54934e1f65c40dad724a6d70f6420c5e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Case Study Integrated Metadata Driven Statistical Data Management System (IMD SDMS) CSB of Latvia Julija. Drozdova@csb. gov. lv METIS 2010 1
Case Study Integrated Metadata Driven Statistical Data Management System (IMD SDMS) CSB of Latvia Julija. Drozdova@csb. gov. lv METIS 2010 1
 Outline • • The main steps for IMD SDMS creation IMD SDMS fundamental elements Costs & benefits IMD SDMS implementation strategy GSBPM versus SBPM of CSB Current situation and further developments The main lessons learned Proposal for GSBPM 2
Outline • • The main steps for IMD SDMS creation IMD SDMS fundamental elements Costs & benefits IMD SDMS implementation strategy GSBPM versus SBPM of CSB Current situation and further developments The main lessons learned Proposal for GSBPM 2
 The main steps for IMD SDMS creation (1) • Data and metadata collection (1999) • Thoughtful analysis of data and metadata flows (1999) • To set the requirements to the system (19971999) 3
The main steps for IMD SDMS creation (1) • Data and metadata collection (1999) • Thoughtful analysis of data and metadata flows (1999) • To set the requirements to the system (19971999) 3
 The main steps for IMD SDMS creation (2) the main requirements to IMD SDMS were: • covers full cycle of statistical data processing; • uses process oriented approach; • IMD SDMS must be: - standardized; - integrated; - meta data-driven; - allows automated generation of user application forms (incl. web); - centralized; - has a modular structure; - transparent; 4
The main steps for IMD SDMS creation (2) the main requirements to IMD SDMS were: • covers full cycle of statistical data processing; • uses process oriented approach; • IMD SDMS must be: - standardized; - integrated; - meta data-driven; - allows automated generation of user application forms (incl. web); - centralized; - has a modular structure; - transparent; 4
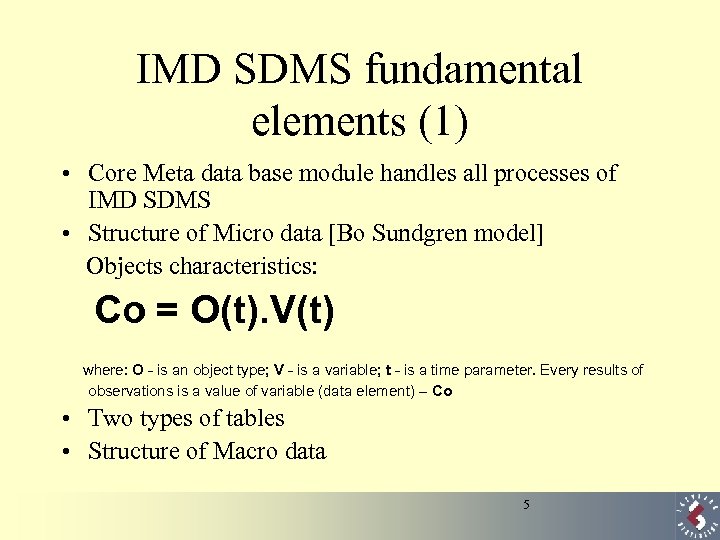 IMD SDMS fundamental elements (1) • Core Meta data base module handles all processes of IMD SDMS • Structure of Micro data [Bo Sundgren model] Objects characteristics: Co = O(t). V(t) where: O - is an object type; V - is a variable; t - is a time parameter. Every results of observations is a value of variable (data element) – Co • Two types of tables • Structure of Macro data 5
IMD SDMS fundamental elements (1) • Core Meta data base module handles all processes of IMD SDMS • Structure of Micro data [Bo Sundgren model] Objects characteristics: Co = O(t). V(t) where: O - is an object type; V - is a variable; t - is a time parameter. Every results of observations is a value of variable (data element) – Co • Two types of tables • Structure of Macro data 5
