10a-Mitosis.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
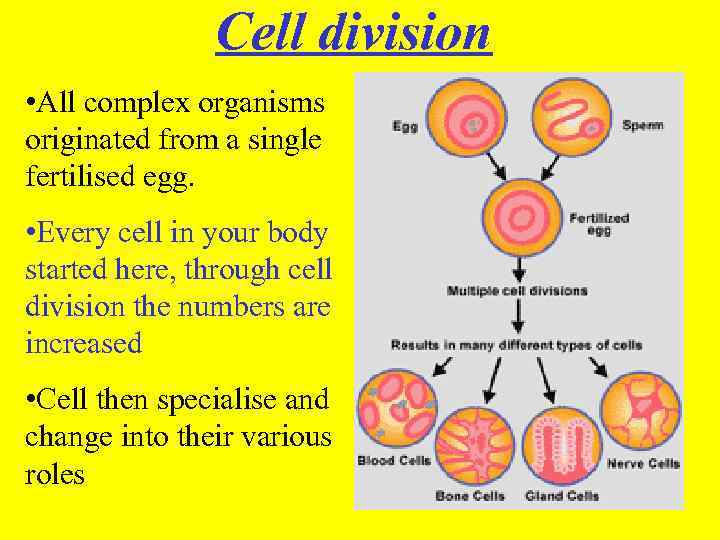 Cell division • All complex organisms originated from a single fertilised egg. • Every cell in your body started here, through cell division the numbers are increased • Cell then specialise and change into their various roles
Cell division • All complex organisms originated from a single fertilised egg. • Every cell in your body started here, through cell division the numbers are increased • Cell then specialise and change into their various roles
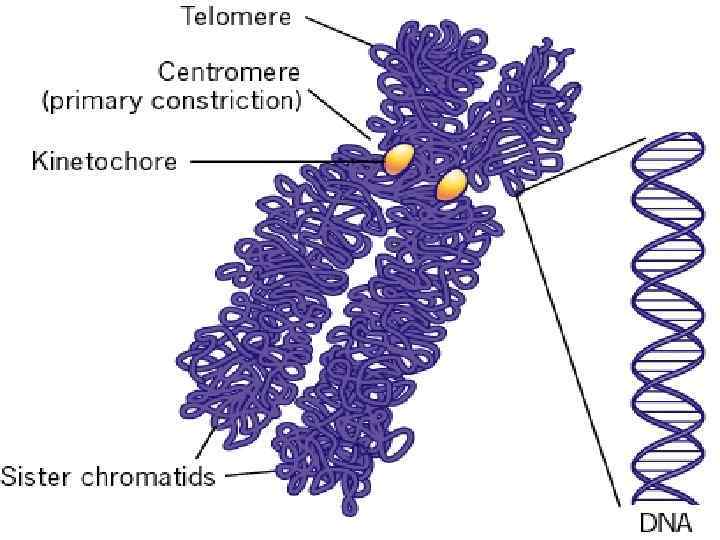
 • During the cell division, chromatin is condenced to form CHROMOSOMES. • Each chromosome contains two chromatids. • Chromatids join together by means of Centromers (Chinetochores).
• During the cell division, chromatin is condenced to form CHROMOSOMES. • Each chromosome contains two chromatids. • Chromatids join together by means of Centromers (Chinetochores).
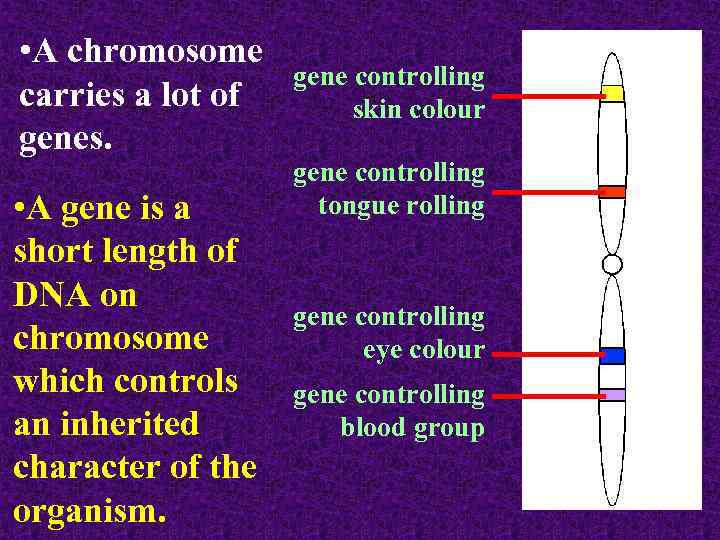 • A chromosome carries a lot of genes. • A gene is a short length of DNA on chromosome which controls an inherited character of the organism. gene controlling skin colour gene controlling tongue rolling gene controlling eye colour gene controlling blood group
• A chromosome carries a lot of genes. • A gene is a short length of DNA on chromosome which controls an inherited character of the organism. gene controlling skin colour gene controlling tongue rolling gene controlling eye colour gene controlling blood group
 Cell Cycle • Each cell has a life cycle or cellular program. • Mainly cell cycle is divided by 2 : 1 - Interphase (G 1, S and G 2) 2 - M-phase (Division phase)
Cell Cycle • Each cell has a life cycle or cellular program. • Mainly cell cycle is divided by 2 : 1 - Interphase (G 1, S and G 2) 2 - M-phase (Division phase)
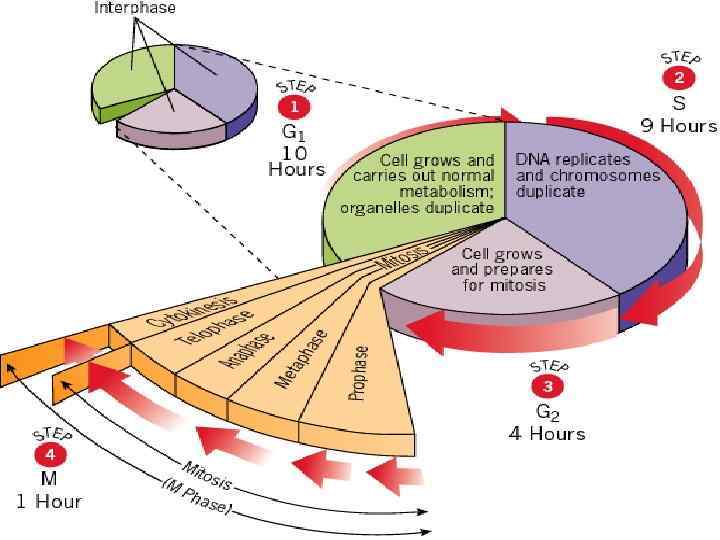
 INTERPHASE There are three steps in the interphase: – G 1: (Cell growth phase). m. RNA, Protein and ATP are produced. – S: (Duplication phase) DNA & Centrosome make copy themself (2 Duplication occur). – G 2: (Preperation phase). The replicated DNA condences.
