463f778abd661fa81a07da9e294783df.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards for point-of-care device communication: Overview SCATA, London, 5 th May, 2005 Melvin Reynolds, AMS Consulting, Ross-on-Wye, UK Chair CEN TC 251 WGIV Health informatics – Technologies for interoperability, Chair ISO TC 215 WG 2 Health informatics – Messages and communications; Past-chair ISO TC 215 WG 2. 1 Health informatics – Device communications, Co-chair IEEE 1073 Medical device communications. with thanks to: Thomas Norgall, Fraunhofer Institute, Erlangen, Todd Cooper, Breakthrough Solutions, San Diego and
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards for point-of-care device communication: Overview SCATA, London, 5 th May, 2005 Melvin Reynolds, AMS Consulting, Ross-on-Wye, UK Chair CEN TC 251 WGIV Health informatics – Technologies for interoperability, Chair ISO TC 215 WG 2 Health informatics – Messages and communications; Past-chair ISO TC 215 WG 2. 1 Health informatics – Device communications, Co-chair IEEE 1073 Medical device communications. with thanks to: Thomas Norgall, Fraunhofer Institute, Erlangen, Todd Cooper, Breakthrough Solutions, San Diego and
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Overview v v v Requirements Interoperability History The (content) standards Conclusions Discussion
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Overview v v v Requirements Interoperability History The (content) standards Conclusions Discussion
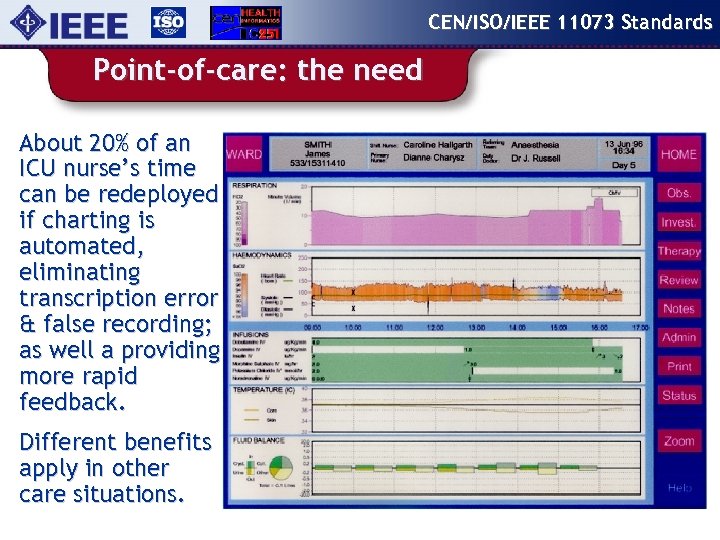 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Point-of-care: the need About 20% of an ICU nurse’s time can be redeployed if charting is automated, eliminating transcription error & false recording; as well a providing more rapid feedback. Different benefits apply in other care situations.
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Point-of-care: the need About 20% of an ICU nurse’s time can be redeployed if charting is automated, eliminating transcription error & false recording; as well a providing more rapid feedback. Different benefits apply in other care situations.
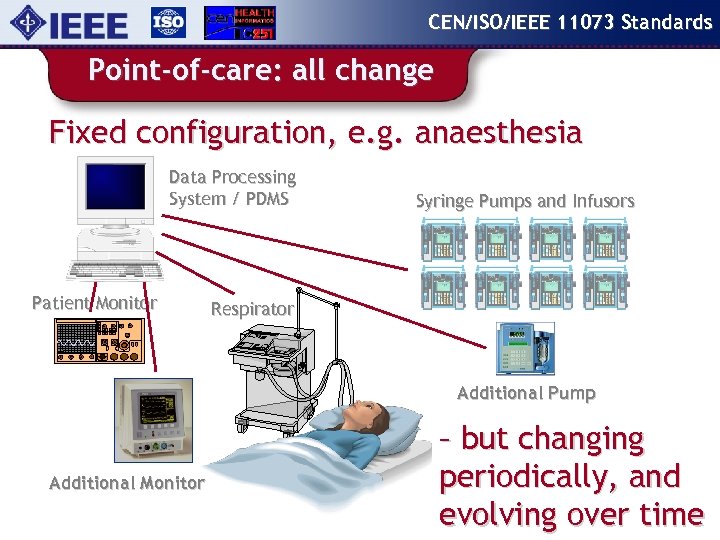 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Point-of-care: all change Fixed configuration, e. g. anaesthesia Data Processing System / PDMS Patient Monitor Syringe Pumps and Infusors Respirator Additional Pump Additional Monitor – but changing periodically, and evolving over time
