7c4b16f7e83495b33f09d437231146a2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 85
 Central Station Operator Course
Central Station Operator Course
 Digi. Com, Inc Central Station Operator Course WELCOME!
Digi. Com, Inc Central Station Operator Course WELCOME!
 Course Schedule Day 1 Introduction and Administration Unit One: Operational Overview Unit Two: The Central Station Operator Role Day 2 Unit Three: Alarm Verification Unit Four: Personnel Guidelines for the Central Station Operator Day 3 Unit Five: Communications Unit Six: Central Station Equipment Day 4 Unit Seven: Underwriter’s Laboratories/ Factory Mutual Unit Eight: Telephone and Radio Communications Day 5 Unit Nine: Emergency Procedures Final Examination and Course Evaluations
Course Schedule Day 1 Introduction and Administration Unit One: Operational Overview Unit Two: The Central Station Operator Role Day 2 Unit Three: Alarm Verification Unit Four: Personnel Guidelines for the Central Station Operator Day 3 Unit Five: Communications Unit Six: Central Station Equipment Day 4 Unit Seven: Underwriter’s Laboratories/ Factory Mutual Unit Eight: Telephone and Radio Communications Day 5 Unit Nine: Emergency Procedures Final Examination and Course Evaluations
 Unit One: Operational Overview Know your objectives!
Unit One: Operational Overview Know your objectives!
 People of the Alarm Industry Customer-End User, Subscriber, SB’s Alarm Installer Central Station Operator Authorities
People of the Alarm Industry Customer-End User, Subscriber, SB’s Alarm Installer Central Station Operator Authorities
 Alarm Systems by Security Function • Burglar Alarm Systems • Fire Alarm Systems • Emergency Alarm Systems • Specialized Supervisory Alarm Systems
Alarm Systems by Security Function • Burglar Alarm Systems • Fire Alarm Systems • Emergency Alarm Systems • Specialized Supervisory Alarm Systems
 Alarm Equipment Detection Devices Control Panels Alarm Receivers
Alarm Equipment Detection Devices Control Panels Alarm Receivers
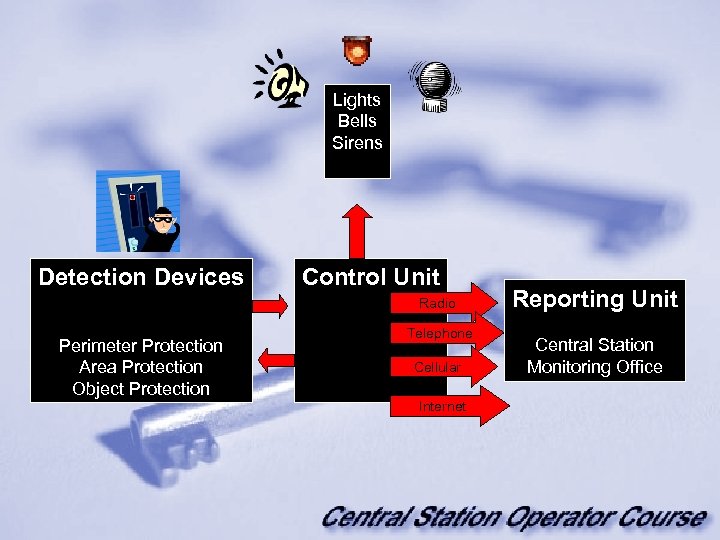 Lights Bells Sirens Detection Devices Control Unit Radio Perimeter Protection Area Protection Object Protection Telephone Cellular Internet Reporting Unit Central Station Monitoring Office
Lights Bells Sirens Detection Devices Control Unit Radio Perimeter Protection Area Protection Object Protection Telephone Cellular Internet Reporting Unit Central Station Monitoring Office