INTERPHASE There are three steps in the interphase: – G 1: (Cell growth phase). m. RNA, Protein and ATP are produced. – S: (Duplication phase) DNA & Centrosome make copy themself (2 Duplication occur). – G 2: (Preperation phase). The replicated DNA condences.
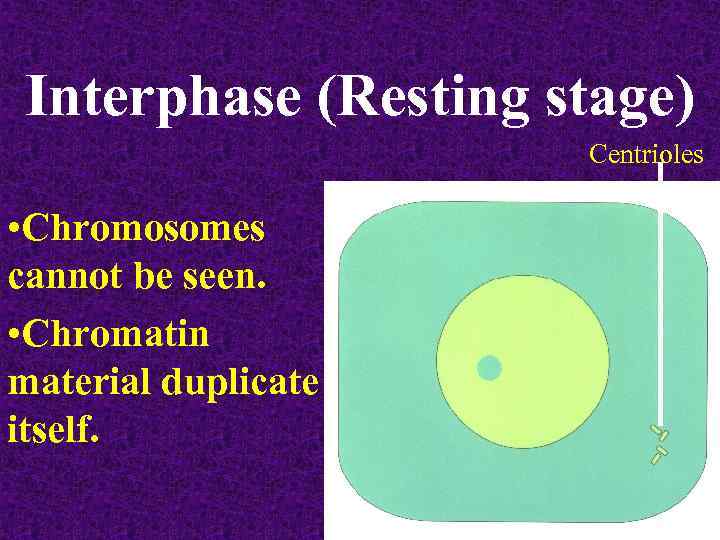 Interphase (Resting stage) Centrioles • Chromosomes cannot be seen. • Chromatin material duplicate itself.
Interphase (Resting stage) Centrioles • Chromosomes cannot be seen. • Chromatin material duplicate itself.
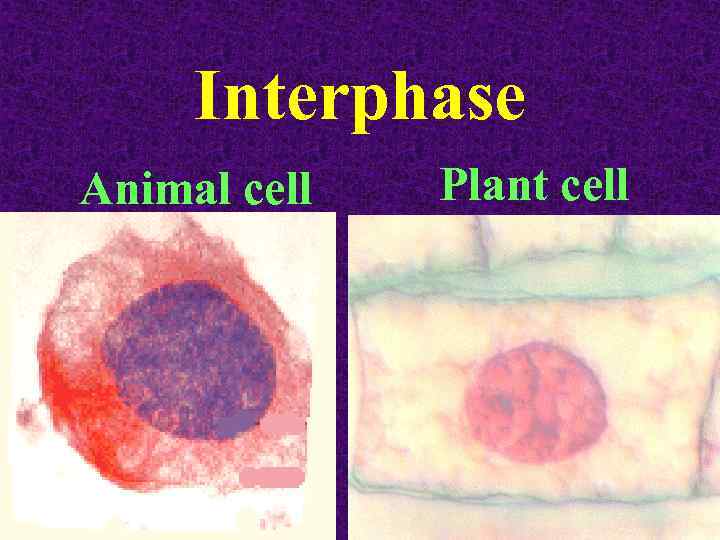 Interphase Animal cell Plant cell
Interphase Animal cell Plant cell
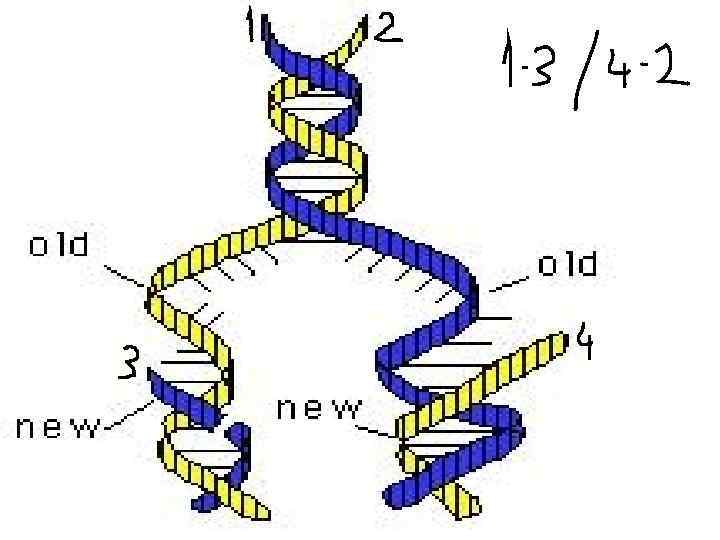
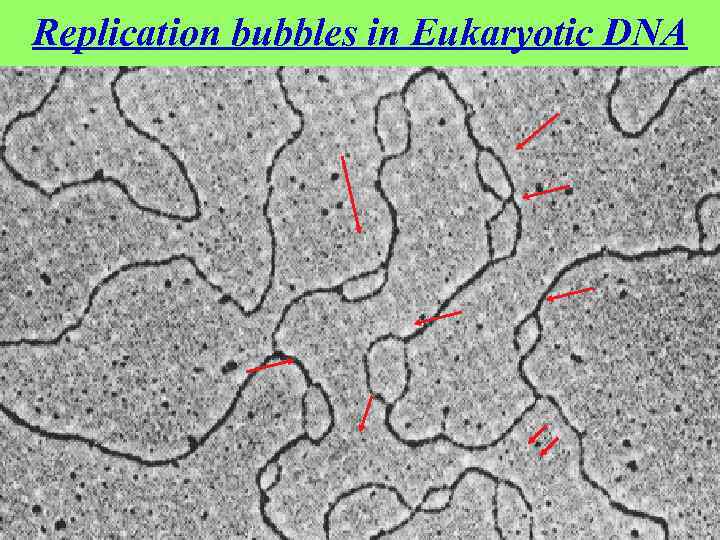 Replication bubbles in Eukaryotic DNA
Replication bubbles in Eukaryotic DNA

 Purposes of Mitosis • Increasing the number of cells for Growth, • Repairing of worn out tissues.
