edbe1f710c2da39de9fc0d3121ed024a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 169
 CAUSES, MOOD, AND SETTING THE COLD WAR, 1945 -1991
CAUSES, MOOD, AND SETTING THE COLD WAR, 1945 -1991
 The Cold War Imagine you are in a classroom in 1955… A Siren goes off indicating a nuclear bomb could be being dropped… What will you do? “Duck-and-Cover”!!!!
The Cold War Imagine you are in a classroom in 1955… A Siren goes off indicating a nuclear bomb could be being dropped… What will you do? “Duck-and-Cover”!!!!
 The Cold War World
The Cold War World
 What was the “Cold War”?
What was the “Cold War”?
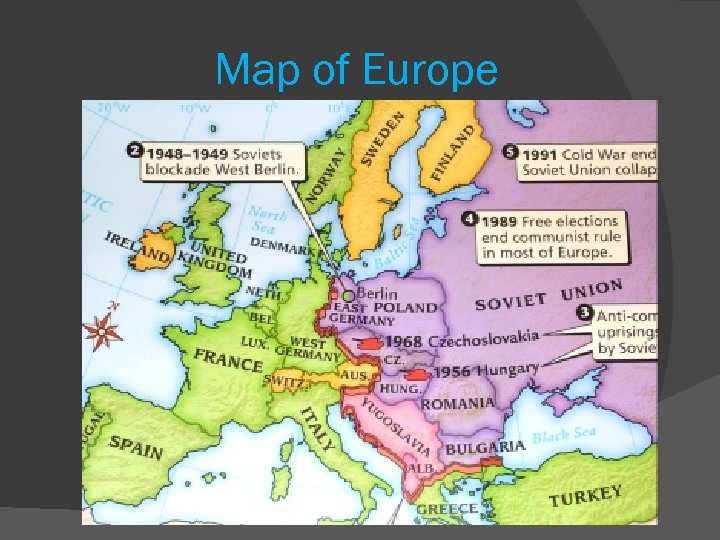 Map of Europe
Map of Europe
 US/USSR Relationship during WWII 1. 2. 3. 4. Before the end of the World War II, Stalin, Churchill and Roosevelt met at Yalta to plan what should happen when the war ended. They agreed on many points: The establishment of the United Nations Division of Germany into four zones Free elections allowed in the states of Eastern Europe Russia’s promise to join the war against Japan Winston Churchill (England), Franklin Roosevelt (US) and Joseph Stalin (USSR) meet in Yalta in 1945 to decide the fate of post-war Europe. No agreement was reached on Poland. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=y 9 Hjv. HZf. CUI 6
US/USSR Relationship during WWII 1. 2. 3. 4. Before the end of the World War II, Stalin, Churchill and Roosevelt met at Yalta to plan what should happen when the war ended. They agreed on many points: The establishment of the United Nations Division of Germany into four zones Free elections allowed in the states of Eastern Europe Russia’s promise to join the war against Japan Winston Churchill (England), Franklin Roosevelt (US) and Joseph Stalin (USSR) meet in Yalta in 1945 to decide the fate of post-war Europe. No agreement was reached on Poland. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=y 9 Hjv. HZf. CUI 6
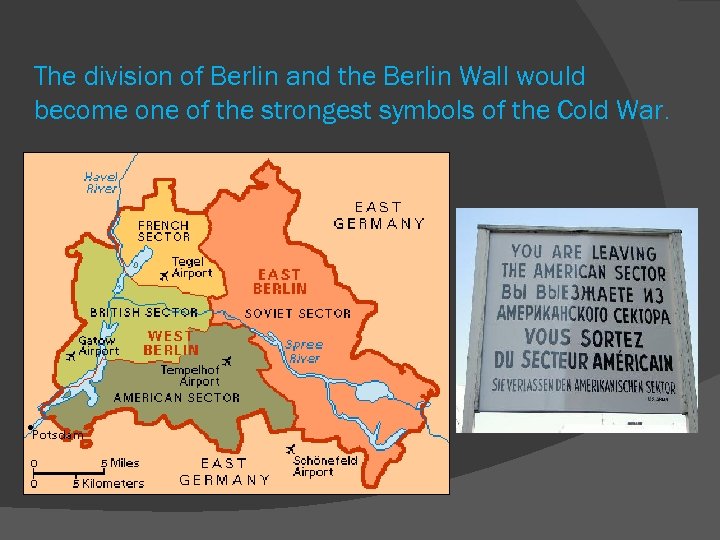 The division of Berlin and the Berlin Wall would become one of the strongest symbols of the Cold War.
The division of Berlin and the Berlin Wall would become one of the strongest symbols of the Cold War.
 Cold War Confrontations: Berlin Wall Construction of the Berlin Wall (1961): Soviet leader Khrushchev built the Berlin Wall to prevent people from fleeing communist East Germany to capitalist West Germany. Came to signify the Cold War divisions: The Iron Curtain.
Cold War Confrontations: Berlin Wall Construction of the Berlin Wall (1961): Soviet leader Khrushchev built the Berlin Wall to prevent people from fleeing communist East Germany to capitalist West Germany. Came to signify the Cold War divisions: The Iron Curtain.
 The Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall
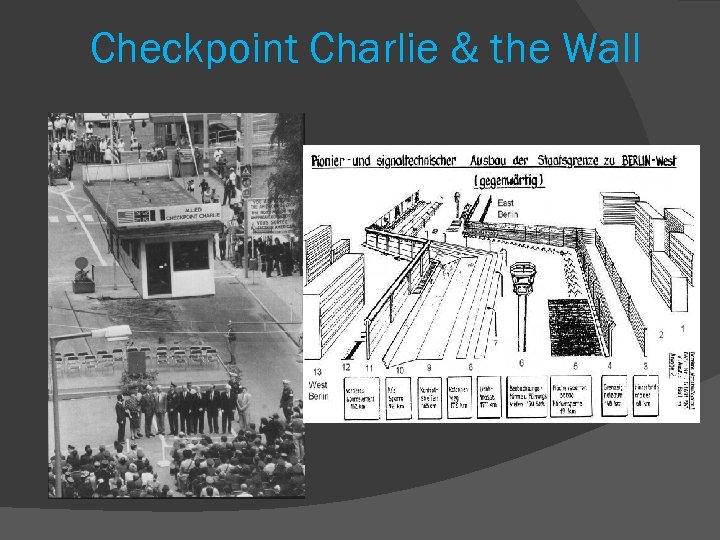 Checkpoint Charlie & the Wall
Checkpoint Charlie & the Wall
 Why was there a Difference between the US and the USSR? Ideological differences: Democracy vs. Authoritarianism / Communism.
Why was there a Difference between the US and the USSR? Ideological differences: Democracy vs. Authoritarianism / Communism.
 Why was there a Difference between the US and the USSR? Economic differences: Free market economy (capitalist) vs. Communist planning and control of the economy.
Why was there a Difference between the US and the USSR? Economic differences: Free market economy (capitalist) vs. Communist planning and control of the economy.
 Why was there a Difference between the US and the USSR? Imperialistic, Military, Nuclear Weapon differences: The US (West) fears a Communist world revolution (Soviet military strength) while the Soviets fear and invasion/nuclear war and an overthrow of their Communist government.
Why was there a Difference between the US and the USSR? Imperialistic, Military, Nuclear Weapon differences: The US (West) fears a Communist world revolution (Soviet military strength) while the Soviets fear and invasion/nuclear war and an overthrow of their Communist government.
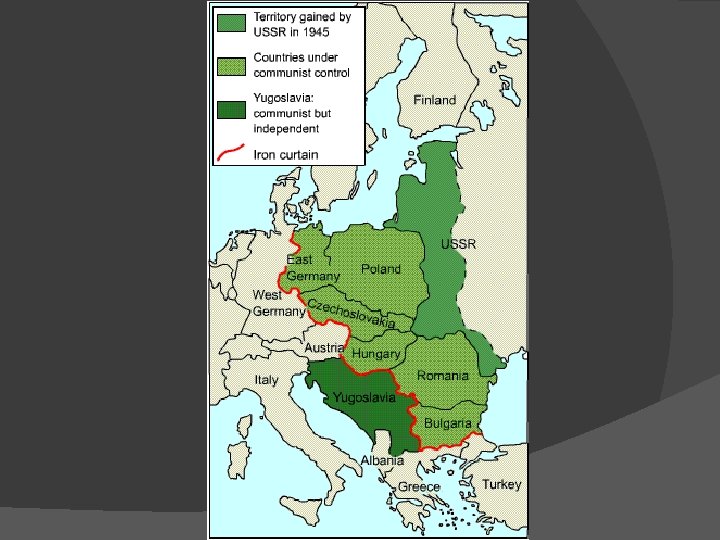
 How did the bi-polar world develop? These countries then became soviet satellite states after the war ended when Stalin refused them democratic elections. Satellite states = formally independent but under heavy political + economic influence of the USSR.
How did the bi-polar world develop? These countries then became soviet satellite states after the war ended when Stalin refused them democratic elections. Satellite states = formally independent but under heavy political + economic influence of the USSR.
 Lead to the phrase: “The Iron Curtain” This phrase “Iron Curtain” was coined by Winston Churchill, in a speech he made shortly after the end of WWII. He was referring to the fact that eastern Europe was controlled by the Soviet Union, and under communist rule. The world was divided between the West (democracy) and the East (communism).
Lead to the phrase: “The Iron Curtain” This phrase “Iron Curtain” was coined by Winston Churchill, in a speech he made shortly after the end of WWII. He was referring to the fact that eastern Europe was controlled by the Soviet Union, and under communist rule. The world was divided between the West (democracy) and the East (communism).
 Churchill’s Speech
Churchill’s Speech
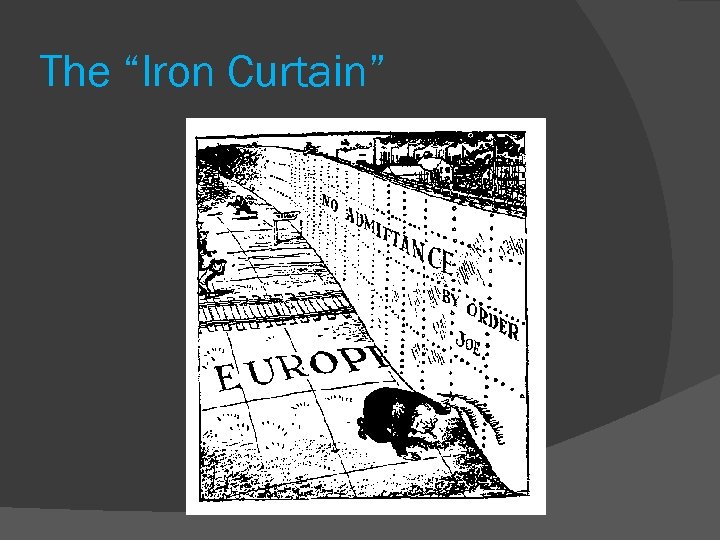 The “Iron Curtain”
The “Iron Curtain”
 Lead to the phrase: “The Iron Curtain” The countries in Eastern Europe were controlled by Soviet dictators and military troops, and were forced to belong to the Warsaw Pact – the communist equivalent to NATO.
