074cf5959f89e709430fcd1d1ca282cb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Central tracker for 12 Ge. V upgrade in Hall. B P. Konczykowski CEA Saclay 06/28/08 n. Micromégas : a new detector for CLAS 12 ü Detector’s principle ü GARFIELD simulation ü Spatial resolution measurement n Long Micromégas prototype tests n Integration to the CLAS magnet Saclay team: S. Aune, J. Ball, M. Combet, M. El Yakoubi, P. Konczykowski, C. Lacombe-Hamdoun, S. Procureur, F. Sabatié
Central tracker for 12 Ge. V upgrade in Hall. B P. Konczykowski CEA Saclay 06/28/08 n. Micromégas : a new detector for CLAS 12 ü Detector’s principle ü GARFIELD simulation ü Spatial resolution measurement n Long Micromégas prototype tests n Integration to the CLAS magnet Saclay team: S. Aune, J. Ball, M. Combet, M. El Yakoubi, P. Konczykowski, C. Lacombe-Hamdoun, S. Procureur, F. Sabatié
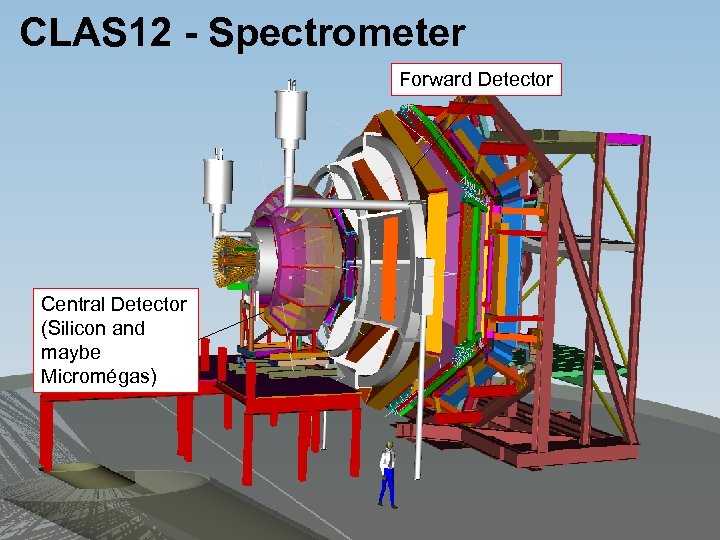 CLAS 12 - Spectrometer Forward Detector Central Detector (Silicon and maybe Micromégas)
CLAS 12 - Spectrometer Forward Detector Central Detector (Silicon and maybe Micromégas)
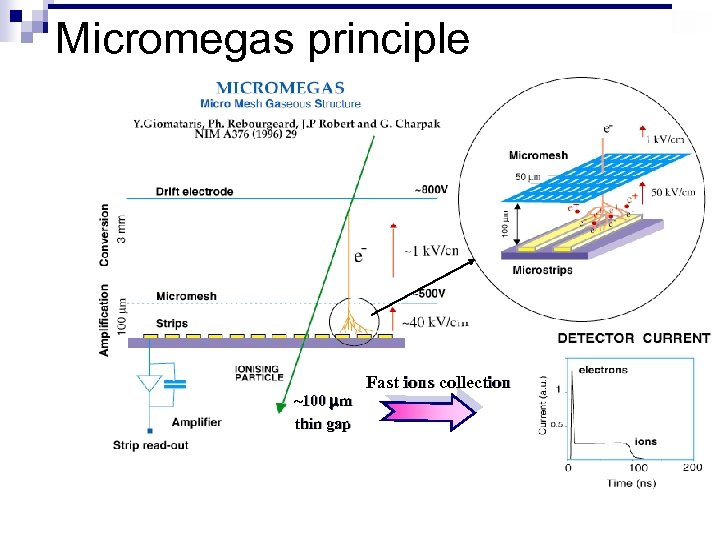 Micromegas principle ~100 mm thin gap Fast ions collection
Micromegas principle ~100 mm thin gap Fast ions collection
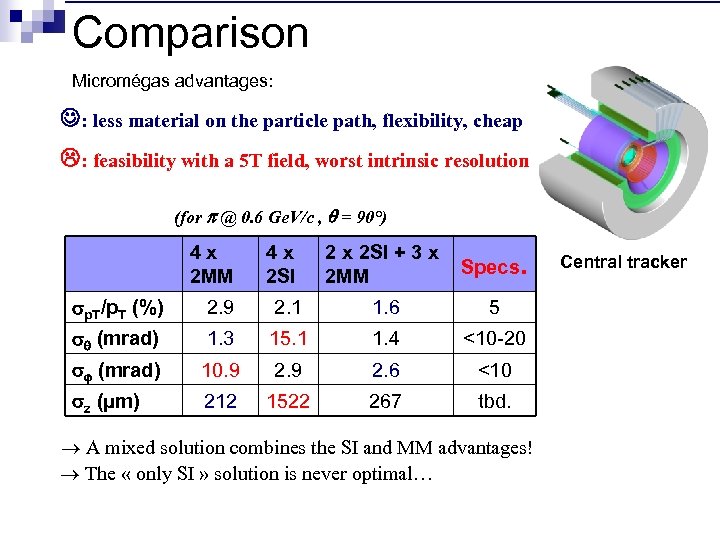 Comparison Micromégas advantages: : less material on the particle path, flexibility, cheap : feasibility with a 5 T field, worst intrinsic resolution (for @ 0. 6 Ge. V/c , = 90°) 4 x 2 MM 4 x 2 SI 2 x 2 SI + 3 x 2 MM Specs. p. T/p. T (%) 2. 9 2. 1 1. 6 5 (mrad) 1. 3 15. 1 1. 4 <10 -20 (mrad) 10. 9 2. 6 <10 z (μm) 212 1522 267 tbd. A mixed solution combines the SI and MM advantages! The « only SI » solution is never optimal… Central tracker
Comparison Micromégas advantages: : less material on the particle path, flexibility, cheap : feasibility with a 5 T field, worst intrinsic resolution (for @ 0. 6 Ge. V/c , = 90°) 4 x 2 MM 4 x 2 SI 2 x 2 SI + 3 x 2 MM Specs. p. T/p. T (%) 2. 9 2. 1 1. 6 5 (mrad) 1. 3 15. 1 1. 4 <10 -20 (mrad) 10. 9 2. 6 <10 z (μm) 212 1522 267 tbd. A mixed solution combines the SI and MM advantages! The « only SI » solution is never optimal… Central tracker
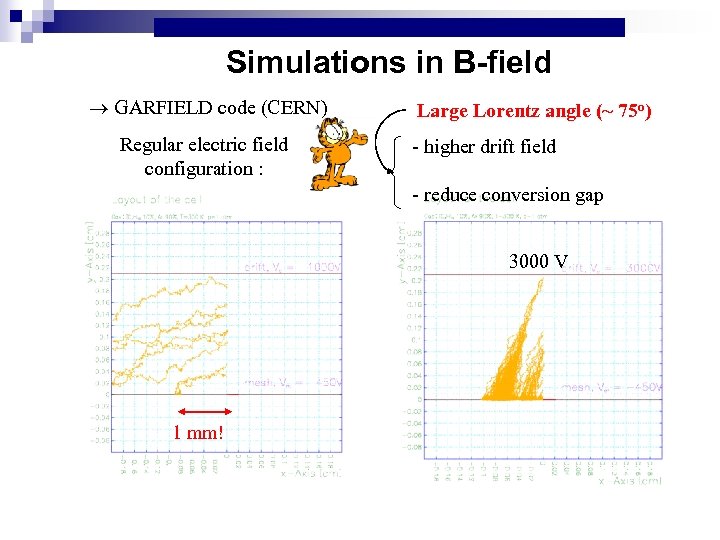 Simulations in B-field GARFIELD code (CERN) Regular electric field configuration : Large Lorentz angle (~ 75 o) - higher drift field - reduce conversion gap 2500 V 2000 V 3000 V 1500 V 1000 V 1 mm!