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Point-of-care: all change Fixed configuration, e. g. anaesthesia Data Processing System / PDMS Patient Monitor Syringe Pumps and Infusors Respirator Additional Pump Additional Monitor – but changing periodically, and evolving over time
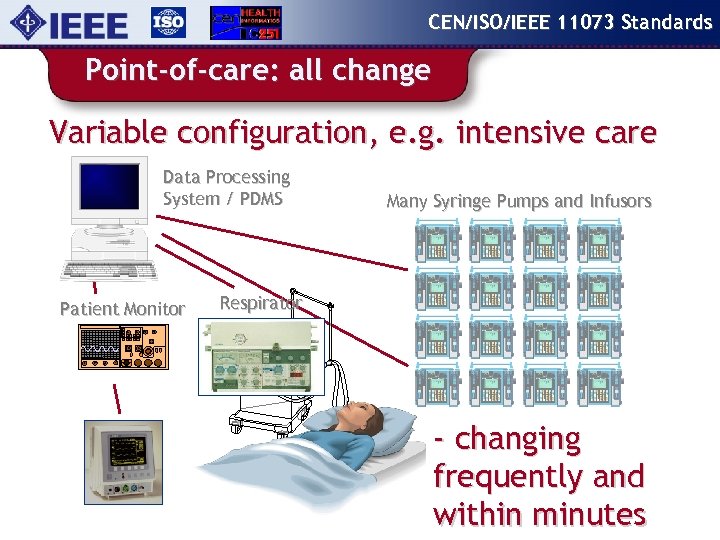 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Point-of-care: all change Variable configuration, e. g. intensive care Data Processing System / PDMS Patient Monitor Many Syringe Pumps and Infusors Respirator - changing frequently and within minutes
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Point-of-care: all change Variable configuration, e. g. intensive care Data Processing System / PDMS Patient Monitor Many Syringe Pumps and Infusors Respirator - changing frequently and within minutes
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Interoperability: ability of two or more systems or components to exchange information and to use the information that has been exchanged source: IEEE Standard Computer Dictionary: A Compilation of IEEE Standard Computer Glossaries, IEEE, 1990 Functional interoperability: Shared Architectures, Methods & Frameworks Semantic interoperability: Shared Data types, Terminologies, Codings
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Interoperability: ability of two or more systems or components to exchange information and to use the information that has been exchanged source: IEEE Standard Computer Dictionary: A Compilation of IEEE Standard Computer Glossaries, IEEE, 1990 Functional interoperability: Shared Architectures, Methods & Frameworks Semantic interoperability: Shared Data types, Terminologies, Codings
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Interoperability Point-of-care medical device communication (IEEE 1073) Charter: v v Provide real-time plug-and-play interoperability for patient-connected medical devices Facilitate the efficient exchange of vital signs and medical device data, acquired at the point-of-care, in all health care environments … Leveraging off-the-shelf technologies, scaling across a wide range of system complexities, and supporting commercially viable implementations.
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Interoperability Point-of-care medical device communication (IEEE 1073) Charter: v v Provide real-time plug-and-play interoperability for patient-connected medical devices Facilitate the efficient exchange of vital signs and medical device data, acquired at the point-of-care, in all health care environments … Leveraging off-the-shelf technologies, scaling across a wide range of system complexities, and supporting commercially viable implementations.
