cc584cb0c3a227587cca14bd6de9ad3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 88
 CE-01: 1 Efaproxiral (RSR 13) as an Adjunct to Whole Brain Radiation Therapy for the Treatment of Brain Metastases Originating from Breast Cancer Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting May 3, 2004
CE-01: 1 Efaproxiral (RSR 13) as an Adjunct to Whole Brain Radiation Therapy for the Treatment of Brain Metastases Originating from Breast Cancer Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting May 3, 2004
 CE-01: 2 RSR 13 Introduction Pablo J. Cagnoni, MD Vice President, Clinical Development Allos Therapeutics
CE-01: 2 RSR 13 Introduction Pablo J. Cagnoni, MD Vice President, Clinical Development Allos Therapeutics
 CE-01: 3 Agenda § Introduction Pablo J. Cagnoni, MD § Brain Metastases John H. Suh, MD § Science of RSR 13 Brian D. Kavanagh, MD § Clinical Efficacy Pablo J. Cagnoni, MD § Clinical Safety Pablo J. Cagnoni, MD § Conclusions Paul A. Bunn, Jr, MD
CE-01: 3 Agenda § Introduction Pablo J. Cagnoni, MD § Brain Metastases John H. Suh, MD § Science of RSR 13 Brian D. Kavanagh, MD § Clinical Efficacy Pablo J. Cagnoni, MD § Clinical Safety Pablo J. Cagnoni, MD § Conclusions Paul A. Bunn, Jr, MD
 CE-01: 4 Experts Available for Q&A § Paul A. Bunn, Jr, MD, Director, University of Colorado Cancer Center § Walter J. Curran Jr, MD, Group Chairman, Radiation Therapy Oncology Group § Anthony D. Elias, MD, Medical Director, Breast Cancer Program, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center
CE-01: 4 Experts Available for Q&A § Paul A. Bunn, Jr, MD, Director, University of Colorado Cancer Center § Walter J. Curran Jr, MD, Group Chairman, Radiation Therapy Oncology Group § Anthony D. Elias, MD, Medical Director, Breast Cancer Program, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center
 CE-01: 5 Experts Available for Q&A (cont. ) § Henry Friedman, MD, Director, James B. Powell Professor of Neuro-oncology, Brain Tumor Center Duke University Medical Center § Marc Gastonguay, Ph. D, Clinical Pharmacology Consultant § Charles Scott, Ph. D, Biostatistics, CBS Squared § Baldassarre D. Stea, MD, Ph. D, Chairman, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Arizona Health Sciences Center
CE-01: 5 Experts Available for Q&A (cont. ) § Henry Friedman, MD, Director, James B. Powell Professor of Neuro-oncology, Brain Tumor Center Duke University Medical Center § Marc Gastonguay, Ph. D, Clinical Pharmacology Consultant § Charles Scott, Ph. D, Biostatistics, CBS Squared § Baldassarre D. Stea, MD, Ph. D, Chairman, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Arizona Health Sciences Center
 CE-01: 6 Experts Available from Allos Therapeutics § Adam P. Boyd, Biostatistics § John O. Hackman, Biostatistics § Markus F. Herzig, Regulatory Affairs § Doug G. Johnson, Ph. D, CMC § Carrie L. Kass, Pharm. D, Clinical Safety § Robert P. Steffen, Ph. D, Pharmacology and Toxicology § Michael E. Saunders, MD, Clinical Development
CE-01: 6 Experts Available from Allos Therapeutics § Adam P. Boyd, Biostatistics § John O. Hackman, Biostatistics § Markus F. Herzig, Regulatory Affairs § Doug G. Johnson, Ph. D, CMC § Carrie L. Kass, Pharm. D, Clinical Safety § Robert P. Steffen, Ph. D, Pharmacology and Toxicology § Michael E. Saunders, MD, Clinical Development
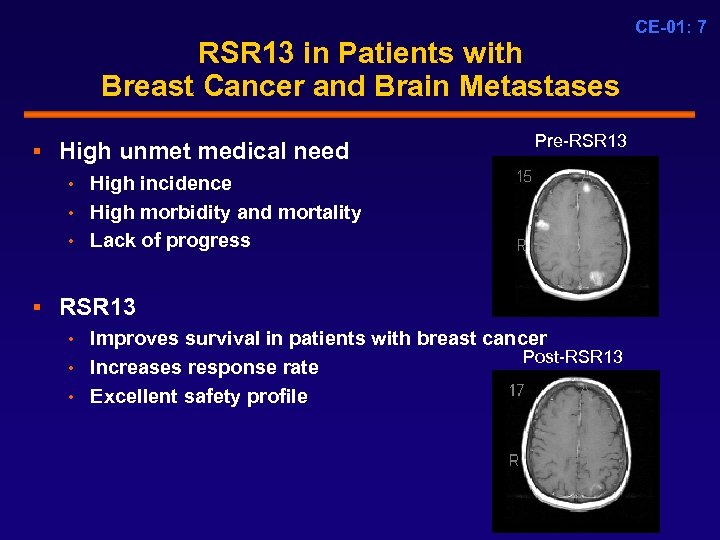 RSR 13 in Patients with Breast Cancer and Brain Metastases § High unmet medical need • High incidence • High morbidity and mortality • Lack of progress Pre-RSR 13 § RSR 13 • Improves survival in patients with breast cancer Post-RSR 13 • Increases response rate • Excellent safety profile CE-01: 7
RSR 13 in Patients with Breast Cancer and Brain Metastases § High unmet medical need • High incidence • High morbidity and mortality • Lack of progress Pre-RSR 13 § RSR 13 • Improves survival in patients with breast cancer Post-RSR 13 • Increases response rate • Excellent safety profile CE-01: 7
 CE-01: 8 Proposed Indication and Dosage RSR 13 is indicated as an adjunct to whole brain radiation for the treatment of brain metastases originating from breast cancer RSR 13 75 -100 mg/kg/d IV over 30 minutes with supplemental oxygen immediately prior to each of 10 fractions of whole brain radiation therapy
CE-01: 8 Proposed Indication and Dosage RSR 13 is indicated as an adjunct to whole brain radiation for the treatment of brain metastases originating from breast cancer RSR 13 75 -100 mg/kg/d IV over 30 minutes with supplemental oxygen immediately prior to each of 10 fractions of whole brain radiation therapy
 CE-01: 9 Brain Metastases John H. Suh, MD Clinical Director of Radiation Oncology Director, Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Center Brain Tumor Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio
CE-01: 9 Brain Metastases John H. Suh, MD Clinical Director of Radiation Oncology Director, Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Center Brain Tumor Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio
 CE-01: 10 Brain Metastases Incidence on the Rise § 170, 000 cancer patients develop brain metastases annually in the United States § 20 -40% of cancer patients develop brain metastases § Incidence is rising due to: • Longer survival resulting from earlier diagnosis • Better systemic therapy for extracranial disease • Improved neuroimaging techniques contribute to higher detection rate Nussbaum et al. Cancer. 1996; 78: 1781 -1788; Posner JB Neurologic complications of cancer: 1995.
CE-01: 10 Brain Metastases Incidence on the Rise § 170, 000 cancer patients develop brain metastases annually in the United States § 20 -40% of cancer patients develop brain metastases § Incidence is rising due to: • Longer survival resulting from earlier diagnosis • Better systemic therapy for extracranial disease • Improved neuroimaging techniques contribute to higher detection rate Nussbaum et al. Cancer. 1996; 78: 1781 -1788; Posner JB Neurologic complications of cancer: 1995.
 Brain Metastases in Patients With Breast Cancer CE-01: 11 § Up to 35, 000 patients per year § Afflicts younger patients (median age 53) § Systemic agents have benefit for extracranial disease § Current treatment strategies provide limited benefit More effective treatment options are needed
Brain Metastases in Patients With Breast Cancer CE-01: 11 § Up to 35, 000 patients per year § Afflicts younger patients (median age 53) § Systemic agents have benefit for extracranial disease § Current treatment strategies provide limited benefit More effective treatment options are needed
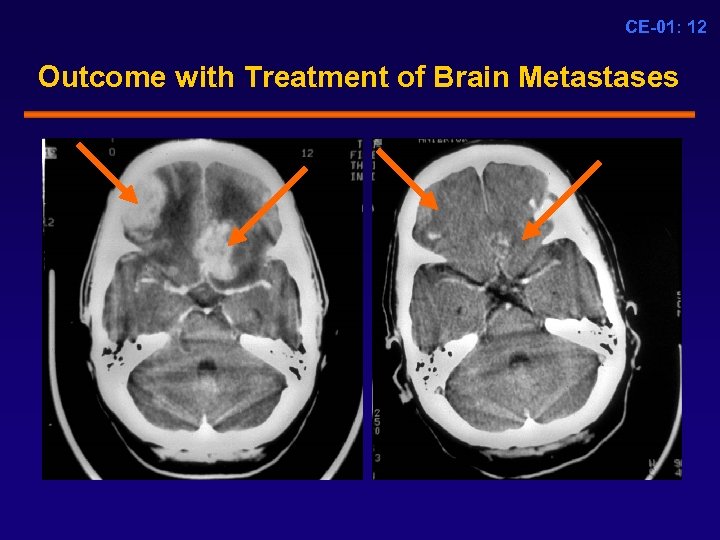 CE-01: 12 Outcome with Treatment of Brain Metastases
CE-01: 12 Outcome with Treatment of Brain Metastases
 CE-01: 13 Current Management of Patients With Brain Metastases § Steroids (eg. dexamethasone) § Anticonvulsant medication (symptom control) § Surgical resection (single) § Stereotactic radiosurgery (single) § Chemotherapy (limited use) § Whole brain radiation therapy (gold standard)
CE-01: 13 Current Management of Patients With Brain Metastases § Steroids (eg. dexamethasone) § Anticonvulsant medication (symptom control) § Surgical resection (single) § Stereotactic radiosurgery (single) § Chemotherapy (limited use) § Whole brain radiation therapy (gold standard)
 CE-01: 14 Whole Brain Radiation Therapy (WBRT) § Improves survival (approximately 4. 5 months) § Improves/stabilizes neurologic function § Standard dosing scheme: 30 Gy in 10 fractions § No benefit to altered fractionation schemes