Lead to the phrase: “The Iron Curtain” The countries in Eastern Europe were controlled by Soviet dictators and military troops, and were forced to belong to the Warsaw Pact – the communist equivalent to NATO.

 Strategies of Competition 1. Domino Theory – Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania, Poland, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia were liberated/overtaken by the Communists during the last few years of the war. - Domino was a metaphor used by the US to show if one country falls, the next country will fall too.
Strategies of Competition 1. Domino Theory – Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania, Poland, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia were liberated/overtaken by the Communists during the last few years of the war. - Domino was a metaphor used by the US to show if one country falls, the next country will fall too.
 Domino Theory in Asia
Domino Theory in Asia
 Strategies of Competition 2. Containment – Part of the Truman Doctrine. - The USA would support those countries that were resisting Communist takeovers such as Taiwan = China, South Korea = North Korea. - Used the Marshall Plan in Western Europe to prevent to Domino Effect.
Strategies of Competition 2. Containment – Part of the Truman Doctrine. - The USA would support those countries that were resisting Communist takeovers such as Taiwan = China, South Korea = North Korea. - Used the Marshall Plan in Western Europe to prevent to Domino Effect.
 Strategies of Competition (continued) § 3. Satellite States – Counties under the control of the USSR (Eastern Europe) and USA. § Gaining global influence/backyards – have many nations on your side (in your backyard) as allies. § 1946: Churchill referred to the division of Europe by claiming that an Iron Curtain had fallen across Europe;
Strategies of Competition (continued) § 3. Satellite States – Counties under the control of the USSR (Eastern Europe) and USA. § Gaining global influence/backyards – have many nations on your side (in your backyard) as allies. § 1946: Churchill referred to the division of Europe by claiming that an Iron Curtain had fallen across Europe;
 Strategies of Competition (continued) 4. Arms Race - the build up of nuclear weapons: - 1949: NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization; mutual defense.
Strategies of Competition (continued) 4. Arms Race - the build up of nuclear weapons: - 1949: NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization; mutual defense.
 Strategies of Competition (continued) 4. Arms Race - 1955: Warsaw Pact – Defense alliance of Eastern European communist states; both side trying to develop the latest war technology. - Nuclear Parity: same level of nuclear weapons, MAD (mutually assured destruction).
Strategies of Competition (continued) 4. Arms Race - 1955: Warsaw Pact – Defense alliance of Eastern European communist states; both side trying to develop the latest war technology. - Nuclear Parity: same level of nuclear weapons, MAD (mutually assured destruction).
 Strategies of Competition (continued) 5. Space Race – Sputnik: first satellite to orbit earth 1957 by the Soviets, Man on the Moon in 1969, Laika (Soviet space dog): first animal to orbit the Earth and the first orbital death. 6. Espionage – CIA vs. KGB. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=w. Vqzi. NV 7 d. GY
Strategies of Competition (continued) 5. Space Race – Sputnik: first satellite to orbit earth 1957 by the Soviets, Man on the Moon in 1969, Laika (Soviet space dog): first animal to orbit the Earth and the first orbital death. 6. Espionage – CIA vs. KGB. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=w. Vqzi. NV 7 d. GY
 NEXT: Canada + the Cold War
NEXT: Canada + the Cold War
 CANADA + THE COLD WAR 1945 -1991: SIDES ARE CHOSEN
CANADA + THE COLD WAR 1945 -1991: SIDES ARE CHOSEN
 The United Nations Building, NYC
The United Nations Building, NYC
 The Creation of the United Nations Created in 1945. International agency that would prevent another international conflict = the idea of collective security and world peace. Not a perfect system.
The Creation of the United Nations Created in 1945. International agency that would prevent another international conflict = the idea of collective security and world peace. Not a perfect system.
 United Nations Security Council UN Security Council: 5 permanent members: ○ USSR (Russia Today) ○ USA ○ Britain ○ France ○ China ○ Plus 10 non permanent members (2 yr terms)
United Nations Security Council UN Security Council: 5 permanent members: ○ USSR (Russia Today) ○ USA ○ Britain ○ France ○ China ○ Plus 10 non permanent members (2 yr terms)
 The United Nations Canada was a very involved member of the United Nations Organization. We were members of all thirteen of the Specialized Agencies. Between 1947 and 1967 we were three times a non-permanent member of the Security Council.
The United Nations Canada was a very involved member of the United Nations Organization. We were members of all thirteen of the Specialized Agencies. Between 1947 and 1967 we were three times a non-permanent member of the Security Council.

 The Gouzenko Affair Canada was placed at the centre of the Cold War in 1945 due to the Gouzenko Affair, which exposed a Soviet spy ring in the Canadian government.
The Gouzenko Affair Canada was placed at the centre of the Cold War in 1945 due to the Gouzenko Affair, which exposed a Soviet spy ring in the Canadian government.
 The Gouzenko Affair As a result of the Red Scare/Menace in Canada, RCMP carried out illegal and secret inquiries regarding potential communists in Canada. Potential immigrants were denied entry to Canada and members of the communist party were deported.
The Gouzenko Affair As a result of the Red Scare/Menace in Canada, RCMP carried out illegal and secret inquiries regarding potential communists in Canada. Potential immigrants were denied entry to Canada and members of the communist party were deported.
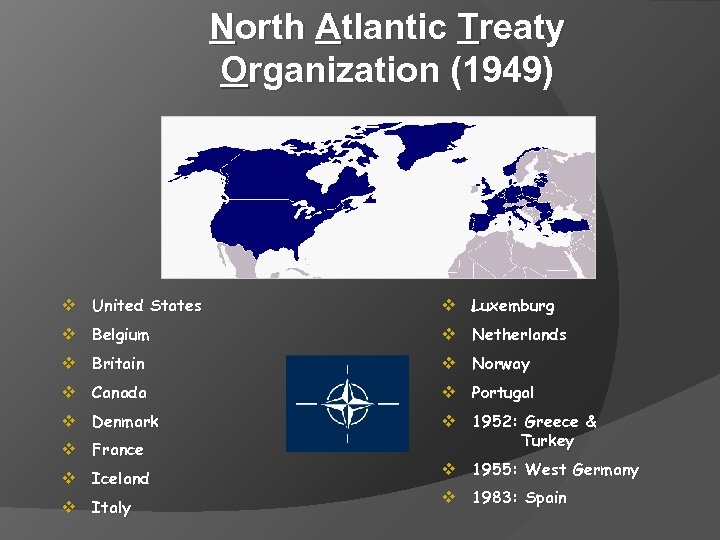 North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) v United States v Luxemburg v Belgium v Netherlands v Britain v Norway v Canada v Portugal v Denmark v 1952: Greece & v France v Iceland v Italy Turkey v 1955: West Germany v 1983: Spain
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) v United States v Luxemburg v Belgium v Netherlands v Britain v Norway v Canada v Portugal v Denmark v 1952: Greece & v France v Iceland v Italy Turkey v 1955: West Germany v 1983: Spain
 Cold War Military Alliances 1. NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization), 1949. Provided for the collective security of Western Europe against the threat of Soviet invasion/spread of communism. ○ Any attack on one NATO member was considered to be an attack on all. Founding Members: Canada
Cold War Military Alliances 1. NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization), 1949. Provided for the collective security of Western Europe against the threat of Soviet invasion/spread of communism. ○ Any attack on one NATO member was considered to be an attack on all. Founding Members: Canada
 NATO: The Agreement NATO Agreement: Tactical nuclear weapons could be used if conventional weapons failed. As a last resort, total nuclear would be waged.
NATO: The Agreement NATO Agreement: Tactical nuclear weapons could be used if conventional weapons failed. As a last resort, total nuclear would be waged.
 Canada and NATO: Commitment Canadian forces participated in regular military exercises with NATO allies. Canada adapted its defence policy to those of its allies. Had to keep Canadian troops based in Europe. All this meant that, to some extent, Canada’s autonomy was sacrificed.
Canada and NATO: Commitment Canadian forces participated in regular military exercises with NATO allies. Canada adapted its defence policy to those of its allies. Had to keep Canadian troops based in Europe. All this meant that, to some extent, Canada’s autonomy was sacrificed.
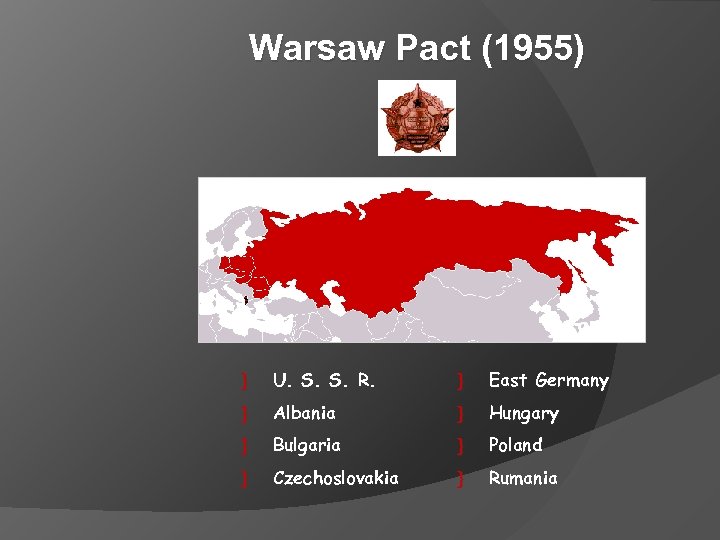 Warsaw Pact (1955) } U. S. S. R. } East Germany } Albania } Hungary } Bulgaria } Poland } Czechoslovakia } Rumania
Warsaw Pact (1955) } U. S. S. R. } East Germany } Albania } Hungary } Bulgaria } Poland } Czechoslovakia } Rumania
 Cold War Military Alliances 2. The USSR created the Warsaw Pact in 1955 to counter/rival NATO. Alliance of Eastern European Communist countries was officially called 'The Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance. ' Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and the Soviet Union.
