aa637b45b16f46a76eb8813f164a06c1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Certainty comes from the courage to follow uncertain paths Business Model Design Tarek Fahim
Certainty comes from the courage to follow uncertain paths Business Model Design Tarek Fahim
 Breaking the ICE Tarek Fahim 1
Breaking the ICE Tarek Fahim 1
 Iqbal Quadir Had a Dream Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Tarek Fahim 2
Iqbal Quadir Had a Dream Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Tarek Fahim 2
 Achieving the Dream Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Tarek Fahim 3
Achieving the Dream Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Tarek Fahim 3
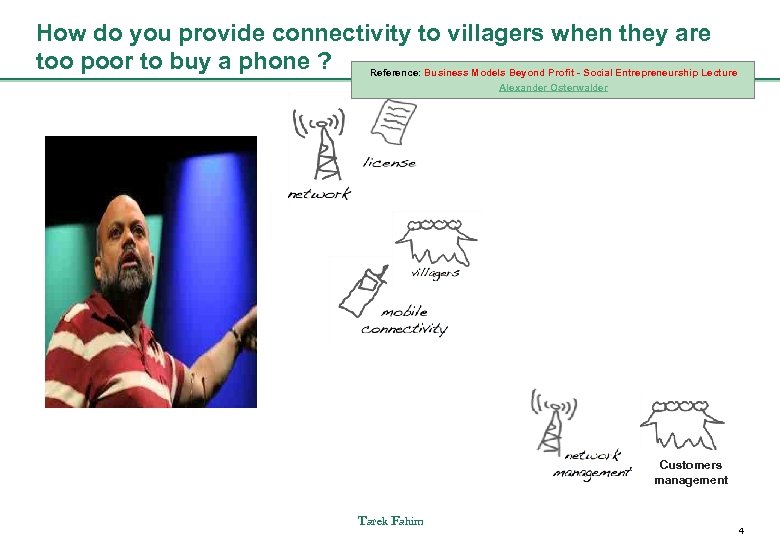 How do you provide connectivity to villagers when they are too poor to buy a phone ? Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Customers management Tarek Fahim 4
How do you provide connectivity to villagers when they are too poor to buy a phone ? Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Customers management Tarek Fahim 4
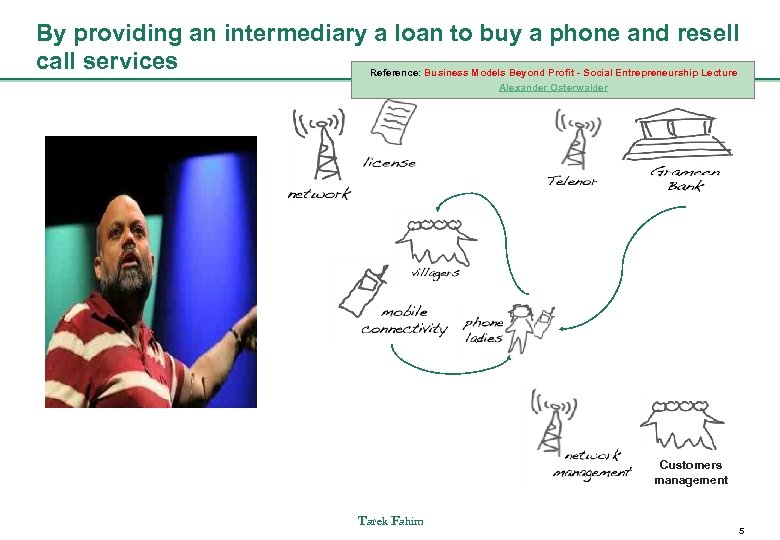 By providing an intermediary a loan to buy a phone and resell call services Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Customers management Tarek Fahim 5
By providing an intermediary a loan to buy a phone and resell call services Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Customers management Tarek Fahim 5
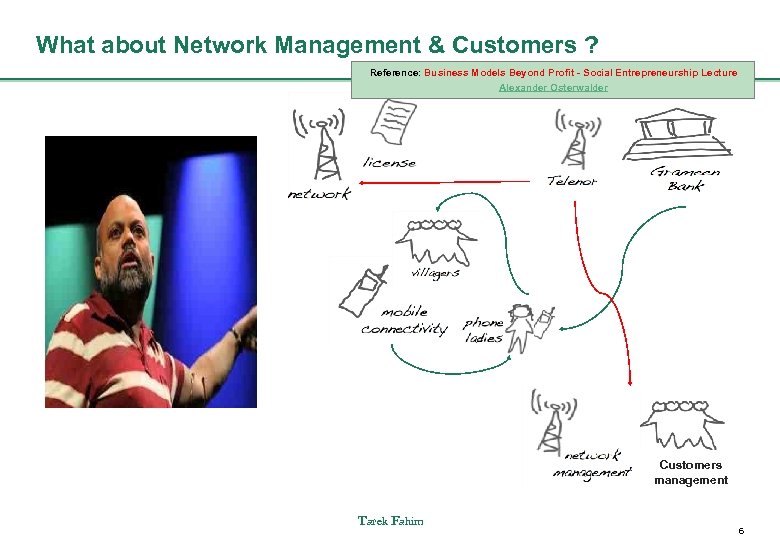 What about Network Management & Customers ? Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Customers management Tarek Fahim 6
What about Network Management & Customers ? Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Customers management Tarek Fahim 6
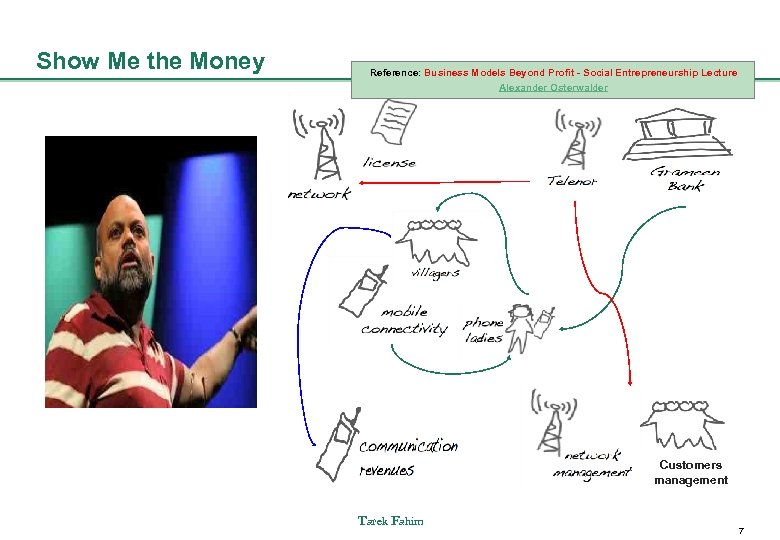 Show Me the Money Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Customers management Tarek Fahim 7
Show Me the Money Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Customers management Tarek Fahim 7
