3efdea305c6b75dcb8cb5f2959c2ee29.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67
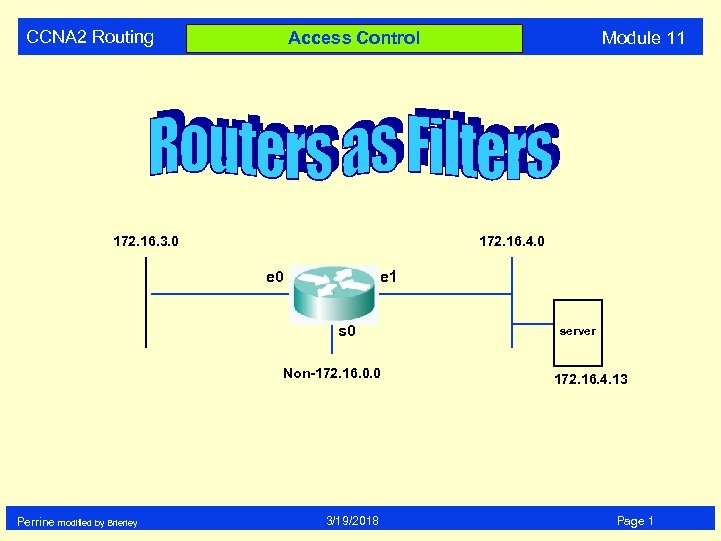 CCNA 2 Routing 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 Perrine modified by Brierley Module 11 Access Control 3/19/2018 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Page 1
CCNA 2 Routing 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 Perrine modified by Brierley Module 11 Access Control 3/19/2018 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Page 1
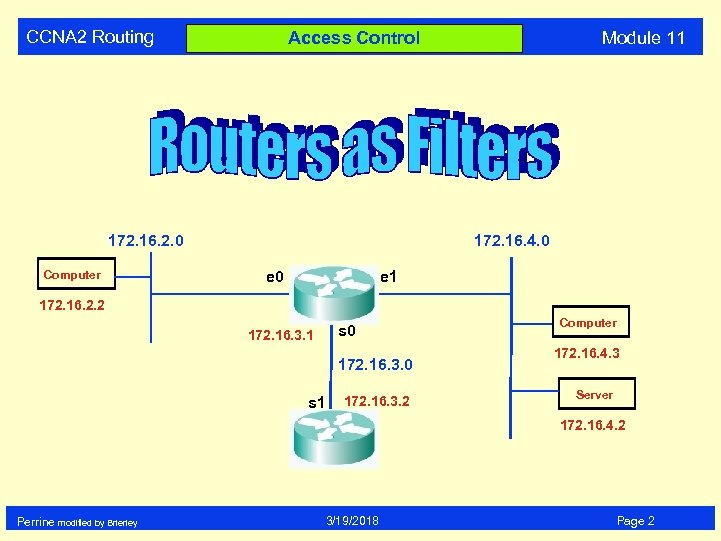 CCNA 2 Routing 172. 16. 2. 0 Computer Module 11 Access Control 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 172. 16. 2. 2 172. 16. 3. 1 s 0 172. 16. 3. 0 s 1 172. 16. 3. 2 Computer 172. 16. 4. 3 Server 172. 16. 4. 2 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 2
CCNA 2 Routing 172. 16. 2. 0 Computer Module 11 Access Control 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 172. 16. 2. 2 172. 16. 3. 1 s 0 172. 16. 3. 0 s 1 172. 16. 3. 2 Computer 172. 16. 4. 3 Server 172. 16. 4. 2 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 2
 CCNA 2 Routing High Level View Module 11 A HIGH LEVEL VIEW of ACLs Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 3
CCNA 2 Routing High Level View Module 11 A HIGH LEVEL VIEW of ACLs Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 3
 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Access Control Lists Standard Extended Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 4
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Access Control Lists Standard Extended Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 4
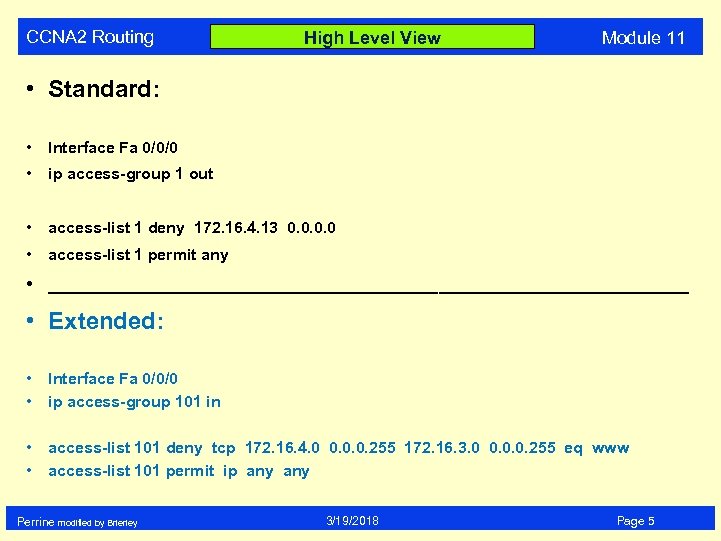 CCNA 2 Routing High Level View Module 11 • Standard: • Interface Fa 0/0/0 • ip access-group 1 out • access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 13 0. 0 • access-list 1 permit any • ________________________________ • Extended: • • Interface Fa 0/0/0 ip access-group 101 in • • access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq www access-list 101 permit ip any Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 5
CCNA 2 Routing High Level View Module 11 • Standard: • Interface Fa 0/0/0 • ip access-group 1 out • access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 13 0. 0 • access-list 1 permit any • ________________________________ • Extended: • • Interface Fa 0/0/0 ip access-group 101 in • • access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq www access-list 101 permit ip any Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 5
 CCNA 2 Routing Standard Access Control Lists Module 11 ACLs are instructions that are applied to a router interfaces. The ACLs describe the kind of packets that are to be permitted or denied. Permitted or Denial testing can be based on: • source address • destination address • port number ACLs are configured on the router Interfaces to control access to a network. ACLs must be defined separately for each protocol; Unique for IP, Unique for IPX; Unique for Apple. Talk, etc. Some times ACLs are called packet filters. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 6
CCNA 2 Routing Standard Access Control Lists Module 11 ACLs are instructions that are applied to a router interfaces. The ACLs describe the kind of packets that are to be permitted or denied. Permitted or Denial testing can be based on: • source address • destination address • port number ACLs are configured on the router Interfaces to control access to a network. ACLs must be defined separately for each protocol; Unique for IP, Unique for IPX; Unique for Apple. Talk, etc. Some times ACLs are called packet filters. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 6
 CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Standard Access Control Lists 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 7
CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Standard Access Control Lists 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 7
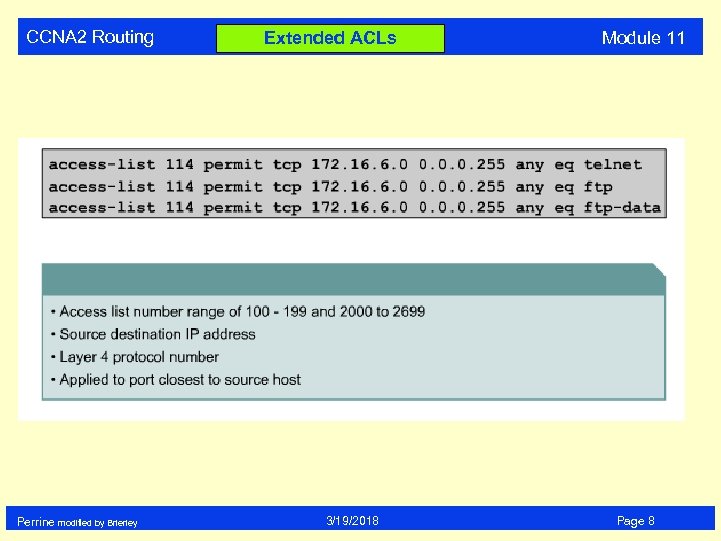 CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Extended ACLs 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 8
CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Extended ACLs 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 8
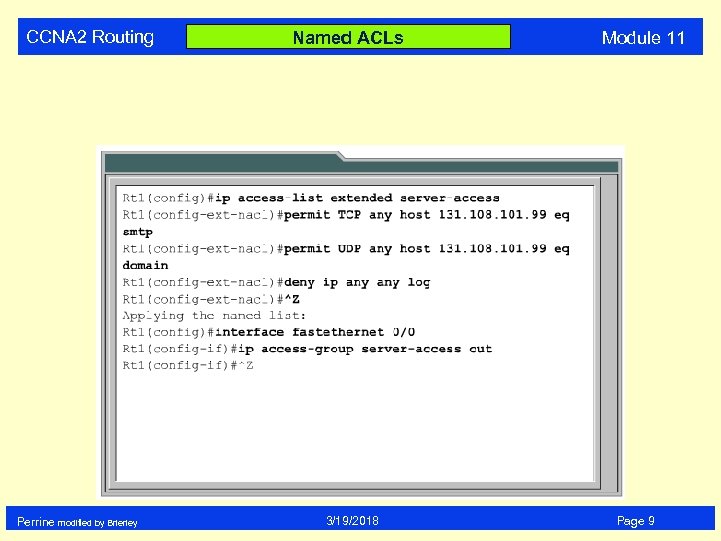 CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Named ACLs 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 9
CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Named ACLs 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 9
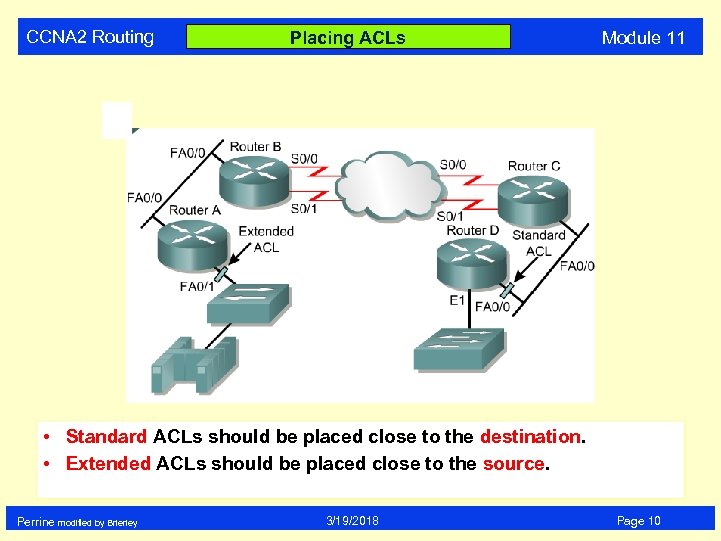 CCNA 2 Routing Placing ACLs Module 11 • Standard ACLs should be placed close to the destination. • Extended ACLs should be placed close to the source. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 10
CCNA 2 Routing Placing ACLs Module 11 • Standard ACLs should be placed close to the destination. • Extended ACLs should be placed close to the source. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 10
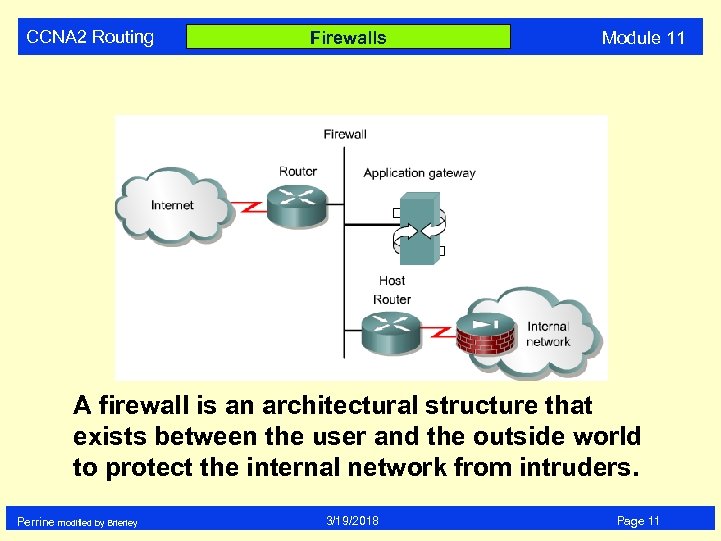 CCNA 2 Routing Firewalls Module 11 A firewall is an architectural structure that exists between the user and the outside world to protect the internal network from intruders. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 11
CCNA 2 Routing Firewalls Module 11 A firewall is an architectural structure that exists between the user and the outside world to protect the internal network from intruders. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 11
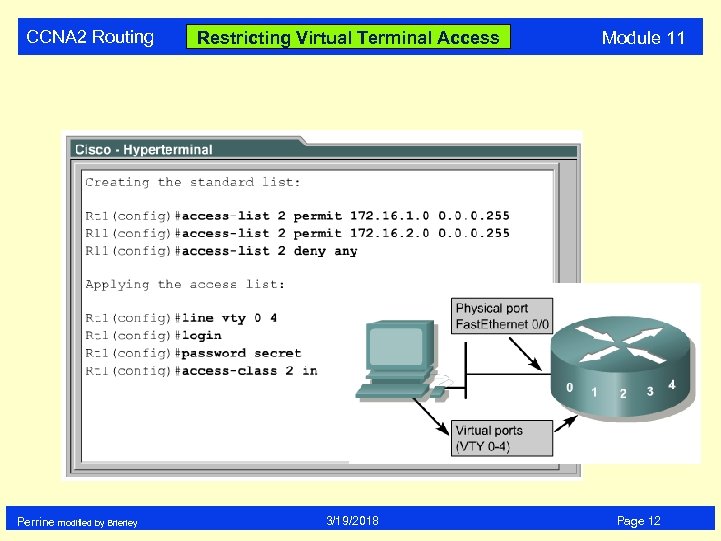 CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Restricting Virtual Terminal Access 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 12
CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Restricting Virtual Terminal Access 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 12
 CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Summary 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 13
CCNA 2 Routing Perrine modified by Brierley Summary 3/19/2018 Module 11 Page 13
 CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 Reasons to create ACLs: • limit network traffic - hence increase network performance • provide traffic flow - limit traffic through the network • provide for security • ACLs establish • which traffic is blocked • which traffic is not blocked Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 14
CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 Reasons to create ACLs: • limit network traffic - hence increase network performance • provide traffic flow - limit traffic through the network • provide for security • ACLs establish • which traffic is blocked • which traffic is not blocked Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 14
 CCNA 2 Routing DETAIL Module 11 A MORE DETAILED VIEW of ACLs Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 15
CCNA 2 Routing DETAIL Module 11 A MORE DETAILED VIEW of ACLs Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 15
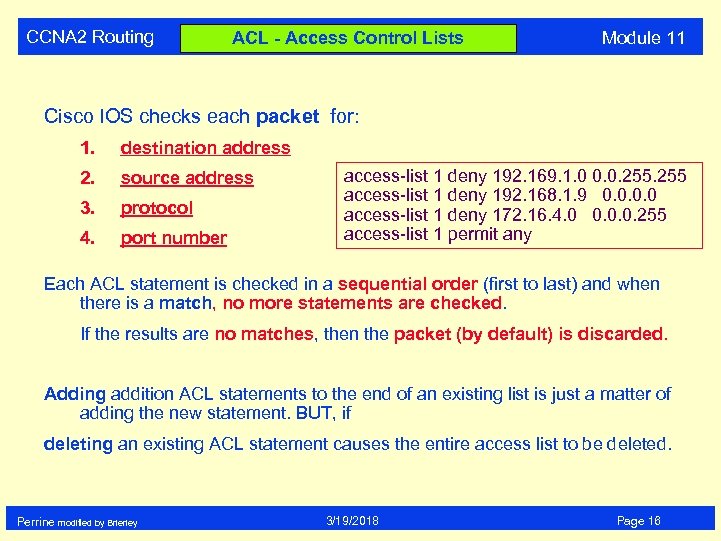 CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 Cisco IOS checks each packet for: 1. destination address 2. source address 3. protocol 4. port number access-list 1 deny 192. 169. 1. 0 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 deny 192. 168. 1. 9 0. 0 access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 permit any Each ACL statement is checked in a sequential order (first to last) and when there is a match, no more statements are checked. If the results are no matches, then the packet (by default) is discarded. Adding addition ACL statements to the end of an existing list is just a matter of adding the new statement. BUT, if deleting an existing ACL statement causes the entire access list to be deleted. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 16
CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 Cisco IOS checks each packet for: 1. destination address 2. source address 3. protocol 4. port number access-list 1 deny 192. 169. 1. 0 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 deny 192. 168. 1. 9 0. 0 access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 permit any Each ACL statement is checked in a sequential order (first to last) and when there is a match, no more statements are checked. If the results are no matches, then the packet (by default) is discarded. Adding addition ACL statements to the end of an existing list is just a matter of adding the new statement. BUT, if deleting an existing ACL statement causes the entire access list to be deleted. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 16
 CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 When a packet enters a router’s interface: “IN” (inbound) checking is required. The packet: 1) Is checked against the ACL list (if one exists) 2) Here It can be interrogated to permit or deny. 3) If denied the packet is dropped else, 4) It is matched against the routing table and passed to an “OUT” (outbound interface) 1) “OUT” (outbound) checking is required. Here It can be interrogated to permit or deny. 2) If denied the packet is dropped 3) If permitted then packet is allowed “OUT” (outbound). The Outbound interface’s ACL is a different list from the inbound) Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 17
CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 When a packet enters a router’s interface: “IN” (inbound) checking is required. The packet: 1) Is checked against the ACL list (if one exists) 2) Here It can be interrogated to permit or deny. 3) If denied the packet is dropped else, 4) It is matched against the routing table and passed to an “OUT” (outbound interface) 1) “OUT” (outbound) checking is required. Here It can be interrogated to permit or deny. 2) If denied the packet is dropped 3) If permitted then packet is allowed “OUT” (outbound). The Outbound interface’s ACL is a different list from the inbound) Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 17
 CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 ACL statements operate in a logical, sequential order. When a match is made the rest of the statements are not checked. If none the ACL statements match, then there is an implicit deny any rule. access-list 10 { permit | deny } { test conditions } access-list 1 deny 192. 169. 1. 0 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 deny 192. 168. 1. 9 0. 0 access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 access-list 10 deny access-list 1 permit any Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 18
CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 ACL statements operate in a logical, sequential order. When a match is made the rest of the statements are not checked. If none the ACL statements match, then there is an implicit deny any rule. access-list 10 { permit | deny } { test conditions } access-list 1 deny 192. 169. 1. 0 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 deny 192. 168. 1. 9 0. 0 access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 access-list 10 deny access-list 1 permit any Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 18
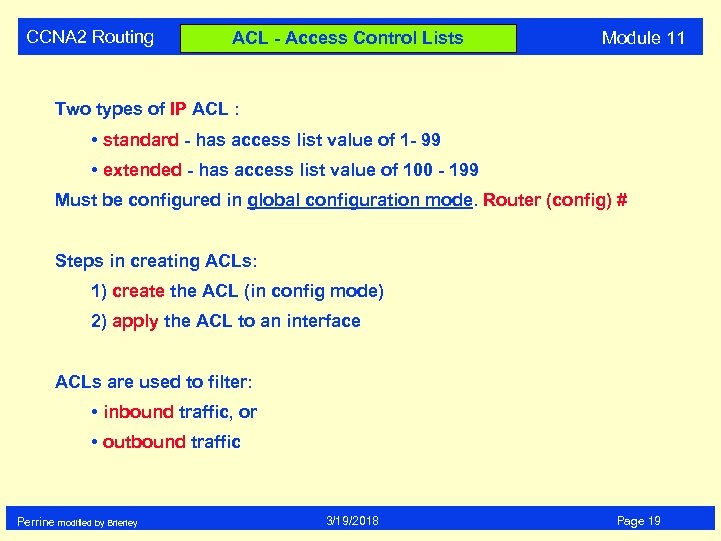 CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 Two types of IP ACL : • standard - has access list value of 1 - 99 • extended - has access list value of 100 - 199 Must be configured in global configuration mode. Router (config) # Steps in creating ACLs: 1) create the ACL (in config mode) 2) apply the ACL to an interface ACLs are used to filter: • inbound traffic, or • outbound traffic Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 19
