423a1a87254abb738959b9f245887fa0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Centre Marocain de Promotion des Exportations Nous emmenons le Maroc vers le monde 1
Centre Marocain de Promotion des Exportations Nous emmenons le Maroc vers le monde 1
 INVESTING IN MOROCCO 2
INVESTING IN MOROCCO 2
 Agenda n Why Invest in Morocco? n Key Information n Political Overview n Main Transport Infrastructures n Legal Form of Companies n Exchange Regulations n Labor Regulations n Customs n Tax System n Investment Incentives n Accounting Standards 3
Agenda n Why Invest in Morocco? n Key Information n Political Overview n Main Transport Infrastructures n Legal Form of Companies n Exchange Regulations n Labor Regulations n Customs n Tax System n Investment Incentives n Accounting Standards 3
 Why Invest in Morocco? n Morocco offers low labor costs, an interesting geographic location, and a high quality of life n 3 hours from Paris and 80 minutes from Spain (Madrid) n A stable socio-political environment n A liberal orientation of its economy n Sound infrastructure n A multicultural population n A fast and efficient customs service n Excellent tourist attractions 4
Why Invest in Morocco? n Morocco offers low labor costs, an interesting geographic location, and a high quality of life n 3 hours from Paris and 80 minutes from Spain (Madrid) n A stable socio-political environment n A liberal orientation of its economy n Sound infrastructure n A multicultural population n A fast and efficient customs service n Excellent tourist attractions 4
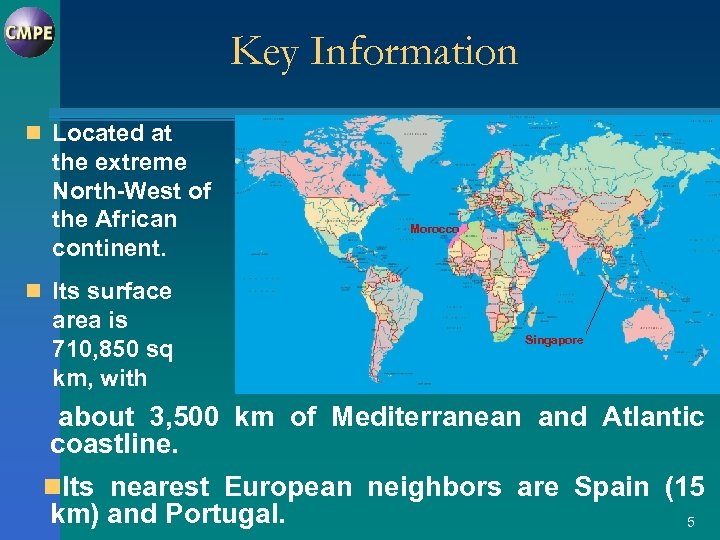 Key Information n Located at the extreme North-West of the African continent. Morocco n Its surface area is 710, 850 sq km, with Singapore about 3, 500 km of Mediterranean and Atlantic coastline. n. Its nearest European neighbors are Spain (15 km) and Portugal. 5
Key Information n Located at the extreme North-West of the African continent. Morocco n Its surface area is 710, 850 sq km, with Singapore about 3, 500 km of Mediterranean and Atlantic coastline. n. Its nearest European neighbors are Spain (15 km) and Portugal. 5
 Key Information n Climate: – Mediterranean, more extreme in the interior than on the coast – The mean temperature is 16. 4°C to 23°C on the west coast and 10°C to 27°C in the interior n Natural resources: phosphates, iron ore, manganese, lead, zinc, fish, salt 6
Key Information n Climate: – Mediterranean, more extreme in the interior than on the coast – The mean temperature is 16. 4°C to 23°C on the west coast and 10°C to 27°C in the interior n Natural resources: phosphates, iron ore, manganese, lead, zinc, fish, salt 6
 Key Information n Population: – – – Population: 30 million inhabitants 37% less than 15 years old, 56% between 15 and 60 Population growth rate: 1. 55% (2006 est. ) Life expectancy at birth: 70. 94 years Labor force: 11. 19 million (2005 est. ) Labor force by sector (2003 est. ) : v agriculture: 40% v industry: 15% v services: 45% – Unemployment (2005): 11% (rural 3. 6%, urban 18. 3%) 7
Key Information n Population: – – – Population: 30 million inhabitants 37% less than 15 years old, 56% between 15 and 60 Population growth rate: 1. 55% (2006 est. ) Life expectancy at birth: 70. 94 years Labor force: 11. 19 million (2005 est. ) Labor force by sector (2003 est. ) : v agriculture: 40% v industry: 15% v services: 45% – Unemployment (2005): 11% (rural 3. 6%, urban 18. 3%) 7
 Key Information n Main Cities: Casablanca 3. 5 million inhabitants Rabat 1. 5 million inhabitants Kenitra 994, 000 inhabitants Agadir 925, 000 inhabitants Marrakech 900, 000 inhabitants Settat 852, 000 inhabitants Nador 690, 000 inhabitants Tangiers 650, 000 inhabitants 8
Key Information n Main Cities: Casablanca 3. 5 million inhabitants Rabat 1. 5 million inhabitants Kenitra 994, 000 inhabitants Agadir 925, 000 inhabitants Marrakech 900, 000 inhabitants Settat 852, 000 inhabitants Nador 690, 000 inhabitants Tangiers 650, 000 inhabitants 8
 Key Information n Language: – Official language: Arabic – Language of business: French – The use of English is spreading n Religions: Muslim 98. 7%, Christian 1. 1%, Jewish 0. 2% n Working week: Monday to Friday, generally 8: 30 am-3: 30 pm. Some private entities’ working hours are 8: 30 am-12: 30 pm and 2: 30 -6: 30 pm 9
Key Information n Language: – Official language: Arabic – Language of business: French – The use of English is spreading n Religions: Muslim 98. 7%, Christian 1. 1%, Jewish 0. 2% n Working week: Monday to Friday, generally 8: 30 am-3: 30 pm. Some private entities’ working hours are 8: 30 am-12: 30 pm and 2: 30 -6: 30 pm 9
