 Cell Reproduction Mitosis
Cell Reproduction Mitosis
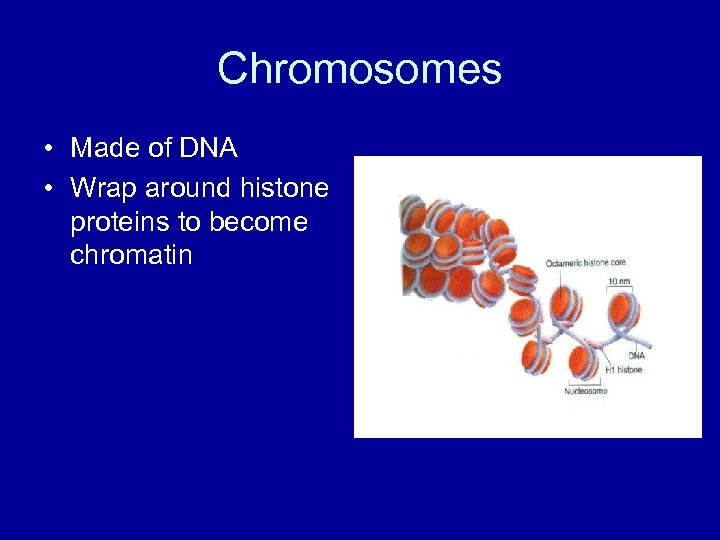 Chromosomes • Made of DNA • Wrap around histone proteins to become chromatin
Chromosomes • Made of DNA • Wrap around histone proteins to become chromatin
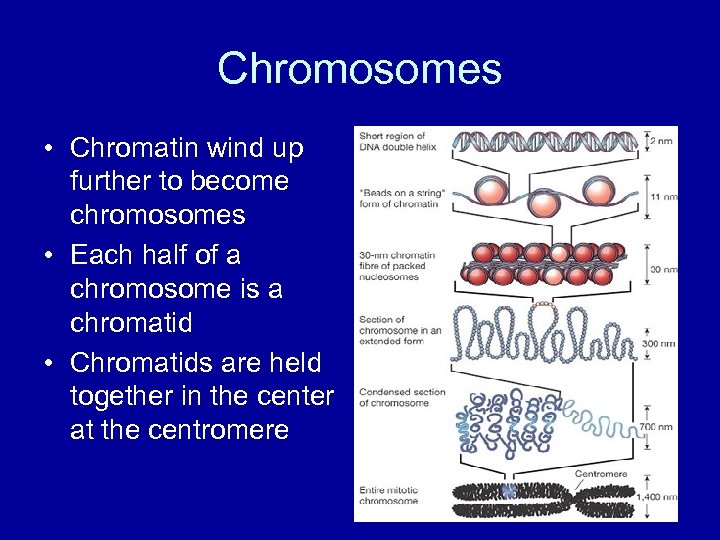 Chromosomes • Chromatin wind up further to become chromosomes • Each half of a chromosome is a chromatid • Chromatids are held together in the center at the centromere
Chromosomes • Chromatin wind up further to become chromosomes • Each half of a chromosome is a chromatid • Chromatids are held together in the center at the centromere
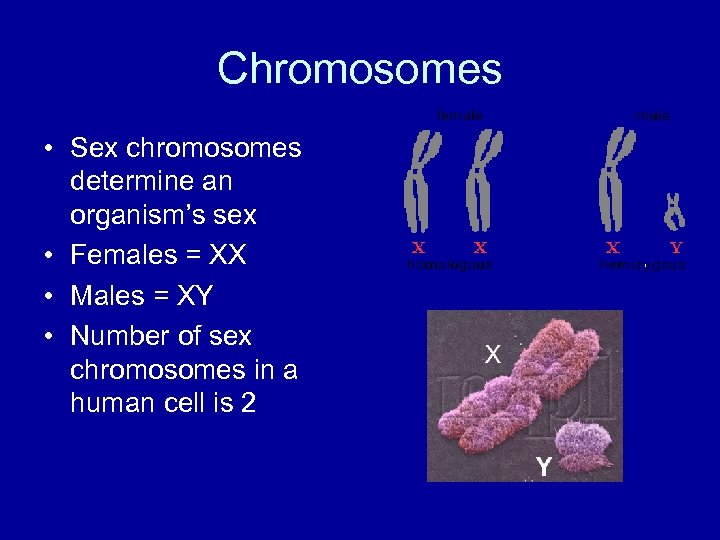 Chromosomes • Sex chromosomes determine an organism’s sex • Females = XX • Males = XY • Number of sex chromosomes in a human cell is 2
Chromosomes • Sex chromosomes determine an organism’s sex • Females = XX • Males = XY • Number of sex chromosomes in a human cell is 2
 Chromosomes • Autosomes – all the chromosomes except for the sex chromosomes • Number of autosomes in humans = 44
Chromosomes • Autosomes – all the chromosomes except for the sex chromosomes • Number of autosomes in humans = 44