Purposes of Mitosis • Increasing the number of cells for Growth, • Repairing of worn out tissues.
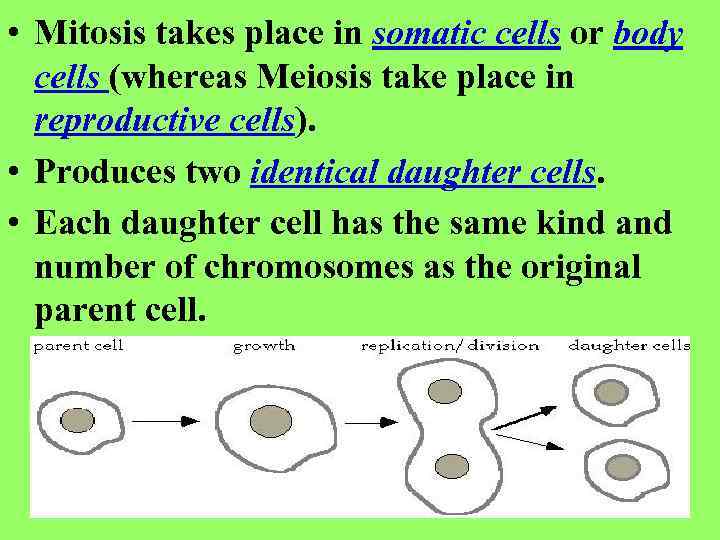 • Mitosis takes place in somatic cells or body cells (whereas Meiosis take place in reproductive cells). • Produces two identical daughter cells. • Each daughter cell has the same kind and number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
• Mitosis takes place in somatic cells or body cells (whereas Meiosis take place in reproductive cells). • Produces two identical daughter cells. • Each daughter cell has the same kind and number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
 • KARYOKINESIS Another name of mitosis is Karyokinesis • Karyokinesis is division of nucleus. • There are 4 steps in karyokinesis: 1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase
• KARYOKINESIS Another name of mitosis is Karyokinesis • Karyokinesis is division of nucleus. • There are 4 steps in karyokinesis: 1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase
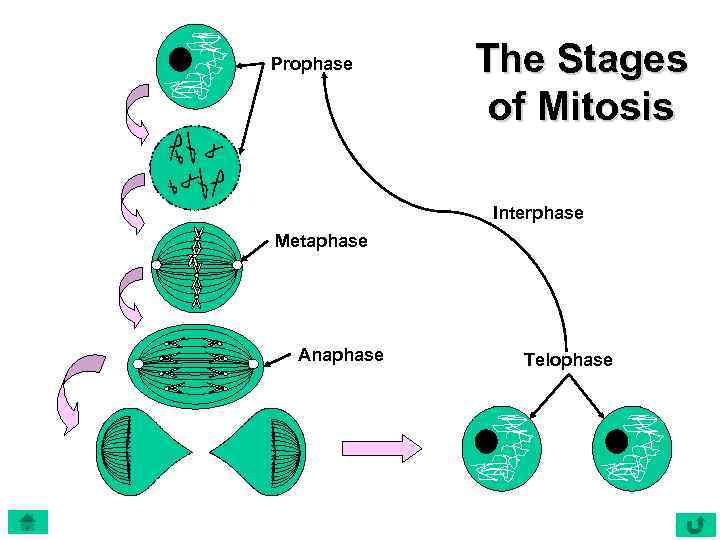 Prophase The Stages of Mitosis Interphase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
Prophase The Stages of Mitosis Interphase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
 PROPHASE • At the beginning of prophase two centrioles move to opposite poles of cell. • Centrioles start to form spindle fibers. • Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear. • DNA molecules are shortened and thickened to form chromosome.
