02a24d19d3c54010d30a76934a09093e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 97
 CCM inter-hospital grand-round th March 2011 15 Cannot eat, cannot breathe then cannot see! Dr Alfred Chan Caritas Medical Centre
CCM inter-hospital grand-round th March 2011 15 Cannot eat, cannot breathe then cannot see! Dr Alfred Chan Caritas Medical Centre
 Clinical History (1) 21 year old girl, born in HK, student n Normal full-term spontaneous delivery n Unremarkable past health n Non drinker and never smoke n No history of drug abuse n “Flu-like illness” in early June 2010 n weak left face + nasal regurgitation on fluid drinking ~ 2 weeks later n
Clinical History (1) 21 year old girl, born in HK, student n Normal full-term spontaneous delivery n Unremarkable past health n Non drinker and never smoke n No history of drug abuse n “Flu-like illness” in early June 2010 n weak left face + nasal regurgitation on fluid drinking ~ 2 weeks later n
 Clinical History (2) Visited acupuncture experts Reluctant to quit from school examination n Attended AED of hospital A on 9 th July 2010 for choking after drinking n Facial weakness became bilateral n Subjective weak voice and slurred speech n
Clinical History (2) Visited acupuncture experts Reluctant to quit from school examination n Attended AED of hospital A on 9 th July 2010 for choking after drinking n Facial weakness became bilateral n Subjective weak voice and slurred speech n
 AED of Hospital A BP 106/85; P 112 regular; temp 37; n GCS 15/15; PERL n No ophthalmoplegia n Limb power and sensation normal n Otoscopy and hearing normal n Bilateral VII palsy, LMN type n Markedly diminished gag reflex n
AED of Hospital A BP 106/85; P 112 regular; temp 37; n GCS 15/15; PERL n No ophthalmoplegia n Limb power and sensation normal n Otoscopy and hearing normal n Bilateral VII palsy, LMN type n Markedly diminished gag reflex n
 Admit M&G of hospital A No ocular movement deficit n Normal facial sensation/ hearing n Tongue movement intact n Poor gag reflex + bilateral LMN VII palsy n Tandem-walking unsteady n WC 13. 4 (80% neutrophil); normal R/LFT n ESR 73; CRP 27 n CT Brain: ? Right pons hypodense spots n
Admit M&G of hospital A No ocular movement deficit n Normal facial sensation/ hearing n Tongue movement intact n Poor gag reflex + bilateral LMN VII palsy n Tandem-walking unsteady n WC 13. 4 (80% neutrophil); normal R/LFT n ESR 73; CRP 27 n CT Brain: ? Right pons hypodense spots n
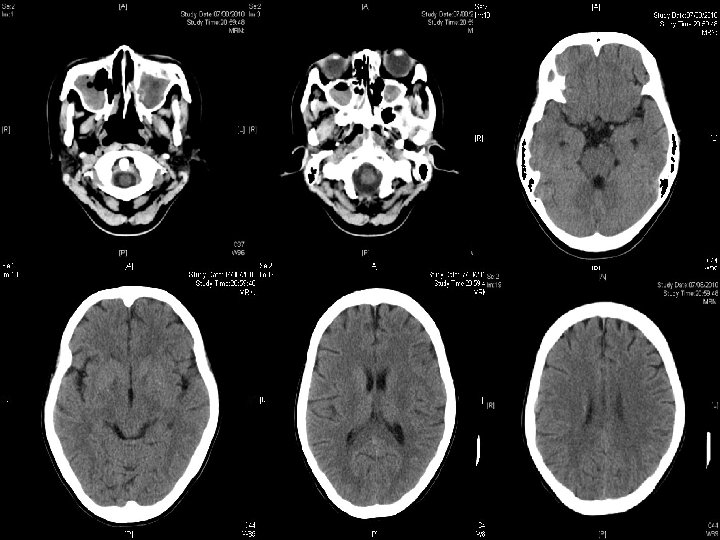
 Initial list of differential diagnosis Viral brainstem encephalitis n Gullain-barre syndrome n Myasthenia gravis n Vertebral artery dissection n Sarcoidosis n Nasopharyngeal carcinoma lower cranial nerve invasion n
Initial list of differential diagnosis Viral brainstem encephalitis n Gullain-barre syndrome n Myasthenia gravis n Vertebral artery dissection n Sarcoidosis n Nasopharyngeal carcinoma lower cranial nerve invasion n
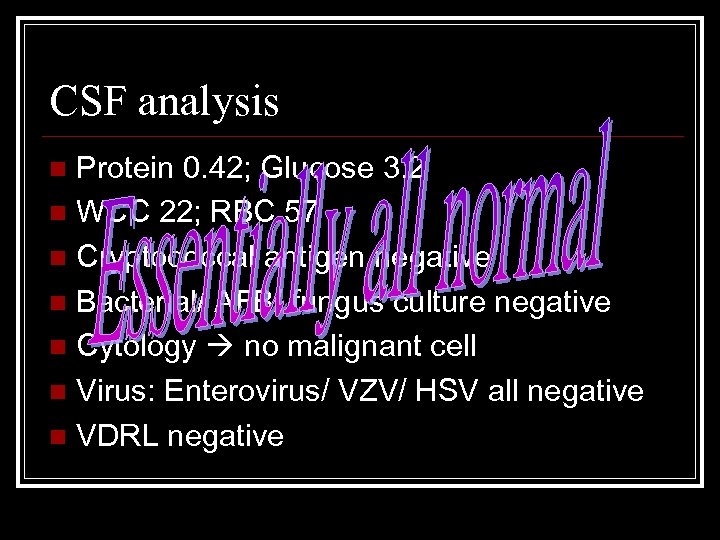 CSF analysis Protein 0. 42; Glucose 3. 2 n WCC 22; RBC 57 n Cryptococcal antigen negative n Bacterial/ AFB/ fungus culture negative n Cytology no malignant cell n Virus: Enterovirus/ VZV/ HSV all negative n VDRL negative n
CSF analysis Protein 0. 42; Glucose 3. 2 n WCC 22; RBC 57 n Cryptococcal antigen negative n Bacterial/ AFB/ fungus culture negative n Cytology no malignant cell n Virus: Enterovirus/ VZV/ HSV all negative n VDRL negative n
 Is it MG crisis? 20 Jan 2009, CCM grand-round
Is it MG crisis? 20 Jan 2009, CCM grand-round
 Private MRI Hyperintense spots in antero-superior part of lateral end of both IAM n Short hyperintense line in labyrinthine portion of right facial nerve n Suggestive of bilateral facial neuritis n MRA showed normal vasculature n Incidentally retention change over bilateral paranasal sinuses n
Private MRI Hyperintense spots in antero-superior part of lateral end of both IAM n Short hyperintense line in labyrinthine portion of right facial nerve n Suggestive of bilateral facial neuritis n MRA showed normal vasculature n Incidentally retention change over bilateral paranasal sinuses n
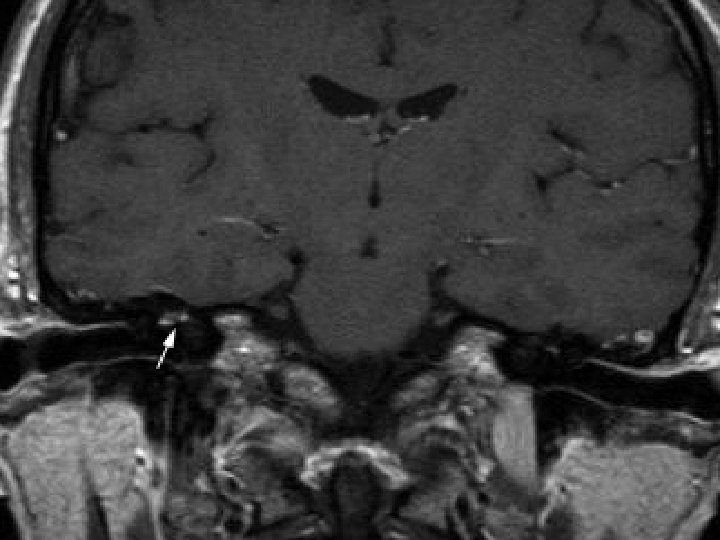
 Neurology workup Tensilon test negative n Anti-Ach receptor antibody negative n Immune markers and ANCA negative n Urine porphobilinogen negative n Nerve conduction test Conduction block at Lt tibial/ Rt peroneal Sural nerve intact bilaterally n
Neurology workup Tensilon test negative n Anti-Ach receptor antibody negative n Immune markers and ANCA negative n Urine porphobilinogen negative n Nerve conduction test Conduction block at Lt tibial/ Rt peroneal Sural nerve intact bilaterally n
