76e0ebfe7bd7511a60eb888694691051.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 CENTRE FOR MULTIMEDIA EDUCATION DEVELOPMENT (CMED)
CENTRE FOR MULTIMEDIA EDUCATION DEVELOPMENT (CMED)
 CENTRE FOR MULTIMEDIA EDUCATION DEVELOPMENT To design and develop innovative applications for the university n To develop and package R&D ideas and concepts n To conduct training in software engineering n To develop software products for clients n
CENTRE FOR MULTIMEDIA EDUCATION DEVELOPMENT To design and develop innovative applications for the university n To develop and package R&D ideas and concepts n To conduct training in software engineering n To develop software products for clients n
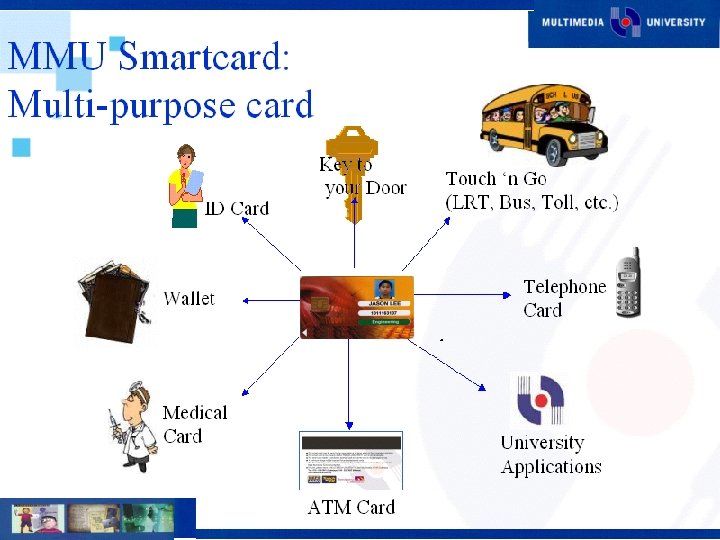
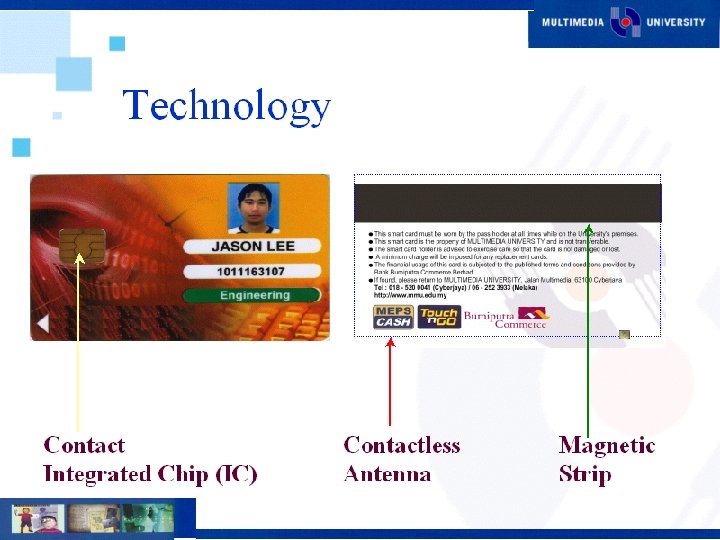
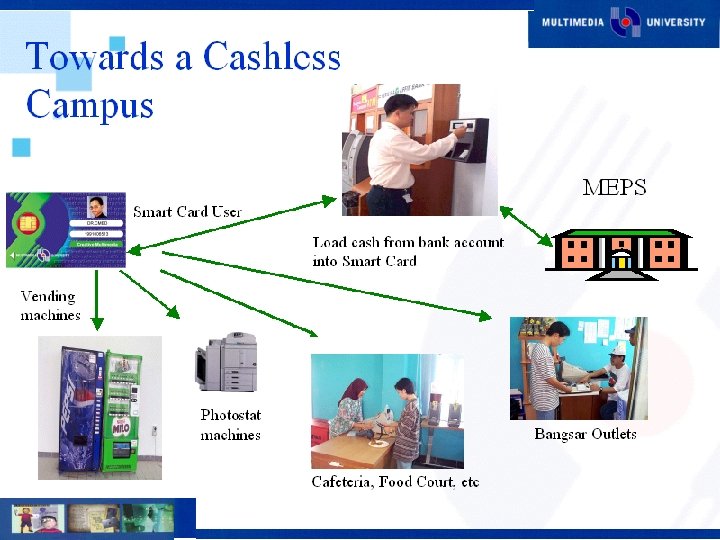
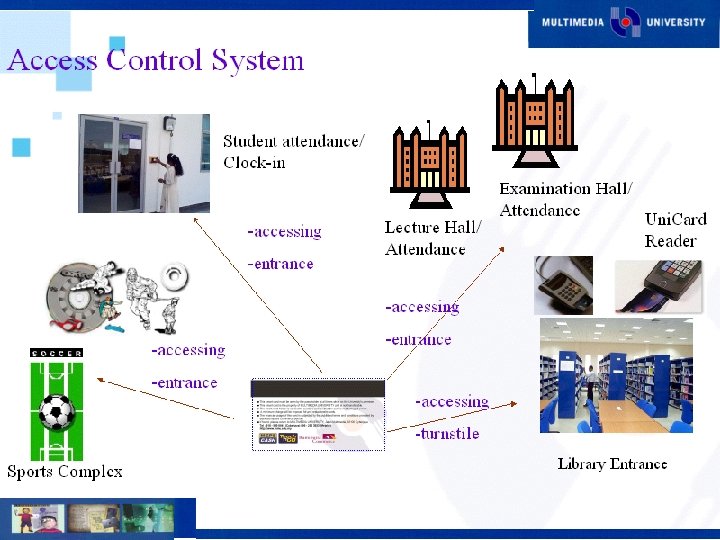
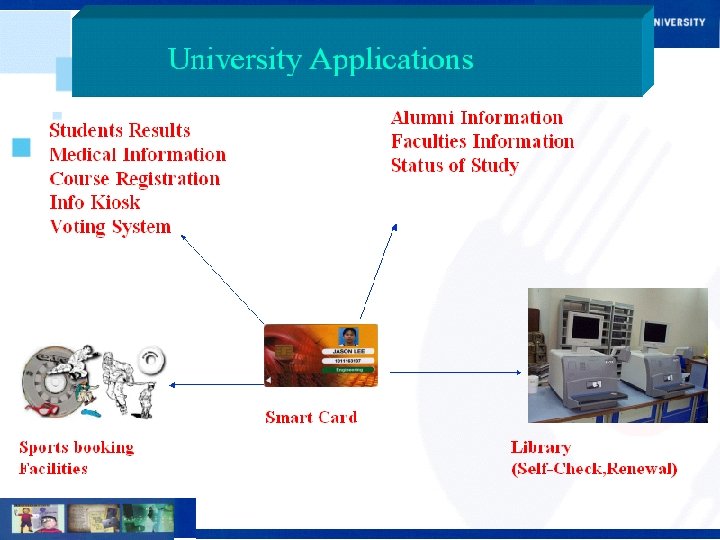
 Current Projects Multimedia Learning System (MMLS) n Smart Card n Document Management System (DMS) n Interactive Voice Response (IVR) n Digital Content Development n E-Procurement System n SMS n
Current Projects Multimedia Learning System (MMLS) n Smart Card n Document Management System (DMS) n Interactive Voice Response (IVR) n Digital Content Development n E-Procurement System n SMS n
 MMU E-scroll n n n First university in the world to introduce the escroll All graduates receive an e-scroll during the university’s convocation ceremony The e-scroll is digitally signed and stored in a CD-ROM
MMU E-scroll n n n First university in the world to introduce the escroll All graduates receive an e-scroll during the university’s convocation ceremony The e-scroll is digitally signed and stored in a CD-ROM