CCNA 2 Routing ACL - Access Control Lists Module 11 Two types of IP ACL : • standard - has access list value of 1 - 99 • extended - has access list value of 100 - 199 Must be configured in global configuration mode. Router (config) # Steps in creating ACLs: 1) create the ACL (in config mode) 2) apply the ACL to an interface ACLs are used to filter: • inbound traffic, or • outbound traffic Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 19
 CCNA 2 Routing Where to place ACLs Module 11 Standard ACLs are place as close as possible to the destination. Extended ACLs are place as close as possible to the source. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 20
CCNA 2 Routing Where to place ACLs Module 11 Standard ACLs are place as close as possible to the destination. Extended ACLs are place as close as possible to the source. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 20
 CCNA 2 Routing Where to place ACLs Module 11 Configuring an Access List: Router(config)# access-list
CCNA 2 Routing Where to place ACLs Module 11 Configuring an Access List: Router(config)# access-list
 CCNA 2 Routing Wildcard Module 11 A wildcard is matched with an IP address or protocol address. It is a 32 bit mask divided into 4 octet, each containing 8 bits. A 0 in the wildcard means to check the bit in the IP you are testing. A 1 in the wildcard means ignore the bit in the IP you are testing. NOTE!!! Do NOT think subnet mask – that is a totally different meaning not related to the WILDCARD Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 22
CCNA 2 Routing Wildcard Module 11 A wildcard is matched with an IP address or protocol address. It is a 32 bit mask divided into 4 octet, each containing 8 bits. A 0 in the wildcard means to check the bit in the IP you are testing. A 1 in the wildcard means ignore the bit in the IP you are testing. NOTE!!! Do NOT think subnet mask – that is a totally different meaning not related to the WILDCARD Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 22
 CCNA 2 Routing Abbreviations Module 11 To permit or deny address: 0. 0 255 Address Wildcard Use the abbreviation any Router(config)# access-list 1 permit 0. 0 255 Router(config)# access-list 1 permit any Router(config)# access-list 1 deny 0. 0 255 Router(config)# access-list 1 deny any Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 23
CCNA 2 Routing Abbreviations Module 11 To permit or deny address: 0. 0 255 Address Wildcard Use the abbreviation any Router(config)# access-list 1 permit 0. 0 255 Router(config)# access-list 1 permit any Router(config)# access-list 1 deny 0. 0 255 Router(config)# access-list 1 deny any Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 23
 CCNA 2 Routing Abbreviations Module 11 To match all the bits of IP address use host: EX: 172. 30. 16. 29 0. 0 Router(config)# access-list 1 permit host 172. 30. 16. 29 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 24
CCNA 2 Routing Abbreviations Module 11 To match all the bits of IP address use host: EX: 172. 30. 16. 29 0. 0 Router(config)# access-list 1 permit host 172. 30. 16. 29 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 24
 CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 Criteria: • block all traffic from a network • allow all traffic from a network • deny entire protocol suits Standard ACLs only check the source address. Router(config)# access-list
CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 Criteria: • block all traffic from a network • allow all traffic from a network • deny entire protocol suits Standard ACLs only check the source address. Router(config)# access-list
 CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 What does this statement accomplish? Access-list 33 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 log Permits all traffic from 172. 16. 0. 0 and sends messages to the console every time the access list is executed. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 26
CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 What does this statement accomplish? Access-list 33 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 log Permits all traffic from 172. 16. 0. 0 and sends messages to the console every time the access list is executed. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 26
 CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 What does this statement accomplish? Access-list 44 deny 172. 16. 13. 7 0. 0 log Denies traffic from host 172. 16. 13. 7 and sends message to the console every time the access list is hit. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 27
CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 What does this statement accomplish? Access-list 44 deny 172. 16. 13. 7 0. 0 log Denies traffic from host 172. 16. 13. 7 and sends message to the console every time the access list is hit. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 27
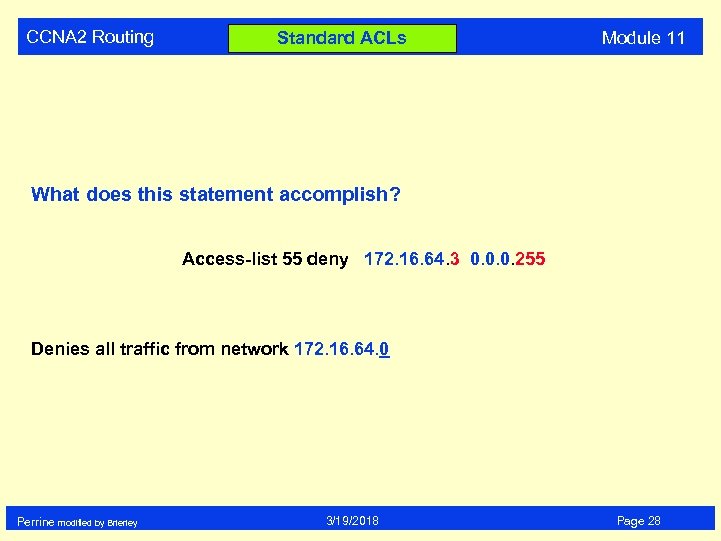 CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 What does this statement accomplish? Access-list 55 deny 172. 16. 64. 3 0. 0. 0. 255 Denies all traffic from network 172. 16. 64. 0 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 28
CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 What does this statement accomplish? Access-list 55 deny 172. 16. 64. 3 0. 0. 0. 255 Denies all traffic from network 172. 16. 64. 0 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 28
 CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 The log command: Prints messages to the console which includes the ACL number, whether the packet was permitted or denied, the source address, and the number of packets. The message is generated for the first packet that matches, and then at five-minute intervals, including the number of packets permitted or denied in the prior five-minute interval. Log is used for debugging only not to be left active on live networks. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 29
CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 The log command: Prints messages to the console which includes the ACL number, whether the packet was permitted or denied, the source address, and the number of packets. The message is generated for the first packet that matches, and then at five-minute intervals, including the number of packets permitted or denied in the prior five-minute interval. Log is used for debugging only not to be left active on live networks. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 29
 CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 Example of applying the access-list: Router(config-if)# ip access-group 33 in Router(config-if)# ip access-group 44 out Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 30
CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 Example of applying the access-list: Router(config-if)# ip access-group 33 in Router(config-if)# ip access-group 44 out Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 30
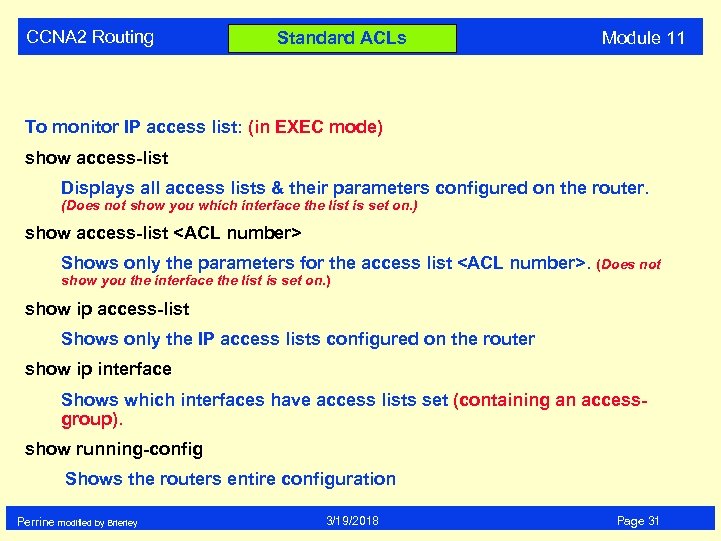 CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 To monitor IP access list: (in EXEC mode) show access-list Displays all access lists & their parameters configured on the router. (Does not show you which interface the list is set on. ) show access-list
CCNA 2 Routing Standard ACLs Module 11 To monitor IP access list: (in EXEC mode) show access-list Displays all access lists & their parameters configured on the router. (Does not show you which interface the list is set on. ) show access-list
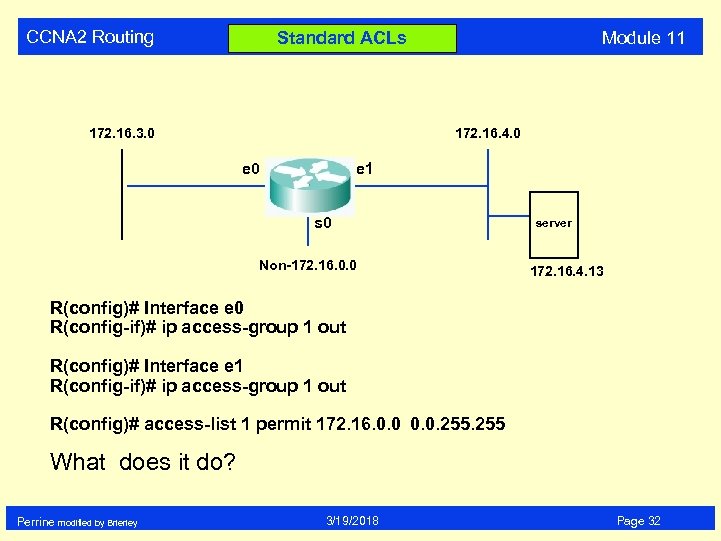 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 R(config)# Interface e 0 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# Interface e 1 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 What does it do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 32
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 R(config)# Interface e 0 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# Interface e 1 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 What does it do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 32
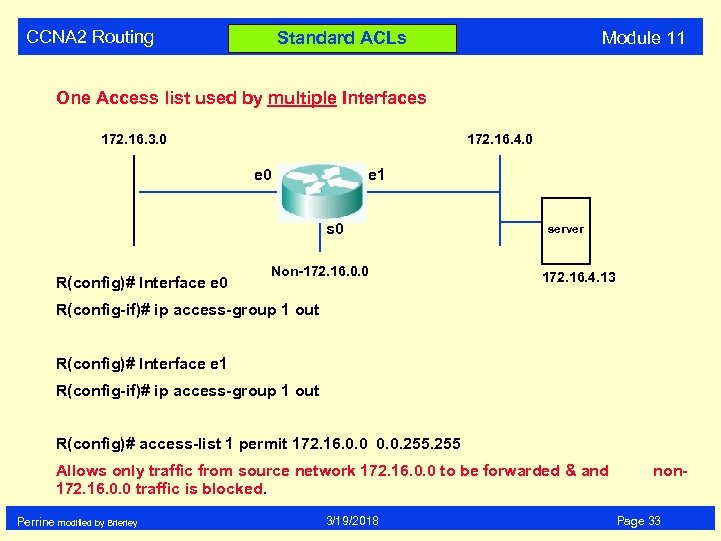 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs One Access list used by multiple Interfaces 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 R(config)# Interface e 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# Interface e 1 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 Allows only traffic from source network 172. 16. 0. 0 to be forwarded & and 172. 16. 0. 0 traffic is blocked. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 non. Page 33
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs One Access list used by multiple Interfaces 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 R(config)# Interface e 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# Interface e 1 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 Allows only traffic from source network 172. 16. 0. 0 to be forwarded & and 172. 16. 0. 0 traffic is blocked. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 non. Page 33
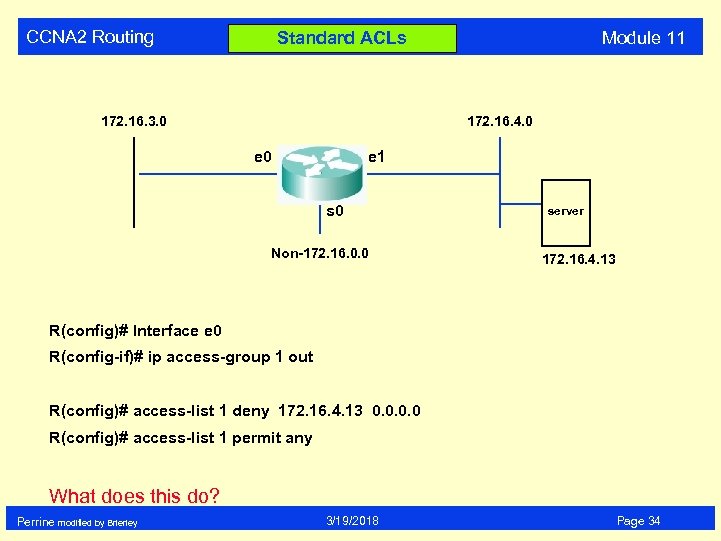 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 R(config)# Interface e 0 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 13 0. 0 R(config)# access-list 1 permit any What does this do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 34
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 R(config)# Interface e 0 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 13 0. 0 R(config)# access-list 1 permit any What does this do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 34
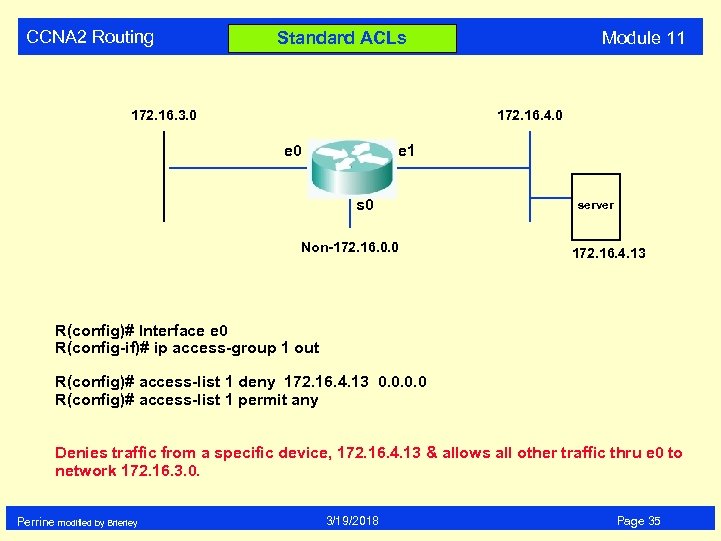 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 R(config)# Interface e 0 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 13 0. 0 R(config)# access-list 1 permit any Denies traffic from a specific device, 172. 16. 4. 13 & allows all other traffic thru e 0 to network 172. 16. 3. 0. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 35
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 R(config)# Interface e 0 R(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out R(config)# access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 13 0. 0 R(config)# access-list 1 permit any Denies traffic from a specific device, 172. 16. 4. 13 & allows all other traffic thru e 0 to network 172. 16. 3. 0. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 35
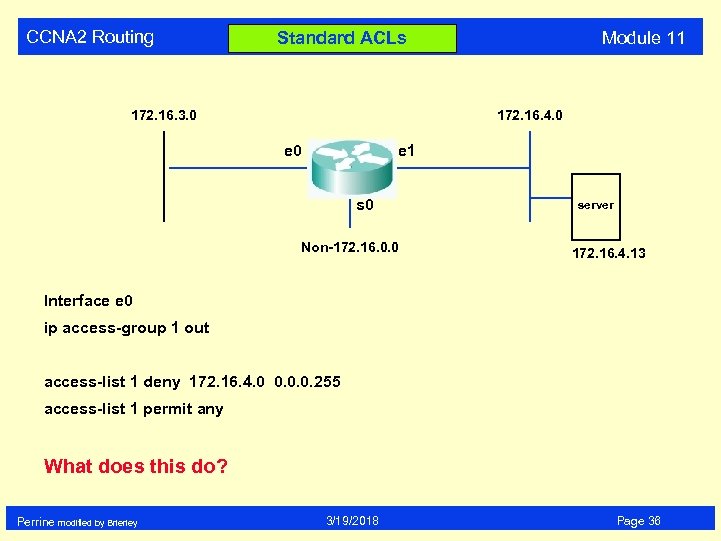 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 1 out access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 permit any What does this do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 36
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 1 out access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 permit any What does this do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 36
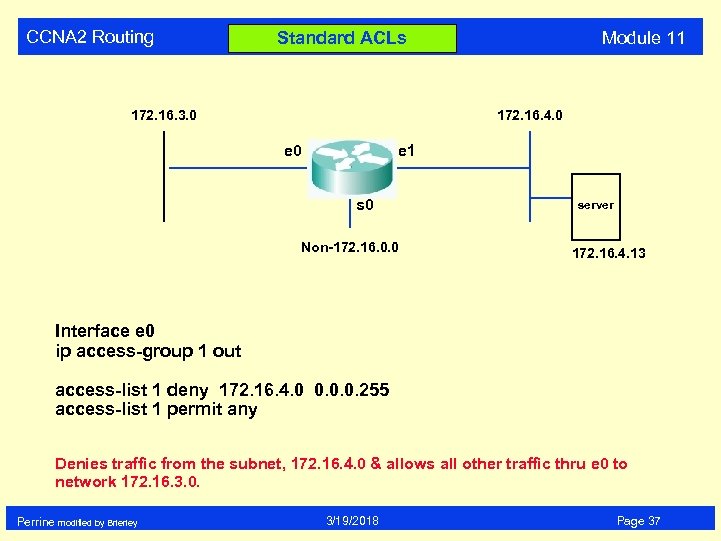 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 1 out access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 permit any Denies traffic from the subnet, 172. 16. 4. 0 & allows all other traffic thru e 0 to network 172. 16. 3. 0. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 37
