 12 km/s. Neglecting the effects of the Earth's atmosphere on the rock, find the speed of the rock just before it hits the surface of Earth. (Ans: 16 km/s)
Ch-13 q T 052 q Q#19: Three identical particles each of mass m are distributed along the circumference of a circle of radius R as shown in Fig 7. The gravitational force of m 2 on m 1 is 1. 0 x 10 -6 N. The magnitude of the net gravitational force on m 1 due to m 2, m 3 is (Ans: 1. 4 x 10 -6 N) q Q#20: Calculate the mass of the Sun using the fact that Earth is rotating around the Sun in a circular orbit of radius 1. 496 x 1011 m with a period of one year (1 year =3. 156 x 107 s). (Ans: 1. 99 x 1030 kg). q Q#21: Calculate the work require to move an Earth satellite of mass m from a circular orbit of radius 2 RE to one of radius 3 RE. (Consider ME = mass of Earth, RE = radius of Earth, G = universal Gravitational constant) (Ans: G ME m /(12 RE)). q Q#22: A 100 -kg rock from outer space is heading directly toward Earth. When the rock is at a distance of (9 RE) from the Earth's surface, its speed is 12 km/s. Neglecting the effects of the Earth's atmosphere on the rock, find the speed of the rock just before it hits the surface of Earth. (Ans: 16 km/s)
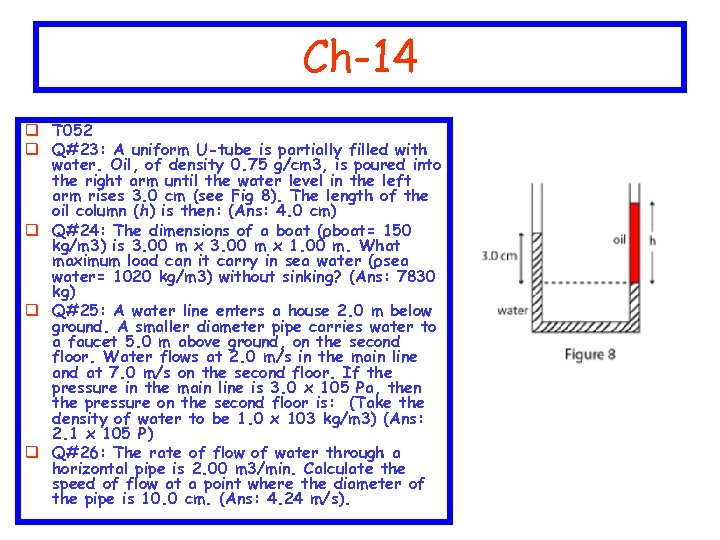 Ch-14 q T 052 q Q#23: A uniform U-tube is partially filled with water. Oil, of density 0. 75 g/cm 3, is poured into the right arm until the water level in the left arm rises 3. 0 cm (see Fig 8). The length of the oil column (h) is then: (Ans: 4. 0 cm) q Q#24: The dimensions of a boat (ρboat= 150 kg/m 3) is 3. 00 m x 1. 00 m. What maximum load can it carry in sea water (ρsea water= 1020 kg/m 3) without sinking? (Ans: 7830 kg) q Q#25: A water line enters a house 2. 0 m below ground. A smaller diameter pipe carries water to a faucet 5. 0 m above ground, on the second floor. Water flows at 2. 0 m/s in the main line and at 7. 0 m/s on the second floor. If the pressure in the main line is 3. 0 x 105 Pa, then the pressure on the second floor is: (Take the density of water to be 1. 0 x 103 kg/m 3) (Ans: 2. 1 x 105 P) q Q#26: The rate of flow of water through a horizontal pipe is 2. 00 m 3/min. Calculate the speed of flow at a point where the diameter of the pipe is 10. 0 cm. (Ans: 4. 24 m/s).
