ffb96e150f98aae33c695037d51b8acf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 CEd. MA Toolset 2004 ROI in Training Norman Buckberry Chairman CEd. MA Europe www. cedma-europe. org 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
CEd. MA Toolset 2004 ROI in Training Norman Buckberry Chairman CEd. MA Europe www. cedma-europe. org 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 ROI Contents • • • Purpose of ROI, and Value of training What is ROI Why ROI Methodology Toolkit 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
ROI Contents • • • Purpose of ROI, and Value of training What is ROI Why ROI Methodology Toolkit 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 The Value of Training • Training consumes resources, but: • It is critical to maximising the value gained from an IT project • It adds value throughout the lifecycle of any IT investment • Training needs to be included early in the decision making cycle if it is to be really successful • ROI techniques can be used to help you to: • understand justify the need to invest properly and comprehensively in training • present the comparative benefits of different approaches to training 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
The Value of Training • Training consumes resources, but: • It is critical to maximising the value gained from an IT project • It adds value throughout the lifecycle of any IT investment • Training needs to be included early in the decision making cycle if it is to be really successful • ROI techniques can be used to help you to: • understand justify the need to invest properly and comprehensively in training • present the comparative benefits of different approaches to training 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 The Value of Human Capital • We all know Human Capital (and its development) is vital • Human Capital is often much undervalued as an investment opportunity • ROI can be very high • Phillips refers to 800% being achievable regularly • Tennessee Valley authority claim 1000%+ • A world-class corporate university claimed 5, 612% 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
The Value of Human Capital • We all know Human Capital (and its development) is vital • Human Capital is often much undervalued as an investment opportunity • ROI can be very high • Phillips refers to 800% being achievable regularly • Tennessee Valley authority claim 1000%+ • A world-class corporate university claimed 5, 612% 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Inhibitors to ROI measurement • Typical inhibitors to carrying out an ROI exercise • Fear of a negative ROI, and the implications this might entail • Reluctance to commit the necessary budget to carrying out the exercise • The fact that this process takes time, and only really demonstrates results some months, or even longer, after the completion of the training • But ROI measurement can provide some valuable returns • • 2/5/2004 Measuring contribution of HRD Setting priorities Focusing on results Altering management’s appreciation and perceptions of training CEd. MA Europe
Inhibitors to ROI measurement • Typical inhibitors to carrying out an ROI exercise • Fear of a negative ROI, and the implications this might entail • Reluctance to commit the necessary budget to carrying out the exercise • The fact that this process takes time, and only really demonstrates results some months, or even longer, after the completion of the training • But ROI measurement can provide some valuable returns • • 2/5/2004 Measuring contribution of HRD Setting priorities Focusing on results Altering management’s appreciation and perceptions of training CEd. MA Europe
 “ROI on Upgrade” example • ROI comes from a number of sources during a typical upgrade exercise: • The user and the organisation increase productivity purely from use of new and enhanced functionality in the hardware and software or better performance of the application or system. • Reducing as much as possible the time taken to achieve these benefits, and achieving further increases in productivity due to training on the use of the new functionality (compared to the productivity the users might experience without the training). • Avoiding or minimising a negative productivity impact due to the typical decrease in productivity during the early days or weeks of using new software (as people have to learn new and changed facilities in order to regain their previous level of performance) 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
“ROI on Upgrade” example • ROI comes from a number of sources during a typical upgrade exercise: • The user and the organisation increase productivity purely from use of new and enhanced functionality in the hardware and software or better performance of the application or system. • Reducing as much as possible the time taken to achieve these benefits, and achieving further increases in productivity due to training on the use of the new functionality (compared to the productivity the users might experience without the training). • Avoiding or minimising a negative productivity impact due to the typical decrease in productivity during the early days or weeks of using new software (as people have to learn new and changed facilities in order to regain their previous level of performance) 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Why ROI? • Pressure on training functions to show demonstrable return • • Value for money from training activity Value of HRD to the business; e. g. • Financial benefits • Staff productivity • Staff retention Clear alignment with corporate goals In-house vs outsourced training • ROI analysis is a tool to support the contention that training is valuable; demonstrate benefits vs cost • Pressure to reduce costs must be balanced by visibility of benefit • 2/5/2004 “Warm and fuzzy” is no longer any good! (in most cases) • Jay Cross alternative view CEd. MA Europe
