8d9005273a06424a1b9db23f3434f22b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59

CH 1: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS (Reference Book: Computers for Nursing by S. Y. Vaishampayan) Vaishampayan

CONTENTS: q 1. 1 Introduction q 1. 2 Characteristics q 1. 3 Block Diagram

1. 1 Introduction:

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) o Dfn: • Computer is a machine made up of electronic devices to process data. o The word ‘Computer’ is formed from the verb “compute”. o Computers were “huge special purpose machines”. o These machines were used for ‘complex numerical tasks’.

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) o All these machines can carry out logical & mathematical action & can decide further action. o Computers play a very important role in the progress of science and technology. o Computers are widely used in the fields of: § Business, Medicine, Health Care, Engineering, Manufacturing, Government, Music, Entertainment, Banking, Defense, Research and Share Market.

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Business: (Pictures)

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Medicine:

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Health Care:

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Engineering :

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Manufacturing :

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Government:
1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Music:

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Entertainment:

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Banking:

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Defense:

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Research:

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use Of Computers in Share Market:

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use of Computers in Medical Science: i. Medical Aid by means of hospitals is not possible in remote and rural areas, due to insufficient human resource. • Hence, well equipped Mobile hospitals can be used for medical help camps in the remote and rural areas. ii. The use of computers in medical science is essential.

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use of Computers in Medical Science: (contd. . ): iii. Many useful machines are developed to help medical diagnosis & treatment. Such as: – X-Ray Machine – ECG – Sonography – CT Scan – 2 D Doppler etc.

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use of Computers in Medical Science: (contd. . ): iv. Many Statistical Packages and Hospital Management Systems are developed. • They are very useful and used in many hospitals. • The websites like www. csmpl. com, www. quasarit. com, gives the idea of the hospital management system. • These systems are very useful, for all departments and all resources management. • The retrieval of the information is very fast and helps a lot for the health care of the patient.
1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use of Computers in Medical Science: (contd. . ): v. Hospital Management System softwares are used for registration of patient, when he is admitted to hospital, all other administrative work, billing up to discharge of patient, report generation. • These softwares are also useful for Data Base management for Parma center, blood bank etc.

1. 1 Introduction: (Contd. . ) • Use of Computers in Medical Science: (contd. . ):

1. 2 Characteristics: – Computers are used to help man make complex and difficult intellectual task simple and fast. – Computers are used widely in many applications due to the following characteristics: A. Automation: B. Speed: C. Accuracy: D. Continuity: E. Memory:

1. 2 Characteristics: (contd. . ) – Computers are used widely in many applications due to the following characteristics: (Contd. . ) F. Storage Power: G. Versatility: H. Reliability: I. Micro-Size: J. Thoughtless or Emotion less:
A. Automation: • An operator operates different parts of a machine in the typical sequence of steps to perform the work. • For example, while moving along curved road the handle of a bicycle is turned first and then it is made straight to move along the straight road. There is no automation in this process. • Scientist, Engineers are trying for automation from many years as it is the nature of the man. • Today we use many automatic machines. The best example is of ATM (AUTOMATED TELLER MACHINE).
A. Automation: (contd. . ) • In this, when a person withdraws amount from ATM centre, ATM machine counts exact denomination, notes come out of the machine, its proper entry is made in persons account and even person gets printout of his balance amount statement. • All these steps are automated. Such type of complex, crucial work can be automated by computer.

A. Automation: (contd. . ) • ATM : (Picture)
B. Speed: • The speed of execution of commands of the computer is tremendous. Computers are popular mainly due its speed. • The speed of calculation of a computer is so high that it can perform millions of operations per second. • Suppose for a certain task, the processing and calculations is carried by more than thousand people, i. e. few thousand man hours required.

B. Speed: (contd. . ) • The same can be completed by a suitable computer within a minute. • The speed of a computer is considered as computers power. • The speed of the computer mainly depends on CPU (central processing unit).