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Context Health informatics: Generally interpreted as being in ISO/OSI Level 7 Medical device communication: Works at all ISO/OSI Levels, Directly in ISO/OSI Levels 7 – 5 In Levels 1 – 4, chiefly by reference to other standards (such as Ir. DA or 802. 11)
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Context Health informatics: Generally interpreted as being in ISO/OSI Level 7 Medical device communication: Works at all ISO/OSI Levels, Directly in ISO/OSI Levels 7 – 5 In Levels 1 – 4, chiefly by reference to other standards (such as Ir. DA or 802. 11)
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Architecture Requirements: v v v True interoperability across all 7 -layers from the ‘connector’ to the end application Mechanisms to support the strong quality of service requirements placed on regulated medical devices Maintainability as communications technology and applications change
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Architecture Requirements: v v v True interoperability across all 7 -layers from the ‘connector’ to the end application Mechanisms to support the strong quality of service requirements placed on regulated medical devices Maintainability as communications technology and applications change
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Series title (National, e. g. BS) EN ISO/IEEE 11073 -xyyzz Health informatics Point-of-care medical device communication x partition (general): yy subsection (group) zz detail (specialised)
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Series title (National, e. g. BS) EN ISO/IEEE 11073 -xyyzz Health informatics Point-of-care medical device communication x partition (general): yy subsection (group) zz detail (specialised)
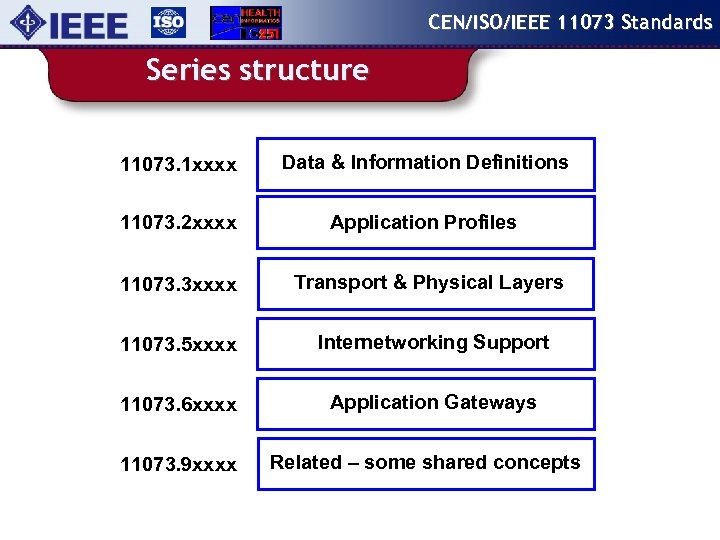 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Series structure 11073. 1 xxxx Data & Information Definitions 11073. 2 xxxx Application Profiles 11073. 3 xxxx Transport & Physical Layers 11073. 5 xxxx Internetworking Support 11073. 6 xxxx Application Gateways 11073. 9 xxxx Related – some shared concepts
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Series structure 11073. 1 xxxx Data & Information Definitions 11073. 2 xxxx Application Profiles 11073. 3 xxxx Transport & Physical Layers 11073. 5 xxxx Internetworking Support 11073. 6 xxxx Application Gateways 11073. 9 xxxx Related – some shared concepts
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -1 xxxx content 11073. 1 xxxx Data & Information Definitions Semantics needed to communicate a device’s application data, status and control information. Three main components: v Nomenclature: 11073. 10101 v Domain Information Model (DIM): 11073. 10201 v Device Specialisations: 11073. 103 xx
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -1 xxxx content 11073. 1 xxxx Data & Information Definitions Semantics needed to communicate a device’s application data, status and control information. Three main components: v Nomenclature: 11073. 10101 v Domain Information Model (DIM): 11073. 10201 v Device Specialisations: 11073. 103 xx
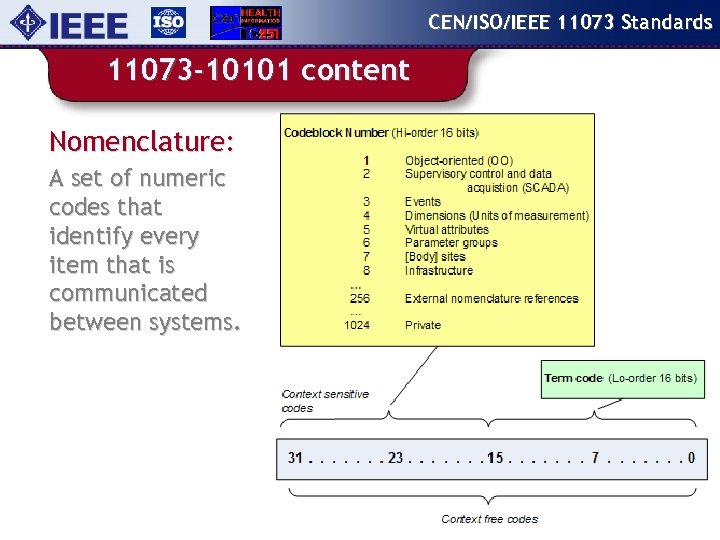 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -10101 content Nomenclature: A set of numeric codes that identify every item that is communicated between systems.
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -10101 content Nomenclature: A set of numeric codes that identify every item that is communicated between systems.