Cold War Military Alliances 2. The USSR created the Warsaw Pact in 1955 to counter/rival NATO. Alliance of Eastern European Communist countries was officially called 'The Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance. ' Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and the Soviet Union.
 Canada is stuck in the middle of nuclear warhead stockpiles
Canada is stuck in the middle of nuclear warhead stockpiles
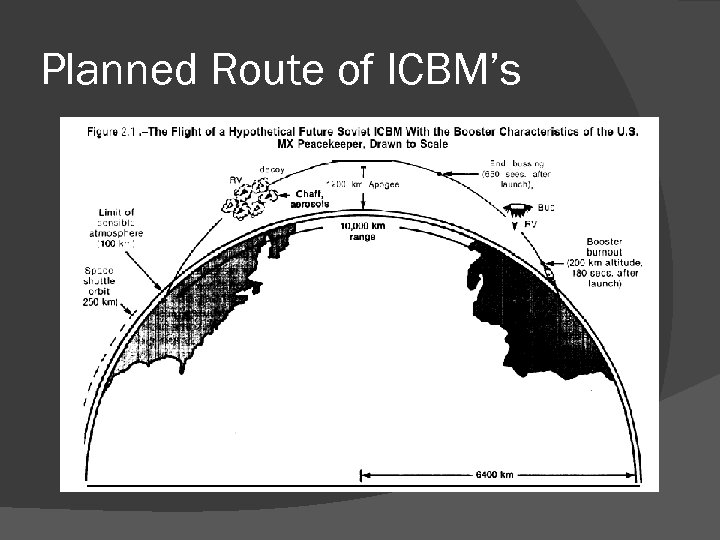
 Defence : ICBMs (intercontinental ballistic missiles): development meant nuclear missiles launched from the USSR could reach North American cities within 30 minutes.
Defence : ICBMs (intercontinental ballistic missiles): development meant nuclear missiles launched from the USSR could reach North American cities within 30 minutes.
 Planned Route of ICBM’s
Planned Route of ICBM’s
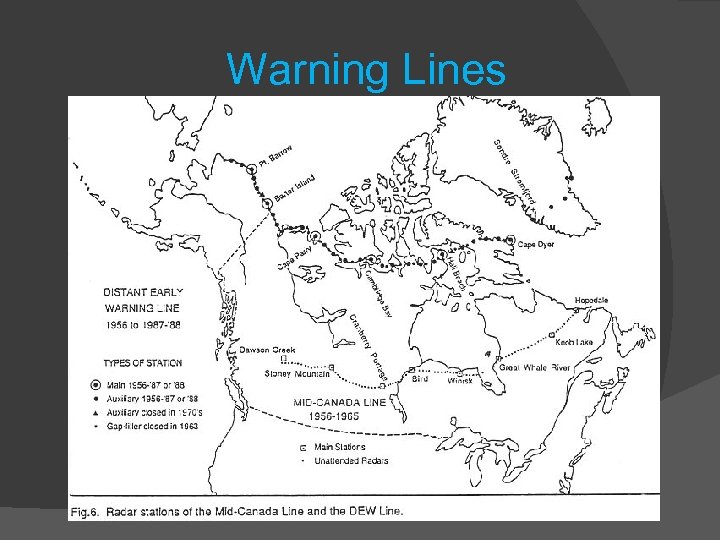
 Defence: NORAD (North American Aerospace Defense Command): Joint fighter forces. Missile bases All controlled by a central command station built in Cheyenne Mountain, Colorado. Radar Stations: the US built three lines of radar stations across Canada between 1950 -57 (stop USSR attacks from north)
Defence: NORAD (North American Aerospace Defense Command): Joint fighter forces. Missile bases All controlled by a central command station built in Cheyenne Mountain, Colorado. Radar Stations: the US built three lines of radar stations across Canada between 1950 -57 (stop USSR attacks from north)
 How does Canada respond? Places Distant Early Warning Line Stations (DEW) in northern Canada. US and Canada form NORAD (North American Defense Agreement); gets involved in Korean War (1950 -53).
How does Canada respond? Places Distant Early Warning Line Stations (DEW) in northern Canada. US and Canada form NORAD (North American Defense Agreement); gets involved in Korean War (1950 -53).
 Warning Lines
Warning Lines
 North American Defense: BOMARC Missiles BOMARC Missile Crisis: 1958 PM Diefenbaker announced an agreement with the US to deploy in Canada 2 squadrons of the American ramjet-powered "Bomarc" antiaircraft missile. This controversial defence decision came from the 1957 NORAD agreement with the US.
North American Defense: BOMARC Missiles BOMARC Missile Crisis: 1958 PM Diefenbaker announced an agreement with the US to deploy in Canada 2 squadrons of the American ramjet-powered "Bomarc" antiaircraft missile. This controversial defence decision came from the 1957 NORAD agreement with the US.
 North American Defense BOMARC Missile Crisis: Fifty-six missiles were deployed in Ontario and Québec. The Canadian government did not make it clear that the Bomarc-B, was to be fitted with nuclear warheads.
North American Defense BOMARC Missile Crisis: Fifty-six missiles were deployed in Ontario and Québec. The Canadian government did not make it clear that the Bomarc-B, was to be fitted with nuclear warheads.
 Defence and Canadian Autonomy These radar stations were manned by US military personnel on Canadian soil. Many Canadians feared this also compromised Canada’s autonomy, but most accepted this as the price of better security against a Soviet attack.
Defence and Canadian Autonomy These radar stations were manned by US military personnel on Canadian soil. Many Canadians feared this also compromised Canada’s autonomy, but most accepted this as the price of better security against a Soviet attack.
 CONFLICTS OF THE COLD WAR: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS, 1945 -1991
CONFLICTS OF THE COLD WAR: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS, 1945 -1991
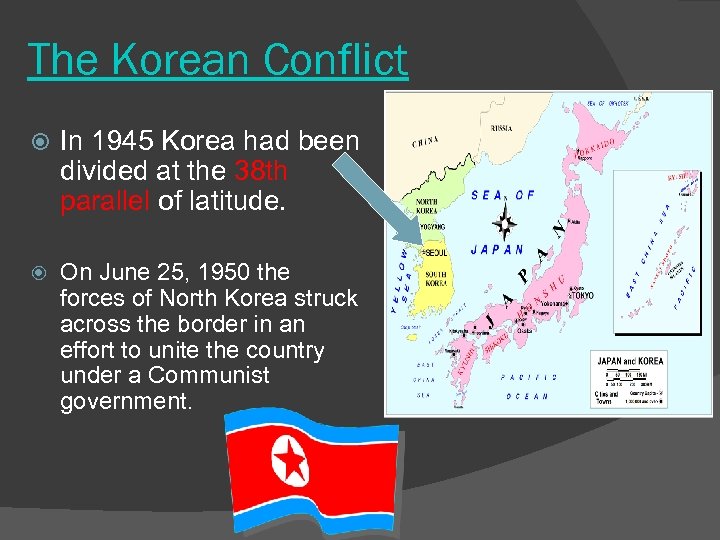 The Korean Conflict In 1945 Korea had been divided at the 38 th parallel of latitude. On June 25, 1950 the forces of North Korea struck across the border in an effort to unite the country under a Communist government.
The Korean Conflict In 1945 Korea had been divided at the 38 th parallel of latitude. On June 25, 1950 the forces of North Korea struck across the border in an effort to unite the country under a Communist government.
 Korean War N. Korea received helped from USSR & China. S. Korea was aided by USA & UN: USA considered use of atomic bomb. http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Kx. D 5 Azt. Iv 1 k http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=l. Tnw 8 YQ 89 dw
Korean War N. Korea received helped from USSR & China. S. Korea was aided by USA & UN: USA considered use of atomic bomb. http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Kx. D 5 Azt. Iv 1 k http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=l. Tnw 8 YQ 89 dw
 Korea and the United Nations 1950 - 1953 The UN Security Council was able to act without fear of the Russian veto Russian representative had absented himself. Troops were authorized in a “police action” to support South Korea. The major contributor of troops was the United States but Canada, along with many other nations, sent over 25, 000 soldiers and sailors to fight in Korea. Future PM Lester Pearson as president of the UN
Korea and the United Nations 1950 - 1953 The UN Security Council was able to act without fear of the Russian veto Russian representative had absented himself. Troops were authorized in a “police action” to support South Korea. The major contributor of troops was the United States but Canada, along with many other nations, sent over 25, 000 soldiers and sailors to fight in Korea. Future PM Lester Pearson as president of the UN
 CANADA AS A MIDDLE POWER “leading from beside. ” http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=cyd 8 KZBt. ZN 0 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=W_9 CMTfr. VFs
CANADA AS A MIDDLE POWER “leading from beside. ” http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=cyd 8 KZBt. ZN 0 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=W_9 CMTfr. VFs
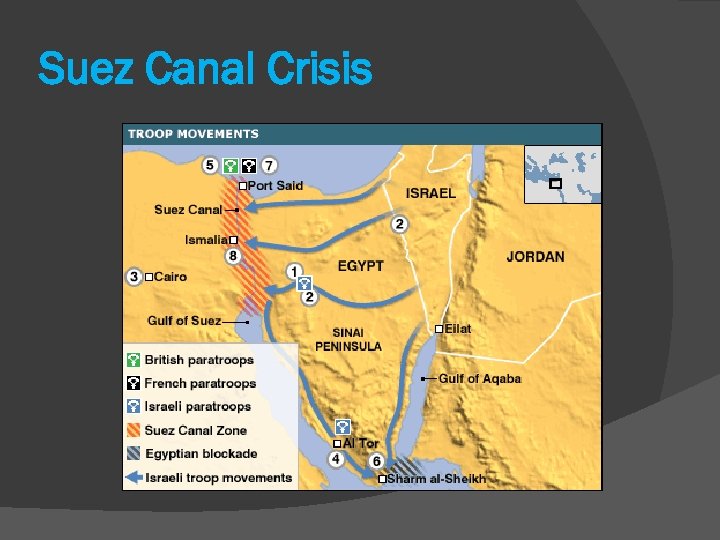
 Cold War Confrontations: CANADA and the Suez Canal Crisis The Suez Crisis (1956): Israel (aided by GB and france) and Egypt (aided by USSR) were at the brink of war over control of the Suez Canal (a major trade route).
Cold War Confrontations: CANADA and the Suez Canal Crisis The Suez Crisis (1956): Israel (aided by GB and france) and Egypt (aided by USSR) were at the brink of war over control of the Suez Canal (a major trade route).