 Achieving the Dream Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Tarek Fahim 8
Achieving the Dream Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Tarek Fahim 8
 Rashmi, 24 Bangladeshi village phone lady 2 -3 $ daily income Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder • There about 250ʼ 000 women retailing telephone services in 60ʼ 000 villages giving access to about 100 million people • The 250ʼ 000 telephones are producing revenues at an annual rate of well over $100 million for Grameen. Phone • Each entrepreneur makes about $2 in profits per day or about $700 per year • $50 million net profit for Grameen. Phone Tarek Fahim 9
Rashmi, 24 Bangladeshi village phone lady 2 -3 $ daily income Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder • There about 250ʼ 000 women retailing telephone services in 60ʼ 000 villages giving access to about 100 million people • The 250ʼ 000 telephones are producing revenues at an annual rate of well over $100 million for Grameen. Phone • Each entrepreneur makes about $2 in profits per day or about $700 per year • $50 million net profit for Grameen. Phone Tarek Fahim 9
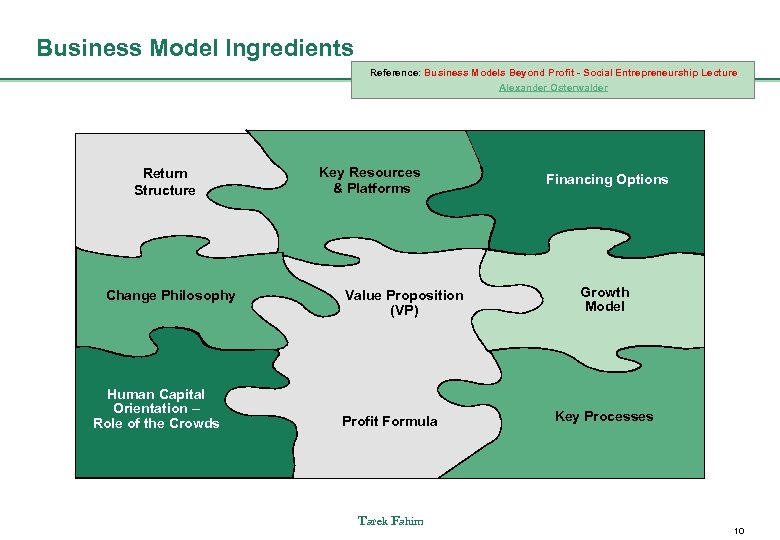 Business Model Ingredients Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Return Structure Change Philosophy Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Key Resources & Platforms Value Proposition (VP) Profit Formula Tarek Fahim Financing Options Growth Model Key Processes 10
Business Model Ingredients Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder Return Structure Change Philosophy Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Key Resources & Platforms Value Proposition (VP) Profit Formula Tarek Fahim Financing Options Growth Model Key Processes 10