PROPHASE • At the beginning of prophase two centrioles move to opposite poles of cell. • Centrioles start to form spindle fibers. • Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear. • DNA molecules are shortened and thickened to form chromosome.
 CENTRIOLES
CENTRIOLES
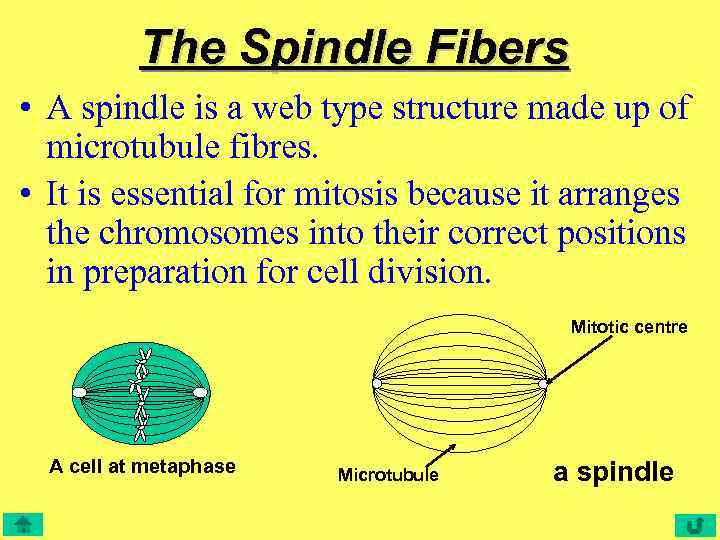 The Spindle Fibers • A spindle is a web type structure made up of microtubule fibres. • It is essential for mitosis because it arranges the chromosomes into their correct positions in preparation for cell division. Mitotic centre A cell at metaphase Microtubule a spindle
The Spindle Fibers • A spindle is a web type structure made up of microtubule fibres. • It is essential for mitosis because it arranges the chromosomes into their correct positions in preparation for cell division. Mitotic centre A cell at metaphase Microtubule a spindle
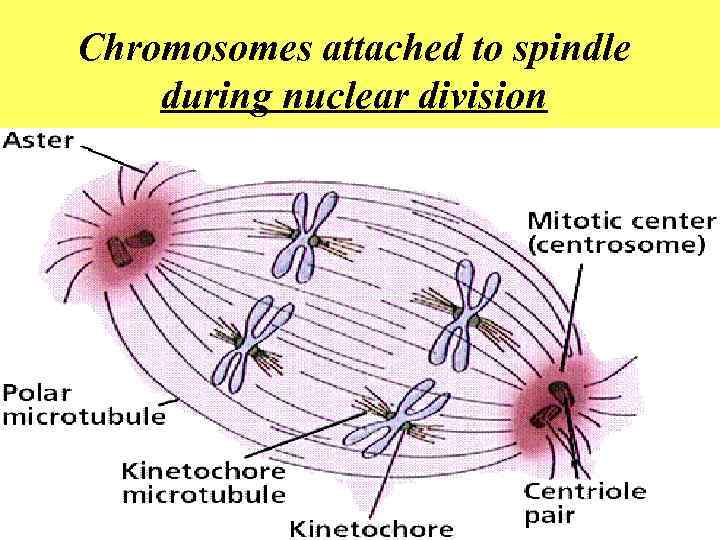 Chromosomes attached to spindle during nuclear division
Chromosomes attached to spindle during nuclear division
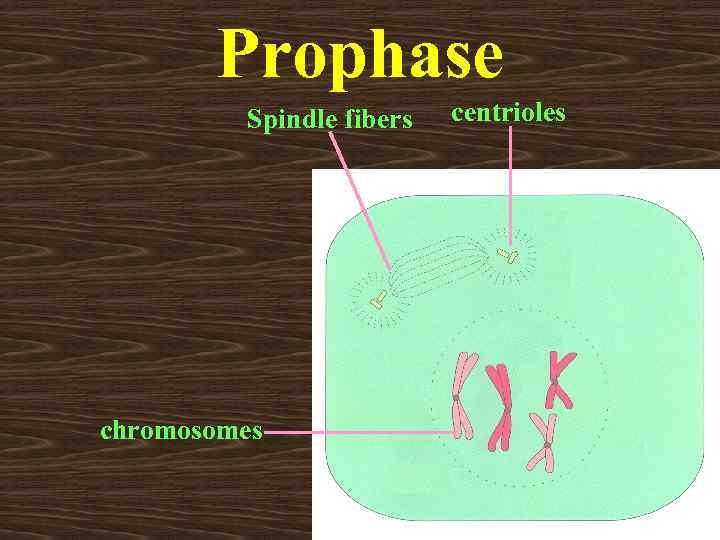 Prophase Spindle fibers chromosomes centrioles
Prophase Spindle fibers chromosomes centrioles
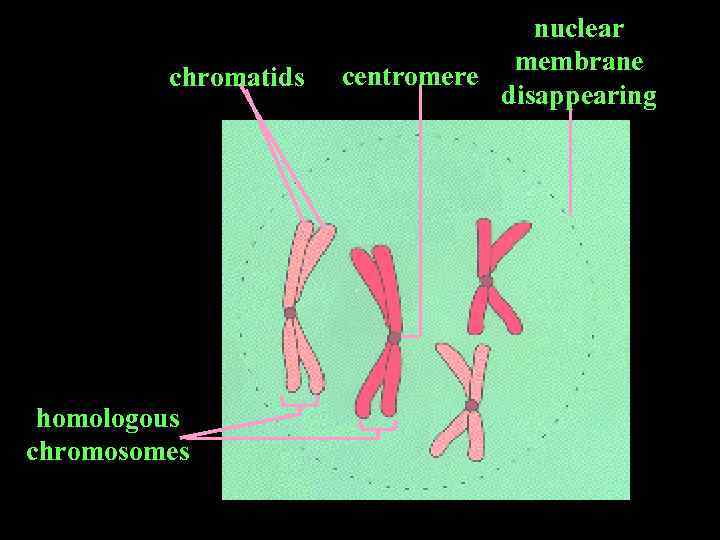 chromatids homologous chromosomes nuclear membrane centromere disappearing
chromatids homologous chromosomes nuclear membrane centromere disappearing
 Prophase Animal cell Plant cell
Prophase Animal cell Plant cell
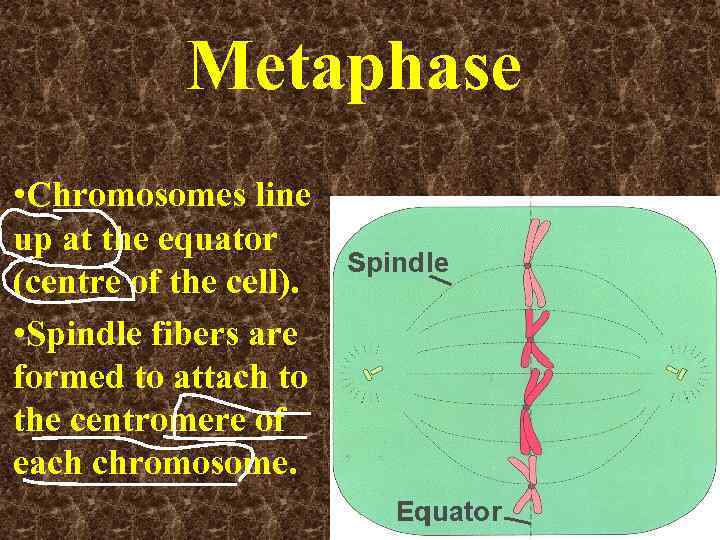 Metaphase • Chromosomes line up at the equator (centre of the cell). • Spindle fibers are formed to attach to the centromere of each chromosome.
Metaphase • Chromosomes line up at the equator (centre of the cell). • Spindle fibers are formed to attach to the centromere of each chromosome.