 Key Information n Currency: Moroccan Dirham, MAD (1 USD= about 9 MAD) n GDP (2005 est. ): 457. 6 billion MAD (50. 84 billion USD) n GDP - composition by sector (2005 est. ): – agriculture: 14. 1% – industry: 30. 0% – services: 55. 9% n Inflation rate: between 2. 1% and 2. 8% (est. 2007) 10
Key Information n Currency: Moroccan Dirham, MAD (1 USD= about 9 MAD) n GDP (2005 est. ): 457. 6 billion MAD (50. 84 billion USD) n GDP - composition by sector (2005 est. ): – agriculture: 14. 1% – industry: 30. 0% – services: 55. 9% n Inflation rate: between 2. 1% and 2. 8% (est. 2007) 10
 Key Information n Main exports: phosphates, fertilizers, phosphoric acid, fruits and vegetables, sea products, garments n Main imports: oil, wheat, sugar, vegetable oils and wood 11
Key Information n Main exports: phosphates, fertilizers, phosphoric acid, fruits and vegetables, sea products, garments n Main imports: oil, wheat, sugar, vegetable oils and wood 11
 Political Overview n Morocco is a constitutional monarchy. n The King names the 1 st Minister and the members of the n n n government on proposal of the 1 st Minister. About fifteen political parties freely deploy their activities in the Kingdom. Legislative elections are held every 5 years to indicate the 2 rooms; House of Commons and Room of the Advisers. Three large trade-union represent the world of work. Companies are gathered within the framework of a Confederation; CGEM. The number of non governmental organizations (estimated at 20. 000), continues to increase 12
Political Overview n Morocco is a constitutional monarchy. n The King names the 1 st Minister and the members of the n n n government on proposal of the 1 st Minister. About fifteen political parties freely deploy their activities in the Kingdom. Legislative elections are held every 5 years to indicate the 2 rooms; House of Commons and Room of the Advisers. Three large trade-union represent the world of work. Companies are gathered within the framework of a Confederation; CGEM. The number of non governmental organizations (estimated at 20. 000), continues to increase 12
 Political Overview n Morocco is a member of the majority of the international institutions: United Nations, Arab League, IMF, World Bank, World Trade Organization, African Development Bank and Arab Monetary Fund n Morocco is also member of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) 13
Political Overview n Morocco is a member of the majority of the international institutions: United Nations, Arab League, IMF, World Bank, World Trade Organization, African Development Bank and Arab Monetary Fund n Morocco is also member of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) 13
 Main Transport Infrastructures Ports n 24 ports ensure 98% of the country's foreign trade. Each year, 40 million tons of merchandise is handled. n A deep water port at Tangier is under construction; its main task will be to break up heavy cargoes into smaller consignments bound for the ports of the region (USA - Middle East traffic). The infrastructure, superstructure and equipment works would require an investment of about 250 million USD 14
Main Transport Infrastructures Ports n 24 ports ensure 98% of the country's foreign trade. Each year, 40 million tons of merchandise is handled. n A deep water port at Tangier is under construction; its main task will be to break up heavy cargoes into smaller consignments bound for the ports of the region (USA - Middle East traffic). The infrastructure, superstructure and equipment works would require an investment of about 250 million USD 14
 Main Transport Infrastructures Airports n There are 15 main airports (in a total of 27 civil airports), 10 of them international n They handle 2, 741, 000 passengers on regular flights and 1, 090, 000 passengers on charter flights. 15
Main Transport Infrastructures Airports n There are 15 main airports (in a total of 27 civil airports), 10 of them international n They handle 2, 741, 000 passengers on regular flights and 1, 090, 000 passengers on charter flights. 15
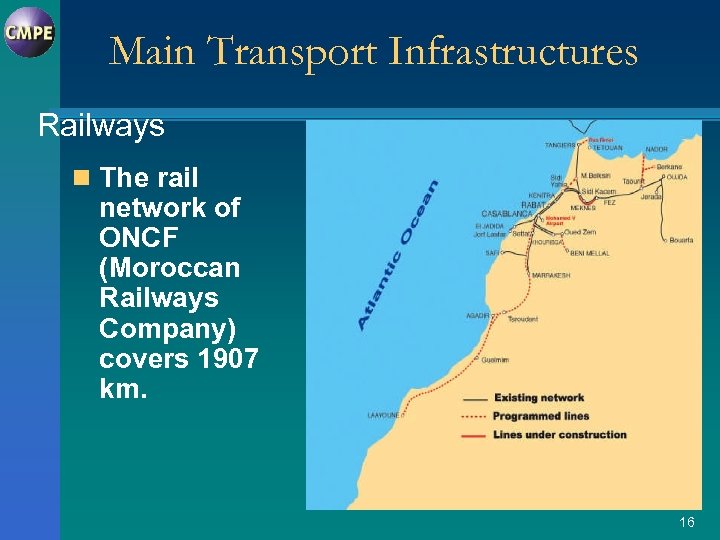 Main Transport Infrastructures Railways n The rail network of ONCF (Moroccan Railways Company) covers 1907 km. 16
Main Transport Infrastructures Railways n The rail network of ONCF (Moroccan Railways Company) covers 1907 km. 16
 Main Transport Infrastructures Roads n The road network is composed of about 62, 000 km of roads, of which more than 50% are paved. The country's road network is one of the biggest in Africa. Highways: 530 km (2004 est. ) 17