 E-Learning Project: Multimedia Learning System http: //mmls. mmu. edu. my
E-Learning Project: Multimedia Learning System http: //mmls. mmu. edu. my
 Higher Education: Challenges for Malaysia n n n Growing number of students Increasing cost of education Demand for quality education Shortage of academic (ICT) staff Limited facilities/tools
Higher Education: Challenges for Malaysia n n n Growing number of students Increasing cost of education Demand for quality education Shortage of academic (ICT) staff Limited facilities/tools
 Education Market in Malaysia A big growth is expected in the education market In Malaysia, with one university in 1957 to over 38 public and private universities today Malaysia targets to have 40% of those finishing secondary school to enter tertiary education by 2020 (currently the figure stands at about 18%)
Education Market in Malaysia A big growth is expected in the education market In Malaysia, with one university in 1957 to over 38 public and private universities today Malaysia targets to have 40% of those finishing secondary school to enter tertiary education by 2020 (currently the figure stands at about 18%)
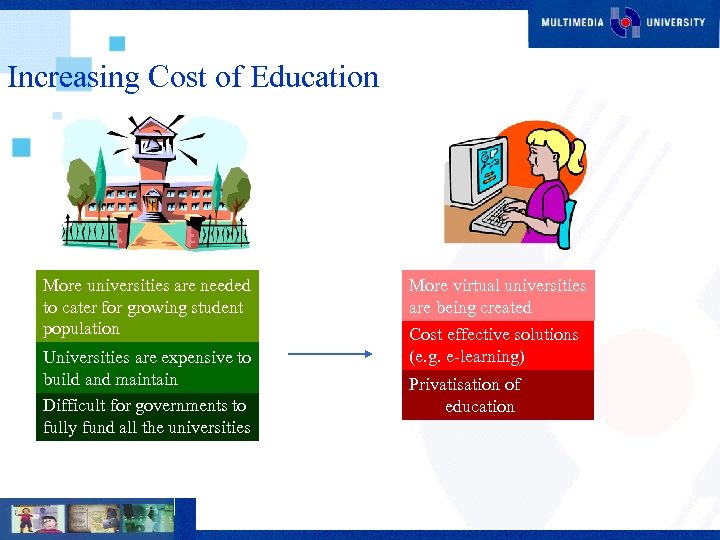 Increasing Cost of Education More universities are needed to cater for growing student population Universities are expensive to build and maintain Difficult for governments to fully fund all the universities More virtual universities are being created Cost effective solutions (e. g. e-learning) Privatisation of education