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -10201 content Domain Information Model: An object oriented data model that specifies objects, attribute groups, event reports, and services that may be used to communicate device data and to control / configure the reporting of information. . . v v v Medical Devices and Functionalities Measured Data and Settings Alert Information v v v Remote Control Patient Information Communication
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -10201 content Domain Information Model: An object oriented data model that specifies objects, attribute groups, event reports, and services that may be used to communicate device data and to control / configure the reporting of information. . . v v v Medical Devices and Functionalities Measured Data and Settings Alert Information v v v Remote Control Patient Information Communication
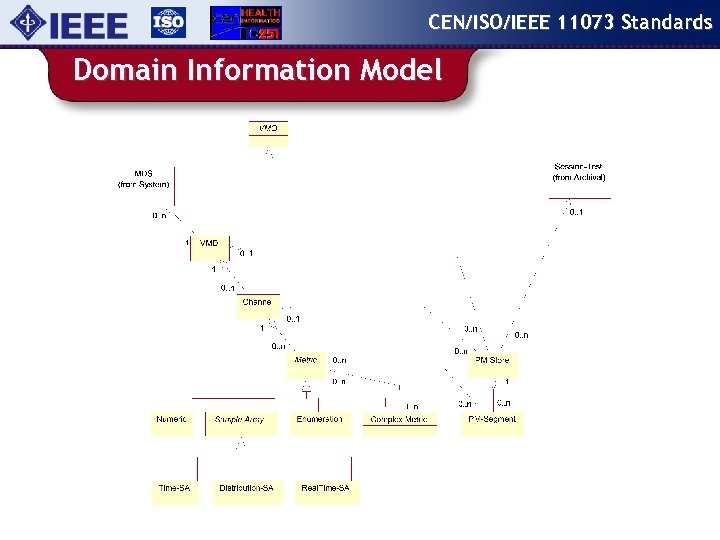 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Domain Information Model
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Domain Information Model
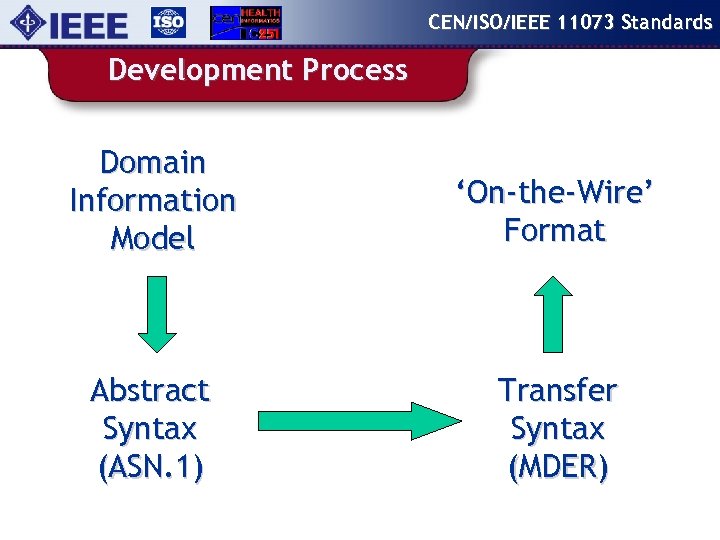 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Development Process Domain Information Model ‘On-the-Wire’ Format Abstract Syntax (ASN. 1) Transfer Syntax (MDER)
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Development Process Domain Information Model ‘On-the-Wire’ Format Abstract Syntax (ASN. 1) Transfer Syntax (MDER)
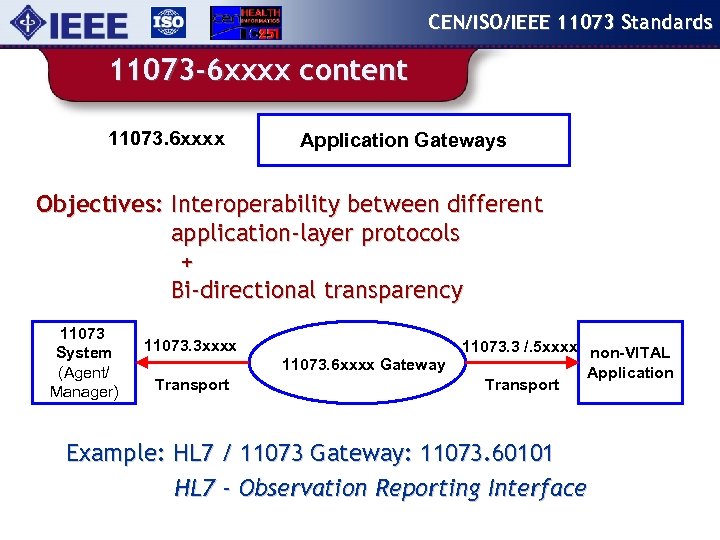 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -6 xxxx content 11073. 6 xxxx Application Gateways Objectives: Interoperability between different application-layer protocols + Bi-directional transparency 11073 System (Agent/ Manager) 11073. 3 xxxx 11073. 6 xxxx Gateway Transport 11073. 3 /. 5 xxxx non-VITAL Application Transport Example: HL 7 / 11073 Gateway: 11073. 60101 HL 7 - Observation Reporting Interface
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -6 xxxx content 11073. 6 xxxx Application Gateways Objectives: Interoperability between different application-layer protocols + Bi-directional transparency 11073 System (Agent/ Manager) 11073. 3 xxxx 11073. 6 xxxx Gateway Transport 11073. 3 /. 5 xxxx non-VITAL Application Transport Example: HL 7 / 11073 Gateway: 11073. 60101 HL 7 - Observation Reporting Interface
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -60101 content HL 7 - Observation Reporting Interface Objective: To ensure that … information … from devices using … 11073 standards is conveyed with appropriate … identification of source device system, medical device, channel and metric (… with required annotation …). For traceability, and to enable safe computation from data, the 11073… nomenclature is retained … payload of the HL 7 message/document that carries the information to the target information system.