Main Transport Infrastructures Roads n The road network is composed of about 62, 000 km of roads, of which more than 50% are paved. The country's road network is one of the biggest in Africa. Highways: 530 km (2004 est. ) 17
 Legal Forms of Companies (most common) The Société Anonyme (SA) (Limited Company) n The minimum share capital is 300’ 000 MAD (about 33’ 000 USD) and 3 millions MAD in case the company call-up funds publicly n The number of shareholders cannot be less than 5 n The liability of the partners is limited to their contributions n The appointment of a statutory auditor is mandatory n The full subscription of capital is required (pay-up at least ¼ of the shares’ face value, the remaining part must be paid-up within 3 years after the registration of the company) n Management: either a Board of Directors or a Management Committee with a Supervisory Board 18
Legal Forms of Companies (most common) The Société Anonyme (SA) (Limited Company) n The minimum share capital is 300’ 000 MAD (about 33’ 000 USD) and 3 millions MAD in case the company call-up funds publicly n The number of shareholders cannot be less than 5 n The liability of the partners is limited to their contributions n The appointment of a statutory auditor is mandatory n The full subscription of capital is required (pay-up at least ¼ of the shares’ face value, the remaining part must be paid-up within 3 years after the registration of the company) n Management: either a Board of Directors or a Management Committee with a Supervisory Board 18
 Legal Forms of Companies (most common) Société à Responsabilité Limitée (SARL) (Limited Liability Company) n The minimum capital is 10’ 000 MAD (about 1’ 100 USD) n Set up by one or several individuals or companies up to 50, n n n otherwise, it should be changed to a Société Anonyme (SA) The liability of the partners is limited to their contributions The full subscription of capital is required (pay-up at least ¼ of the shares’ face value, the remaining part must be paid-up within 5 years after the registration of the company) Appointing a statutory auditor is not mandatory unless the turnover at the end of a financial year exceeds 50 millions MAD VAT excluded The shares cannot be transferable without the agreement of the majority of the partners, representing at least ¾ of the share capital One or more individuals may be appointed as manager (s) 19
Legal Forms of Companies (most common) Société à Responsabilité Limitée (SARL) (Limited Liability Company) n The minimum capital is 10’ 000 MAD (about 1’ 100 USD) n Set up by one or several individuals or companies up to 50, n n n otherwise, it should be changed to a Société Anonyme (SA) The liability of the partners is limited to their contributions The full subscription of capital is required (pay-up at least ¼ of the shares’ face value, the remaining part must be paid-up within 5 years after the registration of the company) Appointing a statutory auditor is not mandatory unless the turnover at the end of a financial year exceeds 50 millions MAD VAT excluded The shares cannot be transferable without the agreement of the majority of the partners, representing at least ¾ of the share capital One or more individuals may be appointed as manager (s) 19
 Legal Forms of Companies (most common) The Branch n No capital contribution n The branch does not have a distinct legal personality from the company which creates it n The appointment of a statutory auditor is not mandatory 20
Legal Forms of Companies (most common) The Branch n No capital contribution n The branch does not have a distinct legal personality from the company which creates it n The appointment of a statutory auditor is not mandatory 20
 Legal Forms of Companies (Incorporation Procedure) n The setting up of an entity is subject to several formalities prescribed by the Moroccan legislation, mainly registration to the license tax, corporate tax, VAT, with the trade register and the Social Security Department (CNSS). The incorporation procedure would take 3 weeks n The required documents for the setting up are provided to the Regional Investment Center which will provide the necessary registrations and assistance. n There are 16 Regional Investment Centers (one-shop for company registration and investment assistance) which assist investment projects. 21