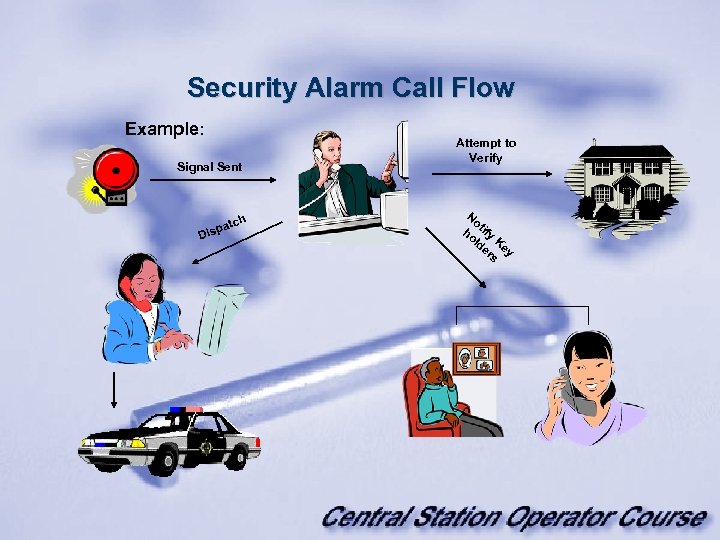 Security Alarm Call Flow Example: Signal Sent h atc isp D Attempt to Verify No ho tify ld Ke er y s
Security Alarm Call Flow Example: Signal Sent h atc isp D Attempt to Verify No ho tify ld Ke er y s
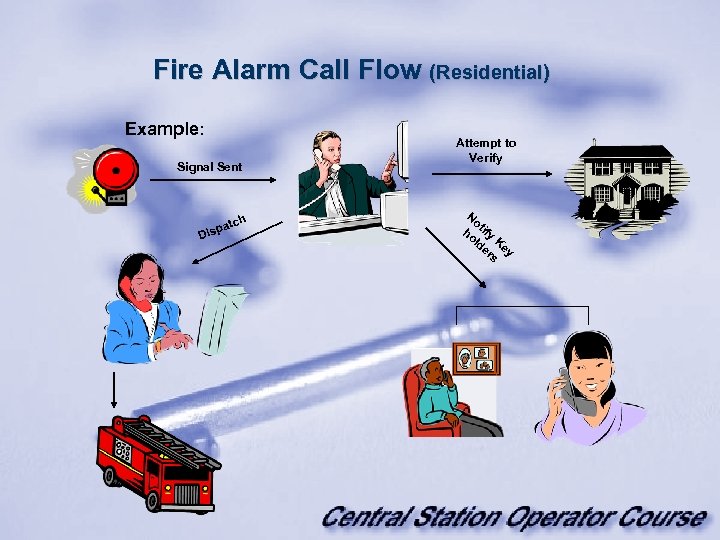 Fire Alarm Call Flow (Residential) Example: Signal Sent h atc isp D Attempt to Verify No ho tify ld Ke er y s
Fire Alarm Call Flow (Residential) Example: Signal Sent h atc isp D Attempt to Verify No ho tify ld Ke er y s
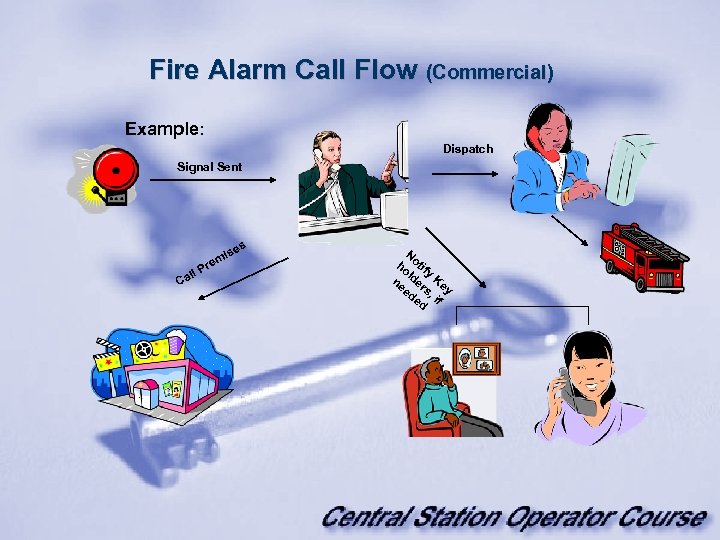 Fire Alarm Call Flow (Commercial) Example: Dispatch Signal Sent s Ca ll P ise em r N ho otif l y ne der Ke ed s, y ed if
Fire Alarm Call Flow (Commercial) Example: Dispatch Signal Sent s Ca ll P ise em r N ho otif l y ne der Ke ed s, y ed if
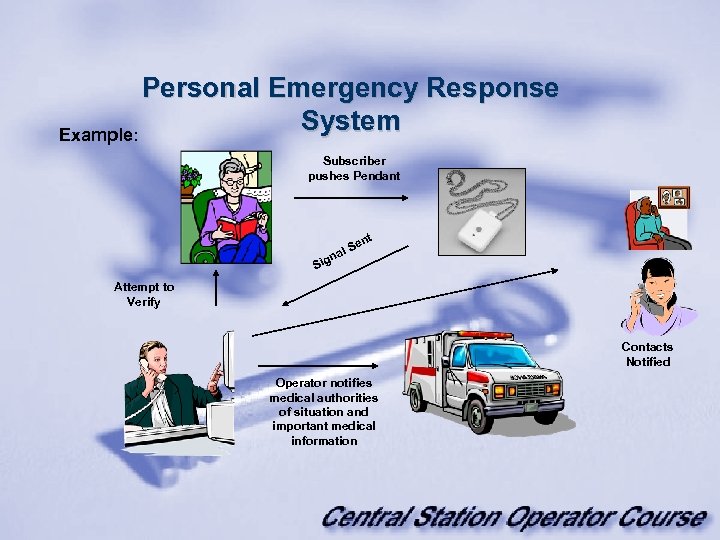 Personal Emergency Response System Example: Subscriber pushes Pendant n Sig t en S al Attempt to Verify Contacts Notified Operator notifies medical authorities of situation and important medical information
Personal Emergency Response System Example: Subscriber pushes Pendant n Sig t en S al Attempt to Verify Contacts Notified Operator notifies medical authorities of situation and important medical information
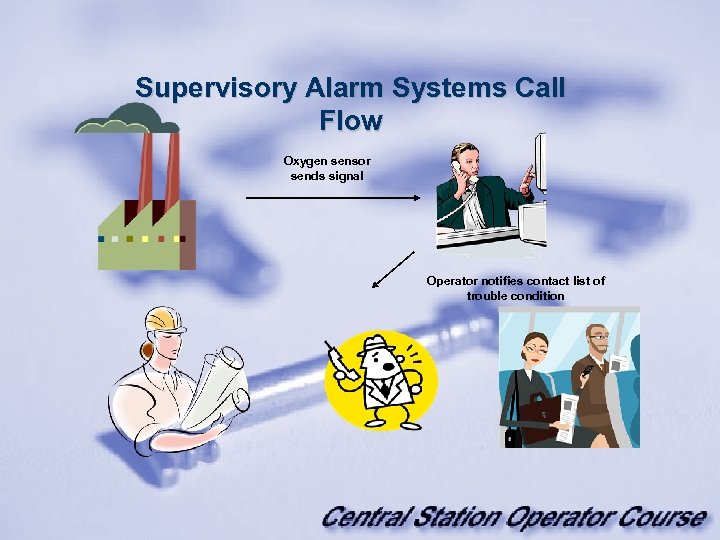 Supervisory Alarm Systems Call Flow Oxygen sensor sends signal Operator notifies contact list of trouble condition
Supervisory Alarm Systems Call Flow Oxygen sensor sends signal Operator notifies contact list of trouble condition
 Chapter 1 Review Questions 1. WHAT ARE THE FOUR SETS OF PEOPLE THAT MAKE UP THE ALARM INDUSTRY? 2. WHAT ARE FOUR TYPES OF ALARM SYSTEMS? 3. WHAT IS THE CALL FLOW FOR A COMMERCIAL FIRE ALARM SYSTEM?
Chapter 1 Review Questions 1. WHAT ARE THE FOUR SETS OF PEOPLE THAT MAKE UP THE ALARM INDUSTRY? 2. WHAT ARE FOUR TYPES OF ALARM SYSTEMS? 3. WHAT IS THE CALL FLOW FOR A COMMERCIAL FIRE ALARM SYSTEM?
 Chapter 1 Review Questions 4. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CATEGORIES OF ALARM EQUIPMENT? DESCRIBE THEM AND PROVIDE AN EXAMPLE OF EACH. 5. DESCRIBE CALL FLOW FOR A SECURITY ALARM.
Chapter 1 Review Questions 4. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CATEGORIES OF ALARM EQUIPMENT? DESCRIBE THEM AND PROVIDE AN EXAMPLE OF EACH. 5. DESCRIBE CALL FLOW FOR A SECURITY ALARM.
 Unit Two: Verification Procedures Know your objectives!
Unit Two: Verification Procedures Know your objectives!
 Why do we have Humans monitoring alarms?
Why do we have Humans monitoring alarms?