CE-01: 14 Whole Brain Radiation Therapy (WBRT) § Improves survival (approximately 4. 5 months) § Improves/stabilizes neurologic function § Standard dosing scheme: 30 Gy in 10 fractions § No benefit to altered fractionation schemes
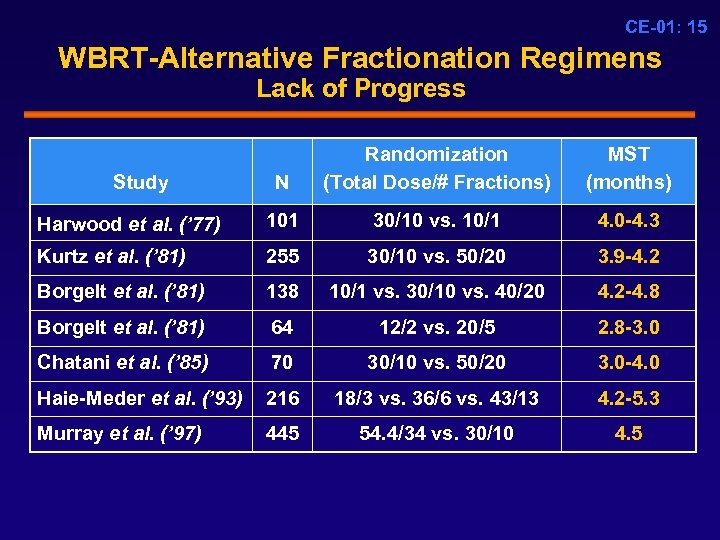 CE-01: 15 WBRT-Alternative Fractionation Regimens Lack of Progress N Randomization (Total Dose/# Fractions) MST (months) Harwood et al. (’ 77) 101 30/10 vs. 10/1 4. 0 -4. 3 Kurtz et al. (’ 81) 255 30/10 vs. 50/20 3. 9 -4. 2 Borgelt et al. (’ 81) 138 10/1 vs. 30/10 vs. 40/20 4. 2 -4. 8 Borgelt et al. (’ 81) 64 12/2 vs. 20/5 2. 8 -3. 0 Chatani et al. (’ 85) 70 30/10 vs. 50/20 3. 0 -4. 0 Haie-Meder et al. (’ 93) 216 18/3 vs. 36/6 vs. 43/13 4. 2 -5. 3 Murray et al. (’ 97) 445 54. 4/34 vs. 30/10 4. 5 Study
CE-01: 15 WBRT-Alternative Fractionation Regimens Lack of Progress N Randomization (Total Dose/# Fractions) MST (months) Harwood et al. (’ 77) 101 30/10 vs. 10/1 4. 0 -4. 3 Kurtz et al. (’ 81) 255 30/10 vs. 50/20 3. 9 -4. 2 Borgelt et al. (’ 81) 138 10/1 vs. 30/10 vs. 40/20 4. 2 -4. 8 Borgelt et al. (’ 81) 64 12/2 vs. 20/5 2. 8 -3. 0 Chatani et al. (’ 85) 70 30/10 vs. 50/20 3. 0 -4. 0 Haie-Meder et al. (’ 93) 216 18/3 vs. 36/6 vs. 43/13 4. 2 -5. 3 Murray et al. (’ 97) 445 54. 4/34 vs. 30/10 4. 5 Study
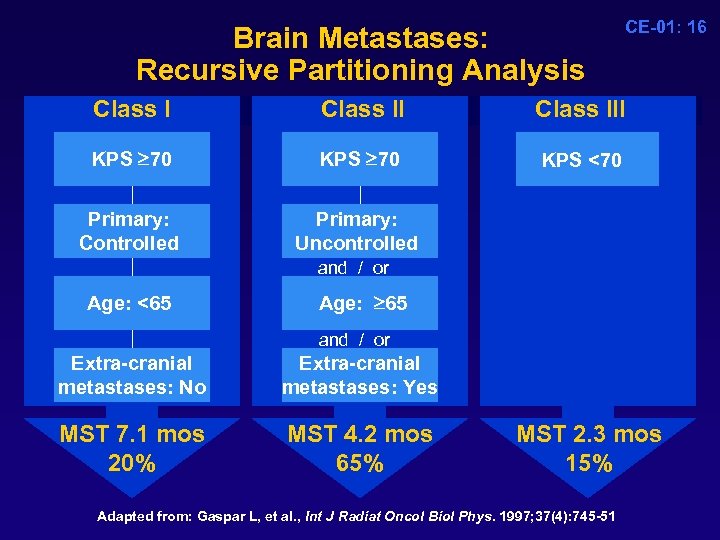 Brain Metastases: Recursive Partitioning Analysis Class II KPS 70 KPS 70 Primary: Controlled CE-01: 16 Class III KPS <70 KPS 70 Primary: Uncontrolled and / or Age: <65 Age: 65 and / or Extra-cranial metastases: No Extra-cranial metastases: Yes MST 7. 1 mos 20% MST 4. 2 mos 65% MST 2. 3 mos 15% Adapted from: Gaspar L, et al. , Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997; 37(4): 745 -51
Brain Metastases: Recursive Partitioning Analysis Class II KPS 70 KPS 70 Primary: Controlled CE-01: 16 Class III KPS <70 KPS 70 Primary: Uncontrolled and / or Age: <65 Age: 65 and / or Extra-cranial metastases: No Extra-cranial metastases: Yes MST 7. 1 mos 20% MST 4. 2 mos 65% MST 2. 3 mos 15% Adapted from: Gaspar L, et al. , Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997; 37(4): 745 -51
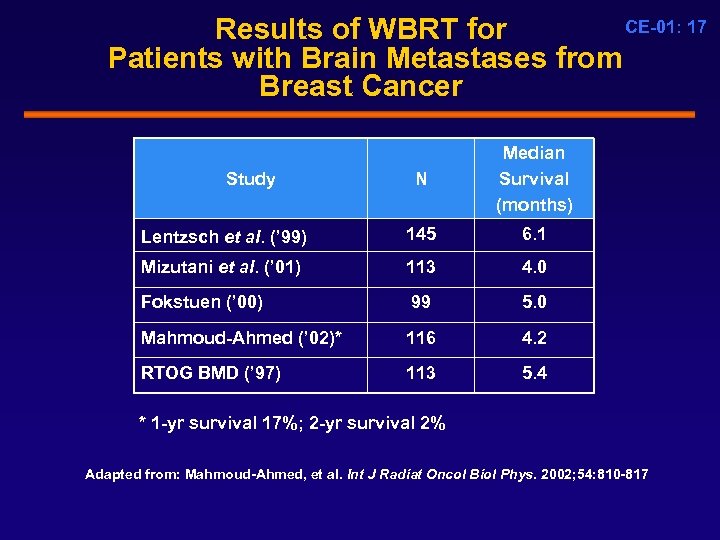 CE-01: 17 Results of WBRT for Patients with Brain Metastases from Breast Cancer N Median Survival (months) Lentzsch et al. (’ 99) 145 6. 1 Mizutani et al. (’ 01) 113 4. 0 Fokstuen (’ 00) 99 5. 0 Mahmoud-Ahmed (’ 02)* 116 4. 2 RTOG BMD (’ 97) 113 5. 4 Study * 1 -yr survival 17%; 2 -yr survival 2% Adapted from: Mahmoud-Ahmed, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 54: 810 -817
CE-01: 17 Results of WBRT for Patients with Brain Metastases from Breast Cancer N Median Survival (months) Lentzsch et al. (’ 99) 145 6. 1 Mizutani et al. (’ 01) 113 4. 0 Fokstuen (’ 00) 99 5. 0 Mahmoud-Ahmed (’ 02)* 116 4. 2 RTOG BMD (’ 97) 113 5. 4 Study * 1 -yr survival 17%; 2 -yr survival 2% Adapted from: Mahmoud-Ahmed, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 54: 810 -817
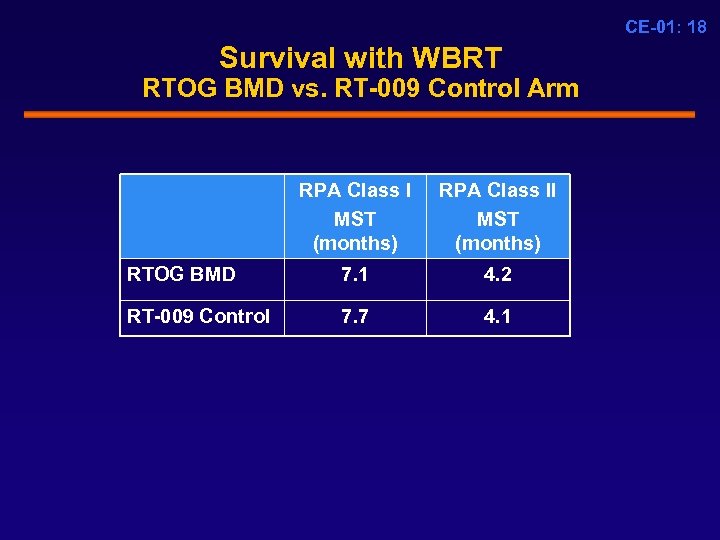 CE-01: 18 Survival with WBRT RTOG BMD vs. RT-009 Control Arm RPA Class I MST (months) RPA Class II MST (months) RTOG BMD 7. 1 4. 2 RT-009 Control 7. 7 4. 1
CE-01: 18 Survival with WBRT RTOG BMD vs. RT-009 Control Arm RPA Class I MST (months) RPA Class II MST (months) RTOG BMD 7. 1 4. 2 RT-009 Control 7. 7 4. 1
 CE-01: 19 Conclusions § Brain metastases from breast cancer are common § Current treatment options yield poor results § Treatment options are available for extra-cranial metastases § Compelling need for more effective treatment options
CE-01: 19 Conclusions § Brain metastases from breast cancer are common § Current treatment options yield poor results § Treatment options are available for extra-cranial metastases § Compelling need for more effective treatment options
 CE-01: 20 The Science of RSR 13 Drug Design Rationale, Mechanism of Action, and Initial Translation into the Clinic Brian D. Kavanagh, MD, MPH Vice-Chairman Department of Radiation Oncology University of Colorado Comprehensive Cancer Center
CE-01: 20 The Science of RSR 13 Drug Design Rationale, Mechanism of Action, and Initial Translation into the Clinic Brian D. Kavanagh, MD, MPH Vice-Chairman Department of Radiation Oncology University of Colorado Comprehensive Cancer Center
 CE-01: 21 The Science of RSR 13 § The clinical problem of tumor hypoxia § RSR 13 drug design rationale § RSR 13 -mediated tumor oxygenation § Translation into the clinic
CE-01: 21 The Science of RSR 13 § The clinical problem of tumor hypoxia § RSR 13 drug design rationale § RSR 13 -mediated tumor oxygenation § Translation into the clinic
 CE-01: 22 Oxygen is the Most Efficient Radiosensitizer § The cytotoxicity of radiation is increased by a factor of 3 or more in the presence of O 2 § O 2 enhances radiation-induced DNA damage by increasing the half-life of toxic free radicals § Hypoxic regions of low p. O 2 exist in all solid tumors § Clinical measurements of tumor hypoxia correlate with lower tumor control rates after radiotherarpy
CE-01: 22 Oxygen is the Most Efficient Radiosensitizer § The cytotoxicity of radiation is increased by a factor of 3 or more in the presence of O 2 § O 2 enhances radiation-induced DNA damage by increasing the half-life of toxic free radicals § Hypoxic regions of low p. O 2 exist in all solid tumors § Clinical measurements of tumor hypoxia correlate with lower tumor control rates after radiotherarpy
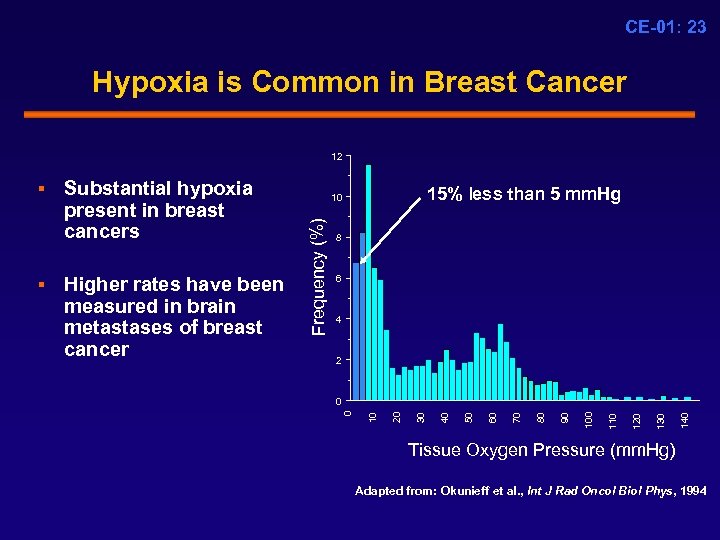 CE-01: 23 Hypoxia is Common in Breast Cancer 12 8 6 4 2 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 0 30 0 20 Higher rates have been measured in brain metastases of breast cancer 15% less than 5 mm. Hg 10 10 § Substantial hypoxia present in breast cancers Frequency (%) § Tissue Oxygen Pressure (mm. Hg) Adapted from: Okunieff et al. , Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys, 1994
CE-01: 23 Hypoxia is Common in Breast Cancer 12 8 6 4 2 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 0 30 0 20 Higher rates have been measured in brain metastases of breast cancer 15% less than 5 mm. Hg 10 10 § Substantial hypoxia present in breast cancers Frequency (%) § Tissue Oxygen Pressure (mm. Hg) Adapted from: Okunieff et al. , Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys, 1994
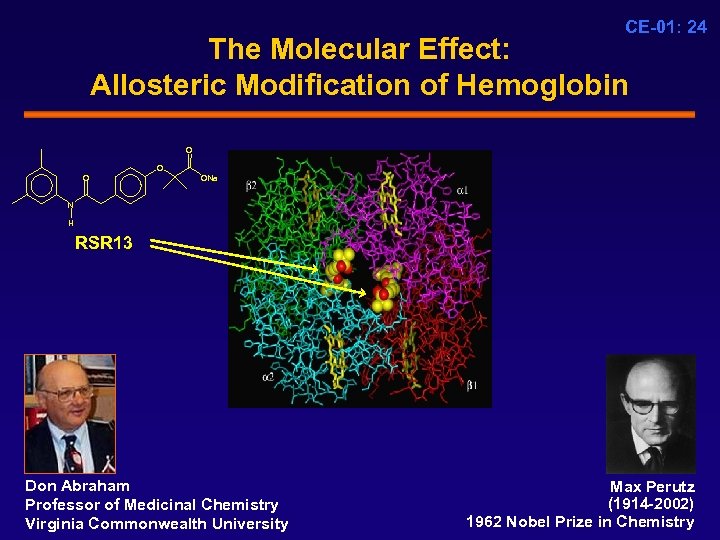 CE-01: 24 The Molecular Effect: Allosteric Modification of Hemoglobin O ONa N H RSR 13 Don Abraham Professor of Medicinal Chemistry Virginia Commonwealth University Max Perutz (1914 -2002) 1962 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
CE-01: 24 The Molecular Effect: Allosteric Modification of Hemoglobin O ONa N H RSR 13 Don Abraham Professor of Medicinal Chemistry Virginia Commonwealth University Max Perutz (1914 -2002) 1962 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
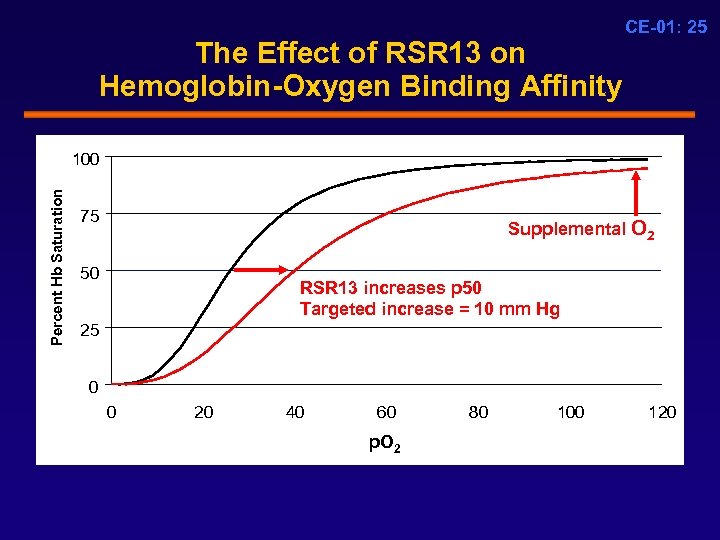 The Effect of RSR 13 on Hemoglobin-Oxygen Binding Affinity CE-01: 25 Percent Hb Saturation 100 75 Supplemental O 2 50 RSR 13 increases p 50 Targeted increase = 10 mm Hg 25 0 0 20 40 60 p. O 2 80 100 120
The Effect of RSR 13 on Hemoglobin-Oxygen Binding Affinity CE-01: 25 Percent Hb Saturation 100 75 Supplemental O 2 50 RSR 13 increases p 50 Targeted increase = 10 mm Hg 25 0 0 20 40 60 p. O 2 80 100 120
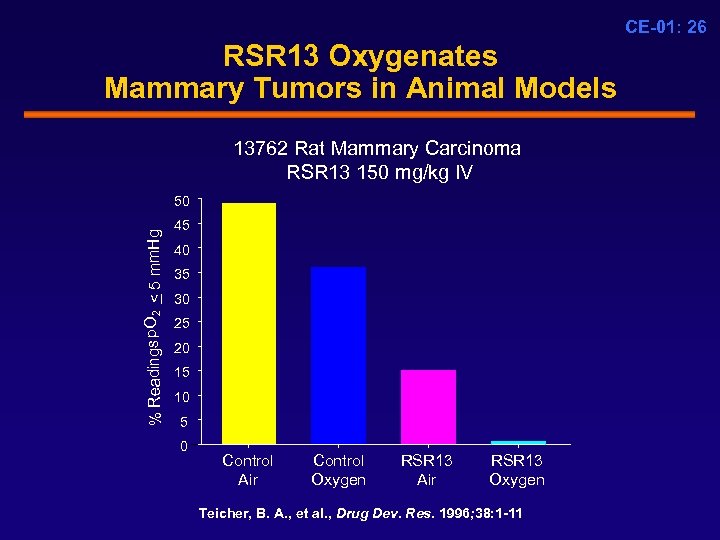 CE-01: 26 RSR 13 Oxygenates Mammary Tumors in Animal Models 13762 Rat Mammary Carcinoma RSR 13 150 mg/kg IV % Readings p. O 2 < 5 mm. Hg 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Control Air Control Oxygen RSR 13 Air RSR 13 Oxygen Teicher, B. A. , et al. , Drug Dev. Res. 1996; 38: 1 -11