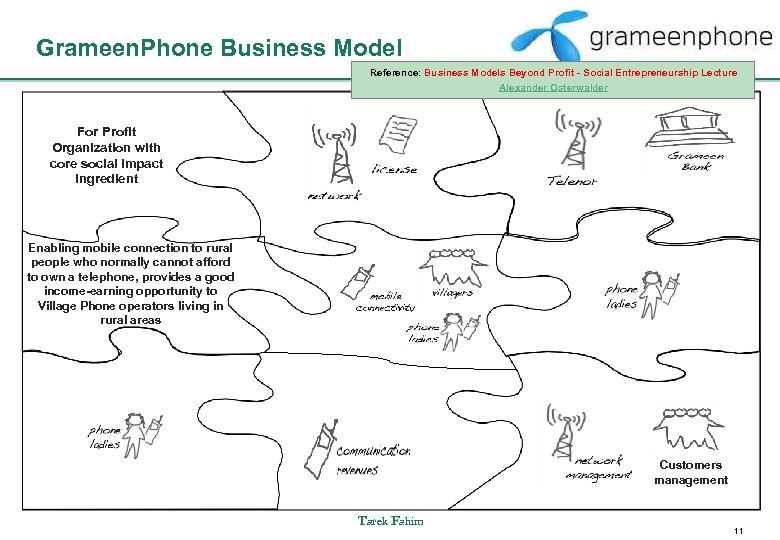 Grameen. Phone Business Model Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder For Profit Organization with core social impact ingredient Enabling mobile connection to rural people who normally cannot afford to own a telephone, provides a good income-earning opportunity to Village Phone operators living in rural areas Customers management Tarek Fahim 11
Grameen. Phone Business Model Reference: Business Models Beyond Profit - Social Entrepreneurship Lecture Alexander Osterwalder For Profit Organization with core social impact ingredient Enabling mobile connection to rural people who normally cannot afford to own a telephone, provides a good income-earning opportunity to Village Phone operators living in rural areas Customers management Tarek Fahim 11
 1 Change Philosophy Tarek Fahim 12
1 Change Philosophy Tarek Fahim 12
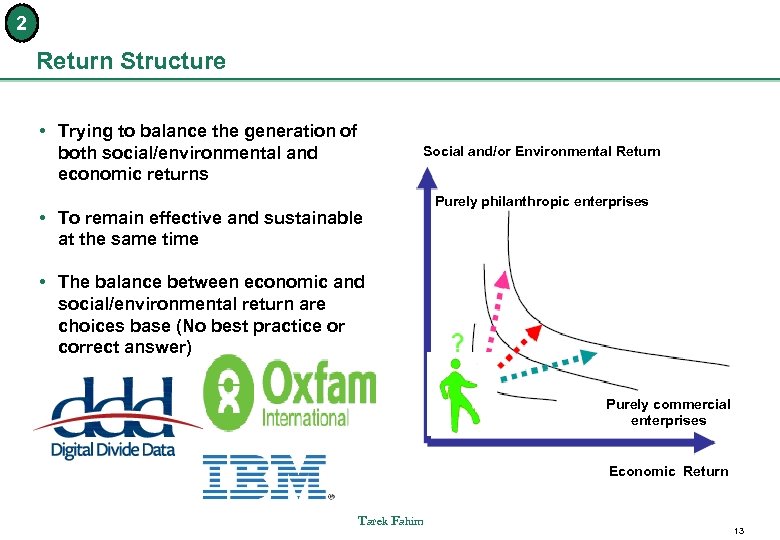 2 Return Structure • Trying to balance the generation of both social/environmental and economic returns Social and/or Environmental Return • To remain effective and sustainable at the same time Purely philanthropic enterprises • The balance between economic and social/environmental return are choices base (No best practice or correct answer) Purely commercial enterprises Economic Return Tarek Fahim 13
2 Return Structure • Trying to balance the generation of both social/environmental and economic returns Social and/or Environmental Return • To remain effective and sustainable at the same time Purely philanthropic enterprises • The balance between economic and social/environmental return are choices base (No best practice or correct answer) Purely commercial enterprises Economic Return Tarek Fahim 13
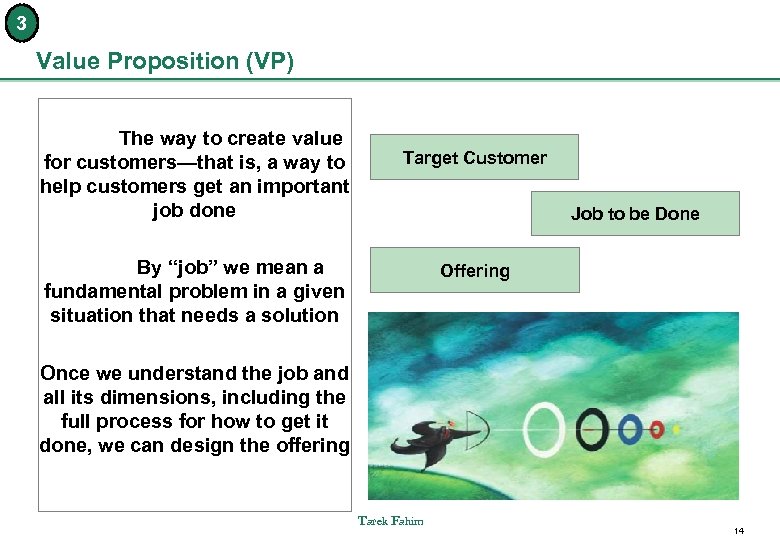 3 Value Proposition (VP) The way to create value for customers—that is, a way to help customers get an important job done Target Customer Job to be Done By “job” we mean a fundamental problem in a given situation that needs a solution Offering Once we understand the job and all its dimensions, including the full process for how to get it done, we can design the offering Tarek Fahim 14