 Assisting Technicians • Place accounts on test • Report signal history • Diagnosing Possible Problems • Caller Id Mismatch • Transmission Errors • AHS Table
Assisting Technicians • Place accounts on test • Report signal history • Diagnosing Possible Problems • Caller Id Mismatch • Transmission Errors • AHS Table
 Assisting Customers • Placing Account on Test • Giving Signal History • Contact Info for Service • Changing or Updating Account Info
Assisting Customers • Placing Account on Test • Giving Signal History • Contact Info for Service • Changing or Updating Account Info
 Alarm History Information Know Digi. Com’s procedure regarding confidentiality and release of information Data Entry and Automation Know Digi. Com’s procedure regarding data entry
Alarm History Information Know Digi. Com’s procedure regarding confidentiality and release of information Data Entry and Automation Know Digi. Com’s procedure regarding data entry
 Unit Two: Review Questions 1. WHY ARE CENTRAL STATION OPERATORS NEEDED? 2. GENERALLY DESCRIBE THREE ALARM VERIFICATION PROCEDURES. 3. HOW MIGHT YOU ASSIST A CUSTOMER? 4. WHAT PROCEDURES ARE USED IN YOUR COMPANY TO RESEARCH, COMPILE AND RELAY ALARM HISTORY INFORMATION? WHO IS ALLOWED TO HAVE THIS INFORMATION?
Unit Two: Review Questions 1. WHY ARE CENTRAL STATION OPERATORS NEEDED? 2. GENERALLY DESCRIBE THREE ALARM VERIFICATION PROCEDURES. 3. HOW MIGHT YOU ASSIST A CUSTOMER? 4. WHAT PROCEDURES ARE USED IN YOUR COMPANY TO RESEARCH, COMPILE AND RELAY ALARM HISTORY INFORMATION? WHO IS ALLOWED TO HAVE THIS INFORMATION?
 Unit Two: Review Questions 5. WHAT RESPONSIBILITIES DO YOU HAVE FOR THE ENTRY OF DATA INTO THE AUTOMATION SYSTEM? WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU USE?
Unit Two: Review Questions 5. WHAT RESPONSIBILITIES DO YOU HAVE FOR THE ENTRY OF DATA INTO THE AUTOMATION SYSTEM? WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU USE?
 Unit Three: Alarm Verification Know your objectives!
Unit Three: Alarm Verification Know your objectives!
 Verification ELECTRONIC VERBAL
Verification ELECTRONIC VERBAL
 Verification Procedures Operator will call premises and attempt to obtain the pass code. 5 Rings and two attempts 3 calls if phone is busy Recalls made immediately one after another If no pass code is given or an incorrect pass code, we attempt to verify the person’s authority to be on premise. If dispatch is made, police should be informed of a possible unauthorized person on premises.
Verification Procedures Operator will call premises and attempt to obtain the pass code. 5 Rings and two attempts 3 calls if phone is busy Recalls made immediately one after another If no pass code is given or an incorrect pass code, we attempt to verify the person’s authority to be on premise. If dispatch is made, police should be informed of a possible unauthorized person on premises.
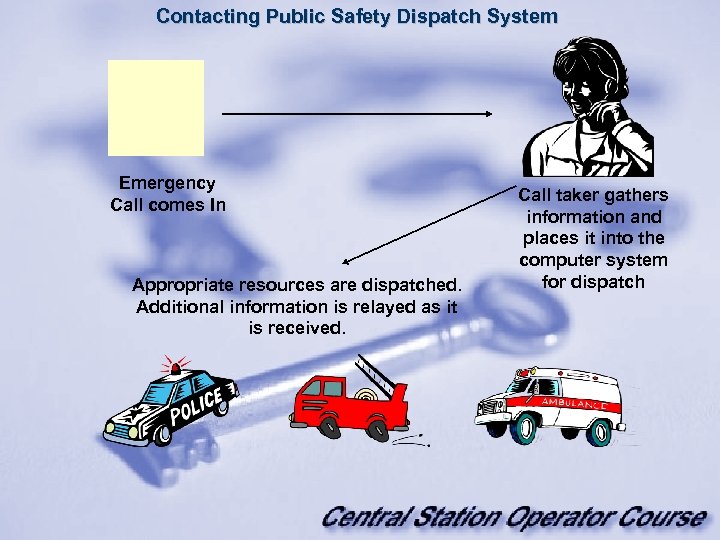 Contacting Public Safety Dispatch System Emergency Call comes In Appropriate resources are dispatched. Additional information is relayed as it is received. Call taker gathers information and places it into the computer system for dispatch
Contacting Public Safety Dispatch System Emergency Call comes In Appropriate resources are dispatched. Additional information is relayed as it is received. Call taker gathers information and places it into the computer system for dispatch
 Information Relay: Be Quick, Accurate & Clear • Identify your company • Provide the location on the alarm • Provide a short description of the nature of the alarm • Provide specific information about the alarm system, if available The Call Taker will “lead the call, asking questions as needed.
Information Relay: Be Quick, Accurate & Clear • Identify your company • Provide the location on the alarm • Provide a short description of the nature of the alarm • Provide specific information about the alarm system, if available The Call Taker will “lead the call, asking questions as needed.
 Notifying Key Holders and Contact Persons Tell the key holder: • Who you are • Why you are calling • What the situation is • Not to enter the protected premises • Wait for the response agent(s)
Notifying Key Holders and Contact Persons Tell the key holder: • Who you are • Why you are calling • What the situation is • Not to enter the protected premises • Wait for the response agent(s)
 Notifying Key Holders and Contact Persons, know Digi. Com’s procedures • What to say • Company policies on leaving messages on answering machines • Company policy on leaving messages with people • Company policy when unable to locate anyone
Notifying Key Holders and Contact Persons, know Digi. Com’s procedures • What to say • Company policies on leaving messages on answering machines • Company policy on leaving messages with people • Company policy when unable to locate anyone
 Verification Procedures • Residential Panic Alarm • Fire Alarm Signals – Household – Commercial • Personal Emergency Response – Panic – Medical • Specialized Supervisory Alarm Systems
Verification Procedures • Residential Panic Alarm • Fire Alarm Signals – Household – Commercial • Personal Emergency Response – Panic – Medical • Specialized Supervisory Alarm Systems
 Unit Three: Review Questions 1. WHAT DO THE TERMS ELECTRONIC VERIFICATION AND VERBAL VERIFICATION MEAN? 2. WHY IS VERIFICATION NECESSARY? 3. THERE ARE THREE PRIMARY RULES TO BE FOLLOWED WHEN RELAYING INFORMATION TO THE PUBLIC SAFETY COMMUNICATIONS CENTER. WHAT ARE THEY? 4. WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU USE TO NOTIFY EMERGENCY RESPONSE SERVICES?
