4fa26064f22fd0f5d7de064a68defb4e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

CFD-based Liquid Flow Calculations for Modular Sample Systems John J. Wawrowski Swagelok Solon, Ohio IFPAC 2004 Arlington, Virginia January 12 -15, 2004 © Swagelok Company, 2004

Agenda Review of Previous Work Flow Testing Description Flow Testing Results Is a larger standard required? Important Considerations Conclusions © Swagelok Company, 2004
Previous Work Studied The flow capacity (Cv) of a three-position Swagelok MPC system The effects of using different surface-mount components on the total system Cv An analytical method for predicting the total system Cv The effect of the fluid type on the pressure drop through a substrate flow component The pressure required for a liquid sample to flow through a three-position Swagelok MPC system © Swagelok Company, 2004
Previous Work Results Created and validated a mathematical model for predicting flow capacity of a Swagelok MPC system The surface-mount component has the largest effect on total system Cv Developed a valid equation for predicting pressure to drive liquids Based on kinematic viscosity MPC requires minimal driving pressure © Swagelok Company, 2004
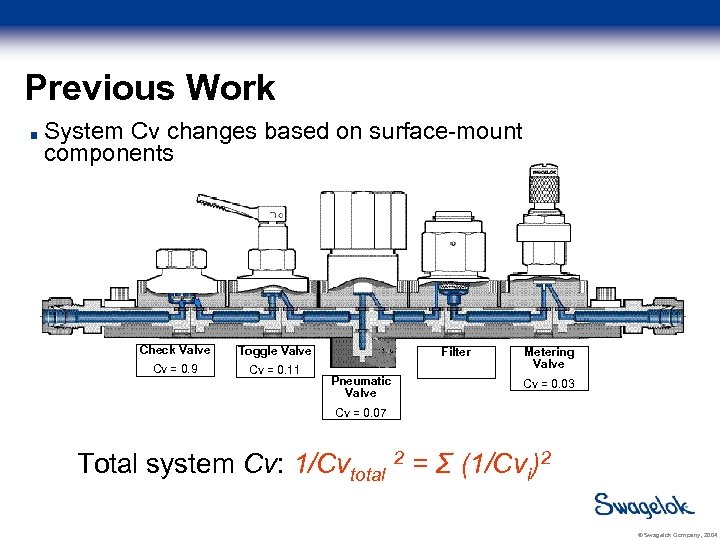
Previous Work System Cv changes based on surface-mount components Check Valve Toggle Valve Cv = 0. 9 Cv = 0. 11 Filter Pneumatic Valve Metering Valve Cv = 0. 03 Cv = 0. 07 Total system Cv: 1/Cvtotal 2 = Σ (1/Cvi)2 © Swagelok Company, 2004
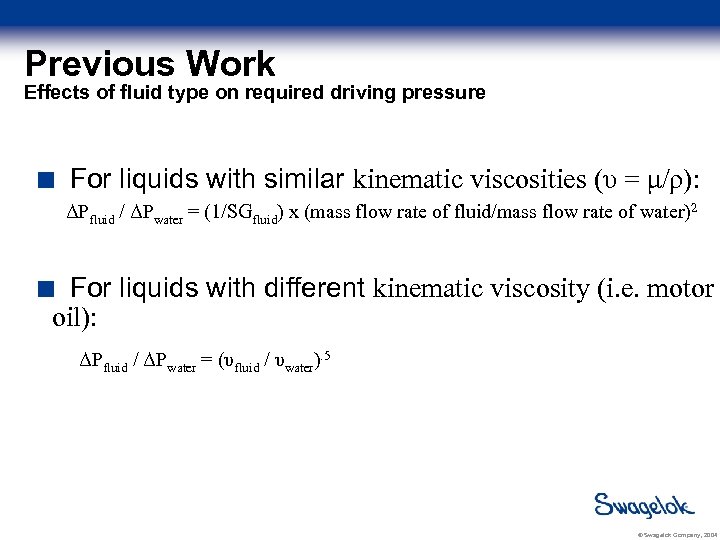
Previous Work Effects of fluid type on required driving pressure For liquids with similar kinematic viscosities (υ = μ/ρ): ΔPfluid / ΔPwater = (1/SGfluid) x (mass flow rate of fluid/mass flow rate of water)2 For liquids with different kinematic viscosity (i. e. motor oil): ΔPfluid / ΔPwater = (υfluid / υwater). 5 © Swagelok Company, 2004
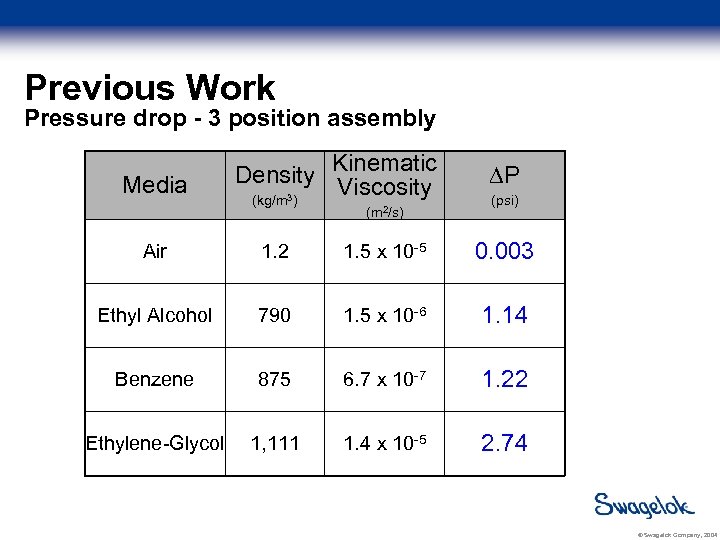
Previous Work Pressure drop - 3 position assembly Media Density (kg/m 3) Kinematic Viscosity (m 2/s) P (psi) Air 1. 2 1. 5 x 10 -5 0. 003 Ethyl Alcohol 790 1. 5 x 10 -6 1. 14 Benzene 875 6. 7 x 10 -7 1. 22 Ethylene-Glycol 1, 111 1. 4 x 10 -5 2. 74 © Swagelok Company, 2004
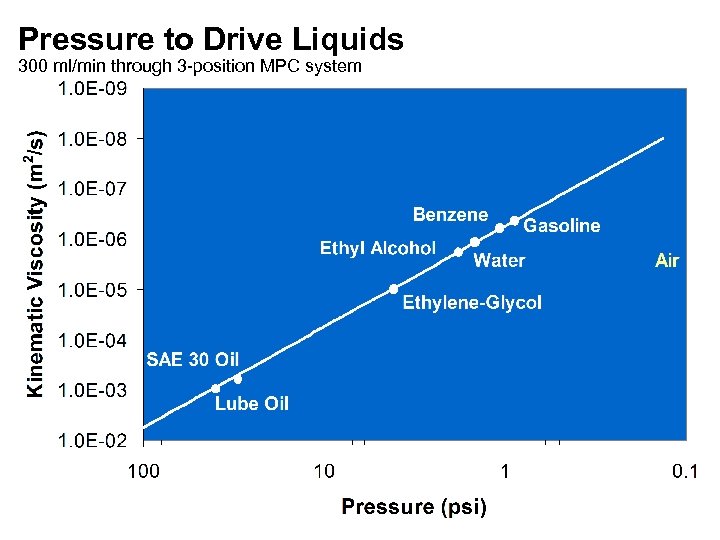
Pressure to Drive Liquids 300 ml/min through 3 -position MPC system