3 Value Proposition (VP) The way to create value for customers—that is, a way to help customers get an important job done Target Customer Job to be Done By “job” we mean a fundamental problem in a given situation that needs a solution Offering Once we understand the job and all its dimensions, including the full process for how to get it done, we can design the offering Tarek Fahim 14
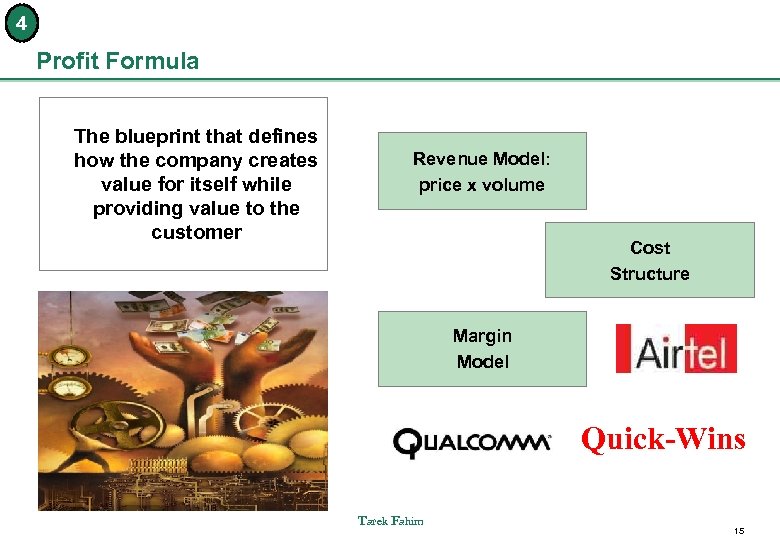 4 Profit Formula The blueprint that defines how the company creates value for itself while providing value to the customer Revenue Model: price x volume Cost Structure Margin Model Quick-Wins Tarek Fahim 15
4 Profit Formula The blueprint that defines how the company creates value for itself while providing value to the customer Revenue Model: price x volume Cost Structure Margin Model Quick-Wins Tarek Fahim 15
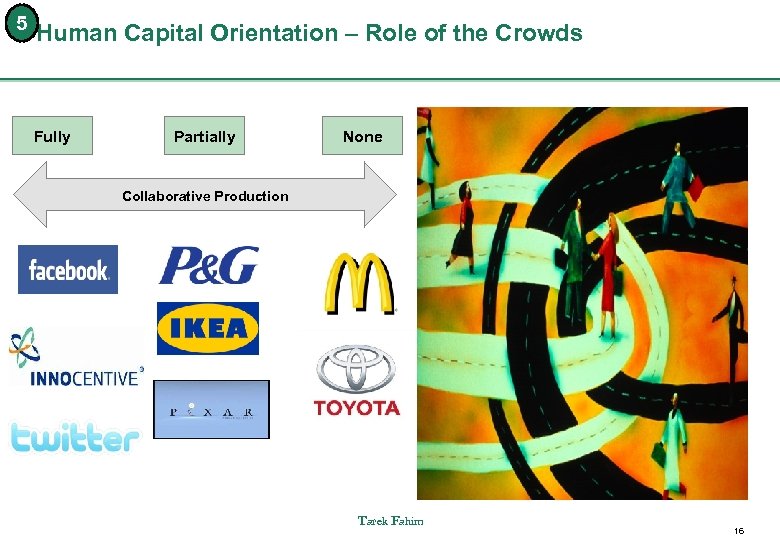 5 Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Fully Partially None Collaborative Production Tarek Fahim 16
5 Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Fully Partially None Collaborative Production Tarek Fahim 16
 6 Key Resources & Platforms The key resources are assets such as technology, products, facilities, equipment, and channels required to deliver the value proposition to the targeted customer. The focus here is on the key elements that create value for the customer and the company, and the way those elements interact Every company also has generic resources that do not create competitive differentiation Tarek Fahim 17
6 Key Resources & Platforms The key resources are assets such as technology, products, facilities, equipment, and channels required to deliver the value proposition to the targeted customer. The focus here is on the key elements that create value for the customer and the company, and the way those elements interact Every company also has generic resources that do not create competitive differentiation Tarek Fahim 17