Unit Three: Review Questions 1. WHAT DO THE TERMS ELECTRONIC VERIFICATION AND VERBAL VERIFICATION MEAN? 2. WHY IS VERIFICATION NECESSARY? 3. THERE ARE THREE PRIMARY RULES TO BE FOLLOWED WHEN RELAYING INFORMATION TO THE PUBLIC SAFETY COMMUNICATIONS CENTER. WHAT ARE THEY? 4. WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU USE TO NOTIFY EMERGENCY RESPONSE SERVICES?
 Unit Three: Review Questions 5. WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU USE TO NOTIFY A CONTACT PERSON OR THE SUBSCRIBER? 6. WHEN DO YOU MAKE FOLLOW UP CALLS? WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU USE TO MAKE THESE CALLS?
Unit Three: Review Questions 5. WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU USE TO NOTIFY A CONTACT PERSON OR THE SUBSCRIBER? 6. WHEN DO YOU MAKE FOLLOW UP CALLS? WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU USE TO MAKE THESE CALLS?
 Unit Four: Personnel Guidelines For the Central Station Operator Know your objectives!
Unit Four: Personnel Guidelines For the Central Station Operator Know your objectives!
 Licensing Requirements Licensing requirements vary from state to state, city to city, and company to company. Know the licensing requirements for the areas your company monitors.
Licensing Requirements Licensing requirements vary from state to state, city to city, and company to company. Know the licensing requirements for the areas your company monitors.
 Moral and Legal Obligations A homeowner has her house burglarized. The television and stereo are missing, but so are the antique coins the her grandfather gave her on her eighteenth birthday they can not be replaced. A small retail clothing store catches fire from faulty electrical hookups in the back of the store. The store smolders for about five hours, then violently explodes into flame. The entire inventory is lost. A 72 year old man is ready to go home from the hospital, but needs to be able to contact help immediately in an emergency. He wouldn’t have to go to a nursing home for the next four months if there was only a way he could just press a button to summon help.
Moral and Legal Obligations A homeowner has her house burglarized. The television and stereo are missing, but so are the antique coins the her grandfather gave her on her eighteenth birthday they can not be replaced. A small retail clothing store catches fire from faulty electrical hookups in the back of the store. The store smolders for about five hours, then violently explodes into flame. The entire inventory is lost. A 72 year old man is ready to go home from the hospital, but needs to be able to contact help immediately in an emergency. He wouldn’t have to go to a nursing home for the next four months if there was only a way he could just press a button to summon help.
 Everything that happens in the central station, including subscriber’s names, addresses, alarm types, passwords, account numbers, client schedules, phone numbers and any other information is strictly confidential. Should any of this information be disseminated, it is a breach of confidentiality and may also have legal consequences.
Everything that happens in the central station, including subscriber’s names, addresses, alarm types, passwords, account numbers, client schedules, phone numbers and any other information is strictly confidential. Should any of this information be disseminated, it is a breach of confidentiality and may also have legal consequences.
 Minimizing Liability Exposure • Treat each alarm as if it was coming from your home or business • Report problems with equipment immediately, follow up as needed • Report problems and conflicts with policy and procedure, and follow up as needed • Ask questions, get training, and understand everything that you are doing
Minimizing Liability Exposure • Treat each alarm as if it was coming from your home or business • Report problems with equipment immediately, follow up as needed • Report problems and conflicts with policy and procedure, and follow up as needed • Ask questions, get training, and understand everything that you are doing
 Stress- Causes and Solutions Mental Physical
Stress- Causes and Solutions Mental Physical
 Cleanliness Keep Your Work Area Clean Know your company’s procedures! • Use a spill proof cup • If you snack at console remember crumbs cause bugs! • Wipe Down all surfaces in your work area: monitors, keyboards, phone, console surface. • Know your company’s dress code • Report any problems to your supervisor: Broken, Dirty, needs to be repaired or cleaned.
Cleanliness Keep Your Work Area Clean Know your company’s procedures! • Use a spill proof cup • If you snack at console remember crumbs cause bugs! • Wipe Down all surfaces in your work area: monitors, keyboards, phone, console surface. • Know your company’s dress code • Report any problems to your supervisor: Broken, Dirty, needs to be repaired or cleaned.
 Personal Safety Know your company’s procedures! • Work Place Violence • Release of Central Station employee schedules • Restriction on visitors • Unscheduled Technicians • Release of Central Station Address • Food Delivery
Personal Safety Know your company’s procedures! • Work Place Violence • Release of Central Station employee schedules • Restriction on visitors • Unscheduled Technicians • Release of Central Station Address • Food Delivery
 Personal Hygiene The Unspeakable Topic!
Personal Hygiene The Unspeakable Topic!
 Additional Personal Information Know your company’s procedures! • Tardiness • Sick leave and policy about calling in sick • Vacation leave • Breaks • Kitchens, if appropriate • Restroom Locations • Smoking and smoking breaks
Additional Personal Information Know your company’s procedures! • Tardiness • Sick leave and policy about calling in sick • Vacation leave • Breaks • Kitchens, if appropriate • Restroom Locations • Smoking and smoking breaks
 Central Station and Company Facility Security and Safety IT IS EVERY OPERATORS RESPONSIBILITY TO ENSURE THE SECURITY AND SAFETY OF THE CENTRAL STATION! Identify any visitors to ensure they are authorized Escort visitors at all times Computers require logins, passwords and logouts Facility and equipment security is essential
Central Station and Company Facility Security and Safety IT IS EVERY OPERATORS RESPONSIBILITY TO ENSURE THE SECURITY AND SAFETY OF THE CENTRAL STATION! Identify any visitors to ensure they are authorized Escort visitors at all times Computers require logins, passwords and logouts Facility and equipment security is essential
 Unit Four: Review Questions 1. WHAT ARE YOUR COMPANY’S REQUIREMENTS FOR LICENSING? 2. WHAT IS MEANT BY MORAL AND LEGAL OBLIGATIONS? HOW DO THESE OBLIGATIONS AFFECT YOU AND YOUR JOB? 3. WHY IS LIABILITY A CONCERN FOR CENTRAL STATION? HOW DOES IT AFFECT YOUR JOB? 4. WHAT ARE TWO TYPES OF STRESS THAT YOU MAY EXPERIENCE? HOW CAN YOU CONTROL THEM? 5. WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO KEEP THE EQUIPMENT AND YOUR WORK AREA CLEAN?