 Treat as ? Bickerstaff encephalitis IV ampicillin + IV Acyclovir > 9/7 to 15/7 n IVIG at 0. 4 g/ kg weight > 14/7 to 18/7 n Hydrocortisone 100 mg Q 8 H > 20/7 to 25/7 n Prednisolone (tapering dose)> 26/7 to 5/8 n CT brain 7 th Aug putamen lesions+ n Rt dilated pupil FU eye as uveitis n She wants to withhold invasive treatment/ workup if cancer diagnosed n
Treat as ? Bickerstaff encephalitis IV ampicillin + IV Acyclovir > 9/7 to 15/7 n IVIG at 0. 4 g/ kg weight > 14/7 to 18/7 n Hydrocortisone 100 mg Q 8 H > 20/7 to 25/7 n Prednisolone (tapering dose)> 26/7 to 5/8 n CT brain 7 th Aug putamen lesions+ n Rt dilated pupil FU eye as uveitis n She wants to withhold invasive treatment/ workup if cancer diagnosed n
 End Cannot Eat
End Cannot Eat
 Unexpected problems (1) TSH <0. 01 and T 4 30. 4 n Carbimazole 10 mg BD + inderal 10 mg tds since 10 th Aug to 14 th Aug n Complete heart block on 15 th Aug temp pacing at CCU on 16 th Aug n Sputum retention and respiratory failure intubated at ICU on 17 th Aug n Started Sulperazon + Amikacin for HAP n
Unexpected problems (1) TSH <0. 01 and T 4 30. 4 n Carbimazole 10 mg BD + inderal 10 mg tds since 10 th Aug to 14 th Aug n Complete heart block on 15 th Aug temp pacing at CCU on 16 th Aug n Sputum retention and respiratory failure intubated at ICU on 17 th Aug n Started Sulperazon + Amikacin for HAP n
 Sputum culture 15 th Aug Acinetobacter species (Heavy growth) n Gentamicin Resistant n Ciprofloxacin Resistant n Cotrimoxazole Resistant n Unasyn Resistant n Piperacillin + Tazobactam Resistant n Tienam Resistant n Sulperazon Resistant n Amikacin Susceptible n Colistin Susceptible
Sputum culture 15 th Aug Acinetobacter species (Heavy growth) n Gentamicin Resistant n Ciprofloxacin Resistant n Cotrimoxazole Resistant n Unasyn Resistant n Piperacillin + Tazobactam Resistant n Tienam Resistant n Sulperazon Resistant n Amikacin Susceptible n Colistin Susceptible
 Unexpected problems (2) Weaned off ventilator since 21 st Aug n Fever 40 degree + unconscious 25 th Aug resume ventilator support n Change pacing wire to LIJV n Stop Sulperazon and Amikacin change to Cloxacillin (ETA grew MSSA 24 th Aug) n EEG generalized encephalopathy n
Unexpected problems (2) Weaned off ventilator since 21 st Aug n Fever 40 degree + unconscious 25 th Aug resume ventilator support n Change pacing wire to LIJV n Stop Sulperazon and Amikacin change to Cloxacillin (ETA grew MSSA 24 th Aug) n EEG generalized encephalopathy n
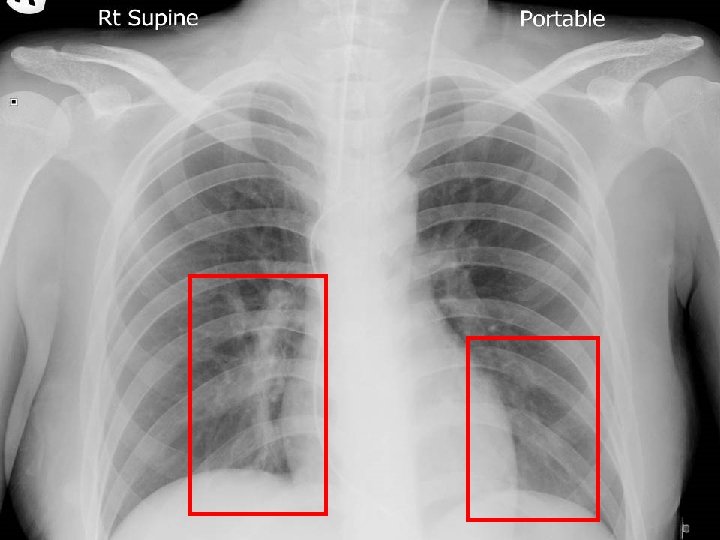
 End Cannot Breath
End Cannot Breath
 Unexpected problems (3) Seen by eye for increasing redness Right endophthalmitis diagnosed 25 th Aug Bedside Intravitreous Vancomycin + Amikacin performed n CT orbit 25 th Aug Increased Rt vitreous chamber hypodensities at bilateral basal ganglia n
Unexpected problems (3) Seen by eye for increasing redness Right endophthalmitis diagnosed 25 th Aug Bedside Intravitreous Vancomycin + Amikacin performed n CT orbit 25 th Aug Increased Rt vitreous chamber hypodensities at bilateral basal ganglia n
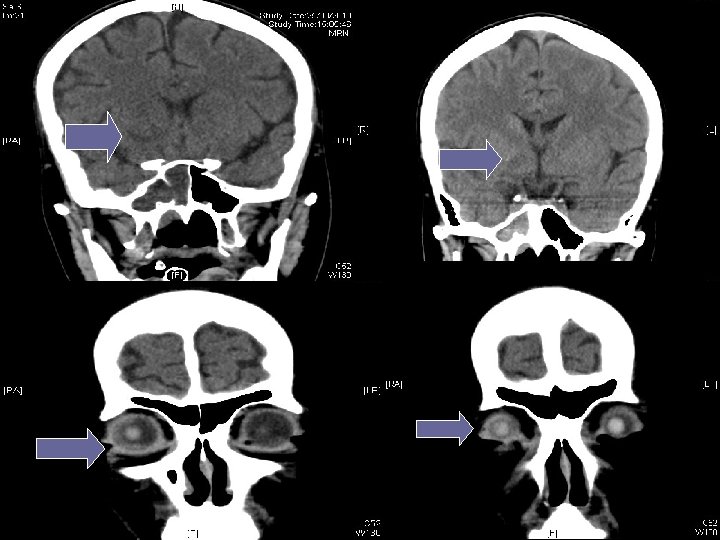
 Eye review on 26 th Aug Vision-saving procedure has to be done in CMC due to restriction on the portability of instruments. n Hopefully to remove sepsis focus n Patient was escorted to ICU of CMC on 27 th Aug, under specialty of M&G, to manage ophthalmological emergency n Plan back to Hospital A after eye OT n
Eye review on 26 th Aug Vision-saving procedure has to be done in CMC due to restriction on the portability of instruments. n Hopefully to remove sepsis focus n Patient was escorted to ICU of CMC on 27 th Aug, under specialty of M&G, to manage ophthalmological emergency n Plan back to Hospital A after eye OT n
 CMC ICU admission 27 th Aug GCS E 2 Vt. M 1 n Under sedation of Dormicum/ fentanyl n Pulse rate 90 sinus, not pacing dependent n Minimal motor response to pain for limbs n Lines not inflamed and CXR clear n Eye OT not available on same day n ? Primary sepsis foci n
CMC ICU admission 27 th Aug GCS E 2 Vt. M 1 n Under sedation of Dormicum/ fentanyl n Pulse rate 90 sinus, not pacing dependent n Minimal motor response to pain for limbs n Lines not inflamed and CXR clear n Eye OT not available on same day n ? Primary sepsis foci n
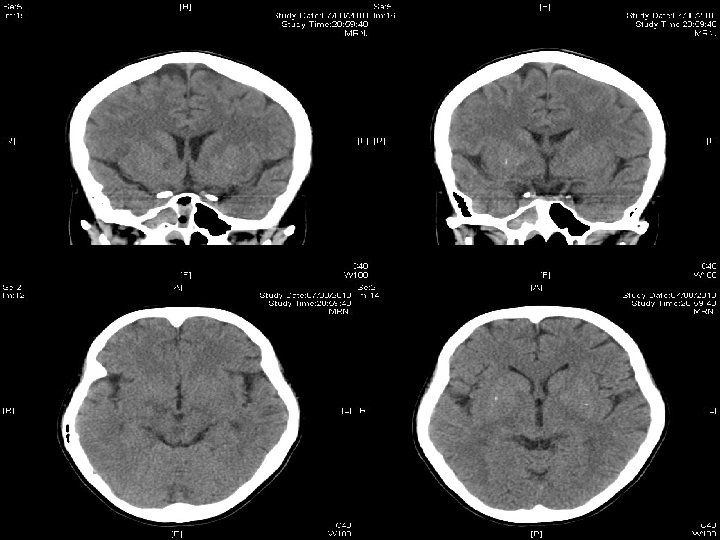
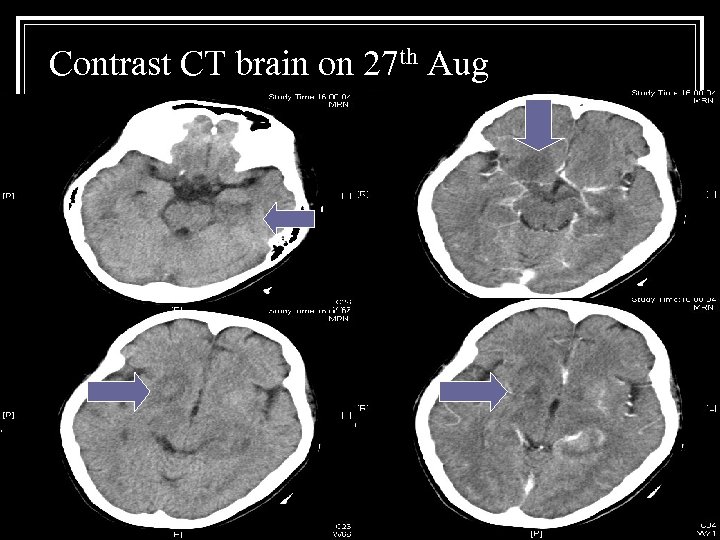 Contrast CT brain on 27 th Aug
Contrast CT brain on 27 th Aug