Simulations in B-field GARFIELD code (CERN) Regular electric field configuration : Large Lorentz angle (~ 75 o) - higher drift field - reduce conversion gap 2500 V 2000 V 3000 V 1500 V 1000 V 1 mm!
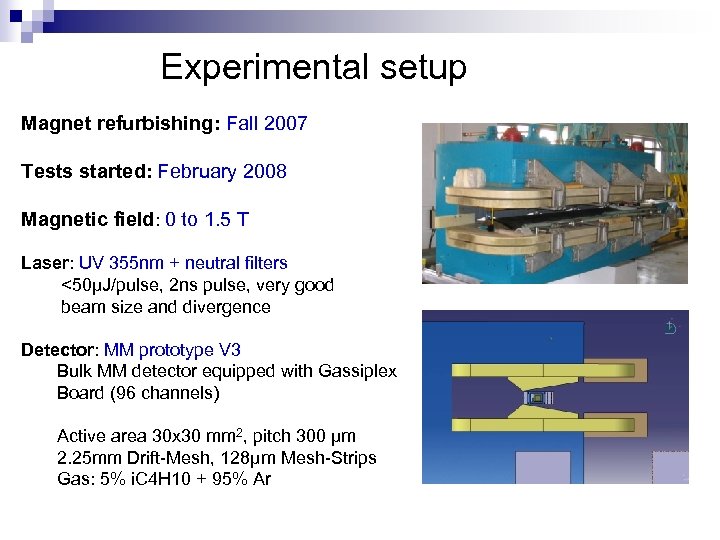 Experimental setup Magnet refurbishing: Fall 2007 Tests started: February 2008 Magnetic field: 0 to 1. 5 T Laser: UV 355 nm + neutral filters <50µJ/pulse, 2 ns pulse, very good beam size and divergence Detector: MM prototype V 3 Bulk MM detector equipped with Gassiplex Board (96 channels) Active area 30 x 30 mm 2, pitch 300 μm 2. 25 mm Drift-Mesh, 128µm Mesh-Strips Gas: 5% i. C 4 H 10 + 95% Ar
Experimental setup Magnet refurbishing: Fall 2007 Tests started: February 2008 Magnetic field: 0 to 1. 5 T Laser: UV 355 nm + neutral filters <50µJ/pulse, 2 ns pulse, very good beam size and divergence Detector: MM prototype V 3 Bulk MM detector equipped with Gassiplex Board (96 channels) Active area 30 x 30 mm 2, pitch 300 μm 2. 25 mm Drift-Mesh, 128µm Mesh-Strips Gas: 5% i. C 4 H 10 + 95% Ar
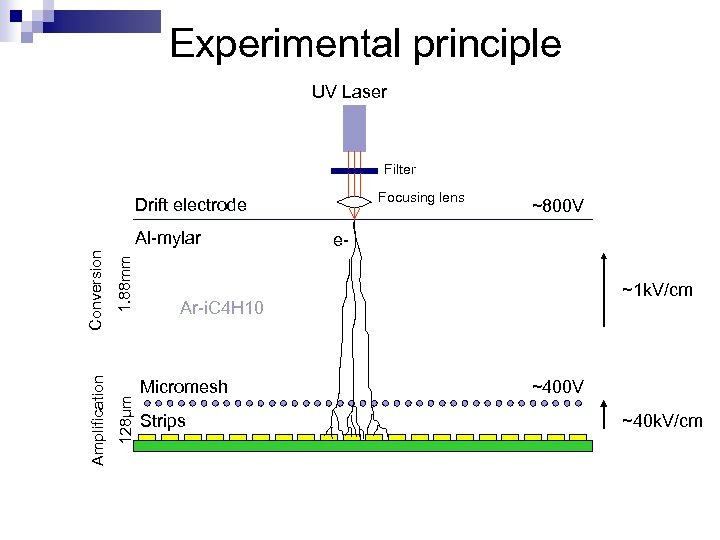 Experimental principle UV Laser Filter Focusing lens Drift electrode 1. 88 mm 128μm Amplification Conversion Al-mylar ~800 V e~1 k. V/cm Ar-i. C 4 H 10 Micromesh Strips ~400 V ~40 k. V/cm
Experimental principle UV Laser Filter Focusing lens Drift electrode 1. 88 mm 128μm Amplification Conversion Al-mylar ~800 V e~1 k. V/cm Ar-i. C 4 H 10 Micromesh Strips ~400 V ~40 k. V/cm
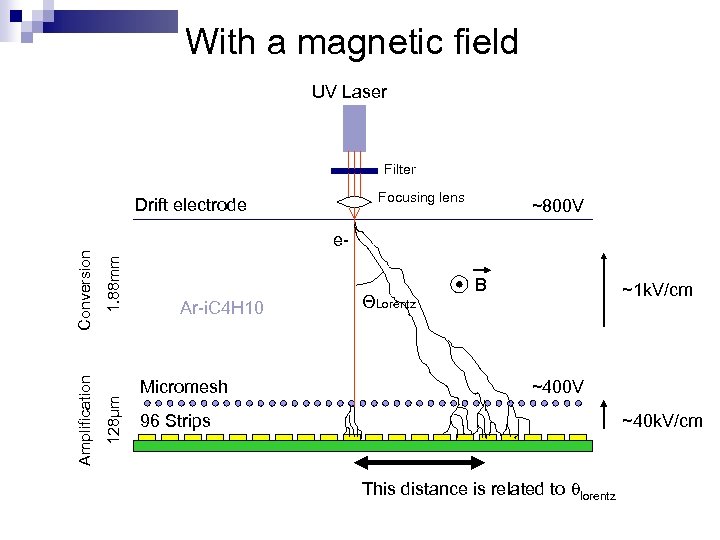 With a magnetic field UV Laser Filter Focusing lens Drift electrode ~800 V 1. 88 mm 128μm Amplification Conversion e- Ar-i. C 4 H 10 Micromesh ΘLorentz B ~1 k. V/cm ~400 V ~40 k. V/cm 96 Strips This distance is related to qlorentz