Unit Four: Review Questions 1. WHAT ARE YOUR COMPANY’S REQUIREMENTS FOR LICENSING? 2. WHAT IS MEANT BY MORAL AND LEGAL OBLIGATIONS? HOW DO THESE OBLIGATIONS AFFECT YOU AND YOUR JOB? 3. WHY IS LIABILITY A CONCERN FOR CENTRAL STATION? HOW DOES IT AFFECT YOUR JOB? 4. WHAT ARE TWO TYPES OF STRESS THAT YOU MAY EXPERIENCE? HOW CAN YOU CONTROL THEM? 5. WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO KEEP THE EQUIPMENT AND YOUR WORK AREA CLEAN?
 Unit Four: Review Questions 6. WHY IS PERSONAL SAFETY IMPORTANT? 7. WHY IS PERSONAL HYGIENE IMPORTANT? 8. WHAT POLICIES ARE IN EFFECT REGARDING ISSUES SUCH AS TARDINESS, SICK LEAVE, ETC. ? 9. WHAT IS YOUR ROLE IN ENSURING THE SAFETY AND SECURITY OF THE CENTRAL STATION FACILITIES?
Unit Four: Review Questions 6. WHY IS PERSONAL SAFETY IMPORTANT? 7. WHY IS PERSONAL HYGIENE IMPORTANT? 8. WHAT POLICIES ARE IN EFFECT REGARDING ISSUES SUCH AS TARDINESS, SICK LEAVE, ETC. ? 9. WHAT IS YOUR ROLE IN ENSURING THE SAFETY AND SECURITY OF THE CENTRAL STATION FACILITIES?
 Unit Five: Communications Know your objectives!
Unit Five: Communications Know your objectives!
 Inference vs. Fact Communication is the art of transmitting an idea from the mind of one to the mind of another, with understanding Inferences- make assumptions or guesses based on the content of the communication received. Facts- based on observations
Inference vs. Fact Communication is the art of transmitting an idea from the mind of one to the mind of another, with understanding Inferences- make assumptions or guesses based on the content of the communication received. Facts- based on observations
 A businessman had just turned off the lights in the store when a man appeared and demanded money. The owner opened the cash register. The contents of the cash register were scooped up, and the man sped away. The robbery alarm activated, and the police force was promptly notified.
A businessman had just turned off the lights in the store when a man appeared and demanded money. The owner opened the cash register. The contents of the cash register were scooped up, and the man sped away. The robbery alarm activated, and the police force was promptly notified.
 A fire alarm activated and connected to the Central Station. The automation system indicated that the alarm was in installed at 1312 Bay Avenue, Constitution, Maryland. The Central Station Operator called the contact number, 427 -3461; the woman who answered properly identified herself as the contact person and reported that there was a house fire, that she observed what appeared to be smoke coming from an open upstairs window, and that she observed a man run from the side of the house and disappear around the corner.
A fire alarm activated and connected to the Central Station. The automation system indicated that the alarm was in installed at 1312 Bay Avenue, Constitution, Maryland. The Central Station Operator called the contact number, 427 -3461; the woman who answered properly identified herself as the contact person and reported that there was a house fire, that she observed what appeared to be smoke coming from an open upstairs window, and that she observed a man run from the side of the house and disappear around the corner.
 Implications for Central Station Operators • Observations vs. Inferences • Why is it so important to distinguish between a fact and an inference?
Implications for Central Station Operators • Observations vs. Inferences • Why is it so important to distinguish between a fact and an inference?
 Statements of Fact Can be made only after observation Must stay within what one observes and not go beyond Can be made only by the observer Approaches certainty Can be made only to the extent of the observer’s capabilities and competency
Statements of Fact Can be made only after observation Must stay within what one observes and not go beyond Can be made only by the observer Approaches certainty Can be made only to the extent of the observer’s capabilities and competency
 Statements of Inferences Can be made anytime Can go beyond; only limited by one’s imagination Can be made by anyone Deal only with probability Can be made by the incompetent Beware of inferences. Be careful about making assumptions!
Statements of Inferences Can be made anytime Can go beyond; only limited by one’s imagination Can be made by anyone Deal only with probability Can be made by the incompetent Beware of inferences. Be careful about making assumptions!
 What is communication? Transfer ideas from the mind of one to the mind of another with understanding!
What is communication? Transfer ideas from the mind of one to the mind of another with understanding!
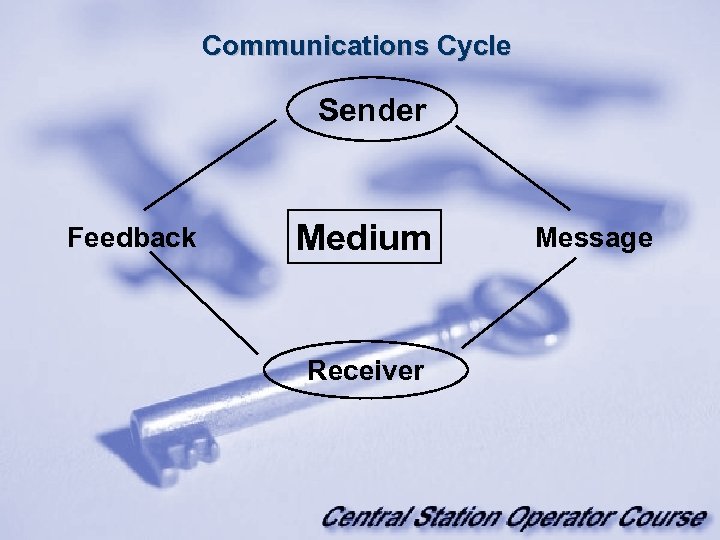 Communications Cycle Sender Feedback Medium Receiver Message
Communications Cycle Sender Feedback Medium Receiver Message
 The words that you use: “All units, 10 -65 signal 95 reference signal 10 just occurred, South and Main, 2 suspects northbound signal 0. ” “November 943, turn left to 240 for approach. Wind 15 at 190, altimeter 29. 04. You have a heavy seven miles ahead on final. ” Lingo: Terms and standards of a specific application
The words that you use: “All units, 10 -65 signal 95 reference signal 10 just occurred, South and Main, 2 suspects northbound signal 0. ” “November 943, turn left to 240 for approach. Wind 15 at 190, altimeter 29. 04. You have a heavy seven miles ahead on final. ” Lingo: Terms and standards of a specific application
 Unit Five: Review Questions 1. WHAT IS THE DEFINITION OF COMMUNICATIONS? 2. WHAT IS AN INFERENCE? HOW DOES IT DIFFER FROM FACT? 3. ALMOST EVERYTHING WE DO IS BASED ON SOME ASSUMPTION AT SOME POINT. WHY? HOW DOES THAT AFFECT OUR PERCEPTION OF FACT? 4. WHY ARE FACTS 100% CERTAIN? 5. WHAT CAN HAPPEN WHEN WE TRUST AN ASSUMPUTION TO BE FACT?