 Blood result on CMC arrival Hb 7. 2 NCMC; Platelet 146 n WCC 5. 9 (neutrophil 5. 1; lymphocyte 0. 5) n INR 1. 0; APTT 28 n RFT normal, A/G= 19/34, ALT 56 n TSH 0. 13, T 4 at 23. 9 n ABG p. H 7. 49; CO 2 31. 5; p. O 2 185 (0. 3 O 2) n G 6 PD negative (May need Septrin later) n
Blood result on CMC arrival Hb 7. 2 NCMC; Platelet 146 n WCC 5. 9 (neutrophil 5. 1; lymphocyte 0. 5) n INR 1. 0; APTT 28 n RFT normal, A/G= 19/34, ALT 56 n TSH 0. 13, T 4 at 23. 9 n ABG p. H 7. 49; CO 2 31. 5; p. O 2 185 (0. 3 O 2) n G 6 PD negative (May need Septrin later) n
 Management strategy 1. 2. 3. 4. Eye intervention as planned Sepsis: second lumbar puncture for CSF sample + taking other specimens Consult ENT for assessment Consult neurology for (a) Primary event leading to bulbar palsy; and (b) Workup of current CNS severe dysfunction
Management strategy 1. 2. 3. 4. Eye intervention as planned Sepsis: second lumbar puncture for CSF sample + taking other specimens Consult ENT for assessment Consult neurology for (a) Primary event leading to bulbar palsy; and (b) Workup of current CNS severe dysfunction
 (1) Eye intervention 28 th Aug Right eye: dense fibrin/ pus in anterior chamber + dense vitritis + inferior rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) n Left eye: chronic RRD n Impression: Rt endophthalmitis + Lt RRT n Procedure: right eye AC washout + Phacoemulsification of cataract + endolaser vitrectomy + Repair of RRD + Intravitreal Vanco & Amikan n
(1) Eye intervention 28 th Aug Right eye: dense fibrin/ pus in anterior chamber + dense vitritis + inferior rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) n Left eye: chronic RRD n Impression: Rt endophthalmitis + Lt RRT n Procedure: right eye AC washout + Phacoemulsification of cataract + endolaser vitrectomy + Repair of RRD + Intravitreal Vanco & Amikan n
 (1) Eye intervention: plan Poor visual prognosis of right eye n Aim to preserve left eye vision n Local antimicrobial to right eye Hourly Gutt Vancomycin and Gutt Gentamycin n Right vitreous matter for bacterial and fungal culture subsequently negative n Need daily assessment at ICU n
(1) Eye intervention: plan Poor visual prognosis of right eye n Aim to preserve left eye vision n Local antimicrobial to right eye Hourly Gutt Vancomycin and Gutt Gentamycin n Right vitreous matter for bacterial and fungal culture subsequently negative n Need daily assessment at ICU n
 Never end Cannot see
Never end Cannot see
 (2) Sepsis workup CSF glucose 2. 0; protein 2. 57; WCC 3; no bacterial/ fungus/ AFB growth n Nasal fluid aspirate: Candida albicans + MRSA + Enterococci + Acinetobacter n ETA Acinetobacter species n CSU Candida albicans + Enterocci n Blood culture negative for bacteria/ fungus n Vitreus matter nil bacteria/ fungus n
(2) Sepsis workup CSF glucose 2. 0; protein 2. 57; WCC 3; no bacterial/ fungus/ AFB growth n Nasal fluid aspirate: Candida albicans + MRSA + Enterococci + Acinetobacter n ETA Acinetobacter species n CSU Candida albicans + Enterocci n Blood culture negative for bacteria/ fungus n Vitreus matter nil bacteria/ fungus n
 (2) Sepsis what to cover? After a bit discussion: Vancomycin 1 g Q 8 H Fluconazole 400 mg stat then 200 mg daily Netromycin 150 mg daily IV n Serum Beta-D-Glucan 173. 7 (<80) Possible systemic candidiasis n
(2) Sepsis what to cover? After a bit discussion: Vancomycin 1 g Q 8 H Fluconazole 400 mg stat then 200 mg daily Netromycin 150 mg daily IV n Serum Beta-D-Glucan 173. 7 (<80) Possible systemic candidiasis n
 (3) ENT intervention 27 th Aug: to refer back hospital A when fit n 30 th Aug: bedside endoscopy showed tiny streak of mucus in Rt middle meatus swab taken for culture (MDR-Acinetobacter + MRSA + enterococci) n 3 rd Sept: Persistent fever despite broad coverage Right maxillary sinus antrotomy only straw colour fluid !! n
(3) ENT intervention 27 th Aug: to refer back hospital A when fit n 30 th Aug: bedside endoscopy showed tiny streak of mucus in Rt middle meatus swab taken for culture (MDR-Acinetobacter + MRSA + enterococci) n 3 rd Sept: Persistent fever despite broad coverage Right maxillary sinus antrotomy only straw colour fluid !! n
 (3) ENT intervention Comments 3 rd Sept 2010: “Based on the clear colour character of antral washout and negative local sign around he head & neck/ peri-nasal Chance of frank sinusitis is low Further procedure e. g. biopsy not helpful” n