With a magnetic field UV Laser Filter Focusing lens Drift electrode ~800 V 1. 88 mm 128μm Amplification Conversion e- Ar-i. C 4 H 10 Micromesh ΘLorentz B ~1 k. V/cm ~400 V ~40 k. V/cm 96 Strips This distance is related to qlorentz
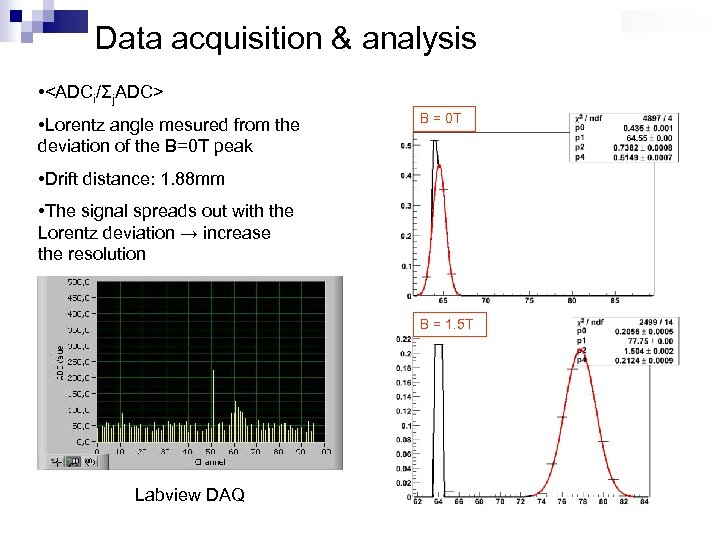 Data acquisition & analysis •
Data acquisition & analysis •
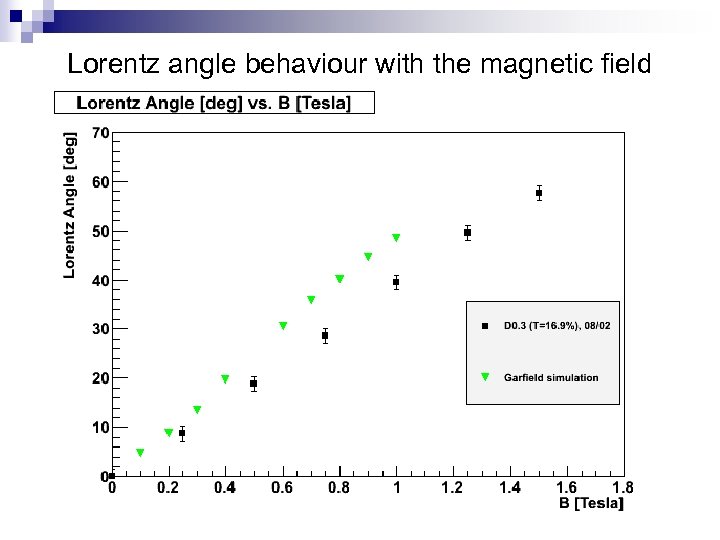 Lorentz angle behaviour with the magnetic field
Lorentz angle behaviour with the magnetic field
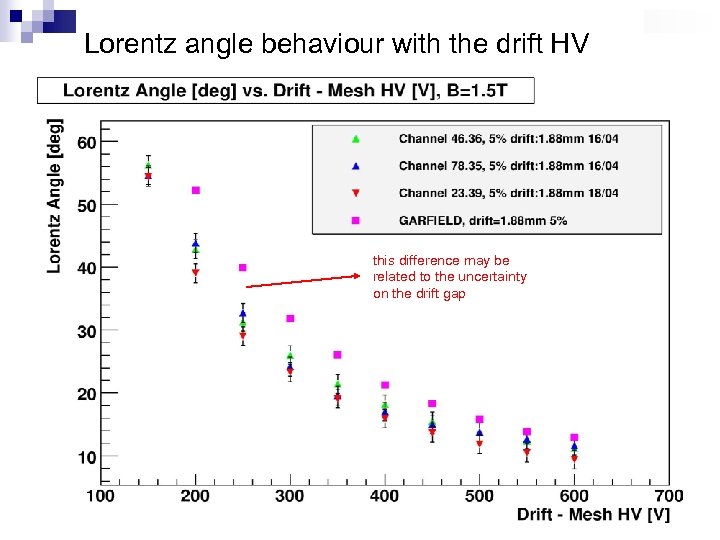 Lorentz angle behaviour with the drift HV this difference may be related to the uncertainty on the drift gap
Lorentz angle behaviour with the drift HV this difference may be related to the uncertainty on the drift gap
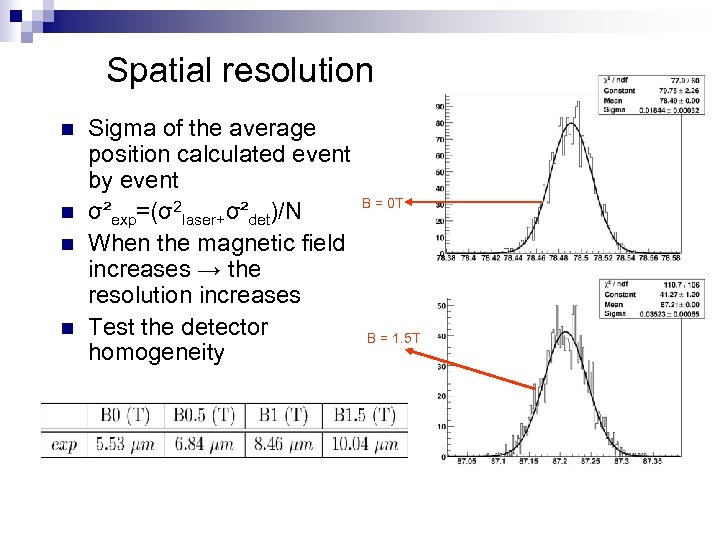 Spatial resolution n n Sigma of the average position calculated event by event B = 0 T σ²exp=(σ2 laser+σ²det)/N When the magnetic field increases → the resolution increases Test the detector B = 1. 5 T homogeneity
Spatial resolution n n Sigma of the average position calculated event by event B = 0 T σ²exp=(σ2 laser+σ²det)/N When the magnetic field increases → the resolution increases Test the detector B = 1. 5 T homogeneity
 Micromégas prototype for the central tracker
Micromégas prototype for the central tracker
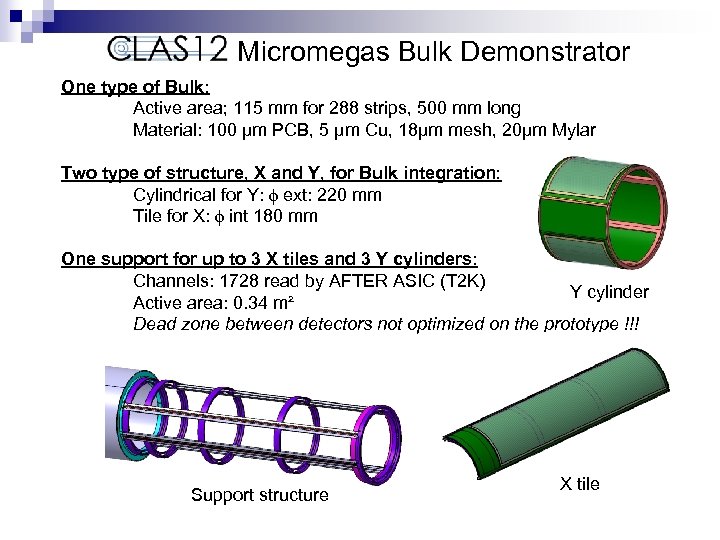 Micromegas Bulk Demonstrator One type of Bulk: Active area; 115 mm for 288 strips, 500 mm long Material: 100 µm PCB, 5 µm Cu, 18µm mesh, 20µm Mylar Two type of structure, X and Y, for Bulk integration: Cylindrical for Y: f ext: 220 mm Tile for X: f int 180 mm One support for up to 3 X tiles and 3 Y cylinders: Channels: 1728 read by AFTER ASIC (T 2 K) Y cylinder Active area: 0. 34 m² Dead zone between detectors not optimized on the prototype !!! Support structure X tile