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -60101 content HL 7 - Observation Reporting Interface Objective: To ensure that … information … from devices using … 11073 standards is conveyed with appropriate … identification of source device system, medical device, channel and metric (… with required annotation …). For traceability, and to enable safe computation from data, the 11073… nomenclature is retained … payload of the HL 7 message/document that carries the information to the target information system.
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -60101 HL 7 ORI Example HL 7 v 2. 6 message: MSH|||^~&|Vendor_name||NUR||200312021203||ORU^R 01|02110212073000458038 |P|2. 3| |||||| PID|||999 -99 -9999 ||Smith^John^L |||||||999 -99 -9999 |||||| PV 1|||CU 1^^BED 1||||^^^||||||||||||||||||||||| OBR|||||||2003120235||||||||||||||||||| OBX||SN|147842^MDC_ECG_HEART_RATE^MDC^^HR^local||=^83|264864^MDC_DIM_BEAT_PER_MIN^MDC^^beat/min^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|134276^MDC_EVT_ECG_V_P_C^MDC^^PVC rate^local||=^0|264864^MDC_DIM_BEAT_PER_MIN^MDC^^beat/min^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|131841^MDC_ECG_AMPL_ST_LEAD_I^MDC^^ST elev lead I^local||=^0. 01|266418^MDC_DIM_X_VOLT^MDC^^m. V^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|131842^MDC_ECG_AMPL_ST LEAD_II^MDC^^ST elev lead II^local||=^0. 01|266418^MDC_DIM_X_VOLT^MDC^^m. V^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|131901^MDC_ECG_AMPL_ST_LEAD_III^MDC^^ST elev lead III^local||=^0. 01|266418^MDC_DIM_X_VOLT^MDC^^m. V^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|150324^MDC_SAT_O 2_ART^MDC^^SPO 2^local||=^97|262688^MDC_DIM_PERCENT^MDC^^%sat^local|||||R|||2003120235|||||460230^MDC _UPEXT_FINGER^MDC^Finger NOS^local^^1 OBX||SN|149538^MDC_PLETH_PULS_RATE^MDC^^Pulse rate^local||=^83|264896^MDC_DIM_PULS_PER_MIN^MDC^^Pulse/min^local|||||R|||2003120235|||||460230^MDC_UPEXT_FINGER^MDC^Finger NOS^local^^1 OBX||ST|150302^MDC_PRESS_CUFF_DIA^MDC^^NIBP dia^local||=^80|266016^MDC_DIM_MMHG^MDC^^mm. Hg^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||||458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1 OBX||ST|150303^MDC_PRESS_CUFF_MEAN^MDC^^NIBP mean^local||=^93|266016^MDC_DIM_MMHG^MDC^^mm. Hg^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||||458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1 OBX||ST|150301^MDC_PRESS_CUFF_SYS^MDC^^NIBP sys^local||=^120|266016^MDC_DIM_MMHG^MDC^^mm. Hg^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||||458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1 OBX||ST|149546^MDC_PULS_RATE_NON_INV^MDC^^Pulse rate^local||=^83|264896^MDC_DIM_PULS_PER_MIN^MDC^^Pulse/min^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||||458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -60101 HL 7 ORI Example HL 7 v 2. 6 message: MSH|||^~&|Vendor_name||NUR||200312021203||ORU^R 01|02110212073000458038 |P|2. 3| |||||| PID|||999 -99 -9999 ||Smith^John^L |||||||999 -99 -9999 |||||| PV 1|||CU 1^^BED 1||||^^^||||||||||||||||||||||| OBR|||||||2003120235||||||||||||||||||| OBX||SN|147842^MDC_ECG_HEART_RATE^MDC^^HR^local||=^83|264864^MDC_DIM_BEAT_PER_MIN^MDC^^beat/min^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|134276^MDC_EVT_ECG_V_P_C^MDC^^PVC rate^local||=^0|264864^MDC_DIM_BEAT_PER_MIN^MDC^^beat/min^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|131841^MDC_ECG_AMPL_ST_LEAD_I^MDC^^ST elev lead I^local||=^0. 