cceeefc0ea0670a78b9fb82205914d33.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Cepheid Gene. Xpert clinical value and product details 佑康公司 楊瑞萍 Kelly
Cepheid Gene. Xpert clinical value and product details 佑康公司 楊瑞萍 Kelly
 The System Approach: It’s All about the Efficiency Product availability based on timing of FDA submission in US *Exclusively distributed worldwide by Instrumentation Laboratories INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 2
The System Approach: It’s All about the Efficiency Product availability based on timing of FDA submission in US *Exclusively distributed worldwide by Instrumentation Laboratories INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 2
 Cepheid Gene. Xpert Product offer Oct. 2009 – CE IVD Menu of Xpert Assays • • • Xpert MRSA , Preventing MRSA infections and transmission Xpert MRSA/SA Nasal , Pre-surgical screening to prevent surgical site infection Xpert MRSA/SA BC , Diagnosing S. aureus blood stream infections Xpert MRSA/SA SSTI , Diagnosing S. aureus skin and soft tissues infections Xpert C. difficile , Diagnosing CDI (Clostridium difficile infection) Xpert van. A/van. B , Preventing VRE spread and outbreaks • Xpert MTB/RIF , Diagnosing tuberculosis and drug resistance • Xpert GBS , GBS screening to prevent neonatal Group B Strep disease • Xpert EV , Diagnosing Enterovirus meningitis • Xpert BCR ABL , CML treatment monitoring • Xpert Factor II and V , Deep venous thrombosis
Cepheid Gene. Xpert Product offer Oct. 2009 – CE IVD Menu of Xpert Assays • • • Xpert MRSA , Preventing MRSA infections and transmission Xpert MRSA/SA Nasal , Pre-surgical screening to prevent surgical site infection Xpert MRSA/SA BC , Diagnosing S. aureus blood stream infections Xpert MRSA/SA SSTI , Diagnosing S. aureus skin and soft tissues infections Xpert C. difficile , Diagnosing CDI (Clostridium difficile infection) Xpert van. A/van. B , Preventing VRE spread and outbreaks • Xpert MTB/RIF , Diagnosing tuberculosis and drug resistance • Xpert GBS , GBS screening to prevent neonatal Group B Strep disease • Xpert EV , Diagnosing Enterovirus meningitis • Xpert BCR ABL , CML treatment monitoring • Xpert Factor II and V , Deep venous thrombosis
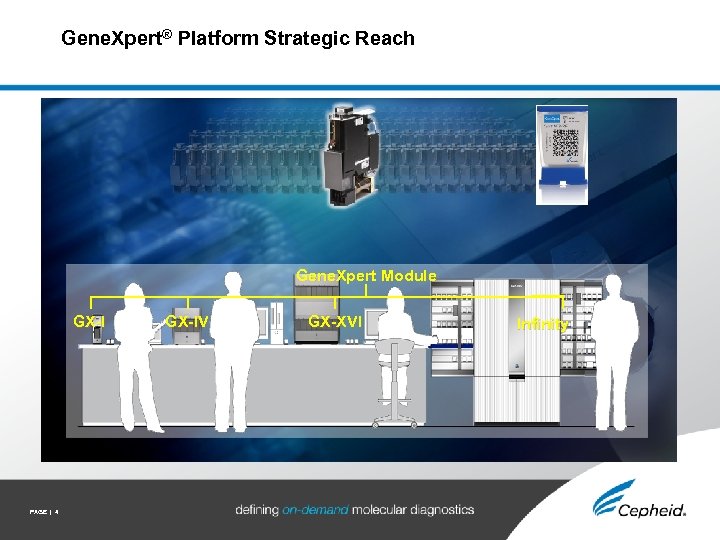 Gene. Xpert® Platform Strategic Reach Gene. Xpert Module GX-I PAGE | 4 GX-IV GX-XVI Infinity
Gene. Xpert® Platform Strategic Reach Gene. Xpert Module GX-I PAGE | 4 GX-IV GX-XVI Infinity
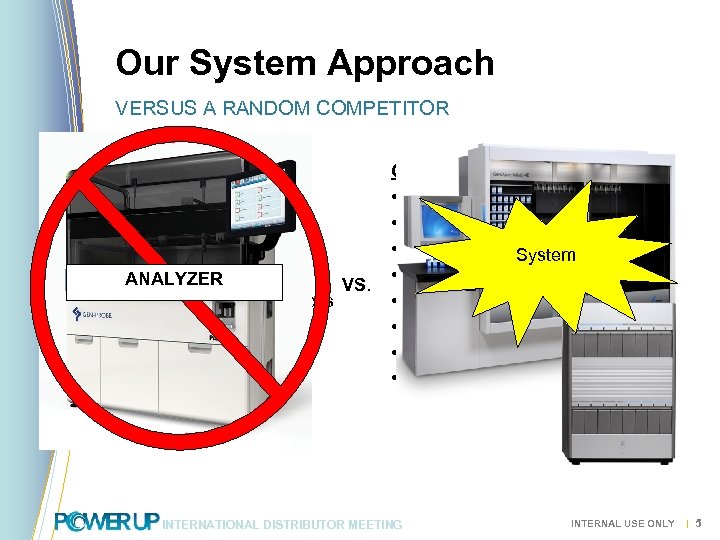 Our System Approach VERSUS A RANDOM COMPETITOR Gen-Probe • Fixed Analyzer Format • Old “batch” Technology • 4 Assays On-board • 1 Test on Menu ANALYZER VS. • Narrow Future Menu Focus • Single Technology (dated) • Labor Intensive • Low Test / m 2 Cepheid • Scalable Configuration • Total Random Access • Limited only by Menu System • 13 Tests on Menu • Broad Future Menu • Multiple Technologies • Easy to Use • High Tests / m 2 INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 5
Our System Approach VERSUS A RANDOM COMPETITOR Gen-Probe • Fixed Analyzer Format • Old “batch” Technology • 4 Assays On-board • 1 Test on Menu ANALYZER VS. • Narrow Future Menu Focus • Single Technology (dated) • Labor Intensive • Low Test / m 2 Cepheid • Scalable Configuration • Total Random Access • Limited only by Menu System • 13 Tests on Menu • Broad Future Menu • Multiple Technologies • Easy to Use • High Tests / m 2 INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 5
 Patient Care Continuum dm A it Triage E m xa t g ab L Im n gi a l su on C Time & Resources INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING a m ar h P r e sf n ra T Dispo INTERNAL USE ONLY | 6
Patient Care Continuum dm A it Triage E m xa t g ab L Im n gi a l su on C Time & Resources INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING a m ar h P r e sf n ra T Dispo INTERNAL USE ONLY | 6
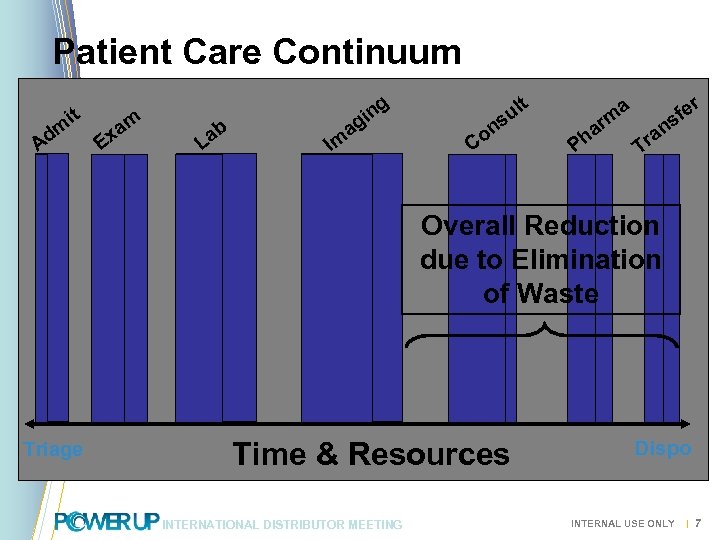 Patient Care Continuum dm A it E m xa t g ab L Im n gi a l su on C a m ar h P r e sf n ra T Overall Reduction due to Elimination of Waste Triage Time & Resources INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING Dispo INTERNAL USE ONLY | 7
Patient Care Continuum dm A it E m xa t g ab L Im n gi a l su on C a m ar h P r e sf n ra T Overall Reduction due to Elimination of Waste Triage Time & Resources INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING Dispo INTERNAL USE ONLY | 7