 7 Key Processes Operational and managerial processes that allow them to deliver value in a way they can successfully repeat and increase in scale. These may include such recurrent tasks as training, development, manufacturing, budgeting, planning, sales, and service. Rules & Metrics Processes & Norms Tarek Fahim 18
7 Key Processes Operational and managerial processes that allow them to deliver value in a way they can successfully repeat and increase in scale. These may include such recurrent tasks as training, development, manufacturing, budgeting, planning, sales, and service. Rules & Metrics Processes & Norms Tarek Fahim 18
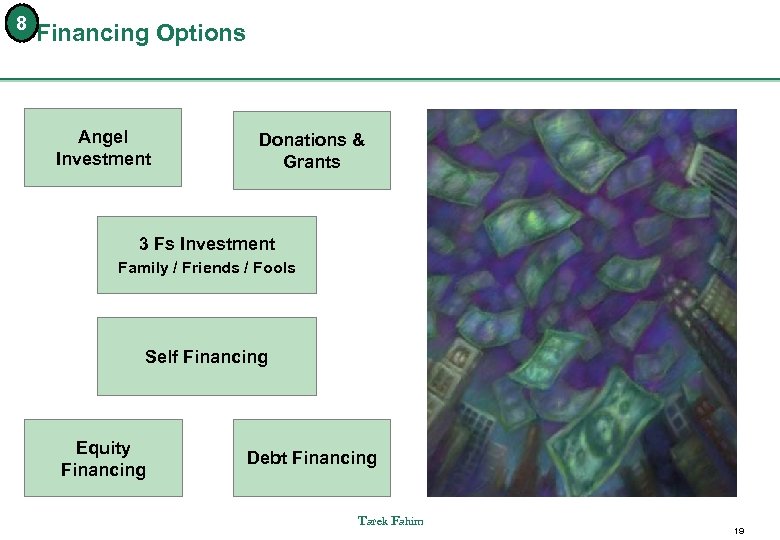 8 Financing Options Angel Investment Donations & Grants 3 Fs Investment Family / Friends / Fools Self Financing Equity Financing Debt Financing Tarek Fahim 19
8 Financing Options Angel Investment Donations & Grants 3 Fs Investment Family / Friends / Fools Self Financing Equity Financing Debt Financing Tarek Fahim 19
 9 Growth Model Different Perspective By Concept One Self Franchise Tarek Fahim 20
9 Growth Model Different Perspective By Concept One Self Franchise Tarek Fahim 20
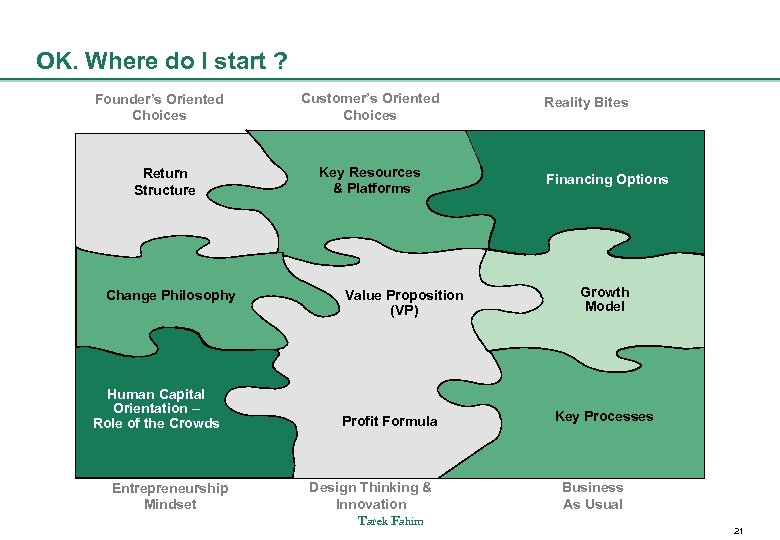 OK. Where do I start ? Founder’s Oriented Choices Return Structure Change Philosophy Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Entrepreneurship Mindset Customer’s Oriented Choices Key Resources & Platforms Value Proposition (VP) Profit Formula Design Thinking & Innovation Tarek Fahim Reality Bites Financing Options Growth Model Key Processes Business As Usual 21
OK. Where do I start ? Founder’s Oriented Choices Return Structure Change Philosophy Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Entrepreneurship Mindset Customer’s Oriented Choices Key Resources & Platforms Value Proposition (VP) Profit Formula Design Thinking & Innovation Tarek Fahim Reality Bites Financing Options Growth Model Key Processes Business As Usual 21