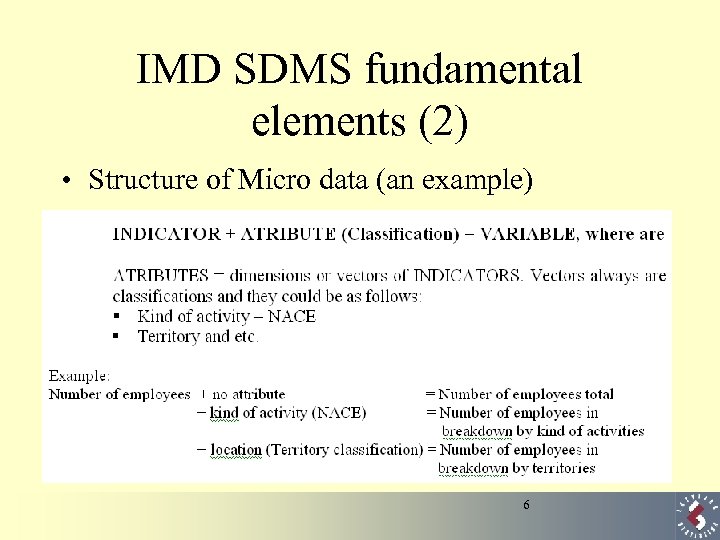 IMD SDMS fundamental elements (2) • Structure of Micro data (an example) 6
IMD SDMS fundamental elements (2) • Structure of Micro data (an example) 6
 IMD SDMS fundamental elements (3) • Two types of tables: - fixed table (data matrix); - open table (data matrix with various number of rows or columns); Questionnaire consists of chapters and chapters consist of tables. 7
IMD SDMS fundamental elements (3) • Two types of tables: - fixed table (data matrix); - open table (data matrix with various number of rows or columns); Questionnaire consists of chapters and chapters consist of tables. 7
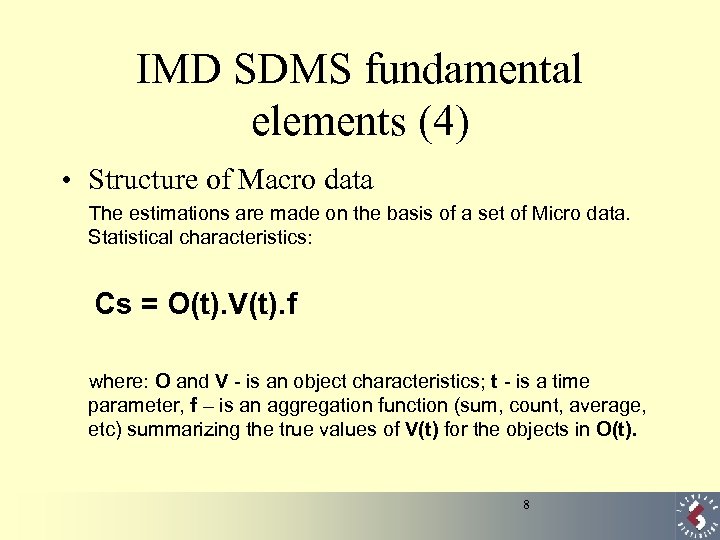 IMD SDMS fundamental elements (4) • Structure of Macro data The estimations are made on the basis of a set of Micro data. Statistical characteristics: Cs = O(t). V(t). f where: O and V - is an object characteristics; t - is a time parameter, f – is an aggregation function (sum, count, average, etc) summarizing the true values of V(t) for the objects in O(t). 8
IMD SDMS fundamental elements (4) • Structure of Macro data The estimations are made on the basis of a set of Micro data. Statistical characteristics: Cs = O(t). V(t). f where: O and V - is an object characteristics; t - is a time parameter, f – is an aggregation function (sum, count, average, etc) summarizing the true values of V(t) for the objects in O(t). 8
 Costs & benefits • Standardization of statistical data production processes • The basis for the CSB regional restructuring (2003 -2004): 5 Data Collection and processing centres replaced previously existing 26 Statistical Regional offices and city Riga office; • Decreasing of statisticians from 180 to 115 9
Costs & benefits • Standardization of statistical data production processes • The basis for the CSB regional restructuring (2003 -2004): 5 Data Collection and processing centres replaced previously existing 26 Statistical Regional offices and city Riga office; • Decreasing of statisticians from 180 to 115 9
 IMD SDMS implementation strategy (1) • Step-wise approach • 1997 – 1999 CSB and Pricewaterhouse. Coopers experts were prepared General Technical Requirements for the project “Modernisation of CSB – Data Management System” 10
IMD SDMS implementation strategy (1) • Step-wise approach • 1997 – 1999 CSB and Pricewaterhouse. Coopers experts were prepared General Technical Requirements for the project “Modernisation of CSB – Data Management System” 10
