d562306ff0bdbe80d28407f149a5fa0a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Cell Depletion in Young Pediatric Patients Laura Cooling MD, MS Associate Director, Transfusion Medicine (no financial disclosures except my salary) Pediatric Hem/Onc 12 -12 -12
Cell Depletion in Young Pediatric Patients Laura Cooling MD, MS Associate Director, Transfusion Medicine (no financial disclosures except my salary) Pediatric Hem/Onc 12 -12 -12
 Outline • Basics of automated leukapheresis • Literature review: whole blood exchange • Technical differences for < 10 kg – UM experience with leukapheresis <10 kg – Mock procedure results – Time/risk assessment: • WBEx vs leukapheresis in <10 kg
Outline • Basics of automated leukapheresis • Literature review: whole blood exchange • Technical differences for < 10 kg – UM experience with leukapheresis <10 kg – Mock procedure results – Time/risk assessment: • WBEx vs leukapheresis in <10 kg
 Automated Leukapheresis Adult Patients • Stem cells (MNC) – 3 BV* • Therapeutic depletion – 2 BV process – Myeloid leukemias • Symptomatic leukostasis • Prophylactic, WBC > 180 -200 K – Lymphoid (rarely done) • WBC > 500 K planned rituximab tx *BV, blood volume Cobe Spectra
Automated Leukapheresis Adult Patients • Stem cells (MNC) – 3 BV* • Therapeutic depletion – 2 BV process – Myeloid leukemias • Symptomatic leukostasis • Prophylactic, WBC > 180 -200 K – Lymphoid (rarely done) • WBC > 500 K planned rituximab tx *BV, blood volume Cobe Spectra
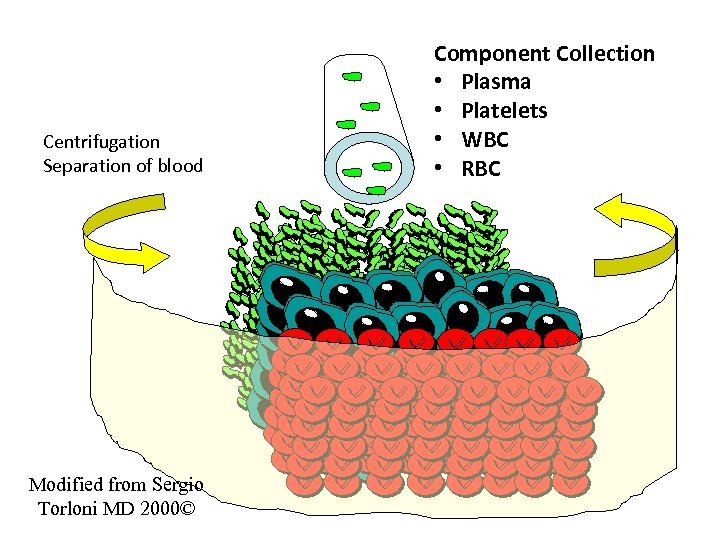 Centrifugation Separation of blood Modified from Sergio Torloni MD 2000© Component Collection • Plasma • Platelets • WBC • RBC 3 D-Studio Max
Centrifugation Separation of blood Modified from Sergio Torloni MD 2000© Component Collection • Plasma • Platelets • WBC • RBC 3 D-Studio Max