Unit Five: Review Questions 1. WHAT IS THE DEFINITION OF COMMUNICATIONS? 2. WHAT IS AN INFERENCE? HOW DOES IT DIFFER FROM FACT? 3. ALMOST EVERYTHING WE DO IS BASED ON SOME ASSUMPTION AT SOME POINT. WHY? HOW DOES THAT AFFECT OUR PERCEPTION OF FACT? 4. WHY ARE FACTS 100% CERTAIN? 5. WHAT CAN HAPPEN WHEN WE TRUST AN ASSUMPUTION TO BE FACT?
 Unit Five: Review Questions 6. WHAT ARE THE COMPONENTS OF THE COMMUNICATION CYCLE? 7. WHAT IS LINGO? SHOULD IT BE USED? WHY OR WHY NOT?
Unit Five: Review Questions 6. WHAT ARE THE COMPONENTS OF THE COMMUNICATION CYCLE? 7. WHAT IS LINGO? SHOULD IT BE USED? WHY OR WHY NOT?
 Unit Six: Central Station Equipment Know your objectives!
Unit Six: Central Station Equipment Know your objectives!
 Glossary of Terms AUTOMATION SYSTEM: A COMPUTER SYSTEM THAT CONSISTS OF HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE COMPONENTS TO ENABLE THE PROCESSING AND RECORDING OF ALARMS AND ACCOUNT DATA. AUTHORITIES (CALL TAKER): EMPLOYEE OF A PUBLIC SAFETY COMMUNICATIONS CENTER WHO ANSWERS THE TELEPHONE AND RECORDS CALL FOR SERVICE. CENTRAL STATION: A BUILDING OR SUITE OF OFFICES THAT HOUSES A COMPANY ENGAGED IN THE MONITORING OF ALARM SYSTEMS. THE CENTRAL STATION CAN NOT RUN WITHOUT POWER SUPPLIES, INCLUDING BACKUP POWER SUPPLIES, ARE ESSENTIAL TO PROPER, CONTINUOUS OPERATION OF THE CENTRAL STATION.
Glossary of Terms AUTOMATION SYSTEM: A COMPUTER SYSTEM THAT CONSISTS OF HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE COMPONENTS TO ENABLE THE PROCESSING AND RECORDING OF ALARMS AND ACCOUNT DATA. AUTHORITIES (CALL TAKER): EMPLOYEE OF A PUBLIC SAFETY COMMUNICATIONS CENTER WHO ANSWERS THE TELEPHONE AND RECORDS CALL FOR SERVICE. CENTRAL STATION: A BUILDING OR SUITE OF OFFICES THAT HOUSES A COMPANY ENGAGED IN THE MONITORING OF ALARM SYSTEMS. THE CENTRAL STATION CAN NOT RUN WITHOUT POWER SUPPLIES, INCLUDING BACKUP POWER SUPPLIES, ARE ESSENTIAL TO PROPER, CONTINUOUS OPERATION OF THE CENTRAL STATION.
 Glossary of Terms CONTROL PANEL: EQUIPMENT THAT IS LOCATED AT THE PROTECTED PREMISES AND THAT CONTROLS THE ALARM SYSTEMS, SENDS SIGNALS TO THE CENTRAL STATION AND ALLOWS THE SUSCRIBER TO TURN THE ALARM SYSTEM OFF. DEALER: COMPANY WHICH SELLS, INSTALLS, LEASES, AND SERVICES ALARM SYSTEMS. OPERATING ROOM: THE AREA WITHIN A CENTRAL STATION THAT IS PHYSICALLY SECURE AND TO WHICH REMOTE ALARM CIRCUITS ARE CONNECTED. PERSONNEL ARE IN ATTENDANCE AT ALL TIMES TO OVERSEE THE CIRCUITS AND INVESTIGATE THE SIGNALS.
Glossary of Terms CONTROL PANEL: EQUIPMENT THAT IS LOCATED AT THE PROTECTED PREMISES AND THAT CONTROLS THE ALARM SYSTEMS, SENDS SIGNALS TO THE CENTRAL STATION AND ALLOWS THE SUSCRIBER TO TURN THE ALARM SYSTEM OFF. DEALER: COMPANY WHICH SELLS, INSTALLS, LEASES, AND SERVICES ALARM SYSTEMS. OPERATING ROOM: THE AREA WITHIN A CENTRAL STATION THAT IS PHYSICALLY SECURE AND TO WHICH REMOTE ALARM CIRCUITS ARE CONNECTED. PERSONNEL ARE IN ATTENDANCE AT ALL TIMES TO OVERSEE THE CIRCUITS AND INVESTIGATE THE SIGNALS.
 Glossary of Terms OPERATOR: AN EMPLOYEE WORKING AT THE CENTRAL STATION WHOSE DUTIES ARE TO PROVIDE IMMEDIATE ATTENTION TO AND PROCESSING OF ALL SIGNALS RECEIVED. PASSWORD/PASS CODE: SECRET CODE NUMBER OR WORD THAT GIVES YOU ACCESS TO A CONTROL UNIT OR A COMPUTER. RECEIVER: ELECTRICALLY OPERATED UNIT LOCATED AT A CENTRAL STATION WHICH MONITORS THE STATUS OF A PROTECTED PREMISES. THE RECEIVING EQUIPMENT CONNECTED TO AN AUTOMATION SYSTEM RECEIVES SIGNALS FROM THE PROTECTED PREMISES AND TRANSMITS THEM TO THE AUTOMATION SYSTEM.
Glossary of Terms OPERATOR: AN EMPLOYEE WORKING AT THE CENTRAL STATION WHOSE DUTIES ARE TO PROVIDE IMMEDIATE ATTENTION TO AND PROCESSING OF ALL SIGNALS RECEIVED. PASSWORD/PASS CODE: SECRET CODE NUMBER OR WORD THAT GIVES YOU ACCESS TO A CONTROL UNIT OR A COMPUTER. RECEIVER: ELECTRICALLY OPERATED UNIT LOCATED AT A CENTRAL STATION WHICH MONITORS THE STATUS OF A PROTECTED PREMISES. THE RECEIVING EQUIPMENT CONNECTED TO AN AUTOMATION SYSTEM RECEIVES SIGNALS FROM THE PROTECTED PREMISES AND TRANSMITS THEM TO THE AUTOMATION SYSTEM.
