929fd322ff44e10932751cef23e94712.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Centre for Fuel Studies and Research Forum of Indian Regulators Role of Natural Gas in the Emerging Energy Scenario May 2013 1
Centre for Fuel Studies and Research Forum of Indian Regulators Role of Natural Gas in the Emerging Energy Scenario May 2013 1
 Preamble q Three Key Issues v Continued Growth at 8 to 9% v Energy Security v Sustainability q Paradigm Shift in Approach v What role NG should play o Supply Constraints o Efficiency § Economy and CO 2 Emission o Priority to divert to desirable sectors o Roadmap q Prepared to take unpleasant decisions 2
Preamble q Three Key Issues v Continued Growth at 8 to 9% v Energy Security v Sustainability q Paradigm Shift in Approach v What role NG should play o Supply Constraints o Efficiency § Economy and CO 2 Emission o Priority to divert to desirable sectors o Roadmap q Prepared to take unpleasant decisions 2
 Enhance Domestic Production q Maximize E&P Activities v 25% present to 75% by 2015 and 100% by 2030!! q E&P Efforts for Crude Oil / Natural Gas same q Key Issues v International and Private Sector participation o Risk Capital o Technology § o Big and Small Companies Price Benchmark and Risk Capital q Short and long term supply options v Imports, Coal as source of complete sol. 3
Enhance Domestic Production q Maximize E&P Activities v 25% present to 75% by 2015 and 100% by 2030!! q E&P Efforts for Crude Oil / Natural Gas same q Key Issues v International and Private Sector participation o Risk Capital o Technology § o Big and Small Companies Price Benchmark and Risk Capital q Short and long term supply options v Imports, Coal as source of complete sol. 3
 Plan for Infrastructure & Markets q Logistics, Natural Monopoly v From Source to Consumer v Transmission Distribution q Natural Gas Ideal Fuel for all markets v Energy – all application v Fossil Fuel interchangeable o Availability /economics v Feedstock o Fertilizer, Petrochemicals q Exporting & Importing Countries v Pricing Mechanism q Transit fuel to low CO 2 era v How? 4