Micromegas Bulk Demonstrator One type of Bulk: Active area; 115 mm for 288 strips, 500 mm long Material: 100 µm PCB, 5 µm Cu, 18µm mesh, 20µm Mylar Two type of structure, X and Y, for Bulk integration: Cylindrical for Y: f ext: 220 mm Tile for X: f int 180 mm One support for up to 3 X tiles and 3 Y cylinders: Channels: 1728 read by AFTER ASIC (T 2 K) Y cylinder Active area: 0. 34 m² Dead zone between detectors not optimized on the prototype !!! Support structure X tile
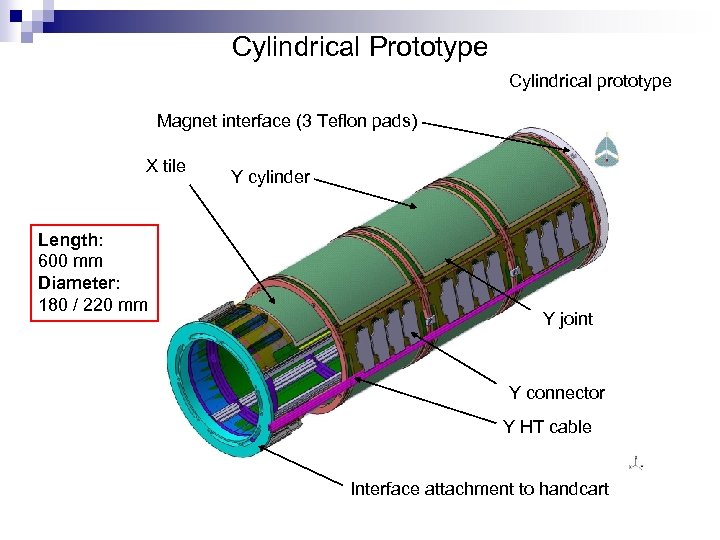 Cylindrical Prototype Cylindrical prototype Magnet interface (3 Teflon pads) X tile Length: 600 mm Diameter: 180 / 220 mm Y cylinder Y joint Y connector Y HT cable Interface attachment to handcart
Cylindrical Prototype Cylindrical prototype Magnet interface (3 Teflon pads) X tile Length: 600 mm Diameter: 180 / 220 mm Y cylinder Y joint Y connector Y HT cable Interface attachment to handcart
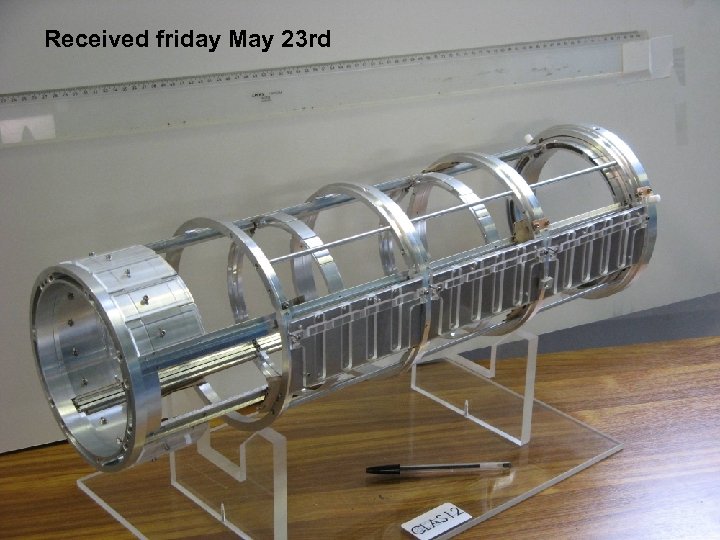 Received friday May 23 rd
Received friday May 23 rd
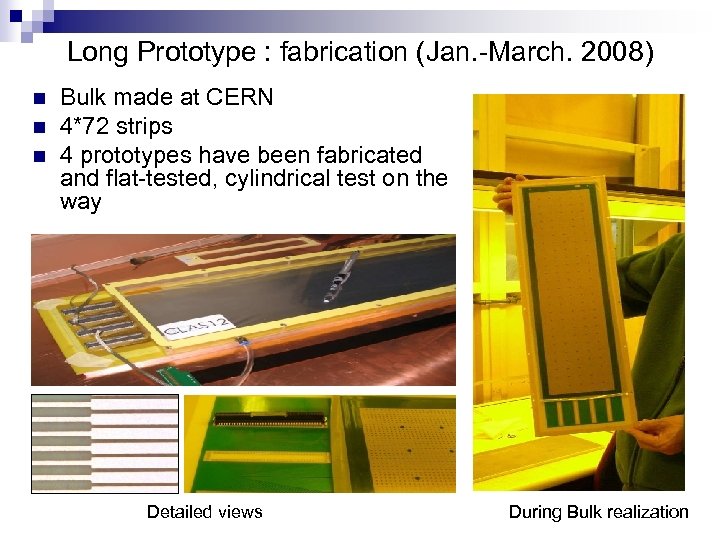 Long Prototype : fabrication (Jan. -March. 2008) n n n Bulk made at CERN 4*72 strips 4 prototypes have been fabricated and flat-tested, cylindrical test on the way Detailed views During Bulk realization
Long Prototype : fabrication (Jan. -March. 2008) n n n Bulk made at CERN 4*72 strips 4 prototypes have been fabricated and flat-tested, cylindrical test on the way Detailed views During Bulk realization
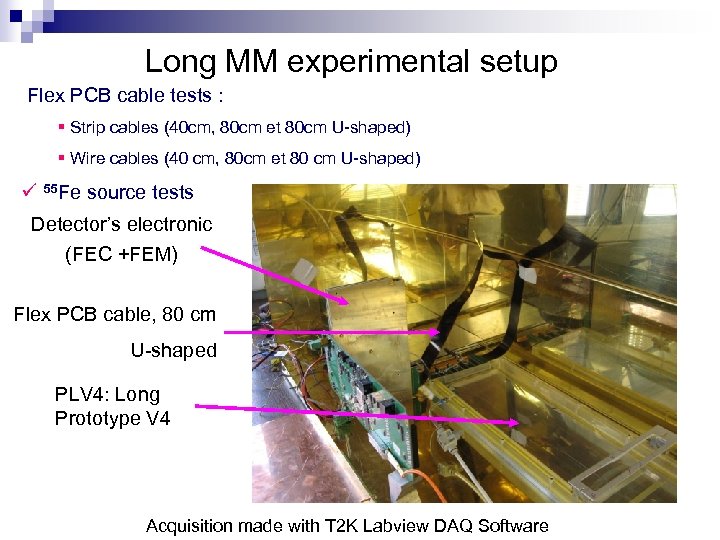 Long MM experimental setup Flex PCB cable tests : § Strip cables (40 cm, 80 cm et 80 cm U-shaped) § Wire cables (40 cm, 80 cm et 80 cm U-shaped) ü 55 Fe source tests Detector’s electronic (FEC +FEM) Flex PCB cable, 80 cm U-shaped PLV 4: Long Prototype V 4 Acquisition made with T 2 K Labview DAQ Software