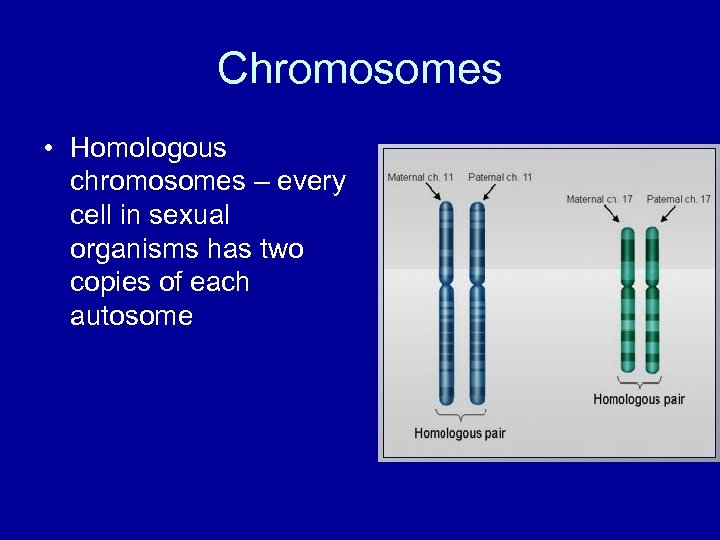 Chromosomes • Homologous chromosomes – every cell in sexual organisms has two copies of each autosome
Chromosomes • Homologous chromosomes – every cell in sexual organisms has two copies of each autosome
 Chromosomes • Humans have 44 autosomes so they have 22 homologous pairs. • Dogs have 76 autosomes so they have 38 homologous pairs. – Goat = 58 – Armidillo = 62 – Chicken = 78 – House fly = 12 – Mosquito = 6
Chromosomes • Humans have 44 autosomes so they have 22 homologous pairs. • Dogs have 76 autosomes so they have 38 homologous pairs. – Goat = 58 – Armidillo = 62 – Chicken = 78 – House fly = 12 – Mosquito = 6
 Diploid • Cells with 2 sets of chromosomes (homologous prs. ) are diploid. • In humans, the diploid number is 46 (2 n)
Diploid • Cells with 2 sets of chromosomes (homologous prs. ) are diploid. • In humans, the diploid number is 46 (2 n)
 Haploid • Cells with one set of chromosomes are haploid. • In humans, the haploid number is 23 (1 n).
Haploid • Cells with one set of chromosomes are haploid. • In humans, the haploid number is 23 (1 n).
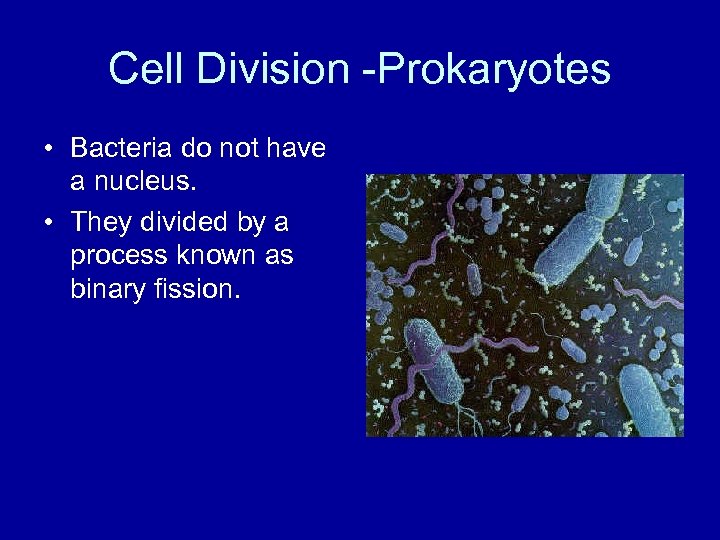 Cell Division -Prokaryotes • Bacteria do not have a nucleus. • They divided by a process known as binary fission.