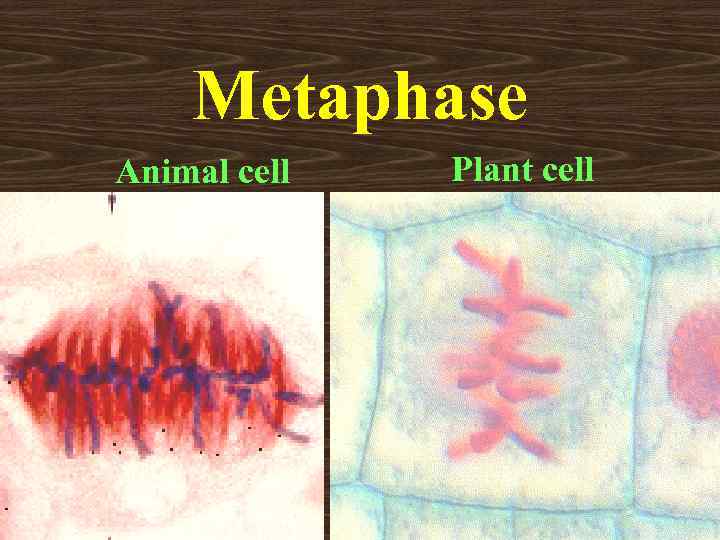 Metaphase Animal cell Plant cell
Metaphase Animal cell Plant cell
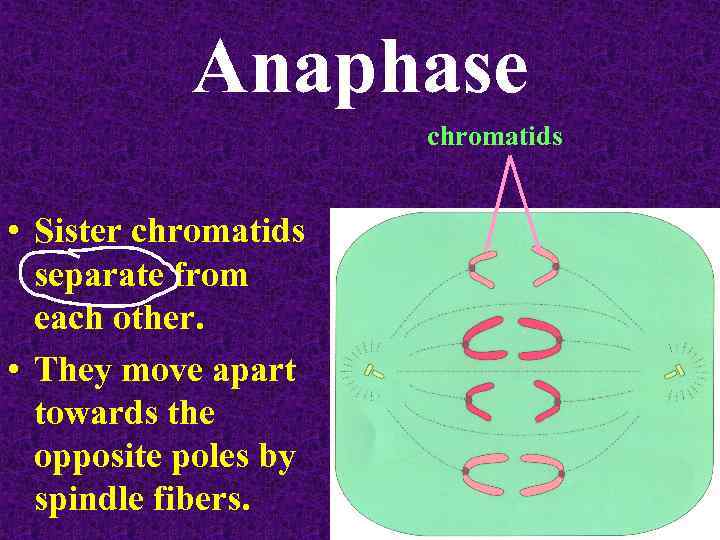 Anaphase chromatids • Sister chromatids separate from each other. • They move apart towards the opposite poles by spindle fibers.
Anaphase chromatids • Sister chromatids separate from each other. • They move apart towards the opposite poles by spindle fibers.
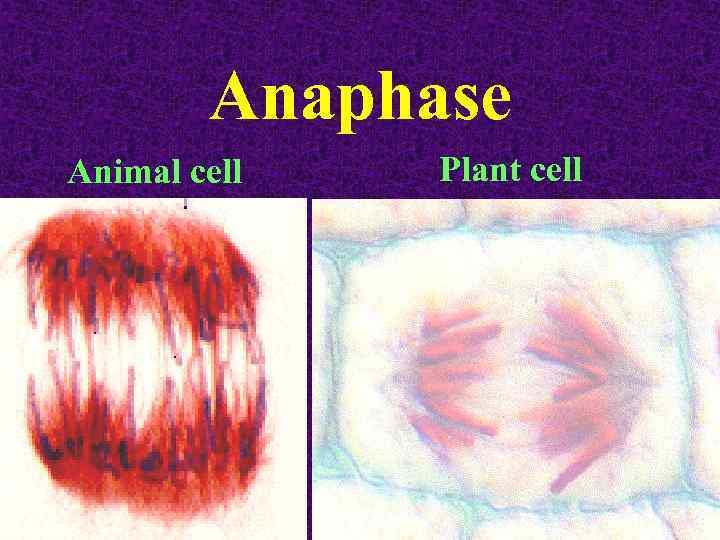 Anaphase Animal cell Plant cell
Anaphase Animal cell Plant cell
 TELOPHASE • A new nuclear membrane is formed at each pole. • Spindle fibers disappear. • Each chromatid • Karyokinesis is begins to uncoil, completed at the becoming less end of the telophase. condenced.
TELOPHASE • A new nuclear membrane is formed at each pole. • Spindle fibers disappear. • Each chromatid • Karyokinesis is begins to uncoil, completed at the becoming less end of the telophase. condenced.
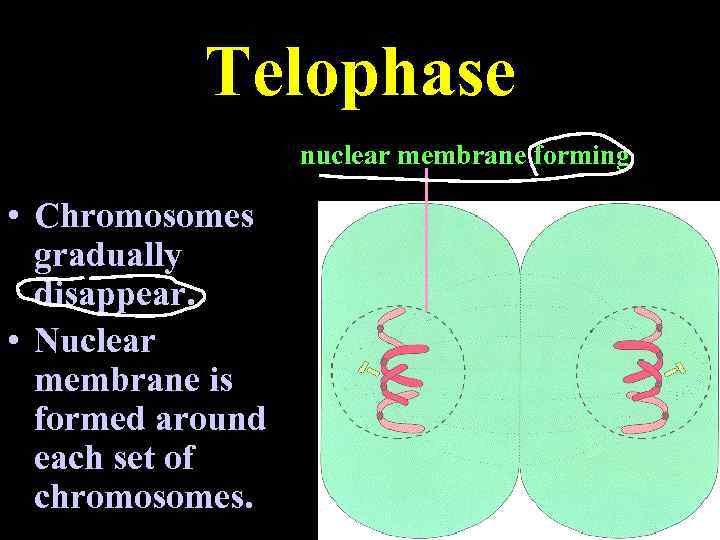 Telophase nuclear membrane forming • Chromosomes gradually disappear. • Nuclear membrane is formed around each set of chromosomes.
Telophase nuclear membrane forming • Chromosomes gradually disappear. • Nuclear membrane is formed around each set of chromosomes.