(3) ENT intervention Comments 3 rd Sept 2010: “Based on the clear colour character of antral washout and negative local sign around he head & neck/ peri-nasal Chance of frank sinusitis is low Further procedure e. g. biopsy not helpful” n
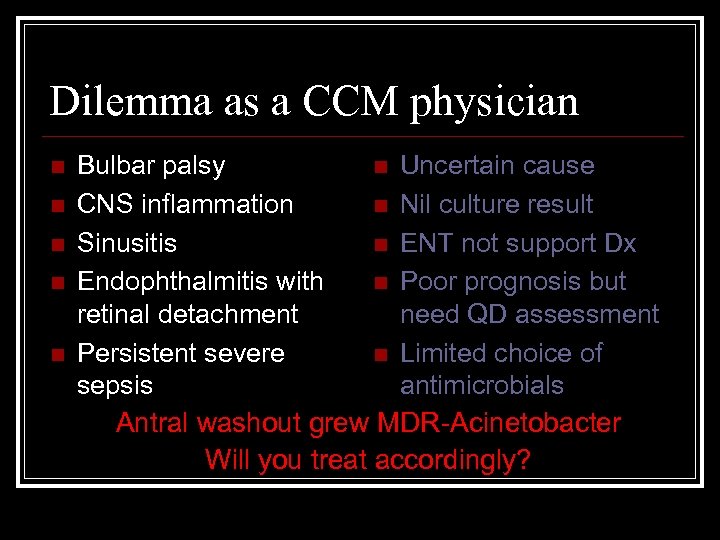 Dilemma as a CCM physician n n Bulbar palsy n Uncertain cause CNS inflammation n Nil culture result Sinusitis n ENT not support Dx Endophthalmitis with n Poor prognosis but retinal detachment need QD assessment Persistent severe n Limited choice of sepsis antimicrobials Antral washout grew MDR-Acinetobacter Will you treat accordingly?
Dilemma as a CCM physician n n Bulbar palsy n Uncertain cause CNS inflammation n Nil culture result Sinusitis n ENT not support Dx Endophthalmitis with n Poor prognosis but retinal detachment need QD assessment Persistent severe n Limited choice of sepsis antimicrobials Antral washout grew MDR-Acinetobacter Will you treat accordingly?
 (4) Neurologist assessment A. B. Review the initial diagnosis leading to admission to Hospital A Assess the current neurological status
(4) Neurologist assessment A. B. Review the initial diagnosis leading to admission to Hospital A Assess the current neurological status
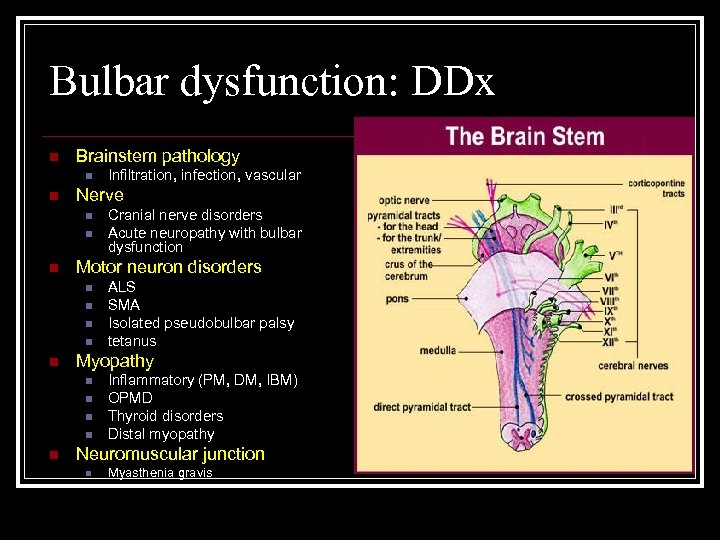 Bulbar dysfunction: DDx n Brainstem pathology n n Nerve n n n ALS SMA Isolated pseudobulbar palsy tetanus Myopathy n n n Cranial nerve disorders Acute neuropathy with bulbar dysfunction Motor neuron disorders n n Infiltration, infection, vascular Inflammatory (PM, DM, IBM) OPMD Thyroid disorders Distal myopathy Neuromuscular junction n Myasthenia gravis
Bulbar dysfunction: DDx n Brainstem pathology n n Nerve n n n ALS SMA Isolated pseudobulbar palsy tetanus Myopathy n n n Cranial nerve disorders Acute neuropathy with bulbar dysfunction Motor neuron disorders n n Infiltration, infection, vascular Inflammatory (PM, DM, IBM) OPMD Thyroid disorders Distal myopathy Neuromuscular junction n Myasthenia gravis
 Miller Fisher Syndrome A clinical variant of GBS; acute postinfectious paralytic illness n Triad: ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, areflexia n Pupillary abnormalities, ptosis, bulbar symptoms, facial weakness n CSF: Albumino-cytological dissociation n Anti-GQ 1 b anti-ganglioside antibodies: sensitive for FS and its variants n
Miller Fisher Syndrome A clinical variant of GBS; acute postinfectious paralytic illness n Triad: ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, areflexia n Pupillary abnormalities, ptosis, bulbar symptoms, facial weakness n CSF: Albumino-cytological dissociation n Anti-GQ 1 b anti-ganglioside antibodies: sensitive for FS and its variants n
 Bickerstaff’s brainstem encephalitis (BBE) Closely related to MFS n Additional: Altered consciousness, long tract signs n Similar CSF and anti-GQ 1 b Antibody findings as in MFS n MRI brain abnormality present in 30% n
Bickerstaff’s brainstem encephalitis (BBE) Closely related to MFS n Additional: Altered consciousness, long tract signs n Similar CSF and anti-GQ 1 b Antibody findings as in MFS n MRI brain abnormality present in 30% n
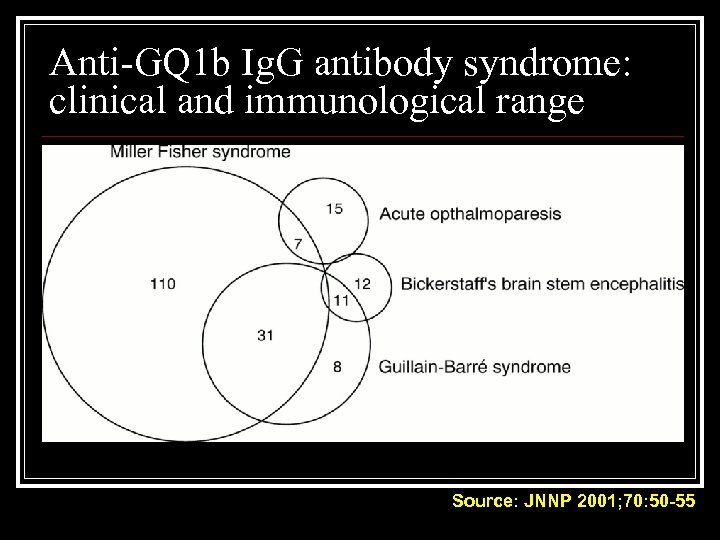 Anti-GQ 1 b Ig. G antibody syndrome: clinical and immunological range Source: JNNP 2001; 70: 50 -55
Anti-GQ 1 b Ig. G antibody syndrome: clinical and immunological range Source: JNNP 2001; 70: 50 -55
 What is unusual in this patient? No ophthalmoplegia ever documented n No alteration of consciousness on presentation til very late phase n CSF: normal protein + raised WCC n Nerve conduction study: normal n Fever persists n
What is unusual in this patient? No ophthalmoplegia ever documented n No alteration of consciousness on presentation til very late phase n CSF: normal protein + raised WCC n Nerve conduction study: normal n Fever persists n
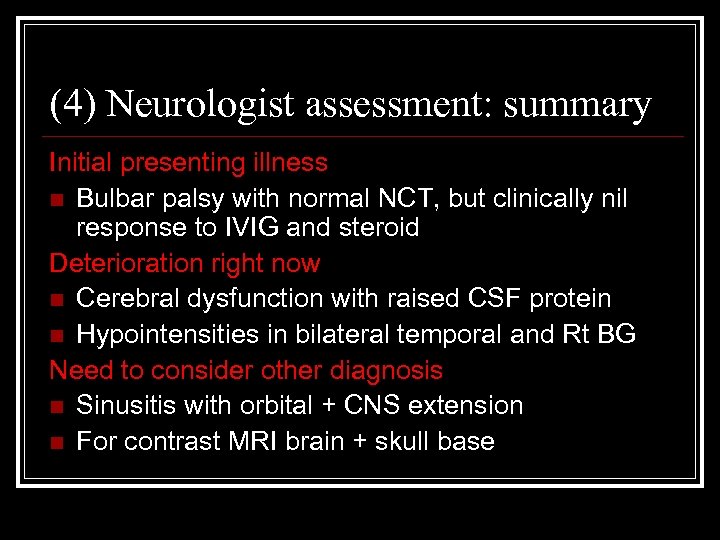 (4) Neurologist assessment: summary Initial presenting illness n Bulbar palsy with normal NCT, but clinically nil response to IVIG and steroid Deterioration right now n Cerebral dysfunction with raised CSF protein n Hypointensities in bilateral temporal and Rt BG Need to consider other diagnosis n Sinusitis with orbital + CNS extension n For contrast MRI brain + skull base
(4) Neurologist assessment: summary Initial presenting illness n Bulbar palsy with normal NCT, but clinically nil response to IVIG and steroid Deterioration right now n Cerebral dysfunction with raised CSF protein n Hypointensities in bilateral temporal and Rt BG Need to consider other diagnosis n Sinusitis with orbital + CNS extension n For contrast MRI brain + skull base