Increasing Cost of Education More universities are needed to cater for growing student population Universities are expensive to build and maintain Difficult for governments to fully fund all the universities More virtual universities are being created Cost effective solutions (e. g. e-learning) Privatisation of education
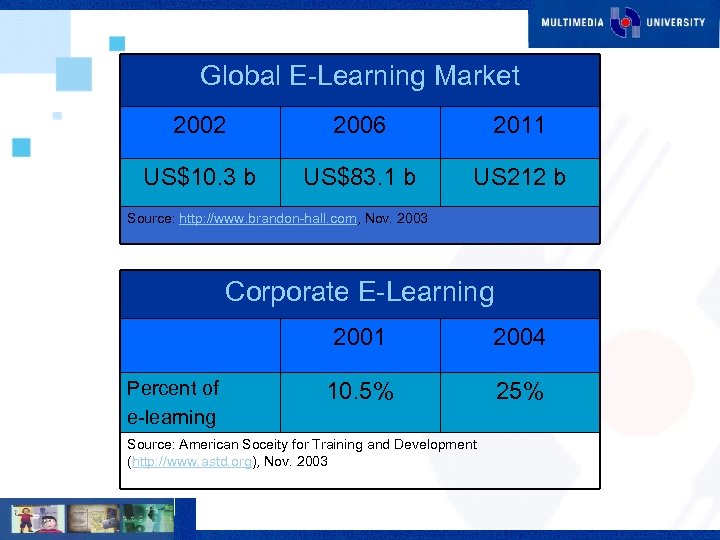 Global E-Learning Market 2002 2006 2011 US$10. 3 b US$83. 1 b US 212 b Source: http: //www. brandon-hall. com, Nov. 2003 Corporate E-Learning 2001 Percent of e-learning 2004 10. 5% 25% Source: American Soceity for Training and Development (http: //www. astd. org), Nov. 2003
Global E-Learning Market 2002 2006 2011 US$10. 3 b US$83. 1 b US 212 b Source: http: //www. brandon-hall. com, Nov. 2003 Corporate E-Learning 2001 Percent of e-learning 2004 10. 5% 25% Source: American Soceity for Training and Development (http: //www. astd. org), Nov. 2003
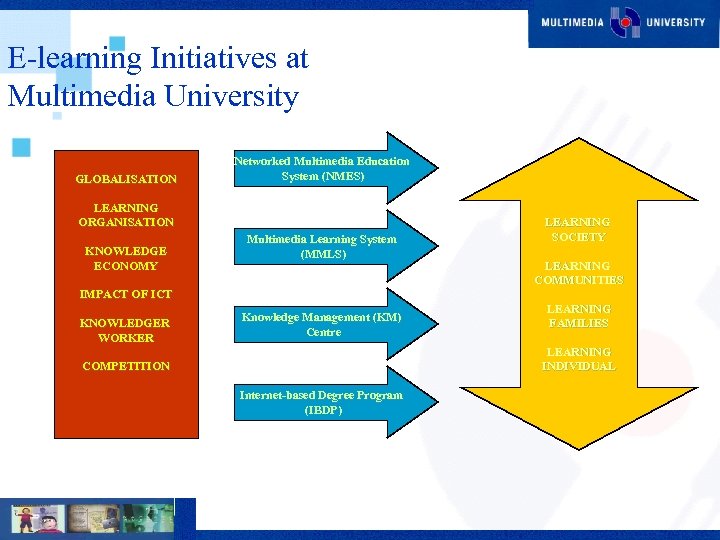 E-learning Initiatives at Multimedia University GLOBALISATION Networked Multimedia Education System (NMES) LEARNING ORGANISATION KNOWLEDGE ECONOMY Multimedia Learning System (MMLS) LEARNING SOCIETY LEARNING COMMUNITIES IMPACT OF ICT KNOWLEDGER WORKER Knowledge Management (KM) Centre LEARNING FAMILIES LEARNING INDIVIDUAL COMPETITION Internet-based Degree Program (IBDP)
E-learning Initiatives at Multimedia University GLOBALISATION Networked Multimedia Education System (NMES) LEARNING ORGANISATION KNOWLEDGE ECONOMY Multimedia Learning System (MMLS) LEARNING SOCIETY LEARNING COMMUNITIES IMPACT OF ICT KNOWLEDGER WORKER Knowledge Management (KM) Centre LEARNING FAMILIES LEARNING INDIVIDUAL COMPETITION Internet-based Degree Program (IBDP)