Why ROI? • Pressure on training functions to show demonstrable return • • Value for money from training activity Value of HRD to the business; e. g. • Financial benefits • Staff productivity • Staff retention Clear alignment with corporate goals In-house vs outsourced training • ROI analysis is a tool to support the contention that training is valuable; demonstrate benefits vs cost • Pressure to reduce costs must be balanced by visibility of benefit • 2/5/2004 “Warm and fuzzy” is no longer any good! (in most cases) • Jay Cross alternative view CEd. MA Europe
 ROI as Process • Use evaluation techniques to acquire performance data • Use Training Needs Analysis to direct the project to the right data • Use analytical techniques to calculate ROI from the data • Use ROI results to review training effectiveness • Use the reviews to inform future decisions 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
ROI as Process • Use evaluation techniques to acquire performance data • Use Training Needs Analysis to direct the project to the right data • Use analytical techniques to calculate ROI from the data • Use ROI results to review training effectiveness • Use the reviews to inform future decisions 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 ROI as Perception • Which of these perceptions indicate your client’s view of ROI (which you need to address)? • The Board may see a big picture of how the training affects the company’s ability to achieve its corporate goals • The finance department may be looking to see how training stacks up financially against other ways to invest the company’s money, and whether the training, as carried out, was financially more effective than alternative forms of development • The business unit manager may be solely concerned with the impact on performance and productivity in achieving the goals of their department • The training and development manager may be concerned with the impact training programmes are having on the credibility and status as the training function within the company and its ability to secure investment in the future to drive further business performance enhancements 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
ROI as Perception • Which of these perceptions indicate your client’s view of ROI (which you need to address)? • The Board may see a big picture of how the training affects the company’s ability to achieve its corporate goals • The finance department may be looking to see how training stacks up financially against other ways to invest the company’s money, and whether the training, as carried out, was financially more effective than alternative forms of development • The business unit manager may be solely concerned with the impact on performance and productivity in achieving the goals of their department • The training and development manager may be concerned with the impact training programmes are having on the credibility and status as the training function within the company and its ability to secure investment in the future to drive further business performance enhancements 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 What is ROI? • Elements of “Total ROI” • Reducing costs • Increasing benefits/performance/capability • Use of ROI • ROI of a training project’s contribution to business or project • ROI of one delivery method vs. another (e. g. ILT vs. e-learning) • Role of ROI • Pre-training assessment and expectation setting • Post-training feedback • Post-experience value measurement 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
What is ROI? • Elements of “Total ROI” • Reducing costs • Increasing benefits/performance/capability • Use of ROI • ROI of a training project’s contribution to business or project • ROI of one delivery method vs. another (e. g. ILT vs. e-learning) • Role of ROI • Pre-training assessment and expectation setting • Post-training feedback • Post-experience value measurement 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
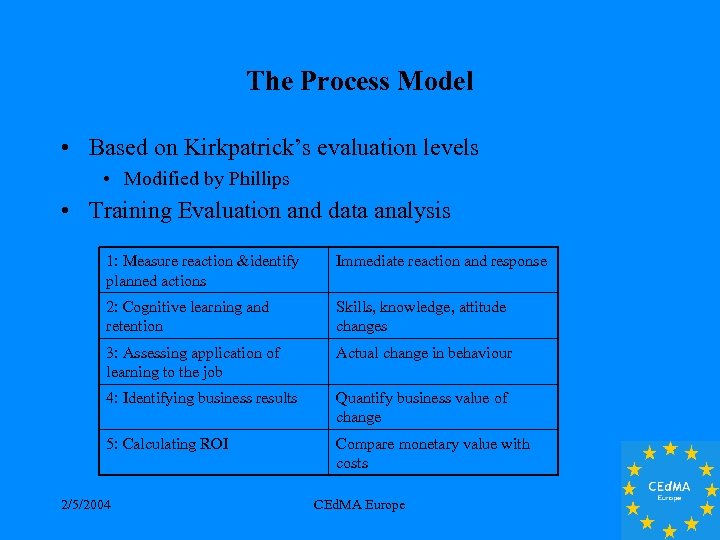 The Process Model • Based on Kirkpatrick’s evaluation levels • Modified by Phillips • Training Evaluation and data analysis 1: Measure reaction &identify planned actions Immediate reaction and response 2: Cognitive learning and retention Skills, knowledge, attitude changes 3: Assessing application of learning to the job Actual change in behaviour 4: Identifying business results Quantify business value of change 5: Calculating ROI Compare monetary value with costs 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
The Process Model • Based on Kirkpatrick’s evaluation levels • Modified by Phillips • Training Evaluation and data analysis 1: Measure reaction &identify planned actions Immediate reaction and response 2: Cognitive learning and retention Skills, knowledge, attitude changes 3: Assessing application of learning to the job Actual change in behaviour 4: Identifying business results Quantify business value of change 5: Calculating ROI Compare monetary value with costs 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Criteria for effective ROI measurement • The ROI measurement must be simple and easily understandable. • The ROI process must be economical to implement. • The assumptions, methodology and techniques must be credible, logical, methodical and practical. • The ROI process must be theoretically sound, without being overcomplex. • The ROI process must account for other factors, which can influence the measured outcomes after training. • The ROI process must be appropriate in the context of other HRD programs. • The ROI process must be flexible enough to be applied pre and post training. • The ROI process must be applicable with all types of data collected. • The ROI process must include the costs of the training and measurement program. 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