New Testing Re-tested original three-position system Nine-position system Stream Selector valve included Ethylene-Glycol and 10 W-30 Oil Determine pressure required to achieve 300 cc/min Tested by an independent third party © Swagelok Company, 2004
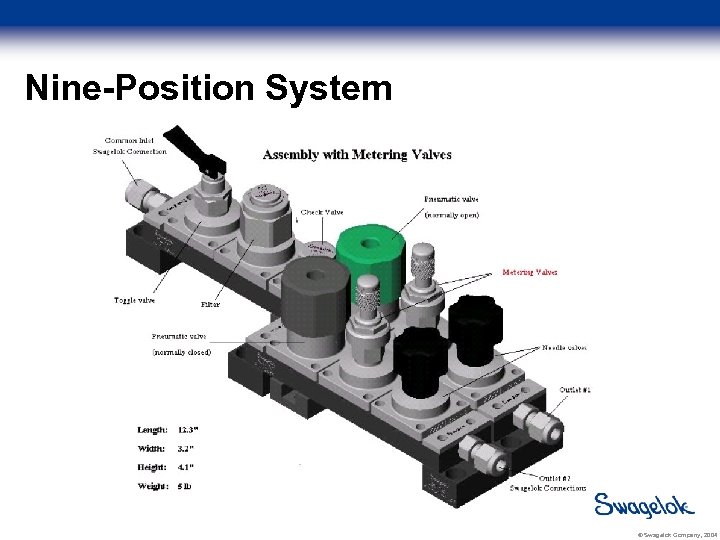
Nine-Position System © Swagelok Company, 2004
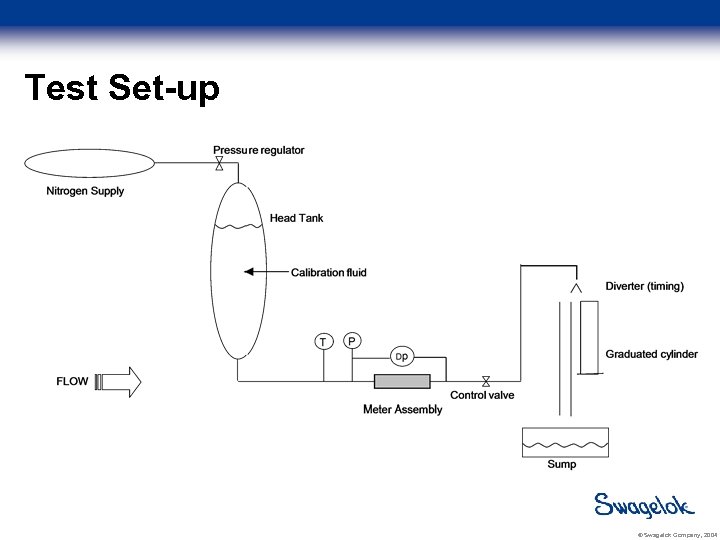
Test Set-up © Swagelok Company, 2004
Preliminary Results Drive pressure to achieve 300 cc/min Ethylene Glycol 3 -position system: 10 psig 9 -position system: 20+ psig Depending on metering valve position 10 W-30 Oil 3 -position system: 30 psig 9 -position system: 40+ psig © Swagelok Company, 2004

New Standard Needed? Component with the lowest Cv has the greatest affect on the total system Cv Surface mount components on the market have the same Cv’s as their traditional configurations Stream Select Valve Needle Valves Filters Check and Relief Valves 0. 1 is typical © Swagelok Company, 2004
Important Considerations Regardless of the size of the flow passages, all sample systems will eventually need to be maintained Plugging Corrosion Leakage You should choose a substrate design that facilitates fast, easy maintenance or expansion Replace or add components without disassembly or removal of the entire system Convenient access to internal components Fewest number of o-rings Ease the burden on instrument and maintenance technicians Lower cost of spare parts © Swagelok Company, 2004

Wrap-Up Please visit us in Booth 315/317 Automated System Demonstration p. H and conductivity sensor array Laboratory GC carrier gas metering system New surface-mount components Regulator Solenoid Valve p. H and conductivity sensors Discuss the topics presented © Swagelok Company, 2004

4fa26064f22fd0f5d7de064a68defb4e.ppt