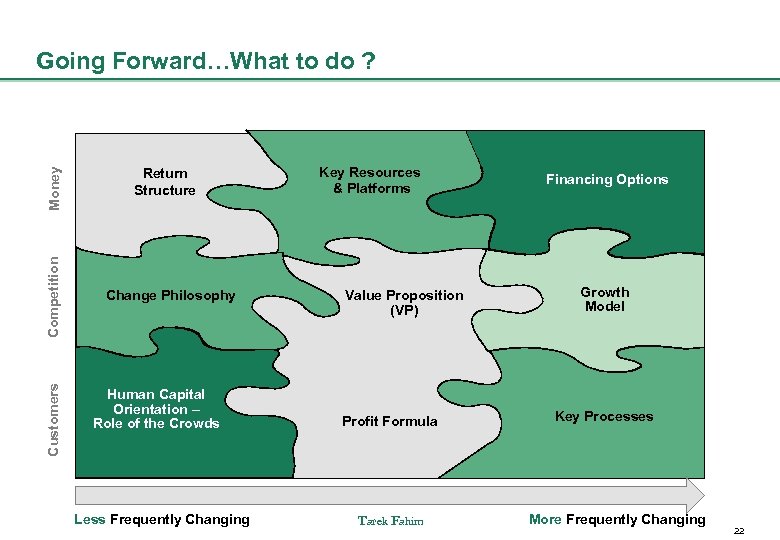 Customers Competition Money Going Forward…What to do ? Return Structure Change Philosophy Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Less Frequently Changing Key Resources & Platforms Value Proposition (VP) Profit Formula Tarek Fahim Financing Options Growth Model Key Processes More Frequently Changing 22
Customers Competition Money Going Forward…What to do ? Return Structure Change Philosophy Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Less Frequently Changing Key Resources & Platforms Value Proposition (VP) Profit Formula Tarek Fahim Financing Options Growth Model Key Processes More Frequently Changing 22
 Constrained Innovation !! Tarek Fahim 23
Constrained Innovation !! Tarek Fahim 23
 Case In Point : Tata Motors Nano Car Providing a safer alternative for scooter families. The cheapest car available in India cost five times what a scooter did and that many of these families could not afford one. “Offering an affordable, safer, allweather alternative for scooter families, one with the potential to reach tens of millions of people who were not yet part of the car-buying market” Tarek Fahim 24
Case In Point : Tata Motors Nano Car Providing a safer alternative for scooter families. The cheapest car available in India cost five times what a scooter did and that many of these families could not afford one. “Offering an affordable, safer, allweather alternative for scooter families, one with the potential to reach tens of millions of people who were not yet part of the car-buying market” Tarek Fahim 24
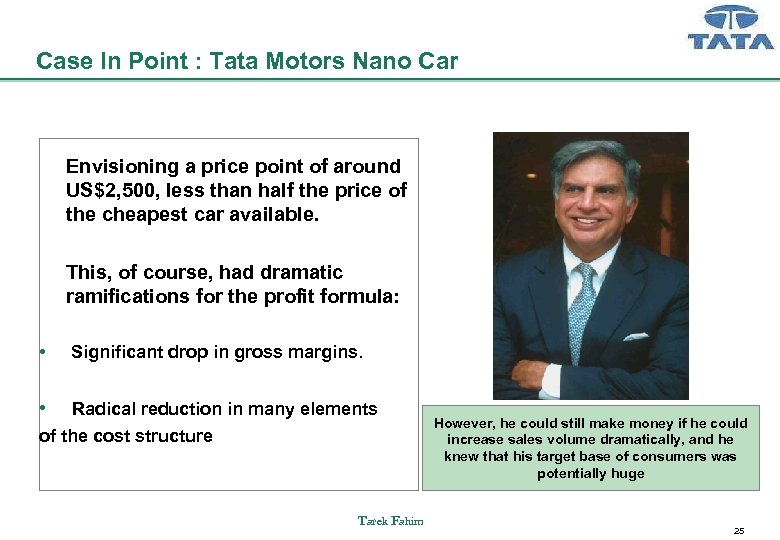 Case In Point : Tata Motors Nano Car Envisioning a price point of around US$2, 500, less than half the price of the cheapest car available. This, of course, had dramatic ramifications for the profit formula: • Significant drop in gross margins. • Radical reduction in many elements of the cost structure Tarek Fahim However, he could still make money if he could increase sales volume dramatically, and he knew that his target base of consumers was potentially huge 25