Plan for Infrastructure & Markets q Logistics, Natural Monopoly v From Source to Consumer v Transmission Distribution q Natural Gas Ideal Fuel for all markets v Energy – all application v Fossil Fuel interchangeable o Availability /economics v Feedstock o Fertilizer, Petrochemicals q Exporting & Importing Countries v Pricing Mechanism q Transit fuel to low CO 2 era v How? 4
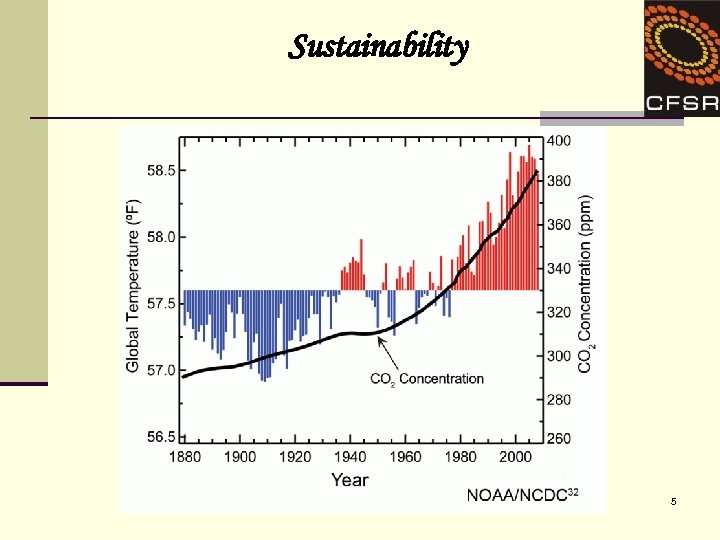 Sustainability 5
Sustainability 5
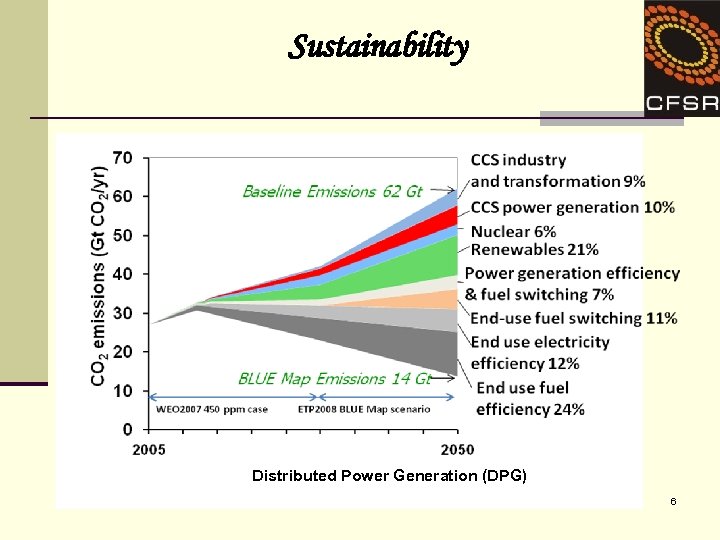 Sustainability Distributed Power Generation (DPG) 6
Sustainability Distributed Power Generation (DPG) 6
 Sustainability 7
Sustainability 7
 Supply Options q Domestic Availability Conventional/Shale Gas v 130 MMM 3/day domestic v 30 MMM 3/day imports q Domestic Options (Conventional and Non-Conventional) v ≈400 MMM 3/day v Rigorous E&P Activities v R&D Efforts for non-conventional sources q Imports (Short term to medium term) v Present World Trade v ME, Africa, SE Asia, Israel, Russia & CIS Countries o World Trade: 3000 MMM 3/day (Pipeline & LNG) q No. of actions on hand o o GAIL tie-up supplies Petronet LNG TAPI Pipeline SAGE Initiative 8
Supply Options q Domestic Availability Conventional/Shale Gas v 130 MMM 3/day domestic v 30 MMM 3/day imports q Domestic Options (Conventional and Non-Conventional) v ≈400 MMM 3/day v Rigorous E&P Activities v R&D Efforts for non-conventional sources q Imports (Short term to medium term) v Present World Trade v ME, Africa, SE Asia, Israel, Russia & CIS Countries o World Trade: 3000 MMM 3/day (Pipeline & LNG) q No. of actions on hand o o GAIL tie-up supplies Petronet LNG TAPI Pipeline SAGE Initiative 8
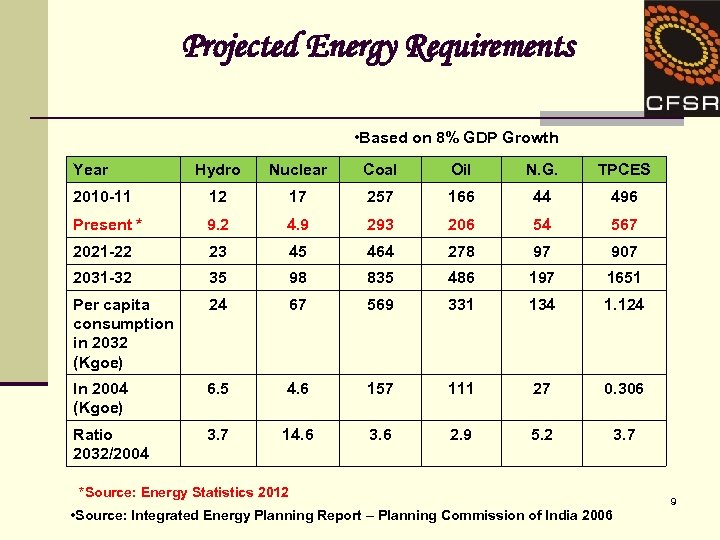 Projected Energy Requirements • Based on 8% GDP Growth Year Hydro Nuclear Coal Oil N. G. TPCES 2010 -11 12 17 257 166 44 496 Present * 9. 2 4. 9 293 206 54 567 2021 -22 23 45 464 278 97 907 2031 -32 35 98 835 486 197 1651 Per capita consumption in 2032 (Kgoe) 24 67 569 331 134 1. 124 In 2004 (Kgoe) 6. 5 4. 6 157 111 27 0. 306 Ratio 2032/2004 3. 7 14. 6 3. 6 2. 9 5. 2 3. 7 *Source: Energy Statistics 2012 • Source: Integrated Energy Planning Report – Planning Commission of India 2006 9