Long MM experimental setup Flex PCB cable tests : § Strip cables (40 cm, 80 cm et 80 cm U-shaped) § Wire cables (40 cm, 80 cm et 80 cm U-shaped) ü 55 Fe source tests Detector’s electronic (FEC +FEM) Flex PCB cable, 80 cm U-shaped PLV 4: Long Prototype V 4 Acquisition made with T 2 K Labview DAQ Software
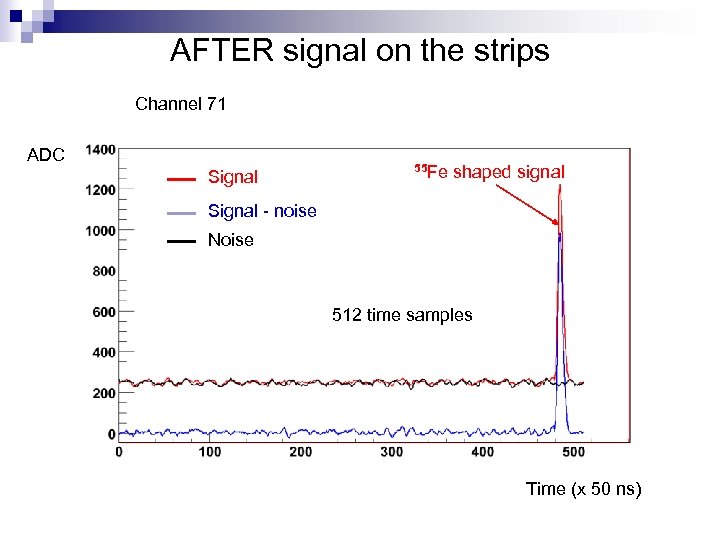 AFTER signal on the strips Channel 71 ADC Signal 55 Fe shaped signal Signal - noise Noise 512 time samples Time (x 50 ns)
AFTER signal on the strips Channel 71 ADC Signal 55 Fe shaped signal Signal - noise Noise 512 time samples Time (x 50 ns)
 Integration to the CLAS magnet
Integration to the CLAS magnet
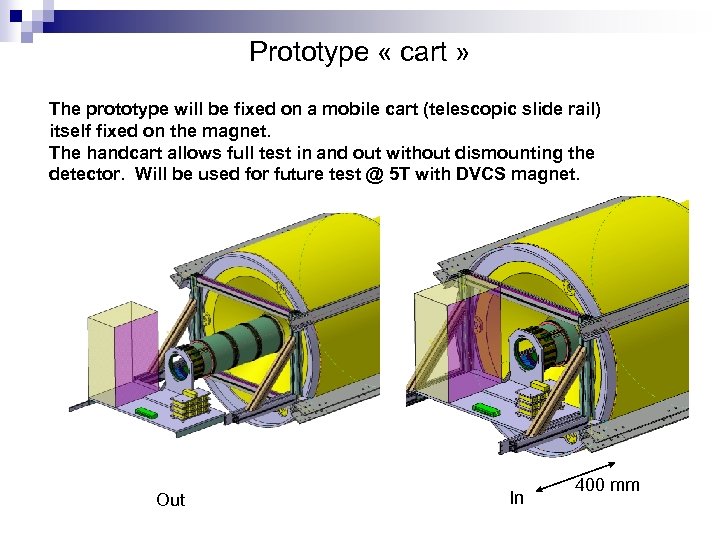 Prototype « cart » The prototype will be fixed on a mobile cart (telescopic slide rail) itself fixed on the magnet. The handcart allows full test in and out without dismounting the detector. Will be used for future test @ 5 T with DVCS magnet. Out In 400 mm
Prototype « cart » The prototype will be fixed on a mobile cart (telescopic slide rail) itself fixed on the magnet. The handcart allows full test in and out without dismounting the detector. Will be used for future test @ 5 T with DVCS magnet. Out In 400 mm
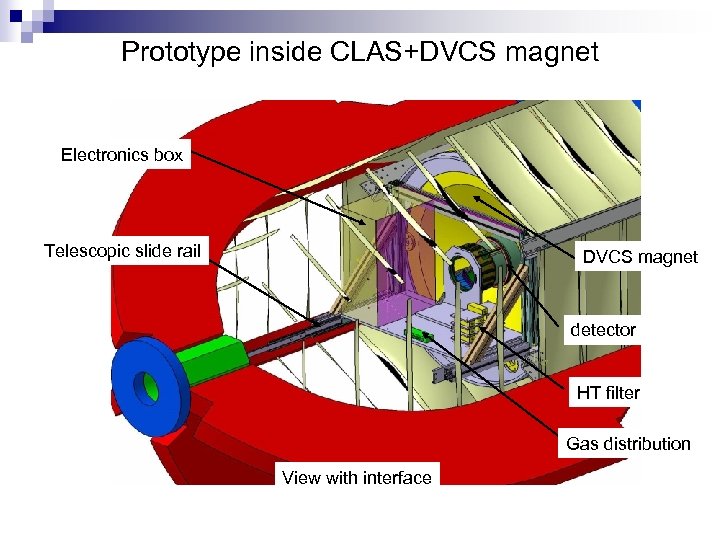 Prototype inside CLAS+DVCS magnet Electronics box Telescopic slide rail DVCS magnet detector HT filter Gas distribution View with interface
Prototype inside CLAS+DVCS magnet Electronics box Telescopic slide rail DVCS magnet detector HT filter Gas distribution View with interface
 2000 -channel tests #1 and 2 1. During fall 2008, 5 T test inside DVCS solenoid: Goals: • Dry test for test beam end 2008: full prototype on handcart • Lorentz angle @ 5 T: one X tile with UV laser • Cosmic test @ 5 T: Three X tiles. 2. During change-out between e 1 -dvcs and eg 1 -dvcs(? ), beam test: Goals: • Beam test: full cylindrical prototype on cart • Beam test: Forward prototype if possible