CE-01: 26 RSR 13 Oxygenates Mammary Tumors in Animal Models 13762 Rat Mammary Carcinoma RSR 13 150 mg/kg IV % Readings p. O 2 < 5 mm. Hg 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Control Air Control Oxygen RSR 13 Air RSR 13 Oxygen Teicher, B. A. , et al. , Drug Dev. Res. 1996; 38: 1 -11
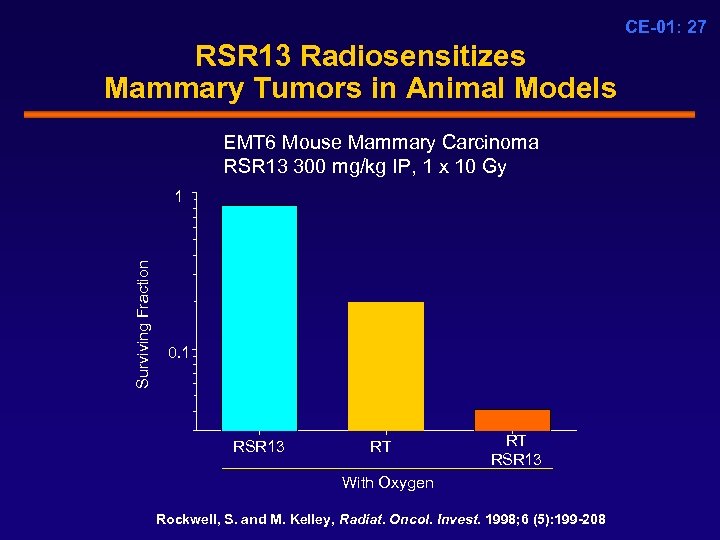 CE-01: 27 RSR 13 Radiosensitizes Mammary Tumors in Animal Models EMT 6 Mouse Mammary Carcinoma RSR 13 300 mg/kg IP, 1 x 10 Gy Surviving Fraction 1 0. 1 RSR 13 RT RT RSR 13 With Oxygen Rockwell, S. and M. Kelley, Radiat. Oncol. Invest. 1998; 6 (5): 199 -208
CE-01: 27 RSR 13 Radiosensitizes Mammary Tumors in Animal Models EMT 6 Mouse Mammary Carcinoma RSR 13 300 mg/kg IP, 1 x 10 Gy Surviving Fraction 1 0. 1 RSR 13 RT RT RSR 13 With Oxygen Rockwell, S. and M. Kelley, Radiat. Oncol. Invest. 1998; 6 (5): 199 -208
 CE-01: 28 Healthy Volunteer Study HV-001 § Targeted pharmacodynamic endpoint: • p 50 increase of 10 mm. Hg § Phase 1 Study, Single IV dose of RSR 13 • RSR 13: 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 mg/kg • N = 19 § Result: • an increase in p 50 of 10 mm. Hg was achieved consistently at a dose of 100 mg/kg
CE-01: 28 Healthy Volunteer Study HV-001 § Targeted pharmacodynamic endpoint: • p 50 increase of 10 mm. Hg § Phase 1 Study, Single IV dose of RSR 13 • RSR 13: 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 mg/kg • N = 19 § Result: • an increase in p 50 of 10 mm. Hg was achieved consistently at a dose of 100 mg/kg
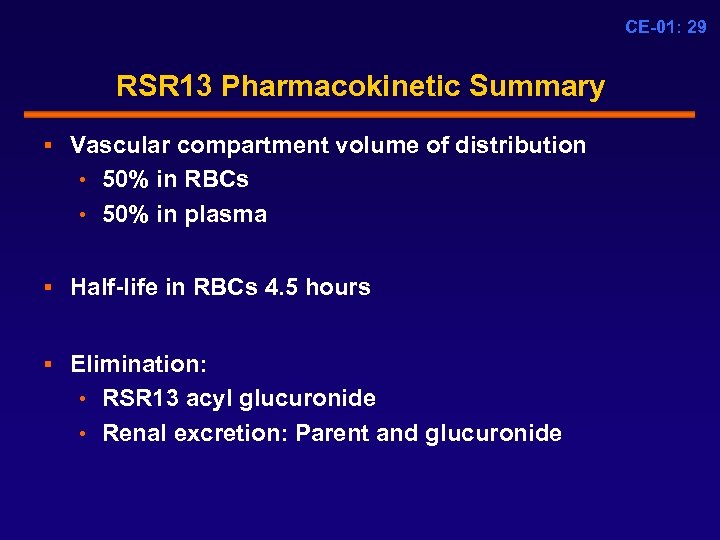 CE-01: 29 RSR 13 Pharmacokinetic Summary § Vascular compartment volume of distribution • 50% in RBCs • 50% in plasma § Half-life in RBCs 4. 5 hours § Elimination: • RSR 13 acyl glucuronide • Renal excretion: Parent and glucuronide
CE-01: 29 RSR 13 Pharmacokinetic Summary § Vascular compartment volume of distribution • 50% in RBCs • 50% in plasma § Half-life in RBCs 4. 5 hours § Elimination: • RSR 13 acyl glucuronide • Renal excretion: Parent and glucuronide
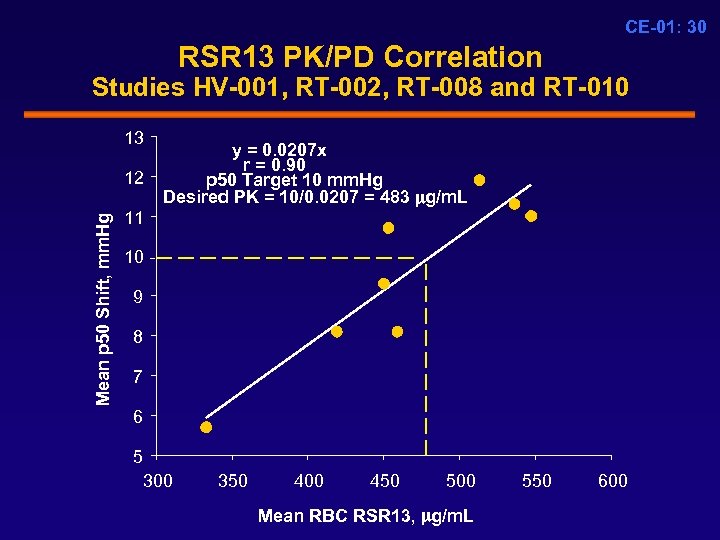 CE-01: 30 RSR 13 PK/PD Correlation Studies HV-001, RT-002, RT-008 and RT-010 13 Mean p 50 Shift, mm. Hg 12 y = 0. 0207 x r = 0. 90 p 50 Target 10 mm. Hg Desired PK = 10/0. 0207 = 483 g/m. L 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 300 350 400 450 500 Mean RBC RSR 13, g/m. L 550 600
CE-01: 30 RSR 13 PK/PD Correlation Studies HV-001, RT-002, RT-008 and RT-010 13 Mean p 50 Shift, mm. Hg 12 y = 0. 0207 x r = 0. 90 p 50 Target 10 mm. Hg Desired PK = 10/0. 0207 = 483 g/m. L 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 300 350 400 450 500 Mean RBC RSR 13, g/m. L 550 600
 CE-01: 31 Conclusions § Tumor hypoxia is associated with radioresistance § RSR 13 reduces tumor hypoxia and increases radiosensitivity § The pharmacodynamic effect of RSR 13 is quantified by the increase in p 50 § Linear correlation between RSR 13 RBC concentration and the p 50 increase § RSR 13 100 mg/kg selected for future study based on ability to induce desired p 50 increase
CE-01: 31 Conclusions § Tumor hypoxia is associated with radioresistance § RSR 13 reduces tumor hypoxia and increases radiosensitivity § The pharmacodynamic effect of RSR 13 is quantified by the increase in p 50 § Linear correlation between RSR 13 RBC concentration and the p 50 increase § RSR 13 100 mg/kg selected for future study based on ability to induce desired p 50 increase
 CE-01: 32 RSR 13 as Adjunct to WBRT Clinical Efficacy in Patients with Brain Metastases
CE-01: 32 RSR 13 as Adjunct to WBRT Clinical Efficacy in Patients with Brain Metastases
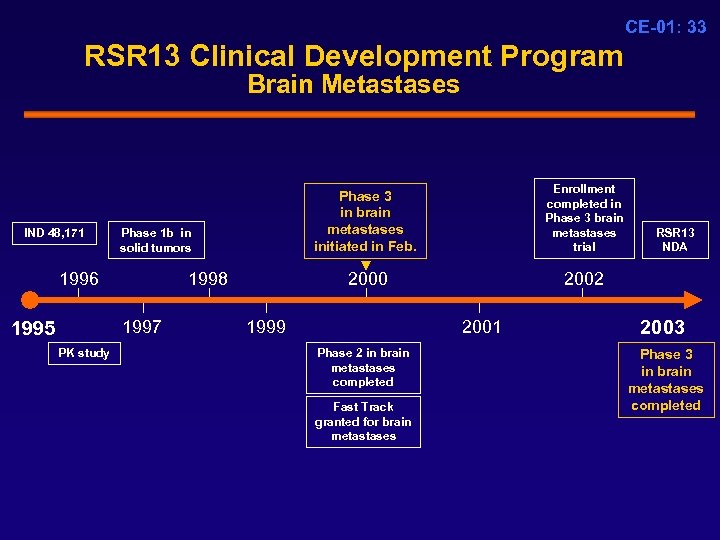 CE-01: 33 RSR 13 Clinical Development Program Brain Metastases IND 48, 171 Phase 1 b in solid tumors 1996 1998 1997 1995 PK study Enrollment completed in Phase 3 brain metastases trial Phase 3 in brain metastases initiated in Feb. 2000 1999 2002 2001 Phase 2 in brain metastases completed Fast Track granted for brain metastases RSR 13 NDA 2003 Phase 3 in brain metastases completed
CE-01: 33 RSR 13 Clinical Development Program Brain Metastases IND 48, 171 Phase 1 b in solid tumors 1996 1998 1997 1995 PK study Enrollment completed in Phase 3 brain metastases trial Phase 3 in brain metastases initiated in Feb. 2000 1999 2002 2001 Phase 2 in brain metastases completed Fast Track granted for brain metastases RSR 13 NDA 2003 Phase 3 in brain metastases completed
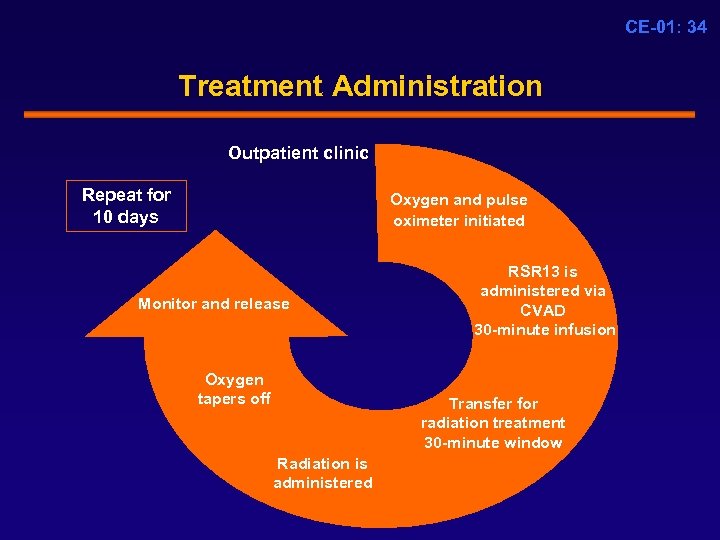 CE-01: 34 Treatment Administration Outpatient clinic Repeat for 10 days Oxygen and pulse oximeter initiated Monitor and release Oxygen tapers off RSR 13 is administered via CVAD 30 -minute infusion Transfer for radiation treatment 30 -minute window Radiation is administered
CE-01: 34 Treatment Administration Outpatient clinic Repeat for 10 days Oxygen and pulse oximeter initiated Monitor and release Oxygen tapers off RSR 13 is administered via CVAD 30 -minute infusion Transfer for radiation treatment 30 -minute window Radiation is administered
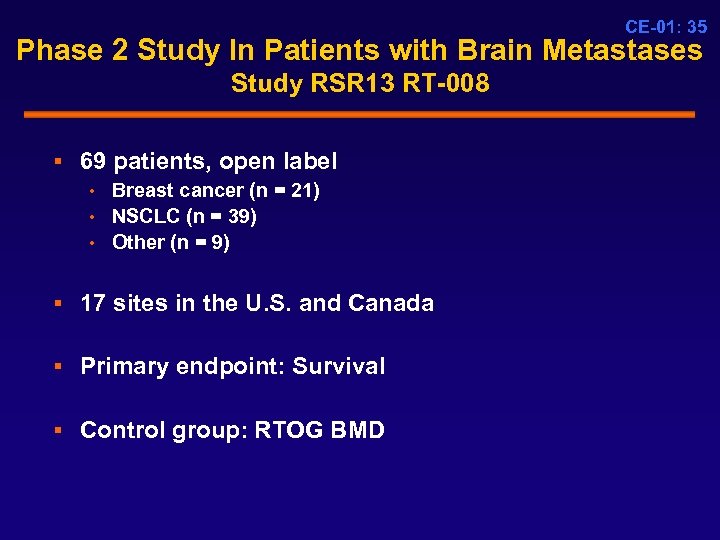 CE-01: 35 Phase 2 Study In Patients with Brain Metastases Study RSR 13 RT-008 § 69 patients, open label • Breast cancer (n = 21) • NSCLC (n = 39) • Other (n = 9) § 17 sites in the U. S. and Canada § Primary endpoint: Survival § Control group: RTOG BMD
CE-01: 35 Phase 2 Study In Patients with Brain Metastases Study RSR 13 RT-008 § 69 patients, open label • Breast cancer (n = 21) • NSCLC (n = 39) • Other (n = 9) § 17 sites in the U. S. and Canada § Primary endpoint: Survival § Control group: RTOG BMD
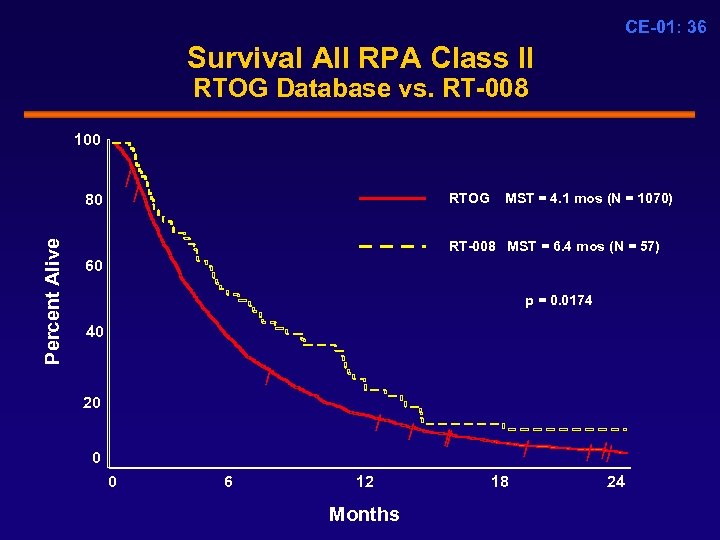 CE-01: 36 Survival All RPA Class II RTOG Database vs. RT-008 100 / Percent Alive 80 / RTOG MST = 4. 1 mos (N = 1070) RT-008 MST = 6. 4 mos (N = 57) 60 p = 0. 0174 40 / 20 / 0 0 6 12 Months / / / 18 / // 24
CE-01: 36 Survival All RPA Class II RTOG Database vs. RT-008 100 / Percent Alive 80 / RTOG MST = 4. 1 mos (N = 1070) RT-008 MST = 6. 4 mos (N = 57) 60 p = 0. 0174 40 / 20 / 0 0 6 12 Months / / / 18 / // 24
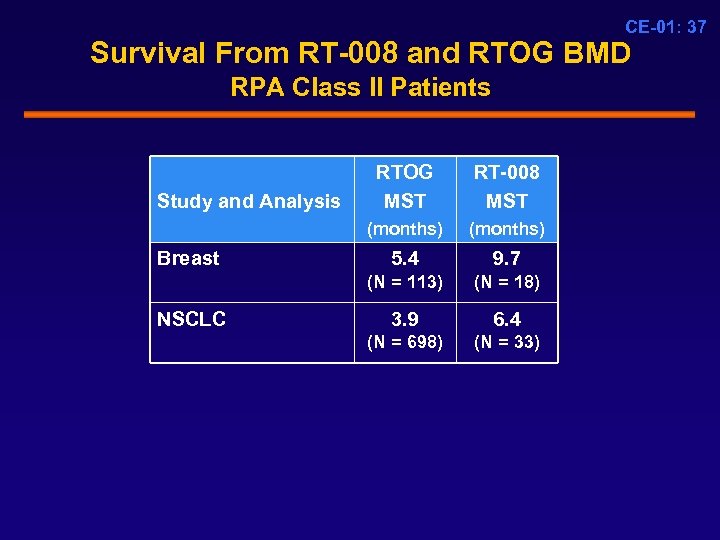 CE-01: 37 Survival From RT-008 and RTOG BMD RPA Class II Patients Breast RT-008 MST (months) Study and Analysis RTOG MST (months) 5. 4 9. 7 (N = 113) NSCLC (N = 18) 3. 9 6. 4 (N = 698) (N = 33)
CE-01: 37 Survival From RT-008 and RTOG BMD RPA Class II Patients Breast RT-008 MST (months) Study and Analysis RTOG MST (months) 5. 4 9. 7 (N = 113) NSCLC (N = 18) 3. 9 6. 4 (N = 698) (N = 33)
 CE-01: 38 Study RSR 13 RT- 009 A phase 3, randomized, open-label, comparative study of standard whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) with supplemental oxygen, with or without efaproxiral (RSR 13), in patients with brain metastases Study chairs: John H. Suh, MD; Cleveland Clinic Foundation Edward G. Shaw, MD; Wake Forest University
CE-01: 38 Study RSR 13 RT- 009 A phase 3, randomized, open-label, comparative study of standard whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) with supplemental oxygen, with or without efaproxiral (RSR 13), in patients with brain metastases Study chairs: John H. Suh, MD; Cleveland Clinic Foundation Edward G. Shaw, MD; Wake Forest University
 CE-01: 39 Key Eligibility Criteria § KPS 70 § Excluded histologies: SCLC, NHL, germ cell § No prior treatment for brain metastases (except surgery if only partial resection performed); prior and concurrent corticosteroids allowed § Adequate hematologic, renal, hepatic and pulmonary function § Resting and exercise Sp. O 2 90% on room air § No cytotoxic chemotherapy (within 7 days)