Projected Energy Requirements • Based on 8% GDP Growth Year Hydro Nuclear Coal Oil N. G. TPCES 2010 -11 12 17 257 166 44 496 Present * 9. 2 4. 9 293 206 54 567 2021 -22 23 45 464 278 97 907 2031 -32 35 98 835 486 197 1651 Per capita consumption in 2032 (Kgoe) 24 67 569 331 134 1. 124 In 2004 (Kgoe) 6. 5 4. 6 157 111 27 0. 306 Ratio 2032/2004 3. 7 14. 6 3. 6 2. 9 5. 2 3. 7 *Source: Energy Statistics 2012 • Source: Integrated Energy Planning Report – Planning Commission of India 2006 9
 Compelling Reasons to increase Role of NG q Why increased role of Natural Gas? v Compelling Reasons o Sustainability § § Efficiency § o Environment CO 2 emission Worldwide Availability § § o India well placed ME, Africa, CIS countries, Israel India’s exploration potential § Conventional / Non-conventional o World average 25% § § o IEP Report availability based(480 mmm 3/day) Target at least 25% Long Term Options 10
Compelling Reasons to increase Role of NG q Why increased role of Natural Gas? v Compelling Reasons o Sustainability § § Efficiency § o Environment CO 2 emission Worldwide Availability § § o India well placed ME, Africa, CIS countries, Israel India’s exploration potential § Conventional / Non-conventional o World average 25% § § o IEP Report availability based(480 mmm 3/day) Target at least 25% Long Term Options 10
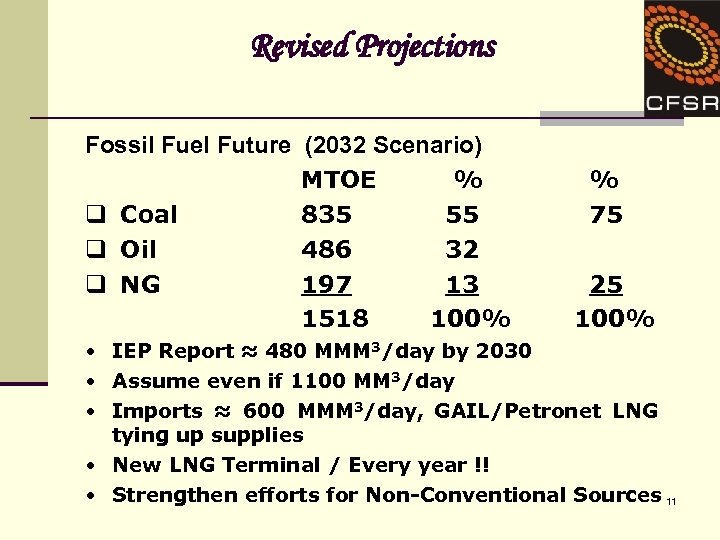 Revised Projections Fossil Fuel Future (2032 Scenario) MTOE % q Coal 835 55 q Oil 486 32 q NG 197 13 1518 100% % 75 25 100% • IEP Report ≈ 480 MMM 3/day by 2030 • Assume even if 1100 MM 3/day • Imports ≈ 600 MMM 3/day, GAIL/Petronet LNG tying up supplies • New LNG Terminal / Every year !! • Strengthen efforts for Non-Conventional Sources 11
Revised Projections Fossil Fuel Future (2032 Scenario) MTOE % q Coal 835 55 q Oil 486 32 q NG 197 13 1518 100% % 75 25 100% • IEP Report ≈ 480 MMM 3/day by 2030 • Assume even if 1100 MM 3/day • Imports ≈ 600 MMM 3/day, GAIL/Petronet LNG tying up supplies • New LNG Terminal / Every year !! • Strengthen efforts for Non-Conventional Sources 11
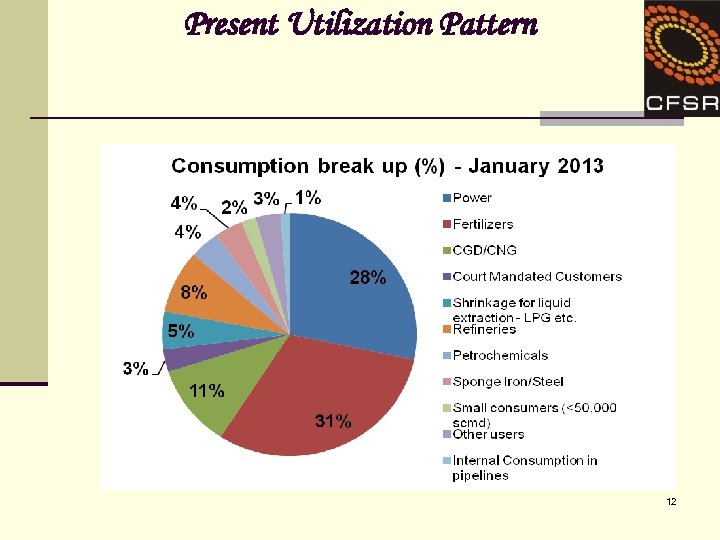 Present Utilization Pattern 12
Present Utilization Pattern 12