Criteria for effective ROI measurement • The ROI measurement must be simple and easily understandable. • The ROI process must be economical to implement. • The assumptions, methodology and techniques must be credible, logical, methodical and practical. • The ROI process must be theoretically sound, without being overcomplex. • The ROI process must account for other factors, which can influence the measured outcomes after training. • The ROI process must be appropriate in the context of other HRD programs. • The ROI process must be flexible enough to be applied pre and post training. • The ROI process must be applicable with all types of data collected. • The ROI process must include the costs of the training and measurement program. 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Getting Started • Select your project to measure • Select a significant project; align with significant goals • Start with a project that has clearly definable metrics • ROI measurement Plan • Data Collection Plan • Identify the “returns” • Identify the investment factors • Select the survey audiences and sources of data • Select your data collection methods • 2/5/2004 Analysis Plan CEd. MA Europe
Getting Started • Select your project to measure • Select a significant project; align with significant goals • Start with a project that has clearly definable metrics • ROI measurement Plan • Data Collection Plan • Identify the “returns” • Identify the investment factors • Select the survey audiences and sources of data • Select your data collection methods • 2/5/2004 Analysis Plan CEd. MA Europe
 Identifying Returns • Cost savings (reductions in costs incurred for a given result) • Cost savings (business benefits from time saved and resources redeployed) • New opportunities made possible • Benefits can be hard to quantify (but these are often the most valuable • Competitive advantage • Improved customer satisfaction • Company image 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
Identifying Returns • Cost savings (reductions in costs incurred for a given result) • Cost savings (business benefits from time saved and resources redeployed) • New opportunities made possible • Benefits can be hard to quantify (but these are often the most valuable • Competitive advantage • Improved customer satisfaction • Company image 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Investment Factors • Costs incurred • • • 2/5/2004 Payments to suppliers and service providers Time and attention to create and deliver the training Opportunity cost Time and costs involved in the ROI measurement exercise Other Internal costs CEd. MA Europe
Investment Factors • Costs incurred • • • 2/5/2004 Payments to suppliers and service providers Time and attention to create and deliver the training Opportunity cost Time and costs involved in the ROI measurement exercise Other Internal costs CEd. MA Europe
 Process Summary – Data Collection Plan • Data collected at different times to provide: • Pre-training baseline • Post-training change analysis • Post-experience change analysis • Data Collection Plan • State the objectives of the training / learning • State the objectives of each phase of data collection at each evaluation Level • Identify any previously used metrics, values or methodologies used by the client, and determine suitability for the current exercise • Select the appropriate evaluation methods • Identify the audiences who will be surveyed for data • Set the timing for the data collection • Allocate responsibilities for data collection and analysis 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
Process Summary – Data Collection Plan • Data collected at different times to provide: • Pre-training baseline • Post-training change analysis • Post-experience change analysis • Data Collection Plan • State the objectives of the training / learning • State the objectives of each phase of data collection at each evaluation Level • Identify any previously used metrics, values or methodologies used by the client, and determine suitability for the current exercise • Select the appropriate evaluation methods • Identify the audiences who will be surveyed for data • Set the timing for the data collection • Allocate responsibilities for data collection and analysis 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Process Summary – ROI Analysis Plan • Continuation of the Data Collection Plan, capturing information on the key items needed to develop the actual ROI calculation. • List Significant Data items (usually Level 4 or 3) to be collected • • 2/5/2004 Benefit Factors Cost Factors Methods to isolate effects of the learning/training from other influences Methods to convert data to numerical values Intangible benefits Other influences Communication targets CEd. MA Europe
Process Summary – ROI Analysis Plan • Continuation of the Data Collection Plan, capturing information on the key items needed to develop the actual ROI calculation. • List Significant Data items (usually Level 4 or 3) to be collected • • 2/5/2004 Benefit Factors Cost Factors Methods to isolate effects of the learning/training from other influences Methods to convert data to numerical values Intangible benefits Other influences Communication targets CEd. MA Europe