B. Speed: (contd. . ) • Speed (Picture):

C. Accuracy: • All computers process up to desired precision according to the requirement. • In case of analog computers computer accuracy is up to 9 parts out of 10 to 9999 parts out of 10000 i. e. 90% to 99. 9999%. • These analog computers mainly work on counting process, accuracy more than this is not possible.

C. Accuracy: (contd. . ) • Accuracy (Picture):

D. Continuity: • Most of the instruments do not have continuity in their processes due to wear and tear. • The saw will not have continuity in cutting because its edge becomes blunt and it is not as sharp as in beginning, hence the process of cutting with same speed will not be continued. • In case of computers, continuity is observed, provided there are no changes in it. • It will continue process for ever with the same speed till there is power.

D. Continuity: (contd. . ) • Continuity (Picture):

E. Memory: • Memory is the important characteristic of a computer. • Programs are loaded into and run from memory. Data used by program is also loaded into memory for fast access. • Memory of a computer can increase the speed of a computer. • A standard personal computer can store about 32 million of alphabets i. e. Say 10000 pages in its memory. • Some other computers designed for special purpose can have 100 times greater memory. • In case of other machines, they can store 1 page in memory.

E. Memory: (contd. . ) • Memory (Picture):

F. Storage Power: • One can have notes on paper for reference or as reminder. • Similarly computers use storage media. • Such media are called storage devices like diskette, hard disk, CD ROM drive. • They can easily store about 3, 000 pages information. This storage capacity is very vast.

F. Storage Power: (contd. . ) • Storage Power (Picture):

G. Versatility: • Computers are creative tools for musicians. • Motion pictures industry uses computers for special effects. • Actions of robot are controlled by a computer; engineering work like CAD is very useful. • In short computer can be used for multimedia, mathematical calculations, engineering design and many more which tells it’s about versatility.

G. Versatility: (contd. . ) • Versatility (Picture):
H. Reliability: • A computer is reliable machine. • It works non-stop and accurately till there is power supply to it. • The mistakes in the execution are not due to computer but due to improper assembly or architecture and/or wrong programming. • The reliability of the computer is obtained by systematic approach in its architecture, mechanism and design.
H. Reliability: (contd. . ) • Reliability (Picture):

I. Micro-Size: • Now days the nano technology is very important. Nano means miniature. • From the point of number system nano means 109, means one part of 10000, 000.

I. Micro-Size: (contd. . ) • Micro-Size (Picture):

J. Thoughtless or Emotion less: • A computer is an electronic device. • It is not intelligent like a man. • It cannot think and it has no emotions. • Decisions given by a computer is not because of its own thought process, but it works according to the instruction given by the programmer. • Scientist are trying to develop a computer which will have its own though process. • In other words scientists are developing Artificial Intelligence like human beings.

J. Thoughtless or Emotion less: (contd. . ) • Thoughtless or Emotion less (Picture):
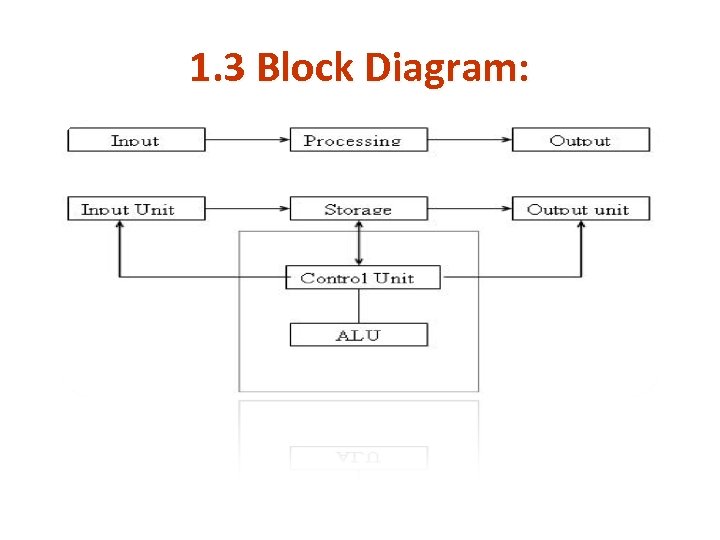
1. 3 Block Diagram:

1. 3 Block Diagram: Explanation 1. The control unit and ALU of the computer are together known as the Central Processing Unit (CPU). 2. All calculations are performed in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) of the computer. 3. Control Unit controls all other units in the computer.
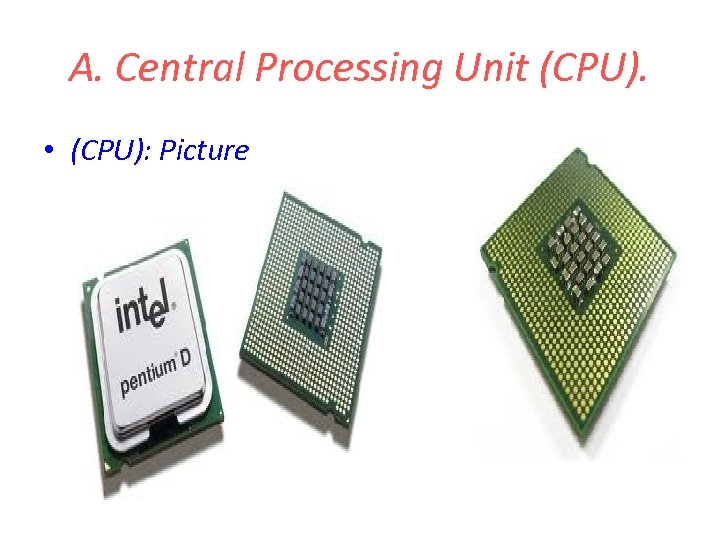
A. Central Processing Unit (CPU). • (CPU): Picture
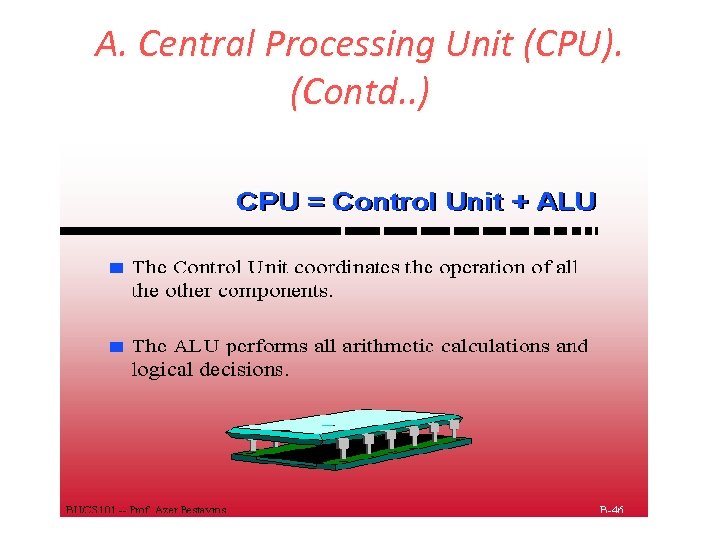
A. Central Processing Unit (CPU). (Contd. . )
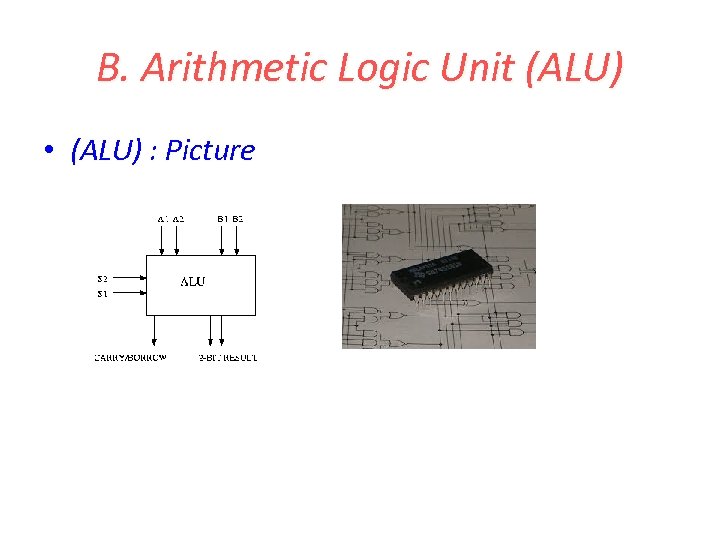
B. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) • (ALU) : Picture
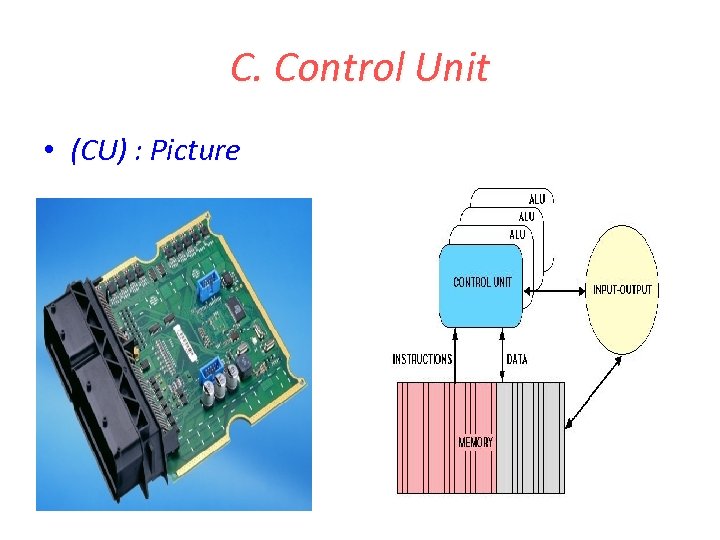
C. Control Unit • (CU) : Picture
1. 3 Block Diagram: Explanation (contd. . ) 4. The Storage Unit of the computer holds data and instructions that are entered through the input unit, before they are processed. • It preserves the intermediate and final results before these are sent to the output devices.