 Glossary of Terms SIGNAL: MESSAGE RELAYED FROM A CONTROL PANEL TO ITS CORRESPONDING RECEIVER AT THE CENTRAL STATION. SUBSCRIBER: THE USER OF A PREMISES PROTECTED BY THE CENTRAL STATION BURGLAR ALARM SYSTEM. AN AUTHORIZED REPRESENTIVE OF THE USER MAY ALSO BE CONSIDERED A SUBSCRIBER. WORKSTATION: SCREEN AND KEYBOARD AT WHICH THE OPERATOR WORKS. A TERMINAL IS CONNECTED TO THE MAIN COMPUTER. IN A PC ENVIRONMENT, IT IS CONNECTED TO THE PC.
Glossary of Terms SIGNAL: MESSAGE RELAYED FROM A CONTROL PANEL TO ITS CORRESPONDING RECEIVER AT THE CENTRAL STATION. SUBSCRIBER: THE USER OF A PREMISES PROTECTED BY THE CENTRAL STATION BURGLAR ALARM SYSTEM. AN AUTHORIZED REPRESENTIVE OF THE USER MAY ALSO BE CONSIDERED A SUBSCRIBER. WORKSTATION: SCREEN AND KEYBOARD AT WHICH THE OPERATOR WORKS. A TERMINAL IS CONNECTED TO THE MAIN COMPUTER. IN A PC ENVIRONMENT, IT IS CONNECTED TO THE PC.
 Automation Systems Telephone Systems
Automation Systems Telephone Systems
 Alternate Alarm Signal Delivery • Radio Network • Cellular Telephone • Packet Switched Network • Dedicated Line • Internet
Alternate Alarm Signal Delivery • Radio Network • Cellular Telephone • Packet Switched Network • Dedicated Line • Internet
 Unit Six: Review Questions 1. WHAT IS AN ALARM RECEIVER? HOW ARE THEY USED IN YOUR COMPANY? 2. HOW IS THE AUTOMATION SYSTEM USED IN YOUR COMPANY? 3. DESCRIBERTHE PHONE SYSTEM THAT YOUR COMPANY USES, INCLUDING KEY FEATURES AND EXTENSION NUMBERS WHERE APPLICABLE. 4. WHAT ALTERNATE ALARM SIGNAL DELIVERY SYSTEMS DOES YOUR COMPANY USE? HOW ARE THEY USED? 5. WHAT OTHER SYSTEMS ARE IN USE IN YOUR COMPANY?
Unit Six: Review Questions 1. WHAT IS AN ALARM RECEIVER? HOW ARE THEY USED IN YOUR COMPANY? 2. HOW IS THE AUTOMATION SYSTEM USED IN YOUR COMPANY? 3. DESCRIBERTHE PHONE SYSTEM THAT YOUR COMPANY USES, INCLUDING KEY FEATURES AND EXTENSION NUMBERS WHERE APPLICABLE. 4. WHAT ALTERNATE ALARM SIGNAL DELIVERY SYSTEMS DOES YOUR COMPANY USE? HOW ARE THEY USED? 5. WHAT OTHER SYSTEMS ARE IN USE IN YOUR COMPANY?
 Unit Seven: Underwriter’s Laboratories/ Factory Mutual Know your objectives!
Unit Seven: Underwriter’s Laboratories/ Factory Mutual Know your objectives!
 Underwriter’s Laboratories and Factory Mutual’s Role in the Alarm Industry • Test Components • Inspect and certificate the installed alarm systems. • Inspect and certificate Central Stations
Underwriter’s Laboratories and Factory Mutual’s Role in the Alarm Industry • Test Components • Inspect and certificate the installed alarm systems. • Inspect and certificate Central Stations
 Verification Procedures for Systems with UL/FM Certificated Line Security Vs. Verification for Systems without UL/FM Certificated Line Security
Verification Procedures for Systems with UL/FM Certificated Line Security Vs. Verification for Systems without UL/FM Certificated Line Security
 Underwriter’s Laboratories/Factory Mutual • Central Station Facilities • Central Station Fire Protection • Central Station Emergency Lighting • Central Station Alarm Receivers • Central Station Power Systems • Remote Site Operations • Inspections
Underwriter’s Laboratories/Factory Mutual • Central Station Facilities • Central Station Fire Protection • Central Station Emergency Lighting • Central Station Alarm Receivers • Central Station Power Systems • Remote Site Operations • Inspections
 Unit Seven: Review Questions 1. WHAT IS UNDERWRITER’S LABORATORIES ROLE IN THE ALARM INDUSTRY? 2. WHAT IS FACTORY MUTUAL’S ROLE IN THE ALARM INDUSTRY? 3. WHAT DOES YOUR CENTRAL STATION USE FOR ITS MAIN POWER SUPPLY? STANDBY POWER SUPPLY? 4. DOES YOUR COMPANY HAVE ANY REMOTE SITES? WHAT DO THEY DO? 5. WHAT ARE YOUR RESPONSIBILITIES DURING AN INSPECTION?
Unit Seven: Review Questions 1. WHAT IS UNDERWRITER’S LABORATORIES ROLE IN THE ALARM INDUSTRY? 2. WHAT IS FACTORY MUTUAL’S ROLE IN THE ALARM INDUSTRY? 3. WHAT DOES YOUR CENTRAL STATION USE FOR ITS MAIN POWER SUPPLY? STANDBY POWER SUPPLY? 4. DOES YOUR COMPANY HAVE ANY REMOTE SITES? WHAT DO THEY DO? 5. WHAT ARE YOUR RESPONSIBILITIES DURING AN INSPECTION?
 Unit Eight: Telephone and Radio Communications Know your objectives!
Unit Eight: Telephone and Radio Communications Know your objectives!
 Telephone Techniques General Telephone Handling Procedures Answering Multiple Telephone Calls Speak Distinctly Observe Telephone Courtesy Terminate Calls Positively and Courteously Specific Call Handling Procedures
Telephone Techniques General Telephone Handling Procedures Answering Multiple Telephone Calls Speak Distinctly Observe Telephone Courtesy Terminate Calls Positively and Courteously Specific Call Handling Procedures
 Emotional Subscribers • Stay in control of yourself • Be firm and in Charge • Be generic • Don’t antagonize the subscriber • Acknowledge concerns and work to a solution
Emotional Subscribers • Stay in control of yourself • Be firm and in Charge • Be generic • Don’t antagonize the subscriber • Acknowledge concerns and work to a solution
 Telephone Messages: Receiving, Recording, Notifying Personnel • Take all information in reference to the person calling • Write it down- Never leave details to memory! • Verify the information • Use message books • Identify yourself on the message so that the person may contact you with any questions.