CE-01: 39 Key Eligibility Criteria § KPS 70 § Excluded histologies: SCLC, NHL, germ cell § No prior treatment for brain metastases (except surgery if only partial resection performed); prior and concurrent corticosteroids allowed § Adequate hematologic, renal, hepatic and pulmonary function § Resting and exercise Sp. O 2 90% on room air § No cytotoxic chemotherapy (within 7 days)
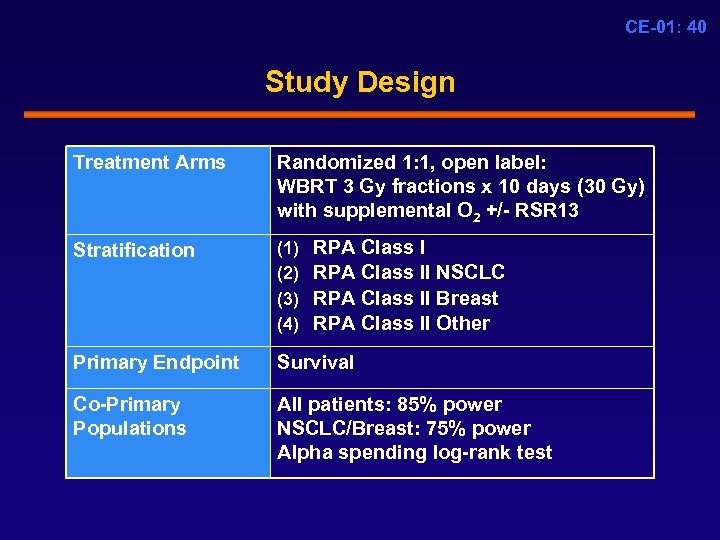 CE-01: 40 Study Design Treatment Arms Randomized 1: 1, open label: WBRT 3 Gy fractions x 10 days (30 Gy) with supplemental O 2 +/- RSR 13 Stratification (1) (2) (3) (4) Primary Endpoint Survival Co-Primary Populations All patients: 85% power NSCLC/Breast: 75% power Alpha spending log-rank test RPA Class II NSCLC RPA Class II Breast RPA Class II Other
CE-01: 40 Study Design Treatment Arms Randomized 1: 1, open label: WBRT 3 Gy fractions x 10 days (30 Gy) with supplemental O 2 +/- RSR 13 Stratification (1) (2) (3) (4) Primary Endpoint Survival Co-Primary Populations All patients: 85% power NSCLC/Breast: 75% power Alpha spending log-rank test RPA Class II NSCLC RPA Class II Breast RPA Class II Other
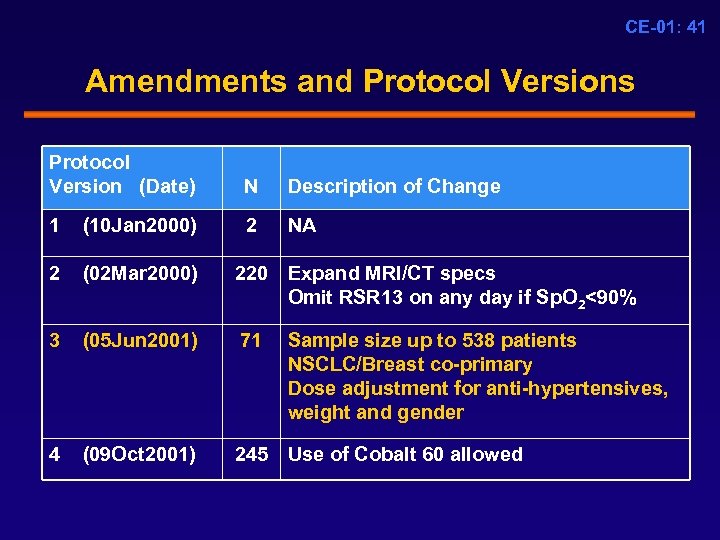 CE-01: 41 Amendments and Protocol Versions Protocol Version (Date) N Description of Change 1 (10 Jan 2000) 2 NA 2 (02 Mar 2000) 220 Expand MRI/CT specs Omit RSR 13 on any day if Sp. O 2<90% 3 (05 Jun 2001) 71 4 (09 Oct 2001) 245 Use of Cobalt 60 allowed Sample size up to 538 patients NSCLC/Breast co-primary Dose adjustment for anti-hypertensives, weight and gender
CE-01: 41 Amendments and Protocol Versions Protocol Version (Date) N Description of Change 1 (10 Jan 2000) 2 NA 2 (02 Mar 2000) 220 Expand MRI/CT specs Omit RSR 13 on any day if Sp. O 2<90% 3 (05 Jun 2001) 71 4 (09 Oct 2001) 245 Use of Cobalt 60 allowed Sample size up to 538 patients NSCLC/Breast co-primary Dose adjustment for anti-hypertensives, weight and gender
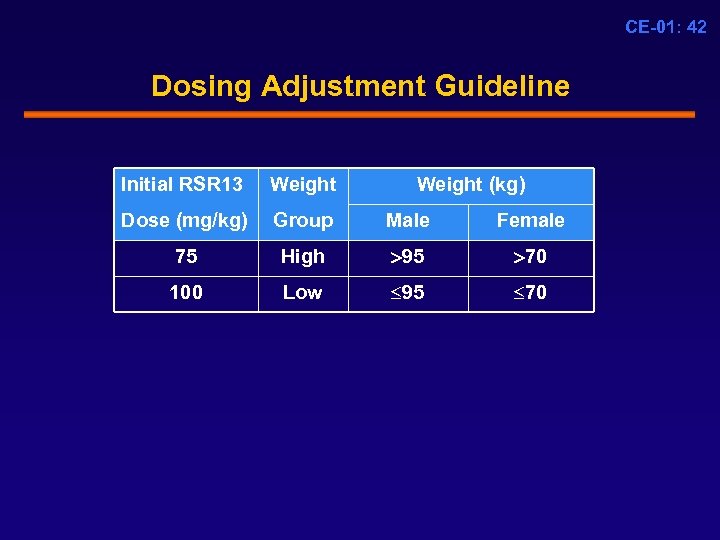 CE-01: 42 Dosing Adjustment Guideline Initial RSR 13 Weight (kg) Dose (mg/kg) Group Male Female 75 High 95 70 100 Low 95 70
CE-01: 42 Dosing Adjustment Guideline Initial RSR 13 Weight (kg) Dose (mg/kg) Group Male Female 75 High 95 70 100 Low 95 70
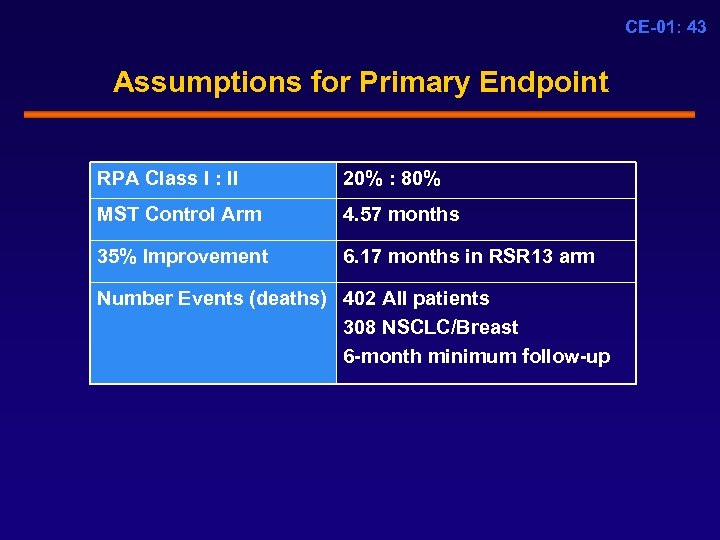 CE-01: 43 Assumptions for Primary Endpoint RPA Class I : II 20% : 80% MST Control Arm 4. 57 months 35% Improvement 6. 17 months in RSR 13 arm Number Events (deaths) 402 All patients 308 NSCLC/Breast 6 -month minimum follow-up
CE-01: 43 Assumptions for Primary Endpoint RPA Class I : II 20% : 80% MST Control Arm 4. 57 months 35% Improvement 6. 17 months in RSR 13 arm Number Events (deaths) 402 All patients 308 NSCLC/Breast 6 -month minimum follow-up
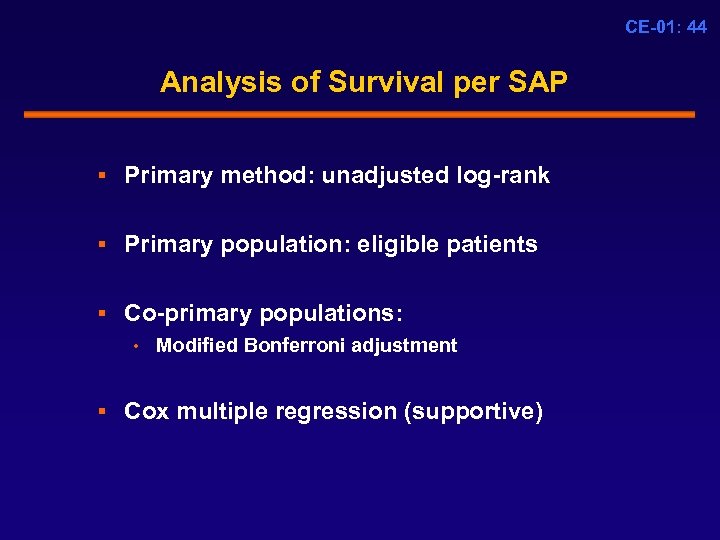 CE-01: 44 Analysis of Survival per SAP § Primary method: unadjusted log-rank § Primary population: eligible patients § Co-primary populations: • Modified Bonferroni adjustment § Cox multiple regression (supportive)
CE-01: 44 Analysis of Survival per SAP § Primary method: unadjusted log-rank § Primary population: eligible patients § Co-primary populations: • Modified Bonferroni adjustment § Cox multiple regression (supportive)
 CE-01: 45 Benefits of Adjusted Survival Analyses § Adjusted analyses provide the most accurate treatment estimate in heterogeneous populations: • Cox multiple regression • Stratified log-rank § RT-009 population very heterogeneous § Omitting strong covariates reduces power to detect treatment effects
CE-01: 45 Benefits of Adjusted Survival Analyses § Adjusted analyses provide the most accurate treatment estimate in heterogeneous populations: • Cox multiple regression • Stratified log-rank § RT-009 population very heterogeneous § Omitting strong covariates reduces power to detect treatment effects
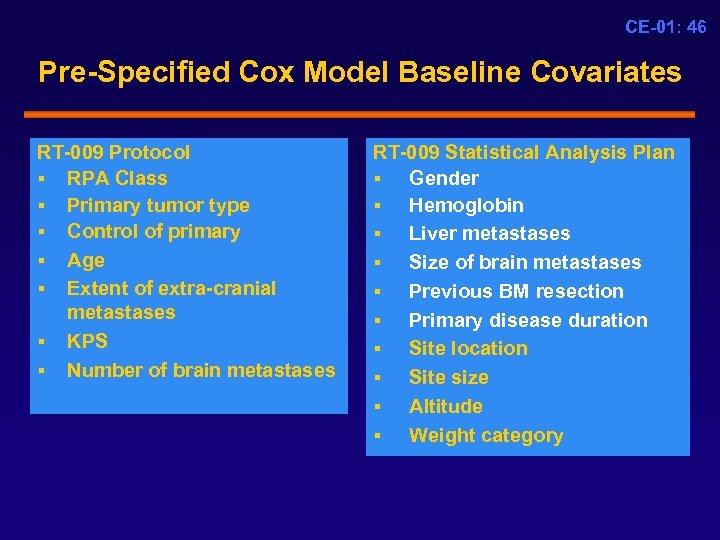 CE-01: 46 Pre-Specified Cox Model Baseline Covariates RT-009 Protocol § RPA Class § Primary tumor type § Control of primary § Age § Extent of extra-cranial metastases § KPS § Number of brain metastases RT-009 Statistical Analysis Plan § Gender § Hemoglobin § Liver metastases § Size of brain metastases § Previous BM resection § Primary disease duration § Site location § Site size § Altitude § Weight category
CE-01: 46 Pre-Specified Cox Model Baseline Covariates RT-009 Protocol § RPA Class § Primary tumor type § Control of primary § Age § Extent of extra-cranial metastases § KPS § Number of brain metastases RT-009 Statistical Analysis Plan § Gender § Hemoglobin § Liver metastases § Size of brain metastases § Previous BM resection § Primary disease duration § Site location § Site size § Altitude § Weight category
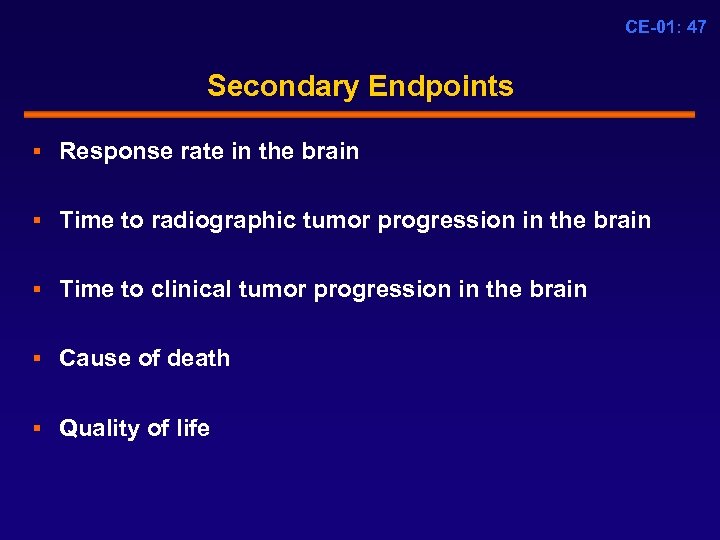 CE-01: 47 Secondary Endpoints § Response rate in the brain § Time to radiographic tumor progression in the brain § Time to clinical tumor progression in the brain § Cause of death § Quality of life
CE-01: 47 Secondary Endpoints § Response rate in the brain § Time to radiographic tumor progression in the brain § Time to clinical tumor progression in the brain § Cause of death § Quality of life
 Radiology Evaluation CE-01: 48 CT/MRI Scans of the Brain § Performed at baseline, initial follow-up 1 month after WBRT Day 10, 3 months after WBRT Day 10, and every 3 months thereafter, until progression § Central, independent radiologic review blinded to study arm and treatment outcome conducted for all scans • Neuroimaging Core Laboratory (Cleveland Clinic)
Radiology Evaluation CE-01: 48 CT/MRI Scans of the Brain § Performed at baseline, initial follow-up 1 month after WBRT Day 10, 3 months after WBRT Day 10, and every 3 months thereafter, until progression § Central, independent radiologic review blinded to study arm and treatment outcome conducted for all scans • Neuroimaging Core Laboratory (Cleveland Clinic)
 CE-01: 49 Phase 3 Study RSR 13 RT-009 Results
CE-01: 49 Phase 3 Study RSR 13 RT-009 Results
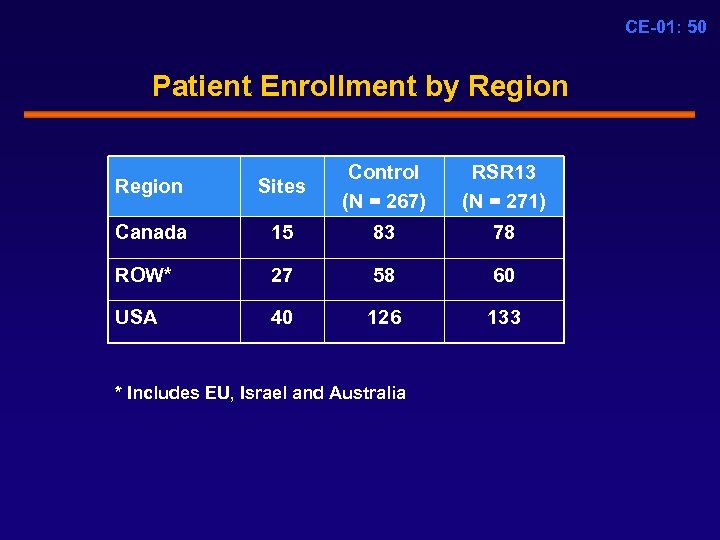 CE-01: 50 Patient Enrollment by Region Sites Control (N = 267) Canada 15 83 78 ROW* 27 58 60 USA 40 126 133 * Includes EU, Israel and Australia RSR 13 (N = 271)
CE-01: 50 Patient Enrollment by Region Sites Control (N = 267) Canada 15 83 78 ROW* 27 58 60 USA 40 126 133 * Includes EU, Israel and Australia RSR 13 (N = 271)
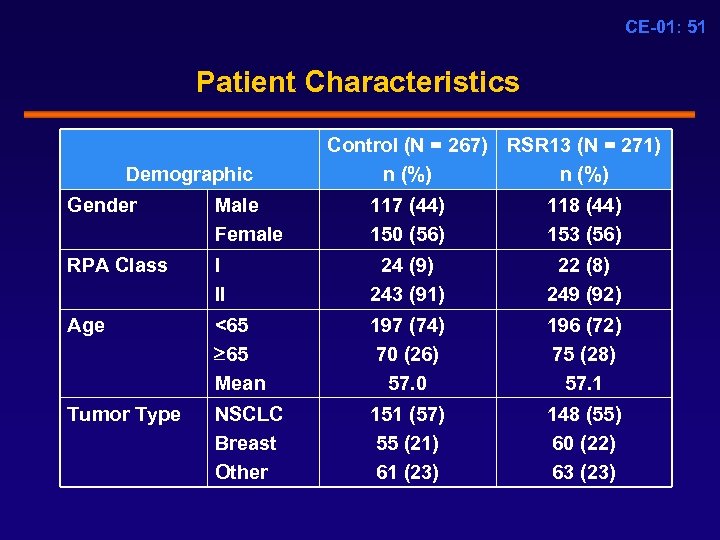 CE-01: 51 Patient Characteristics Demographic Control (N = 267) RSR 13 (N = 271) n (%) Gender Male Female 117 (44) 150 (56) 118 (44) 153 (56) RPA Class I II 24 (9) 243 (91) 22 (8) 249 (92) Age <65 65 Mean 197 (74) 70 (26) 57. 0 196 (72) 75 (28) 57. 1 Tumor Type NSCLC Breast Other 151 (57) 55 (21) 61 (23) 148 (55) 60 (22) 63 (23)
CE-01: 51 Patient Characteristics Demographic Control (N = 267) RSR 13 (N = 271) n (%) Gender Male Female 117 (44) 150 (56) 118 (44) 153 (56) RPA Class I II 24 (9) 243 (91) 22 (8) 249 (92) Age <65 65 Mean 197 (74) 70 (26) 57. 0 196 (72) 75 (28) 57. 1 Tumor Type NSCLC Breast Other 151 (57) 55 (21) 61 (23) 148 (55) 60 (22) 63 (23)
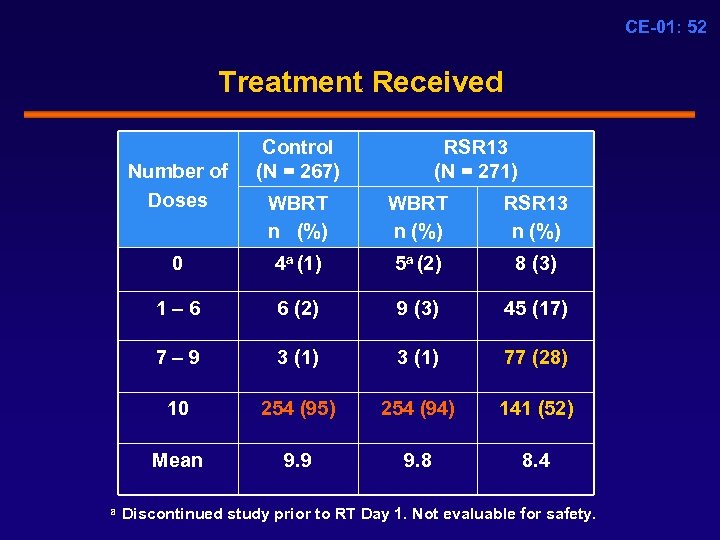 CE-01: 52 Treatment Received Number of Doses Control (N = 267) RSR 13 (N = 271) WBRT n (%) WBRT n (%) RSR 13 n (%) 0 4 a (1) 5 a (2) 8 (3) 1 – 6 6 (2) 9 (3) 45 (17) 7 – 9 3 (1) 77 (28) 10 254 (95) 254 (94) 141 (52) Mean 9. 9 9. 8 8. 4 a Discontinued study prior to RT Day 1. Not evaluable for safety.