 MRSA超菌 孩童鼻腔帶菌高 2011/04/19 中央社記者陳麗婷台北 19日電 • 金黃色葡萄球菌是臨床上相當重要的致病菌,抗藥性金黃色葡萄球菌( MRSA)也被 歸類為超級細菌之一,近 10年來曾在社區出現流行,尤其造成兒童感染嚴重病例 不少,甚至造成死亡。 • 林口長庚兒童醫院兒童感染科醫師陳志榮在 2005到 2008年研究,針對 6000多名孩 童採鼻腔檢體分析,結果發現,台灣 5歲(含)以下健康兒童,有 7. 8%鼻腔帶菌,且帶 菌率在 3年間顯著上升。 • 值得注意的是,前 陣子 H 1 N 1新型流感疫情高峰時,臨床發現患者續發細菌性肺炎 也是近 10年來最嚴峻的,其中有些就是 MRSA細菌感染引起 。 • 此外,陳志榮分析院內 2004年到 2006年間重覆感染 MRSA的病童與感染菌株,共有 48位孩童有 2次以上 MRSA感染,且 7成是由同一株 MRSA引起,甚至有病童在相隔 超過 11個月後再次感染 MRSA,仍是同一株細菌,顯示細菌未被根除,仍在鼻腔等 處帶菌,等待孩童免疫力低下時,又再度造成感染。 • 這項研究顯示, 大多數的重複感染來自於病患自身所帶的細菌,因此,醫師積極主 動篩檢,並有效投藥去除帶菌,例如鼻腔抹藥或以特定殺菌劑讓患者洗澡,才是杜 絕大部分 MRSA重複感染的有效方法。 INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 8
MRSA超菌 孩童鼻腔帶菌高 2011/04/19 中央社記者陳麗婷台北 19日電 • 金黃色葡萄球菌是臨床上相當重要的致病菌,抗藥性金黃色葡萄球菌( MRSA)也被 歸類為超級細菌之一,近 10年來曾在社區出現流行,尤其造成兒童感染嚴重病例 不少,甚至造成死亡。 • 林口長庚兒童醫院兒童感染科醫師陳志榮在 2005到 2008年研究,針對 6000多名孩 童採鼻腔檢體分析,結果發現,台灣 5歲(含)以下健康兒童,有 7. 8%鼻腔帶菌,且帶 菌率在 3年間顯著上升。 • 值得注意的是,前 陣子 H 1 N 1新型流感疫情高峰時,臨床發現患者續發細菌性肺炎 也是近 10年來最嚴峻的,其中有些就是 MRSA細菌感染引起 。 • 此外,陳志榮分析院內 2004年到 2006年間重覆感染 MRSA的病童與感染菌株,共有 48位孩童有 2次以上 MRSA感染,且 7成是由同一株 MRSA引起,甚至有病童在相隔 超過 11個月後再次感染 MRSA,仍是同一株細菌,顯示細菌未被根除,仍在鼻腔等 處帶菌,等待孩童免疫力低下時,又再度造成感染。 • 這項研究顯示, 大多數的重複感染來自於病患自身所帶的細菌,因此,醫師積極主 動篩檢,並有效投藥去除帶菌,例如鼻腔抹藥或以特定殺菌劑讓患者洗澡,才是杜 絕大部分 MRSA重複感染的有效方法。 INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 8
 C. difficile (梭狀芽胞桿菌)是最常見可被辨識出來會導致感染愛滋病患者腹瀉 的細菌 • 細菌性腹瀉的發生率為每年每 1000人中有 7. 2人,且直接和患者的免疫力被抑 制有關連 • 在引起疾病的有機物中, C. difficile (梭狀芽胞桿菌)佔了54%, ,賀氏菌(Shigella species)佔了 14% • 主要的復發危險因子有年紀增長,使用抗生素及住院治療 • • 及時檢測成本效益 : 降低抗生素使用、 減少腸道檢查 (結腸鏡檢查、 影像診斷 學 )以及不必要手術干預 • C. difficle感染平均將增加病患在醫院 醫療成本 • Xpert C. difficle 除針對懷疑 CDI感染患者作快速篩檢之外, 更能針對 GDH(+)檢 體進行確認 C. difficle產毒菌種是否存在 5 -6天的留置時間,將增加病患在醫院的 INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 9
C. difficile (梭狀芽胞桿菌)是最常見可被辨識出來會導致感染愛滋病患者腹瀉 的細菌 • 細菌性腹瀉的發生率為每年每 1000人中有 7. 2人,且直接和患者的免疫力被抑 制有關連 • 在引起疾病的有機物中, C. difficile (梭狀芽胞桿菌)佔了54%, ,賀氏菌(Shigella species)佔了 14% • 主要的復發危險因子有年紀增長,使用抗生素及住院治療 • • 及時檢測成本效益 : 降低抗生素使用、 減少腸道檢查 (結腸鏡檢查、 影像診斷 學 )以及不必要手術干預 • C. difficle感染平均將增加病患在醫院 醫療成本 • Xpert C. difficle 除針對懷疑 CDI感染患者作快速篩檢之外, 更能針對 GDH(+)檢 體進行確認 C. difficle產毒菌種是否存在 5 -6天的留置時間,將增加病患在醫院的 INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 9
 Xpert MTB Agenda • Background: tuberculosis infection and disease • Current testing algorithms • Clinical value of Xpert MTB/RIF • Xpert MTB/RIF: product details • Xpert MTB/RIF: latest clinical experience
Xpert MTB Agenda • Background: tuberculosis infection and disease • Current testing algorithms • Clinical value of Xpert MTB/RIF • Xpert MTB/RIF: product details • Xpert MTB/RIF: latest clinical experience
 Tuberculosis: an important public health concern • Bacterial disease, airborne – transmitted caused by M. tuberculosis • 1/3 world population latently infected: 2 billion people • ~9. 3 million of new cases in 2007 and 1. 8 million deaths • TB the second most deadly infectious disease worldwide after HIV/AIDS. • Most of the cases occur in the developing world. PAGE | 11
Tuberculosis: an important public health concern • Bacterial disease, airborne – transmitted caused by M. tuberculosis • 1/3 world population latently infected: 2 billion people • ~9. 3 million of new cases in 2007 and 1. 8 million deaths • TB the second most deadly infectious disease worldwide after HIV/AIDS. • Most of the cases occur in the developing world. PAGE | 11
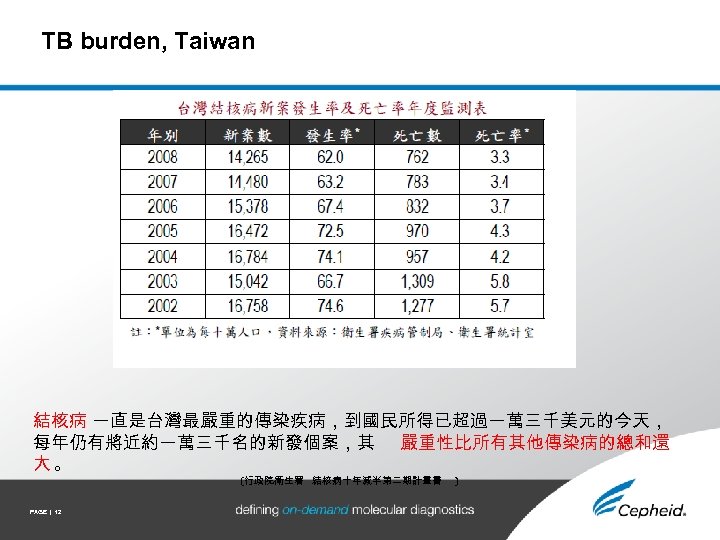 TB burden, Taiwan 結核病 一直是台灣最嚴重的傳染疾病,到國民所得已超過一萬三千美元的今天, 每年仍有將近約一萬三千名的新發個案,其 嚴重性比所有其他傳染病的總和還 大。 (行政院衛生署 結核病十年減半第二期計畫書 PAGE | 12 )
TB burden, Taiwan 結核病 一直是台灣最嚴重的傳染疾病,到國民所得已超過一萬三千美元的今天, 每年仍有將近約一萬三千名的新發個案,其 嚴重性比所有其他傳染病的總和還 大。 (行政院衛生署 結核病十年減半第二期計畫書 PAGE | 12 )
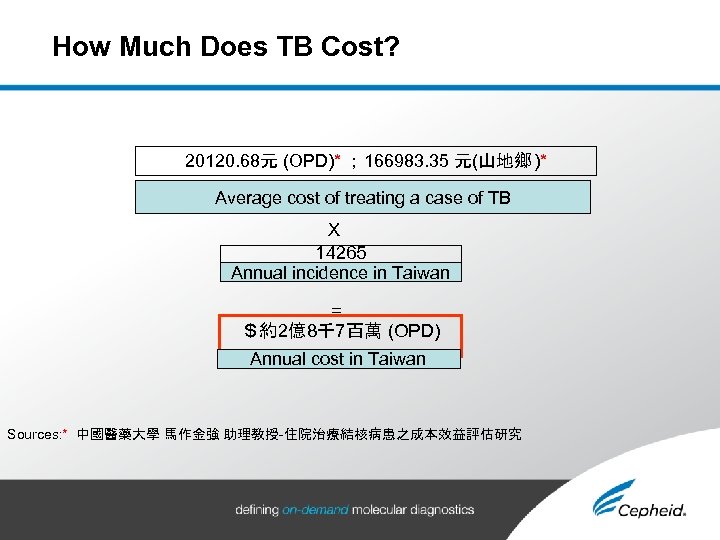 How Much Does TB Cost? 20120. 68元 (OPD)* ; 166983. 35 元(山地鄉 )* Average cost of treating a case of TB X 14265 Annual incidence in Taiwan = $約2億8千7百萬 (OPD) Annual cost in Taiwan Sources: * 中國醫藥大學 馬作金強 助理教授-住院治療結核病患之成本效益評估研究
How Much Does TB Cost? 20120. 68元 (OPD)* ; 166983. 35 元(山地鄉 )* Average cost of treating a case of TB X 14265 Annual incidence in Taiwan = $約2億8千7百萬 (OPD) Annual cost in Taiwan Sources: * 中國醫藥大學 馬作金強 助理教授-住院治療結核病患之成本效益評估研究
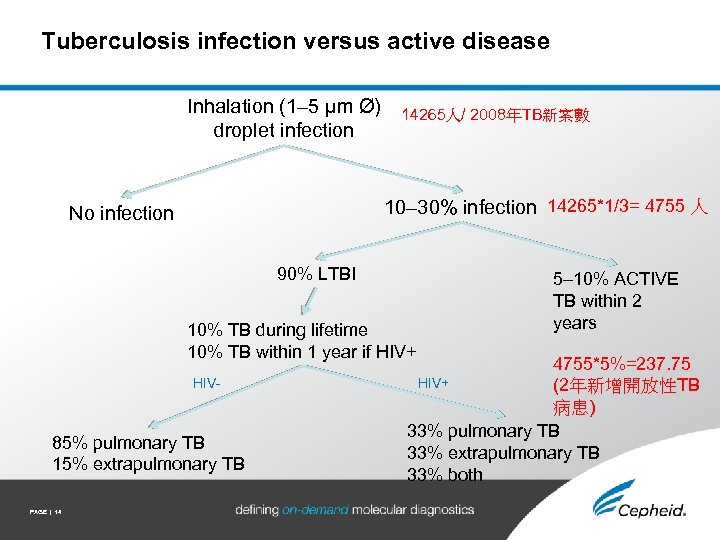 Tuberculosis infection versus active disease Inhalation (1– 5 μm Ø) droplet infection 14265人/ 2008年TB新案數 10– 30% infection 14265*1/3= 4755 人 No infection 90% LTBI 10% TB during lifetime 10% TB within 1 year if HIV+ HIV- 85% pulmonary TB 15% extrapulmonary TB PAGE | 14 5– 10% ACTIVE TB within 2 years 4755*5%=237. 75 HIV+ (2年新增開放性TB 病患) 33% pulmonary TB 33% extrapulmonary TB 33% both
Tuberculosis infection versus active disease Inhalation (1– 5 μm Ø) droplet infection 14265人/ 2008年TB新案數 10– 30% infection 14265*1/3= 4755 人 No infection 90% LTBI 10% TB during lifetime 10% TB within 1 year if HIV+ HIV- 85% pulmonary TB 15% extrapulmonary TB PAGE | 14 5– 10% ACTIVE TB within 2 years 4755*5%=237. 75 HIV+ (2年新增開放性TB 病患) 33% pulmonary TB 33% extrapulmonary TB 33% both