Cell Division -Prokaryotes • Bacteria do not have a nucleus. • They divided by a process known as binary fission.
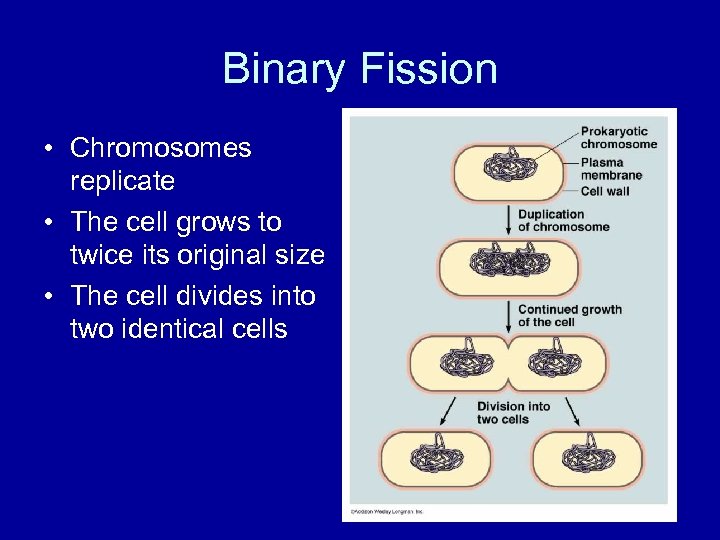 Binary Fission • Chromosomes replicate • The cell grows to twice its original size • The cell divides into two identical cells
Binary Fission • Chromosomes replicate • The cell grows to twice its original size • The cell divides into two identical cells
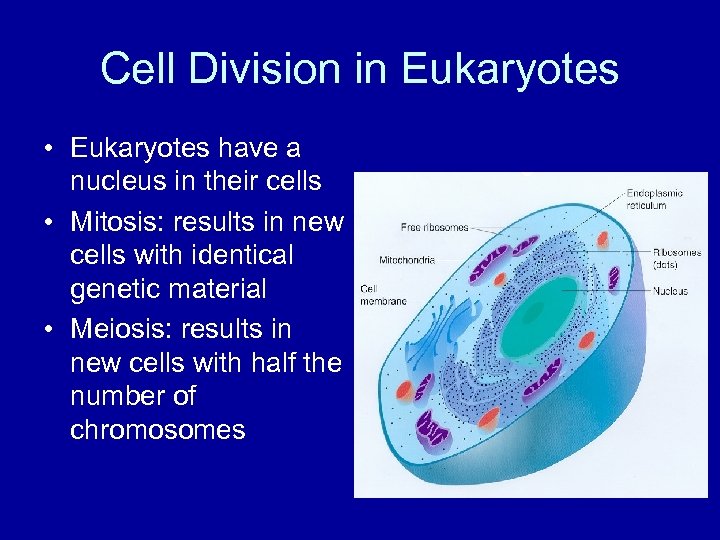 Cell Division in Eukaryotes • Eukaryotes have a nucleus in their cells • Mitosis: results in new cells with identical genetic material • Meiosis: results in new cells with half the number of chromosomes