Legal Forms of Companies (Incorporation Procedure) n The setting up of an entity is subject to several formalities prescribed by the Moroccan legislation, mainly registration to the license tax, corporate tax, VAT, with the trade register and the Social Security Department (CNSS). The incorporation procedure would take 3 weeks n The required documents for the setting up are provided to the Regional Investment Center which will provide the necessary registrations and assistance. n There are 16 Regional Investment Centers (one-shop for company registration and investment assistance) which assist investment projects. 21
 Exchange Regulations n There is an exchange control over the Moroccan currency n If the original investment is made in foreign currency, n n foreign investors can freely: – Transfer income derived from their investment – Transfer disposal revenue of their investment Exchange Control Office should be notified with the inward investment within 6 months from the investment The Moroccan Dirham is convertible for all current transactions, notably technical assistance provided by non -residents Expatriates are allowed to repatriate 100% of their salaries Other transfers are subject to the prior authorization of the Exchange Office 22
Exchange Regulations n There is an exchange control over the Moroccan currency n If the original investment is made in foreign currency, n n foreign investors can freely: – Transfer income derived from their investment – Transfer disposal revenue of their investment Exchange Control Office should be notified with the inward investment within 6 months from the investment The Moroccan Dirham is convertible for all current transactions, notably technical assistance provided by non -residents Expatriates are allowed to repatriate 100% of their salaries Other transfers are subject to the prior authorization of the Exchange Office 22
 Labour Regulations n Working hours: 44 hours per week or 2288 hours per year n Minimum legal salary for workers and employees employed in industrial and commercial activities: 9. 66 MAD per hour. n Legal minimum number of holidays: 1. 5 days per month worked by the employee n Employment contracts: – “Contrat à durée indéterminé” (CDI): permanent contract – “Contrat à durée déterminé” (CDD): fixed-term contract – “Contrat de travail temporaire”: temporary contract (short term) 23
Labour Regulations n Working hours: 44 hours per week or 2288 hours per year n Minimum legal salary for workers and employees employed in industrial and commercial activities: 9. 66 MAD per hour. n Legal minimum number of holidays: 1. 5 days per month worked by the employee n Employment contracts: – “Contrat à durée indéterminé” (CDI): permanent contract – “Contrat à durée déterminé” (CDD): fixed-term contract – “Contrat de travail temporaire”: temporary contract (short term) 23
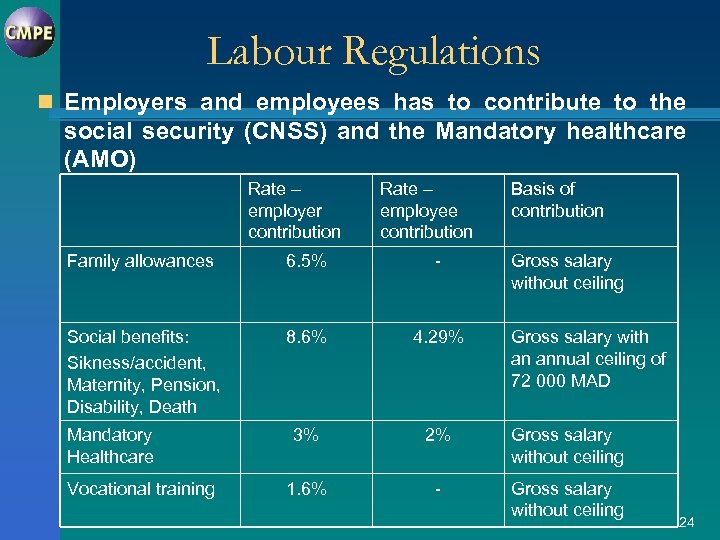 Labour Regulations n Employers and employees has to contribute to the social security (CNSS) and the Mandatory healthcare (AMO) Rate – employer contribution Rate – employee contribution Basis of contribution Family allowances 6. 5% - Social benefits: Sikness/accident, Maternity, Pension, Disability, Death 8. 6% 4. 29% 3% 2% Gross salary without ceiling 1. 6% - Gross salary without ceiling Mandatory Healthcare Vocational training Gross salary without ceiling Gross salary with an annual ceiling of 72 000 MAD 24
Labour Regulations n Employers and employees has to contribute to the social security (CNSS) and the Mandatory healthcare (AMO) Rate – employer contribution Rate – employee contribution Basis of contribution Family allowances 6. 5% - Social benefits: Sikness/accident, Maternity, Pension, Disability, Death 8. 6% 4. 29% 3% 2% Gross salary without ceiling 1. 6% - Gross salary without ceiling Mandatory Healthcare Vocational training Gross salary without ceiling Gross salary with an annual ceiling of 72 000 MAD 24
 Customs n The customs tariff schedule is based on the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (HS) n Customs duties are calculation ad valorem on the CIF value of the goods n Customs base rates varies between 2. 5% and 45% n In addition to the customs duties, there are Import Tax (Prélèvement Fiscal à l’Importation, PFI) which general rate is 15% on the customs value and the Para-Fiscal Import Tax of 0. 25% of the value of the import n For all imports into Morocco, the import certificate must be registered with an authorized bank, which make the necessary payments upon submission of the required documents. 25