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Standard ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 1 out access-list 1 deny 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 access-list 1 permit any Denies traffic from the subnet, 172. 16. 4. 0 & allows all other traffic thru e 0 to network 172. 16. 3. 0. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 37
 CCNA 2 Routing Extended ACLs Module 11 Criteria: • checks both the packet’s source & destination addresses • check for specific protocol • check for specific port numbers • permit or denied applications – pings, telnets, FTP, etc. • ACL values range between 100 – 199 (for IP) Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 38
CCNA 2 Routing Extended ACLs Module 11 Criteria: • checks both the packet’s source & destination addresses • check for specific protocol • check for specific port numbers • permit or denied applications – pings, telnets, FTP, etc. • ACL values range between 100 – 199 (for IP) Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 38
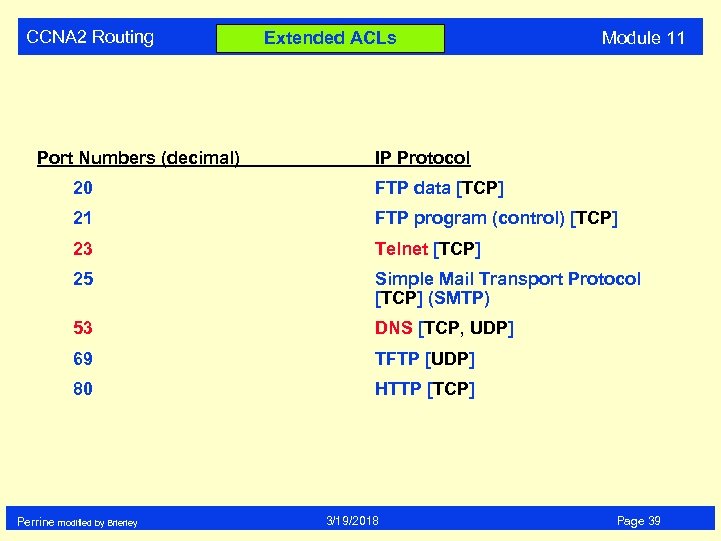 CCNA 2 Routing Port Numbers (decimal) Extended ACLs Module 11 IP Protocol 20 FTP data [TCP] 21 FTP program (control) [TCP] 23 Telnet [TCP] 25 Simple Mail Transport Protocol [TCP] (SMTP) 53 DNS [TCP, UDP] 69 TFTP [UDP] 80 HTTP [TCP] Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 39
CCNA 2 Routing Port Numbers (decimal) Extended ACLs Module 11 IP Protocol 20 FTP data [TCP] 21 FTP program (control) [TCP] 23 Telnet [TCP] 25 Simple Mail Transport Protocol [TCP] (SMTP) 53 DNS [TCP, UDP] 69 TFTP [UDP] 80 HTTP [TCP] Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 39
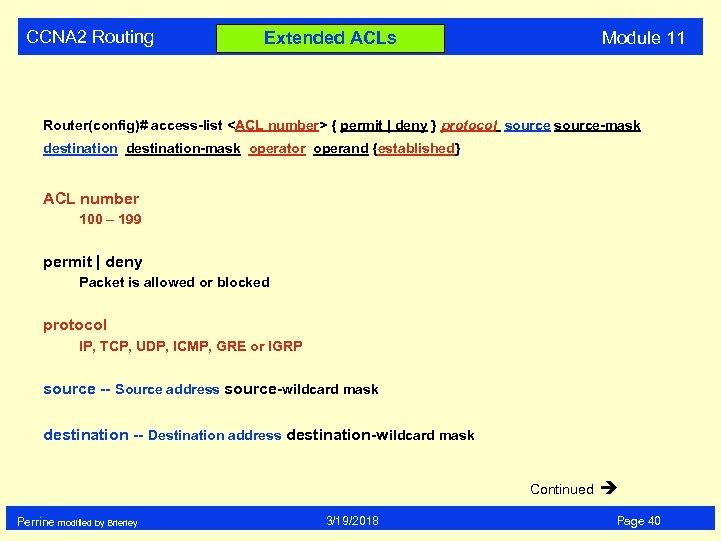 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs Router(config)# access-list
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs Router(config)# access-list
 CCNA 2 Routing Extended ACLs Module 11 Router(config)# access-list
CCNA 2 Routing Extended ACLs Module 11 Router(config)# access-list
 CCNA 2 Routing Extended ACLs Module 11 Configuring an extended ACL to an interface: Router(config-if)# ip access-group
CCNA 2 Routing Extended ACLs Module 11 Configuring an extended ACL to an interface: Router(config-if)# ip access-group
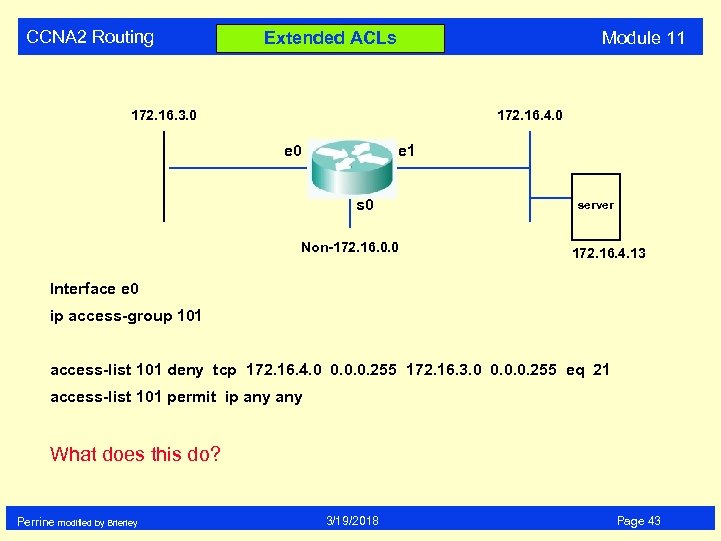 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 101 access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq 21 access-list 101 permit ip any What does this do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 43
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 101 access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq 21 access-list 101 permit ip any What does this do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 43
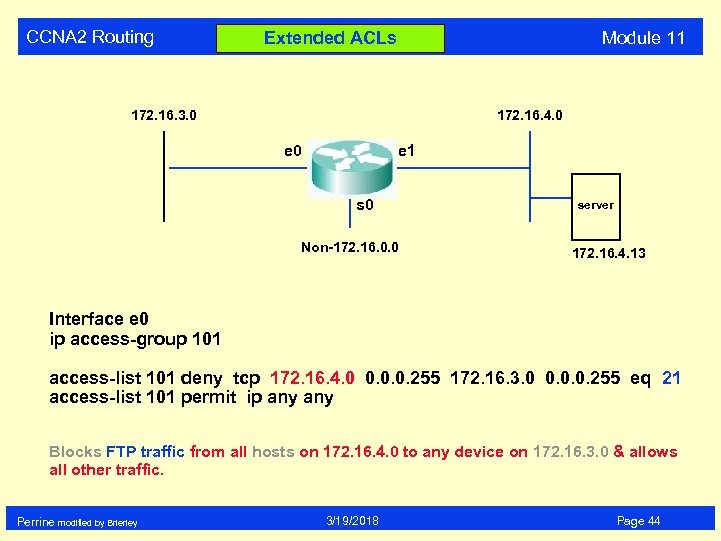 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 101 access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq 21 access-list 101 permit ip any Blocks FTP traffic from all hosts on 172. 16. 4. 0 to any device on 172. 16. 3. 0 & allows all other traffic. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 44
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 101 access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq 21 access-list 101 permit ip any Blocks FTP traffic from all hosts on 172. 16. 4. 0 to any device on 172. 16. 3. 0 & allows all other traffic. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 44
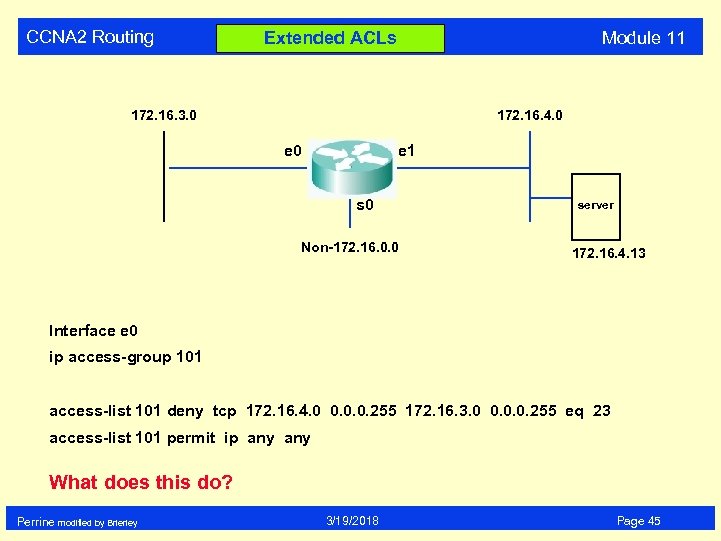 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 101 access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq 23 access-list 101 permit ip any What does this do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 45
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 101 access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq 23 access-list 101 permit ip any What does this do? Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 45
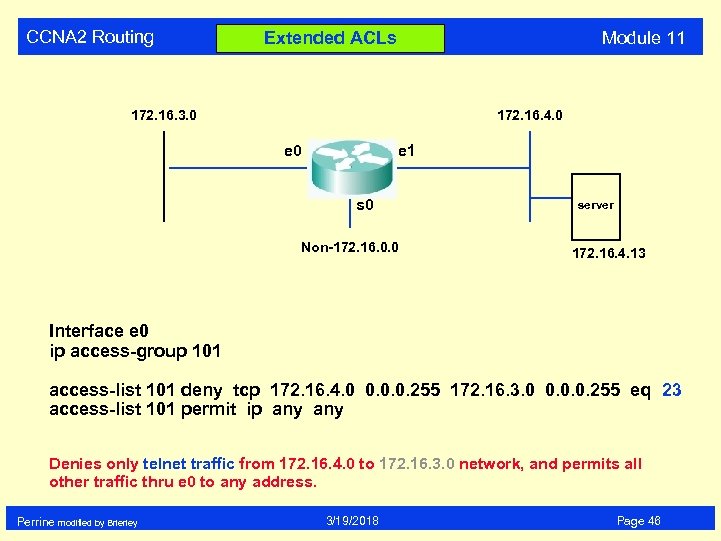 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 101 access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq 23 access-list 101 permit ip any Denies only telnet traffic from 172. 16. 4. 0 to 172. 16. 3. 0 network, and permits all other traffic thru e 0 to any address. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 46
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Extended ACLs 172. 16. 3. 0 172. 16. 4. 0 e 1 s 0 Non-172. 16. 0. 0 server 172. 16. 4. 13 Interface e 0 ip access-group 101 access-list 101 deny tcp 172. 16. 4. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq 23 access-list 101 permit ip any Denies only telnet traffic from 172. 16. 4. 0 to 172. 16. 3. 0 network, and permits all other traffic thru e 0 to any address. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 46
 CCNA 2 Routing Extended/Standard ACL numbers for IP Module 11 NOTE: Standard ACL numbers: 1 -99; 1300 -1999 Extended ACL numbers: 100 -199; Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 2000 -2699 Page 47
CCNA 2 Routing Extended/Standard ACL numbers for IP Module 11 NOTE: Standard ACL numbers: 1 -99; 1300 -1999 Extended ACL numbers: 100 -199; Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 2000 -2699 Page 47
 CCNA 2 Routing Standard/Extended ACL Module 11 You can not add ACL statements into the body of the access-list (ONLY at the end of the list). Otherwise the access list must be deleted first, and then rewritten. Therefore it is prudent to write your access-list in text format using “notepad”, and then transfer it to your router. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 48