 Process Summary – Data Collection • Identify the purposes of the evaluation. • • • Select the evaluation instruments and methodology. Establish the timing for the data collection. • • State clearly what the evaluations are to measure and what the goals of the training are intended to be. Be as specific as possible about the goals of the training Ensure goals address the performance enhancement, business improvement or cost savings expectations. Decide whether pre-training analysis is required, or post training analysis, or both. (e. g. pre-training and multiple post-training assessments may be necessary to effectively identify the skills changes in Levels 2, 3 and 4. ) Carry out the data collection at the levels 1 -4 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
Process Summary – Data Collection • Identify the purposes of the evaluation. • • • Select the evaluation instruments and methodology. Establish the timing for the data collection. • • State clearly what the evaluations are to measure and what the goals of the training are intended to be. Be as specific as possible about the goals of the training Ensure goals address the performance enhancement, business improvement or cost savings expectations. Decide whether pre-training analysis is required, or post training analysis, or both. (e. g. pre-training and multiple post-training assessments may be necessary to effectively identify the skills changes in Levels 2, 3 and 4. ) Carry out the data collection at the levels 1 -4 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Process Summary – Sources of Data • Organisational Performance Records, showing outputs and measurements taken as part of the business’ normal reporting process • Testing and certification assessment records • Participant feedback • Instructor feedback • Feedback from participants’ supervisors/managers • Feedback from participants’ subordinates • Team/group peer feedback • Feedback from other internal or external groups (eg HR training departments) 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
Process Summary – Sources of Data • Organisational Performance Records, showing outputs and measurements taken as part of the business’ normal reporting process • Testing and certification assessment records • Participant feedback • Instructor feedback • Feedback from participants’ supervisors/managers • Feedback from participants’ subordinates • Team/group peer feedback • Feedback from other internal or external groups (eg HR training departments) 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Process Summary – Evaluation Methods • • • Identify how the data will be collected analysed Surveys On the job Observation Interviews Focus groups Action plans (or Performance contracts) and Program assignments • Performance data monitoring 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
Process Summary – Evaluation Methods • • • Identify how the data will be collected analysed Surveys On the job Observation Interviews Focus groups Action plans (or Performance contracts) and Program assignments • Performance data monitoring 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Process Summary – Isolate effects of training • Separate training (personal productivity) component of performance change, from new software/systems/processes • Essential for credibility • Potential methods • Use control groups • Impact assessments and estimates by participants, managers, peers • Trend lines • Discount/adjust for over-estimates • Apply “inflation adjustment” for estimates and assessments 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
Process Summary – Isolate effects of training • Separate training (personal productivity) component of performance change, from new software/systems/processes • Essential for credibility • Potential methods • Use control groups • Impact assessments and estimates by participants, managers, peers • Trend lines • Discount/adjust for over-estimates • Apply “inflation adjustment” for estimates and assessments 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
 Process Summary – Convert to money • Convert data to monetary value • • • 2/5/2004 Specific costs and time incurred Costs and time saved Quality increase, reduced waste Improved customer service and satisfaction “Intangible” benefits (retention, commitment, fewer complaints, reduced conflicts etc) CEd. MA Europe
Process Summary – Convert to money • Convert data to monetary value • • • 2/5/2004 Specific costs and time incurred Costs and time saved Quality increase, reduced waste Improved customer service and satisfaction “Intangible” benefits (retention, commitment, fewer complaints, reduced conflicts etc) CEd. MA Europe
 Process Summary - ROI • Calculate ROI • Benefit-cost ratio=Program Benefits Program Costs • ROI % = Net Program Benefits Program Costs • Break-even time = Investment Benefit 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe x 100 x Period in months
Process Summary - ROI • Calculate ROI • Benefit-cost ratio=Program Benefits Program Costs • ROI % = Net Program Benefits Program Costs • Break-even time = Investment Benefit 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe x 100 x Period in months
 ROI Tools • ROI Overview and process summary • Powerpoint presentation • ROI calculator • Worksheets 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe
ROI Tools • ROI Overview and process summary • Powerpoint presentation • ROI calculator • Worksheets 2/5/2004 CEd. MA Europe