Case In Point : Tata Motors Nano Car Envisioning a price point of around US$2, 500, less than half the price of the cheapest car available. This, of course, had dramatic ramifications for the profit formula: • Significant drop in gross margins. • Radical reduction in many elements of the cost structure Tarek Fahim However, he could still make money if he could increase sales volume dramatically, and he knew that his target base of consumers was potentially huge 25
 Case In Point : Tata Motors Nano Car For Tata Motors to fulfill the requirements of its customer value proposition and profit formula for the Nano, it had to reconceived how a car is designed, manufactured, and distributed Tarek Fahim 26
Case In Point : Tata Motors Nano Car For Tata Motors to fulfill the requirements of its customer value proposition and profit formula for the Nano, it had to reconceived how a car is designed, manufactured, and distributed Tarek Fahim 26
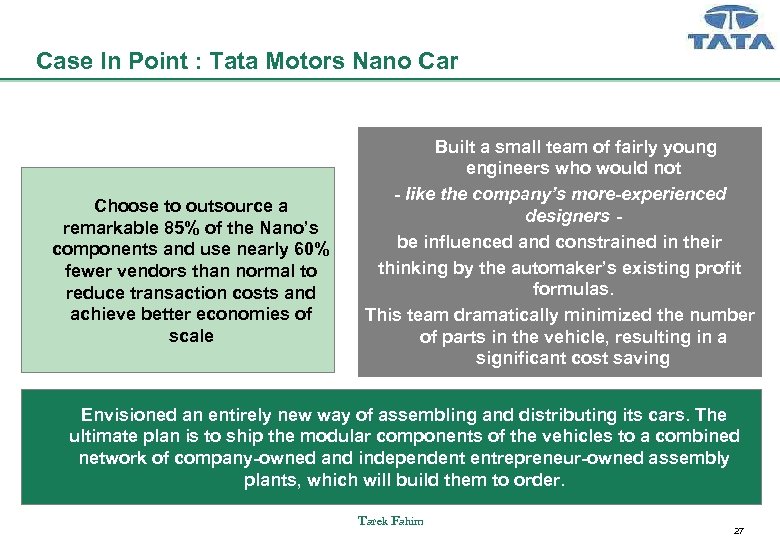 Case In Point : Tata Motors Nano Car Choose to outsource a remarkable 85% of the Nano’s components and use nearly 60% fewer vendors than normal to reduce transaction costs and achieve better economies of scale Built a small team of fairly young engineers who would not - like the company’s more-experienced designers be influenced and constrained in their thinking by the automaker’s existing profit formulas. This team dramatically minimized the number of parts in the vehicle, resulting in a significant cost saving Envisioned an entirely new way of assembling and distributing its cars. The ultimate plan is to ship the modular components of the vehicles to a combined network of company-owned and independent entrepreneur-owned assembly plants, which will build them to order. Tarek Fahim 27