 Searching for an answer…. n n n n n Anti-HIV negative, VDRL negative Blood fungal culture/ bacterial negative Paired serum viral titer not raised CMV pp 65 antigen negative 2 nd porphyria screen negative Immune markers all negative Anti-Ganglioside Q 1 b & anti-GM 1 not raised Serum Vancomycin trough 21. 3 Hb 9. 9; Plt 123; WCC 5. 6; ALT 63 (3/9/10)
Searching for an answer…. n n n n n Anti-HIV negative, VDRL negative Blood fungal culture/ bacterial negative Paired serum viral titer not raised CMV pp 65 antigen negative 2 nd porphyria screen negative Immune markers all negative Anti-Ganglioside Q 1 b & anti-GM 1 not raised Serum Vancomycin trough 21. 3 Hb 9. 9; Plt 123; WCC 5. 6; ALT 63 (3/9/10)
 Searching for an answer, again…. . n n n n n 9 th July: Plain CT Brain (Hospital A) 7 th Aug: Plain CT Brain (Hospital A) 25 th August: Plain CT Orbit (Hospital A) 27 th August: Contrast CT brain + Sinus 4 th September: MRI brain + brainstem 4 th September: Plain CT brain 10 th September: Contrast CT brain 11 th September: Plain CT sinus 15 th September: MRI brain + DWI
Searching for an answer, again…. . n n n n n 9 th July: Plain CT Brain (Hospital A) 7 th Aug: Plain CT Brain (Hospital A) 25 th August: Plain CT Orbit (Hospital A) 27 th August: Contrast CT brain + Sinus 4 th September: MRI brain + brainstem 4 th September: Plain CT brain 10 th September: Contrast CT brain 11 th September: Plain CT sinus 15 th September: MRI brain + DWI
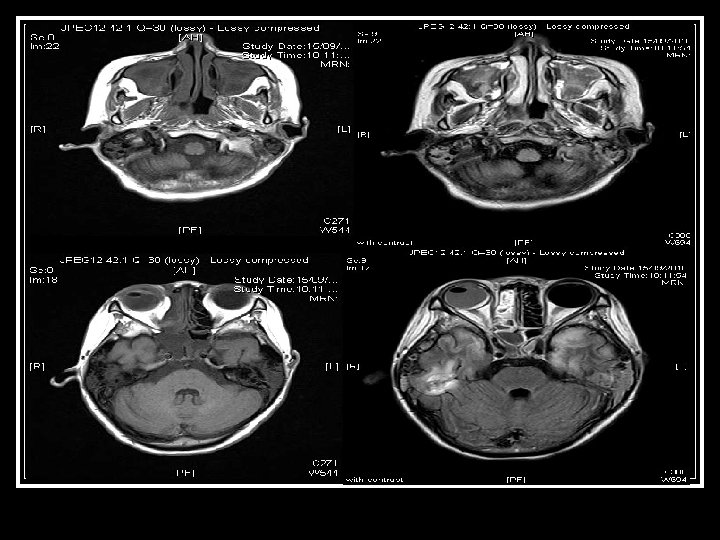
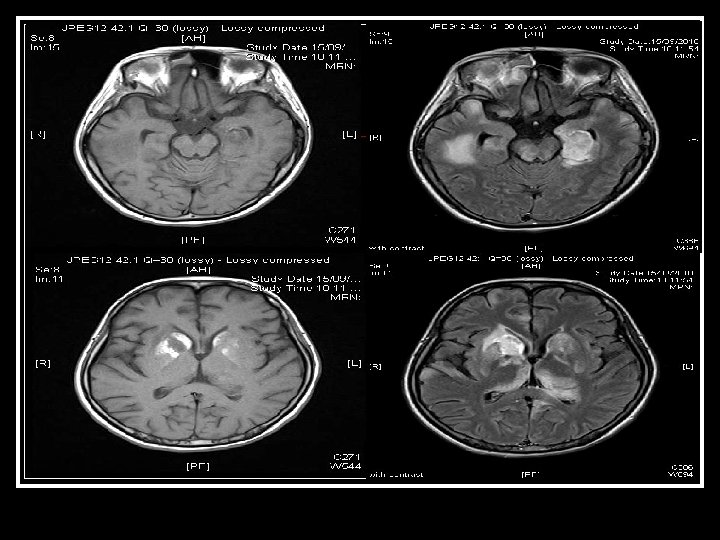
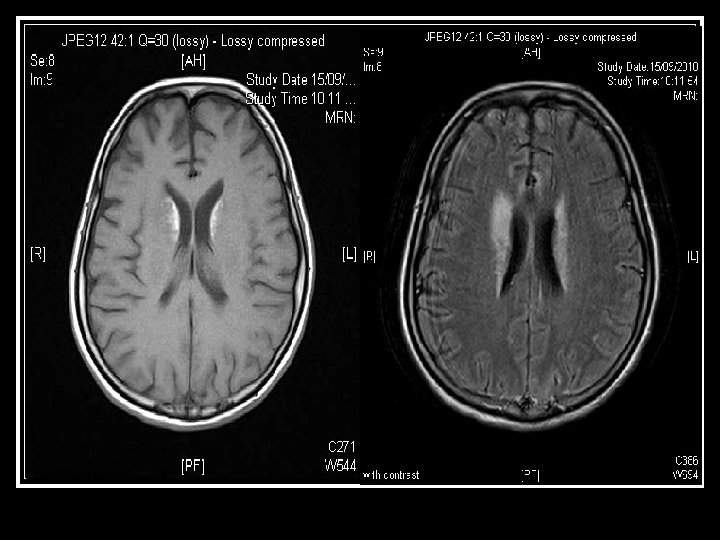
 Brain was so ill, but no answer…. Condition since 4 th September 2010 n Multi-focal inflammatory change over bilateral basal ganglia/ thalamus/ temporal lobes and brainstem on MRI, unlikely due to bacterial infection n GCS E 4 Vt. M 1 and all limbs flaccid n Persistent high fever and tachycardia despite Vanco/netro/fluconazole 14 days
Brain was so ill, but no answer…. Condition since 4 th September 2010 n Multi-focal inflammatory change over bilateral basal ganglia/ thalamus/ temporal lobes and brainstem on MRI, unlikely due to bacterial infection n GCS E 4 Vt. M 1 and all limbs flaccid n Persistent high fever and tachycardia despite Vanco/netro/fluconazole 14 days
 While waiting, do something Temporary tracheostomy on 6 th Sept n Moderately enlarged thyroid n Milky discharge from left thyroid n Thyroid tissue sent for histology n Tracheostomy #8 inserted n
While waiting, do something Temporary tracheostomy on 6 th Sept n Moderately enlarged thyroid n Milky discharge from left thyroid n Thyroid tissue sent for histology n Tracheostomy #8 inserted n
 More aggressive workup? 8 th to 11 th Sept 2010: n PMH neurologist/ CMC neurologist/ KWH neurosurgeon and PMH neurosurgeon n Possible role of brain biopsy to identify pathogen, but result can be negative because of prior multiple antimicrobials n Risk++ n
More aggressive workup? 8 th to 11 th Sept 2010: n PMH neurologist/ CMC neurologist/ KWH neurosurgeon and PMH neurosurgeon n Possible role of brain biopsy to identify pathogen, but result can be negative because of prior multiple antimicrobials n Risk++ n
 Eye: no need for more OT at CMC!! We decided to reconsult ENT n ? Drainage of sinus may help sepsis control better than simply antimicrobial n ENT preferred to have procedure at CMC 12 th Sept: Lt maxillary sinus antral wash Straw colour fluid yielded Opacity “Likely mucosal oedema only” n
Eye: no need for more OT at CMC!! We decided to reconsult ENT n ? Drainage of sinus may help sepsis control better than simply antimicrobial n ENT preferred to have procedure at CMC 12 th Sept: Lt maxillary sinus antral wash Straw colour fluid yielded Opacity “Likely mucosal oedema only” n
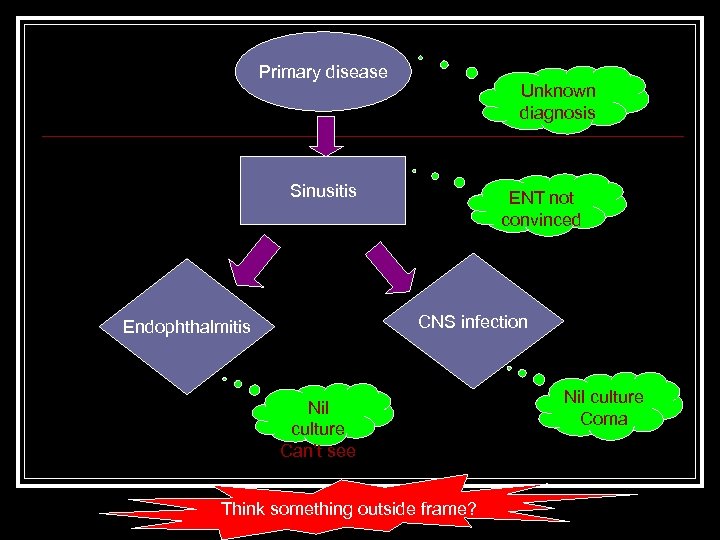 Primary disease Unknown diagnosis Sinusitis ENT not convinced CNS infection Endophthalmitis Nil culture Can’t see Think something outside frame? Nil culture Coma
Primary disease Unknown diagnosis Sinusitis ENT not convinced CNS infection Endophthalmitis Nil culture Can’t see Think something outside frame? Nil culture Coma
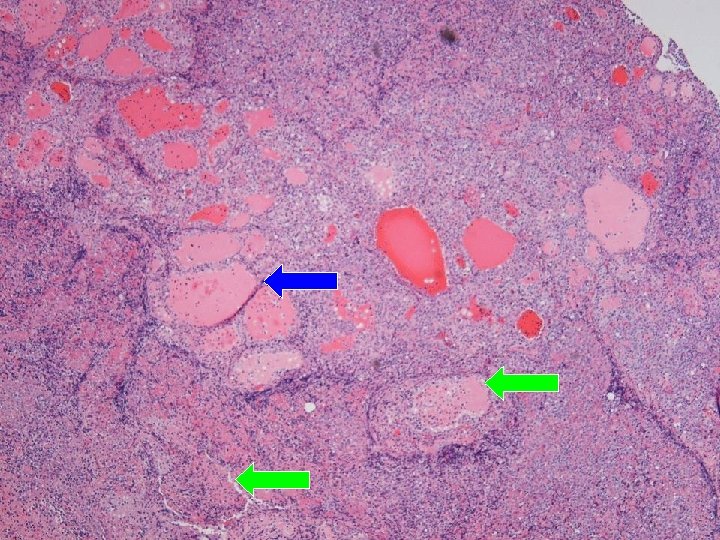
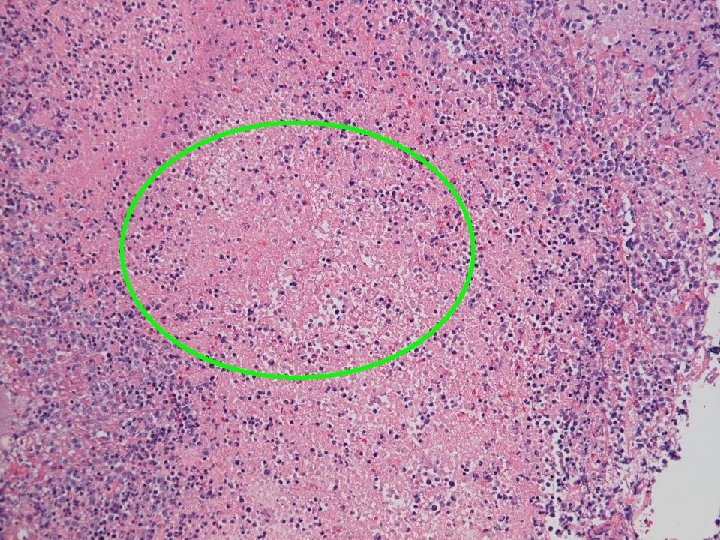
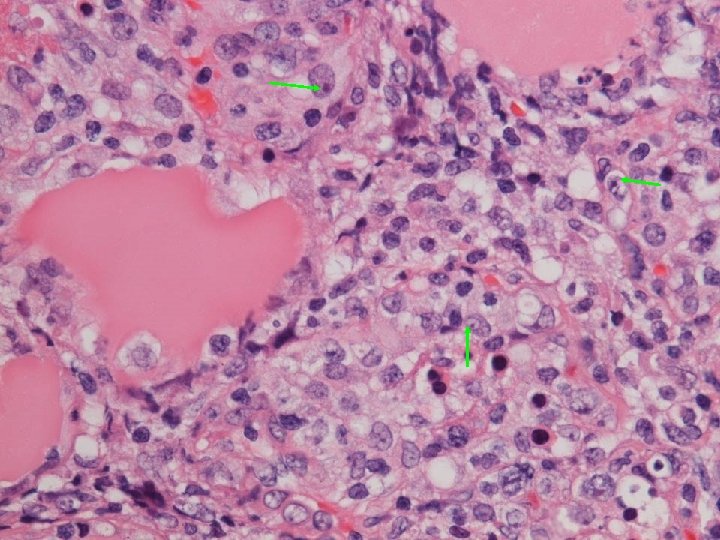
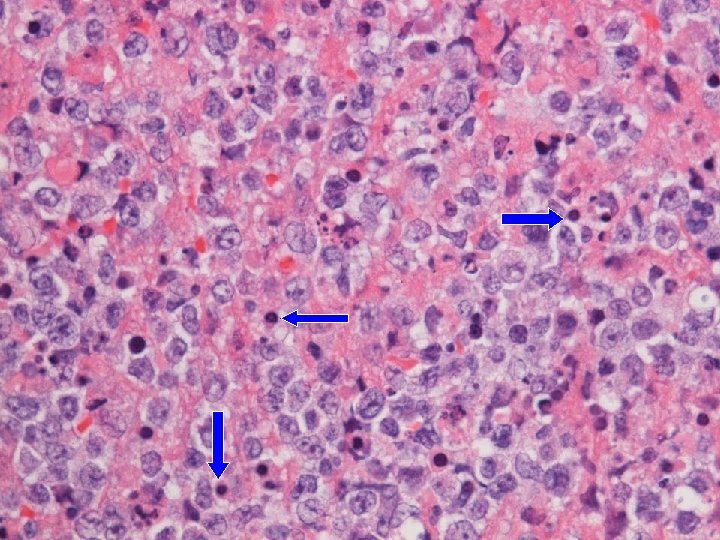
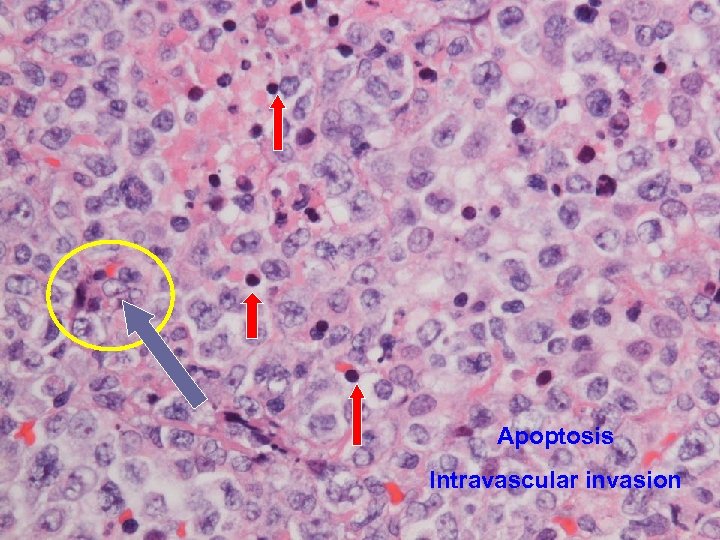 Apoptosis Intravascular invasion
Apoptosis Intravascular invasion
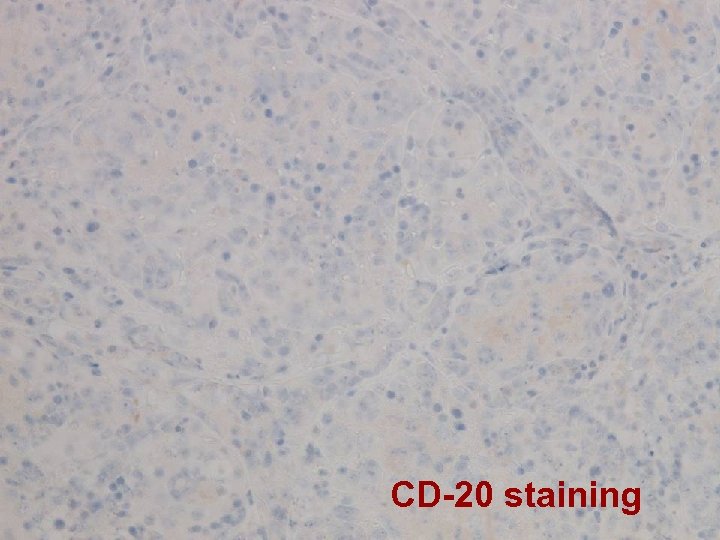 CD-20 staining
CD-20 staining
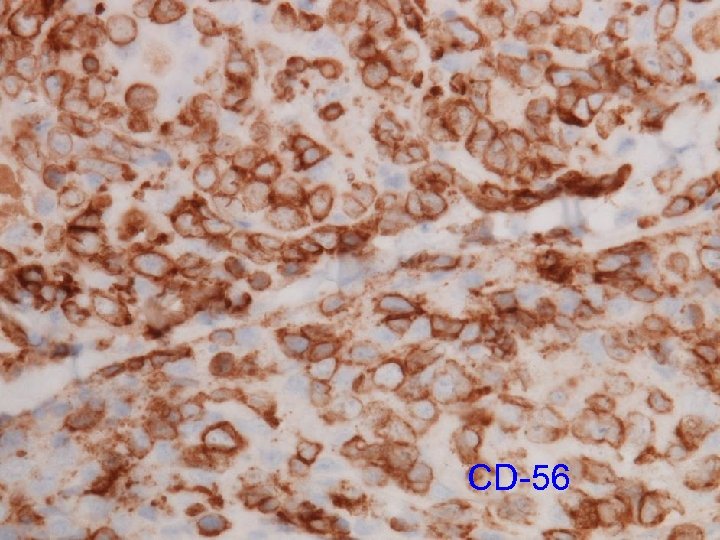 CD-56
CD-56