Telephone Messages: Receiving, Recording, Notifying Personnel • Take all information in reference to the person calling • Write it down- Never leave details to memory! • Verify the information • Use message books • Identify yourself on the message so that the person may contact you with any questions.
 ALPHA LIMA WHISKEY BRAVO MIKE X-RAY CHARLIE NOVEMBER YANKEE DELTA OSCAR ZULU ECHO PAPA FOXTROT QUEBEC GOLF ROMEO HOTEL SIERRA INDIA TANGO JULIETT UNIFORM KILO VICTOR
ALPHA LIMA WHISKEY BRAVO MIKE X-RAY CHARLIE NOVEMBER YANKEE DELTA OSCAR ZULU ECHO PAPA FOXTROT QUEBEC GOLF ROMEO HOTEL SIERRA INDIA TANGO JULIETT UNIFORM KILO VICTOR
 24– HOUR TIME Also known as military time
24– HOUR TIME Also known as military time
 Unit Eight: Review Questions 1. WHAT IMPORTANCE DO YOU PROJECT EVERY TIME YOU ANSWER THE PHONE? 2. WHAT ARE YOUR COMPANY’S POLICIES ON ANSWERING THE PHONE? WHAT DO YOU SAY AND HOW DO YOU SAY IT? 3. HOW DO YOU HANDLE ANSWERING MULTIPLE PHONE LINES AT ONCE? 4. WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU HAVE TO DEAL WITH EXCITED OR HYSTERICAL CALLERS? 5. WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO RECORD ALL INFORMATION ON A CALL BY ENTERING IT INTO THE COMPUTER?
Unit Eight: Review Questions 1. WHAT IMPORTANCE DO YOU PROJECT EVERY TIME YOU ANSWER THE PHONE? 2. WHAT ARE YOUR COMPANY’S POLICIES ON ANSWERING THE PHONE? WHAT DO YOU SAY AND HOW DO YOU SAY IT? 3. HOW DO YOU HANDLE ANSWERING MULTIPLE PHONE LINES AT ONCE? 4. WHAT PROCEDURES DO YOU HAVE TO DEAL WITH EXCITED OR HYSTERICAL CALLERS? 5. WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO RECORD ALL INFORMATION ON A CALL BY ENTERING IT INTO THE COMPUTER?
 Unit Eight: Review Questions 6. WHAT ARE YOUR COMPANY’S PROCEDURES FOR TAKING MESSAGES AND RELAYING THEM TO THE PROPER PERSON? 7. CAN YOU RECITE AND USE THE INTERNATIONAL PHONETIC ALPHABET? 8. CAN YOU EASILY USE 24 -HOUR TIME?
Unit Eight: Review Questions 6. WHAT ARE YOUR COMPANY’S PROCEDURES FOR TAKING MESSAGES AND RELAYING THEM TO THE PROPER PERSON? 7. CAN YOU RECITE AND USE THE INTERNATIONAL PHONETIC ALPHABET? 8. CAN YOU EASILY USE 24 -HOUR TIME?
 Unit Nine: Emergency Procedures Know your objectives!
Unit Nine: Emergency Procedures Know your objectives!
 SYMPTOMS OF PENDING SYSTEM OF COMPUTER PROBLEMS: • The system seems to be slowing down. Information is coming slower than normal. • The display colors are wrong or information is scrambled. • The system suddenly pauses and stops processing information, then starts again. It seems as if it “took a break. ” • The system fails to work at all, i. e. , keyboard inputs, alarm receiver inputs, etc. do not show up on the screen. In effect, the system is frozen.
SYMPTOMS OF PENDING SYSTEM OF COMPUTER PROBLEMS: • The system seems to be slowing down. Information is coming slower than normal. • The display colors are wrong or information is scrambled. • The system suddenly pauses and stops processing information, then starts again. It seems as if it “took a break. ” • The system fails to work at all, i. e. , keyboard inputs, alarm receiver inputs, etc. do not show up on the screen. In effect, the system is frozen.
 Automation Failure Locate the procedures used in the company to deal with partial or full failure of the automation systems, including the location of written instructions for the response to alarm accounts and how to read receiver tapes.
Automation Failure Locate the procedures used in the company to deal with partial or full failure of the automation systems, including the location of written instructions for the response to alarm accounts and how to read receiver tapes.
 Receiver Failure Locate the procedures used for monitoring the condition of alarm receivers and the procedures of non-functioning units.
Receiver Failure Locate the procedures used for monitoring the condition of alarm receivers and the procedures of non-functioning units.
 Personal Shortages Locate your company policy and procedure that is enacted when a personnel shortage occurs! Phone System Failure Locate the procedures for handling failures in the phone system!
Personal Shortages Locate your company policy and procedure that is enacted when a personnel shortage occurs! Phone System Failure Locate the procedures for handling failures in the phone system!
 Environmental and Man-Made Disasters Which occur in your part of the country? Hurricane Tornado Seasonal Flooding Flash Flooding Seasonal High Wind Forest Fire Mudslide Earthquakes Thunderstorm Torrential Rain Blizzard Extreme Cold Ice Storm Extreme Heat
Environmental and Man-Made Disasters Which occur in your part of the country? Hurricane Tornado Seasonal Flooding Flash Flooding Seasonal High Wind Forest Fire Mudslide Earthquakes Thunderstorm Torrential Rain Blizzard Extreme Cold Ice Storm Extreme Heat
 Unit Nine: Review Questions 1. HOW DO YOU DEAL WITH A FAILURE OF THE AUTOMATION SYSTEM? 2. HOW DO YOU DEAL WITH FAILURE OF ALARM RECEIVING EQUIPMENT? 3. WHAT ARE YOU RESPONSIBILITIES FOR DEALING WITH SHORTAGES OF PERSONNEL? HOW ARE THESE SITUATIONS HANDLED? 4. HOW DO YOU DEAL WITH A FAILURE OF THE PHONE SYSTEM? 5. HOW DO YOU DEAL WITH ENVIRONMENTAL AND MAN -MADE DISASTERS?
Unit Nine: Review Questions 1. HOW DO YOU DEAL WITH A FAILURE OF THE AUTOMATION SYSTEM? 2. HOW DO YOU DEAL WITH FAILURE OF ALARM RECEIVING EQUIPMENT? 3. WHAT ARE YOU RESPONSIBILITIES FOR DEALING WITH SHORTAGES OF PERSONNEL? HOW ARE THESE SITUATIONS HANDLED? 4. HOW DO YOU DEAL WITH A FAILURE OF THE PHONE SYSTEM? 5. HOW DO YOU DEAL WITH ENVIRONMENTAL AND MAN -MADE DISASTERS?