2000 -channel tests #1 and 2 1. During fall 2008, 5 T test inside DVCS solenoid: Goals: • Dry test for test beam end 2008: full prototype on handcart • Lorentz angle @ 5 T: one X tile with UV laser • Cosmic test @ 5 T: Three X tiles. 2. During change-out between e 1 -dvcs and eg 1 -dvcs(? ), beam test: Goals: • Beam test: full cylindrical prototype on cart • Beam test: Forward prototype if possible
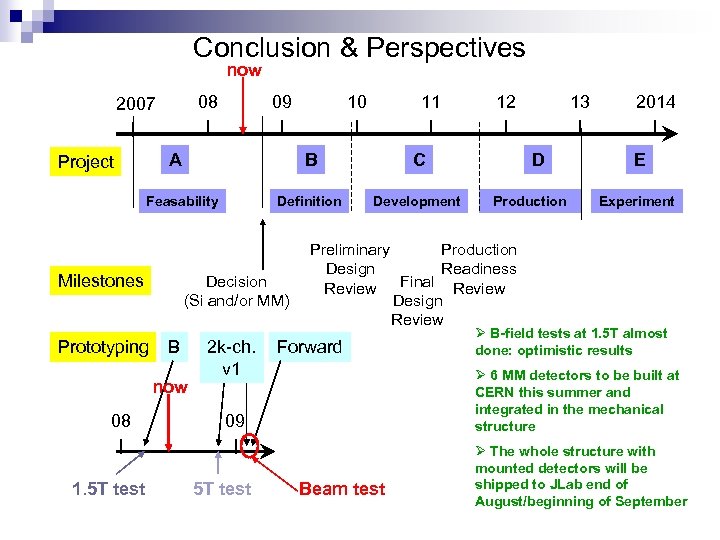 Conclusion & Perspectives now 08 2007 09 A Project Prototyping Definition 1. 5 T test Development B 2 k-ch. v 1 13 D Production 2014 E Experiment Preliminary Production Design Readiness Final Review Design Review Forward Ø B-field tests at 1. 5 T almost done: optimistic results Ø 6 MM detectors to be built at CERN this summer and integrated in the mechanical structure 09 5 T test 12 C Decision (Si and/or MM) now 08 11 B Feasability Milestones 10 Beam test Ø The whole structure with mounted detectors will be shipped to JLab end of August/beginning of September
Conclusion & Perspectives now 08 2007 09 A Project Prototyping Definition 1. 5 T test Development B 2 k-ch. v 1 13 D Production 2014 E Experiment Preliminary Production Design Readiness Final Review Design Review Forward Ø B-field tests at 1. 5 T almost done: optimistic results Ø 6 MM detectors to be built at CERN this summer and integrated in the mechanical structure 09 5 T test 12 C Decision (Si and/or MM) now 08 11 B Feasability Milestones 10 Beam test Ø The whole structure with mounted detectors will be shipped to JLab end of August/beginning of September
 ANNEXES
ANNEXES
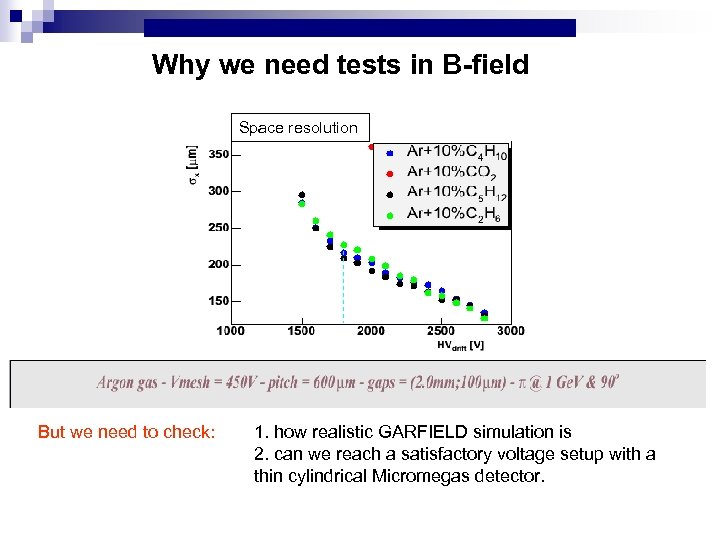 Why we need tests in B-field Space resolution But we need to check: 1. how realistic GARFIELD simulation is 2. can we reach a satisfactory voltage setup with a thin cylindrical Micromegas detector.