Cell Division in Eukaryotes • Eukaryotes have a nucleus in their cells • Mitosis: results in new cells with identical genetic material • Meiosis: results in new cells with half the number of chromosomes
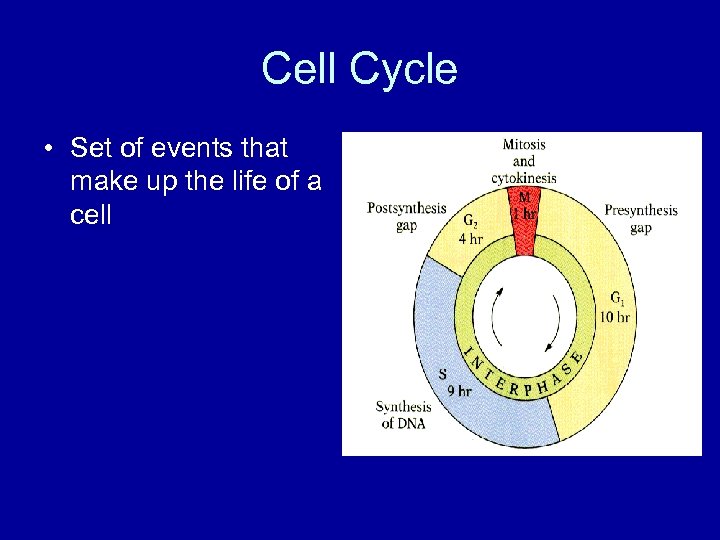 Cell Cycle • Set of events that make up the life of a cell
Cell Cycle • Set of events that make up the life of a cell
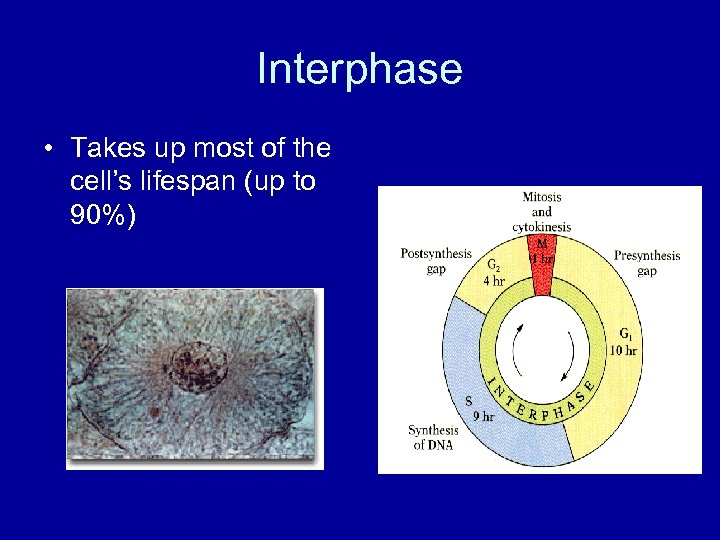 Interphase • Takes up most of the cell’s lifespan (up to 90%)
Interphase • Takes up most of the cell’s lifespan (up to 90%)
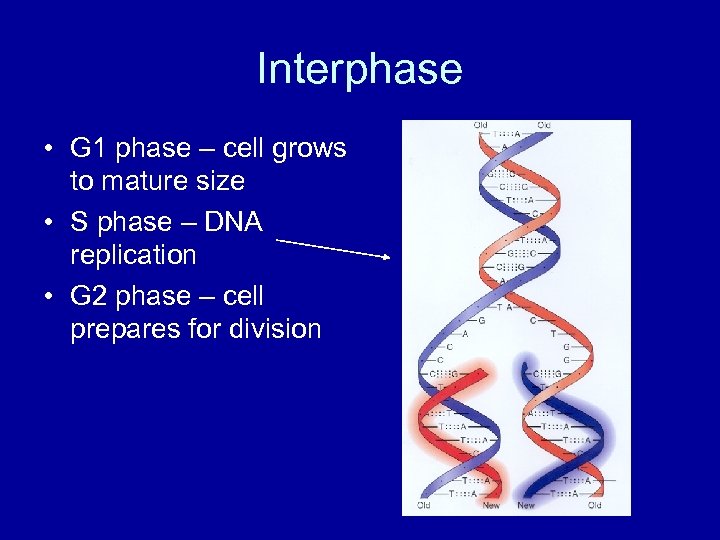 Interphase • G 1 phase – cell grows to mature size • S phase – DNA replication • G 2 phase – cell prepares for division
Interphase • G 1 phase – cell grows to mature size • S phase – DNA replication • G 2 phase – cell prepares for division