Customs n The customs tariff schedule is based on the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (HS) n Customs duties are calculation ad valorem on the CIF value of the goods n Customs base rates varies between 2. 5% and 45% n In addition to the customs duties, there are Import Tax (Prélèvement Fiscal à l’Importation, PFI) which general rate is 15% on the customs value and the Para-Fiscal Import Tax of 0. 25% of the value of the import n For all imports into Morocco, the import certificate must be registered with an authorized bank, which make the necessary payments upon submission of the required documents. 25
 Customs n Morocco has several commercial agreements: – Free Trade Agreements with: EU, USA, UAE, Turkey, Tunisia, Jordan, Egypt – Free trade Agreement with AELE (or EFTA) (Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Island republic, Norway) – Agreement for the development of trade with Arab League (Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Kuwait, Lebanon, Palestine, Qatar, Sudan, Sultanate Oman, Syria, Yemen, Egypt, UAE, Iraq, Jordan, Libya, Tunisia, Morocco) – Bilateral Tariff agreements with Algeria, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Senegal, Libya, Mauritania, Guinea 26
Customs n Morocco has several commercial agreements: – Free Trade Agreements with: EU, USA, UAE, Turkey, Tunisia, Jordan, Egypt – Free trade Agreement with AELE (or EFTA) (Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Island republic, Norway) – Agreement for the development of trade with Arab League (Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Kuwait, Lebanon, Palestine, Qatar, Sudan, Sultanate Oman, Syria, Yemen, Egypt, UAE, Iraq, Jordan, Libya, Tunisia, Morocco) – Bilateral Tariff agreements with Algeria, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Senegal, Libya, Mauritania, Guinea 26
 Tax System n Corporate Tax (impôts sur les sociétés, IS) – Corporate tax rate is 35% (39. 6% for banks and insurance institutions) – There is 10% withholding tax on dividends or after tax profits that are remitted to non-resident companies – Income earned by non resident companies is subject to tax at a rate of 10% – 8. 75% for the companies operating in free zone areas of export during the 20 years following the 5 first years of total exemption – Non resident companies successful tenderers of work contracts may opt for a flat-rate tax of 8% on the total amount of the contract 27
Tax System n Corporate Tax (impôts sur les sociétés, IS) – Corporate tax rate is 35% (39. 6% for banks and insurance institutions) – There is 10% withholding tax on dividends or after tax profits that are remitted to non-resident companies – Income earned by non resident companies is subject to tax at a rate of 10% – 8. 75% for the companies operating in free zone areas of export during the 20 years following the 5 first years of total exemption – Non resident companies successful tenderers of work contracts may opt for a flat-rate tax of 8% on the total amount of the contract 27
 Tax System n Tax treaties signed by Morocco n n n Algeria Bahrain Belgium Bulgaria Canada Denmark Egypt Finland France Germany Hungary n India n South Korea n Italy n Spain n Libya n Sweden n Luxembourg n Switzerland n Netherlands n Tunisia n Norway n MAU (UMA) n Poland n United Arab n Portugal Emirates n Romania n United Kingdom n Russia n United States 28
Tax System n Tax treaties signed by Morocco n n n Algeria Bahrain Belgium Bulgaria Canada Denmark Egypt Finland France Germany Hungary n India n South Korea n Italy n Spain n Libya n Sweden n Luxembourg n Switzerland n Netherlands n Tunisia n Norway n MAU (UMA) n Poland n United Arab n Portugal Emirates n Romania n United Kingdom n Russia n United States 28
 Tax System n Value Added Tax – VAT is levied on goods and services rendered or delivered in Morocco at a common rate of 20%. Reduced VAT rates of 7%, 10% and 14% are available for some goods or services – Taxpayers are assessed on either a monthly or quarterly basis depending on their turnover – Non resident companies performing taxable operations in Morocco must appoint a tax representative in Morocco who will commit to comply with the obligations to which Moroccan taxpayers are subject (paying the VAT due and filing monthly VAT returns on behalf of the non resident company). 29
Tax System n Value Added Tax – VAT is levied on goods and services rendered or delivered in Morocco at a common rate of 20%. Reduced VAT rates of 7%, 10% and 14% are available for some goods or services – Taxpayers are assessed on either a monthly or quarterly basis depending on their turnover – Non resident companies performing taxable operations in Morocco must appoint a tax representative in Morocco who will commit to comply with the obligations to which Moroccan taxpayers are subject (paying the VAT due and filing monthly VAT returns on behalf of the non resident company). 29
