 Cell technologies in plant selection
Cell technologies in plant selection
 One of the priority areas in cell technology is their use in breeding, which and accelerates the traditional process of creating new forms and varieties of plants. Methods of isolated cells and tissues in vitro cultivation can be divided into two groups.
One of the priority areas in cell technology is their use in breeding, which and accelerates the traditional process of creating new forms and varieties of plants. Methods of isolated cells and tissues in vitro cultivation can be divided into two groups.
 1 st group. Supportive technologies of traditional breeding: l l l In vitro fertilization; Cultivation of cotyledons and immature embryos; Haploids obtaining through cultivation of anthers and microspores; Cryoconservation of isolated cells, tissues and organs; Clonal micropropagation of distant hybrids.
1 st group. Supportive technologies of traditional breeding: l l l In vitro fertilization; Cultivation of cotyledons and immature embryos; Haploids obtaining through cultivation of anthers and microspores; Cryoconservation of isolated cells, tissues and organs; Clonal micropropagation of distant hybrids.
 2 nd group. l l l The second group of methods leads to independent from traditional breeding obtaining of a new forms and varieties of plants: Cell selection with usage of callus tissue; Somatic hybridization (protoplasts fusion); Genetic engineering.
2 nd group. l l l The second group of methods leads to independent from traditional breeding obtaining of a new forms and varieties of plants: Cell selection with usage of callus tissue; Somatic hybridization (protoplasts fusion); Genetic engineering.
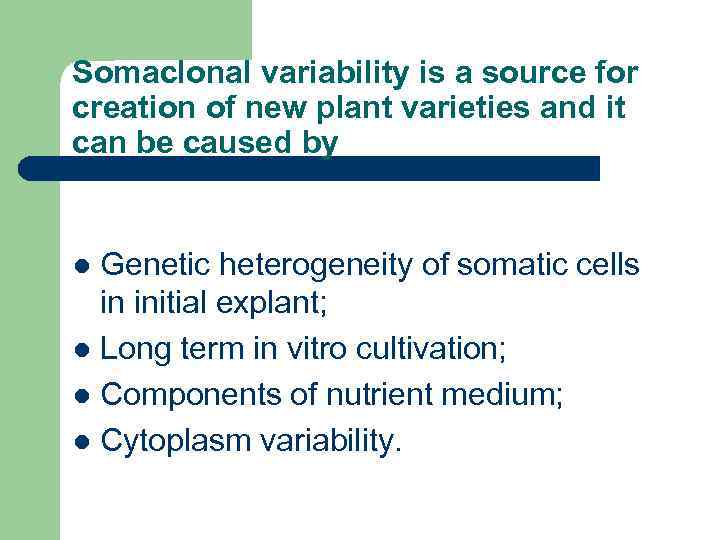 Somaclonal variability is a source for creation of new plant varieties and it can be caused by Genetic heterogeneity of somatic cells in initial explant; l Long term in vitro cultivation; l Components of nutrient medium; l Cytoplasm variability. l
Somaclonal variability is a source for creation of new plant varieties and it can be caused by Genetic heterogeneity of somatic cells in initial explant; l Long term in vitro cultivation; l Components of nutrient medium; l Cytoplasm variability. l
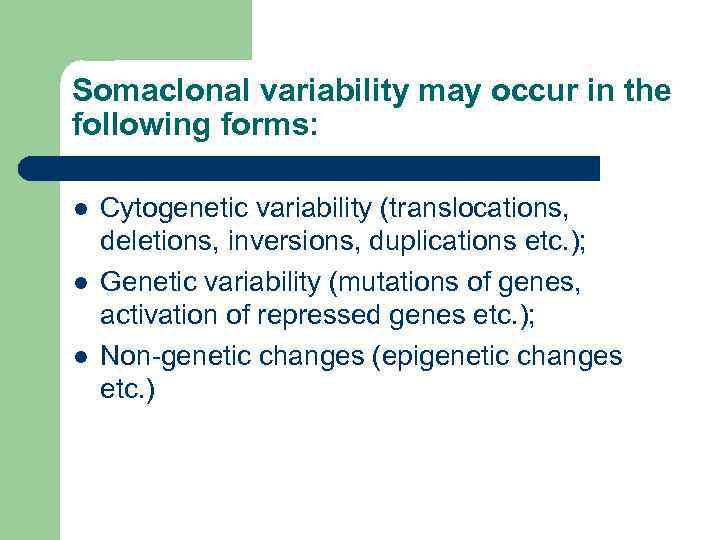 Somaclonal variability may occur in the following forms: l l l Cytogenetic variability (translocations, deletions, inversions, duplications etc. ); Genetic variability (mutations of genes, activation of repressed genes etc. ); Non-genetic changes (epigenetic changes etc. )
Somaclonal variability may occur in the following forms: l l l Cytogenetic variability (translocations, deletions, inversions, duplications etc. ); Genetic variability (mutations of genes, activation of repressed genes etc. ); Non-genetic changes (epigenetic changes etc. )
 Frequency and spectrum of somaclonal variability can be enhanced through usage of chemical (nitrosoguanidine, nitrosomethylurea, methylmethane sulfonate) and physical (UV-light, gamma-ray) mutagens
Frequency and spectrum of somaclonal variability can be enhanced through usage of chemical (nitrosoguanidine, nitrosomethylurea, methylmethane sulfonate) and physical (UV-light, gamma-ray) mutagens
 Cell selection is a set of methods for selection of natural and induced mutants in vitro on a cellular level
Cell selection is a set of methods for selection of natural and induced mutants in vitro on a cellular level
 Objects of selection: l Callus tissues; l Suspension culture; l Protoplasts.