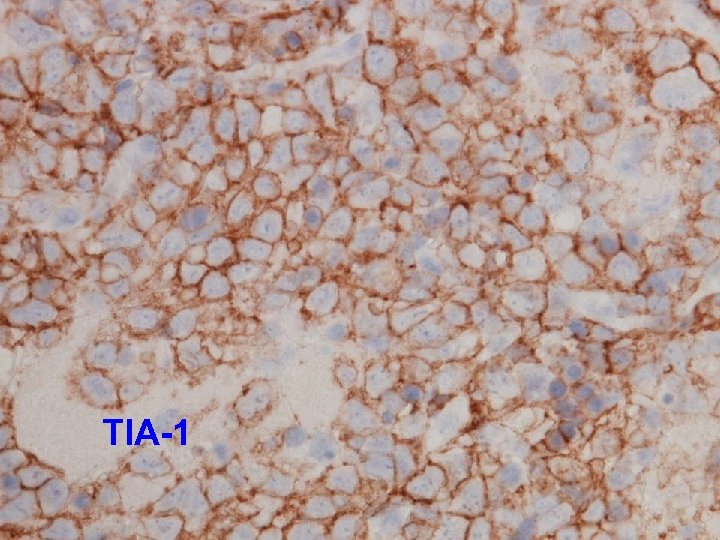 TIA-1
TIA-1
 Final histology Thyroid follicles infiltrated by diffuse destructive sheets of large lymphoid cells n CD 20 -; CD 3+; CD 4 -; CD 8 -; TCR-γNeg n Strongly positive for TIA 1 n Extranodal NK/ T-cell lymphoma with intravascular lymphomatosis n { CSF/ nasal aspirate nil malignant cell } n
Final histology Thyroid follicles infiltrated by diffuse destructive sheets of large lymphoid cells n CD 20 -; CD 3+; CD 4 -; CD 8 -; TCR-γNeg n Strongly positive for TIA 1 n Extranodal NK/ T-cell lymphoma with intravascular lymphomatosis n { CSF/ nasal aspirate nil malignant cell } n
 Final progress (1) PMH Haematology was consulted: Advanced multi-organ involvement by hematological malignancy with the host having extremely poor tolerability to toxic drugs which mean high dose IV Methotrexate & Cytarabine Advised comfort care n
Final progress (1) PMH Haematology was consulted: Advanced multi-organ involvement by hematological malignancy with the host having extremely poor tolerability to toxic drugs which mean high dose IV Methotrexate & Cytarabine Advised comfort care n
 Final progress (2) Adopt DNR after detailed discussion with family, knowing that patient had expressed her wish to withhold invasive treatment/ workup if cancer diagnosed n Put on morphine infusion for distress n To palliative care bed on 18 th Sept (D 23) n Passed away on 20 th Sept (D 25) n
Final progress (2) Adopt DNR after detailed discussion with family, knowing that patient had expressed her wish to withhold invasive treatment/ workup if cancer diagnosed n Put on morphine infusion for distress n To palliative care bed on 18 th Sept (D 23) n Passed away on 20 th Sept (D 25) n
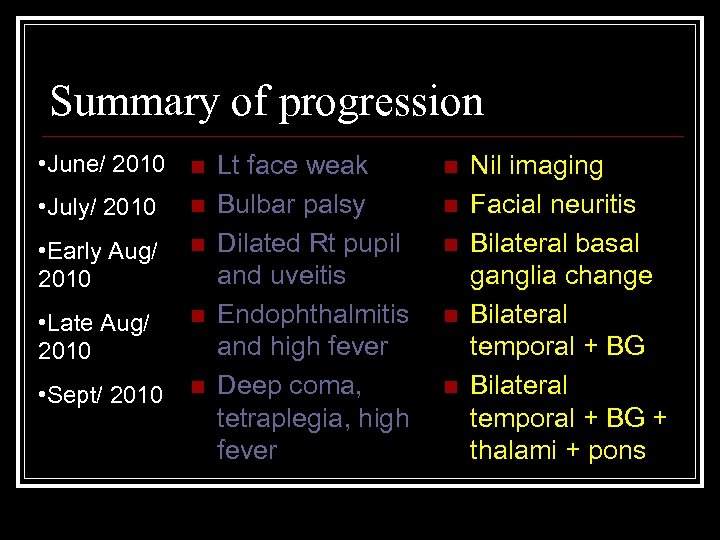 Summary of progression • June/ 2010 n • July/ 2010 n • Early Aug/ 2010 n • Late Aug/ 2010 n • Sept/ 2010 n Lt face weak Bulbar palsy Dilated Rt pupil and uveitis Endophthalmitis and high fever Deep coma, tetraplegia, high fever n n n Nil imaging Facial neuritis Bilateral basal ganglia change Bilateral temporal + BG + thalami + pons
Summary of progression • June/ 2010 n • July/ 2010 n • Early Aug/ 2010 n • Late Aug/ 2010 n • Sept/ 2010 n Lt face weak Bulbar palsy Dilated Rt pupil and uveitis Endophthalmitis and high fever Deep coma, tetraplegia, high fever n n n Nil imaging Facial neuritis Bilateral basal ganglia change Bilateral temporal + BG + thalami + pons
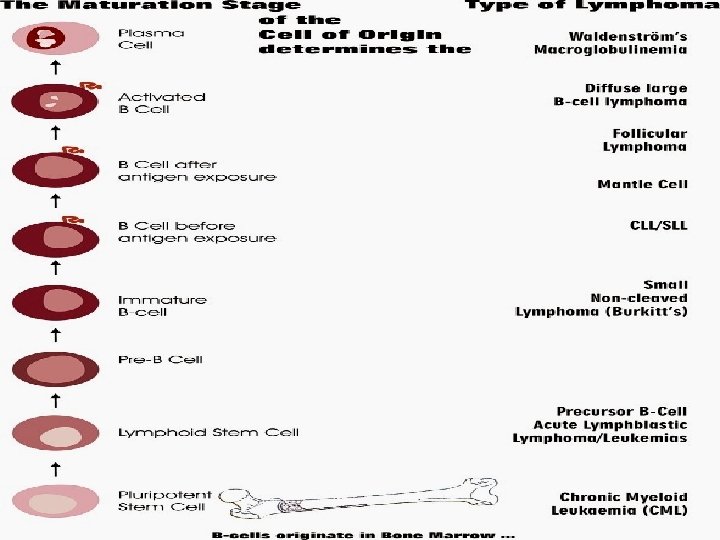
 Natural killer cells (NK Cell) Constitute <15% of peripheral lymphocytes n Large granular cells n Originate from bipotent NK/T-progenitor, therefore also express T markers e. g. CD 2 n Nil TCR genes arrangement n 5 subtypes according to CD 56 and CD 16 n n CD 56 or 16 bright vs. CD 56 or 16 dim vs. CD 56 neg
Natural killer cells (NK Cell) Constitute <15% of peripheral lymphocytes n Large granular cells n Originate from bipotent NK/T-progenitor, therefore also express T markers e. g. CD 2 n Nil TCR genes arrangement n 5 subtypes according to CD 56 and CD 16 n n CD 56 or 16 bright vs. CD 56 or 16 dim vs. CD 56 neg
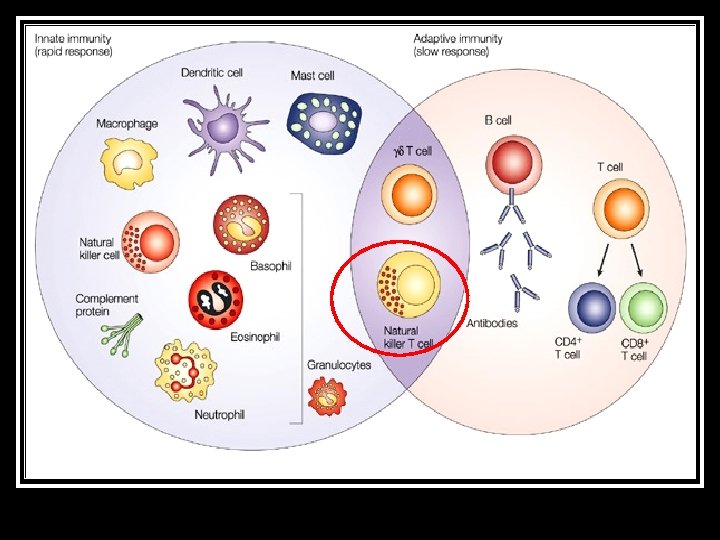
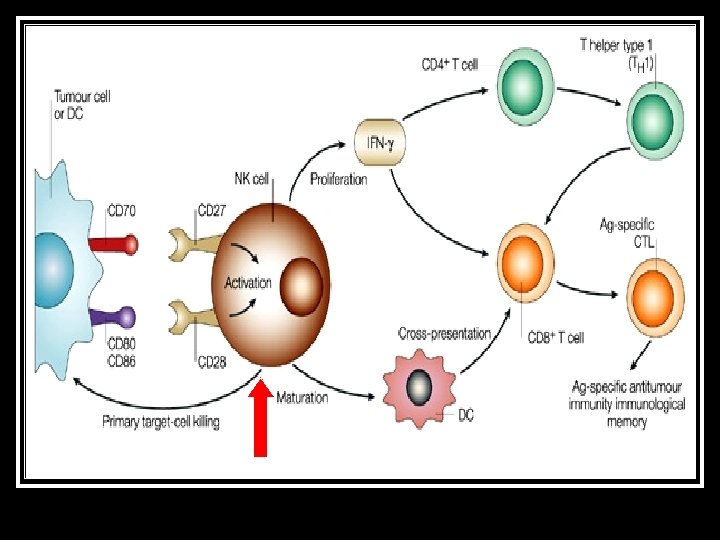
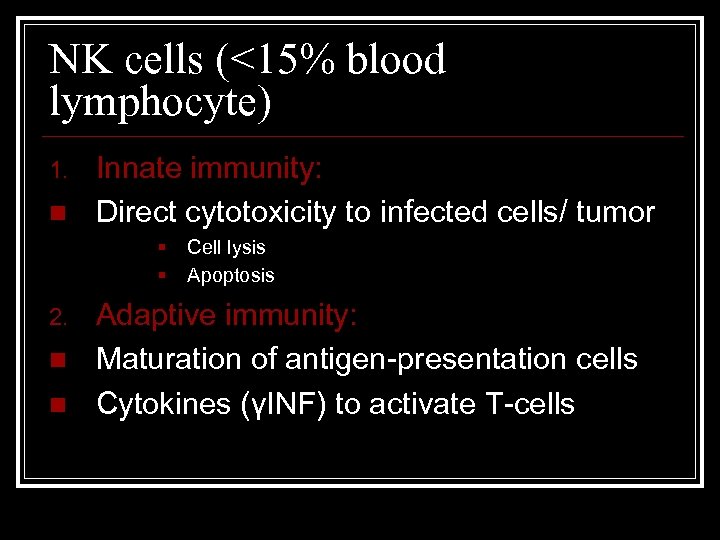 NK cells (<15% blood lymphocyte) 1. n Innate immunity: Direct cytotoxicity to infected cells/ tumor § § 2. n n Cell lysis Apoptosis Adaptive immunity: Maturation of antigen-presentation cells Cytokines (γINF) to activate T-cells
NK cells (<15% blood lymphocyte) 1. n Innate immunity: Direct cytotoxicity to infected cells/ tumor § § 2. n n Cell lysis Apoptosis Adaptive immunity: Maturation of antigen-presentation cells Cytokines (γINF) to activate T-cells
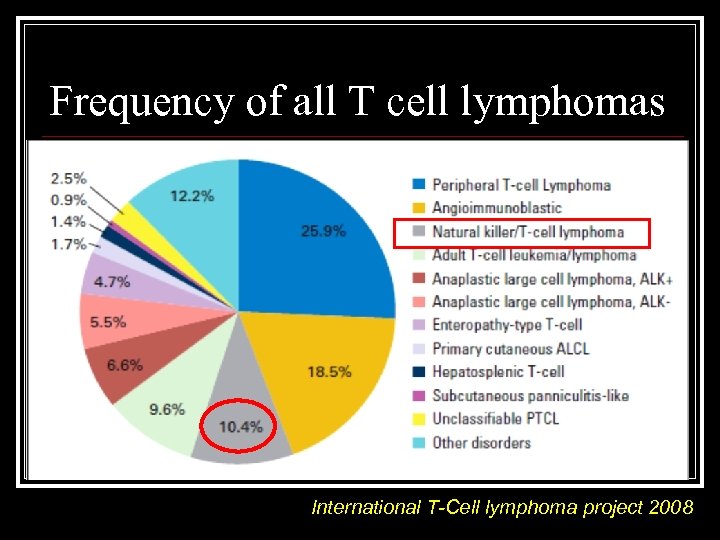 Frequency of all T cell lymphomas International T-Cell lymphoma project 2008
Frequency of all T cell lymphomas International T-Cell lymphoma project 2008
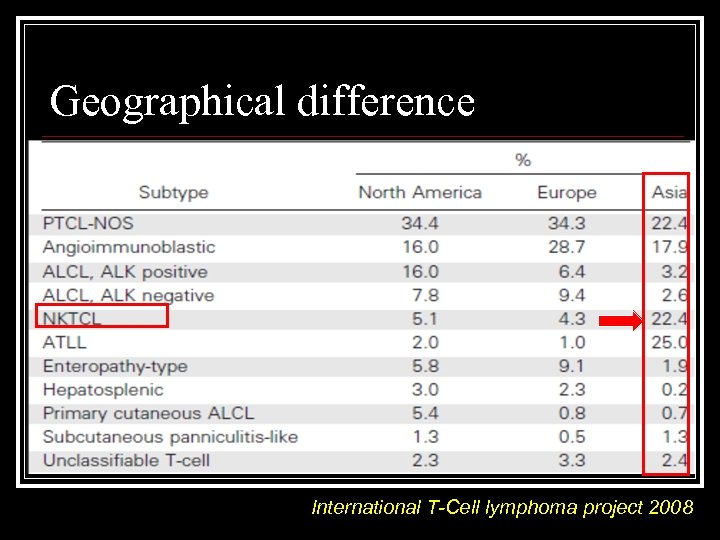 Geographical difference International T-Cell lymphoma project 2008
Geographical difference International T-Cell lymphoma project 2008
 Histology of extranodal NK/T-cell Polymorphous infiltration by atypical lymphocytes with accompanying inflammatory cells n Size of neoplastic cells vary widely n Small neoplastic cells easily missed Read as “Chronic inflammation” n Necrosis and angio-invasion common n
Histology of extranodal NK/T-cell Polymorphous infiltration by atypical lymphocytes with accompanying inflammatory cells n Size of neoplastic cells vary widely n Small neoplastic cells easily missed Read as “Chronic inflammation” n Necrosis and angio-invasion common n