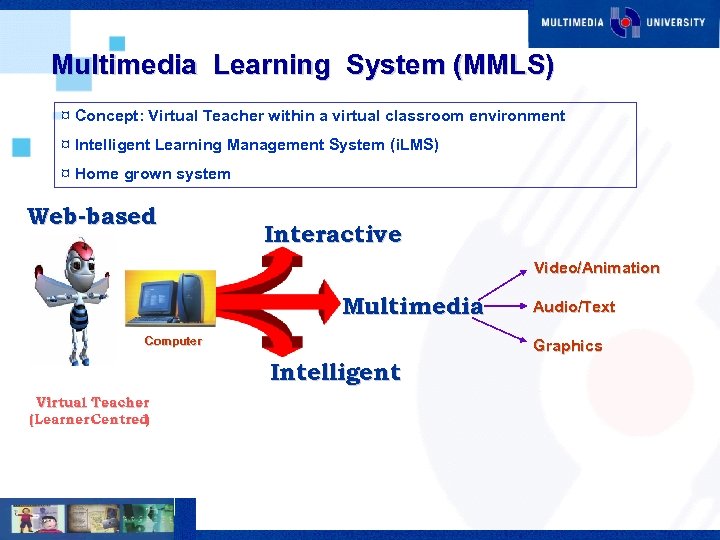 Multimedia Learning System (MMLS) ¤ Concept: Virtual Teacher within a virtual classroom environment ¤ Intelligent Learning Management System (i. LMS) ¤ Home grown system Web-based Interactive Video/Animation Multimedia Computer Graphics Intelligent Virtual Teacher (Learner Centred ) Audio/Text
Multimedia Learning System (MMLS) ¤ Concept: Virtual Teacher within a virtual classroom environment ¤ Intelligent Learning Management System (i. LMS) ¤ Home grown system Web-based Interactive Video/Animation Multimedia Computer Graphics Intelligent Virtual Teacher (Learner Centred ) Audio/Text
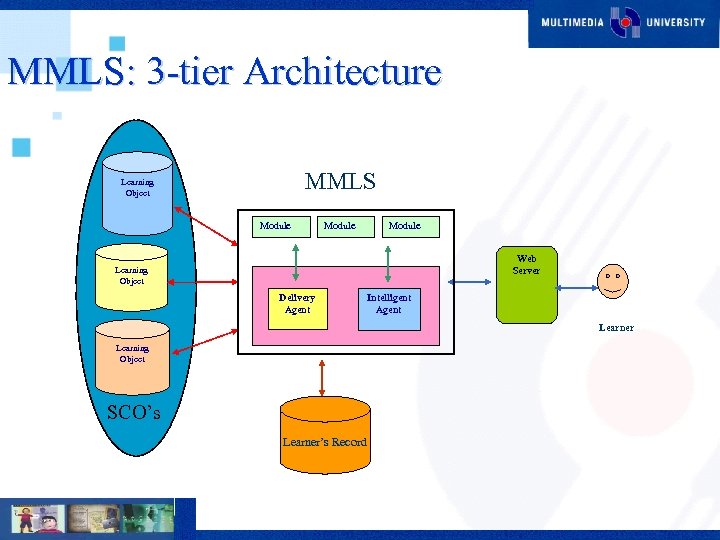 MMLS: 3 -tier Architecture MMLS Learning Object Module Web Server Learning Object Delivery Agent Intelligent Agent Learner Learning Object SCO’s Learner’s Record
MMLS: 3 -tier Architecture MMLS Learning Object Module Web Server Learning Object Delivery Agent Intelligent Agent Learner Learning Object SCO’s Learner’s Record
 MMLS Technology MMLS uses the following: Operating system : Supports Linux, Sun Solaris, Unix and Windows Web server : Apache Database : My. SQL Supports other databases/ODBC Server side script : PHP Client side script : Java. Script
MMLS Technology MMLS uses the following: Operating system : Supports Linux, Sun Solaris, Unix and Windows Web server : Apache Database : My. SQL Supports other databases/ODBC Server side script : PHP Client side script : Java. Script
 Key Features of MMLS * Platform independent * Database independent * Fully web enabled * Intelligent student monitoring * Course management by instructor * Auto-administration (e. g. registration, grouping, etc) * Bulletin board * Newsgroups, by course, for asynchronous interactions * On-line quiz templates and auto-grading & distribution of grades * Customisable