 Paradigm Shift q Revisit Utilization Pattern v Key Issues o Efficiency / Sustainability v Power Generation o Increasing NG Imports – Utility Stations economical? v Fertilizer o Increasing Subsidy o OMIFCO Model (Offshore) o Coal as option v Others o Petroleum Product Replacement – Not an issue o Transport – limited option o CCHP mode 13
Paradigm Shift q Revisit Utilization Pattern v Key Issues o Efficiency / Sustainability v Power Generation o Increasing NG Imports – Utility Stations economical? v Fertilizer o Increasing Subsidy o OMIFCO Model (Offshore) o Coal as option v Others o Petroleum Product Replacement – Not an issue o Transport – limited option o CCHP mode 13
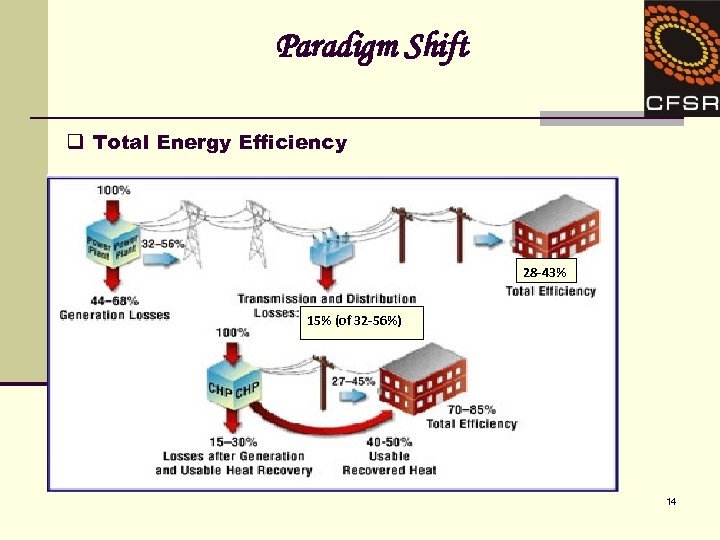 Paradigm Shift q Total Energy Efficiency 28 -43% 15% (of 32 -56%) 14
Paradigm Shift q Total Energy Efficiency 28 -43% 15% (of 32 -56%) 14
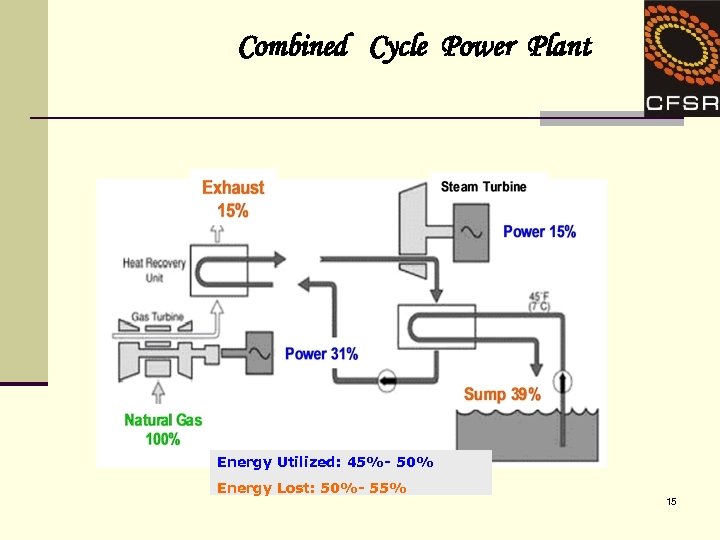 Combined Cycle Power Plant Energy Utilized: 45%- 50% Energy Lost: 50%- 55% 15
Combined Cycle Power Plant Energy Utilized: 45%- 50% Energy Lost: 50%- 55% 15
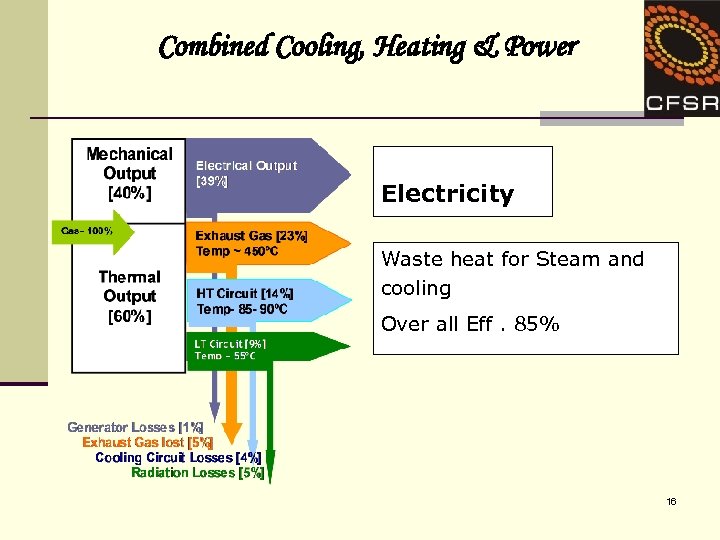 Combined Cooling, Heating & Power Electricity Waste heat for Steam and cooling Over all Eff. 85% 16
Combined Cooling, Heating & Power Electricity Waste heat for Steam and cooling Over all Eff. 85% 16
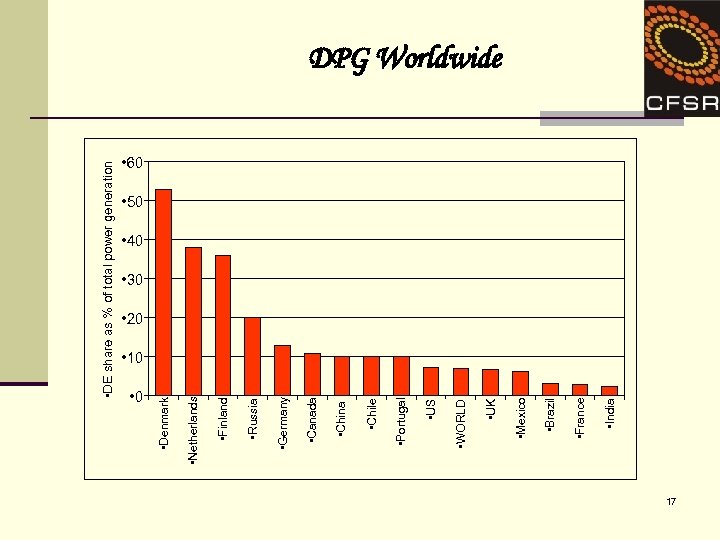 • DE share as % of total power generation • 0 • India • France • Brazil • Mexico • UK • WORLD • US • Portugal • Chile • China • Canada • Germany • Russia • Finland • Netherlands • Denmark DPG Worldwide • 60 • 50 • 40 • 30 • 20 • 10 17
• DE share as % of total power generation • 0 • India • France • Brazil • Mexico • UK • WORLD • US • Portugal • Chile • China • Canada • Germany • Russia • Finland • Netherlands • Denmark DPG Worldwide • 60 • 50 • 40 • 30 • 20 • 10 17
 Paradigm Shift q Revisit Utilization Pattern v Distributed Power Generation o Industry & Commerce (I&C) § § Basis of comparison § 85% Efficiency § Reduction in CO 2 Emission § Avoided T&D Losses § Avoided Capex for T&D expansion § § CCHP Mode Total Energy Efficiency Incentivise efficiency q 50% plus reduction in CO 2 – No additional cost to Economy 18