CCNA 2 Routing Standard/Extended ACL Module 11 You can not add ACL statements into the body of the access-list (ONLY at the end of the list). Otherwise the access list must be deleted first, and then rewritten. Therefore it is prudent to write your access-list in text format using “notepad”, and then transfer it to your router. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 48
 CCNA 2 Routing Configuring Named ACLs Module 11 NOTE: • A NAMED ACL is an alphanumeric string instead of the ACL number (1 - 199 ) • NAMED ACLs are not compatible with Cisco IOS release prior to Release 11. 2 • Named ACLs can be used for either standard & extended • You cannot configure the same name for multiple ACLs. • use Name ACL when you want to intuitively identify ACLs • use Name ACL when you have more than 99 standard & 100 extended ACLs have been configured on a router for a given protocol Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 49
CCNA 2 Routing Configuring Named ACLs Module 11 NOTE: • A NAMED ACL is an alphanumeric string instead of the ACL number (1 - 199 ) • NAMED ACLs are not compatible with Cisco IOS release prior to Release 11. 2 • Named ACLs can be used for either standard & extended • You cannot configure the same name for multiple ACLs. • use Name ACL when you want to intuitively identify ACLs • use Name ACL when you have more than 99 standard & 100 extended ACLs have been configured on a router for a given protocol Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 49
 CCNA 2 Routing Configuring Named ACLs Module 11 Router(config)# ip access-list { standard | extended } name { deny | permit } { commands } ip access-list standard internetfilter deny 172. 10. 15. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 permit 128. 88. 0. 0. 255 permit 36. 0. 0. 0. 255 ip access-list extended marketing-group permit tcp any 171. 69. 0. 0 0. 255 eq telnet deny udp any 171. 69. 0. 0 0. 255 lt 1024 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 50
CCNA 2 Routing Configuring Named ACLs Module 11 Router(config)# ip access-list { standard | extended } name { deny | permit } { commands } ip access-list standard internetfilter deny 172. 10. 15. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 permit 128. 88. 0. 0. 255 permit 36. 0. 0. 0. 255 ip access-list extended marketing-group permit tcp any 171. 69. 0. 0 0. 255 eq telnet deny udp any 171. 69. 0. 0 0. 255 lt 1024 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 50
 CCNA 2 Routing Named ACL Module 11 A named ACL will allow the deletion of statements, but will only allow for the statements to be inserted a the end of the list. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 51
CCNA 2 Routing Named ACL Module 11 A named ACL will allow the deletion of statements, but will only allow for the statements to be inserted a the end of the list. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 51
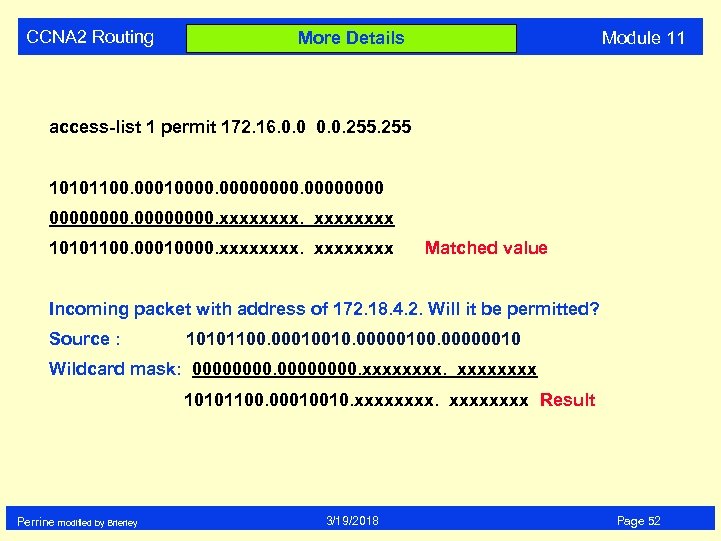 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 More Details access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 10101100. 000100000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxxx Matched value Incoming packet with address of 172. 18. 4. 2. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 00010010. 00000100. 00000010 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010010. xxxxxxxx Result Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 52
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 More Details access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 10101100. 000100000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxxx Matched value Incoming packet with address of 172. 18. 4. 2. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 00010010. 00000100. 00000010 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010010. xxxxxxxx Result Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 52
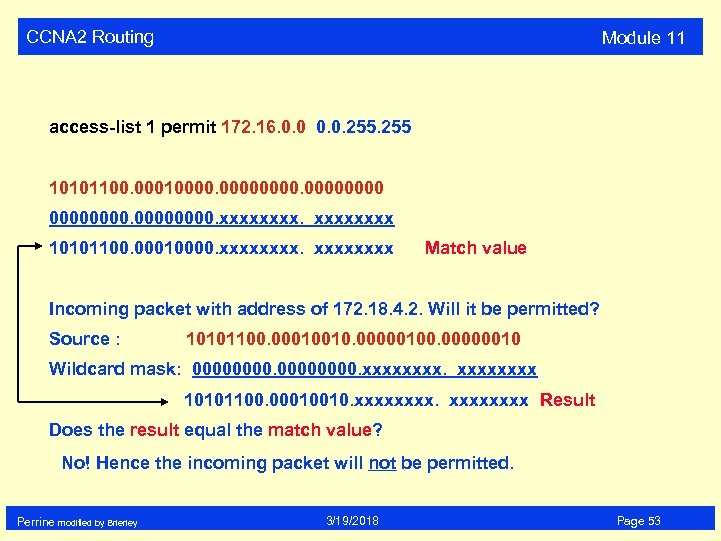 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 10101100. 000100000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxxx Match value Incoming packet with address of 172. 18. 4. 2. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 00010010. 00000100. 00000010 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010010. xxxxxxxx Result Does the result equal the match value? No! Hence the incoming packet will not be permitted. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 53
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 10101100. 000100000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxxx Match value Incoming packet with address of 172. 18. 4. 2. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 00010010. 00000100. 00000010 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010010. xxxxxxxx Result Does the result equal the match value? No! Hence the incoming packet will not be permitted. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 53
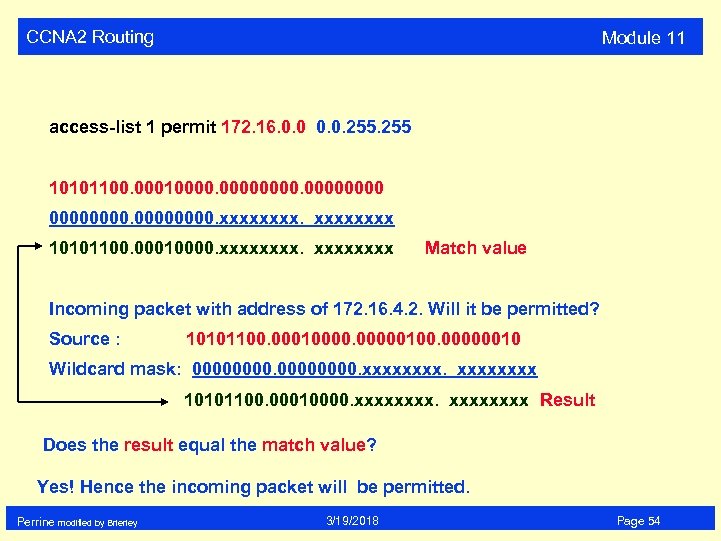 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 10101100. 000100000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxxx Match value Incoming packet with address of 172. 16. 4. 2. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 000100000100. 00000010 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxxx Result Does the result equal the match value? Yes! Hence the incoming packet will be permitted. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 54
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255 10101100. 000100000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxxx Match value Incoming packet with address of 172. 16. 4. 2. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 000100000100. 00000010 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxx 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxxx Result Does the result equal the match value? Yes! Hence the incoming packet will be permitted. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 54