 Limitations of Leukapheresis Overall tumor burden • High proliferative rate – ALL – Rapid rebound in counts (< 8 - 12 hrs) • Large, extravascular tumor burden – Eg. CML, CMML, +/- M 5 – Mobilize extravascular tumor stores • Little or no decrease in peripheral WBC • Higher post-procedure WBC
Limitations of Leukapheresis Overall tumor burden • High proliferative rate – ALL – Rapid rebound in counts (< 8 - 12 hrs) • Large, extravascular tumor burden – Eg. CML, CMML, +/- M 5 – Mobilize extravascular tumor stores • Little or no decrease in peripheral WBC • Higher post-procedure WBC
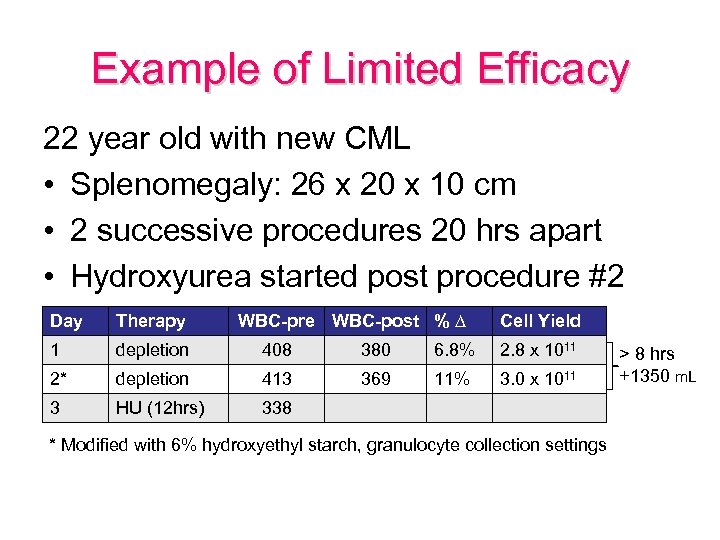 Example of Limited Efficacy 22 year old with new CML • Splenomegaly: 26 x 20 x 10 cm • 2 successive procedures 20 hrs apart • Hydroxyurea started post procedure #2 Day Therapy WBC-pre WBC-post % ∆ Cell Yield 1 depletion 408 380 6. 8% 2. 8 x 1011 2* depletion 413 369 11% 3. 0 x 1011 3 HU (12 hrs) 338 * Modified with 6% hydroxyethyl starch, granulocyte collection settings > 8 hrs +1350 m. L
Example of Limited Efficacy 22 year old with new CML • Splenomegaly: 26 x 20 x 10 cm • 2 successive procedures 20 hrs apart • Hydroxyurea started post procedure #2 Day Therapy WBC-pre WBC-post % ∆ Cell Yield 1 depletion 408 380 6. 8% 2. 8 x 1011 2* depletion 413 369 11% 3. 0 x 1011 3 HU (12 hrs) 338 * Modified with 6% hydroxyethyl starch, granulocyte collection settings > 8 hrs +1350 m. L
 Limitations of Leukapheresis • High tumor burden • Peripheral WBC – Ineffective WBC < 100, 000
Limitations of Leukapheresis • High tumor burden • Peripheral WBC – Ineffective WBC < 100, 000
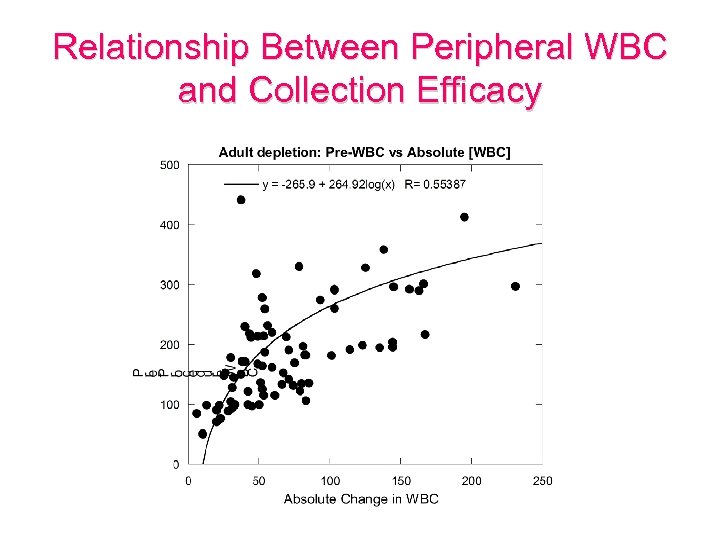 Relationship Between Peripheral WBC and Collection Efficacy
Relationship Between Peripheral WBC and Collection Efficacy
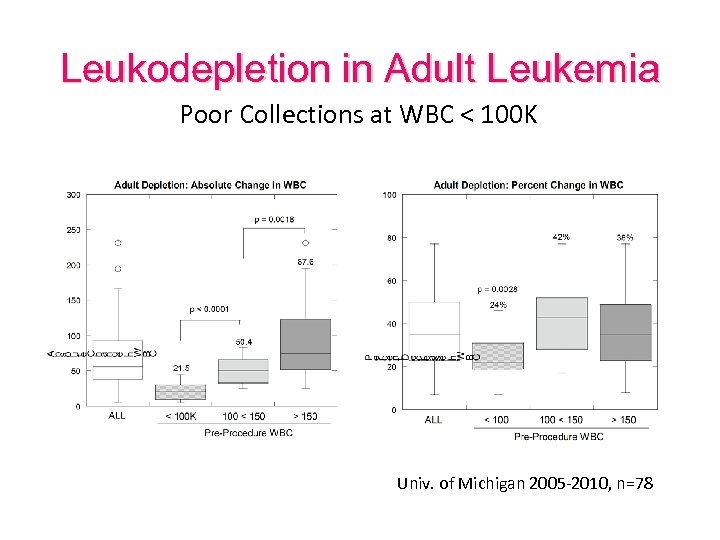 Leukodepletion in Adult Leukemia Poor Collections at WBC < 100 K Univ. of Michigan 2005 -2010, n=78