 Lester B. Pearson Minister of External Affairs 1950 s PM of Canada 1963 -1968 Played a key role in Canada’s relationship with the UN. MULTILATERALISM!!!! http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=j. P 28 u 2 R 9 MHQ
Lester B. Pearson Minister of External Affairs 1950 s PM of Canada 1963 -1968 Played a key role in Canada’s relationship with the UN. MULTILATERALISM!!!! http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=j. P 28 u 2 R 9 MHQ
 Suez Canal Crisis
Suez Canal Crisis
 Suez Canal Crisis Canadian Lester B. Pearson proposed a UN peacekeeping force be sent in to mediate – Canadians + other nations went as peacekeepers. RESULT: Pearson won Nobel Peace Prize. Canada gains reputation as peacekeeping nation. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=b. BNIr. YU 5 G 3 M
Suez Canal Crisis Canadian Lester B. Pearson proposed a UN peacekeeping force be sent in to mediate – Canadians + other nations went as peacekeepers. RESULT: Pearson won Nobel Peace Prize. Canada gains reputation as peacekeeping nation. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=b. BNIr. YU 5 G 3 M
 Canada and the Cuban Missile Crisis Kennedy, Khrushchev, Diefenbaker
Canada and the Cuban Missile Crisis Kennedy, Khrushchev, Diefenbaker
 Cold War Confrontations: Vietnam (1955 -1975): Was a French colony but Japan invaded in WWII and won. The French attempt to come back.
Cold War Confrontations: Vietnam (1955 -1975): Was a French colony but Japan invaded in WWII and won. The French attempt to come back.
 Vietnam War USA and UN supported dictatorship in South to prevent the Domino Theory (dictator was not communist). Fought communists in North who were supplied weapons and training by USSR and China.
Vietnam War USA and UN supported dictatorship in South to prevent the Domino Theory (dictator was not communist). Fought communists in North who were supplied weapons and training by USSR and China.
 Vietnam was the first war recorded by American media.
Vietnam was the first war recorded by American media.
 CANADA: Vietnam Draft Dodgers War was unpopular in US --- hippies and/or anti-war activists. Many draft dodgers fled to Canada = we offered them sanctuary/protection.
CANADA: Vietnam Draft Dodgers War was unpopular in US --- hippies and/or anti-war activists. Many draft dodgers fled to Canada = we offered them sanctuary/protection.
 CANADA: Vietnam Draft Dodgers Many Vietnamese also fled to Canada = we offered them a new home. PM Pearson’s criticism of the US in Vietnam led to problems = bad relations.
CANADA: Vietnam Draft Dodgers Many Vietnamese also fled to Canada = we offered them a new home. PM Pearson’s criticism of the US in Vietnam led to problems = bad relations.
 CANADA Cold War Confrontations: Diefenbaker The US expected Canada to provide unconditional support throughout the Cold War. PM Diefenbaker refused to - he instead: Placed Canada’s NORAD forces on alert. Allowed US planes with A-bombs to land.
CANADA Cold War Confrontations: Diefenbaker The US expected Canada to provide unconditional support throughout the Cold War. PM Diefenbaker refused to - he instead: Placed Canada’s NORAD forces on alert. Allowed US planes with A-bombs to land.
 Diefenbaker RESULT: Canadian independence preserved. But relations with USA were damaged.
Diefenbaker RESULT: Canadian independence preserved. But relations with USA were damaged.
 Cold War Confrontations: Cyprus: 1964 -1993: Canada's longest peacekeeping mission began a few years after the Suez Crisis. In 1959, Cyprus, an island in the Mediterranean, gained its independence from Great Britain = Greek and Turkish communities on the island, however, could not coexist peacefully.
Cold War Confrontations: Cyprus: 1964 -1993: Canada's longest peacekeeping mission began a few years after the Suez Crisis. In 1959, Cyprus, an island in the Mediterranean, gained its independence from Great Britain = Greek and Turkish communities on the island, however, could not coexist peacefully.
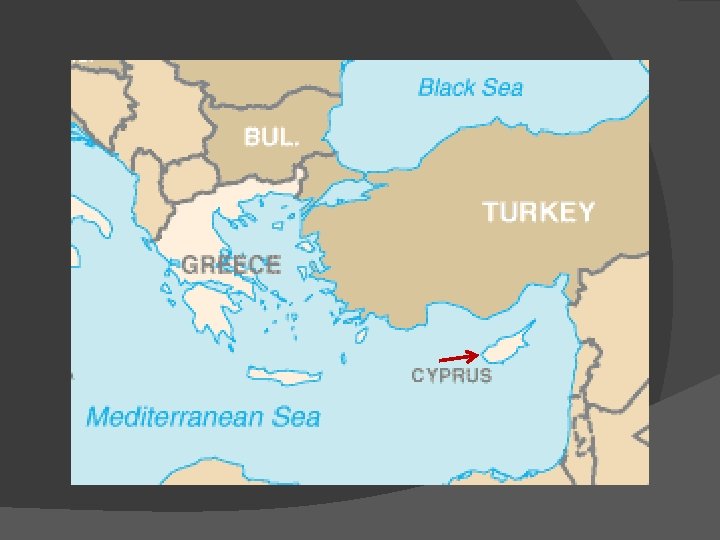
 CANADA Cold War Confrontations: CANADA and Cyprus: 1964 -1993: By 1963, fighting had broken out between the two groups (Greek and Turkish) and an international crisis loomed. UN troops, including a Canadian contingent, were stationed in Cyprus to keep the peace.
CANADA Cold War Confrontations: CANADA and Cyprus: 1964 -1993: By 1963, fighting had broken out between the two groups (Greek and Turkish) and an international crisis loomed. UN troops, including a Canadian contingent, were stationed in Cyprus to keep the peace.
 CANADA Cold War Confrontations: Cyprus: 1964 -1993: The conflict continued, however, and led to the partitioning of Cyprus into Turkish and Greek republics. Canada kept an infantry battalion of varying size in Cyprus until the mid-1990 s and still maintains a small group of observers there.
CANADA Cold War Confrontations: Cyprus: 1964 -1993: The conflict continued, however, and led to the partitioning of Cyprus into Turkish and Greek republics. Canada kept an infantry battalion of varying size in Cyprus until the mid-1990 s and still maintains a small group of observers there.
 CANADIAN NON-VIOLENT RELATIONS IN THE WORLD
CANADIAN NON-VIOLENT RELATIONS IN THE WORLD
 Trudeau and the Cold War Last half of the 20 th century further defined by Pierre Elliott Trudeau: Served four terms as PM of Canada (1968 -1979; 19801984).
Trudeau and the Cold War Last half of the 20 th century further defined by Pierre Elliott Trudeau: Served four terms as PM of Canada (1968 -1979; 19801984).
 Pierre Elliott Trudeau
Pierre Elliott Trudeau
 Pierre Elliott Trudeau: Pirouette
Pierre Elliott Trudeau: Pirouette
 Trudeau’s Foreign Policy In 1968 Pierre Elliott Trudeau would become Prime Minster of Canada following on the heels of L. B. Pearson. He wanted to become less dependent on the U. S. A. and saw the world in a global perspective.
Trudeau’s Foreign Policy In 1968 Pierre Elliott Trudeau would become Prime Minster of Canada following on the heels of L. B. Pearson. He wanted to become less dependent on the U. S. A. and saw the world in a global perspective.
 Trudeau and the Cold War Changed Canada’s defence policies: Removed nukes from Canada’s NATO forces in Europe. Dismantled BOMARC missile sites (surface to air missiles). Removed all nuclear warheads from Canadian soil by 1984. Cut Canada’s European NATO force in half. Set continued to setup Pearson’s role of. Canada up as middle power promoting peace. ○ He officially recognized the communist government of China contrary to American opinion ○ Had relations with Cuba
Trudeau and the Cold War Changed Canada’s defence policies: Removed nukes from Canada’s NATO forces in Europe. Dismantled BOMARC missile sites (surface to air missiles). Removed all nuclear warheads from Canadian soil by 1984. Cut Canada’s European NATO force in half. Set continued to setup Pearson’s role of. Canada up as middle power promoting peace. ○ He officially recognized the communist government of China contrary to American opinion ○ Had relations with Cuba
 VIDEO: The Cold War Ends
VIDEO: The Cold War Ends
 Gorbachev: Glasnost + Perestroika Replaced the old system with: Glasnost = openness, encouraged open debate, transparency, freedom of information. Perestroika = restructured the economy in 1987; main reason for the fall of Communism in the USSR.
Gorbachev: Glasnost + Perestroika Replaced the old system with: Glasnost = openness, encouraged open debate, transparency, freedom of information. Perestroika = restructured the economy in 1987; main reason for the fall of Communism in the USSR.
 The Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989) http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=MM 2 qq 5 J 5 A 1 s
The Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989) http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=MM 2 qq 5 J 5 A 1 s
 Collapse of the Wall in 1989 symbolized the beginning of the end of the Cold War
Collapse of the Wall in 1989 symbolized the beginning of the end of the Cold War
 CANADIAN RELATIONS IN MODERN TIMES: MILITARY
CANADIAN RELATIONS IN MODERN TIMES: MILITARY
 A New World Order? After the US led UN forces in the first Gulf War vs. Iraq (1991), President George Bush (Sr. ) declared a “new world order”: UN serving as a global peace force under US guidance.
A New World Order? After the US led UN forces in the first Gulf War vs. Iraq (1991), President George Bush (Sr. ) declared a “new world order”: UN serving as a global peace force under US guidance.
 New World Order: Failures Today, many question the purpose of the UN (under US “control? ”) after failures regarding genocides in Yugoslavia, Somalia, Bosnia, Rwanda, Darfur and more.
New World Order: Failures Today, many question the purpose of the UN (under US “control? ”) after failures regarding genocides in Yugoslavia, Somalia, Bosnia, Rwanda, Darfur and more.
 Tensions Rise Slobodan Milošević Tito dies in 1980 Serbian Milošević becomes new Yugoslavian President Ethnic Tension Ethnic groups begin to fight Political Changes Glasnost & perestroika in the late 80 s led to end of Cold War As parts of the former USSR declared independence, parts of Yugoslavia do the same
Tensions Rise Slobodan Milošević Tito dies in 1980 Serbian Milošević becomes new Yugoslavian President Ethnic Tension Ethnic groups begin to fight Political Changes Glasnost & perestroika in the late 80 s led to end of Cold War As parts of the former USSR declared independence, parts of Yugoslavia do the same
 Civil War in the Former Yugoslavia Croatia, Slovenia, Macedonia and Bosnia broke away from Yugoslavia (often known as Serbia) and became independent countries. Conflict quickly broke out in this part of Europe which is known as the Balkans. NATO and the UN worked together to try and end the conflict and protect civilians.