Key Features of MMLS * Platform independent * Database independent * Fully web enabled * Intelligent student monitoring * Course management by instructor * Auto-administration (e. g. registration, grouping, etc) * Bulletin board * Newsgroups, by course, for asynchronous interactions * On-line quiz templates and auto-grading & distribution of grades * Customisable
 Users/Collaborators n MMU – Face-to-face or classroom-based training – 15, 000 students used the MMLS – All lecture notes, ref. , tutorials, etc for all subjects are available online – Multimedia content (more than 100 subjects) – 200, 000 hits per month • http: //mmlscyber. mmu. edu. my • http: //mmlsmelaka. mmu. edu. my – Others: IBDP, MBA, DE, and FOSEE. Other Collaborators: Malaysia: APN, CIAST, and 17 Schools France: La Rochelle University Japan: Waseda Uni. , Kyoto Uni. & NTT (SCORM) S. Africa: NEMISA India: Matrushri Academy
Users/Collaborators n MMU – Face-to-face or classroom-based training – 15, 000 students used the MMLS – All lecture notes, ref. , tutorials, etc for all subjects are available online – Multimedia content (more than 100 subjects) – 200, 000 hits per month • http: //mmlscyber. mmu. edu. my • http: //mmlsmelaka. mmu. edu. my – Others: IBDP, MBA, DE, and FOSEE. Other Collaborators: Malaysia: APN, CIAST, and 17 Schools France: La Rochelle University Japan: Waseda Uni. , Kyoto Uni. & NTT (SCORM) S. Africa: NEMISA India: Matrushri Academy
 Three International Awards
Three International Awards