Leukodepletion in Adult Leukemia Poor Collections at WBC < 100 K Univ. of Michigan 2005 -2010, n=78
 Limitations of Leukapheresis • High tumor burden • Peripheral WBC – Ineffective WBC < 100, 000 • Poor/unstable WBC-RBC interface – Patient factors (eg. High retic, cryoglobulins) – Access / alarms – Slow rates
Limitations of Leukapheresis • High tumor burden • Peripheral WBC – Ineffective WBC < 100, 000 • Poor/unstable WBC-RBC interface – Patient factors (eg. High retic, cryoglobulins) – Access / alarms – Slow rates
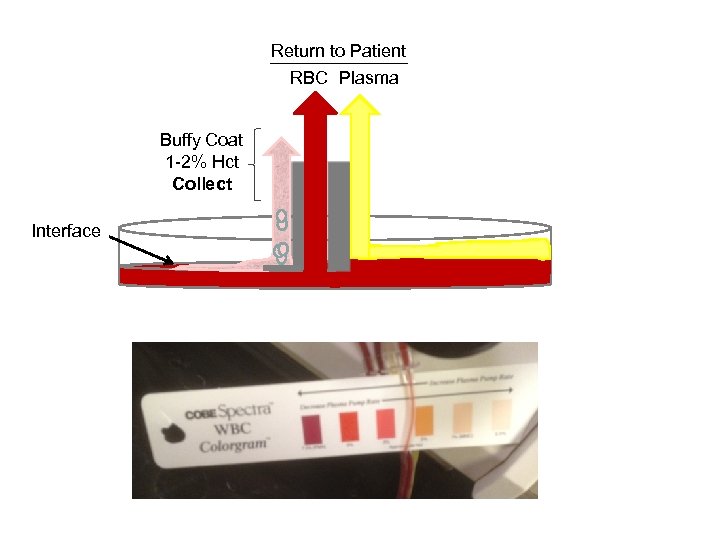 Return to Patient RBC Plasma Buffy Coat 1 -2% Hct Collect Interface
Return to Patient RBC Plasma Buffy Coat 1 -2% Hct Collect Interface
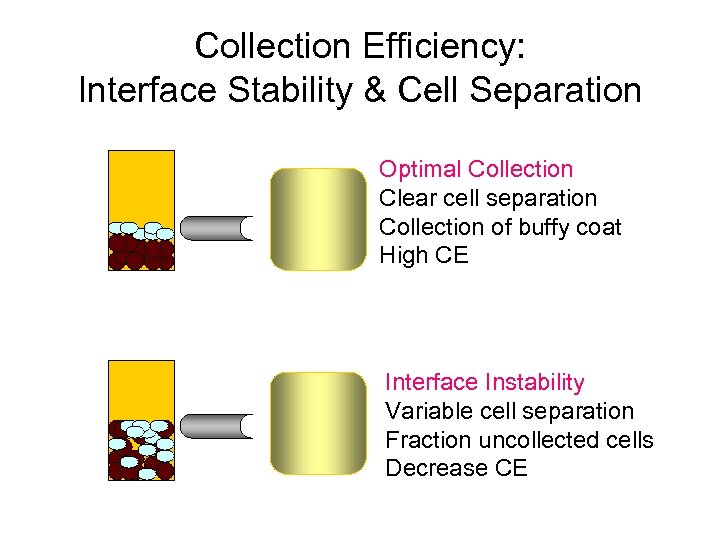 Collection Efficiency: Interface Stability & Cell Separation Optimal Collection Clear cell separation Collection of buffy coat High CE Interface Instability Variable cell separation Fraction uncollected cells Decrease CE
Collection Efficiency: Interface Stability & Cell Separation Optimal Collection Clear cell separation Collection of buffy coat High CE Interface Instability Variable cell separation Fraction uncollected cells Decrease CE
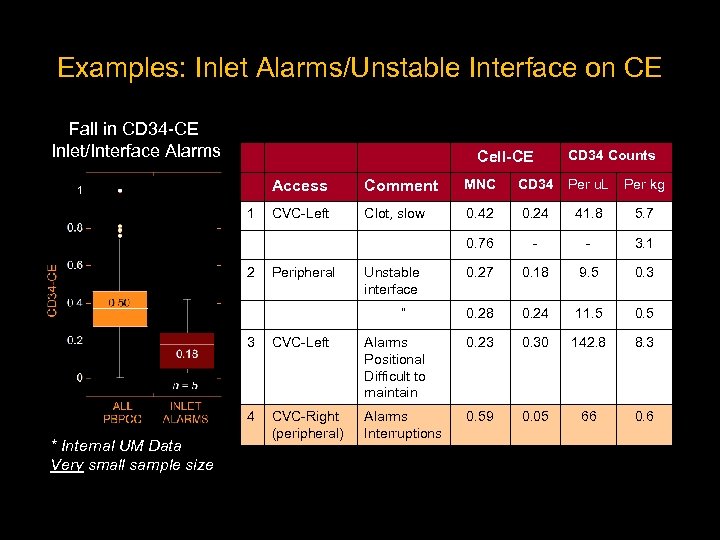 Examples: Inlet Alarms/Unstable Interface on CE Fall in CD 34 -CE Inlet/Interface Alarms Cell-CE CD 34 Counts Access 2 MNC CD 34 Per u. L Per kg CVC-Left Clot, slow 0. 42 0. 24 41. 8 5. 7 0. 76 1 Comment - - 3. 1 0. 27 0. 18 9. 5 0. 3 0. 28 0. 24 11. 5 0. 5 Peripheral Unstable interface “ 3 Alarms Positional Difficult to maintain 0. 23 0. 30 142. 8 8. 3 4 * Internal UM Data Very small sample size CVC-Left CVC-Right (peripheral) Alarms Interruptions 0. 59 0. 05 66 0. 6