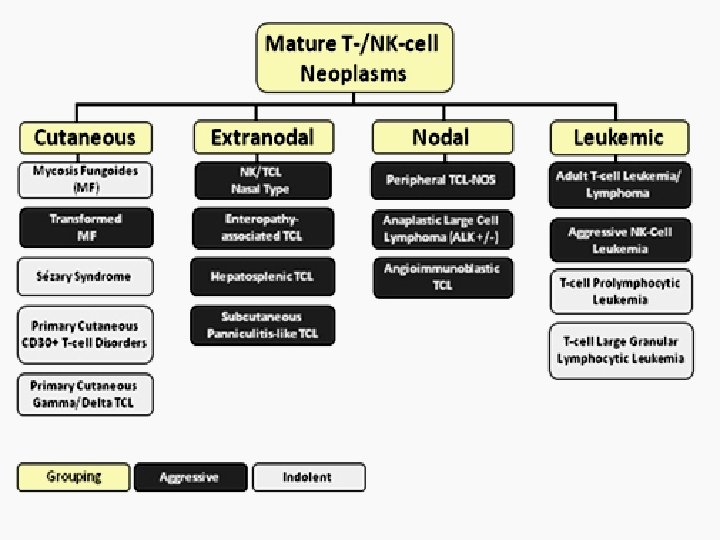
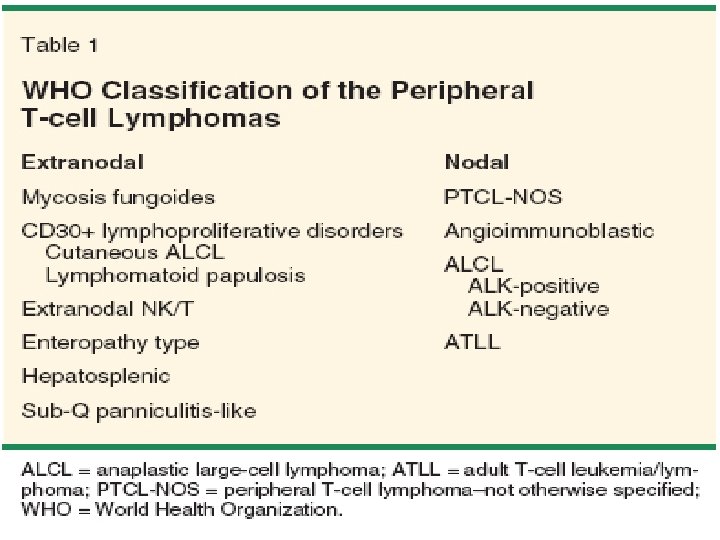
 NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type 1. n n n Nasal 85% of cases Destructive lesion over face and nose “Lethal midline granuloma” Nasal blockage/ discharge/ epistaxis Male dominance, median age onset 50 Associated mosquito bite hypersensitivity
NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type 1. n n n Nasal 85% of cases Destructive lesion over face and nose “Lethal midline granuloma” Nasal blockage/ discharge/ epistaxis Male dominance, median age onset 50 Associated mosquito bite hypersensitivity
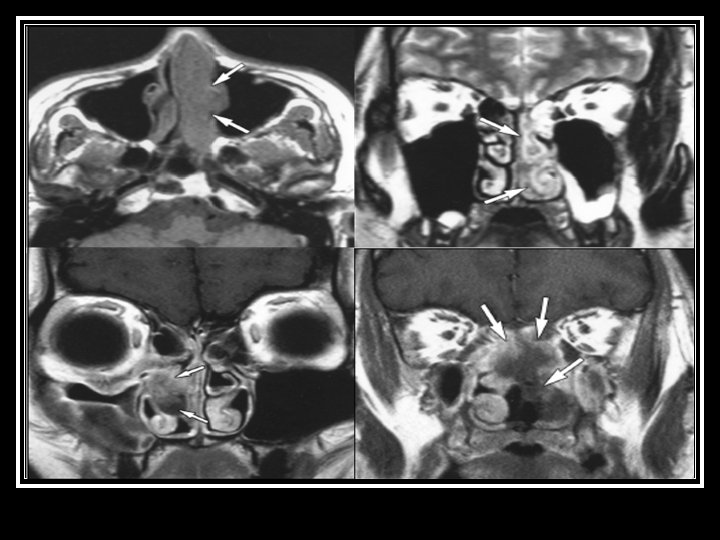
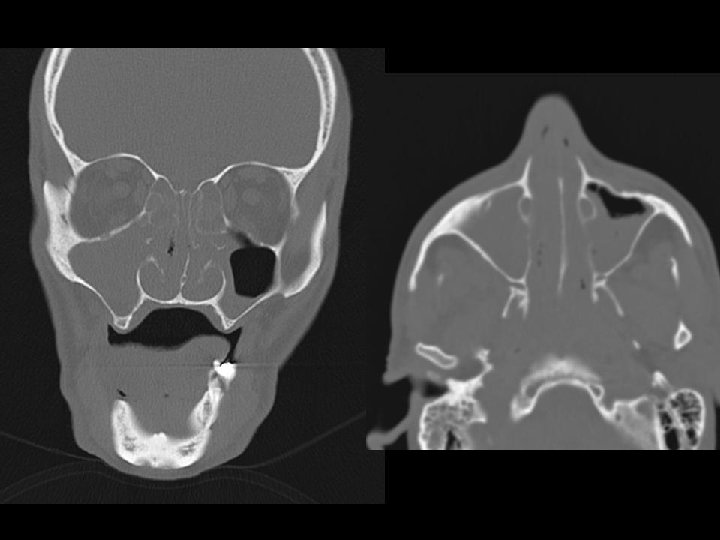
 NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type 2. n n n Extranasal Occurs at any site Commonest skin: multiple ulcers, pyogenic granuloma-like lesions GI tract: polypoid/ fungating/ erosions Liver, lung, testis, even orbit and brain Female and male equally affected
NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type 2. n n n Extranasal Occurs at any site Commonest skin: multiple ulcers, pyogenic granuloma-like lesions GI tract: polypoid/ fungating/ erosions Liver, lung, testis, even orbit and brain Female and male equally affected
 NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type 3. n n Nodal Cervical LN most commonly affected “Very confusing classification: extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma of nasal type with nodal involvement”
NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type 3. n n Nodal Cervical LN most commonly affected “Very confusing classification: extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma of nasal type with nodal involvement”
 Staging of disease Can be difficult n Histology easily mistaken n 18 F-FDG uptake grossly less intense than lymphoma of other cells n Marrow 80% of involved cases had normal study by H&E. n EBER in situ hybridization is essential n
Staging of disease Can be difficult n Histology easily mistaken n 18 F-FDG uptake grossly less intense than lymphoma of other cells n Marrow 80% of involved cases had normal study by H&E. n EBER in situ hybridization is essential n
 Neurological presentation n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Pathologies being reported Intracranial lymphomatous mass Leptomeningeal infiltration, and even along cranial nerves/ spinal nerve roots Demyelination causing polyradiculopathy Vascular insult via angiocentric necrosis GBS-like syndrome Axonal degeneration (unknown pathogenesis)
Neurological presentation n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Pathologies being reported Intracranial lymphomatous mass Leptomeningeal infiltration, and even along cranial nerves/ spinal nerve roots Demyelination causing polyradiculopathy Vascular insult via angiocentric necrosis GBS-like syndrome Axonal degeneration (unknown pathogenesis)
 Case: cranial neuropathy + acute polyradiculopathy 50 year-old man n Left face weakness and paraparesis n Impaired sensation of L 1 -5 dermatomes n MRI enhanced thoracic nerve roots n 2 nd LP CSF +ve for NK-cell lymphoma n 2 nd NCT small amplitude and loss of F n Worsened to tetraplegia in 10 days n J Clin Neuromusc Dis 2000; 1: 137 -140
Case: cranial neuropathy + acute polyradiculopathy 50 year-old man n Left face weakness and paraparesis n Impaired sensation of L 1 -5 dermatomes n MRI enhanced thoracic nerve roots n 2 nd LP CSF +ve for NK-cell lymphoma n 2 nd NCT small amplitude and loss of F n Worsened to tetraplegia in 10 days n J Clin Neuromusc Dis 2000; 1: 137 -140
 Cases: intravascular NK lymphoma Three males and one female n Age 63 -87 n All with skin lesion over trunk/ extremities n One patient with diffuse brain infiltration on presentation and died within one week n Lymphoma cells confined within blood vessels with some lumina occluded n Am J Surg Pathol 2008; 32 (6): 891 -8
Cases: intravascular NK lymphoma Three males and one female n Age 63 -87 n All with skin lesion over trunk/ extremities n One patient with diffuse brain infiltration on presentation and died within one week n Lymphoma cells confined within blood vessels with some lumina occluded n Am J Surg Pathol 2008; 32 (6): 891 -8
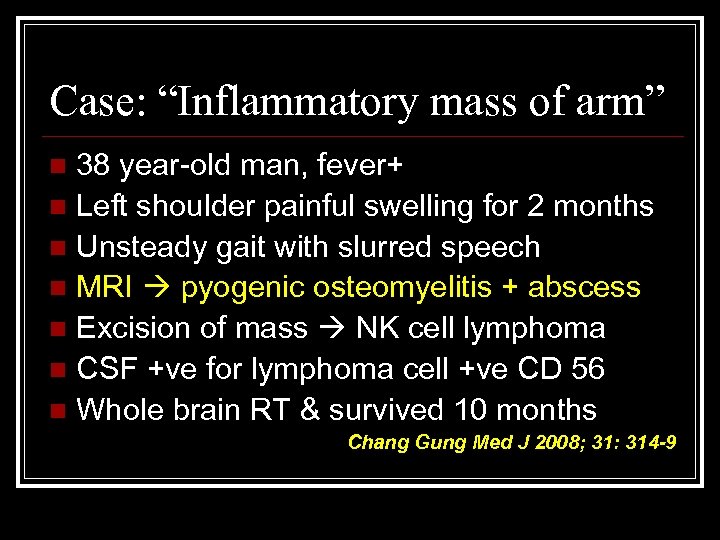 Case: “Inflammatory mass of arm” 38 year-old man, fever+ n Left shoulder painful swelling for 2 months n Unsteady gait with slurred speech n MRI pyogenic osteomyelitis + abscess n Excision of mass NK cell lymphoma n CSF +ve for lymphoma cell +ve CD 56 n Whole brain RT & survived 10 months n Chang Gung Med J 2008; 31: 314 -9