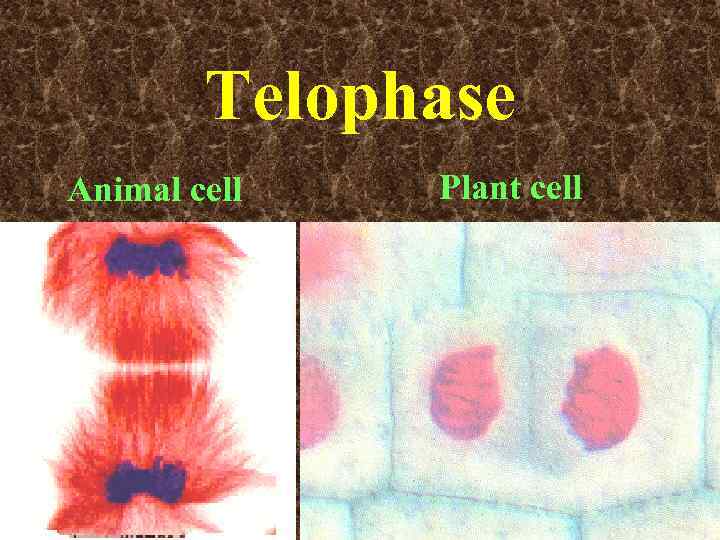 Telophase Animal cell Plant cell
Telophase Animal cell Plant cell
 CYTOKINESIS • Cytokinesis is division of cytoplasm. • It is different in animal and plant cells. • In plant cells, cytokinesis occurs by formation of the CELL PLATE. • In animal cells, cytoplasm is pincked to form CLEAVAGE FURROW, then two new identically similar cells.
CYTOKINESIS • Cytokinesis is division of cytoplasm. • It is different in animal and plant cells. • In plant cells, cytokinesis occurs by formation of the CELL PLATE. • In animal cells, cytoplasm is pincked to form CLEAVAGE FURROW, then two new identically similar cells.
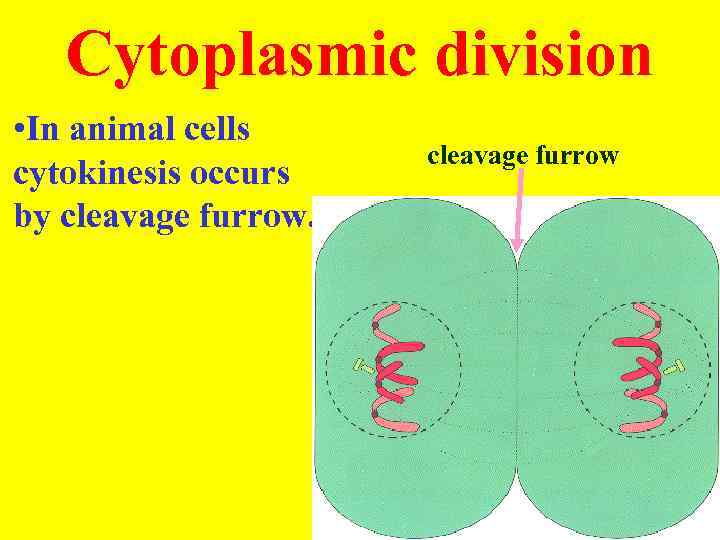 Cytoplasmic division • In animal cells cytokinesis occurs by cleavage furrow
Cytoplasmic division • In animal cells cytokinesis occurs by cleavage furrow
 • In plant cells cytokinesis occurs by cell plate. Cell plate
• In plant cells cytokinesis occurs by cell plate. Cell plate
 MITOSIS ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL • Spindle fibers are formed by centrioles. • Spindle fibers are formed by microtubules. • Cytokinesis occurs by cleavage furrow. • Cytokinesis occurs by cell plate.