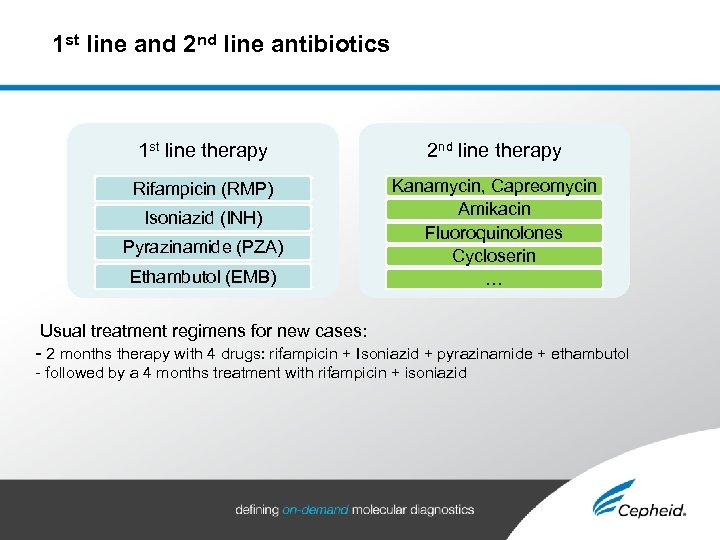 1 st line and 2 nd line antibiotics 1 st line therapy 2 nd line therapy Rifampicin (RMP) Kanamycin, Capreomycin Amikacin Fluoroquinolones Cycloserin … Isoniazid (INH) Pyrazinamide (PZA) Ethambutol (EMB) Usual treatment regimens for new cases: - 2 months therapy with 4 drugs: rifampicin + Isoniazid + pyrazinamide + ethambutol - followed by a 4 months treatment with rifampicin + isoniazid
1 st line and 2 nd line antibiotics 1 st line therapy 2 nd line therapy Rifampicin (RMP) Kanamycin, Capreomycin Amikacin Fluoroquinolones Cycloserin … Isoniazid (INH) Pyrazinamide (PZA) Ethambutol (EMB) Usual treatment regimens for new cases: - 2 months therapy with 4 drugs: rifampicin + Isoniazid + pyrazinamide + ethambutol - followed by a 4 months treatment with rifampicin + isoniazid
 Drug resistant TB • Jeopardizing TB control programmes • MDR TB = Resistance to at least Isoniazid (INH) and Rifampicin (RIF) • XDR TB = Resistance to al least isoniazid and rifampicin + any of the fluoroquinolones + any of the three injectable drugs : Amikacin, Capreomycin , Kanamycin PAGE | 16
Drug resistant TB • Jeopardizing TB control programmes • MDR TB = Resistance to at least Isoniazid (INH) and Rifampicin (RIF) • XDR TB = Resistance to al least isoniazid and rifampicin + any of the fluoroquinolones + any of the three injectable drugs : Amikacin, Capreomycin , Kanamycin PAGE | 16
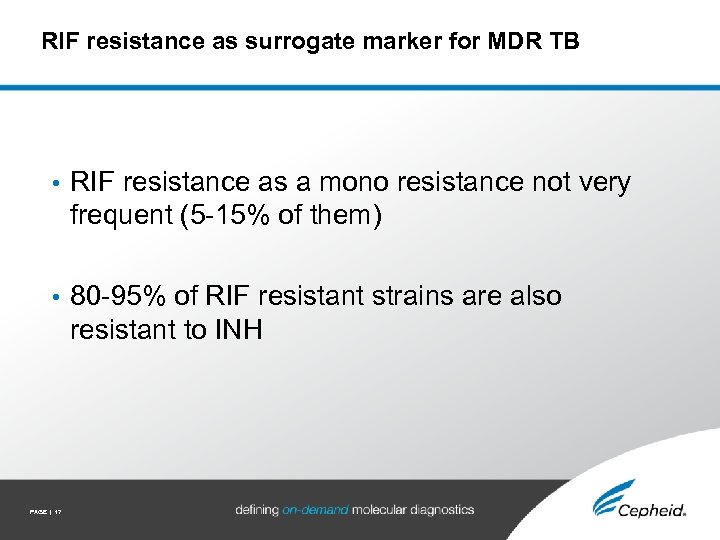 RIF resistance as surrogate marker for MDR TB • RIF resistance as a mono resistance not very frequent (5 -15% of them) • 80 -95% of RIF resistant strains are also resistant to INH PAGE | 17
RIF resistance as surrogate marker for MDR TB • RIF resistance as a mono resistance not very frequent (5 -15% of them) • 80 -95% of RIF resistant strains are also resistant to INH PAGE | 17
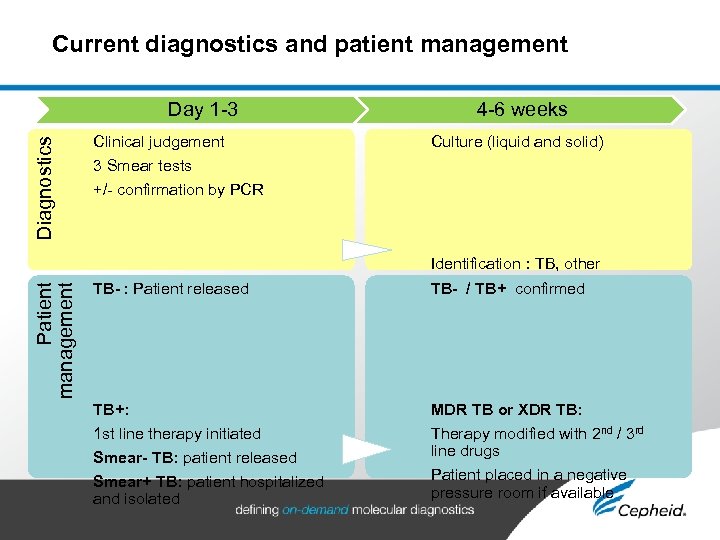 Current diagnostics and patient management Patient management Diagnostics Day 1 -3 Clinical judgement 4 -6 weeks Culture (liquid and solid) 3 Smear tests +/- confirmation by PCR TB- : Patient released No drug susceptibility TB+: 1 st line therapy initiated Smear- TB: patient released Smear+ TB: patient hospitalized and isolated Identification : TB, other mycobacteria… TB- / TB+ confirmed Drug susceptibility testing MDR TB or XDR TB: Therapy modified with 2 nd / 3 rd line drugs Patient placed in a negative pressure room if available
Current diagnostics and patient management Patient management Diagnostics Day 1 -3 Clinical judgement 4 -6 weeks Culture (liquid and solid) 3 Smear tests +/- confirmation by PCR TB- : Patient released No drug susceptibility TB+: 1 st line therapy initiated Smear- TB: patient released Smear+ TB: patient hospitalized and isolated Identification : TB, other mycobacteria… TB- / TB+ confirmed Drug susceptibility testing MDR TB or XDR TB: Therapy modified with 2 nd / 3 rd line drugs Patient placed in a negative pressure room if available
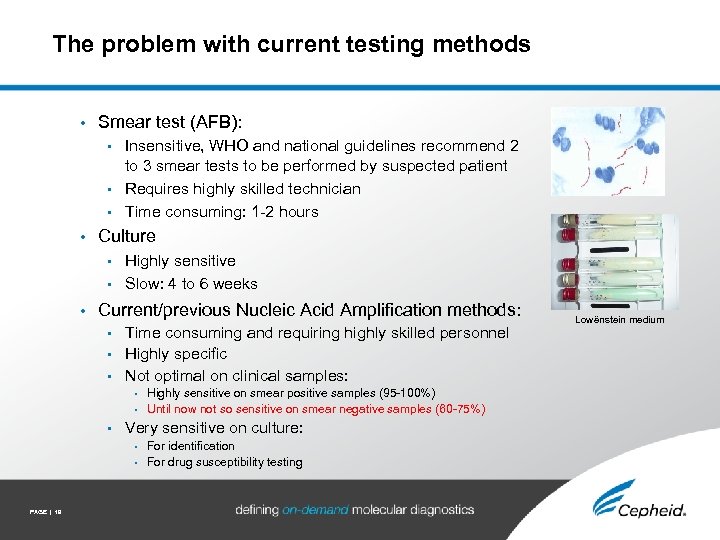 The problem with current testing methods • Smear test (AFB): Insensitive, WHO and national guidelines recommend 2 to 3 smear tests to be performed by suspected patient • Requires highly skilled technician • Time consuming: 1 -2 hours • • Culture Highly sensitive • Slow: 4 to 6 weeks • • Current/previous Nucleic Acid Amplification methods: Time consuming and requiring highly skilled personnel • Highly specific • Not optimal on clinical samples: • • Highly sensitive on smear positive samples (95 -100%) • Until now not so sensitive on smear negative samples (60 -75%) • Very sensitive on culture: • For identification • For drug susceptibility testing PAGE | 19 Lowënstein medium
The problem with current testing methods • Smear test (AFB): Insensitive, WHO and national guidelines recommend 2 to 3 smear tests to be performed by suspected patient • Requires highly skilled technician • Time consuming: 1 -2 hours • • Culture Highly sensitive • Slow: 4 to 6 weeks • • Current/previous Nucleic Acid Amplification methods: Time consuming and requiring highly skilled personnel • Highly specific • Not optimal on clinical samples: • • Highly sensitive on smear positive samples (95 -100%) • Until now not so sensitive on smear negative samples (60 -75%) • Very sensitive on culture: • For identification • For drug susceptibility testing PAGE | 19 Lowënstein medium