 Tax System n Individual Income Tax (Impôt sur le revenu, IR) – Taxable income: professional income, salaries, real estate income and gain, equity investment income and agricultural income (agriculture is exempted until the year 2010) – Income tax on salaries must be withheld monthly by employers domiciled or established in Morocco. 30
Tax System n Individual Income Tax (Impôt sur le revenu, IR) – Taxable income: professional income, salaries, real estate income and gain, equity investment income and agricultural income (agriculture is exempted until the year 2010) – Income tax on salaries must be withheld monthly by employers domiciled or established in Morocco. 30
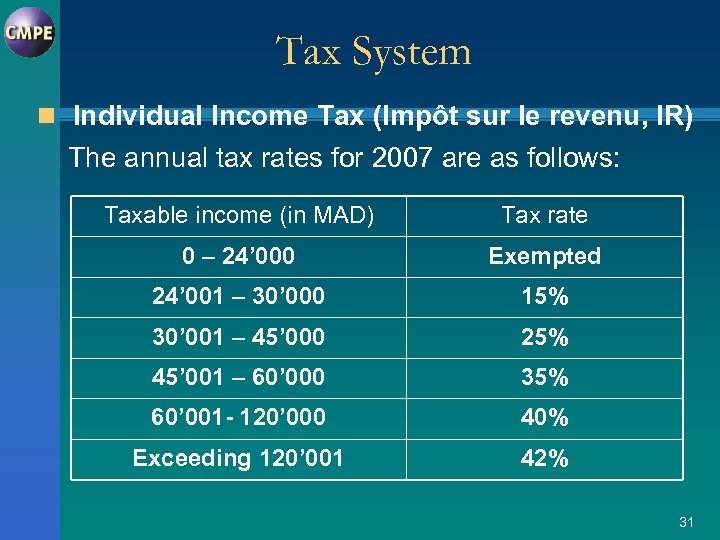 Tax System n Individual Income Tax (Impôt sur le revenu, IR) The annual tax rates for 2007 are as follows: Taxable income (in MAD) Tax rate 0 – 24’ 000 Exempted 24’ 001 – 30’ 000 15% 30’ 001 – 45’ 000 25% 45’ 001 – 60’ 000 35% 60’ 001 - 120’ 000 40% Exceeding 120’ 001 42% 31
Tax System n Individual Income Tax (Impôt sur le revenu, IR) The annual tax rates for 2007 are as follows: Taxable income (in MAD) Tax rate 0 – 24’ 000 Exempted 24’ 001 – 30’ 000 15% 30’ 001 – 45’ 000 25% 45’ 001 – 60’ 000 35% 60’ 001 - 120’ 000 40% Exceeding 120’ 001 42% 31
 Tax System n Urban tax (“taxe urbaine”) – The urban tax applies to land, buildings and their improvement and equipment (with a value limited to MAD 50 million) properties situated within urban areas and their peripheral zones. – An exemption is granted during the 5 first years for the acquisitions of equipment, new buildings or additions except for permanent establishments of foreign companies. – The urban tax is calculated by applying 13. 5% to the rental value. n Communal tax ("taxe d’édilité") – The tax rate is 10% on the rental value (which is determined for the urban tax calculation) for the buildings located in the perimeter of urban communes and delimited centres calculation 32
Tax System n Urban tax (“taxe urbaine”) – The urban tax applies to land, buildings and their improvement and equipment (with a value limited to MAD 50 million) properties situated within urban areas and their peripheral zones. – An exemption is granted during the 5 first years for the acquisitions of equipment, new buildings or additions except for permanent establishments of foreign companies. – The urban tax is calculated by applying 13. 5% to the rental value. n Communal tax ("taxe d’édilité") – The tax rate is 10% on the rental value (which is determined for the urban tax calculation) for the buildings located in the perimeter of urban communes and delimited centres calculation 32
 Tax System n Licence tax (“patente”) – The licence tax applies to entities that carry on professional, industrial or commercial activities in Morocco. Licence tax is determined on the basis of the gross rental value of the premises used – The rental value must not be less than 3% of the market value of the assets of land, buildings and equipment (limited to MAD 50 million) – Licence tax is levied on the rental value at a rate between 10% to 30% according to the type of business. There is a tax exemption for the 5 first years of the start of activities except for permanent establishment 33
Tax System n Licence tax (“patente”) – The licence tax applies to entities that carry on professional, industrial or commercial activities in Morocco. Licence tax is determined on the basis of the gross rental value of the premises used – The rental value must not be less than 3% of the market value of the assets of land, buildings and equipment (limited to MAD 50 million) – Licence tax is levied on the rental value at a rate between 10% to 30% according to the type of business. There is a tax exemption for the 5 first years of the start of activities except for permanent establishment 33
 Investment Incentives n Export: The taxable income corresponding to turnover realized in export benefit from a total exemption from the Corporate tax (or income tax when applicable) during the 5 first years from the financial year during which the first operation of export occurred and from a 50% reduction beyond this period n Tourism: The taxable income corresponding to Hotels’ turnover realized in foreign currency repatriated directly or through travel agencies benefit from total exemption from Corporate tax (or income tax when applicable) during the 5 first years from the financial year during which the first operation of accommodation in foreign currency occurred and from a 50% reduction beyond this period 34