 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255. 254 10101100. 000100000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 0 Matched value Incoming packet with address of 172. 16. 4. 1. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 000100000100. 00000001 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 1 Result Incoming packet with address of 172. 16. 4. 4. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 000100000100 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 0 Result Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 55
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255. 254 10101100. 000100000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 0 Matched value Incoming packet with address of 172. 16. 4. 1. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 000100000100. 00000001 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 1 Result Incoming packet with address of 172. 16. 4. 4. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 000100000100 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 0 Result Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 55
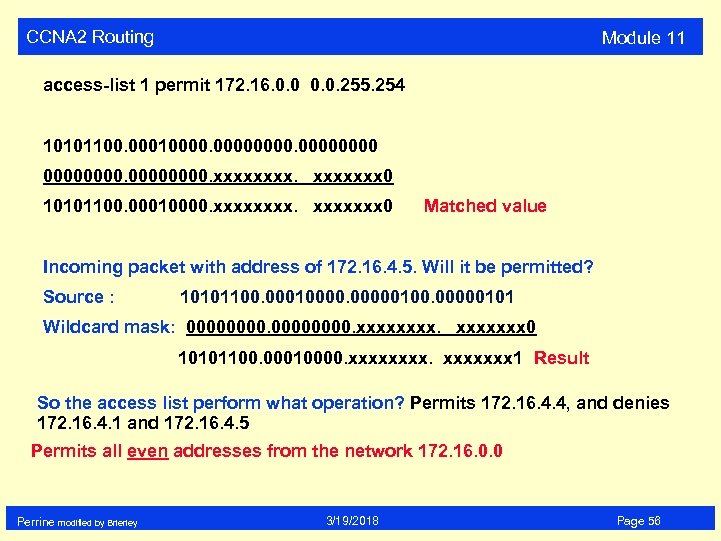 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255. 254 10101100. 000100000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 0 Matched value Incoming packet with address of 172. 16. 4. 5. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 000100000101 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 1 Result So the access list perform what operation? Permits 172. 16. 4. 4, and denies 172. 16. 4. 1 and 172. 16. 4. 5 Permits all even addresses from the network 172. 16. 0. 0 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 56
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 0. 0. 255. 254 10101100. 000100000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 0 Matched value Incoming packet with address of 172. 16. 4. 5. Will it be permitted? Source : 10101100. 000100000101 Wildcard mask: 00000000. xxxxxxx 0 10101100. 00010000. xxxxxxx 1 Result So the access list perform what operation? Permits 172. 16. 4. 4, and denies 172. 16. 4. 1 and 172. 16. 4. 5 Permits all even addresses from the network 172. 16. 0. 0 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 56
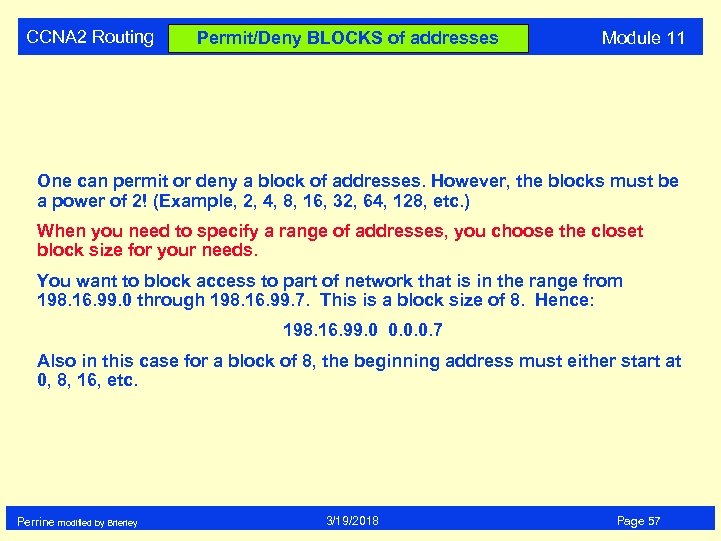 CCNA 2 Routing Permit/Deny BLOCKS of addresses Module 11 One can permit or deny a block of addresses. However, the blocks must be a power of 2! (Example, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, etc. ) When you need to specify a range of addresses, you choose the closet block size for your needs. You want to block access to part of network that is in the range from 198. 16. 99. 0 through 198. 16. 99. 7. This is a block size of 8. Hence: 198. 16. 99. 0 0. 0. 0. 7 Also in this case for a block of 8, the beginning address must either start at 0, 8, 16, etc. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 57
CCNA 2 Routing Permit/Deny BLOCKS of addresses Module 11 One can permit or deny a block of addresses. However, the blocks must be a power of 2! (Example, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, etc. ) When you need to specify a range of addresses, you choose the closet block size for your needs. You want to block access to part of network that is in the range from 198. 16. 99. 0 through 198. 16. 99. 7. This is a block size of 8. Hence: 198. 16. 99. 0 0. 0. 0. 7 Also in this case for a block of 8, the beginning address must either start at 0, 8, 16, etc. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 57
 CCNA 2 Routing Permit/Deny BLOCKS of addresses Module 11 One has a subnet whose addresses range from 200. 17. 2. 128 to 200. 17. 2. 191. One wants to divide this network so the top half are permitted and the bottom half is denied to any other network. What is the access lists? The block range is: 64 What is the access-list for the bottom? access-list 101 deny ip 200. 17. 2. 128 0. 0. 0. 31 any What is the access-list for the top? access-list 101 permit ip 200. 17. 2. 160 0. 0. 0. 31 any Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 58
CCNA 2 Routing Permit/Deny BLOCKS of addresses Module 11 One has a subnet whose addresses range from 200. 17. 2. 128 to 200. 17. 2. 191. One wants to divide this network so the top half are permitted and the bottom half is denied to any other network. What is the access lists? The block range is: 64 What is the access-list for the bottom? access-list 101 deny ip 200. 17. 2. 128 0. 0. 0. 31 any What is the access-list for the top? access-list 101 permit ip 200. 17. 2. 160 0. 0. 0. 31 any Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 58
 CCNA 2 Routing Permit/Deny BLOCKS of addresses Module 11 What does this do? access-list 10 deny 200. 16. 88. 64 0. 0. 0. 63 Denies a block of 64 address starting at 200. 16. 88. 64 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 59
CCNA 2 Routing Permit/Deny BLOCKS of addresses Module 11 What does this do? access-list 10 deny 200. 16. 88. 64 0. 0. 0. 63 Denies a block of 64 address starting at 200. 16. 88. 64 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 59
 CCNA 2 Routing Virtual Terminal ACL Module 11 You can control access via the VTY ports controlling telnet sessions coming into the router. You write the ACL as usual, but use access-class to apply it. As an example: Router(config t)# access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 1. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 Router(config t)# line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)# login Router(config-line)# password cisco Router(config-line)# access-class 1 in Note: only numbered access lists can be applied to VTY virtual lines! Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 60