CE-01: 52 Treatment Received Number of Doses Control (N = 267) RSR 13 (N = 271) WBRT n (%) WBRT n (%) RSR 13 n (%) 0 4 a (1) 5 a (2) 8 (3) 1 – 6 6 (2) 9 (3) 45 (17) 7 – 9 3 (1) 77 (28) 10 254 (95) 254 (94) 141 (52) Mean 9. 9 9. 8 8. 4 a Discontinued study prior to RT Day 1. Not evaluable for safety.
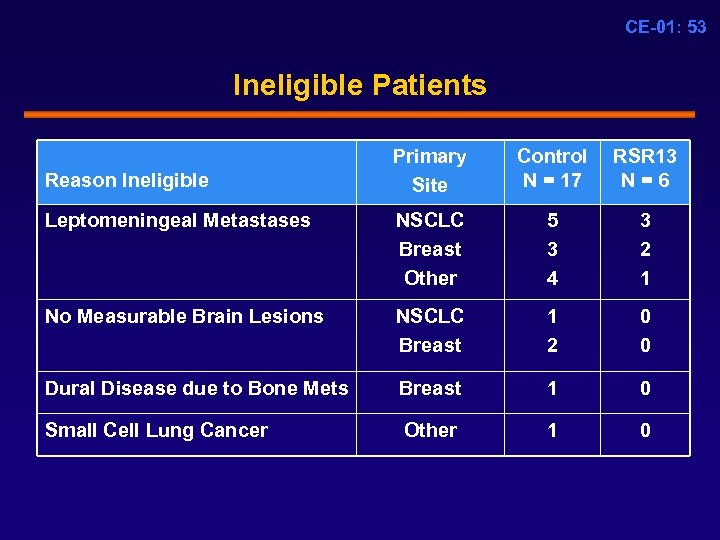 CE-01: 53 Ineligible Patients Primary Site Control N = 17 RSR 13 N = 6 Leptomeningeal Metastases NSCLC Breast Other 5 3 4 3 2 1 No Measurable Brain Lesions NSCLC Breast 1 2 0 0 Dural Disease due to Bone Mets Breast 1 0 Small Cell Lung Cancer Other 1 0 Reason Ineligible
CE-01: 53 Ineligible Patients Primary Site Control N = 17 RSR 13 N = 6 Leptomeningeal Metastases NSCLC Breast Other 5 3 4 3 2 1 No Measurable Brain Lesions NSCLC Breast 1 2 0 0 Dural Disease due to Bone Mets Breast 1 0 Small Cell Lung Cancer Other 1 0 Reason Ineligible
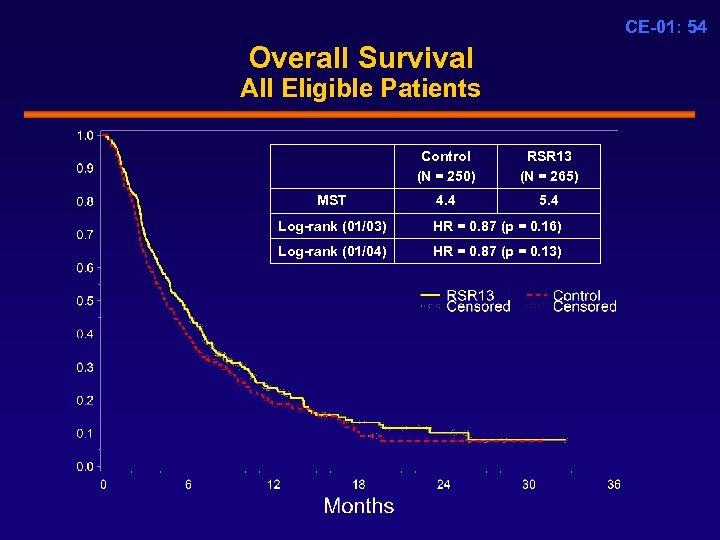 CE-01: 54 Overall Survival All Eligible Patients Control (N = 250) MST RSR 13 (N = 265) 4. 4 5. 4 Log-rank (01/03) HR = 0. 87 (p = 0. 16) Log-rank (01/04) HR = 0. 87 (p = 0. 13)
CE-01: 54 Overall Survival All Eligible Patients Control (N = 250) MST RSR 13 (N = 265) 4. 4 5. 4 Log-rank (01/03) HR = 0. 87 (p = 0. 16) Log-rank (01/04) HR = 0. 87 (p = 0. 13)
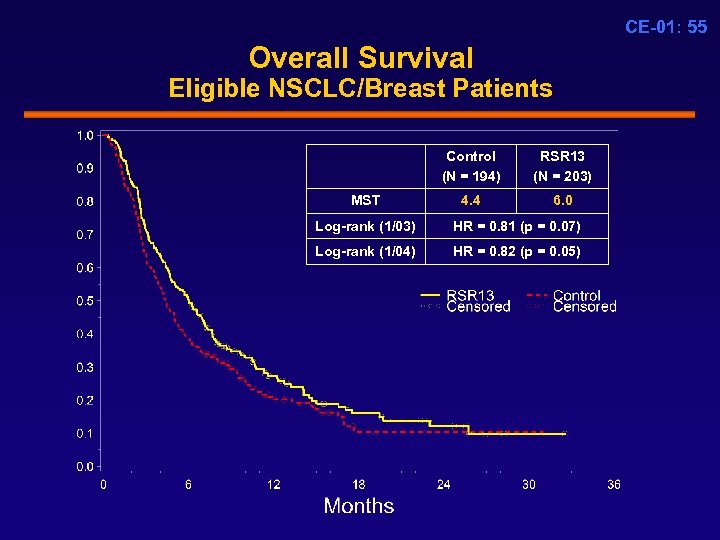 CE-01: 55 Overall Survival Eligible NSCLC/Breast Patients Control (N = 194) MST RSR 13 (N = 203) 4. 4 6. 0 Log-rank (1/03) HR = 0. 81 (p = 0. 07) Log-rank (1/04) HR = 0. 82 (p = 0. 05)
CE-01: 55 Overall Survival Eligible NSCLC/Breast Patients Control (N = 194) MST RSR 13 (N = 203) 4. 4 6. 0 Log-rank (1/03) HR = 0. 81 (p = 0. 07) Log-rank (1/04) HR = 0. 82 (p = 0. 05)
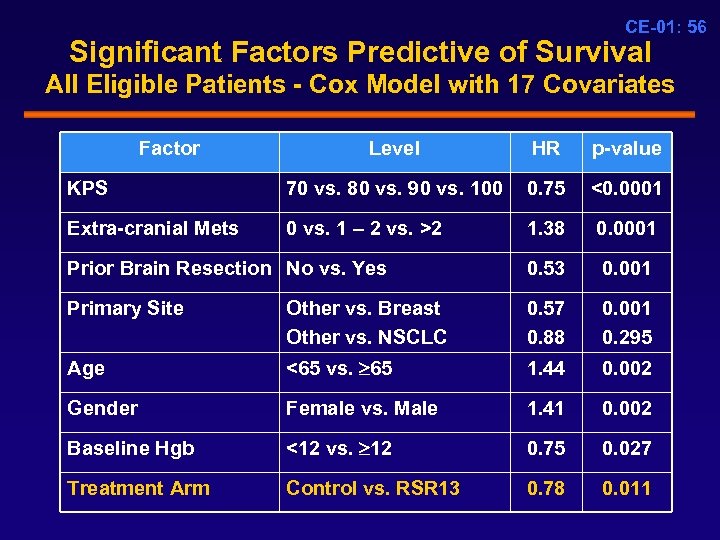 CE-01: 56 Significant Factors Predictive of Survival All Eligible Patients - Cox Model with 17 Covariates Factor Level HR p-value KPS 70 vs. 80 vs. 90 vs. 100 0. 75 <0. 0001 Extra-cranial Mets 0 vs. 1 – 2 vs. >2 1. 38 0. 0001 Prior Brain Resection No vs. Yes 0. 53 0. 001 Primary Site Other vs. Breast Other vs. NSCLC 0. 57 0. 88 0. 001 0. 295 Age <65 vs. 65 1. 44 0. 002 Gender Female vs. Male 1. 41 0. 002 Baseline Hgb <12 vs. 12 0. 75 0. 027 Treatment Arm Control vs. RSR 13 0. 78 0. 011
CE-01: 56 Significant Factors Predictive of Survival All Eligible Patients - Cox Model with 17 Covariates Factor Level HR p-value KPS 70 vs. 80 vs. 90 vs. 100 0. 75 <0. 0001 Extra-cranial Mets 0 vs. 1 – 2 vs. >2 1. 38 0. 0001 Prior Brain Resection No vs. Yes 0. 53 0. 001 Primary Site Other vs. Breast Other vs. NSCLC 0. 57 0. 88 0. 001 0. 295 Age <65 vs. 65 1. 44 0. 002 Gender Female vs. Male 1. 41 0. 002 Baseline Hgb <12 vs. 12 0. 75 0. 027 Treatment Arm Control vs. RSR 13 0. 78 0. 011
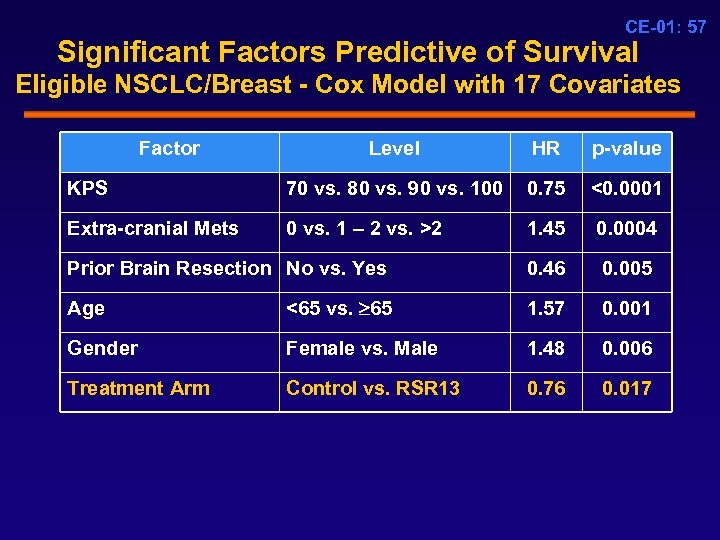 CE-01: 57 Significant Factors Predictive of Survival Eligible NSCLC/Breast - Cox Model with 17 Covariates Factor Level HR p-value KPS 70 vs. 80 vs. 90 vs. 100 0. 75 <0. 0001 Extra-cranial Mets 0 vs. 1 – 2 vs. >2 1. 45 0. 0004 Prior Brain Resection No vs. Yes 0. 46 0. 005 Age <65 vs. 65 1. 57 0. 001 Gender Female vs. Male 1. 48 0. 006 Treatment Arm Control vs. RSR 13 0. 76 0. 017
CE-01: 57 Significant Factors Predictive of Survival Eligible NSCLC/Breast - Cox Model with 17 Covariates Factor Level HR p-value KPS 70 vs. 80 vs. 90 vs. 100 0. 75 <0. 0001 Extra-cranial Mets 0 vs. 1 – 2 vs. >2 1. 45 0. 0004 Prior Brain Resection No vs. Yes 0. 46 0. 005 Age <65 vs. 65 1. 57 0. 001 Gender Female vs. Male 1. 48 0. 006 Treatment Arm Control vs. RSR 13 0. 76 0. 017
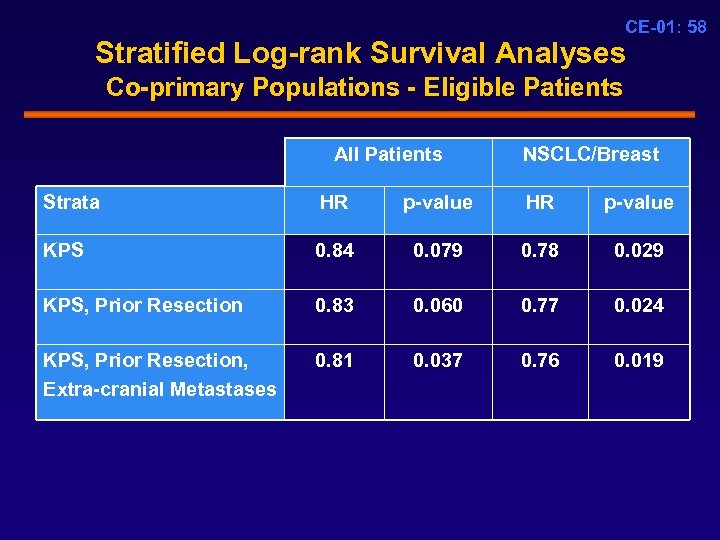 CE-01: 58 Stratified Log-rank Survival Analyses Co-primary Populations - Eligible Patients All Patients NSCLC/Breast Strata HR p-value KPS 0. 84 0. 079 0. 78 0. 029 KPS, Prior Resection 0. 83 0. 060 0. 77 0. 024 KPS, Prior Resection, Extra-cranial Metastases 0. 81 0. 037 0. 76 0. 019
CE-01: 58 Stratified Log-rank Survival Analyses Co-primary Populations - Eligible Patients All Patients NSCLC/Breast Strata HR p-value KPS 0. 84 0. 079 0. 78 0. 029 KPS, Prior Resection 0. 83 0. 060 0. 77 0. 024 KPS, Prior Resection, Extra-cranial Metastases 0. 81 0. 037 0. 76 0. 019
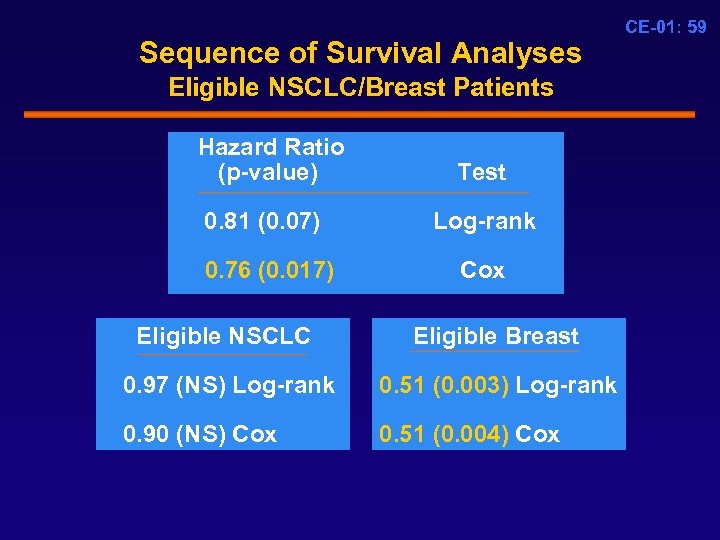 Sequence of Survival Analyses Eligible NSCLC/Breast Patients Hazard Ratio (p-value) Test 0. 81 (0. 07) Log-rank 0. 76 (0. 017) Cox Eligible NSCLC Eligible Breast 0. 97 (NS) Log-rank 0. 51 (0. 003) Log-rank 0. 90 (NS) Cox 0. 51 (0. 004) Cox CE-01: 59
Sequence of Survival Analyses Eligible NSCLC/Breast Patients Hazard Ratio (p-value) Test 0. 81 (0. 07) Log-rank 0. 76 (0. 017) Cox Eligible NSCLC Eligible Breast 0. 97 (NS) Log-rank 0. 51 (0. 003) Log-rank 0. 90 (NS) Cox 0. 51 (0. 004) Cox CE-01: 59
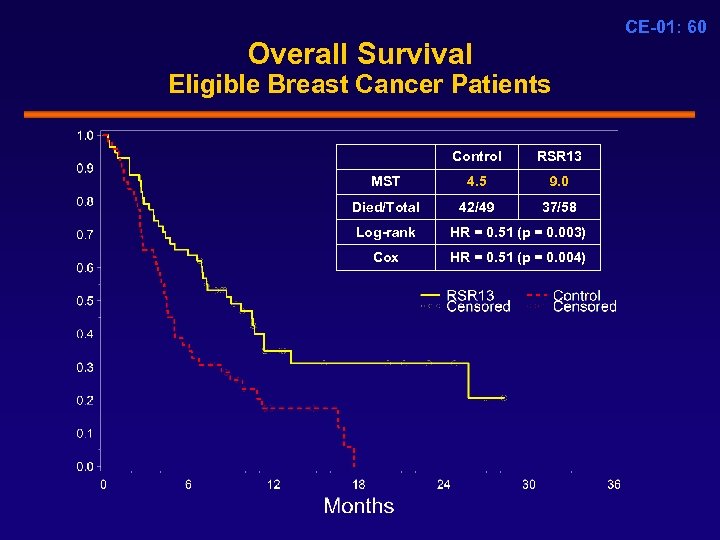 CE-01: 60 Overall Survival Eligible Breast Cancer Patients Control RSR 13 MST 4. 5 9. 0 Died/Total 42/49 37/58 Log-rank HR = 0. 51 (p = 0. 003) Cox HR = 0. 51 (p = 0. 004)
CE-01: 60 Overall Survival Eligible Breast Cancer Patients Control RSR 13 MST 4. 5 9. 0 Died/Total 42/49 37/58 Log-rank HR = 0. 51 (p = 0. 003) Cox HR = 0. 51 (p = 0. 004)