Paradigm Shift q Revisit Utilization Pattern v Distributed Power Generation o Industry & Commerce (I&C) § § Basis of comparison § 85% Efficiency § Reduction in CO 2 Emission § Avoided T&D Losses § Avoided Capex for T&D expansion § § CCHP Mode Total Energy Efficiency Incentivise efficiency q 50% plus reduction in CO 2 – No additional cost to Economy 18
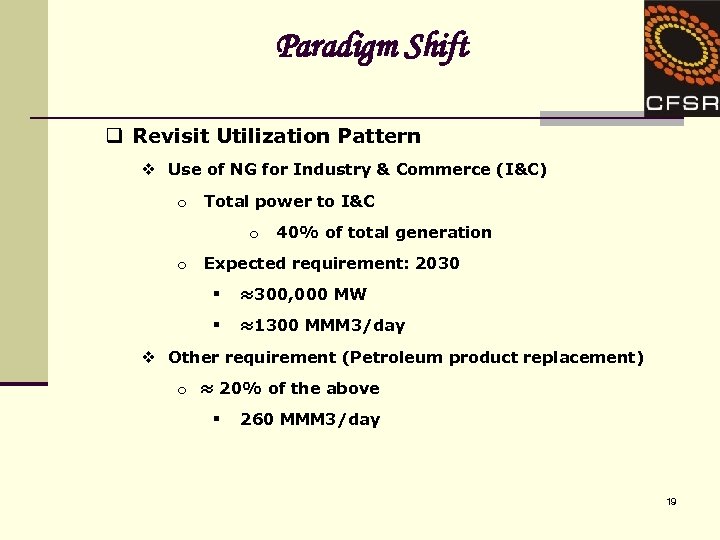 Paradigm Shift q Revisit Utilization Pattern v Use of NG for Industry & Commerce (I&C) o Total power to I&C o o 40% of total generation Expected requirement: 2030 § ≈300, 000 MW § ≈1300 MMM 3/day v Other requirement (Petroleum product replacement) o ≈ 20% of the above § 260 MMM 3/day 19
Paradigm Shift q Revisit Utilization Pattern v Use of NG for Industry & Commerce (I&C) o Total power to I&C o o 40% of total generation Expected requirement: 2030 § ≈300, 000 MW § ≈1300 MMM 3/day v Other requirement (Petroleum product replacement) o ≈ 20% of the above § 260 MMM 3/day 19
 National Gas Grid Seamless Development q Large and Lumpy Investment v Huge Cost of Stranded Investments q Distributed Power Generation (CCHP Mode) v Anchor Load q Load Distribution Zone v Cities with 10 lakh+ population v Include Industrial Centers around the City v Petroleum Product Replacement o Domestic o Generators o Fuel Oil o CNG Transport q Expected 80 LDZs around the country q Each LDZ ≈ 2 to 3 MMM 3/day Anchor Load q NG Grid in next 5 to 7 years possible v Connect supplies to LDZs v GAIL and then unbundle? – BG Model v Revisit NG Price, India hub 20
National Gas Grid Seamless Development q Large and Lumpy Investment v Huge Cost of Stranded Investments q Distributed Power Generation (CCHP Mode) v Anchor Load q Load Distribution Zone v Cities with 10 lakh+ population v Include Industrial Centers around the City v Petroleum Product Replacement o Domestic o Generators o Fuel Oil o CNG Transport q Expected 80 LDZs around the country q Each LDZ ≈ 2 to 3 MMM 3/day Anchor Load q NG Grid in next 5 to 7 years possible v Connect supplies to LDZs v GAIL and then unbundle? – BG Model v Revisit NG Price, India hub 20