CCNA 2 Routing Virtual Terminal ACL Module 11 You can control access via the VTY ports controlling telnet sessions coming into the router. You write the ACL as usual, but use access-class to apply it. As an example: Router(config t)# access-list 1 permit 172. 16. 1. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 Router(config t)# line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)# login Router(config-line)# password cisco Router(config-line)# access-class 1 in Note: only numbered access lists can be applied to VTY virtual lines! Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 60
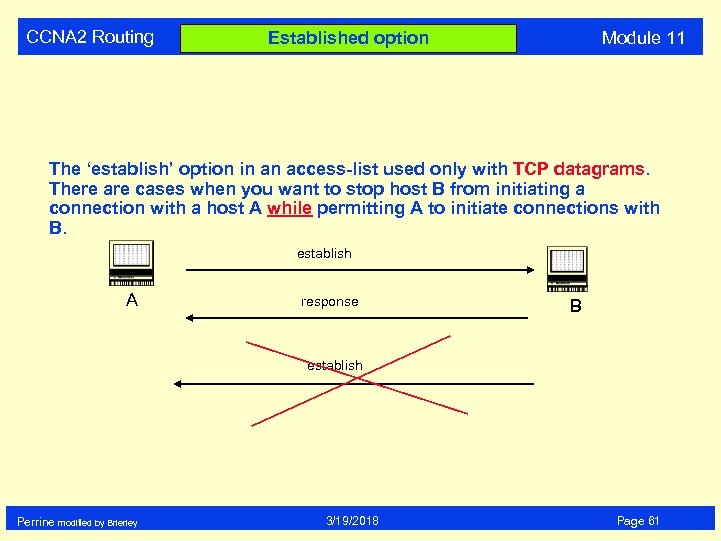 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Established option The ‘establish’ option in an access-list used only with TCP datagrams. There are cases when you want to stop host B from initiating a connection with a host A while permitting A to initiate connections with B. establish A response B establish Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 61
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Established option The ‘establish’ option in an access-list used only with TCP datagrams. There are cases when you want to stop host B from initiating a connection with a host A while permitting A to initiate connections with B. establish A response B establish Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 61
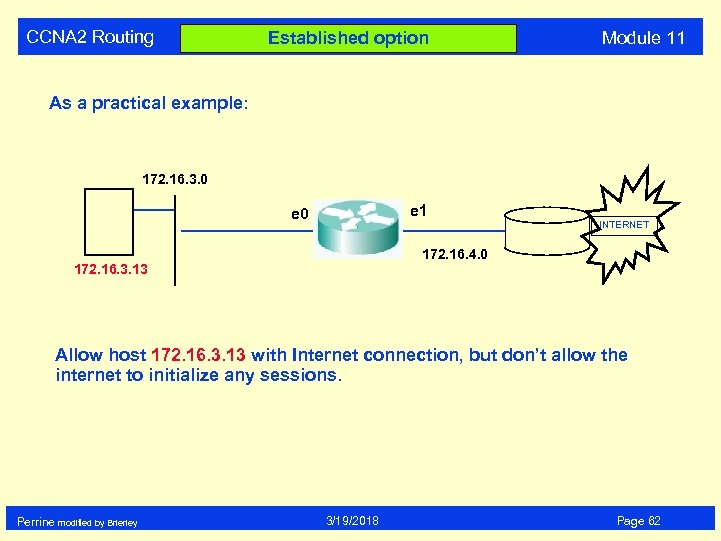 CCNA 2 Routing Established option Module 11 As a practical example: 172. 16. 3. 0 e 1 e 0 INTERNET 172. 16. 4. 0 172. 16. 3. 13 Allow host 172. 16. 3. 13 with Internet connection, but don’t allow the internet to initialize any sessions. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 62
CCNA 2 Routing Established option Module 11 As a practical example: 172. 16. 3. 0 e 1 e 0 INTERNET 172. 16. 4. 0 172. 16. 3. 13 Allow host 172. 16. 3. 13 with Internet connection, but don’t allow the internet to initialize any sessions. Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 62
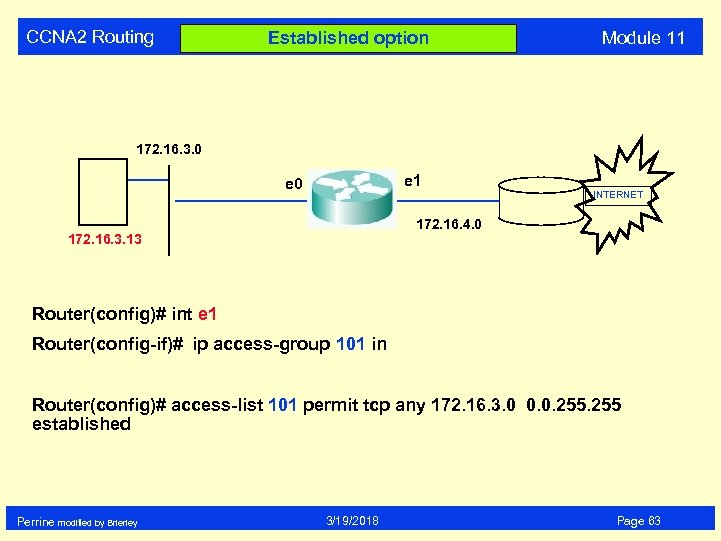 CCNA 2 Routing Established option Module 11 172. 16. 3. 0 e 1 e 0 INTERNET 172. 16. 4. 0 172. 16. 3. 13 Router(config)# int e 1 Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in Router(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 255 established Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 63
CCNA 2 Routing Established option Module 11 172. 16. 3. 0 e 1 e 0 INTERNET 172. 16. 4. 0 172. 16. 3. 13 Router(config)# int e 1 Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in Router(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 255 established Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 63
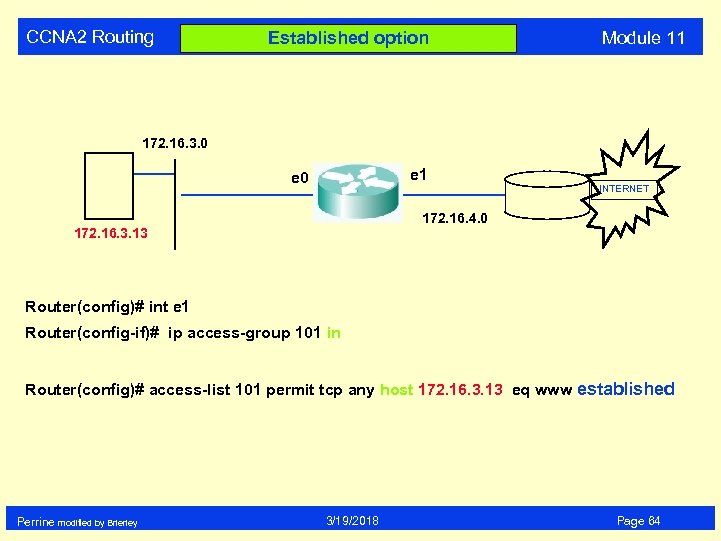 CCNA 2 Routing Established option Module 11 172. 16. 3. 0 e 1 e 0 INTERNET 172. 16. 4. 0 172. 16. 3. 13 Router(config)# int e 1 Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in Router(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any host 172. 16. 3. 13 eq www established Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 64
CCNA 2 Routing Established option Module 11 172. 16. 3. 0 e 1 e 0 INTERNET 172. 16. 4. 0 172. 16. 3. 13 Router(config)# int e 1 Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in Router(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any host 172. 16. 3. 13 eq www established Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 64
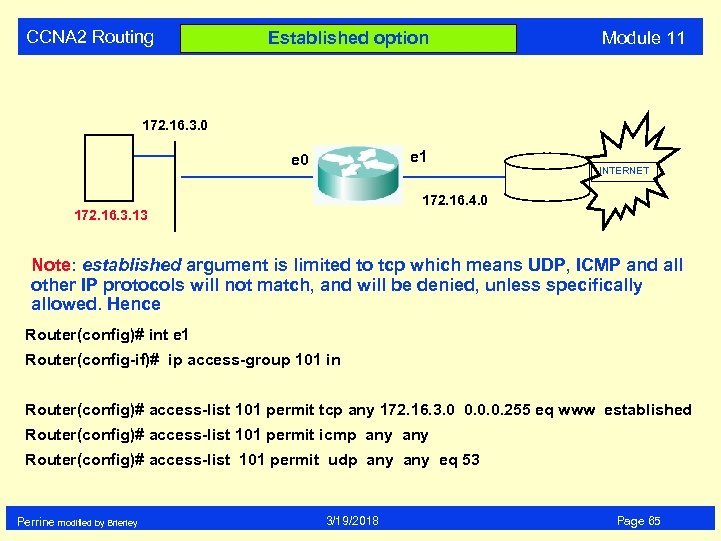 CCNA 2 Routing Established option Module 11 172. 16. 3. 0 e 1 e 0 INTERNET 172. 16. 4. 0 172. 16. 3. 13 Note: established argument is limited to tcp which means UDP, ICMP and all other IP protocols will not match, and will be denied, unless specifically allowed. Hence Router(config)# int e 1 Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in Router(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq www established Router(config)# access-list 101 permit icmp any Router(config)# access-list 101 permit udp any eq 53 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 65
CCNA 2 Routing Established option Module 11 172. 16. 3. 0 e 1 e 0 INTERNET 172. 16. 4. 0 172. 16. 3. 13 Note: established argument is limited to tcp which means UDP, ICMP and all other IP protocols will not match, and will be denied, unless specifically allowed. Hence Router(config)# int e 1 Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in Router(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any 172. 16. 3. 0 0. 0. 0. 255 eq www established Router(config)# access-list 101 permit icmp any Router(config)# access-list 101 permit udp any eq 53 Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 65
 CCNA 2 Routing Where to Place ACLs? Module 11 ACL Rules: Standard ACL Place the ACL as near the destination as possible. Extended ACL Put the ACL as close as possible to the source Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 66
CCNA 2 Routing Where to Place ACLs? Module 11 ACL Rules: Standard ACL Place the ACL as near the destination as possible. Extended ACL Put the ACL as close as possible to the source Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 66
 CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Access Lists Standard Extended End of Session Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 67
CCNA 2 Routing Module 11 Access Lists Standard Extended End of Session Perrine modified by Brierley 3/19/2018 Page 67