Examples: Inlet Alarms/Unstable Interface on CE Fall in CD 34 -CE Inlet/Interface Alarms Cell-CE CD 34 Counts Access 2 MNC CD 34 Per u. L Per kg CVC-Left Clot, slow 0. 42 0. 24 41. 8 5. 7 0. 76 1 Comment - - 3. 1 0. 27 0. 18 9. 5 0. 3 0. 28 0. 24 11. 5 0. 5 Peripheral Unstable interface “ 3 Alarms Positional Difficult to maintain 0. 23 0. 30 142. 8 8. 3 4 * Internal UM Data Very small sample size CVC-Left CVC-Right (peripheral) Alarms Interruptions 0. 59 0. 05 66 0. 6
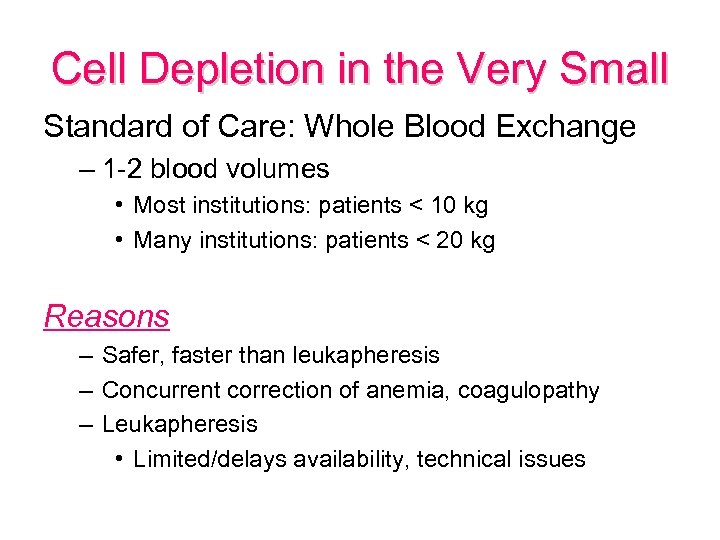 Cell Depletion in the Very Small Standard of Care: Whole Blood Exchange – 1 -2 blood volumes • Most institutions: patients < 10 kg • Many institutions: patients < 20 kg Reasons – Safer, faster than leukapheresis – Concurrent correction of anemia, coagulopathy – Leukapheresis • Limited/delays availability, technical issues
Cell Depletion in the Very Small Standard of Care: Whole Blood Exchange – 1 -2 blood volumes • Most institutions: patients < 10 kg • Many institutions: patients < 20 kg Reasons – Safer, faster than leukapheresis – Concurrent correction of anemia, coagulopathy – Leukapheresis • Limited/delays availability, technical issues
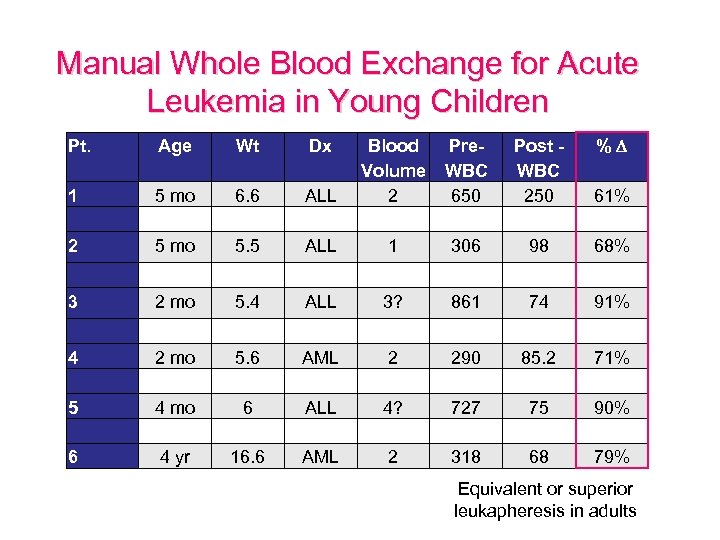 Manual Whole Blood Exchange for Acute Leukemia in Young Children Pt. Age Wt Dx Blood Pre. Volume WBC 2 650 1 306 1 2 5 mo 6. 6 5. 5 ALL 3 2 mo 5. 4 ALL 3? 4 5 6 2 mo 4 yr 5. 6 6 16. 6 AML ALL AML 2 4? 2 Post WBC 250 98 % 61% 68% 861 74 91% 290 727 318 85. 2 75 68 71% 90% 79% Equivalent or superior leukapheresis in adults
Manual Whole Blood Exchange for Acute Leukemia in Young Children Pt. Age Wt Dx Blood Pre. Volume WBC 2 650 1 306 1 2 5 mo 6. 6 5. 5 ALL 3 2 mo 5. 4 ALL 3? 4 5 6 2 mo 4 yr 5. 6 6 16. 6 AML ALL AML 2 4? 2 Post WBC 250 98 % 61% 68% 861 74 91% 290 727 318 85. 2 75 68 71% 90% 79% Equivalent or superior leukapheresis in adults
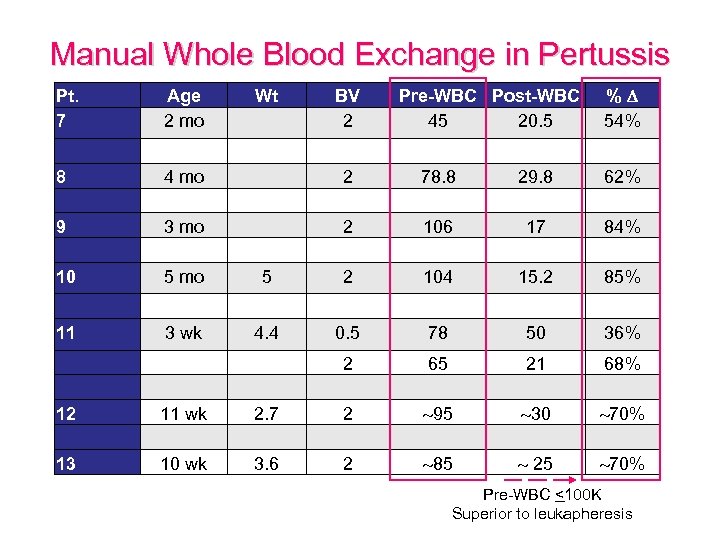 Manual Whole Blood Exchange in Pertussis Pt. 7 Age 2 mo Wt BV 2 Pre-WBC Post-WBC 45 20. 5 % 54% 8 9 10 4 mo 3 mo 5 2 2 2 78. 8 106 104 29. 8 17 15. 2 62% 84% 85% 11 3 wk 4. 4 0. 5 78 50 36% 12 13 11 wk 10 wk 2. 7 3. 6 2 2 2 65 95 85 21 30 25 68% 70% Pre-WBC <100 K Superior to leukapheresis