Civil War in the Former Yugoslavia Croatia, Slovenia, Macedonia and Bosnia broke away from Yugoslavia (often known as Serbia) and became independent countries. Conflict quickly broke out in this part of Europe which is known as the Balkans. NATO and the UN worked together to try and end the conflict and protect civilians.
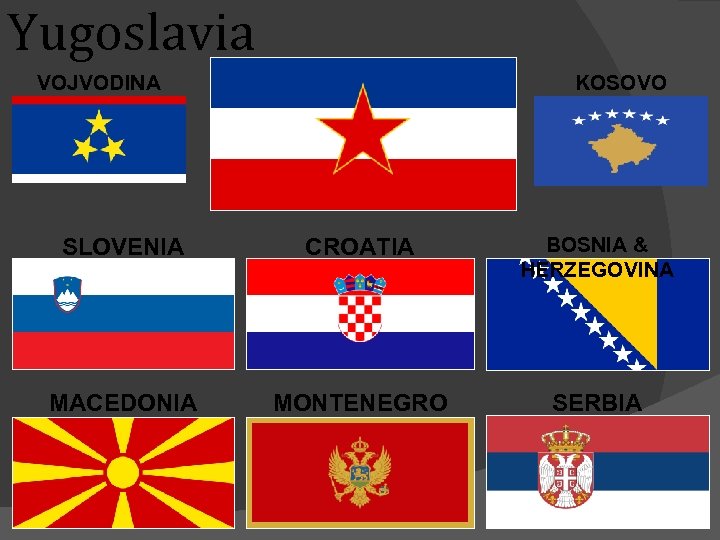 Yugoslavia VOJVODINA KOSOVO SLOVENIA CROATIA BOSNIA & HERZEGOVINA MACEDONIA MONTENEGRO SERBIA
Yugoslavia VOJVODINA KOSOVO SLOVENIA CROATIA BOSNIA & HERZEGOVINA MACEDONIA MONTENEGRO SERBIA
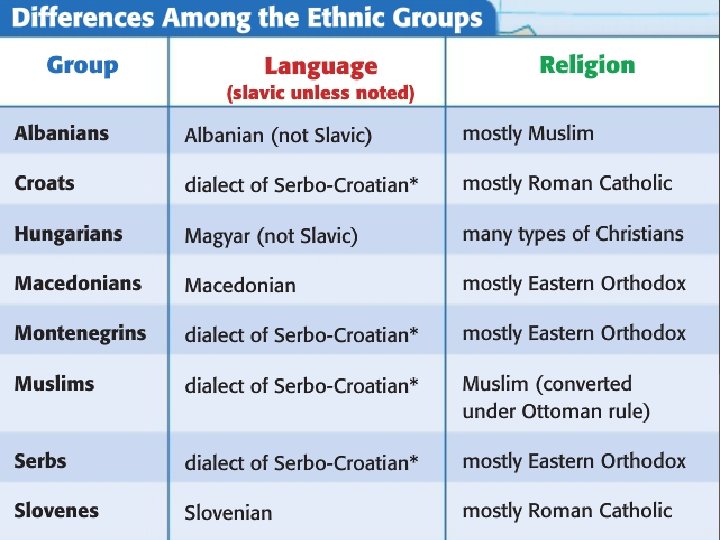
 What do you notice about the location of the different ethnic groups in
What do you notice about the location of the different ethnic groups in
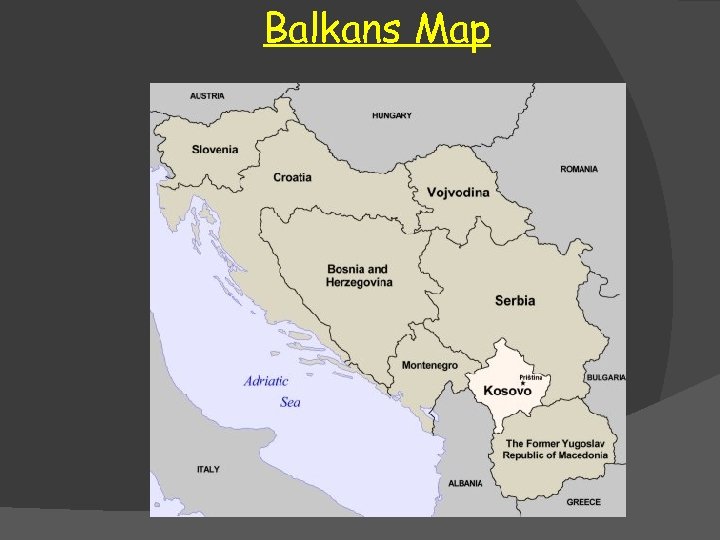 Balkans Map
Balkans Map
 Civil War in Yugoslavia War in Bosnia & Herzegovina declare independence, but arguments break out among the ethnic groups of Bosnia ○ Bosnian Muslims & Croats support independence ○ Bosnian Serbs want to remain part of Yugoslavia Bosnian Serbs form paramilitary units ○ Paramilitary units are supported by Milošević ○ Begin a policy of Ethnic Cleansing against Muslim & Croat people in Bosnia
Civil War in Yugoslavia War in Bosnia & Herzegovina declare independence, but arguments break out among the ethnic groups of Bosnia ○ Bosnian Muslims & Croats support independence ○ Bosnian Serbs want to remain part of Yugoslavia Bosnian Serbs form paramilitary units ○ Paramilitary units are supported by Milošević ○ Begin a policy of Ethnic Cleansing against Muslim & Croat people in Bosnia
 Action in Bosnia There was evidence of ‘ethnic cleansing’ of Bosnian Muslims. The UN tried to negotiate a ceasefire provide aid and put sanctions on Serbia to stop them sending weapons to Bosnia. UN peacekeepers were sent into areas where peace had been negotiated but found it difficult to protect civilians. The UN introduced a no fly zone over Bosnia to stop Serbia sending aircraft on bombing missions to Bosnia.
Action in Bosnia There was evidence of ‘ethnic cleansing’ of Bosnian Muslims. The UN tried to negotiate a ceasefire provide aid and put sanctions on Serbia to stop them sending weapons to Bosnia. UN peacekeepers were sent into areas where peace had been negotiated but found it difficult to protect civilians. The UN introduced a no fly zone over Bosnia to stop Serbia sending aircraft on bombing missions to Bosnia.
 Ethnic Cleansing “Purposeful policy designed by one ethnic or religious group to remove by violent and terror-inspiring means the civilian population of another ethnic or religious group from certain geographic areas” (U. N. ) Mostly blamed on Serbs, but used by all sides in Bosnian conflict Methods Murder, torture, unfair arrests, executions, sexual assaults, ghettos, forcible deportation, etc.
Ethnic Cleansing “Purposeful policy designed by one ethnic or religious group to remove by violent and terror-inspiring means the civilian population of another ethnic or religious group from certain geographic areas” (U. N. ) Mostly blamed on Serbs, but used by all sides in Bosnian conflict Methods Murder, torture, unfair arrests, executions, sexual assaults, ghettos, forcible deportation, etc.
 Results of Ethnic Cleansing Death Toll 100, 000+ estimated killed Refugees A person who leaves his/her home/nation to find safety Near 3 million displaced
Results of Ethnic Cleansing Death Toll 100, 000+ estimated killed Refugees A person who leaves his/her home/nation to find safety Near 3 million displaced
 How Did NATO Get Involved? The UN asked NATO to help them make sure that Serbia obeyed the no-fly zone. NATO threatened to use air strikes if safe havens were attacked In 1995 the civil war came to an end. NATO troops were sent in to supervise the peace agreement – they acted as the ‘muscle’ of the UN.
How Did NATO Get Involved? The UN asked NATO to help them make sure that Serbia obeyed the no-fly zone. NATO threatened to use air strikes if safe havens were attacked In 1995 the civil war came to an end. NATO troops were sent in to supervise the peace agreement – they acted as the ‘muscle’ of the UN.
 Kosovo NATO sent in forces to ensure that peace was maintained in Kosovo. They are still there. They found evidence of mass graves. Hague Trial 2002 – U. N. puts Milošević on trial for genocide & other crimes against humanity 2006 – Milošević dies of a heart attack while in custody Mixed international reaction
Kosovo NATO sent in forces to ensure that peace was maintained in Kosovo. They are still there. They found evidence of mass graves. Hague Trial 2002 – U. N. puts Milošević on trial for genocide & other crimes against humanity 2006 – Milošević dies of a heart attack while in custody Mixed international reaction
 30 for 30: Once Brothers Chronicles the relationship of Yugoslavian and NBA basketball players Vlade Divac (Serbia) and Dražen Petrović (Croatia). They played together on the Yugoslavia national basketball team from 1986– 1990 and were at one time close friends, but the Wars drove them apart as they came from opposing sides/ethnicities. http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=4 u-A 6 b 1 dbtc http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=8 mt. RJppz. Zbg
30 for 30: Once Brothers Chronicles the relationship of Yugoslavian and NBA basketball players Vlade Divac (Serbia) and Dražen Petrović (Croatia). They played together on the Yugoslavia national basketball team from 1986– 1990 and were at one time close friends, but the Wars drove them apart as they came from opposing sides/ethnicities. http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=4 u-A 6 b 1 dbtc http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=8 mt. RJppz. Zbg
 SOMALIA: The New World Order Canadian troops participated in Operation Restore Hope in Somalia (Africa), ravaged by civil war, under the auspices of the United Nations. A teenager was arrested and tortured by the Canadian forces. Compounding the act was efforts made at a cover-up that tarnished the reputation of Canadian forces. The air borne squadron that was involved was completely disbanded as a consequence.
SOMALIA: The New World Order Canadian troops participated in Operation Restore Hope in Somalia (Africa), ravaged by civil war, under the auspices of the United Nations. A teenager was arrested and tortured by the Canadian forces. Compounding the act was efforts made at a cover-up that tarnished the reputation of Canadian forces. The air borne squadron that was involved was completely disbanded as a consequence.
 Operation Restory Hope: Somali Children in Bombed Out Home
Operation Restory Hope: Somali Children in Bombed Out Home
 RWANDA: New World Order Failures Rwandan Genocide (1994): The UN sent in )UNITED NATIONS ASSISTANCE MISSION FOR RWANDA) UNAMIR to keep the peace after a Civil War in Rwanda but soon the genocide began. The mass murder of an estimated 1 Million people in the small East African nation of Rwanda over the course of 100 days.
RWANDA: New World Order Failures Rwandan Genocide (1994): The UN sent in )UNITED NATIONS ASSISTANCE MISSION FOR RWANDA) UNAMIR to keep the peace after a Civil War in Rwanda but soon the genocide began. The mass murder of an estimated 1 Million people in the small East African nation of Rwanda over the course of 100 days.