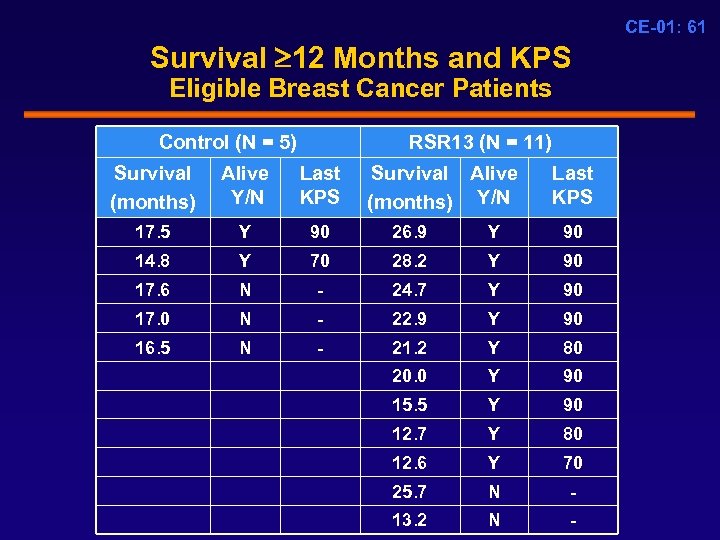 CE-01: 61 Survival 12 Months and KPS Eligible Breast Cancer Patients Control (N = 5) RSR 13 (N = 11) Survival (months) Alive Y/N Last KPS Survival Alive (months) Y/N Last KPS 17. 5 Y 90 26. 9 Y 90 14. 8 Y 70 28. 2 Y 90 17. 6 N - 24. 7 Y 90 17. 0 N - 22. 9 Y 90 16. 5 N - 21. 2 Y 80 20. 0 Y 90 15. 5 Y 90 12. 7 Y 80 12. 6 Y 70 25. 7 N - 13. 2 N -
CE-01: 61 Survival 12 Months and KPS Eligible Breast Cancer Patients Control (N = 5) RSR 13 (N = 11) Survival (months) Alive Y/N Last KPS Survival Alive (months) Y/N Last KPS 17. 5 Y 90 26. 9 Y 90 14. 8 Y 70 28. 2 Y 90 17. 6 N - 24. 7 Y 90 17. 0 N - 22. 9 Y 90 16. 5 N - 21. 2 Y 80 20. 0 Y 90 15. 5 Y 90 12. 7 Y 80 12. 6 Y 70 25. 7 N - 13. 2 N -
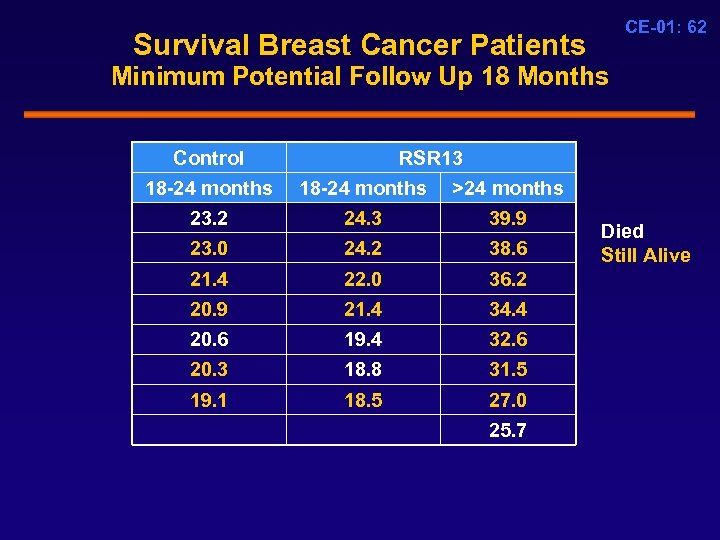 Survival Breast Cancer Patients CE-01: 62 Minimum Potential Follow Up 18 Months Control RSR 13 18 -24 months >24 months 23. 2 23. 0 24. 3 24. 2 39. 9 38. 6 21. 4 22. 0 36. 2 20. 9 20. 6 20. 3 21. 4 19. 4 18. 8 34. 4 32. 6 31. 5 19. 1 18. 5 27. 0 25. 7 Died Still Alive
Survival Breast Cancer Patients CE-01: 62 Minimum Potential Follow Up 18 Months Control RSR 13 18 -24 months >24 months 23. 2 23. 0 24. 3 24. 2 39. 9 38. 6 21. 4 22. 0 36. 2 20. 9 20. 6 20. 3 21. 4 19. 4 18. 8 34. 4 32. 6 31. 5 19. 1 18. 5 27. 0 25. 7 Died Still Alive
 CE-01: 63 Secondary Endpoints All Randomized Patients
CE-01: 63 Secondary Endpoints All Randomized Patients
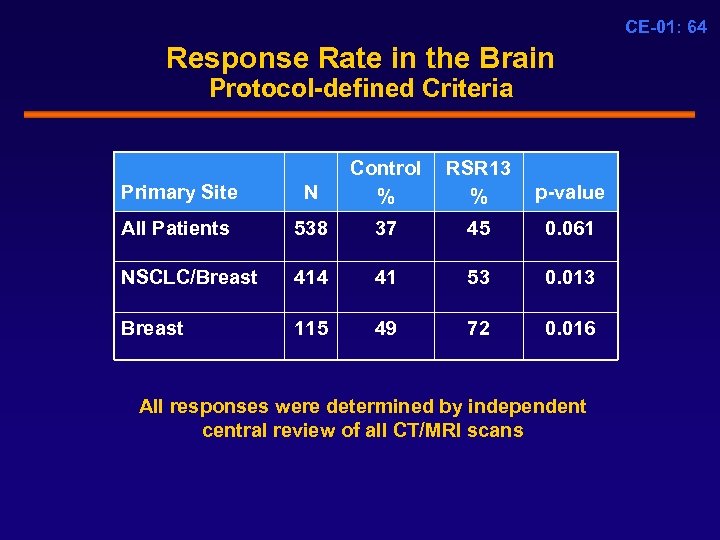 CE-01: 64 Response Rate in the Brain Protocol-defined Criteria Primary Site N Control % RSR 13 % p-value All Patients 538 37 45 0. 061 NSCLC/Breast 414 41 53 0. 013 Breast 115 49 72 0. 016 All responses were determined by independent central review of all CT/MRI scans
CE-01: 64 Response Rate in the Brain Protocol-defined Criteria Primary Site N Control % RSR 13 % p-value All Patients 538 37 45 0. 061 NSCLC/Breast 414 41 53 0. 013 Breast 115 49 72 0. 016 All responses were determined by independent central review of all CT/MRI scans
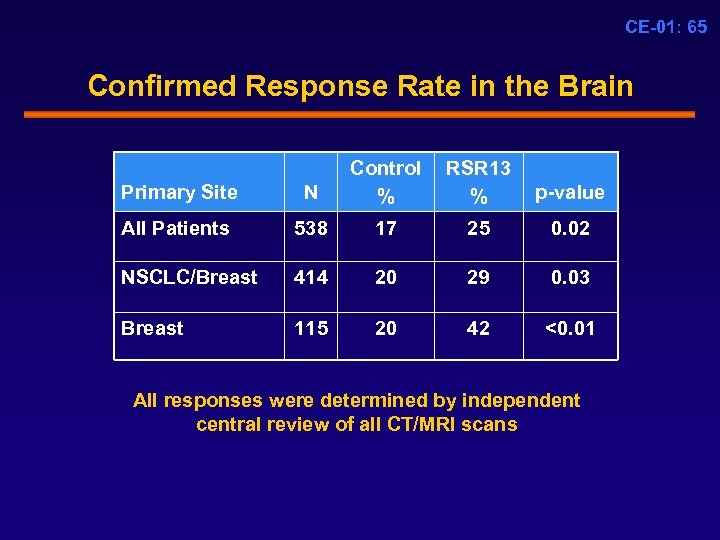 CE-01: 65 Confirmed Response Rate in the Brain Primary Site N Control % RSR 13 % p-value All Patients 538 17 25 0. 02 NSCLC/Breast 414 20 29 0. 03 Breast 115 20 42 <0. 01 All responses were determined by independent central review of all CT/MRI scans
CE-01: 65 Confirmed Response Rate in the Brain Primary Site N Control % RSR 13 % p-value All Patients 538 17 25 0. 02 NSCLC/Breast 414 20 29 0. 03 Breast 115 20 42 <0. 01 All responses were determined by independent central review of all CT/MRI scans
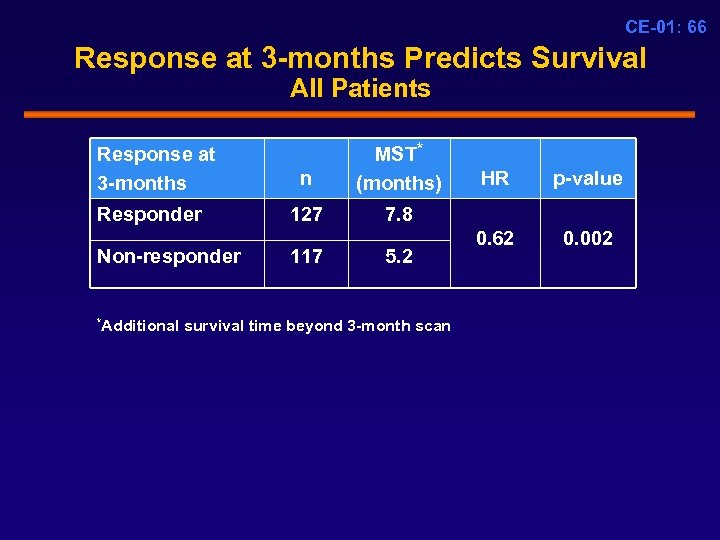 CE-01: 66 Response at 3 -months Predicts Survival All Patients Response at 3 -months Responder Non-responder n MST* (months) 127 7. 8 117 5. 2 *Additional survival time beyond 3 -month scan HR p-value 0. 62 0. 002
CE-01: 66 Response at 3 -months Predicts Survival All Patients Response at 3 -months Responder Non-responder n MST* (months) 127 7. 8 117 5. 2 *Additional survival time beyond 3 -month scan HR p-value 0. 62 0. 002
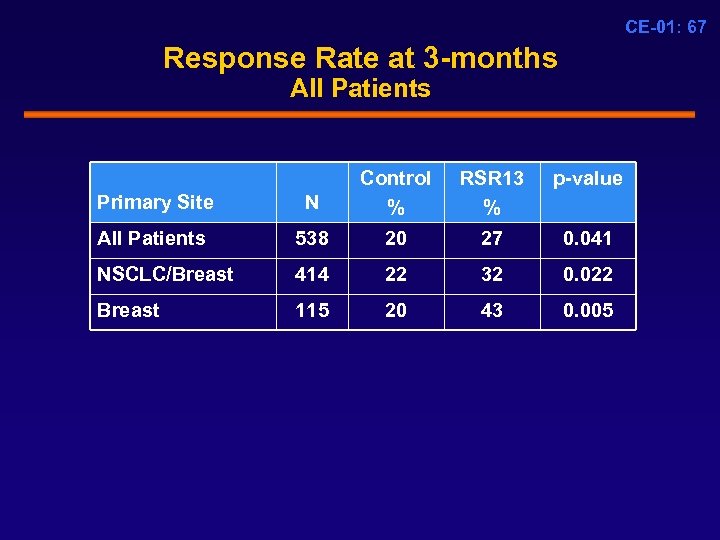 CE-01: 67 Response Rate at 3 -months All Patients Primary Site N Control % RSR 13 % p-value All Patients 538 20 27 0. 041 NSCLC/Breast 414 22 32 0. 022 Breast 115 20 43 0. 005
CE-01: 67 Response Rate at 3 -months All Patients Primary Site N Control % RSR 13 % p-value All Patients 538 20 27 0. 041 NSCLC/Breast 414 22 32 0. 022 Breast 115 20 43 0. 005
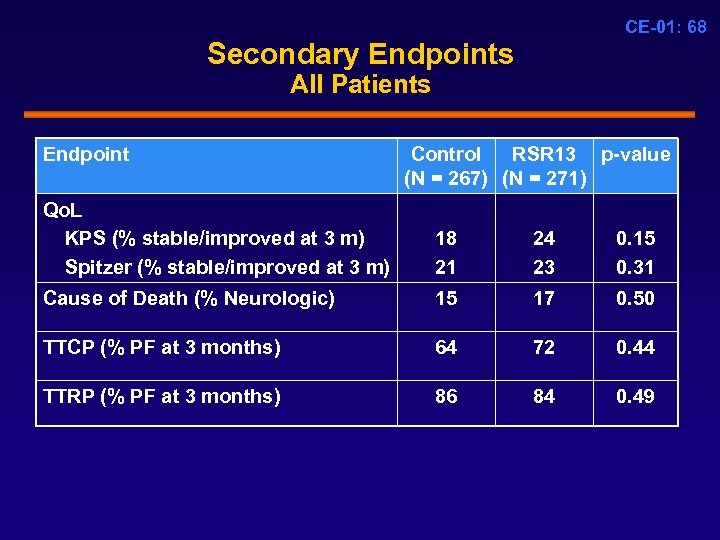 CE-01: 68 Secondary Endpoints All Patients Endpoint Control RSR 13 p-value (N = 267) (N = 271) Qo. L KPS (% stable/improved at 3 m) Spitzer (% stable/improved at 3 m) 18 21 24 23 0. 15 0. 31 Cause of Death (% Neurologic) 15 17 0. 50 TTCP (% PF at 3 months) 64 72 0. 44 TTRP (% PF at 3 months) 86 84 0. 49
CE-01: 68 Secondary Endpoints All Patients Endpoint Control RSR 13 p-value (N = 267) (N = 271) Qo. L KPS (% stable/improved at 3 m) Spitzer (% stable/improved at 3 m) 18 21 24 23 0. 15 0. 31 Cause of Death (% Neurologic) 15 17 0. 50 TTCP (% PF at 3 months) 64 72 0. 44 TTRP (% PF at 3 months) 86 84 0. 49
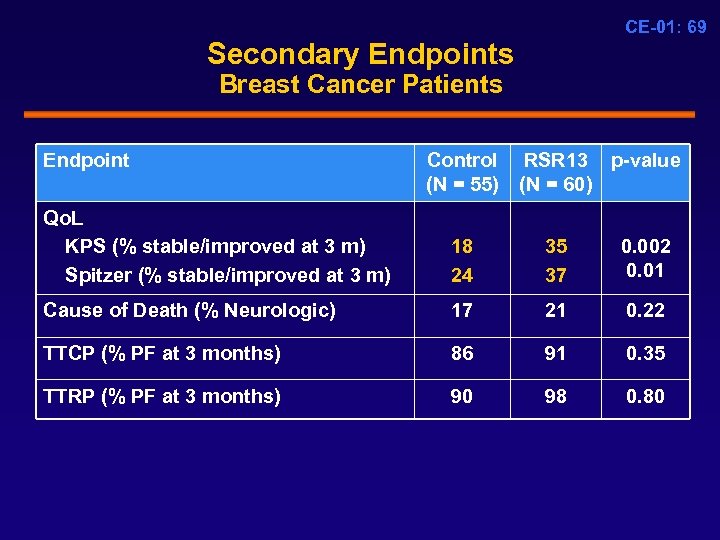 CE-01: 69 Secondary Endpoints Breast Cancer Patients Endpoint Control RSR 13 p-value (N = 55) (N = 60) Qo. L KPS (% stable/improved at 3 m) Spitzer (% stable/improved at 3 m) 18 24 35 37 0. 002 0. 01 Cause of Death (% Neurologic) 17 21 0. 22 TTCP (% PF at 3 months) 86 91 0. 35 TTRP (% PF at 3 months) 90 98 0. 80
CE-01: 69 Secondary Endpoints Breast Cancer Patients Endpoint Control RSR 13 p-value (N = 55) (N = 60) Qo. L KPS (% stable/improved at 3 m) Spitzer (% stable/improved at 3 m) 18 24 35 37 0. 002 0. 01 Cause of Death (% Neurologic) 17 21 0. 22 TTCP (% PF at 3 months) 86 91 0. 35 TTRP (% PF at 3 months) 90 98 0. 80
 CE-01: 70 Treatment Effect Different in Patients with NSCLC and Breast Cancer § Biological differences § Different growth rates § Efficacy of therapy for extra-cranial disease § Body weight differences: RSR 13 PK
CE-01: 70 Treatment Effect Different in Patients with NSCLC and Breast Cancer § Biological differences § Different growth rates § Efficacy of therapy for extra-cranial disease § Body weight differences: RSR 13 PK