 Institutional Requirement q Role of PNGRB v Preparation of National Gas Plan o PSUs, Expertise drawn from Private Sector o Open Access Tariff v Dedicated Technical Group o Market Survey LDZ, economics o Railways o Grid Plan and execution o LDZ Distribution network § State level support v Redefine CGD’s Bids to be based on supplies 21
Institutional Requirement q Role of PNGRB v Preparation of National Gas Plan o PSUs, Expertise drawn from Private Sector o Open Access Tariff v Dedicated Technical Group o Market Survey LDZ, economics o Railways o Grid Plan and execution o LDZ Distribution network § State level support v Redefine CGD’s Bids to be based on supplies 21
 Other Issues q DPG Electricity Act of 2003 Not an issue q Entry Barriers v Level Playing Fields o Duty Structure – Mega Vs. Macro v Awareness o Technology v Electricity Duties, Back-up charges v CDM Credits – State Support (aggregate) v Acceptance and Support from State Electricity Boards 22
Other Issues q DPG Electricity Act of 2003 Not an issue q Entry Barriers v Level Playing Fields o Duty Structure – Mega Vs. Macro v Awareness o Technology v Electricity Duties, Back-up charges v CDM Credits – State Support (aggregate) v Acceptance and Support from State Electricity Boards 22
 Longer Term Perspective q Security of Supplies q Short term supply options v Intensify domestic supplies / capture imports q Long term supply options v Coal as Total Energy Solution o Validate Coal Reserves v Gas Hydrates o Potential o Japan Example o R&D Efforts v Coal gasification o Coal Syngas Methane Syngas to liquids o Catalytic Conversion to Methane o Coal Syngas to power, Chemicals, Fertilizers 23
Longer Term Perspective q Security of Supplies q Short term supply options v Intensify domestic supplies / capture imports q Long term supply options v Coal as Total Energy Solution o Validate Coal Reserves v Gas Hydrates o Potential o Japan Example o R&D Efforts v Coal gasification o Coal Syngas Methane Syngas to liquids o Catalytic Conversion to Methane o Coal Syngas to power, Chemicals, Fertilizers 23