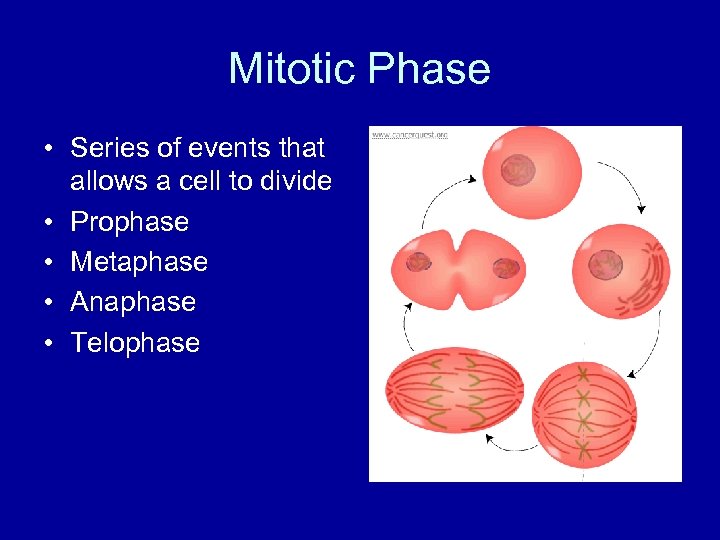 Mitotic Phase • Series of events that allows a cell to divide • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase
Mitotic Phase • Series of events that allows a cell to divide • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase
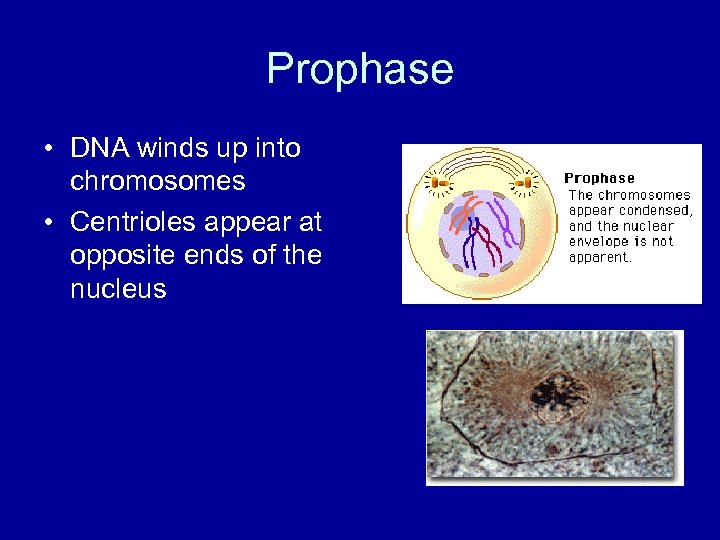 Prophase • DNA winds up into chromosomes • Centrioles appear at opposite ends of the nucleus
Prophase • DNA winds up into chromosomes • Centrioles appear at opposite ends of the nucleus
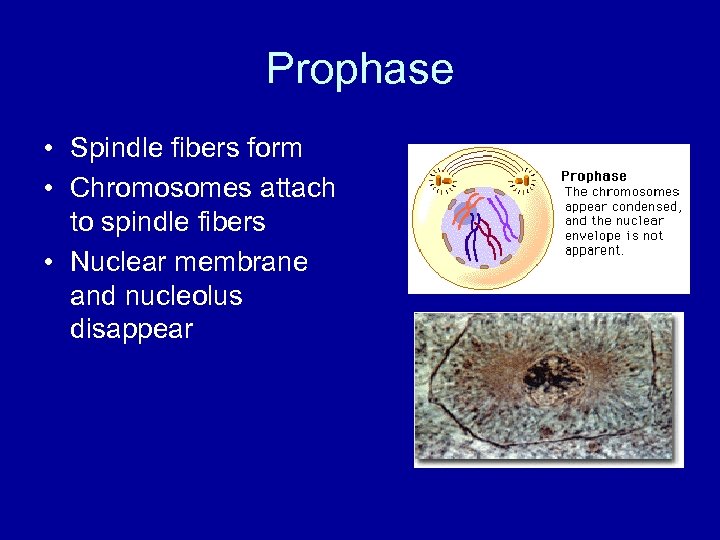 Prophase • Spindle fibers form • Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers • Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear