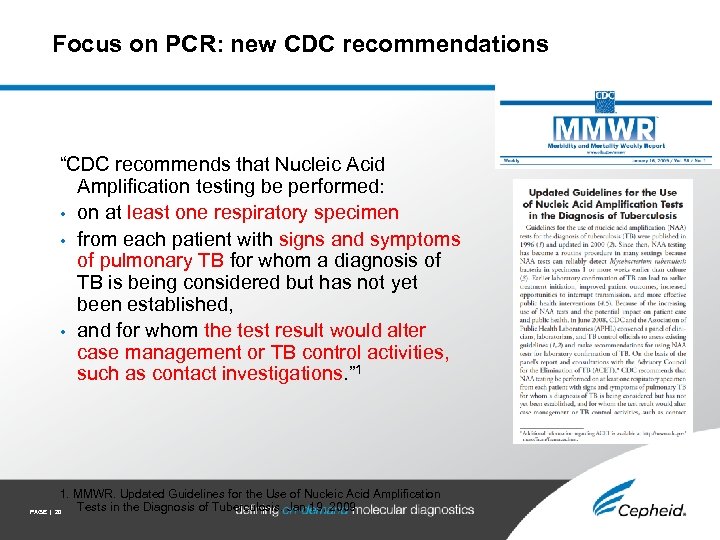 Focus on PCR: new CDC recommendations “CDC recommends that Nucleic Acid Amplification testing be performed: • on at least one respiratory specimen • from each patient with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB for whom a diagnosis of TB is being considered but has not yet been established, • and for whom the test result would alter case management or TB control activities, such as contact investigations. ” 1 1. MMWR. Updated Guidelines for the Use of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests in the Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. Jan 19, 2009 PAGE | 20
Focus on PCR: new CDC recommendations “CDC recommends that Nucleic Acid Amplification testing be performed: • on at least one respiratory specimen • from each patient with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB for whom a diagnosis of TB is being considered but has not yet been established, • and for whom the test result would alter case management or TB control activities, such as contact investigations. ” 1 1. MMWR. Updated Guidelines for the Use of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests in the Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. Jan 19, 2009 PAGE | 20
 Unmet Needs • Early detection of disease TB cases diagnosed without aetiology (smear-, current PCR not sensitive enough) • Limitation of spread • Detection in HIV cases • • Detection of MDR / XDR TB Rapid implementation of the appropriate therapy • Limitation of spread of resistance • Optimisation of expensive isolation facilities • PAGE | 21
Unmet Needs • Early detection of disease TB cases diagnosed without aetiology (smear-, current PCR not sensitive enough) • Limitation of spread • Detection in HIV cases • • Detection of MDR / XDR TB Rapid implementation of the appropriate therapy • Limitation of spread of resistance • Optimisation of expensive isolation facilities • PAGE | 21
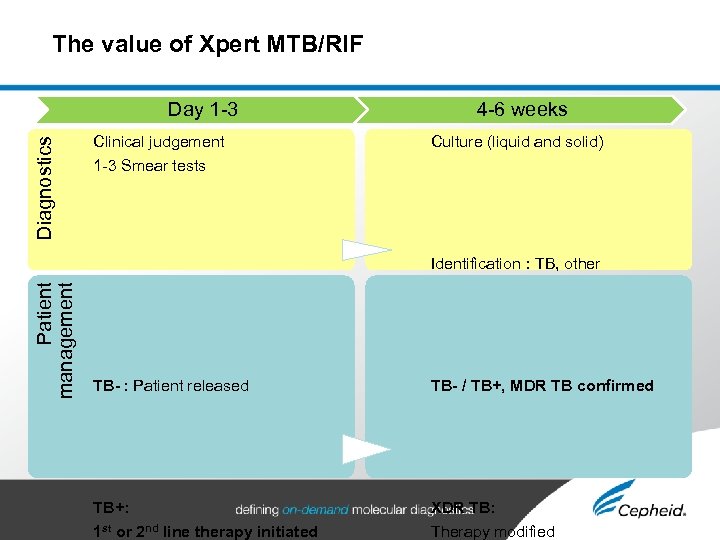 The value of Xpert MTB/RIF Patient management Diagnostics Day 1 -3 Clinical judgement 4 -6 weeks Culture (liquid and solid) 1 -3 Smear tests Xpert MTB/RIF: Smear+ / smear- TB confirmed Rifampicin resistance Identification : TB, other mycobacteria… TB- : Patient released TB- / TB+, MDR TB confirmed Drug susceptibility testing TB+: 1 st or 2 nd line therapy initiated XDR TB: Therapy modified
The value of Xpert MTB/RIF Patient management Diagnostics Day 1 -3 Clinical judgement 4 -6 weeks Culture (liquid and solid) 1 -3 Smear tests Xpert MTB/RIF: Smear+ / smear- TB confirmed Rifampicin resistance Identification : TB, other mycobacteria… TB- : Patient released TB- / TB+, MDR TB confirmed Drug susceptibility testing TB+: 1 st or 2 nd line therapy initiated XDR TB: Therapy modified
 The value of Xpert MTB/RIF: • Xpert MTB/RIF detects simultaneously the tuberculosis complex and rifampicin resistance • Xpert MTB/RIF significantly enhances diagnosis and therapeutic decision making in pulmonary tuberculosis • Xpert MTB/RIF combines rapidity and high sensitivity in a simply performed test PAGE | 23
The value of Xpert MTB/RIF: • Xpert MTB/RIF detects simultaneously the tuberculosis complex and rifampicin resistance • Xpert MTB/RIF significantly enhances diagnosis and therapeutic decision making in pulmonary tuberculosis • Xpert MTB/RIF combines rapidity and high sensitivity in a simply performed test PAGE | 23
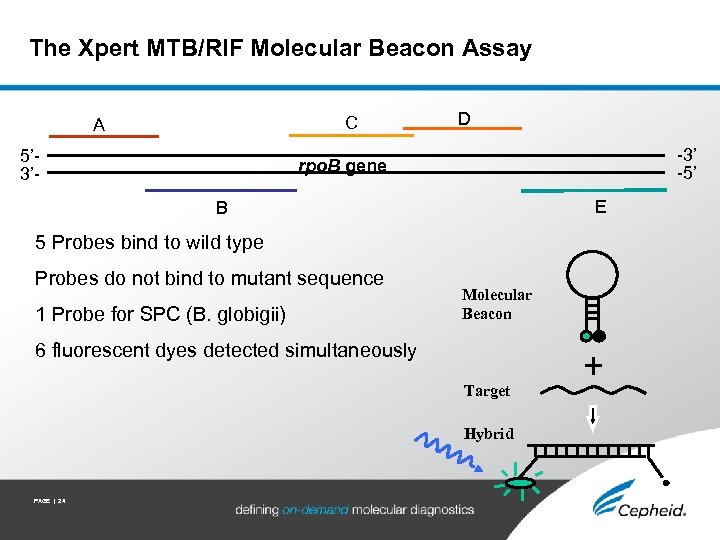 The Xpert MTB/RIF Molecular Beacon Assay C A 5’ 3’- D -3’ -5’ rpo. B gene E B 5 Probes bind to wild type Probes do not bind to mutant sequence 1 Probe for SPC (B. globigii) Molecular Beacon 6 fluorescent dyes detected simultaneously Target Hybrid PAGE | 24
The Xpert MTB/RIF Molecular Beacon Assay C A 5’ 3’- D -3’ -5’ rpo. B gene E B 5 Probes bind to wild type Probes do not bind to mutant sequence 1 Probe for SPC (B. globigii) Molecular Beacon 6 fluorescent dyes detected simultaneously Target Hybrid PAGE | 24
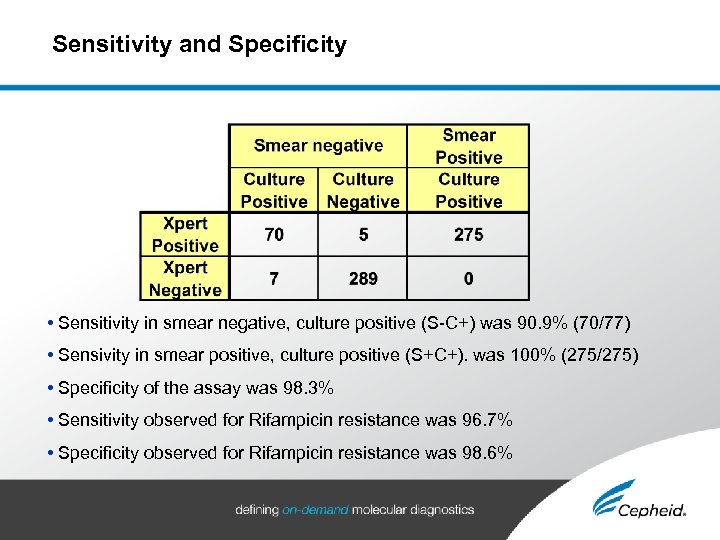 Sensitivity and Specificity • Sensitivity in smear negative, culture positive (S-C+) was 90. 9% (70/77) • Sensivity in smear positive, culture positive (S+C+). was 100% (275/275) • Specificity of the assay was 98. 3% • Sensitivity observed for Rifampicin resistance was 96. 7% • Specificity observed for Rifampicin resistance was 98. 6%
Sensitivity and Specificity • Sensitivity in smear negative, culture positive (S-C+) was 90. 9% (70/77) • Sensivity in smear positive, culture positive (S+C+). was 100% (275/275) • Specificity of the assay was 98. 3% • Sensitivity observed for Rifampicin resistance was 96. 7% • Specificity observed for Rifampicin resistance was 98. 6%
 Specimen Processing Routine Bacteriology BSL 2 Mycobacteriology BSL 3 2 min Incubate 1 -2 days 3 hrs (batch) Incubate up to 8 wks