Investment Incentives n Export: The taxable income corresponding to turnover realized in export benefit from a total exemption from the Corporate tax (or income tax when applicable) during the 5 first years from the financial year during which the first operation of export occurred and from a 50% reduction beyond this period n Tourism: The taxable income corresponding to Hotels’ turnover realized in foreign currency repatriated directly or through travel agencies benefit from total exemption from Corporate tax (or income tax when applicable) during the 5 first years from the financial year during which the first operation of accommodation in foreign currency occurred and from a 50% reduction beyond this period 34
 Investment Incentives n Geographical incentives: Reduction of 50% of the Corporate tax (or income tax when applicable) during the 5 first years from the start of activities of entities established in some provinces set in the decree n° 2 -98 -520: Al Hoceima, Berkane, Boujdour, Chefchaouen, Es-Semara, Guelmim, Laâyoune, Larache, Nador, Oued-Ed-Dahab, Oujda-Angad, Tanger-Assilah, Fahs-Bni-Makada, Tan-Tan, Taounate, Taourirt, Tata, Taza, Tétouan n Tangiers Province: The amounts Corporate tax or income tax for taxpayers having their head office in Tangier and corresponding to their activities carried out mainly within the province are reduced by 50%. 35
Investment Incentives n Geographical incentives: Reduction of 50% of the Corporate tax (or income tax when applicable) during the 5 first years from the start of activities of entities established in some provinces set in the decree n° 2 -98 -520: Al Hoceima, Berkane, Boujdour, Chefchaouen, Es-Semara, Guelmim, Laâyoune, Larache, Nador, Oued-Ed-Dahab, Oujda-Angad, Tanger-Assilah, Fahs-Bni-Makada, Tan-Tan, Taounate, Taourirt, Tata, Taza, Tétouan n Tangiers Province: The amounts Corporate tax or income tax for taxpayers having their head office in Tangier and corresponding to their activities carried out mainly within the province are reduced by 50%. 35
 Investment Incentives Companies can buy materials and equipment which are investments to be recognized within depreciable assets with VAT exemption during the 24 months following the start of their activities (under some conditions) n Investment projects in some sectors (e. g. car product manufacturing) are eligible for Hassan II Fund subsidy consisting of 50% of the cost of the land 30% of the cost of the construction (with ceilings) n Important investments of at least 200 million MAD may benefit from the import VAT and duties exemption on equipments and goods imported directly or on their behalf, under the terms of an agreement with the Government n 36
Investment Incentives Companies can buy materials and equipment which are investments to be recognized within depreciable assets with VAT exemption during the 24 months following the start of their activities (under some conditions) n Investment projects in some sectors (e. g. car product manufacturing) are eligible for Hassan II Fund subsidy consisting of 50% of the cost of the land 30% of the cost of the construction (with ceilings) n Important investments of at least 200 million MAD may benefit from the import VAT and duties exemption on equipments and goods imported directly or on their behalf, under the terms of an agreement with the Government n 36
 Investment Incentives n Companies with important investment can enter into an agreement with the Government and benefit from its participation to the investment costs – The investment should: v be equal or exceeding 200 million MAD v create 250 or more of permanent jobs v be realized in one of regions provided by decree v providing a transfer of technology v contribute to the protection of the environment – The participation of the Government would be: v in the acquisition cost of the land up to 20% v in the expenses for external infrastructures needed for the realization of the investment up to 5% of these expenses v in the professional training costs included in the investment up to 20% of the cost of the training. 37