Ch-14 q T 052 q Q#23: A uniform U-tube is partially filled with water. Oil, of density 0. 75 g/cm 3, is poured into the right arm until the water level in the left arm rises 3. 0 cm (see Fig 8). The length of the oil column (h) is then: (Ans: 4. 0 cm) q Q#24: The dimensions of a boat (ρboat= 150 kg/m 3) is 3. 00 m x 1. 00 m. What maximum load can it carry in sea water (ρsea water= 1020 kg/m 3) without sinking? (Ans: 7830 kg) q Q#25: A water line enters a house 2. 0 m below ground. A smaller diameter pipe carries water to a faucet 5. 0 m above ground, on the second floor. Water flows at 2. 0 m/s in the main line and at 7. 0 m/s on the second floor. If the pressure in the main line is 3. 0 x 105 Pa, then the pressure on the second floor is: (Take the density of water to be 1. 0 x 103 kg/m 3) (Ans: 2. 1 x 105 P) q Q#26: The rate of flow of water through a horizontal pipe is 2. 00 m 3/min. Calculate the speed of flow at a point where the diameter of the pipe is 10. 0 cm. (Ans: 4. 24 m/s).
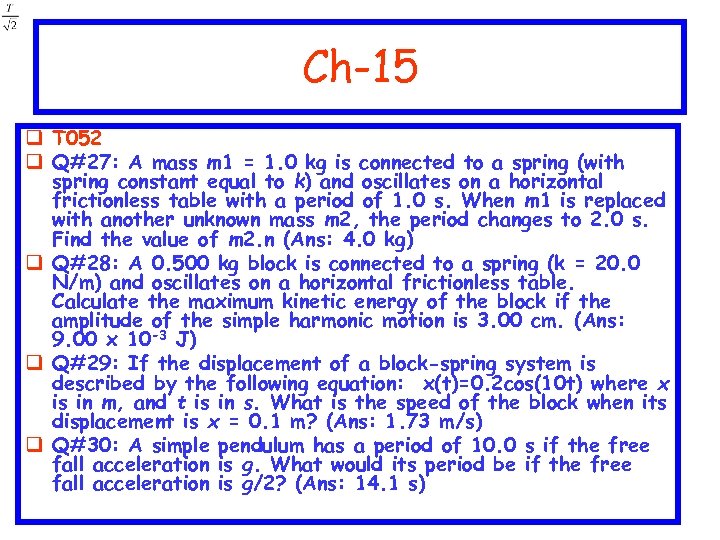 Ch-15 q T 052 q Q#27: A mass m 1 = 1. 0 kg is connected to a spring (with spring constant equal to k) and oscillates on a horizontal frictionless table with a period of 1. 0 s. When m 1 is replaced with another unknown mass m 2, the period changes to 2. 0 s. Find the value of m 2. n (Ans: 4. 0 kg) q Q#28: A 0. 500 kg block is connected to a spring (k = 20. 0 N/m) and oscillates on a horizontal frictionless table. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the block if the amplitude of the simple harmonic motion is 3. 00 cm. (Ans: 9. 00 x 10 -3 J) q Q#29: If the displacement of a block-spring system is described by the following equation: x(t)=0. 2 cos(10 t) where x is in m, and t is in s. What is the speed of the block when its displacement is x = 0. 1 m? (Ans: 1. 73 m/s) q Q#30: A simple pendulum has a period of 10. 0 s if the free fall acceleration is g. What would its period be if the free fall acceleration is g/2? (Ans: 14. 1 s)
Ch-15 q T 052 q Q#27: A mass m 1 = 1. 0 kg is connected to a spring (with spring constant equal to k) and oscillates on a horizontal frictionless table with a period of 1. 0 s. When m 1 is replaced with another unknown mass m 2, the period changes to 2. 0 s. Find the value of m 2. n (Ans: 4. 0 kg) q Q#28: A 0. 500 kg block is connected to a spring (k = 20. 0 N/m) and oscillates on a horizontal frictionless table. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the block if the amplitude of the simple harmonic motion is 3. 00 cm. (Ans: 9. 00 x 10 -3 J) q Q#29: If the displacement of a block-spring system is described by the following equation: x(t)=0. 2 cos(10 t) where x is in m, and t is in s. What is the speed of the block when its displacement is x = 0. 1 m? (Ans: 1. 73 m/s) q Q#30: A simple pendulum has a period of 10. 0 s if the free fall acceleration is g. What would its period be if the free fall acceleration is g/2? (Ans: 14. 1 s)