Specimen Processing Routine Bacteriology BSL 2 Mycobacteriology BSL 3 2 min Incubate 1 -2 days 3 hrs (batch) Incubate up to 8 wks
 Culture Detection and Identification Routine Bacteriology BSL 2 Mycobacteriology BSL 3
Culture Detection and Identification Routine Bacteriology BSL 2 Mycobacteriology BSL 3
 Myobacterial Culture Methods MGIT liquid medium 7 H 11 agar LJ slant Specimen pellet Average TTD: 3 wks
Myobacterial Culture Methods MGIT liquid medium 7 H 11 agar LJ slant Specimen pellet Average TTD: 3 wks
 Automated Liquid Culture Systems MGIT 960 320 tubes per unit Positive Average TTD: 7 days
Automated Liquid Culture Systems MGIT 960 320 tubes per unit Positive Average TTD: 7 days
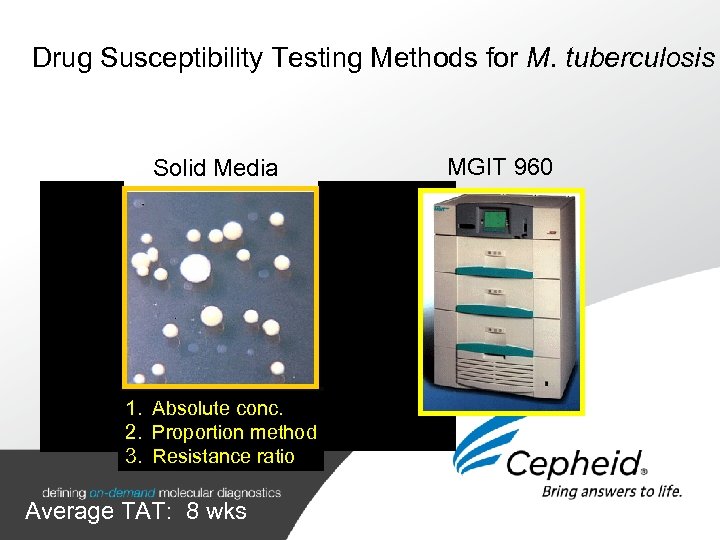 Drug Susceptibility Testing Methods for M. tuberculosis Solid Media MGIT 960 1. Absolute conc. 2. Proportion method 3. Resistance ratio Average TAT: 8 wks 2 -3 weeks
Drug Susceptibility Testing Methods for M. tuberculosis Solid Media MGIT 960 1. Absolute conc. 2. Proportion method 3. Resistance ratio Average TAT: 8 wks 2 -3 weeks
 Specimen Processing is Required for NAATs BSL 3 2 hrs (batched) Real-Time PCR DNA extraction
Specimen Processing is Required for NAATs BSL 3 2 hrs (batched) Real-Time PCR DNA extraction
 Specimen Processing is Required for NAATs BSL 3 2 hrs (batched) Real-Time PCR DNA extraction
Specimen Processing is Required for NAATs BSL 3 2 hrs (batched) Real-Time PCR DNA extraction
 It’s About Time to Stop Transmission! • Approximately 20% of transmitted infections are caused by smear -negative / culture positive patients 1 • Should the patient be isolated until culture results are available? • => cost • Should the patient be released while awaiting culture results? • => transmission risk Sources: 1: Behr MA, Warren SA, Salamon H, et al. Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from patients smear-negative for acid-fast bacilli, Lancet 1999; 353: 444– 449
It’s About Time to Stop Transmission! • Approximately 20% of transmitted infections are caused by smear -negative / culture positive patients 1 • Should the patient be isolated until culture results are available? • => cost • Should the patient be released while awaiting culture results? • => transmission risk Sources: 1: Behr MA, Warren SA, Salamon H, et al. Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from patients smear-negative for acid-fast bacilli, Lancet 1999; 353: 444– 449
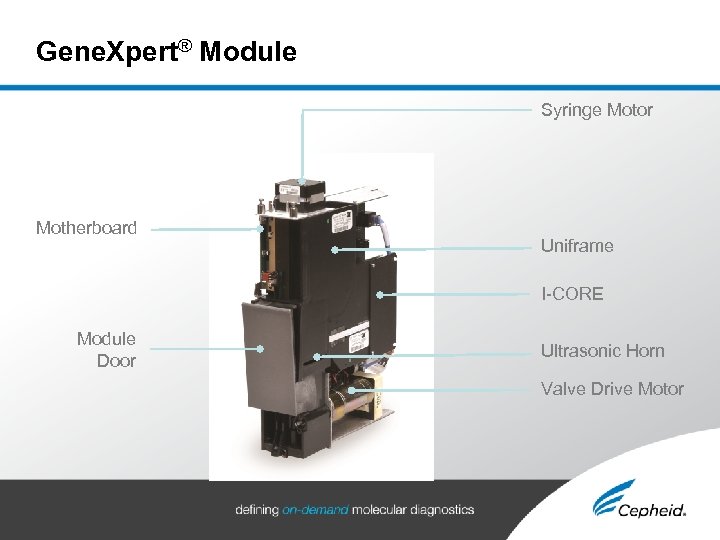 Gene. Xpert® Module Syringe Motor Motherboard Uniframe I-CORE Module Door Ultrasonic Horn Valve Drive Motor
Gene. Xpert® Module Syringe Motor Motherboard Uniframe I-CORE Module Door Ultrasonic Horn Valve Drive Motor
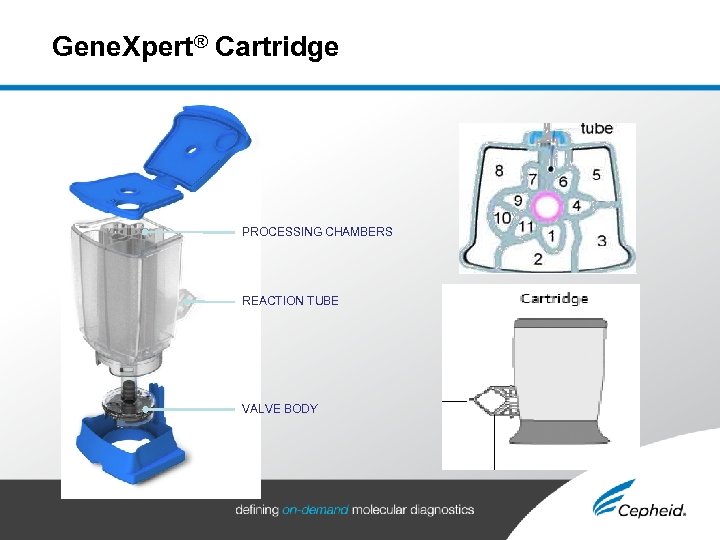 Gene. Xpert® Cartridge PROCESSING CHAMBERS REACTION TUBE VALVE BODY
Gene. Xpert® Cartridge PROCESSING CHAMBERS REACTION TUBE VALVE BODY
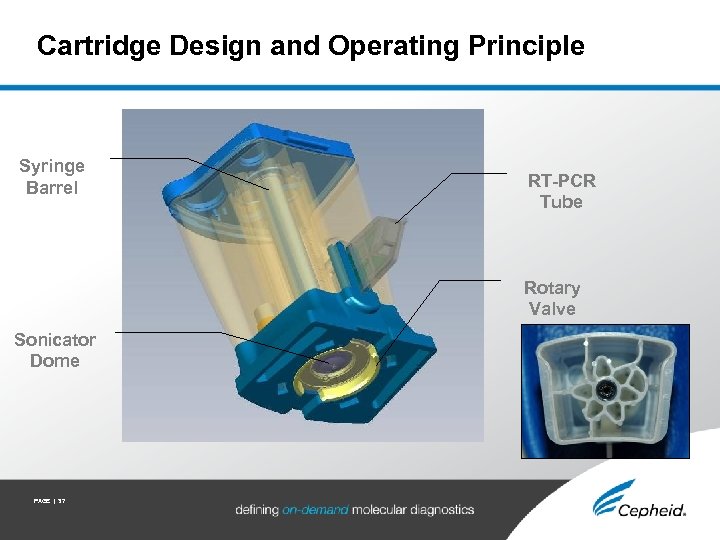 Cartridge Design and Operating Principle Syringe Barrel RT-PCR Tube Rotary Valve Sonicator Dome PAGE | 37
Cartridge Design and Operating Principle Syringe Barrel RT-PCR Tube Rotary Valve Sonicator Dome PAGE | 37
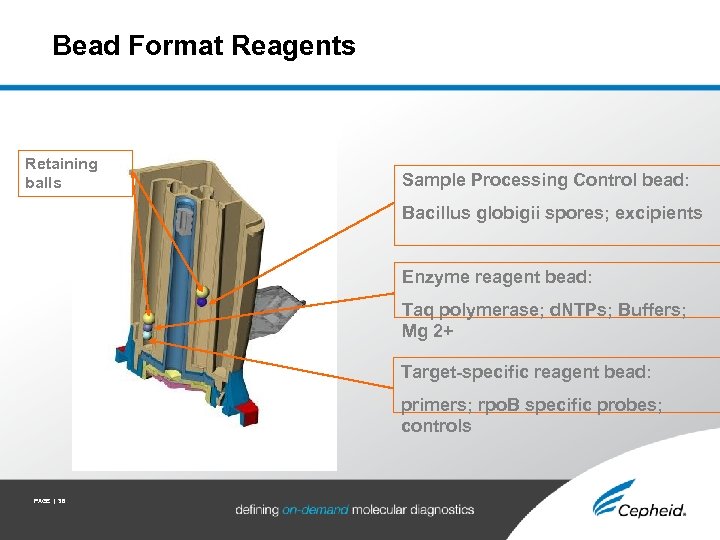 Bead Format Reagents Retaining balls Sample Processing Control bead: Bacillus globigii spores; excipients Enzyme reagent bead: Taq polymerase; d. NTPs; Buffers; Mg 2+ Target-specific reagent bead: primers; rpo. B specific probes; controls PAGE | 38
Bead Format Reagents Retaining balls Sample Processing Control bead: Bacillus globigii spores; excipients Enzyme reagent bead: Taq polymerase; d. NTPs; Buffers; Mg 2+ Target-specific reagent bead: primers; rpo. B specific probes; controls PAGE | 38
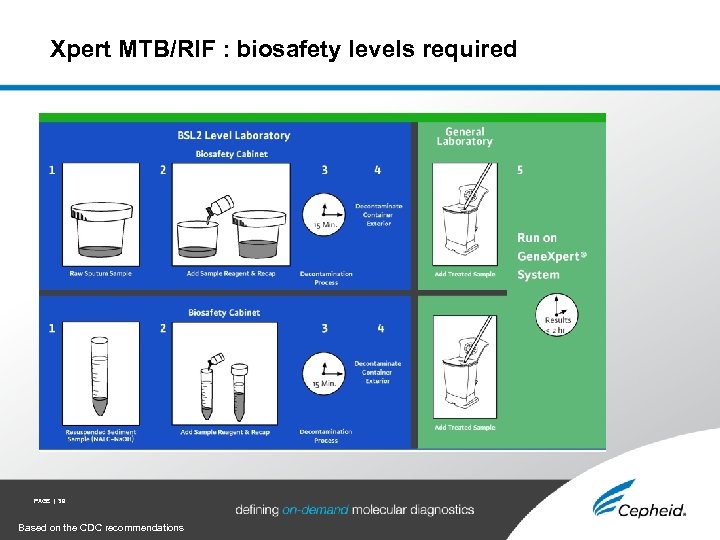 Xpert MTB/RIF : biosafety levels required PAGE | 39 Based on the CDC recommendations
Xpert MTB/RIF : biosafety levels required PAGE | 39 Based on the CDC recommendations
 Novel Technologies Combine Sample Processing and Nucleic Acid Amplification Sputum treated with “buffer” for 15 min 120 minutes
Novel Technologies Combine Sample Processing and Nucleic Acid Amplification Sputum treated with “buffer” for 15 min 120 minutes
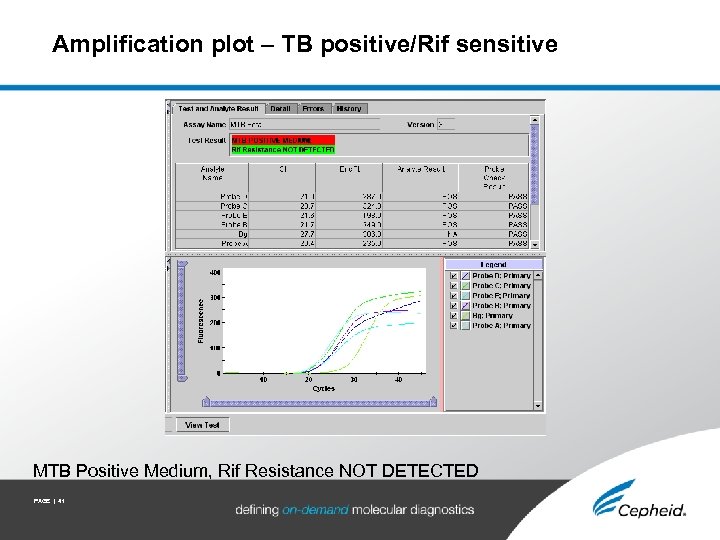 Amplification plot – TB positive/Rif sensitive MTB Positive Medium, Rif Resistance NOT DETECTED PAGE | 41
Amplification plot – TB positive/Rif sensitive MTB Positive Medium, Rif Resistance NOT DETECTED PAGE | 41
 WHO statements PAGE | 42
WHO statements PAGE | 42