01|266418^MDC_DIM_X_VOLT^MDC^^m. V^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|131842^MDC_ECG_AMPL_ST LEAD_II^MDC^^ST elev lead II^local||=^0. 01|266418^MDC_DIM_X_VOLT^MDC^^m. V^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|131901^MDC_ECG_AMPL_ST_LEAD_III^MDC^^ST elev lead III^local||=^0. 01|266418^MDC_DIM_X_VOLT^MDC^^m. V^local|||||R|||2003120235||| OBX||SN|150324^MDC_SAT_O 2_ART^MDC^^SPO 2^local||=^97|262688^MDC_DIM_PERCENT^MDC^^%sat^local|||||R|||2003120235|||||460230^MDC _UPEXT_FINGER^MDC^Finger NOS^local^^1 OBX||SN|149538^MDC_PLETH_PULS_RATE^MDC^^Pulse rate^local||=^83|264896^MDC_DIM_PULS_PER_MIN^MDC^^Pulse/min^local|||||R|||2003120235|||||460230^MDC_UPEXT_FINGER^MDC^Finger NOS^local^^1 OBX||ST|150302^MDC_PRESS_CUFF_DIA^MDC^^NIBP dia^local||=^80|266016^MDC_DIM_MMHG^MDC^^mm. Hg^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||||458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1 OBX||ST|150303^MDC_PRESS_CUFF_MEAN^MDC^^NIBP mean^local||=^93|266016^MDC_DIM_MMHG^MDC^^mm. Hg^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||||458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1 OBX||ST|150301^MDC_PRESS_CUFF_SYS^MDC^^NIBP sys^local||=^120|266016^MDC_DIM_MMHG^MDC^^mm. Hg^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||||458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1 OBX||ST|149546^MDC_PULS_RATE_NON_INV^MDC^^Pulse rate^local||=^83|264896^MDC_DIM_PULS_PER_MIN^MDC^^Pulse/min^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||||458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -60101 HL 7 ORI Example HL 7 v 2. 6 message 11073 payload: OBX||SN|147842^MDC_ECG_HEART_RATE^MDC^^HR^local||=^83| 264864^MDC_DIM_BEAT_PER_MIN^MDC^^beat/min^local|||||R|||2003120235||||| OBX||SN|134276^MDC_EVT_ECG_V_P_C^MDC^^PVC rate^local||=^0| 264864^MDC_DIM_BEAT_PER_MIN^MDC^^beat/min^local|||||R|||2003120235||||| OBX||SN|131841^MDC_ECG_AMPL_ST_LEAD_I^MDC^^ST elev lead I^local||=^0. 01| 266418^MDC_DIM_X_VOLT^MDC^^m. V^local|||||R|||2003120235||||| … OBX||SN|150324^MDC_SAT_O 2_ART^MDC^^SPO 2^local||=^97| 262688^MDC_DIM_PERCENT^MDC ^^%sat^local|||||R|||2003120235||||| 460230^MDC_UPEXT_FINGER^MDC^Finger NOS^local^^1 OBX||SN|149538^MDC_PLETH_PULS_RATE^MDC^^Pulse rate^local||=^83| 264896^MDC_DIM_PULS_PER_MIN^MDC^^Pulse/min^local|||||R|||2003120235|||| |460230^MDC_UPEXT_FINGER^MDC^Finger NOS^local^^1 … OBX||ST|150301^MDC_PRESS_CUFF_SYS^MDC^^NIBP sys^local||=^120| 266016^MDC_DIM_MMHG^MDC^^mm. Hg^local|||||R|||20031202120030||||| 458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1 OBX||ST|149546^MDC_PULS_RATE_NON_INV^MDC^^Pulse rate^local||=^83| 264896^MDC_DIM_PULS_PER_MIN^MDC^^Pulse/min^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||| |458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards 11073 -60101 HL 7 ORI Example HL 7 v 2. 6 message 11073 payload: OBX||SN|147842^MDC_ECG_HEART_RATE^MDC^^HR^local||=^83| 264864^MDC_DIM_BEAT_PER_MIN^MDC^^beat/min^local|||||R|||2003120235||||| OBX||SN|134276^MDC_EVT_ECG_V_P_C^MDC^^PVC rate^local||=^0| 264864^MDC_DIM_BEAT_PER_MIN^MDC^^beat/min^local|||||R|||2003120235||||| OBX||SN|131841^MDC_ECG_AMPL_ST_LEAD_I^MDC^^ST elev lead I^local||=^0. 