Investment Incentives n Companies with important investment can enter into an agreement with the Government and benefit from its participation to the investment costs – The investment should: v be equal or exceeding 200 million MAD v create 250 or more of permanent jobs v be realized in one of regions provided by decree v providing a transfer of technology v contribute to the protection of the environment – The participation of the Government would be: v in the acquisition cost of the land up to 20% v in the expenses for external infrastructures needed for the realization of the investment up to 5% of these expenses v in the professional training costs included in the investment up to 20% of the cost of the training. 37
 Investment Incentives n Real estate developers are exempted for all their deeds, activities and income related to development of social housing from the following: – Registration fee (‘Droits d’enregistrement’) and stamps – Conservation fee (‘Droits fonciers’) – License tax (‘patente’) – VAT – Corporate tax (or income tax when applicable) – Urban tax – Any other taxes or fees collected for local communities These exemptions are granted for real estate developers which realize their operations under an agreement signed with the Government for building programs of 2, 500 low cost housing within a maximum of 5 years starting from the delivery of the building permit. 38
Investment Incentives n Real estate developers are exempted for all their deeds, activities and income related to development of social housing from the following: – Registration fee (‘Droits d’enregistrement’) and stamps – Conservation fee (‘Droits fonciers’) – License tax (‘patente’) – VAT – Corporate tax (or income tax when applicable) – Urban tax – Any other taxes or fees collected for local communities These exemptions are granted for real estate developers which realize their operations under an agreement signed with the Government for building programs of 2, 500 low cost housing within a maximum of 5 years starting from the delivery of the building permit. 38
 Investment Incentives n A customs free zone situated in Tangiers. This export free zone benefits from the following incentives: – The entrance of goods and their exit are not subject to the legislation related to foreign trade and exchange control. – Goods entering or leaving export free zone as well as those obtained or staying in that export free zone, are exempted from all customs duties – Exemption from Corporate tax for the 5 first year and 8. 75% for the 20 following years – Goods and services rendered to the export free zone are exempted from VAT – Exemption for the dividends paid to non-residents and application of a reduced rate of 7. 5% for dividends paid to Moroccan residents – Exemption from registration fee and stamp duty on capital at the incorporation or the increase in capital and on the on acquisition of land for the investment project – Exemption from the License tax for the 15 years from the start of activities from the Urban Tax starting from the achievement 39
Investment Incentives n A customs free zone situated in Tangiers. This export free zone benefits from the following incentives: – The entrance of goods and their exit are not subject to the legislation related to foreign trade and exchange control. – Goods entering or leaving export free zone as well as those obtained or staying in that export free zone, are exempted from all customs duties – Exemption from Corporate tax for the 5 first year and 8. 75% for the 20 following years – Goods and services rendered to the export free zone are exempted from VAT – Exemption for the dividends paid to non-residents and application of a reduced rate of 7. 5% for dividends paid to Moroccan residents – Exemption from registration fee and stamp duty on capital at the incorporation or the increase in capital and on the on acquisition of land for the investment project – Exemption from the License tax for the 15 years from the start of activities from the Urban Tax starting from the achievement 39
 Accounting Standards n The Moroccan accounting standards were introduced by law in 1992 and are based on international standards n These standards differs however, from IFRS for several points n Three of the big international accounting firms are present in Morocco n A Board of chartered accountant was created by law regulating chartered accounting profession in 1993 40
Accounting Standards n The Moroccan accounting standards were introduced by law in 1992 and are based on international standards n These standards differs however, from IFRS for several points n Three of the big international accounting firms are present in Morocco n A Board of chartered accountant was created by law regulating chartered accounting profession in 1993 40