 WHO endorses new rapid tuberculosis test A major milestone for global TB diagnosis and care • 2010. 12. 8 | London | Geneva - Today, WHO endorsed a new and novel rapid test for tuberculosis (TB), especially relevant in countries most affected by the disease. The test could revolutionize TB care and control by providing an accurate diagnosis for many patients in about 100 minutes, compared to current tests that can take up to three months to have results. • "This new test represents a major milestone for global TB diagnosis and care. It also represents new hope for the millions of people who are at the highest risk of TB and drug-resistant disease. " said Dr Mario Raviglione, Director of WHO's Stop TB Department. "We have the scientific evidence, we have defined the policy, and now we aim to support implementation for impact in countries. " PAGE | 43
WHO endorses new rapid tuberculosis test A major milestone for global TB diagnosis and care • 2010. 12. 8 | London | Geneva - Today, WHO endorsed a new and novel rapid test for tuberculosis (TB), especially relevant in countries most affected by the disease. The test could revolutionize TB care and control by providing an accurate diagnosis for many patients in about 100 minutes, compared to current tests that can take up to three months to have results. • "This new test represents a major milestone for global TB diagnosis and care. It also represents new hope for the millions of people who are at the highest risk of TB and drug-resistant disease. " said Dr Mario Raviglione, Director of WHO's Stop TB Department. "We have the scientific evidence, we have defined the policy, and now we aim to support implementation for impact in countries. " PAGE | 43
 NEJM – September 2010 – Rapid Molecular Detection of Tuberculosis and Rifampin Resistance • Large press coverage followed the publication in the US, Europe, many parts of the world • PAGE | 44 Dr Mario Raviglione, Director of the World Health Organization's Stop TB Department, said: “The search for faster and more effective means to diagnose TB, which is the second greatest infectious killer of adults worldwide, is a top priority for the global health community. Over the next few days, WHO will convene independent experts to review the full evidence about the field effectiveness of this novel technology and propose it to country programs. These results suggest that it has the potential to revolutionize TB care, and WHO will treat it as a top priority. ”
NEJM – September 2010 – Rapid Molecular Detection of Tuberculosis and Rifampin Resistance • Large press coverage followed the publication in the US, Europe, many parts of the world • PAGE | 44 Dr Mario Raviglione, Director of the World Health Organization's Stop TB Department, said: “The search for faster and more effective means to diagnose TB, which is the second greatest infectious killer of adults worldwide, is a top priority for the global health community. Over the next few days, WHO will convene independent experts to review the full evidence about the field effectiveness of this novel technology and propose it to country programs. These results suggest that it has the potential to revolutionize TB care, and WHO will treat it as a top priority. ”
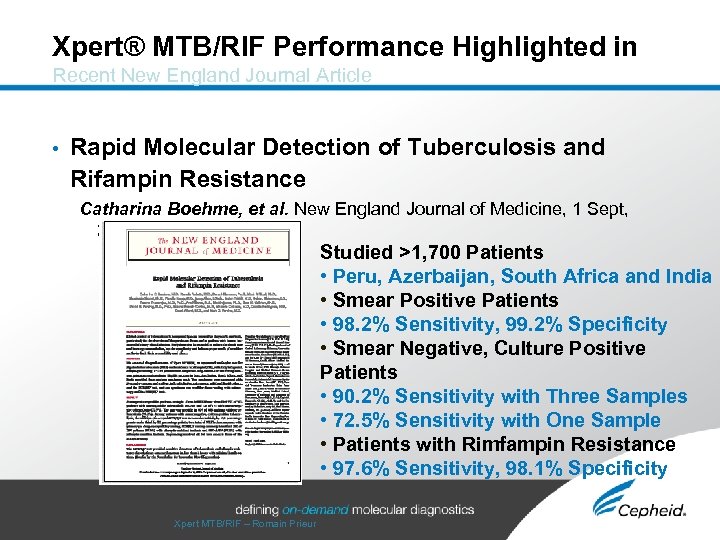 Xpert® MTB/RIF Performance Highlighted in Recent New England Journal Article • Rapid Molecular Detection of Tuberculosis and Rifampin Resistance Catharina Boehme, et al. New England Journal of Medicine, 1 Sept, 2010 Studied >1, 700 Patients • Peru, Azerbaijan, South Africa and India • Smear Positive Patients • 98. 2% Sensitivity, 99. 2% Specificity • Smear Negative, Culture Positive Patients • 90. 2% Sensitivity with Three Samples • 72. 5% Sensitivity with One Sample • Patients with Rimfampin Resistance • 97. 6% Sensitivity, 98. 1% Specificity Xpert MTB/RIF – Romain Prieur
Xpert® MTB/RIF Performance Highlighted in Recent New England Journal Article • Rapid Molecular Detection of Tuberculosis and Rifampin Resistance Catharina Boehme, et al. New England Journal of Medicine, 1 Sept, 2010 Studied >1, 700 Patients • Peru, Azerbaijan, South Africa and India • Smear Positive Patients • 98. 2% Sensitivity, 99. 2% Specificity • Smear Negative, Culture Positive Patients • 90. 2% Sensitivity with Three Samples • 72. 5% Sensitivity with One Sample • Patients with Rimfampin Resistance • 97. 6% Sensitivity, 98. 1% Specificity Xpert MTB/RIF – Romain Prieur
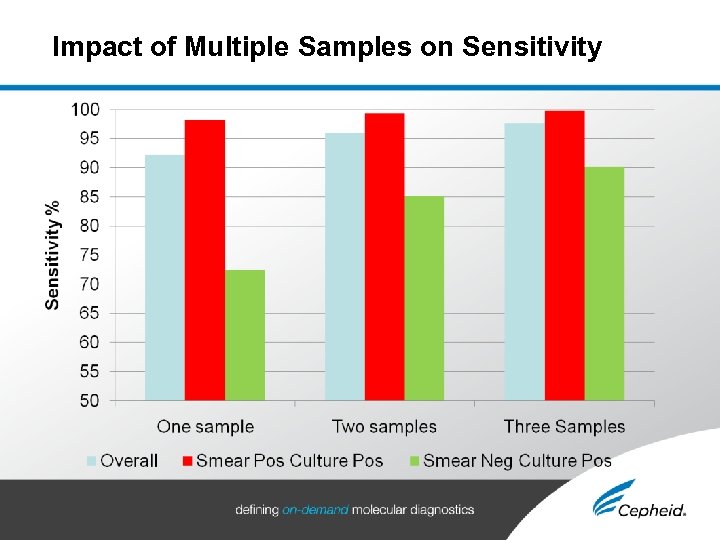 Impact of Multiple Samples on Sensitivity
Impact of Multiple Samples on Sensitivity
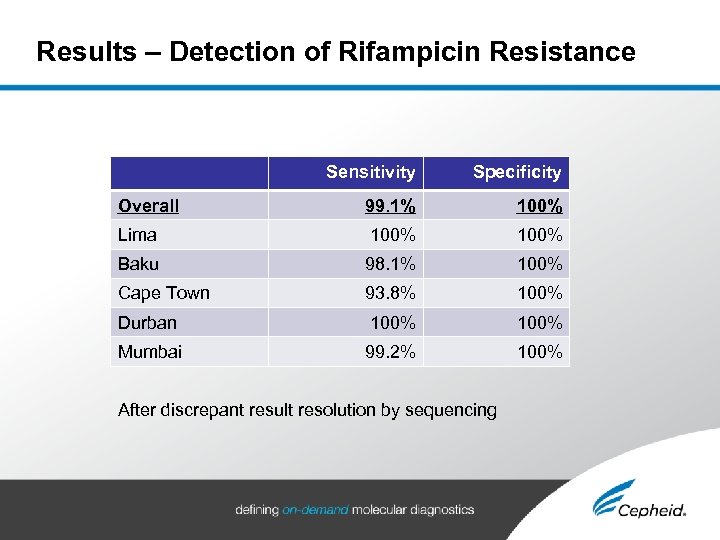 Results – Detection of Rifampicin Resistance Sensitivity Specificity Overall 99. 1% 100% Lima 100% Baku 98. 1% 100% Cape Town 93. 8% 100% Durban 100% Mumbai 99. 2% 100% After discrepant result resolution by sequencing