Prophase • Spindle fibers form • Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers • Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear
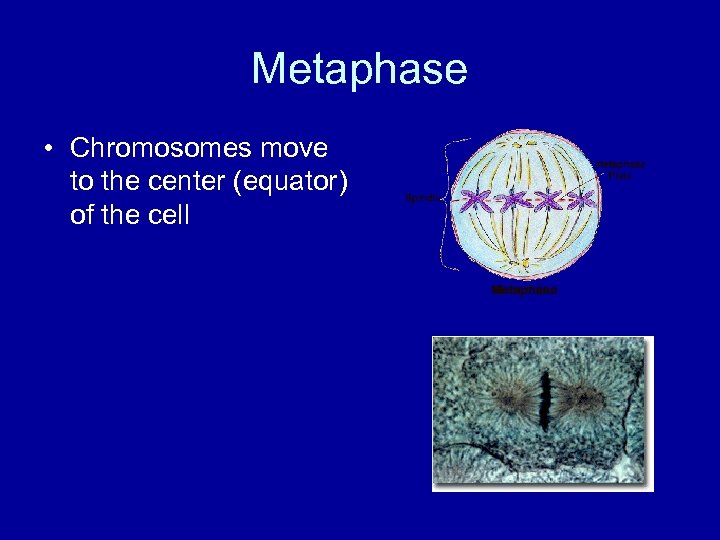 Metaphase • Chromosomes move to the center (equator) of the cell
Metaphase • Chromosomes move to the center (equator) of the cell
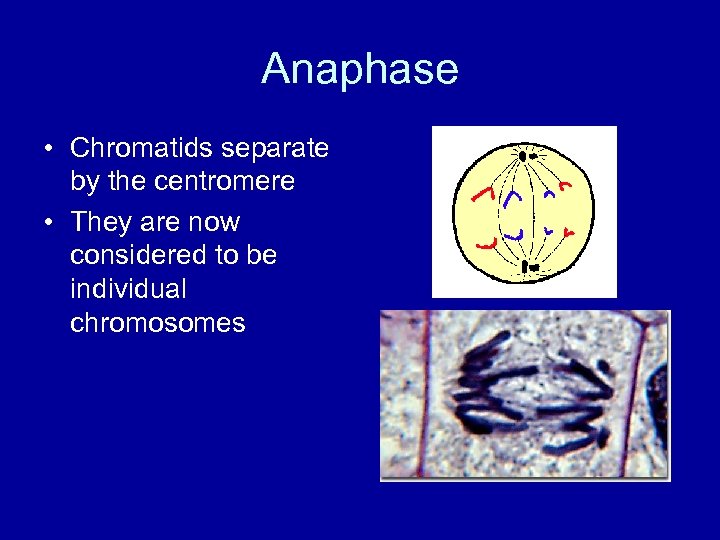 Anaphase • Chromatids separate by the centromere • They are now considered to be individual chromosomes
Anaphase • Chromatids separate by the centromere • They are now considered to be individual chromosomes
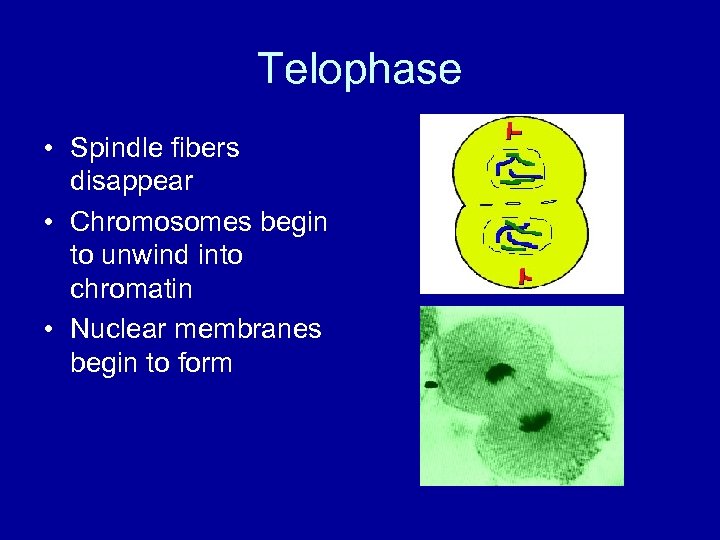 Telophase • Spindle fibers disappear • Chromosomes begin to unwind into chromatin • Nuclear membranes begin to form