Manual Whole Blood Exchange in Pertussis Pt. 7 Age 2 mo Wt BV 2 Pre-WBC Post-WBC 45 20. 5 % 54% 8 9 10 4 mo 3 mo 5 2 2 2 78. 8 106 104 29. 8 17 15. 2 62% 84% 85% 11 3 wk 4. 4 0. 5 78 50 36% 12 13 11 wk 10 wk 2. 7 3. 6 2 2 2 65 95 85 21 30 25 68% 70% Pre-WBC <100 K Superior to leukapheresis
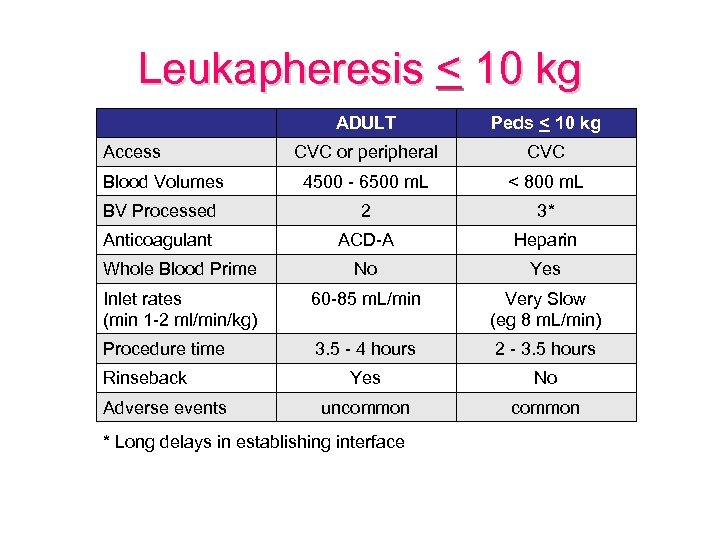 Leukapheresis < 10 kg ADULT Peds < 10 kg CVC or peripheral CVC Blood Volumes 4500 - 6500 m. L < 800 m. L BV Processed 2 3* Anticoagulant ACD-A Heparin Whole Blood Prime No Yes Inlet rates (min 1 -2 ml/min/kg) 60 -85 m. L/min Very Slow (eg 8 m. L/min) Procedure time 3. 5 - 4 hours 2 - 3. 5 hours Yes No uncommon Access Rinseback Adverse events * Long delays in establishing interface
Leukapheresis < 10 kg ADULT Peds < 10 kg CVC or peripheral CVC Blood Volumes 4500 - 6500 m. L < 800 m. L BV Processed 2 3* Anticoagulant ACD-A Heparin Whole Blood Prime No Yes Inlet rates (min 1 -2 ml/min/kg) 60 -85 m. L/min Very Slow (eg 8 m. L/min) Procedure time 3. 5 - 4 hours 2 - 3. 5 hours Yes No uncommon Access Rinseback Adverse events * Long delays in establishing interface
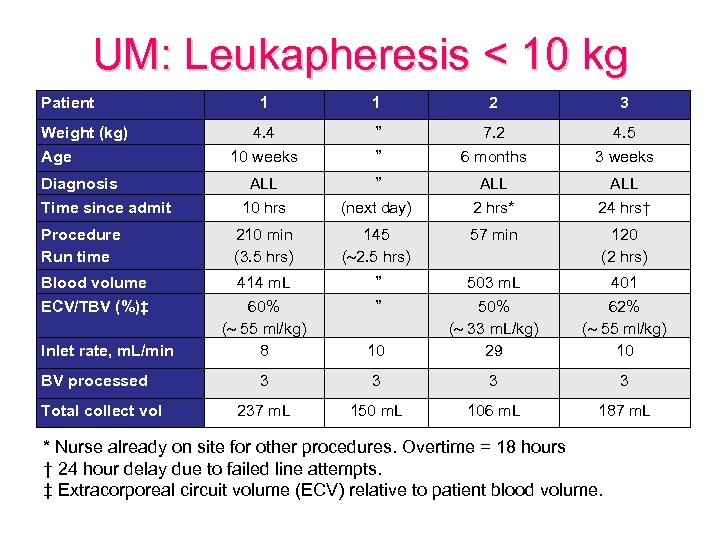 UM: Leukapheresis < 10 kg Patient Weight (kg) Age Diagnosis Time since admit Procedure Run time Blood volume ECV/TBV (%)‡ Inlet rate, m. L/min BV processed Total collect vol 1 1 2 3 4. 4 ” 7. 2 4. 5 10 weeks ” 6 months 3 weeks ALL 10 hrs ” (next day) ALL 2 hrs* ALL 24 hrs† 210 min (3. 5 hrs) 145 ( 2. 5 hrs) 57 min 120 (2 hrs) 414 m. L 60% ( 55 ml/kg) 8 ” ” 10 503 m. L 50% ( 33 m. L/kg) 29 401 62% ( 55 ml/kg) 10 3 3 237 m. L 150 m. L 106 m. L 187 m. L * Nurse already on site for other procedures. Overtime = 18 hours † 24 hour delay due to failed line attempts. ‡ Extracorporeal circuit volume (ECV) relative to patient blood volume.