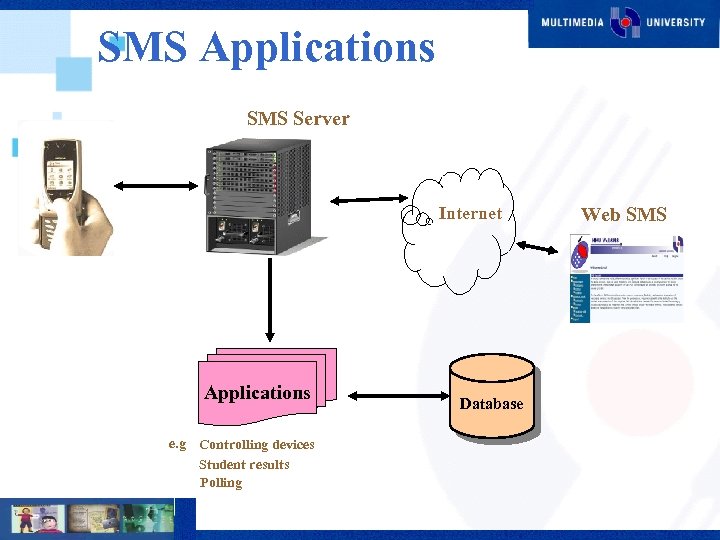 SMS Applications SMS Server Internet Applications e. g Controlling devices Student results Polling Database Web SMS
SMS Applications SMS Server Internet Applications e. g Controlling devices Student results Polling Database Web SMS
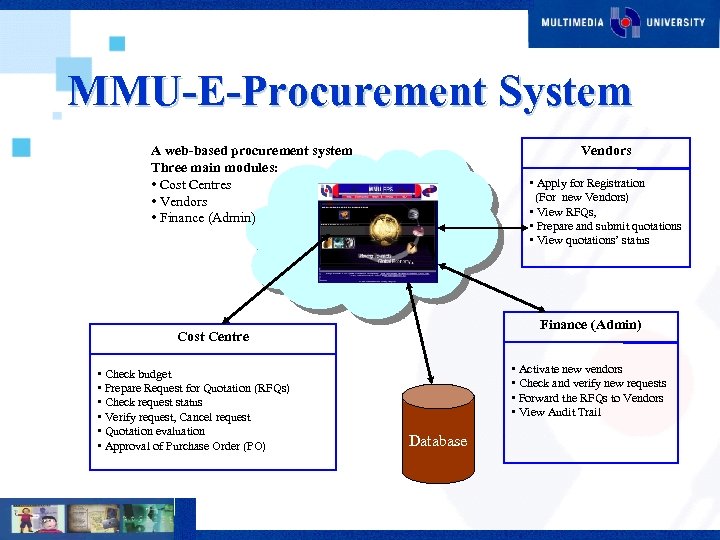 MMU-E-Procurement System A web-based procurement system Three main modules: • Cost Centres • Vendors • Finance (Admin) Vendors • Apply for Registration (For new Vendors) • View RFQs, • Prepare and submit quotations • View quotations’ status Finance (Admin) Cost Centre • Check budget • Prepare Request for Quotation (RFQs) • Check request status • Verify request, Cancel request • Quotation evaluation • Approval of Purchase Order (PO) • Activate new vendors • Check and verify new requests • Forward the RFQs to Vendors • View Audit Trail Database
MMU-E-Procurement System A web-based procurement system Three main modules: • Cost Centres • Vendors • Finance (Admin) Vendors • Apply for Registration (For new Vendors) • View RFQs, • Prepare and submit quotations • View quotations’ status Finance (Admin) Cost Centre • Check budget • Prepare Request for Quotation (RFQs) • Check request status • Verify request, Cancel request • Quotation evaluation • Approval of Purchase Order (PO) • Activate new vendors • Check and verify new requests • Forward the RFQs to Vendors • View Audit Trail Database
 Benefits n Reduced operational costs n Transparency in procurement system n Best price n Efficient Usage As of July 20, 2004
Benefits n Reduced operational costs n Transparency in procurement system n Best price n Efficient Usage As of July 20, 2004