MITOSIS ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL • Spindle fibers are formed by centrioles. • Spindle fibers are formed by microtubules. • Cytokinesis occurs by cleavage furrow. • Cytokinesis occurs by cell plate.
 Let’s Quizzzz. . !!!
Let’s Quizzzz. . !!!
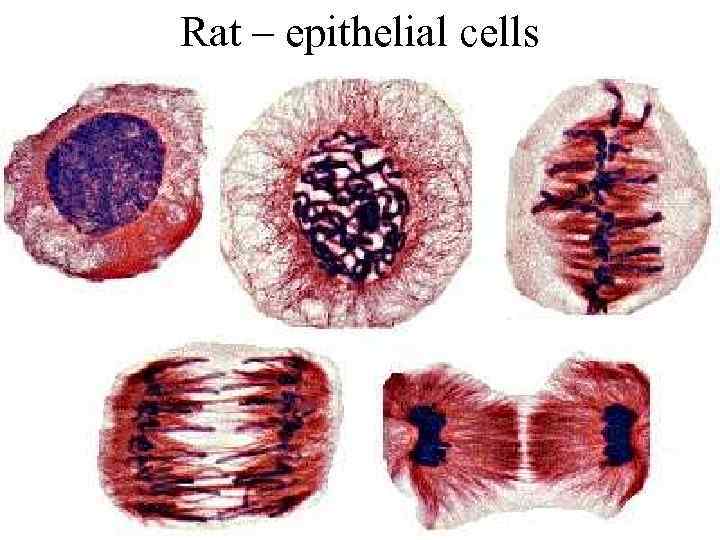 Rat – epithelial cells
Rat – epithelial cells
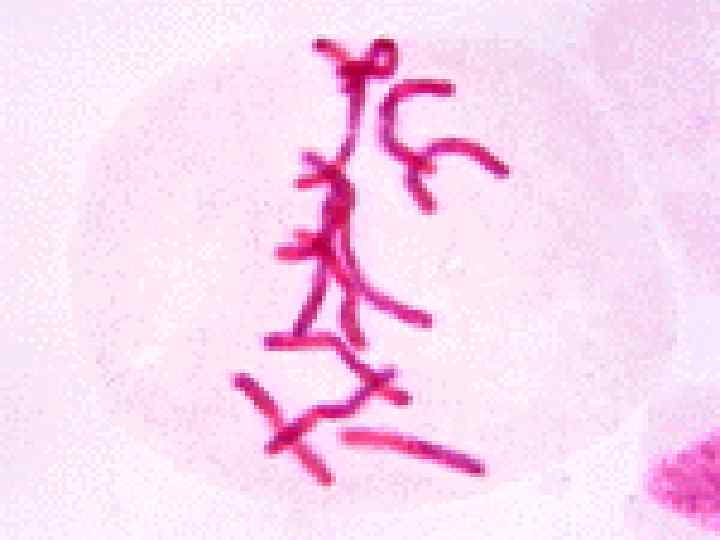
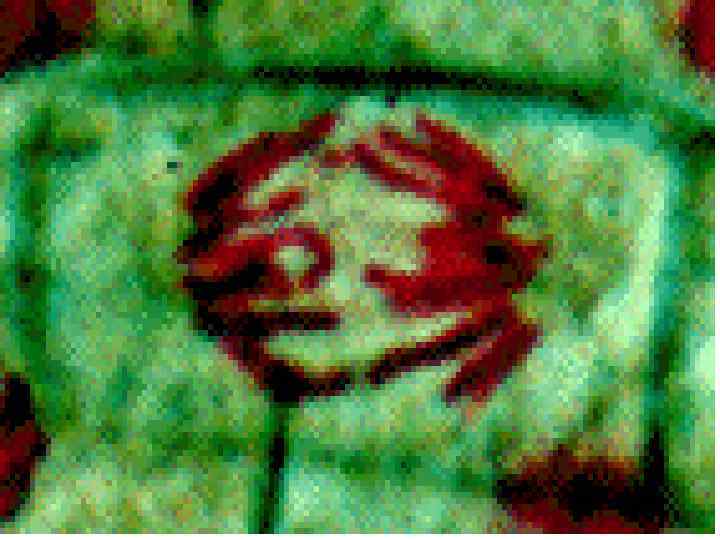
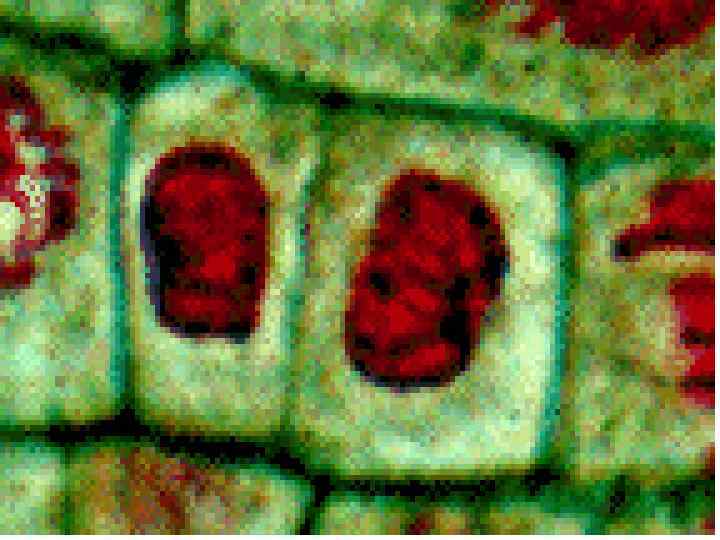
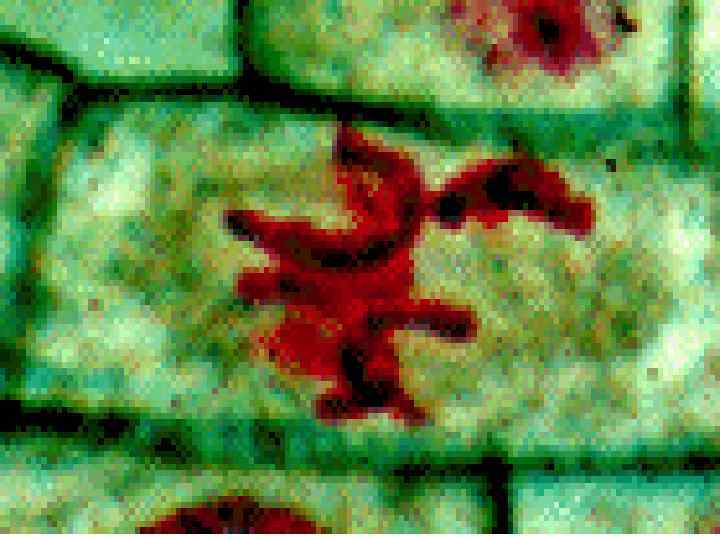
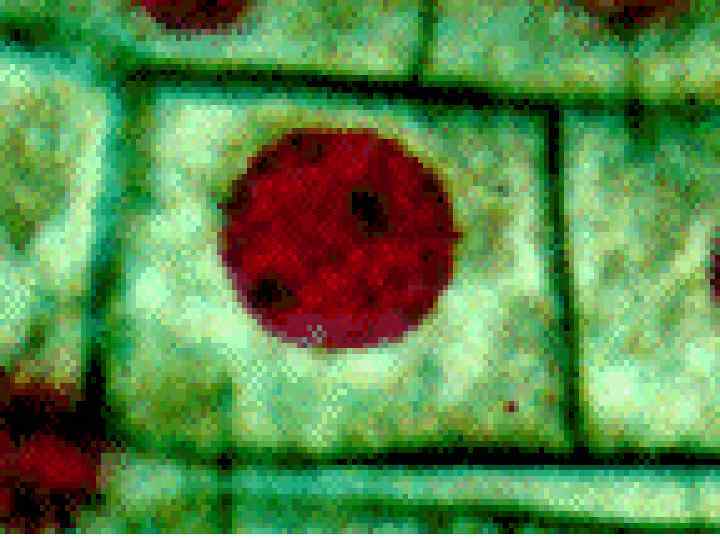


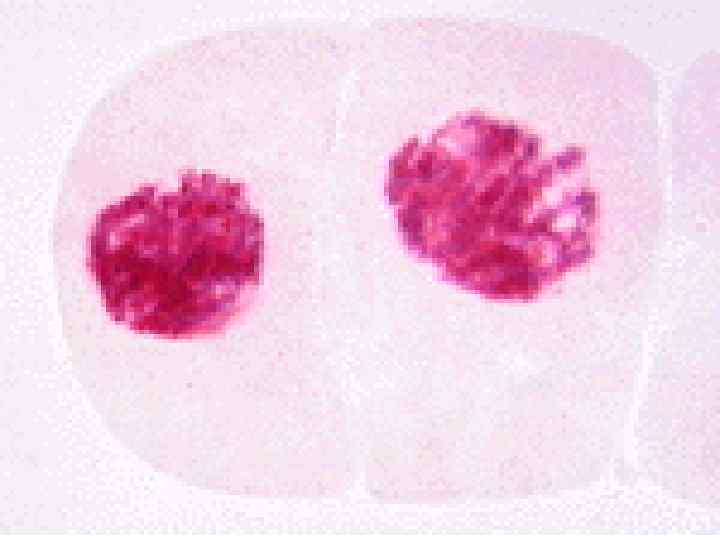

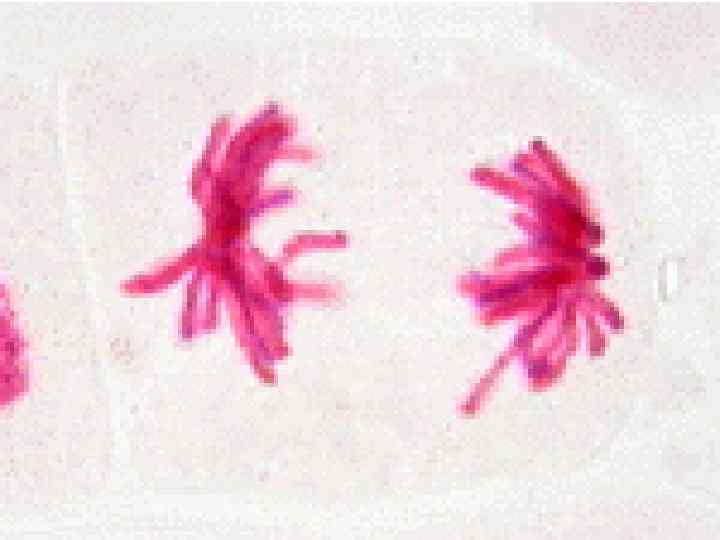

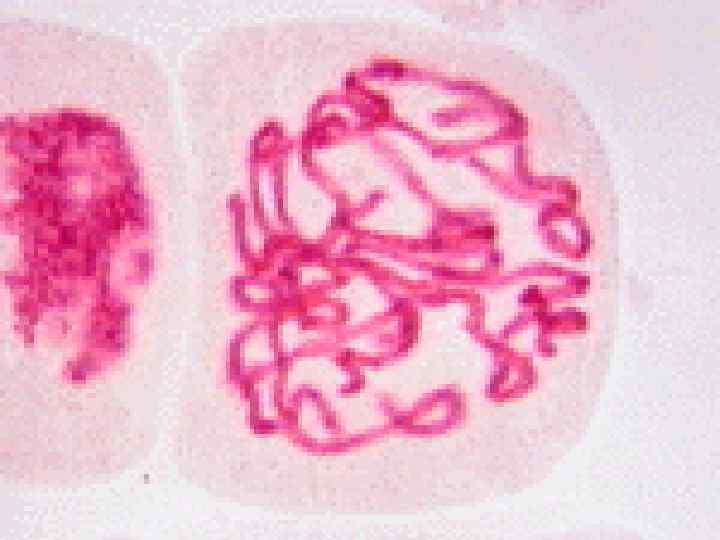
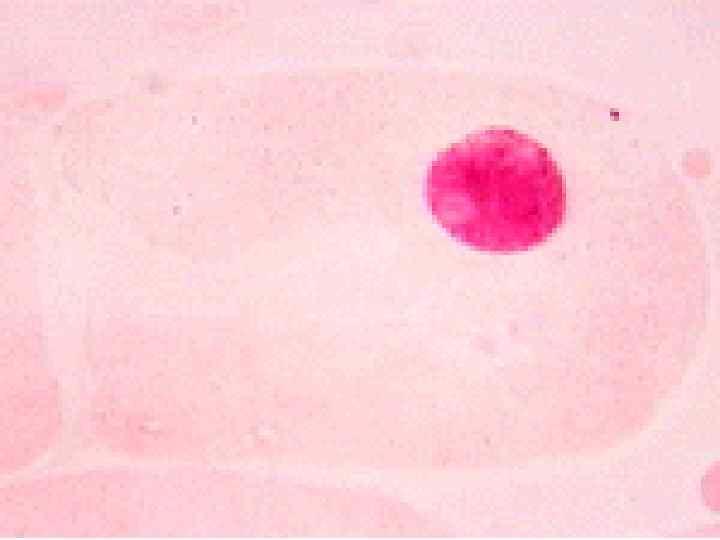



 Cancer • The division of normal cells is precisely controlled. • Cancerous cells divide repeatedly out of control. • They can also destroy the correct functioning of major organs. • Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: • 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer • 1 in 17 cancer deaths are due to lung cancer • Annual lung cancer death rate per 100, 000 men