Results – Detection of Rifampicin Resistance Sensitivity Specificity Overall 99. 1% 100% Lima 100% Baku 98. 1% 100% Cape Town 93. 8% 100% Durban 100% Mumbai 99. 2% 100% After discrepant result resolution by sequencing
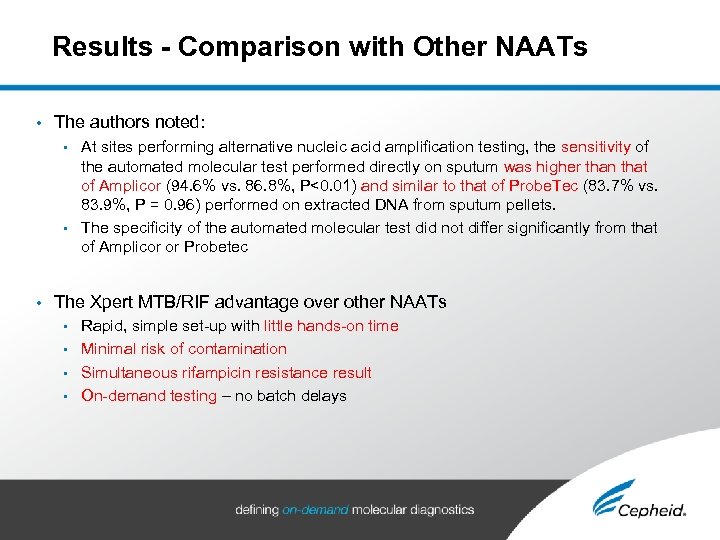 Results - Comparison with Other NAATs • The authors noted: At sites performing alternative nucleic acid amplification testing, the sensitivity of the automated molecular test performed directly on sputum was higher than that of Amplicor (94. 6% vs. 86. 8%, P<0. 01) and similar to that of Probe. Tec (83. 7% vs. 83. 9%, P = 0. 96) performed on extracted DNA from sputum pellets. • The specificity of the automated molecular test did not differ significantly from that of Amplicor or Probetec • • The Xpert MTB/RIF advantage over other NAATs Rapid, simple set-up with little hands-on time • Minimal risk of contamination • Simultaneous rifampicin resistance result • On-demand testing – no batch delays •
Results - Comparison with Other NAATs • The authors noted: At sites performing alternative nucleic acid amplification testing, the sensitivity of the automated molecular test performed directly on sputum was higher than that of Amplicor (94. 6% vs. 86. 8%, P<0. 01) and similar to that of Probe. Tec (83. 7% vs. 83. 9%, P = 0. 96) performed on extracted DNA from sputum pellets. • The specificity of the automated molecular test did not differ significantly from that of Amplicor or Probetec • • The Xpert MTB/RIF advantage over other NAATs Rapid, simple set-up with little hands-on time • Minimal risk of contamination • Simultaneous rifampicin resistance result • On-demand testing – no batch delays •
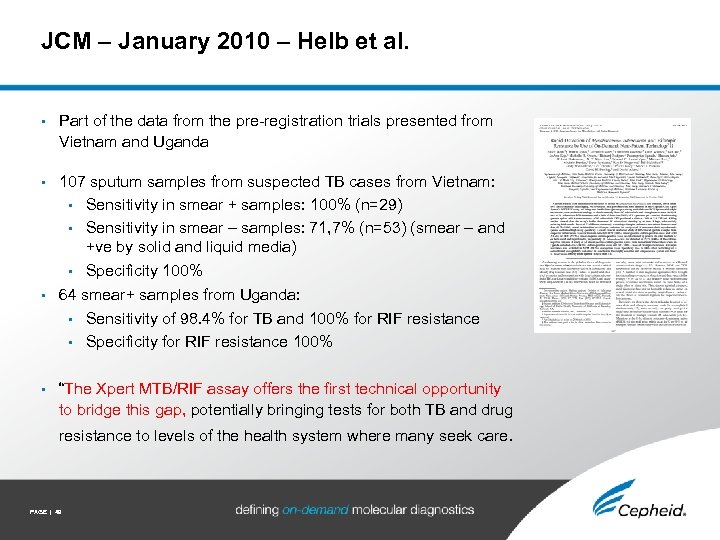 JCM – January 2010 – Helb et al. • Part of the data from the pre-registration trials presented from Vietnam and Uganda • 107 sputum samples from suspected TB cases from Vietnam: • Sensitivity in smear + samples: 100% (n=29) • Sensitivity in smear – samples: 71, 7% (n=53) (smear – and +ve by solid and liquid media) • Specificity 100% • 64 smear+ samples from Uganda: • Sensitivity of 98. 4% for TB and 100% for RIF resistance • Specificity for RIF resistance 100% • “The Xpert MTB/RIF assay offers the first technical opportunity to bridge this gap, potentially bringing tests for both TB and drug resistance to levels of the health system where many seek care. PAGE | 49
JCM – January 2010 – Helb et al. • Part of the data from the pre-registration trials presented from Vietnam and Uganda • 107 sputum samples from suspected TB cases from Vietnam: • Sensitivity in smear + samples: 100% (n=29) • Sensitivity in smear – samples: 71, 7% (n=53) (smear – and +ve by solid and liquid media) • Specificity 100% • 64 smear+ samples from Uganda: • Sensitivity of 98. 4% for TB and 100% for RIF resistance • Specificity for RIF resistance 100% • “The Xpert MTB/RIF assay offers the first technical opportunity to bridge this gap, potentially bringing tests for both TB and drug resistance to levels of the health system where many seek care. PAGE | 49
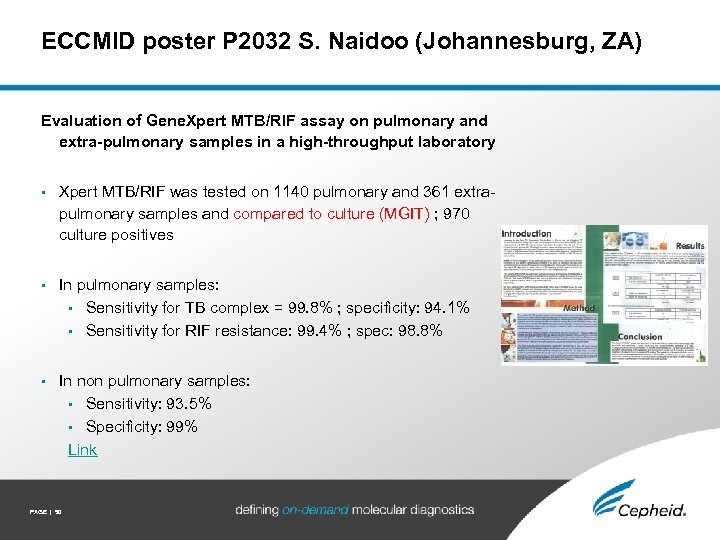 ECCMID poster P 2032 S. Naidoo (Johannesburg, ZA) Evaluation of Gene. Xpert MTB/RIF assay on pulmonary and extra-pulmonary samples in a high-throughput laboratory • Xpert MTB/RIF was tested on 1140 pulmonary and 361 extrapulmonary samples and compared to culture (MGIT) ; 970 culture positives • In pulmonary samples: • Sensitivity for TB complex = 99. 8% ; specificity: 94. 1% • Sensitivity for RIF resistance: 99. 4% ; spec: 98. 8% • In non pulmonary samples: • Sensitivity: 93. 5% • Specificity: 99% Link PAGE | 50
ECCMID poster P 2032 S. Naidoo (Johannesburg, ZA) Evaluation of Gene. Xpert MTB/RIF assay on pulmonary and extra-pulmonary samples in a high-throughput laboratory • Xpert MTB/RIF was tested on 1140 pulmonary and 361 extrapulmonary samples and compared to culture (MGIT) ; 970 culture positives • In pulmonary samples: • Sensitivity for TB complex = 99. 8% ; specificity: 94. 1% • Sensitivity for RIF resistance: 99. 4% ; spec: 98. 8% • In non pulmonary samples: • Sensitivity: 93. 5% • Specificity: 99% Link PAGE | 50
 Other posters presented at ECCMID 2010 P 2048 T. Bodmer, A. Ströhle (Berne, CH) Diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis in a low prevalence setting – the Xpert MTB/RIF test P 2047 - J. S. Lin, C. Lin, R. Hsiao, L. Shih (Changhua, TW) Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF assay and amplified Mycobacterium tuberculosis direct test in direct detection of pulmonary M. tuberculosis complex P 2076 K. Kart Yasar, F. Pehlivanoglu, G. Sengoz, E. R. Ince, S. Sandikci (Istanbul, TR) Tuberculosis meningoencephalitis with severe neurologic sequelae in an immigrant family’s child: PAGE | 51