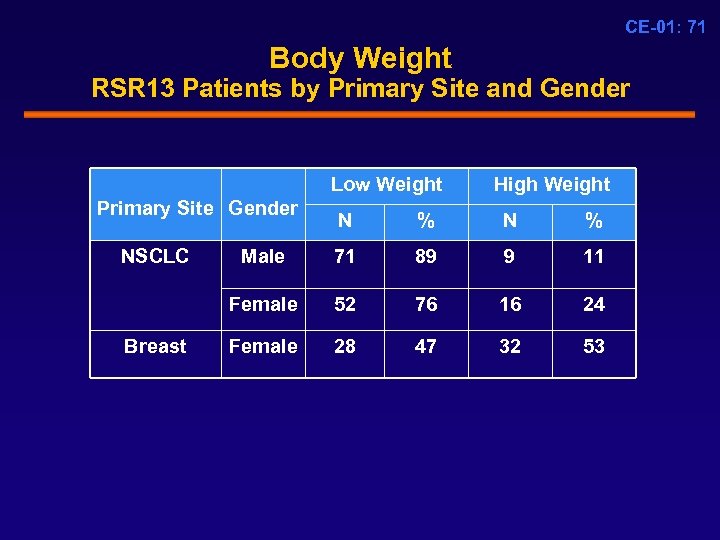 CE-01: 71 Body Weight RSR 13 Patients by Primary Site and Gender Low Weight Primary Site Gender High Weight Breast % N % Male 71 89 9 11 Female NSCLC N 52 76 16 24 Female 28 47 32 53
CE-01: 71 Body Weight RSR 13 Patients by Primary Site and Gender Low Weight Primary Site Gender High Weight Breast % N % Male 71 89 9 11 Female NSCLC N 52 76 16 24 Female 28 47 32 53
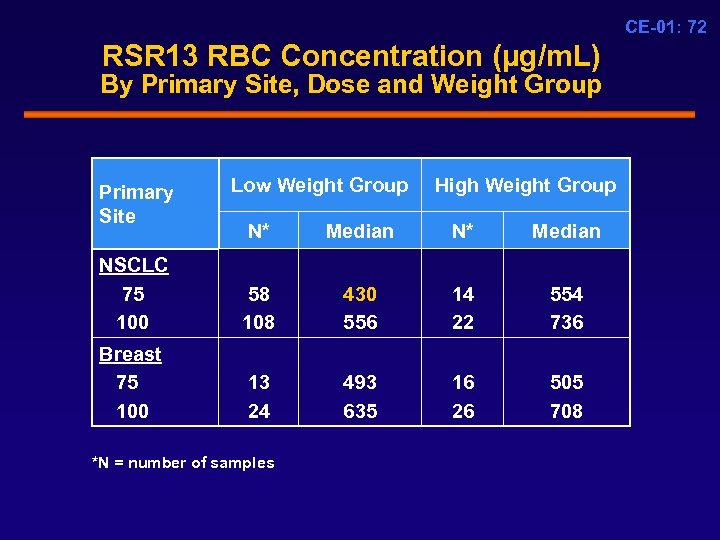 CE-01: 72 RSR 13 RBC Concentration (µg/m. L) By Primary Site, Dose and Weight Group Primary Site Low Weight Group High Weight Group N* Median NSCLC 75 100 58 108 430 556 14 22 554 736 Breast 75 100 13 24 493 635 16 26 505 708 *N = number of samples
CE-01: 72 RSR 13 RBC Concentration (µg/m. L) By Primary Site, Dose and Weight Group Primary Site Low Weight Group High Weight Group N* Median NSCLC 75 100 58 108 430 556 14 22 554 736 Breast 75 100 13 24 493 635 16 26 505 708 *N = number of samples
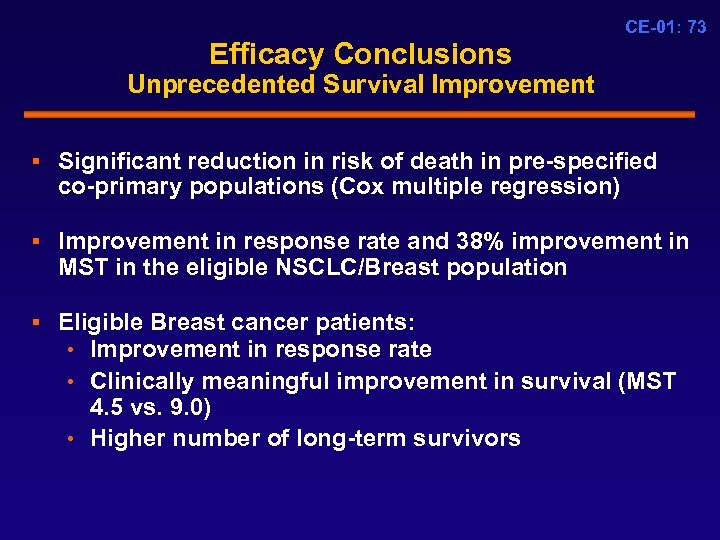 CE-01: 73 Efficacy Conclusions Unprecedented Survival Improvement § Significant reduction in risk of death in pre-specified co-primary populations (Cox multiple regression) § Improvement in response rate and 38% improvement in MST in the eligible NSCLC/Breast population § Eligible Breast cancer patients: • Improvement in response rate • Clinically meaningful improvement in survival (MST 4. 5 vs. 9. 0) • Higher number of long-term survivors
CE-01: 73 Efficacy Conclusions Unprecedented Survival Improvement § Significant reduction in risk of death in pre-specified co-primary populations (Cox multiple regression) § Improvement in response rate and 38% improvement in MST in the eligible NSCLC/Breast population § Eligible Breast cancer patients: • Improvement in response rate • Clinically meaningful improvement in survival (MST 4. 5 vs. 9. 0) • Higher number of long-term survivors
 CE-01: 74 RSR 13 Safety Profile
CE-01: 74 RSR 13 Safety Profile
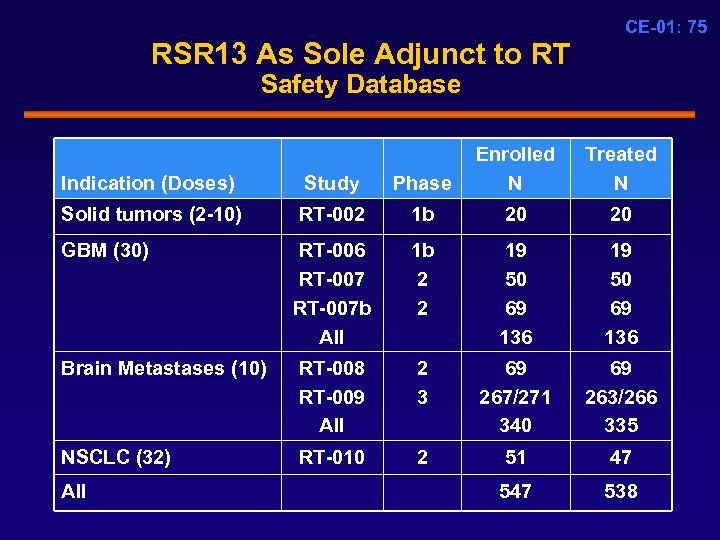 CE-01: 75 RSR 13 As Sole Adjunct to RT Safety Database Indication (Doses) Study Phase Enrolled N Solid tumors (2 -10) RT-002 1 b 20 20 RT-006 RT-007 b All 1 b 2 2 19 50 69 136 Brain Metastases (10) RT-008 RT-009 All 2 3 69 267/271 340 69 263/266 335 NSCLC (32) RT-010 2 51 47 538 GBM (30) All Treated N
CE-01: 75 RSR 13 As Sole Adjunct to RT Safety Database Indication (Doses) Study Phase Enrolled N Solid tumors (2 -10) RT-002 1 b 20 20 RT-006 RT-007 b All 1 b 2 2 19 50 69 136 Brain Metastases (10) RT-008 RT-009 All 2 3 69 267/271 340 69 263/266 335 NSCLC (32) RT-010 2 51 47 538 GBM (30) All Treated N
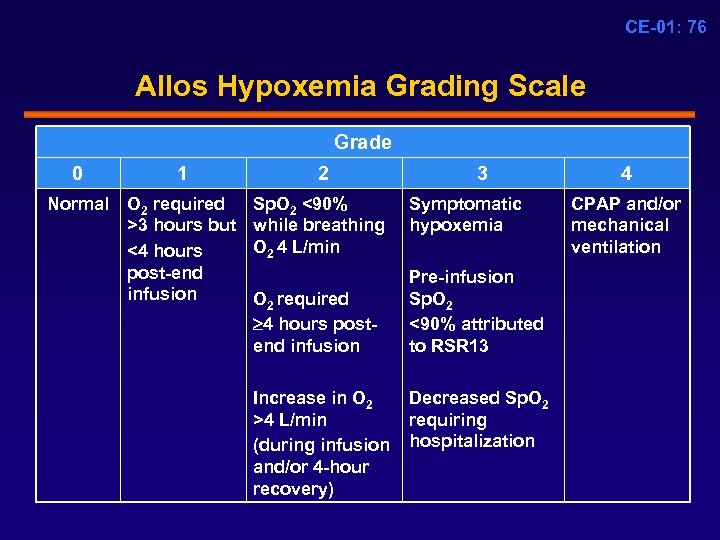 CE-01: 76 Allos Hypoxemia Grading Scale Grade 0 1 2 Normal O 2 required >3 hours but <4 hours post-end infusion Sp. O 2 <90% while breathing O 2 4 L/min O 2 required 4 hours postend infusion Increase in O 2 >4 L/min (during infusion and/or 4 -hour recovery) 3 4 Symptomatic CPAP and/or hypoxemia mechanical ventilation Pre-infusion Sp. O 2 <90% attributed to RSR 13 Decreased Sp. O 2 requiring hospitalization
CE-01: 76 Allos Hypoxemia Grading Scale Grade 0 1 2 Normal O 2 required >3 hours but <4 hours post-end infusion Sp. O 2 <90% while breathing O 2 4 L/min O 2 required 4 hours postend infusion Increase in O 2 >4 L/min (during infusion and/or 4 -hour recovery) 3 4 Symptomatic CPAP and/or hypoxemia mechanical ventilation Pre-infusion Sp. O 2 <90% attributed to RSR 13 Decreased Sp. O 2 requiring hospitalization
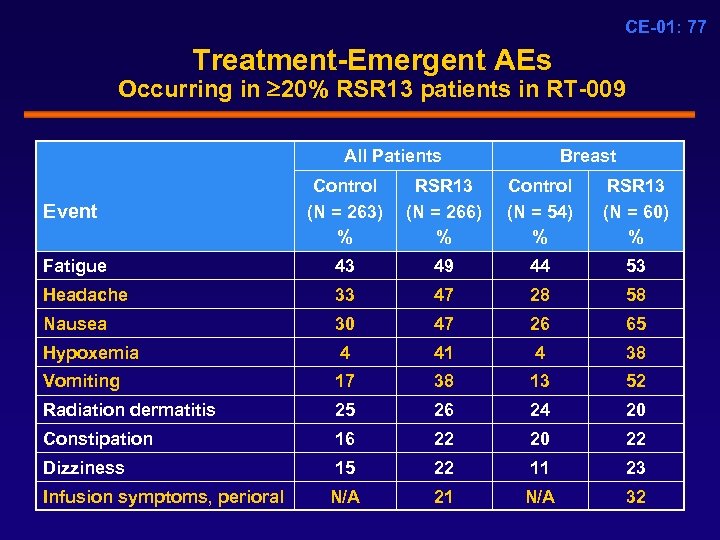 CE-01: 77 Treatment-Emergent AEs Occurring in 20% RSR 13 patients in RT-009 All Patients Breast Event Control (N = 263) % RSR 13 (N = 266) % Control (N = 54) % RSR 13 (N = 60) % Fatigue 43 49 44 53 Headache 33 47 28 58 Nausea 30 47 26 65 Hypoxemia 4 41 4 38 Vomiting 17 38 13 52 Radiation dermatitis 25 26 24 20 Constipation 16 22 20 22 Dizziness 15 22 11 23 N/A 21 N/A 32 Infusion symptoms, perioral
CE-01: 77 Treatment-Emergent AEs Occurring in 20% RSR 13 patients in RT-009 All Patients Breast Event Control (N = 263) % RSR 13 (N = 266) % Control (N = 54) % RSR 13 (N = 60) % Fatigue 43 49 44 53 Headache 33 47 28 58 Nausea 30 47 26 65 Hypoxemia 4 41 4 38 Vomiting 17 38 13 52 Radiation dermatitis 25 26 24 20 Constipation 16 22 20 22 Dizziness 15 22 11 23 N/A 21 N/A 32 Infusion symptoms, perioral
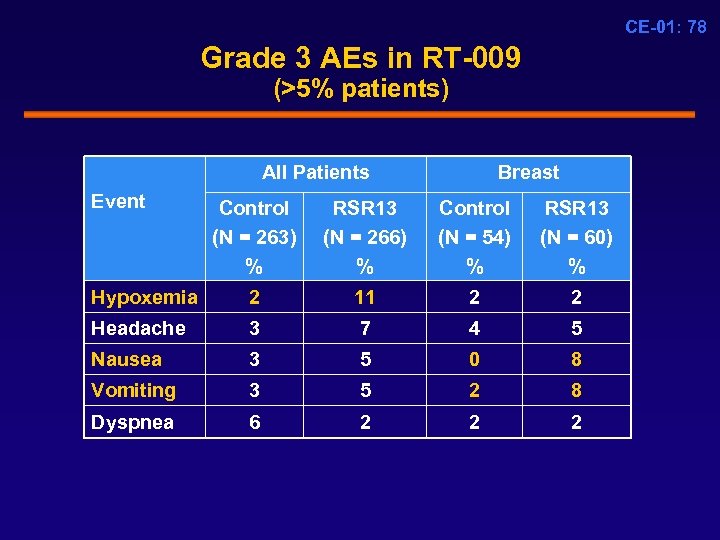 CE-01: 78 Grade 3 AEs in RT-009 (>5% patients) All Patients Event Breast Control (N = 263) % RSR 13 (N = 266) % Control (N = 54) % RSR 13 (N = 60) % Hypoxemia 2 11 2 2 Headache 3 7 4 5 Nausea 3 5 0 8 Vomiting 3 5 2 8 Dyspnea 6 2 2 2
CE-01: 78 Grade 3 AEs in RT-009 (>5% patients) All Patients Event Breast Control (N = 263) % RSR 13 (N = 266) % Control (N = 54) % RSR 13 (N = 60) % Hypoxemia 2 11 2 2 Headache 3 7 4 5 Nausea 3 5 0 8 Vomiting 3 5 2 8 Dyspnea 6 2 2 2
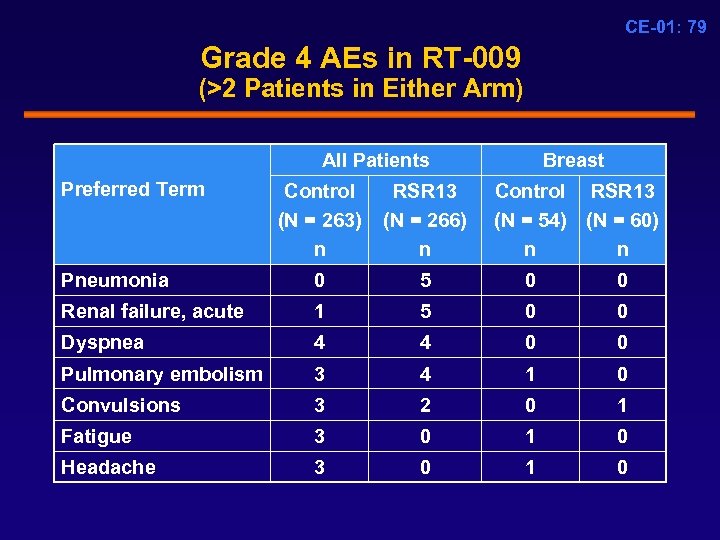 CE-01: 79 Grade 4 AEs in RT-009 (>2 Patients in Either Arm) All Patients Preferred Term Breast Control (N = 263) n RSR 13 (N = 266) n Control RSR 13 (N = 54) (N = 60) n n Pneumonia 0 5 0 0 Renal failure, acute 1 5 0 0 Dyspnea 4 4 0 0 Pulmonary embolism 3 4 1 0 Convulsions 3 2 0 1 Fatigue 3 0 1 0 Headache 3 0 1 0