Telophase • Spindle fibers disappear • Chromosomes begin to unwind into chromatin • Nuclear membranes begin to form
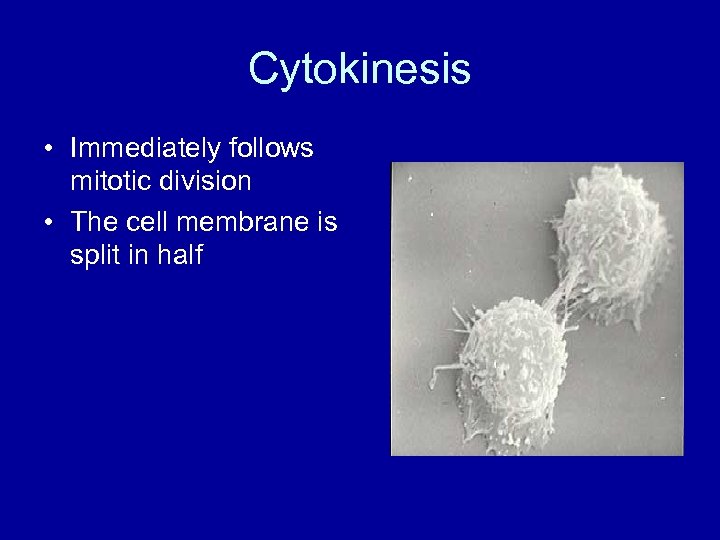 Cytokinesis • Immediately follows mitotic division • The cell membrane is split in half
Cytokinesis • Immediately follows mitotic division • The cell membrane is split in half
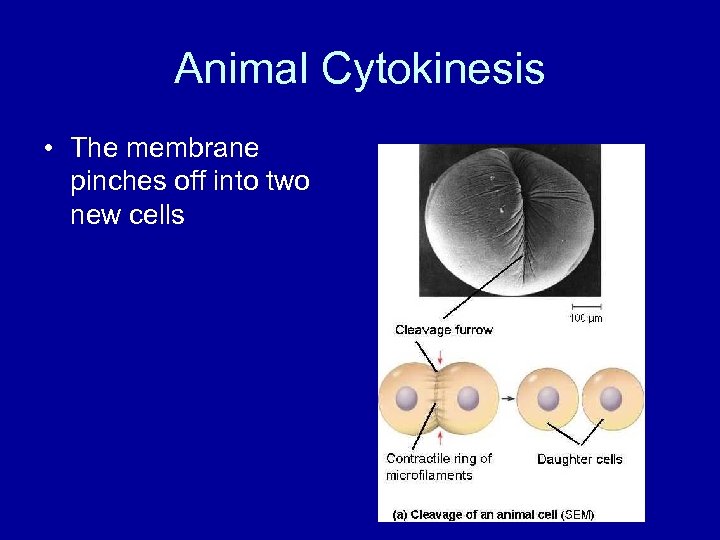 Animal Cytokinesis • The membrane pinches off into two new cells
Animal Cytokinesis • The membrane pinches off into two new cells
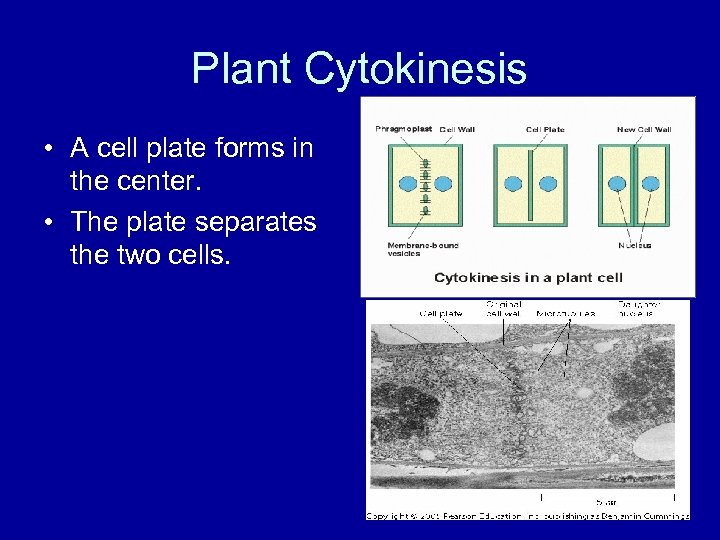 Plant Cytokinesis • A cell plate forms in the center. • The plate separates the two cells.
Plant Cytokinesis • A cell plate forms in the center. • The plate separates the two cells.