Why we need tests in B-field Space resolution But we need to check: 1. how realistic GARFIELD simulation is 2. can we reach a satisfactory voltage setup with a thin cylindrical Micromegas detector.
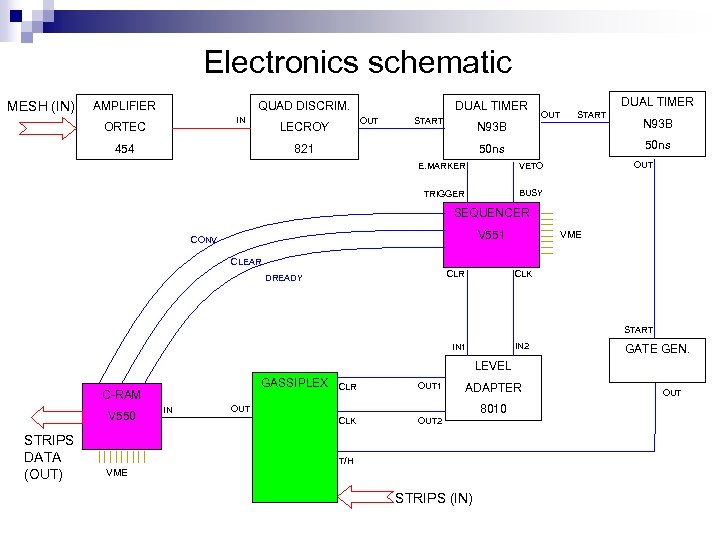 Electronics schematic MESH (IN) AMPLIFIER QUAD DISCRIM. IN ORTEC 454 DUAL TIMER OUT START N 93 B 821 N 93 B 50 ns LECROY 50 ns E. MARKER TRIGGER OUT VETO BUSY SEQUENCER V 551 CONV VME CLEAR CLR DREADY CLK START IN 2 IN 1 GATE GEN. LEVEL GASSIPLEX C-RAM V 550 STRIPS DATA (OUT) IN CLR OUT 1 CLK OUT 2 ADAPTER OUT T/H VME STRIPS (IN) 8010 OUT
Electronics schematic MESH (IN) AMPLIFIER QUAD DISCRIM. IN ORTEC 454 DUAL TIMER OUT START N 93 B 821 N 93 B 50 ns LECROY 50 ns E. MARKER TRIGGER OUT VETO BUSY SEQUENCER V 551 CONV VME CLEAR CLR DREADY CLK START IN 2 IN 1 GATE GEN. LEVEL GASSIPLEX C-RAM V 550 STRIPS DATA (OUT) IN CLR OUT 1 CLK OUT 2 ADAPTER OUT T/H VME STRIPS (IN) 8010 OUT
 Data acquisition (Labview)
Data acquisition (Labview)
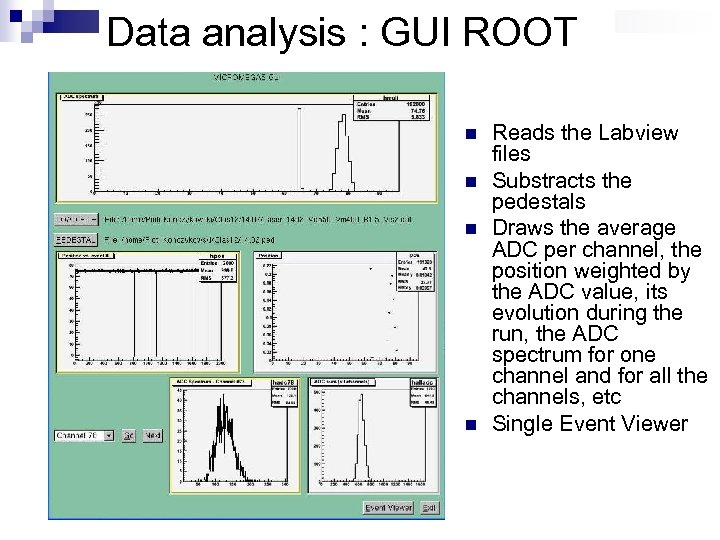 Data analysis : GUI ROOT n n Reads the Labview files Substracts the pedestals Draws the average ADC per channel, the position weighted by the ADC value, its evolution during the run, the ADC spectrum for one channel and for all the channels, etc Single Event Viewer
Data analysis : GUI ROOT n n Reads the Labview files Substracts the pedestals Draws the average ADC per channel, the position weighted by the ADC value, its evolution during the run, the ADC spectrum for one channel and for all the channels, etc Single Event Viewer
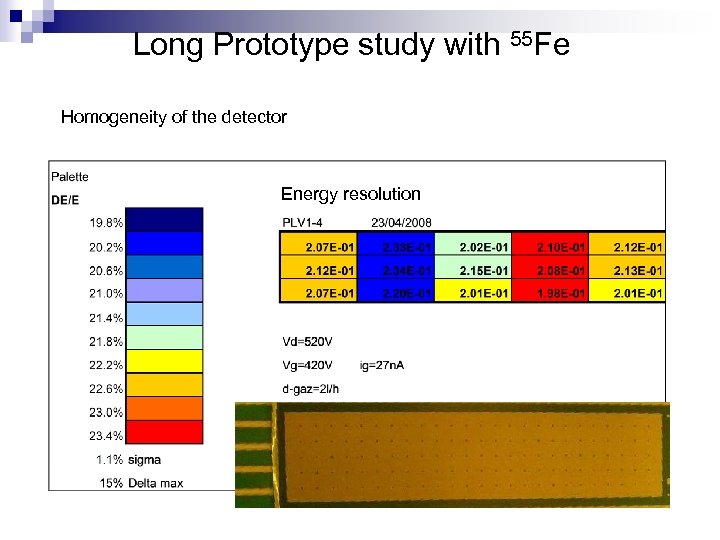 Long Prototype study with 55 Fe Homogeneity of the detector Energy resolution
Long Prototype study with 55 Fe Homogeneity of the detector Energy resolution
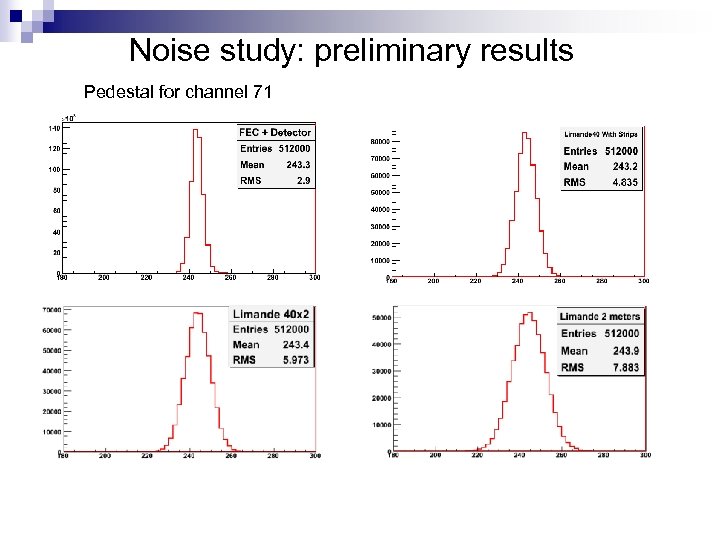 Noise study: preliminary results Pedestal for channel 71
Noise study: preliminary results Pedestal for channel 71