Cancer • The division of normal cells is precisely controlled. • Cancerous cells divide repeatedly out of control. • They can also destroy the correct functioning of major organs. • Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: • 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer • 1 in 17 cancer deaths are due to lung cancer • Annual lung cancer death rate per 100, 000 men
 What causes cancer? • Cancer arises from the mutation of a normal gene. • Mutated genes that cause cancer are called oncogenes. A factor which brings about a mutation is called a mutagen. A mutagen is mutagenic. Any agent that causes cancer is called a carcinogen and is described as carcinogenic.
What causes cancer? • Cancer arises from the mutation of a normal gene. • Mutated genes that cause cancer are called oncogenes. A factor which brings about a mutation is called a mutagen. A mutagen is mutagenic. Any agent that causes cancer is called a carcinogen and is described as carcinogenic.
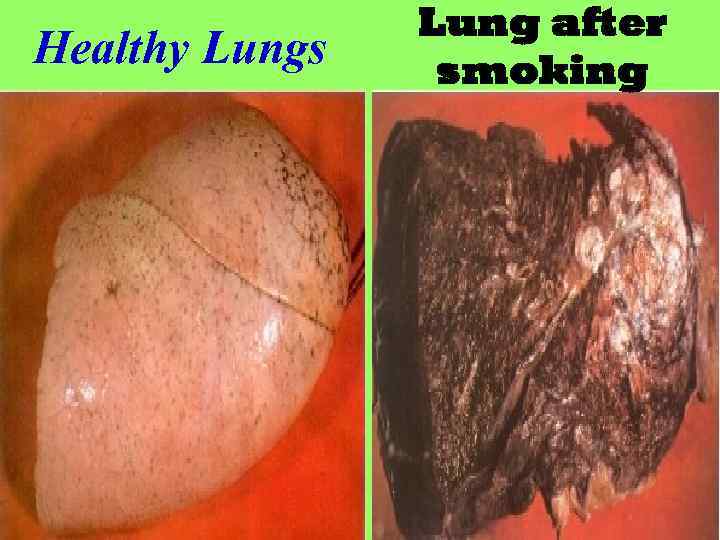 Healthy Lungs Lung after smoking
Healthy Lungs Lung after smoking