UM: Leukapheresis < 10 kg Patient Weight (kg) Age Diagnosis Time since admit Procedure Run time Blood volume ECV/TBV (%)‡ Inlet rate, m. L/min BV processed Total collect vol 1 1 2 3 4. 4 ” 7. 2 4. 5 10 weeks ” 6 months 3 weeks ALL 10 hrs ” (next day) ALL 2 hrs* ALL 24 hrs† 210 min (3. 5 hrs) 145 ( 2. 5 hrs) 57 min 120 (2 hrs) 414 m. L 60% ( 55 ml/kg) 8 ” ” 10 503 m. L 50% ( 33 m. L/kg) 29 401 62% ( 55 ml/kg) 10 3 3 237 m. L 150 m. L 106 m. L 187 m. L * Nurse already on site for other procedures. Overtime = 18 hours † 24 hour delay due to failed line attempts. ‡ Extracorporeal circuit volume (ECV) relative to patient blood volume.
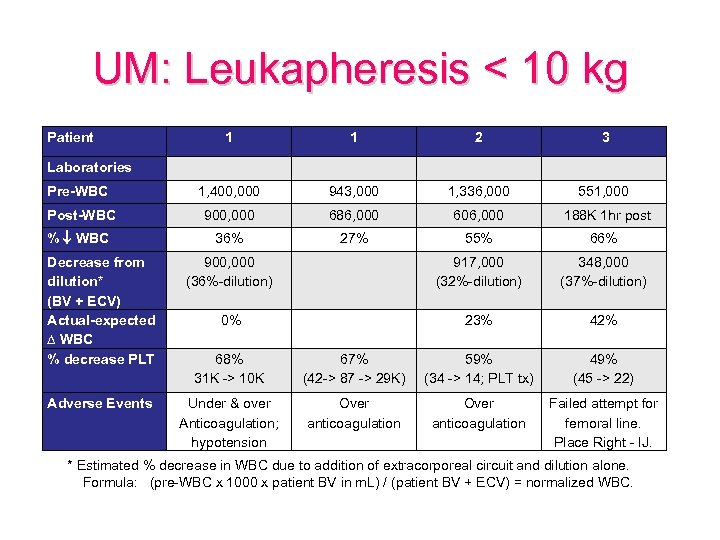 UM: Leukapheresis < 10 kg Patient 1 1 2 3 Laboratories Pre-WBC 1, 400, 000 943, 000 1, 336, 000 551, 000 Post-WBC 900, 000 686, 000 606, 000 188 K 1 hr post % WBC 36% 27% 55% 66% Decrease from dilution* (BV + ECV) Actual-expected ∆ WBC % decrease PLT 900, 000 (36%-dilution) 917, 000 (32%-dilution) 348, 000 (37%-dilution) 0% 23% 42% 68% 31 K -> 10 K 67% (42 -> 87 -> 29 K) 59% (34 -> 14; PLT tx) 49% (45 -> 22) Adverse Events Under & over Anticoagulation; hypotension Over anticoagulation Failed attempt for femoral line. Place Right - IJ. * Estimated % decrease in WBC due to addition of extracorporeal circuit and dilution alone. Formula: (pre-WBC x 1000 x patient BV in m. L) / (patient BV + ECV) = normalized WBC.
UM: Leukapheresis < 10 kg Patient 1 1 2 3 Laboratories Pre-WBC 1, 400, 000 943, 000 1, 336, 000 551, 000 Post-WBC 900, 000 686, 000 606, 000 188 K 1 hr post % WBC 36% 27% 55% 66% Decrease from dilution* (BV + ECV) Actual-expected ∆ WBC % decrease PLT 900, 000 (36%-dilution) 917, 000 (32%-dilution) 348, 000 (37%-dilution) 0% 23% 42% 68% 31 K -> 10 K 67% (42 -> 87 -> 29 K) 59% (34 -> 14; PLT tx) 49% (45 -> 22) Adverse Events Under & over Anticoagulation; hypotension Over anticoagulation Failed attempt for femoral line. Place Right - IJ. * Estimated % decrease in WBC due to addition of extracorporeal circuit and dilution alone. Formula: (pre-WBC x 1000 x patient BV in m. L) / (patient BV + ECV) = normalized WBC.