 Rwandan Refugee Camp
Rwandan Refugee Camp
 New World Order: Failures Rwandan Genocide (1994): (million people had been killed within a few weeks) It was the culmination of longstanding ethnic discrimination/hatred between the minority Tutsi, who had controlled power for centuries, and the majority Hutu peoples. Canadian Lieutenant General Roméo Dallaire attempted to get the UN to react and stop the genocide to no avail. http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=3 vdyeg. Ayre 4 https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=u 3 Drvrr. Sg. HI
New World Order: Failures Rwandan Genocide (1994): (million people had been killed within a few weeks) It was the culmination of longstanding ethnic discrimination/hatred between the minority Tutsi, who had controlled power for centuries, and the majority Hutu peoples. Canadian Lieutenant General Roméo Dallaire attempted to get the UN to react and stop the genocide to no avail. http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=3 vdyeg. Ayre 4 https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=u 3 Drvrr. Sg. HI
 Canada – USA Relations: War on Terror September 11, 2001: A commercial airplane crashed into the North Tower of the World Trade Centre in New York. Shortly after, a second plane hit the South Tower. Another commercial plane that hit the Pentagon, Washington, DC. A fourth plane was shot down in Somerset County, PA.
Canada – USA Relations: War on Terror September 11, 2001: A commercial airplane crashed into the North Tower of the World Trade Centre in New York. Shortly after, a second plane hit the South Tower. Another commercial plane that hit the Pentagon, Washington, DC. A fourth plane was shot down in Somerset County, PA.
 Canada – USA Relations: War on Terror These attacks became known as Terrorist Attacks of 9/11 or just 9/11. They were a series of coordinated suicide attacks by Al-Qaeda (led by Osama bin Laden) upon the United States.
Canada – USA Relations: War on Terror These attacks became known as Terrorist Attacks of 9/11 or just 9/11. They were a series of coordinated suicide attacks by Al-Qaeda (led by Osama bin Laden) upon the United States.
 Canada’s Response: War on Terror Operation Support: 1) Support passengers and crew of aircraft that was diverted to Canadian airfields; 2 increase emergency preparedness in order to respond to requests of humanitarian assistance. 3) placing CF-18 fighter jets at strategic locations throughout our country.
Canada’s Response: War on Terror Operation Support: 1) Support passengers and crew of aircraft that was diverted to Canadian airfields; 2 increase emergency preparedness in order to respond to requests of humanitarian assistance. 3) placing CF-18 fighter jets at strategic locations throughout our country.
 Canada’s Response: War on Terror Operation Apollo: Canada’s military contribution to the “war on terror; ” after 9/11, t. UN issued a resolution the reaffirmed the right of member nations defence. Support the USA’s Operation Enduring Freedom PM Jean Chretien promised air, land, and sea forces to the international campaign.
Canada’s Response: War on Terror Operation Apollo: Canada’s military contribution to the “war on terror; ” after 9/11, t. UN issued a resolution the reaffirmed the right of member nations defence. Support the USA’s Operation Enduring Freedom PM Jean Chretien promised air, land, and sea forces to the international campaign.
 War in Iraq As the fight against Al-Qaeda in Afghanistan was reaching a conclusion (Bin Laden - was shot to death on May 2, 2011 and the War in Afghanistan continues – the USA will pull out by 2014). President Bush declared that Iraq was also part of the “Axis of Evil” and that military action would also be directed toward ousting the regime of Saddam Hussein (was shot in killed by US forces on December 6, 2006).
War in Iraq As the fight against Al-Qaeda in Afghanistan was reaching a conclusion (Bin Laden - was shot to death on May 2, 2011 and the War in Afghanistan continues – the USA will pull out by 2014). President Bush declared that Iraq was also part of the “Axis of Evil” and that military action would also be directed toward ousting the regime of Saddam Hussein (was shot in killed by US forces on December 6, 2006).
 War in Iraq The War in Iraq/Iraq War began on March 20, 2003 – present…. CANADA DID NOT PARTICIPATE (no UN permission) War in Afghanistan began on October 7, 2001 – present. ○ Dec 15, 2011 last rotation of troops returns; March 31, 2014 – training mission ends.
War in Iraq The War in Iraq/Iraq War began on March 20, 2003 – present…. CANADA DID NOT PARTICIPATE (no UN permission) War in Afghanistan began on October 7, 2001 – present. ○ Dec 15, 2011 last rotation of troops returns; March 31, 2014 – training mission ends.
 CANADA: War in Iraq PM Chretien stated that Canada would join military action in Iraq if approved by the UN Security Council. By 2003 the Canadian government, France, and Germany recognized that the Bush administration would wage war with or without approval. Canada choose to provide humanitarian aid to Iraqis not military aid to the USA.
CANADA: War in Iraq PM Chretien stated that Canada would join military action in Iraq if approved by the UN Security Council. By 2003 the Canadian government, France, and Germany recognized that the Bush administration would wage war with or without approval. Canada choose to provide humanitarian aid to Iraqis not military aid to the USA.
 Canada + Afghanistan Canada's role in the Afghanistan War began in late 2001. Canada sent it's first element of Canadian soldiers secretly in October 2001 from Joint Task Force 2, and the first contingents of regular Canadian troops arrived in Afghanistan in 2002.
Canada + Afghanistan Canada's role in the Afghanistan War began in late 2001. Canada sent it's first element of Canadian soldiers secretly in October 2001 from Joint Task Force 2, and the first contingents of regular Canadian troops arrived in Afghanistan in 2002.
 Canada + Afghanistan Canada took on a larger role starting in 2006 after the Canadian troops were redeployed to Kandahar province. There were 2, 500 Canadian Forces (CF) personnel in Afghanistan in 2006, of which 1, 200 comprised the combat battle group. ○ Roughly 950 are currently deployed in Afghanistan as part of International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) = military trainers – ends March 31, 2014.
Canada + Afghanistan Canada took on a larger role starting in 2006 after the Canadian troops were redeployed to Kandahar province. There were 2, 500 Canadian Forces (CF) personnel in Afghanistan in 2006, of which 1, 200 comprised the combat battle group. ○ Roughly 950 are currently deployed in Afghanistan as part of International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) = military trainers – ends March 31, 2014.
 Canada + Afghanistan Canada withdrew the bulk of its military troops from Afghanistan in Dec. of 2011. We are no longer doing combat mission but will be helping Afghans to rebuild Afghanistan via the education of children and youth (especially for women and girls), providing healthcare, training security forces, promoting regional diplomacy, and humanitarian aid.
Canada + Afghanistan Canada withdrew the bulk of its military troops from Afghanistan in Dec. of 2011. We are no longer doing combat mission but will be helping Afghans to rebuild Afghanistan via the education of children and youth (especially for women and girls), providing healthcare, training security forces, promoting regional diplomacy, and humanitarian aid.
 What do you think of Canada’s relationship with the USA? What should change? What should remain the same?
What do you think of Canada’s relationship with the USA? What should change? What should remain the same?
 Peacekeeping (est. 1948, first mission/Suez Crisis 1956) = a technique developed by the UN: "a unique and dynamic instrument developed by the Organization as a way to help countries torn by conflict create the conditions for lasting peace. ”
Peacekeeping (est. 1948, first mission/Suez Crisis 1956) = a technique developed by the UN: "a unique and dynamic instrument developed by the Organization as a way to help countries torn by conflict create the conditions for lasting peace. ”
 Peacekeeping VS peacemaking. Peacekeepers = monitor and observe peace processes (they are not part of the conflict = observers) in post-conflict areas and assist ex-combatants in implementing the peace agreements they may have signed.
Peacekeeping VS peacemaking. Peacekeepers = monitor and observe peace processes (they are not part of the conflict = observers) in post-conflict areas and assist ex-combatants in implementing the peace agreements they may have signed.
 Canadian Troops Overseas In the second half of the 20 th Century, over 100, 000 Canadians have served as peacekeepers under the auspices of the UN. In Canada`s peacekeeping history, over 110 Canadian have been killed.
Canadian Troops Overseas In the second half of the 20 th Century, over 100, 000 Canadians have served as peacekeepers under the auspices of the UN. In Canada`s peacekeeping history, over 110 Canadian have been killed.
 Canadian Troops Overseas Canadians have served in the following recent conflicts: The Persian Gulf War, 1990 Haiti, 1990 + El Salvador, 1991 Cambodia, 1991 + Yugoslavia (Bosnia), 1992 Somalia, 1992 Rwanda, 1994 NATO bombing of Kosovo, 1995 Kosovo, 1999 Afghanistan, 2001 – 2011+ Bosnia-Herzegovina, 2004 Gaza, 2005
Canadian Troops Overseas Canadians have served in the following recent conflicts: The Persian Gulf War, 1990 Haiti, 1990 + El Salvador, 1991 Cambodia, 1991 + Yugoslavia (Bosnia), 1992 Somalia, 1992 Rwanda, 1994 NATO bombing of Kosovo, 1995 Kosovo, 1999 Afghanistan, 2001 – 2011+ Bosnia-Herzegovina, 2004 Gaza, 2005
 The Changing Role of Peacekeepers Modern Peacekeeping = Requires a diversity of skills: Work with police, governments, judges, lawyers, media, health, tax, and social policy advisors, child protection experts, infrastructure specialists and facilitator and mediators.
The Changing Role of Peacekeepers Modern Peacekeeping = Requires a diversity of skills: Work with police, governments, judges, lawyers, media, health, tax, and social policy advisors, child protection experts, infrastructure specialists and facilitator and mediators.
 The Changing Role of Peacekeepers In the past = patrolling contested borders, and unarmed monitoring of ceasefires. Modern Peacekeeping = training and restructuring local police forces, de-mining, conducting elections, facilitating the return of refugees, monitoring human rights, demobilizing and reintegrating former soldiers promoting sustainable democracy and economic development, and humanitarian intervention.
The Changing Role of Peacekeepers In the past = patrolling contested borders, and unarmed monitoring of ceasefires. Modern Peacekeeping = training and restructuring local police forces, de-mining, conducting elections, facilitating the return of refugees, monitoring human rights, demobilizing and reintegrating former soldiers promoting sustainable democracy and economic development, and humanitarian intervention.
 International Law UN International Tribunals, 1993: Set up to try persons accused of war crimes during conflict, the establishment was sparked by the massive human rights violations in the former Yugoslavia, a second tribunal was wet up to hear cases from he Rwandan genocide in 1994.