Other posters presented at ECCMID 2010 P 2048 T. Bodmer, A. Ströhle (Berne, CH) Diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis in a low prevalence setting – the Xpert MTB/RIF test P 2047 - J. S. Lin, C. Lin, R. Hsiao, L. Shih (Changhua, TW) Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF assay and amplified Mycobacterium tuberculosis direct test in direct detection of pulmonary M. tuberculosis complex P 2076 K. Kart Yasar, F. Pehlivanoglu, G. Sengoz, E. R. Ince, S. Sandikci (Istanbul, TR) Tuberculosis meningoencephalitis with severe neurologic sequelae in an immigrant family’s child: PAGE | 51
 Poster presented at ASM 2010
Poster presented at ASM 2010
 Posters presented at ESM 2010 Detection of M. tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance using a commercial PCR real time technique in respiratory and extrapulmonary samples (T. Tortola, N. Martin…Vall d’Hebron Hosp. in Barcelona, Spain) Preliminary evaluation of Xpert MTB RIF kit for tuberculosis detection in nonrespiratory specimens (M. Casal, M. Causse, Reina Sofia hosp in Cordoba, Spain) Evaluation of Gene. Xpert MTB/RIF assay for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis detection and Rifampicin resistance identification in patients with high clinical suspicion of TB. (P. Ioannidis, D. Papaventsis, S. Nikolaou, National reference lab in Athens, Greece) Molecular diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis: a three day experience (M. Peracchi, L. Fallico, Padua, Italy) + oral presentation respiratory and non respitatory samples Evaluation of Genexpert MTB/RIF assay for detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Rifampicin resistance in a routine laboratory setting in Slovenia (Manca Zolnir-Dovc, Golnik, Slovenia)
Posters presented at ESM 2010 Detection of M. tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance using a commercial PCR real time technique in respiratory and extrapulmonary samples (T. Tortola, N. Martin…Vall d’Hebron Hosp. in Barcelona, Spain) Preliminary evaluation of Xpert MTB RIF kit for tuberculosis detection in nonrespiratory specimens (M. Casal, M. Causse, Reina Sofia hosp in Cordoba, Spain) Evaluation of Gene. Xpert MTB/RIF assay for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis detection and Rifampicin resistance identification in patients with high clinical suspicion of TB. (P. Ioannidis, D. Papaventsis, S. Nikolaou, National reference lab in Athens, Greece) Molecular diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis: a three day experience (M. Peracchi, L. Fallico, Padua, Italy) + oral presentation respiratory and non respitatory samples Evaluation of Genexpert MTB/RIF assay for detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Rifampicin resistance in a routine laboratory setting in Slovenia (Manca Zolnir-Dovc, Golnik, Slovenia)
 More to come at ICAAC 2010 Rapid and Efficient detection of Mycobactrium Tuberculosis by the Cepheid Xpert MTB RIF assay (B. Malbruny. . . R. Leclercq, V. Cattoire, CHU Caen, France) Effectiveness Analysis of Integrated Nucleic Acid Amplification System for the Rapid Diagnosis of Smear-negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis (L. Muñoz, …F. Alcaide, M. Santin, Hosp Univ. Bellvitge, Barcelona, Spain)
More to come at ICAAC 2010 Rapid and Efficient detection of Mycobactrium Tuberculosis by the Cepheid Xpert MTB RIF assay (B. Malbruny. . . R. Leclercq, V. Cattoire, CHU Caen, France) Effectiveness Analysis of Integrated Nucleic Acid Amplification System for the Rapid Diagnosis of Smear-negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis (L. Muñoz, …F. Alcaide, M. Santin, Hosp Univ. Bellvitge, Barcelona, Spain)
 • 越短的時間得到正確的藥物治療,對結核病患有較佳的預 後 • 在短時間得到治療,能減低傳染家人及社會的傳播壓力 • 病患短時間確診能改變 • 及時確診是全球結核病控制的重要步驟 TB及 MDR-TB的傳播 NEJM 363; 11 Sep 9, 2010 INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 55
• 越短的時間得到正確的藥物治療,對結核病患有較佳的預 後 • 在短時間得到治療,能減低傳染家人及社會的傳播壓力 • 病患短時間確診能改變 • 及時確診是全球結核病控制的重要步驟 TB及 MDR-TB的傳播 NEJM 363; 11 Sep 9, 2010 INTERNATIONAL DISTRIBUTOR MEETING INTERNAL USE ONLY | 55
 Delivering A Better Way Delivering a Better Way to Realize the Benefits of Molecular Diagnostics ACCURATE FAST EASY Results Answers To Use
Delivering A Better Way Delivering a Better Way to Realize the Benefits of Molecular Diagnostics ACCURATE FAST EASY Results Answers To Use
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!