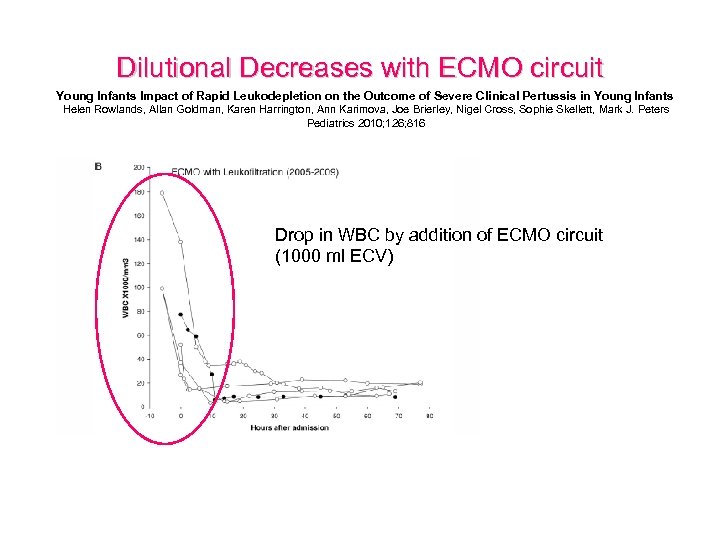 Dilutional Decreases with ECMO circuit Young Infants Impact of Rapid Leukodepletion on the Outcome of Severe Clinical Pertussis in Young Infants Helen Rowlands, Allan Goldman, Karen Harrington, Ann Karimova, Joe Brierley, Nigel Cross, Sophie Skellett, Mark J. Peters Pediatrics 2010; 126; 816 Drop in WBC by addition of ECMO circuit (1000 ml ECV)
Dilutional Decreases with ECMO circuit Young Infants Impact of Rapid Leukodepletion on the Outcome of Severe Clinical Pertussis in Young Infants Helen Rowlands, Allan Goldman, Karen Harrington, Ann Karimova, Joe Brierley, Nigel Cross, Sophie Skellett, Mark J. Peters Pediatrics 2010; 126; 816 Drop in WBC by addition of ECMO circuit (1000 ml ECV)
 The Experiment Mock Leukapheresis 4. 5 kg “neonate” Hct = 15% Measures: • Time to interface/collect • Hematocrit – WB Prime – Return line (machine) – Access line (infant) – ‘Product’
The Experiment Mock Leukapheresis 4. 5 kg “neonate” Hct = 15% Measures: • Time to interface/collect • Hematocrit – WB Prime – Return line (machine) – Access line (infant) – ‘Product’
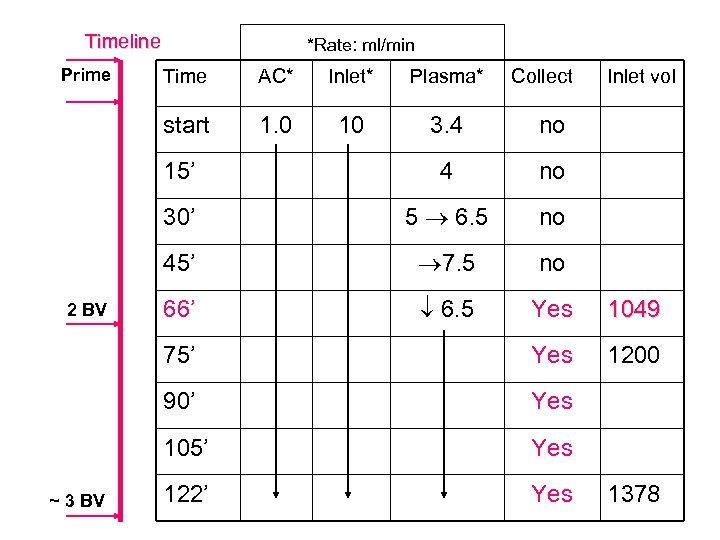 Timeline Prime *Rate: ml/min Inlet* Plasma* 1. 0 10 3. 4 no 15’ 4 no 30’ 5 6. 5 no 45’ 7. 5 no 66’ 6. 5 Yes 1049 75’ Yes 1200 90’ Yes 105’ ~ 3 BV AC* start 2 BV Time Collect Inlet vol Yes 122’ Yes 1378
Timeline Prime *Rate: ml/min Inlet* Plasma* 1. 0 10 3. 4 no 15’ 4 no 30’ 5 6. 5 no 45’ 7. 5 no 66’ 6. 5 Yes 1049 75’ Yes 1200 90’ Yes 105’ ~ 3 BV AC* start 2 BV Time Collect Inlet vol Yes 122’ Yes 1378
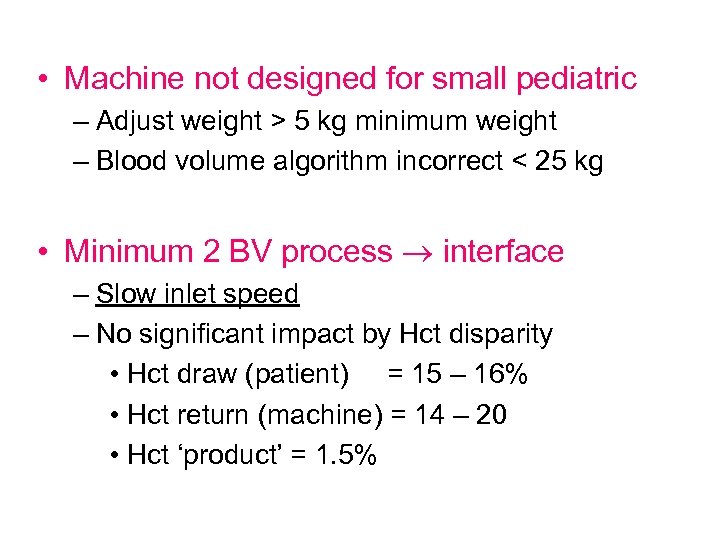 • Machine not designed for small pediatric – Adjust weight > 5 kg minimum weight – Blood volume algorithm incorrect < 25 kg • Minimum 2 BV process interface – Slow inlet speed – No significant impact by Hct disparity • Hct draw (patient) = 15 – 16% • Hct return (machine) = 14 – 20 • Hct ‘product’ = 1. 5%
• Machine not designed for small pediatric – Adjust weight > 5 kg minimum weight – Blood volume algorithm incorrect < 25 kg • Minimum 2 BV process interface – Slow inlet speed – No significant impact by Hct disparity • Hct draw (patient) = 15 – 16% • Hct return (machine) = 14 – 20 • Hct ‘product’ = 1. 5%