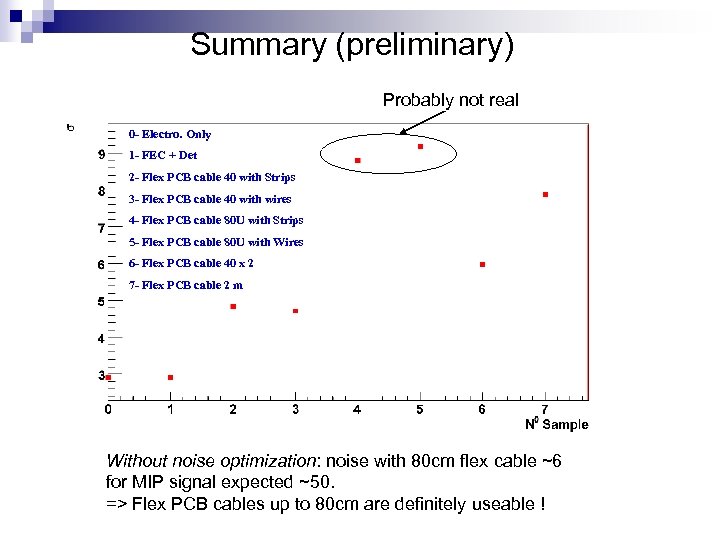 Summary (preliminary) Probably not real 0 - Electro. Only 1 - FEC + Det 2 - Flex PCB cable 40 with Strips 3 - Flex PCB cable 40 with wires 4 - Flex PCB cable 80 U with Strips 5 - Flex PCB cable 80 U with Wires 6 - Flex PCB cable 40 x 2 7 - Flex PCB cable 2 m Without noise optimization: noise with 80 cm flex cable ~6 for MIP signal expected ~50. => Flex PCB cables up to 80 cm are definitely useable !
Summary (preliminary) Probably not real 0 - Electro. Only 1 - FEC + Det 2 - Flex PCB cable 40 with Strips 3 - Flex PCB cable 40 with wires 4 - Flex PCB cable 80 U with Strips 5 - Flex PCB cable 80 U with Wires 6 - Flex PCB cable 40 x 2 7 - Flex PCB cable 2 m Without noise optimization: noise with 80 cm flex cable ~6 for MIP signal expected ~50. => Flex PCB cables up to 80 cm are definitely useable !
 Future plans with B-field tests (June. July + fall ’ 08) -Improved precision tests thanks to a larger drift gap -Direct measurement of gap with the laser setup -Precise variation of the laser intensity with neutral filter wheel -Tests planned in the fall ’ 08 with e 1 -dvcs magnet at 5 T and large-area detectors
Future plans with B-field tests (June. July + fall ’ 08) -Improved precision tests thanks to a larger drift gap -Direct measurement of gap with the laser setup -Precise variation of the laser intensity with neutral filter wheel -Tests planned in the fall ’ 08 with e 1 -dvcs magnet at 5 T and large-area detectors
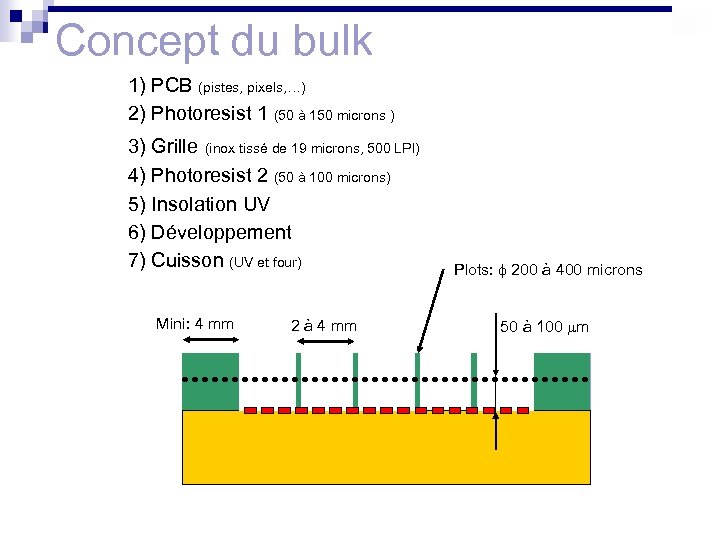 Concept du bulk 1) PCB (pistes, pixels, …) 2) Photoresist 1 (50 à 150 microns ) 3) Grille (inox tissé de 19 microns, 500 LPI) 4) Photoresist 2 (50 à 100 microns) 5) Insolation UV 6) Développement UV 7) Cuisson (UV et four) Mask Photoresist 2 Photoresist 1 Mini: 4 mm 2 à 4 mm Plots: f 200 à 400 microns 50 à 100 mm Mesh PCB
Concept du bulk 1) PCB (pistes, pixels, …) 2) Photoresist 1 (50 à 150 microns ) 3) Grille (inox tissé de 19 microns, 500 LPI) 4) Photoresist 2 (50 à 100 microns) 5) Insolation UV 6) Développement UV 7) Cuisson (UV et four) Mask Photoresist 2 Photoresist 1 Mini: 4 mm 2 à 4 mm Plots: f 200 à 400 microns 50 à 100 mm Mesh PCB