 Summary q Domestic – Enhancing E&P Activities v Conventional and Shale Gas v TOR-I v Treat Oil/Gas alike v NG Benchmark to International Price o Japan LNG less LNG Liq. /Transport v Other Non-Conventional o Coal Reserves o R&D efforts / Long term § Can be source of all fuel even H 2 Eventually § Coal Gasification § Coal to NG (Catalytic) § Underground Coal Gasification • o Technology to suit India Coal Total Energy Solution 24
Summary q Domestic – Enhancing E&P Activities v Conventional and Shale Gas v TOR-I v Treat Oil/Gas alike v NG Benchmark to International Price o Japan LNG less LNG Liq. /Transport v Other Non-Conventional o Coal Reserves o R&D efforts / Long term § Can be source of all fuel even H 2 Eventually § Coal Gasification § Coal to NG (Catalytic) § Underground Coal Gasification • o Technology to suit India Coal Total Energy Solution 24
 Summary q National Gas Grid – next 5 to 7 years v Paradigm Shift o DPG, LDZ o Transit Fuel v Supplies o E&P Efforts o Short, Medium Term § Tie-up imports o Non-conventional R&D Efforts v BG Model v Role of PNGRB v Grid, Market, Supplies q Huge Task v Mindset and Political Will v Can we tell the Truth? 25
Summary q National Gas Grid – next 5 to 7 years v Paradigm Shift o DPG, LDZ o Transit Fuel v Supplies o E&P Efforts o Short, Medium Term § Tie-up imports o Non-conventional R&D Efforts v BG Model v Role of PNGRB v Grid, Market, Supplies q Huge Task v Mindset and Political Will v Can we tell the Truth? 25
 1928 2004 Upasala Glacier, South American Andes, Argentina Thank You 26
1928 2004 Upasala Glacier, South American Andes, Argentina Thank You 26
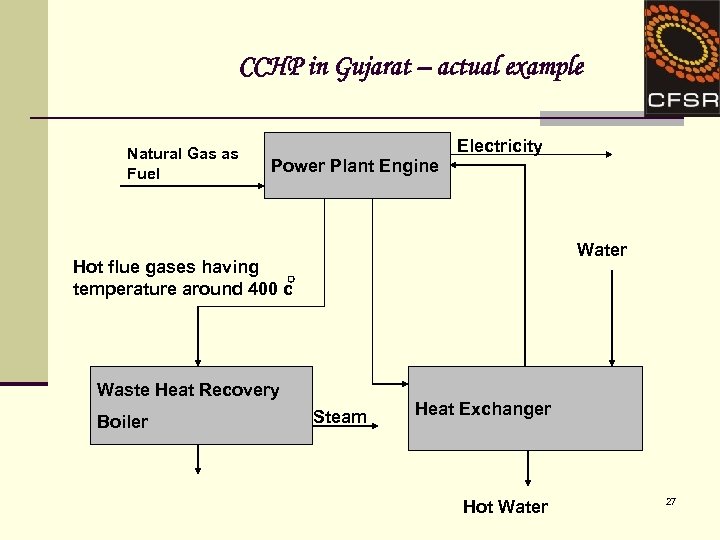 CCHP in Gujarat – actual example Natural Gas as Fuel • Power Plant Engine Electricity Water Hot flue gases having temperature around 400 c Waste Heat Recovery Boiler Steam Heat Exchanger Hot Water 27
CCHP in Gujarat – actual example Natural Gas as Fuel • Power Plant Engine Electricity Water Hot flue gases having temperature around 400 c Waste Heat Recovery Boiler Steam Heat Exchanger Hot Water 27
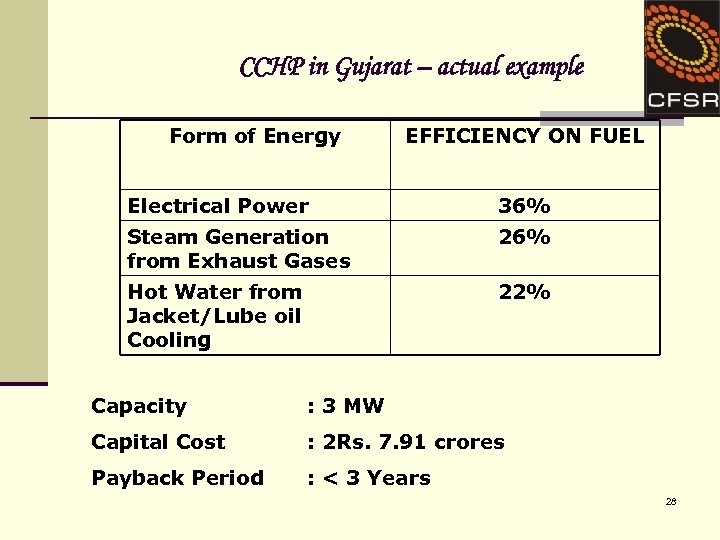 CCHP in Gujarat – actual example Form of Energy EFFICIENCY ON FUEL Electrical Power 36% Steam Generation from Exhaust Gases 26% Hot Water from Jacket/Lube oil Cooling 22% Capacity : 3 MW Capital Cost : 2 Rs. 7. 91 crores Payback Period : < 3 Years 28