Case: “Inflammatory mass of arm” 38 year-old man, fever+ n Left shoulder painful swelling for 2 months n Unsteady gait with slurred speech n MRI pyogenic osteomyelitis + abscess n Excision of mass NK cell lymphoma n CSF +ve for lymphoma cell +ve CD 56 n Whole brain RT & survived 10 months n Chang Gung Med J 2008; 31: 314 -9
 Case: mimic cerebral infarcts 49 year-old man n Fever/ confusion and agitation for 1 week n MRI brain subacute infarct right frontal n Leukopenia and thrombocytopenia n Bone marrow confirmed NK-lymphoma n Brain lesion remitted after RT n Onkologie 2008; 31 (3): 115 -7
Case: mimic cerebral infarcts 49 year-old man n Fever/ confusion and agitation for 1 week n MRI brain subacute infarct right frontal n Leukopenia and thrombocytopenia n Bone marrow confirmed NK-lymphoma n Brain lesion remitted after RT n Onkologie 2008; 31 (3): 115 -7
 Cases: occult nasal NK lymphoma One woman had MS-like lesion with intraocular involvement (Turbid vitreous body) tissue taken 3 years ago for “chronic sinusitis” actually was lymphoma n One man of leptomeningeal NK lymphoma with ocular involvement had nasal polyp 3 years later confirmed to be NK lymphoma n Am J of Hemat 1999; 60(2): 161 -3
Cases: occult nasal NK lymphoma One woman had MS-like lesion with intraocular involvement (Turbid vitreous body) tissue taken 3 years ago for “chronic sinusitis” actually was lymphoma n One man of leptomeningeal NK lymphoma with ocular involvement had nasal polyp 3 years later confirmed to be NK lymphoma n Am J of Hemat 1999; 60(2): 161 -3
 Treatment of NK/T-cell lymphoma No standard chemotherapy n High concentration of P-glycoprotein which mediates multi-drug resistance n n Commonly presents with multi-organ failure
Treatment of NK/T-cell lymphoma No standard chemotherapy n High concentration of P-glycoprotein which mediates multi-drug resistance n n Commonly presents with multi-organ failure
 Treatment of localized disease Localized radiotherapy n Combine with anthracycline-based chemotherapy n Medial overall survival 3 years n ? Uncertain timing of chemotherapy n Studies showed initial RT had superior CR rate and longer overall survival n
Treatment of localized disease Localized radiotherapy n Combine with anthracycline-based chemotherapy n Medial overall survival 3 years n ? Uncertain timing of chemotherapy n Studies showed initial RT had superior CR rate and longer overall survival n
 Treatment of disseminated disease Only 30% CR rate using anthracyclinebased chemotherapy n Overall median survival 4 months n SMILE ( Steroid + MTx + Ifosfamide + Lasparaginase + Etoposide) in phase 1 n High dose chemo. + Hematopoietic SCT need further evaluation n
Treatment of disseminated disease Only 30% CR rate using anthracyclinebased chemotherapy n Overall median survival 4 months n SMILE ( Steroid + MTx + Ifosfamide + Lasparaginase + Etoposide) in phase 1 n High dose chemo. + Hematopoietic SCT need further evaluation n
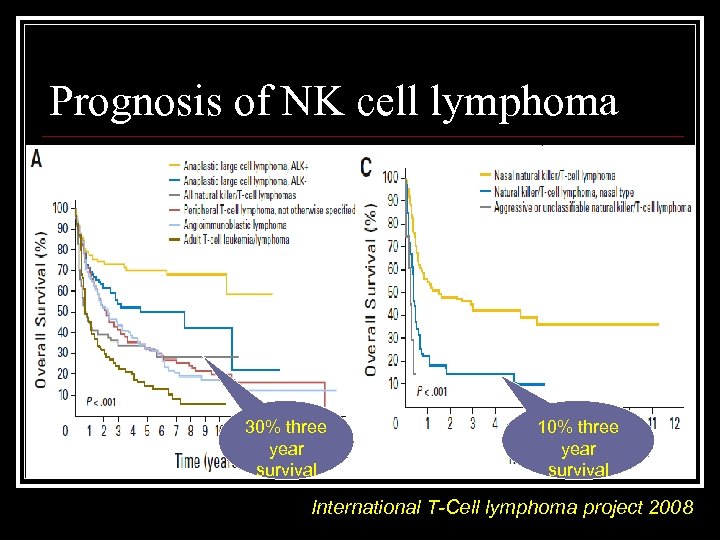 Prognosis of NK cell lymphoma 30% three year survival 10% three year survival International T-Cell lymphoma project 2008
Prognosis of NK cell lymphoma 30% three year survival 10% three year survival International T-Cell lymphoma project 2008
 Prognostic indicators Extranasal location of lesion compared to nasal origin of tumor n Advanced stage (III and IV) n Poor performance status n Stage I disease: 40% 5 year survival n CR rate >80% if RT first followed by chemo n Ann of Onc 2010; 21: 1032 -40
Prognostic indicators Extranasal location of lesion compared to nasal origin of tumor n Advanced stage (III and IV) n Poor performance status n Stage I disease: 40% 5 year survival n CR rate >80% if RT first followed by chemo n Ann of Onc 2010; 21: 1032 -40
 Bring-home……questions ? Genuine neuritis vs. perineural spread n ? Genuine sinusitis vs. lymphoma n ? Genuine endophthalmitis vs. lymphoma n ? Genuine CNS infection vs. lymphoma n ? Positive results if NCT/ LP repeated n ? Aggressive ENT workup or even sinus Bx n ? May be treatable if diagnosed earlier n
Bring-home……questions ? Genuine neuritis vs. perineural spread n ? Genuine sinusitis vs. lymphoma n ? Genuine endophthalmitis vs. lymphoma n ? Genuine CNS infection vs. lymphoma n ? Positive results if NCT/ LP repeated n ? Aggressive ENT workup or even sinus Bx n ? May be treatable if diagnosed earlier n