CE-01: 79 Grade 4 AEs in RT-009 (>2 Patients in Either Arm) All Patients Preferred Term Breast Control (N = 263) n RSR 13 (N = 266) n Control RSR 13 (N = 54) (N = 60) n n Pneumonia 0 5 0 0 Renal failure, acute 1 5 0 0 Dyspnea 4 4 0 0 Pulmonary embolism 3 4 1 0 Convulsions 3 2 0 1 Fatigue 3 0 1 0 Headache 3 0 1 0
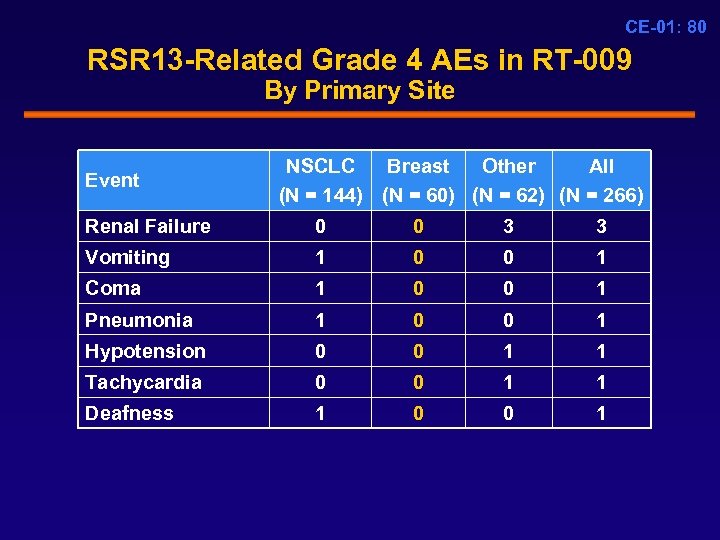 CE-01: 80 RSR 13 -Related Grade 4 AEs in RT-009 By Primary Site Event NSCLC Breast Other All (N = 144) (N = 60) (N = 62) (N = 266) Renal Failure 0 0 3 3 Vomiting 1 0 0 1 Coma 1 0 0 1 Pneumonia 1 0 0 1 Hypotension 0 0 1 1 Tachycardia 0 0 1 1 Deafness 1 0 0 1
CE-01: 80 RSR 13 -Related Grade 4 AEs in RT-009 By Primary Site Event NSCLC Breast Other All (N = 144) (N = 60) (N = 62) (N = 266) Renal Failure 0 0 3 3 Vomiting 1 0 0 1 Coma 1 0 0 1 Pneumonia 1 0 0 1 Hypotension 0 0 1 1 Tachycardia 0 0 1 1 Deafness 1 0 0 1
 CE-01: 81 Hypoxemia § Only 11% patients had a Grade 3 hypoxemia AE § 73% of patients in RT-009 who had Grade 3 hypoxemia as an AE were asymptomatic § Hypoxemia was self-limited and easily managed with supplemental oxygen
CE-01: 81 Hypoxemia § Only 11% patients had a Grade 3 hypoxemia AE § 73% of patients in RT-009 who had Grade 3 hypoxemia as an AE were asymptomatic § Hypoxemia was self-limited and easily managed with supplemental oxygen
 CE-01: 82 Safety Summary § Data from 535 patients indicate that RSR 13 is safe in cancer patients receiving RT § Very low incidence of Grade 3 -4 AEs in a heavily pre -treated population of cancer patients in RT-009 § All AEs in RT-009 resolved within the 1 -month follow -up period and were easily managed with supportive care § Hypoxemia associated with RSR 13: • Self-limited, requires only supplemental O 2 • Asymptomatic in the majority of patients
CE-01: 82 Safety Summary § Data from 535 patients indicate that RSR 13 is safe in cancer patients receiving RT § Very low incidence of Grade 3 -4 AEs in a heavily pre -treated population of cancer patients in RT-009 § All AEs in RT-009 resolved within the 1 -month follow -up period and were easily managed with supportive care § Hypoxemia associated with RSR 13: • Self-limited, requires only supplemental O 2 • Asymptomatic in the majority of patients
 CE-01: 83 Conclusions Paul A. Bunn, Jr. , MD Grohne/Stapp Professor and Director University of Colorado Comprehensive Cancer Center Denver, CO
CE-01: 83 Conclusions Paul A. Bunn, Jr. , MD Grohne/Stapp Professor and Director University of Colorado Comprehensive Cancer Center Denver, CO
 CE-01: 84 RSR 13 in Patients with Brain Metastases (N = 538) High unmet medical need High incidence High morbidity and mortality Lack of progress Pre-RSR 13 Post-RSR 13
CE-01: 84 RSR 13 in Patients with Brain Metastases (N = 538) High unmet medical need High incidence High morbidity and mortality Lack of progress Pre-RSR 13 Post-RSR 13
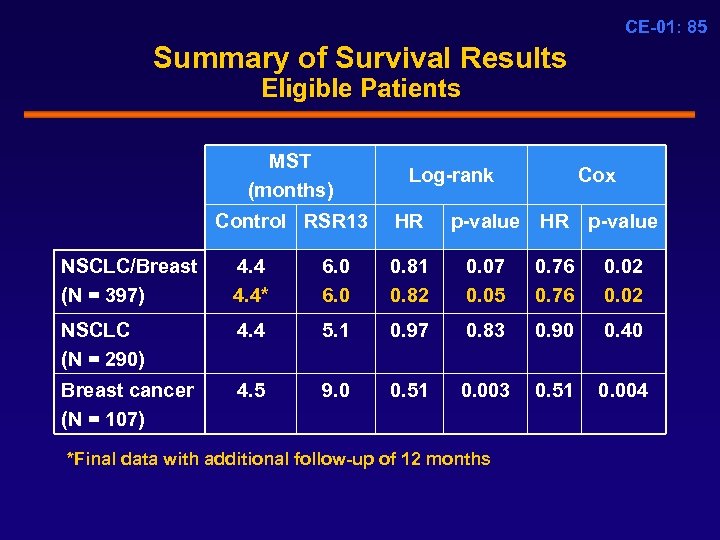 CE-01: 85 Summary of Survival Results Eligible Patients MST (months) Control RSR 13 Log-rank HR Cox p-value HR p-value NSCLC/Breast (N = 397) 4. 4* 6. 0 0. 81 0. 82 0. 07 0. 05 0. 76 0. 02 NSCLC (N = 290) 4. 4 5. 1 0. 97 0. 83 0. 90 0. 40 Breast cancer (N = 107) 4. 5 9. 0 0. 51 0. 003 0. 51 0. 004 *Final data with additional follow-up of 12 months
CE-01: 85 Summary of Survival Results Eligible Patients MST (months) Control RSR 13 Log-rank HR Cox p-value HR p-value NSCLC/Breast (N = 397) 4. 4* 6. 0 0. 81 0. 82 0. 07 0. 05 0. 76 0. 02 NSCLC (N = 290) 4. 4 5. 1 0. 97 0. 83 0. 90 0. 40 Breast cancer (N = 107) 4. 5 9. 0 0. 51 0. 003 0. 51 0. 004 *Final data with additional follow-up of 12 months
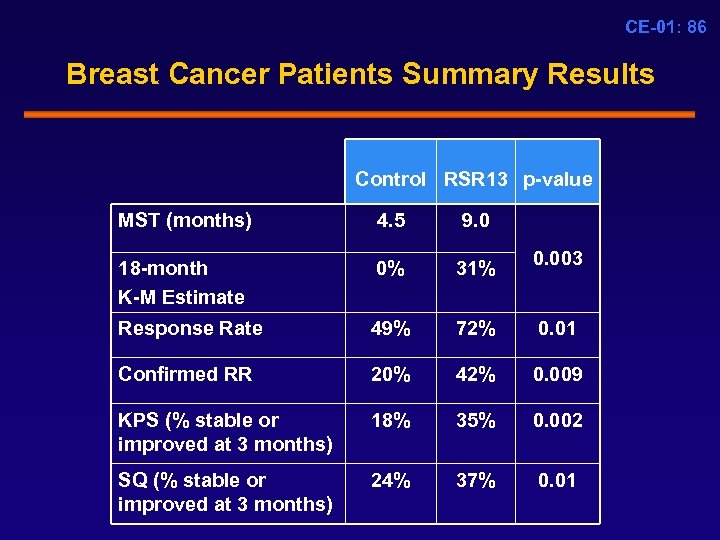 CE-01: 86 Breast Cancer Patients Summary Results Control RSR 13 p-value MST (months) 4. 5 9. 0 18 -month K-M Estimate 0% 31% 0. 003 Response Rate 49% 72% 0. 01 Confirmed RR 20% 42% 0. 009 KPS (% stable or improved at 3 months) 18% 35% 0. 002 SQ (% stable or improved at 3 months) 24% 37% 0. 01
CE-01: 86 Breast Cancer Patients Summary Results Control RSR 13 p-value MST (months) 4. 5 9. 0 18 -month K-M Estimate 0% 31% 0. 003 Response Rate 49% 72% 0. 01 Confirmed RR 20% 42% 0. 009 KPS (% stable or improved at 3 months) 18% 35% 0. 002 SQ (% stable or improved at 3 months) 24% 37% 0. 01
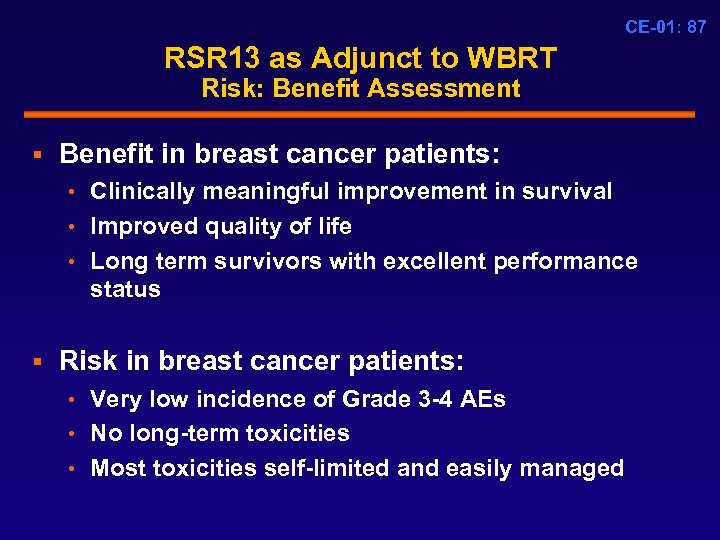 CE-01: 87 RSR 13 as Adjunct to WBRT Risk: Benefit Assessment § Benefit in breast cancer patients: • Clinically meaningful improvement in survival • Improved quality of life • Long term survivors with excellent performance status § Risk in breast cancer patients: • Very low incidence of Grade 3 -4 AEs • No long-term toxicities • Most toxicities self-limited and easily managed
CE-01: 87 RSR 13 as Adjunct to WBRT Risk: Benefit Assessment § Benefit in breast cancer patients: • Clinically meaningful improvement in survival • Improved quality of life • Long term survivors with excellent performance status § Risk in breast cancer patients: • Very low incidence of Grade 3 -4 AEs • No long-term toxicities • Most toxicities self-limited and easily managed
 CE-01: 88 Thank You!
CE-01: 88 Thank You!