 IMD SDMS implementation strategy (2) • The main requirement: Meta data should be used as the key element in statistical data processing • Additional requirements: - Increase efficiency of the production of statistical information; - Avoid hard code programming via standardisation of procedures and use of Meta data within the statistical data processing; - Increase the quality of the information produced; - Improve processes of statistical data analysis; - Modernise and increase the quality of data dissemination; 11
IMD SDMS implementation strategy (2) • The main requirement: Meta data should be used as the key element in statistical data processing • Additional requirements: - Increase efficiency of the production of statistical information; - Avoid hard code programming via standardisation of procedures and use of Meta data within the statistical data processing; - Increase the quality of the information produced; - Improve processes of statistical data analysis; - Modernise and increase the quality of data dissemination; 11
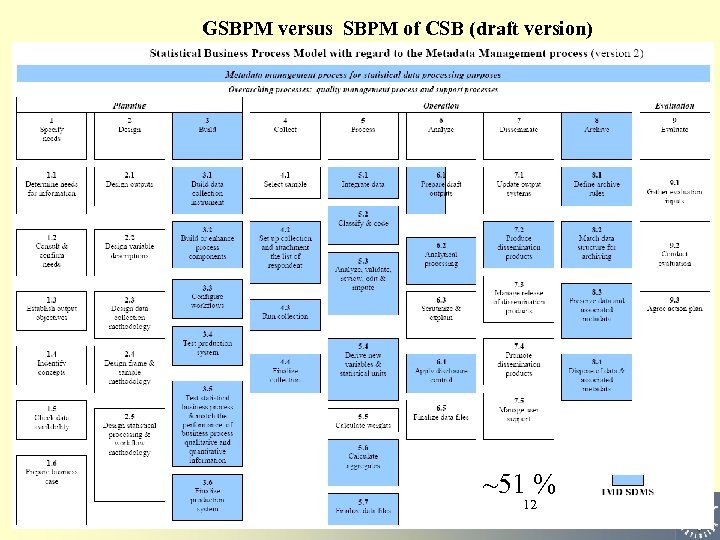 GSBPM versus SBPM of CSB (draft version) GSBPM versus SBPM of CSB ~51 % 12
GSBPM versus SBPM of CSB (draft version) GSBPM versus SBPM of CSB ~51 % 12
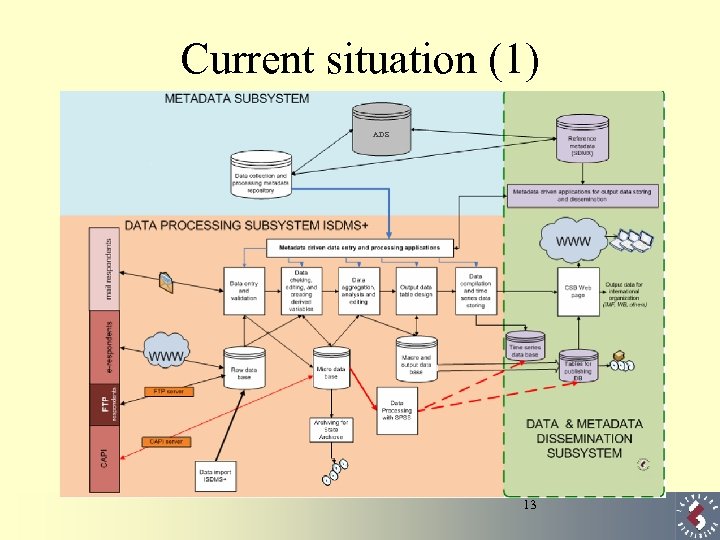 Current situation (1) ADS 13
Current situation (1) ADS 13
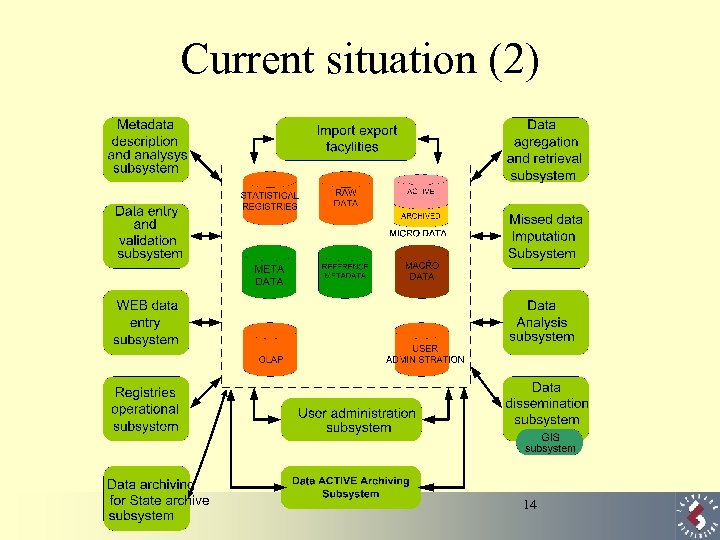 Current situation (2) 14
Current situation (2) 14
 Further developments • Since 2009 a project has been launched for the IMD SDMS to cover Social statistics domain. Starting from: - Population Census; - Agricultural Census; - Labour Force Survey; - EU-SILC … 15
Further developments • Since 2009 a project has been launched for the IMD SDMS to cover Social statistics domain. Starting from: - Population Census; - Agricultural Census; - Labour Force Survey; - EU-SILC … 15
 The main lessons learned (1) • Design of the new information system should be based on the results of deep analysis of statistical surveys: - statistical questionnaires and variables; - statistical processes and data flows; • Statistical data processes and “Variables and questionnaires system” must be harmonized and standardized before creation of the new system; 16
The main lessons learned (1) • Design of the new information system should be based on the results of deep analysis of statistical surveys: - statistical questionnaires and variables; - statistical processes and data flows; • Statistical data processes and “Variables and questionnaires system” must be harmonized and standardized before creation of the new system; 16
 The main lessons learned (2) • The system should provide a full cycle of statistical data processing; • The system should be: - standardized; - integrated; - meta data-driven; - allows automated generation of user application forms (incl. web); - centralized; - has a modular structure; - transparent; 17