Case In Point : Tata Motors Nano Car Choose to outsource a remarkable 85% of the Nano’s components and use nearly 60% fewer vendors than normal to reduce transaction costs and achieve better economies of scale Built a small team of fairly young engineers who would not - like the company’s more-experienced designers be influenced and constrained in their thinking by the automaker’s existing profit formulas. This team dramatically minimized the number of parts in the vehicle, resulting in a significant cost saving Envisioned an entirely new way of assembling and distributing its cars. The ultimate plan is to ship the modular components of the vehicles to a combined network of company-owned and independent entrepreneur-owned assembly plants, which will build them to order. Tarek Fahim 27
 28 FS Tarek Fahim 28
28 FS Tarek Fahim 28
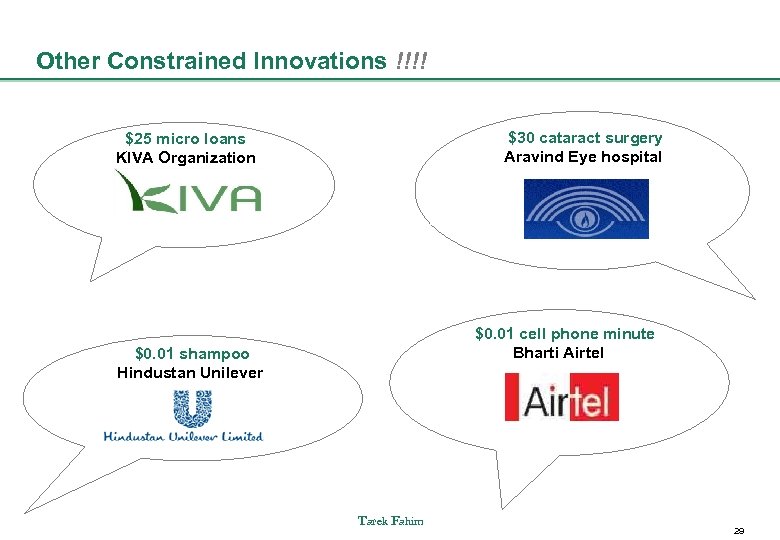 Other Constrained Innovations !!!! $30 cataract surgery Aravind Eye hospital $25 micro loans KIVA Organization $0. 01 cell phone minute Bharti Airtel $0. 01 shampoo Hindustan Unilever Tarek Fahim 29
Other Constrained Innovations !!!! $30 cataract surgery Aravind Eye hospital $25 micro loans KIVA Organization $0. 01 cell phone minute Bharti Airtel $0. 01 shampoo Hindustan Unilever Tarek Fahim 29
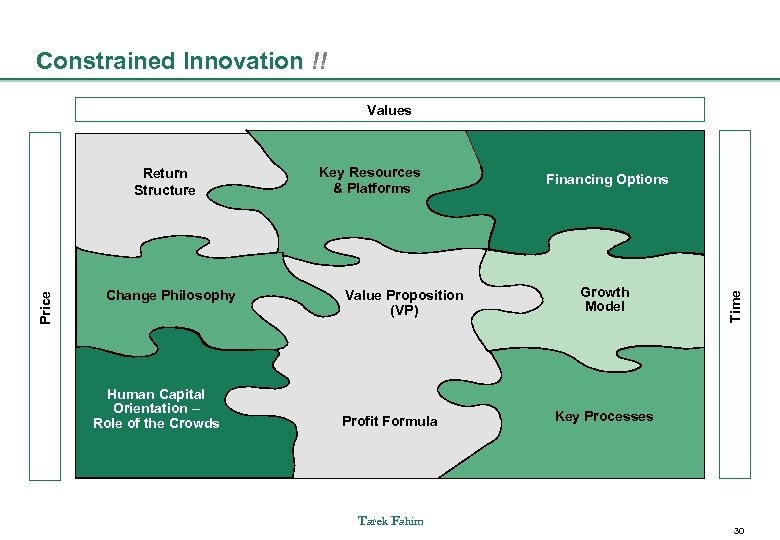 Constrained Innovation !! Values Change Philosophy Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Key Resources & Platforms Value Proposition (VP) Profit Formula Tarek Fahim Financing Options Growth Model Time Price Return Structure Key Processes 30
Constrained Innovation !! Values Change Philosophy Human Capital Orientation – Role of the Crowds Key Resources & Platforms Value Proposition (VP) Profit Formula Tarek Fahim Financing Options Growth Model Time Price Return Structure Key Processes 30
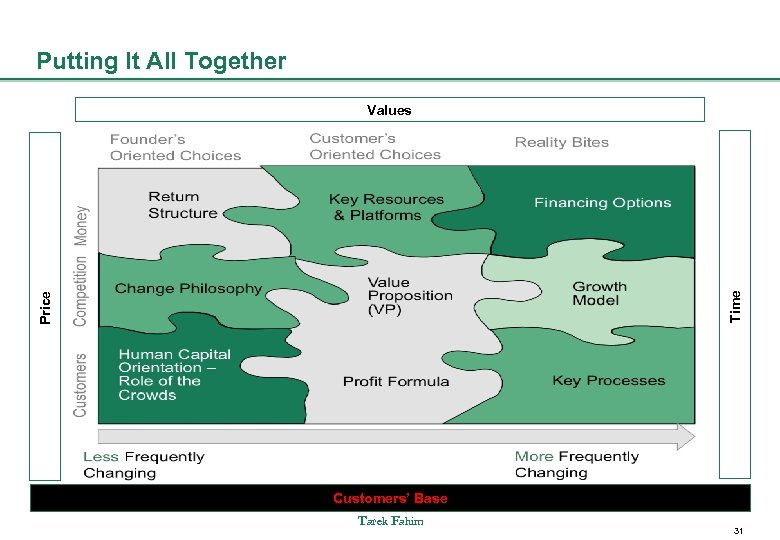 Putting It All Together Price Time Values Customers’ Base Tarek Fahim 31
Putting It All Together Price Time Values Customers’ Base Tarek Fahim 31
 Any Questions ? Tarek Fahim 32
Any Questions ? Tarek Fahim 32