01| 266418^MDC_DIM_X_VOLT^MDC^^m. V^local|||||R|||2003120235||||| … OBX||SN|150324^MDC_SAT_O 2_ART^MDC^^SPO 2^local||=^97| 262688^MDC_DIM_PERCENT^MDC ^^%sat^local|||||R|||2003120235||||| 460230^MDC_UPEXT_FINGER^MDC^Finger NOS^local^^1 OBX||SN|149538^MDC_PLETH_PULS_RATE^MDC^^Pulse rate^local||=^83| 264896^MDC_DIM_PULS_PER_MIN^MDC^^Pulse/min^local|||||R|||2003120235|||| |460230^MDC_UPEXT_FINGER^MDC^Finger NOS^local^^1 … OBX||ST|150301^MDC_PRESS_CUFF_SYS^MDC^^NIBP sys^local||=^120| 266016^MDC_DIM_MMHG^MDC^^mm. Hg^local|||||R|||20031202120030||||| 458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1 OBX||ST|149546^MDC_PULS_RATE_NON_INV^MDC^^Pulse rate^local||=^83| 264896^MDC_DIM_PULS_PER_MIN^MDC^^Pulse/min^local|||||R|||20031202120030|||| |458572^MDC_UPEXT_ARM_UPPER^MDC^Upper arm^local^^1
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Conclusions v v 11073 is a comprehensive system of point-of-care medical device communication standards 11073 device types range from real-time-operating medical equipment to point-of-care test 11073 supports wired, wireless IR (and hopefully future wireless RF) network technologies 11073 provides plug-and-play, internetworking and application gateway capabilities
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Conclusions v v 11073 is a comprehensive system of point-of-care medical device communication standards 11073 device types range from real-time-operating medical equipment to point-of-care test 11073 supports wired, wireless IR (and hopefully future wireless RF) network technologies 11073 provides plug-and-play, internetworking and application gateway capabilities
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Conclusions v v v 11073 is used to a greater or lesser extent by the biggest companies in the business – often not declared! 11073 provides an open way of accessing: device networks data for real time decision support 11073 is being requested by health care providers & management organisations, e. g NHS NPf. IT, US DHHS, as they seek point-of-care to record transparency of information
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Conclusions v v v 11073 is used to a greater or lesser extent by the biggest companies in the business – often not declared! 11073 provides an open way of accessing: device networks data for real time decision support 11073 is being requested by health care providers & management organisations, e. g NHS NPf. IT, US DHHS, as they seek point-of-care to record transparency of information
 CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Contact details Thank you for your attention. Melvin Reynolds AMS Consulting Ashcote, Walford Road, Ross-on-Wye, HR 9 5 PQ, UK melvinr@ams-consulting. co. uk www. ieee 1073. org
CEN/ISO/IEEE 11073 Standards Contact details Thank you for your attention. Melvin Reynolds AMS Consulting Ashcote, Walford Road, Ross-on-Wye, HR 9 5 PQ, UK melvinr@ams-consulting. co. uk www. ieee 1073. org