The main lessons learned (2) • The system should provide a full cycle of statistical data processing; • The system should be: - standardized; - integrated; - meta data-driven; - allows automated generation of user application forms (incl. web); - centralized; - has a modular structure; - transparent; 17
 The main lessons learned (3) • Motivation of the statisticians to move (from stove-pipe to process oriented) to the new data processing environment is essential; • To establish Metadata group; • Data electronic archiving reduces human resources, expenses of CSB for deposition in the State Archives, time of archiving and physical amount of archiving information (In 2000, Population Census - 21 m 3 = 4 DVD) 18
The main lessons learned (3) • Motivation of the statisticians to move (from stove-pipe to process oriented) to the new data processing environment is essential; • To establish Metadata group; • Data electronic archiving reduces human resources, expenses of CSB for deposition in the State Archives, time of archiving and physical amount of archiving information (In 2000, Population Census - 21 m 3 = 4 DVD) 18
 Proposal for GSBPM (1) • Extension of phase 4 – Collect, between subprocesses 4. 1 and 4. 2 • Extension, between sub-processes 4. 3 and 4. 4 Why ? : - statistician’s work with respondents and with the list of respondents is a very difficult, heavy process and time consuming process (…; sending of letters to respondents; conduction of the respondents lists; creation of the sample Matrix; clarifications; response control; reminding process; …); - sometimes statistician’s work is pressed for time (…Business tendencies survey…) 19
Proposal for GSBPM (1) • Extension of phase 4 – Collect, between subprocesses 4. 1 and 4. 2 • Extension, between sub-processes 4. 3 and 4. 4 Why ? : - statistician’s work with respondents and with the list of respondents is a very difficult, heavy process and time consuming process (…; sending of letters to respondents; conduction of the respondents lists; creation of the sample Matrix; clarifications; response control; reminding process; …); - sometimes statistician’s work is pressed for time (…Business tendencies survey…) 19
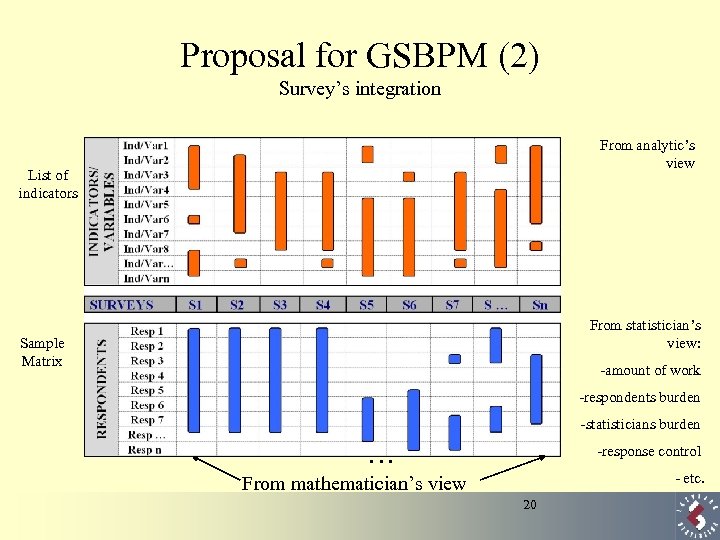 Proposal for GSBPM (2) Survey’s integration From analytic’s view List of indicators From statistician’s view: Sample Matrix -amount of work -respondents burden -statisticians burden … -response control - etc. From mathematician’s view 20
Proposal for GSBPM (2) Survey’s integration From analytic’s view List of indicators From statistician’s view: Sample Matrix -amount of work -respondents burden -statisticians burden … -response control - etc. From mathematician’s view 20