Objects of selection: l Callus tissues; l Suspension culture; l Protoplasts.
 Suspension culture is the system of growing single cells and small cell aggregates in a liquid growth medium that is kept agitated by means of bubbling, shaking, or stirring so the cells do not settle out.
Suspension culture is the system of growing single cells and small cell aggregates in a liquid growth medium that is kept agitated by means of bubbling, shaking, or stirring so the cells do not settle out.
 There are couple methods of cell selection: l Direct selection; l Indirect selection; l Total selection; l Visual selection.
There are couple methods of cell selection: l Direct selection; l Indirect selection; l Total selection; l Visual selection.
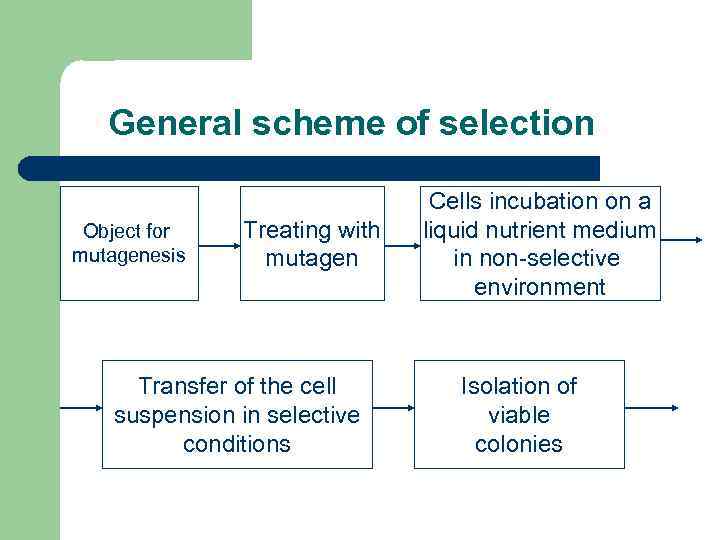 General scheme of selection Object for mutagenesis Treating with mutagen Transfer of the cell suspension in selective conditions Cells incubation on a liquid nutrient medium in non-selective environment Isolation of viable colonies
General scheme of selection Object for mutagenesis Treating with mutagen Transfer of the cell suspension in selective conditions Cells incubation on a liquid nutrient medium in non-selective environment Isolation of viable colonies
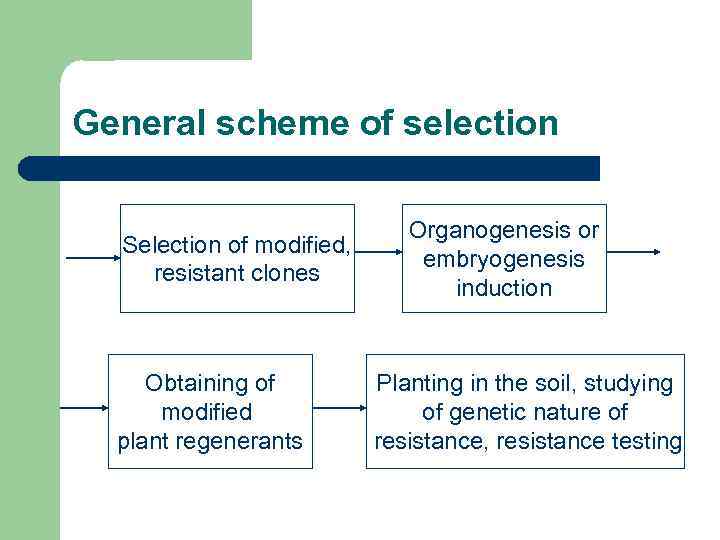 General scheme of selection Selection of modified, resistant clones Obtaining of modified plant regenerants Organogenesis or embryogenesis induction Planting in the soil, studying of genetic nature of resistance, resistance testing
General scheme of selection Selection of modified, resistant clones Obtaining of modified plant regenerants Organogenesis or embryogenesis induction Planting in the soil, studying of genetic nature of resistance, resistance testing
 Negative selection The basis of this method is usage of agents, which are selectively inhibit growth of nonmutant (wild) cells or lead to their death.
Negative selection The basis of this method is usage of agents, which are selectively inhibit growth of nonmutant (wild) cells or lead to their death.
 Total selection is selection with individual testing of all clones
Total selection is selection with individual testing of all clones
 Visual selection and non-selective screening when identification of lines in all population is made visually or through biochemical methods
Visual selection and non-selective screening when identification of lines in all population is made visually or through biochemical methods