CBC-1 вфтф зукувудфттщу.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 5
CBC (Complete Blood Count)
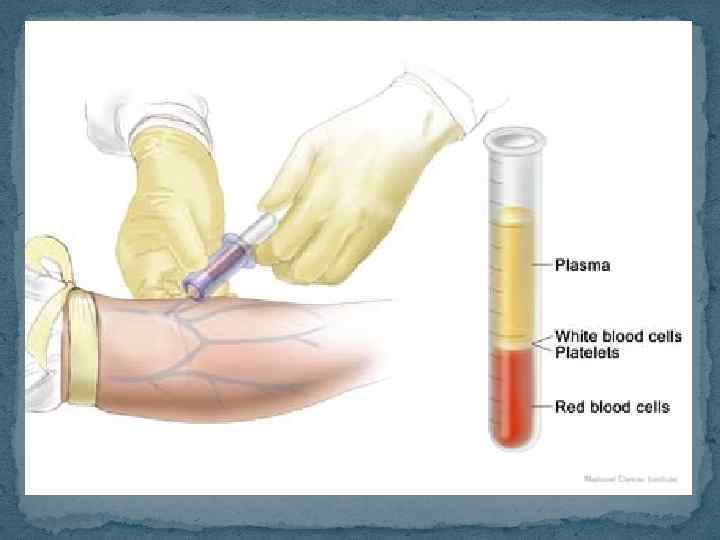
A complete blood count (CBC) is a blood test used to evaluate your overall health and detect a wide range of disorders, including anemia, infection and leukemia. A complete blood count test measures several components and features of your blood, including: Red blood cells, which carry oxygen White blood cells, which fight infection Hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells Hematocrit, the proportion of red blood cells to the fluid component, or plasma, in your blood Platelets, which help with blood clotting Abnormal increases or decreases in cell counts as revealed in a complete blood count may indicate that you have an underlying medical condition that calls for further evaluation.

A complete blood count is a common blood test that's done for a variety of reasons: To assess your overall health. Your doctor may recommend a complete blood count as part of a routine medical examination to monitor your general health and to screen for a variety of disorders, such as anemia or leukemia. To diagnose a medical condition. Your doctor may suggest a complete blood count if you're experiencing weakness, fatigue, fever, inflammation, bruising or bleeding. A complete blood count may help diagnose the cause of these signs and symptoms. If your doctor suspects you have an infection, the test can also help confirm that diagnosis. To monitor a medical condition. If you've been diagnosed with a blood disorder that affects blood cell counts, such as thalassemia or polycythemia vera, your doctor may use complete blood counts to monitor your condition. To monitor medical treatment. A complete blood count may

The following are normal complete blood count results for adults: Red blood cell count Male: 4. 32 -5. 72 trillion cells/L* (4. 32 -5. 72 million cells/mc. L**) Female: 3. 90 -5. 03 trillion cells/L (3. 90 -5. 03 million cells/mc. L) Hemoglobin Hematocrit White blood cell count Platelet count Male: 13. 5 -17. 5 grams/d. L*** (135 -175 grams/L) Female: 12. 0 -15. 5 grams/d. L (120 -155 grams/L) * L = liter ** mc. L = Male: 38. 8 -50. 0 percent microliter *** d. L = deciliter Female: 34. 9 -44. 5 percent **** mmol = micromole 3. 5 -10. 5 billion cells/L (3, 500 to 10, 500 cells/mc. L) 150 -450 billion/L (150, 000 to 450, 000/mmol****)
CBC-1 вфтф зукувудфттщу.pptx