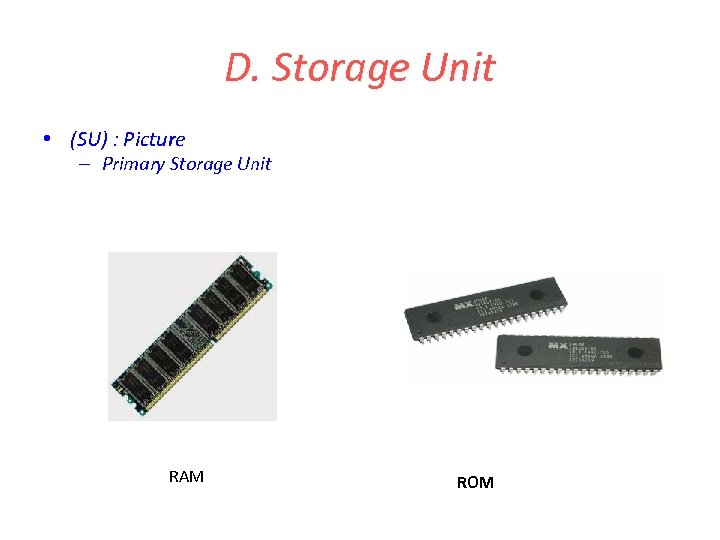
D. Storage Unit • (SU) : Picture – Primary Storage Unit RAM ROM

D. Storage Unit (contd. . ) • SU) : Picture – Secondary Storage Unit Hard Disk CD-ROM
1. 3 Block Diagram: Explanation (contd. . ) 5. Computers need to receive data and instruction in order to solve any problem. • Therefore we need to input the data and instructions into the computers. • These are done through the Input Unit. E. g. : Keyboard, Mouse, Floppy Disk Drive, Magnetic Tape, Scanners etc

E. Input Unit • (IU) : Picture

1. 3 Block Diagram: Explanation (contd. . ) 6. The Output Unit of a computer provides the information and results of a computation to outside world. • For Example: CRT & LCD Monitors, Printer, Plotters, & Speakers.

F. Output Unit • (OU) : Picture
8d9005273a06424a1b9db23f3434f22b.ppt