International Law UN International Tribunals, 1993: Set up to try persons accused of war crimes during conflict, the establishment was sparked by the massive human rights violations in the former Yugoslavia, a second tribunal was wet up to hear cases from he Rwandan genocide in 1994.
 International Law International Criminal Court (ICC), 1998: Became possible to punish mass violations of human rights through the establishment of the ICC, the international community made it clear that those who committed horrible acts would not go unpunished, has jurisdiction over genocides, war crimes, crimes against humanity and aggression.
International Law International Criminal Court (ICC), 1998: Became possible to punish mass violations of human rights through the establishment of the ICC, the international community made it clear that those who committed horrible acts would not go unpunished, has jurisdiction over genocides, war crimes, crimes against humanity and aggression.
 What do you think of Canada’s role as a peacekeeper? Has it been effective? Why or why not? Joe Clark: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=99 Nd. U_p 8 Dk 8
What do you think of Canada’s role as a peacekeeper? Has it been effective? Why or why not? Joe Clark: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=99 Nd. U_p 8 Dk 8
 CANADIAN RELATIONS IN MODERN TIMES: ECONOMICS AND TECHNOLOGY
CANADIAN RELATIONS IN MODERN TIMES: ECONOMICS AND TECHNOLOGY
 TRUDEAU, Canada and the World: Foreign Aid Official Development Assistance (ODA), 1969 = provided financial aid to countries in Africa, the Middle East, the Americas, Asia and some countries in Central and Eastern Europe via: Bilateral/Direct Assistance = government to government. NGOs (Non-governmental organizations). Private sector enterprises Multilateral Institutions = UN, World Bank, La Francophonie.
TRUDEAU, Canada and the World: Foreign Aid Official Development Assistance (ODA), 1969 = provided financial aid to countries in Africa, the Middle East, the Americas, Asia and some countries in Central and Eastern Europe via: Bilateral/Direct Assistance = government to government. NGOs (Non-governmental organizations). Private sector enterprises Multilateral Institutions = UN, World Bank, La Francophonie.
 Canada and the World: Foreign Aid Trudeau’s mission was to improve the economic status of poorer nations. Canadian ODA is at a 30 year low. Canada has reduced its contributions by 34% + ranked 17 th of 22 countries in regards to contributions.
Canada and the World: Foreign Aid Trudeau’s mission was to improve the economic status of poorer nations. Canadian ODA is at a 30 year low. Canada has reduced its contributions by 34% + ranked 17 th of 22 countries in regards to contributions.
 CIDA Canadian International Development Agency (CIDA), 1968. ODA is managed by CIDA, promotes sustainable development in developing countries.
CIDA Canadian International Development Agency (CIDA), 1968. ODA is managed by CIDA, promotes sustainable development in developing countries.
 CIDA Has 7 priorities: 1. Basic human needs, 2. Women in suitable development, 3. Infrastructure services, 4. Human rights, 5. Democracy and good governance, 6. Private sector development, 7. The environment. Also has expanded 4 social development sectors: 1. basic education, 2. health and nutrition, 3. HIV/AIDS, and 4. child protection.
CIDA Has 7 priorities: 1. Basic human needs, 2. Women in suitable development, 3. Infrastructure services, 4. Human rights, 5. Democracy and good governance, 6. Private sector development, 7. The environment. Also has expanded 4 social development sectors: 1. basic education, 2. health and nutrition, 3. HIV/AIDS, and 4. child protection.
 CIDA IN MODERN TIMES http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=r. Gy. Jb 9 g. ECJs http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=LYAV LFCG 6 ww http: //www. youtube. com/user/CIDAACDI ? feature=watch
CIDA IN MODERN TIMES http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=r. Gy. Jb 9 g. ECJs http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=LYAV LFCG 6 ww http: //www. youtube. com/user/CIDAACDI ? feature=watch
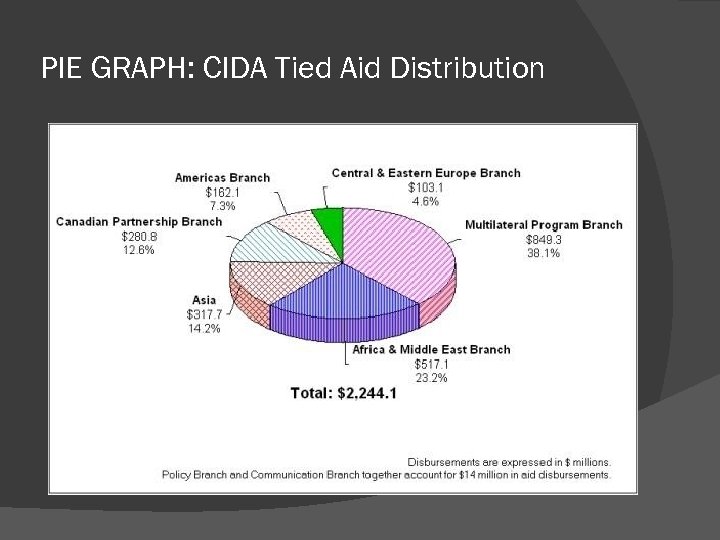 PIE GRAPH: CIDA Tied Aid Distribution
PIE GRAPH: CIDA Tied Aid Distribution
 International Aid We all have a vested interest in solving problems in the “global village. ” Those of us in the developed world have the financial resources to pay for remedies. Solutions to problems may be global or local.
International Aid We all have a vested interest in solving problems in the “global village. ” Those of us in the developed world have the financial resources to pay for remedies. Solutions to problems may be global or local.
 Multilateral Aid directed from many sources to one or more recipients is known as multilateral. Organizations like the World Bank or UNICEF frequently dispense such assistance.
Multilateral Aid directed from many sources to one or more recipients is known as multilateral. Organizations like the World Bank or UNICEF frequently dispense such assistance.
 Bilateral Aid directed from one country directly to another is known as bilateral assistance. Canada
Bilateral Aid directed from one country directly to another is known as bilateral assistance. Canada
 Tied Aid Sometimes aid is given with strings attached. Recipients may have to buy goods or support donor countries politically in return for aid.
Tied Aid Sometimes aid is given with strings attached. Recipients may have to buy goods or support donor countries politically in return for aid.
 Military Aid Much “foreign aid” is given in the form of military equipment. Donors see their equipment in action. They can also dispose of surplus goods.
Military Aid Much “foreign aid” is given in the form of military equipment. Donors see their equipment in action. They can also dispose of surplus goods.
 Grassroots Aid For development aid to work, it must get into the hands of those in need. Too often, corrupt officials skim a portion of the money. Sometimes little is left by the time aid reaches people at the lowest and neediest levels of society.
Grassroots Aid For development aid to work, it must get into the hands of those in need. Too often, corrupt officials skim a portion of the money. Sometimes little is left by the time aid reaches people at the lowest and neediest levels of society.
 Grassroots Aid II “We need to be clear; corruption is not the grease that oils the economy. Corruption undermines economic stability, deters foreign and domestic investment, and erodes support for development assistance. Above all, corruption imposes a disproportionately heavy burden on the poor. ” James D. Wofensohn President, World Bank, July, 1998.
Grassroots Aid II “We need to be clear; corruption is not the grease that oils the economy. Corruption undermines economic stability, deters foreign and domestic investment, and erodes support for development assistance. Above all, corruption imposes a disproportionately heavy burden on the poor. ” James D. Wofensohn President, World Bank, July, 1998.
 Non-Governmental Aid Independent relief agencies are often best placed to ensure the delivery of grassroots aid.
Non-Governmental Aid Independent relief agencies are often best placed to ensure the delivery of grassroots aid.
 Click for hyperlink NGO’s Doctors from around the world volunteer their professional abilities to help in developing countries.
Click for hyperlink NGO’s Doctors from around the world volunteer their professional abilities to help in developing countries.
 NGO’s Oxfam provides technical assistance to help at the grassroots level. Oxfam’s cheap and effective water bucket has been lauded as an outstanding example of British practical design. Oxfam designed, but locally made, these latrine covers markedly improve sanitation.
NGO’s Oxfam provides technical assistance to help at the grassroots level. Oxfam’s cheap and effective water bucket has been lauded as an outstanding example of British practical design. Oxfam designed, but locally made, these latrine covers markedly improve sanitation.
 NGO’s Operation Eyesight Universal Founded by Dr. Ben Gullison, in 1947, OEU sends volunteers to developing countries to perform vision-restoring procedures. Dr. Gullison & his wife
NGO’s Operation Eyesight Universal Founded by Dr. Ben Gullison, in 1947, OEU sends volunteers to developing countries to perform vision-restoring procedures. Dr. Gullison & his wife
 NGO’s Operation Eyesight Universal II Cards are sent to donors, informing them of what their specific donation has accomplished
NGO’s Operation Eyesight Universal II Cards are sent to donors, informing them of what their specific donation has accomplished
 Canada as a Middle Power Canada joined La Francophonie, an organization of French speaking countries, many former colonies of France. Canada also participated in the Colombo Plan, a plan to assist developing countries. Canada invited overseas students to study in Canada and sent experts overseas to give technical assistance.
Canada as a Middle Power Canada joined La Francophonie, an organization of French speaking countries, many former colonies of France. Canada also participated in the Colombo Plan, a plan to assist developing countries. Canada invited overseas students to study in Canada and sent experts overseas to give technical assistance.
 1980 S Brian Mulroney PM of Canada 1984 -1993: Much closer relationship to USA (friends with President Reagan) Introduced major economic reforms such as the Canada. U. S. Free Trade Agreement = FTA = a trade agreement signed by Canada and the United States on October 4, 1988 to eliminate barriers to trade in goods + services and encourage fair competition.
1980 S Brian Mulroney PM of Canada 1984 -1993: Much closer relationship to USA (friends with President Reagan) Introduced major economic reforms such as the Canada. U. S. Free Trade Agreement = FTA = a trade agreement signed by Canada and the United States on October 4, 1988 to eliminate barriers to trade in goods + services and encourage fair competition.
 Brian Mulroney PM of Canada 1984 -1993: NAFTA + North American Free Trade Agreement. Is an agreement signed by the governments of Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994.
Brian Mulroney PM of Canada 1984 -1993: NAFTA + North American Free Trade Agreement. Is an agreement signed by the governments of Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994.


 1990 S: A New Era of Globalization The 1990’s saw Canada actively try to expand its trade initiatives. Canada eagerly organized “Team Canada”, a trade mission to Asia and Latin America to secure deals for investment and exports. Canada has signed free trade deals with Chile and Israel.