CCHP in Gujarat – actual example Form of Energy EFFICIENCY ON FUEL Electrical Power 36% Steam Generation from Exhaust Gases 26% Hot Water from Jacket/Lube oil Cooling 22% Capacity : 3 MW Capital Cost : 2 Rs. 7. 91 crores Payback Period : < 3 Years 28
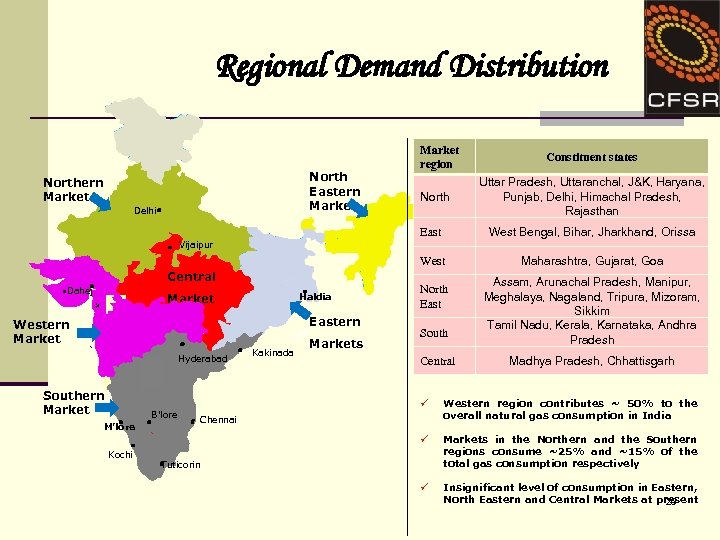 Regional Demand Distribution North Eastern Market Northern Market Delhi Market region North Constituent states Uttar Pradesh, Uttaranchal, J&K, Haryana, Punjab, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan East West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa West Maharashtra, Gujarat, Goa Vijaipur Central • Dahej Market Haldia • Mumbai Western Market Eastern Hyderabad Southern Market Kakinada Markets North East South Central Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Tripura, Mizoram, Sikkim Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh M’lore Kochi ü Western region contributes ~ 50% to the overall natural gas consumption in India ü B’lore Markets in the Northern and the Southern regions consume ~25% and ~15% of the total gas consumption respectively ü Insignificant level of consumption in Eastern, North Eastern and Central Markets at present 29 Chennai Tuticorin
Regional Demand Distribution North Eastern Market Northern Market Delhi Market region North Constituent states Uttar Pradesh, Uttaranchal, J&K, Haryana, Punjab, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan East West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa West Maharashtra, Gujarat, Goa Vijaipur Central • Dahej Market Haldia • Mumbai Western Market Eastern Hyderabad Southern Market Kakinada Markets North East South Central Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Tripura, Mizoram, Sikkim Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh M’lore Kochi ü Western region contributes ~ 50% to the overall natural gas consumption in India ü B’lore Markets in the Northern and the Southern regions consume ~25% and ~15% of the total gas consumption respectively ü Insignificant level of consumption in Eastern, North Eastern and Central Markets at present 29 Chennai Tuticorin