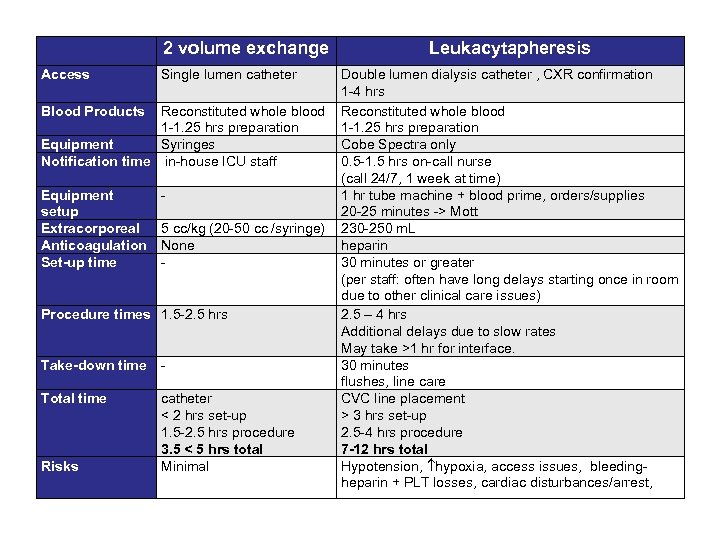 2 volume exchange Access Single lumen catheter Leukacytapheresis Double lumen dialysis catheter , CXR confirmation 1 -4 hrs Blood Products Reconstituted whole blood 1 -1. 25 hrs preparation Equipment Syringes Cobe Spectra only Notification time in-house ICU staff 0. 5 -1. 5 hrs on-call nurse (call 24/7, 1 week at time) Equipment 1 hr tube machine + blood prime, orders/supplies setup 20 -25 minutes -> Mott Extracorporeal 5 cc/kg (20 -50 cc /syringe) 230 -250 m. L Anticoagulation None heparin Set-up time 30 minutes or greater (per staff: often have long delays starting once in room due to other clinical care issues) Procedure times 1. 5 -2. 5 hrs 2. 5 – 4 hrs Additional delays due to slow rates May take >1 hr for interface. Take-down time 30 minutes flushes, line care Total time catheter CVC line placement < 2 hrs set-up > 3 hrs set-up 1. 5 -2. 5 hrs procedure 2. 5 -4 hrs procedure 3. 5 < 5 hrs total 7 -12 hrs total Risks Minimal Hypotension, hypoxia, access issues, bleedingheparin + PLT losses, cardiac disturbances/arrest,
2 volume exchange Access Single lumen catheter Leukacytapheresis Double lumen dialysis catheter , CXR confirmation 1 -4 hrs Blood Products Reconstituted whole blood 1 -1. 25 hrs preparation Equipment Syringes Cobe Spectra only Notification time in-house ICU staff 0. 5 -1. 5 hrs on-call nurse (call 24/7, 1 week at time) Equipment 1 hr tube machine + blood prime, orders/supplies setup 20 -25 minutes -> Mott Extracorporeal 5 cc/kg (20 -50 cc /syringe) 230 -250 m. L Anticoagulation None heparin Set-up time 30 minutes or greater (per staff: often have long delays starting once in room due to other clinical care issues) Procedure times 1. 5 -2. 5 hrs 2. 5 – 4 hrs Additional delays due to slow rates May take >1 hr for interface. Take-down time 30 minutes flushes, line care Total time catheter CVC line placement < 2 hrs set-up > 3 hrs set-up 1. 5 -2. 5 hrs procedure 2. 5 -4 hrs procedure 3. 5 < 5 hrs total 7 -12 hrs total Risks Minimal Hypotension, hypoxia, access issues, bleedingheparin + PLT losses, cardiac disturbances/arrest,
 Summary • < 10 kg – Cell depletions should be done by WBEx • 10 – 15 kg – Gray area, WBEx may be preferable Going Forward • Protocol for WBEx • Responsibility and training
Summary • < 10 kg – Cell depletions should be done by WBEx • 10 – 15 kg – Gray area, WBEx may be preferable Going Forward • Protocol for WBEx • Responsibility and training