1990 S: A New Era of Globalization The 1990’s saw Canada actively try to expand its trade initiatives. Canada eagerly organized “Team Canada”, a trade mission to Asia and Latin America to secure deals for investment and exports. Canada has signed free trade deals with Chile and Israel.
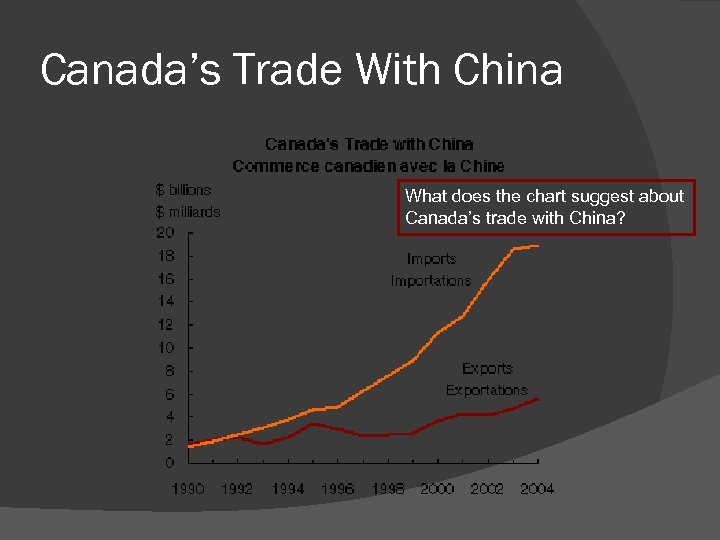 Canada’s Trade With China What does the chart suggest about Canada’s trade with China?
Canada’s Trade With China What does the chart suggest about Canada’s trade with China?
 A New Era of Globalization APEC, the Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation Group, to promote freer trade among Pacific countries. Canada has embraced the process by which regions and countries of the world are becoming interconnected
A New Era of Globalization APEC, the Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation Group, to promote freer trade among Pacific countries. Canada has embraced the process by which regions and countries of the world are becoming interconnected
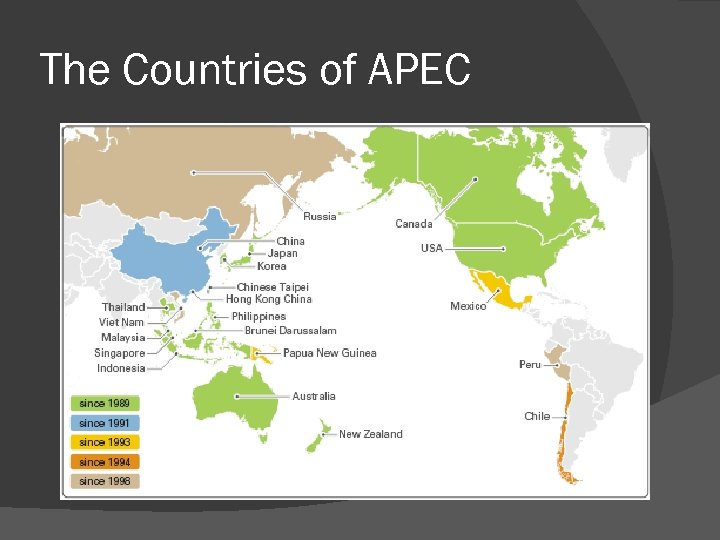 The Countries of APEC
The Countries of APEC
 A New Era of Globalization Proponents of globalization raise living standards for everyone, large corporations will invest in less industrialized countries, and jobs will be created for more people. Opponents of globalization It’s too optimistic, Canadian economy will suffer from failed initiatives, global economy is unstable, workers will lose jobs as corporations will relocated to countries with cheaper labour. other cultures are at risk from the domination of the ways and cultures of Western countries.
A New Era of Globalization Proponents of globalization raise living standards for everyone, large corporations will invest in less industrialized countries, and jobs will be created for more people. Opponents of globalization It’s too optimistic, Canadian economy will suffer from failed initiatives, global economy is unstable, workers will lose jobs as corporations will relocated to countries with cheaper labour. other cultures are at risk from the domination of the ways and cultures of Western countries.
 Globalization as the Americans See It
Globalization as the Americans See It
 A New Era of Globalization To Canada’s credit, it has insisted upon a commitment to human rights packages in countries with which it has made trade deals.
A New Era of Globalization To Canada’s credit, it has insisted upon a commitment to human rights packages in countries with which it has made trade deals.
 SPAR Aerospace Canadarm § Spar Arrowspace: developed the Canadarm for the U. S, space missions.
SPAR Aerospace Canadarm § Spar Arrowspace: developed the Canadarm for the U. S, space missions.
 CANDU Reactor The CANDU (short for CANada Deuterium Uranium) reactor is a Canadian-invented, pressurized heavy water reactor. All power reactors built in Canada are of the CANDU type.
CANDU Reactor The CANDU (short for CANada Deuterium Uranium) reactor is a Canadian-invented, pressurized heavy water reactor. All power reactors built in Canada are of the CANDU type.
 Alouette 1 With the launch of Alouette 1 in September 1962 Canada Canadian Space Agency (CSA) became third country to put a man-made satellite into space.
Alouette 1 With the launch of Alouette 1 in September 1962 Canada Canadian Space Agency (CSA) became third country to put a man-made satellite into space.
 CANADIAN RELATIONS IN MODERN TIMES: ENVIRONMENT
CANADIAN RELATIONS IN MODERN TIMES: ENVIRONMENT
 Canada – USA Relations: Resources - FISH The treaty was successful for 12 years, but in 1997 negotiators were unable to agree on quotas that satisfied all parties = each side was free to set their own limits. American fishing boats were seized an Alaskan ferry was blockaded.
Canada – USA Relations: Resources - FISH The treaty was successful for 12 years, but in 1997 negotiators were unable to agree on quotas that satisfied all parties = each side was free to set their own limits. American fishing boats were seized an Alaskan ferry was blockaded.
 Pacific Salmon Treaty Resolution, June 1999: Canada and the USA signed a new Ottawa, the US government, the states of Washington, Alaska and Oregon, along with representative from 24 Native tribes. BC was absent from the negotiations.
Pacific Salmon Treaty Resolution, June 1999: Canada and the USA signed a new Ottawa, the US government, the states of Washington, Alaska and Oregon, along with representative from 24 Native tribes. BC was absent from the negotiations.
 Salmon Treaty Problem: salmon stocks are in danger people are scared they will go the way of the cod fishery on the East Coast.
Salmon Treaty Problem: salmon stocks are in danger people are scared they will go the way of the cod fishery on the East Coast.
 Canada – USA Relations: Environment 1992 Earth Summit (Rio) got the ball rolling The Kyoto Protocol, 1997/2005: An international agreement linked to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
Canada – USA Relations: Environment 1992 Earth Summit (Rio) got the ball rolling The Kyoto Protocol, 1997/2005: An international agreement linked to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
 Canada – USA Relations: Environment The major feature of the Kyoto Protocol is that it sets binding targets for 37 industrialized countries and the European community for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that cause global warming. Countries use carbon credits (could buy and sell) to reduce emissions.
Canada – USA Relations: Environment The major feature of the Kyoto Protocol is that it sets binding targets for 37 industrialized countries and the European community for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that cause global warming. Countries use carbon credits (could buy and sell) to reduce emissions.
 TAKING ACTION 1992 EARTH SUMMIT – BRAZIL Leaders could not agree on solutions to GHG concentrations. Led to Kyoto. KYOTO 1997 Set average GHG emission targets of 5% of 1990 levels by 2012 (Canada = 6%) USA did not sign. Canada has not met these goals. - Provinces not on board - Harper set his own goals but continues to have worst record of G 8 Nations. FAILURE? ? ? BALI ROAD MAP 2007 New timeline & goals set out. Each country to take “Nationally Appropriate Steps. ” STRONG ENOUGH? ? ? COPENHAGEN 2009 Again tried to finalize an agreement. Developing Nations (China / India) felt Developed nations shouldn’t prevent their progress!!! India trying to increase SOL Obama offered $30 Billion to developing nations to lower emissions Other nations felt unfair & did not pass
TAKING ACTION 1992 EARTH SUMMIT – BRAZIL Leaders could not agree on solutions to GHG concentrations. Led to Kyoto. KYOTO 1997 Set average GHG emission targets of 5% of 1990 levels by 2012 (Canada = 6%) USA did not sign. Canada has not met these goals. - Provinces not on board - Harper set his own goals but continues to have worst record of G 8 Nations. FAILURE? ? ? BALI ROAD MAP 2007 New timeline & goals set out. Each country to take “Nationally Appropriate Steps. ” STRONG ENOUGH? ? ? COPENHAGEN 2009 Again tried to finalize an agreement. Developing Nations (China / India) felt Developed nations shouldn’t prevent their progress!!! India trying to increase SOL Obama offered $30 Billion to developing nations to lower emissions Other nations felt unfair & did not pass
 Kyoto: Success + Failure The Kyoto Protocol was adopted in Kyoto, Japan, on 11 December 1997 and entered into force on 16 February 2005.
Kyoto: Success + Failure The Kyoto Protocol was adopted in Kyoto, Japan, on 11 December 1997 and entered into force on 16 February 2005.
 Kyoto: Success + Failure USA withdrew support for the Protocol – never signed. Little action has been taken by Canada to reduce emissions – FAIL! national self interest Canada refused to re-sign the Kyoto Protocol in 2012! FAIL!
Kyoto: Success + Failure USA withdrew support for the Protocol – never signed. Little action has been taken by Canada to reduce emissions – FAIL! national self interest Canada refused to re-sign the Kyoto Protocol in 2012! FAIL!
 BALI ROAD MAP 2007: 189 nations to replace Kyoto by 2012 Harper against previous admins and didn’t join UN POV. (Canada highest of growth emissions)
BALI ROAD MAP 2007: 189 nations to replace Kyoto by 2012 Harper against previous admins and didn’t join UN POV. (Canada highest of growth emissions)
 COPENHAGEN 2009 Copenhagen 2009: Met again in that split between developing vs developed. Accused the developed of denying progress Obama election in 2008 (more pro environment) impacted Canada as Harper agreed that USA and Canada should have similar policies that reveal the ‘close integration of our economies and geographic proximity’ Promised 30 billion for developing over 3 years (small nations still no happy as no say)
COPENHAGEN 2009 Copenhagen 2009: Met again in that split between developing vs developed. Accused the developed of denying progress Obama election in 2008 (more pro environment) impacted Canada as Harper agreed that USA and Canada should have similar policies that reveal the ‘close integration of our economies and geographic proximity’ Promised 30 billion for developing over 3 years (small nations still no happy as no say)


