 Case study
Case study
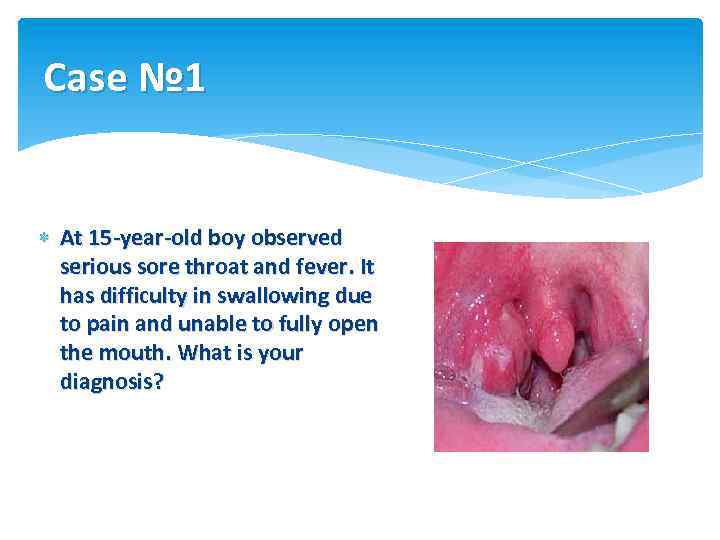 Case № 1 At 15 -year-old boy observed serious sore throat and fever. It has difficulty in swallowing due to pain and unable to fully open the mouth. What is your diagnosis?
Case № 1 At 15 -year-old boy observed serious sore throat and fever. It has difficulty in swallowing due to pain and unable to fully open the mouth. What is your diagnosis?
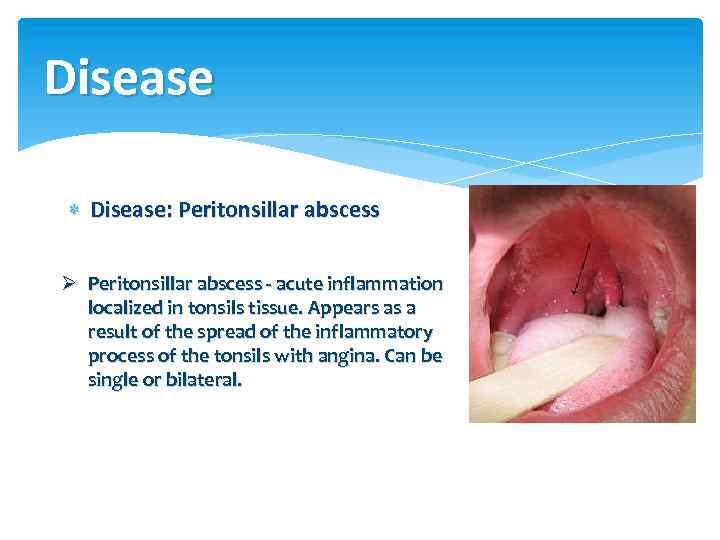 Disease Disease: Peritonsillar abscess Ø Peritonsillar abscess - acute inflammation localized in tonsils tissue. Appears as a result of the spread of the inflammatory process of the tonsils with angina. Can be single or bilateral.
Disease Disease: Peritonsillar abscess Ø Peritonsillar abscess - acute inflammation localized in tonsils tissue. Appears as a result of the spread of the inflammatory process of the tonsils with angina. Can be single or bilateral.
 Classification posterior inferior anterior external • localized between the amygdala and the palatopharyngeal bow, sometimes in the most bow • localized at the lower pole of the tonsils • localized between the upper pole of the tonsil and palato-lingual bow • localized outside of the tonsils. Occurs most rarely
Classification posterior inferior anterior external • localized between the amygdala and the palatopharyngeal bow, sometimes in the most bow • localized at the lower pole of the tonsils • localized between the upper pole of the tonsil and palato-lingual bow • localized outside of the tonsils. Occurs most rarely
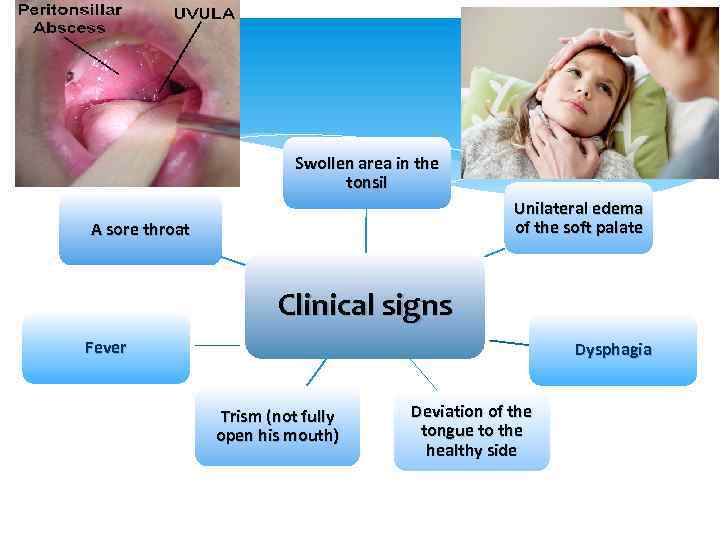 Swollen area in the tonsil Unilateral edema of the soft palate A sore throat Clinical signs Fever Dysphagia Trism (not fully open his mouth) Deviation of the tongue to the healthy side
Swollen area in the tonsil Unilateral edema of the soft palate A sore throat Clinical signs Fever Dysphagia Trism (not fully open his mouth) Deviation of the tongue to the healthy side
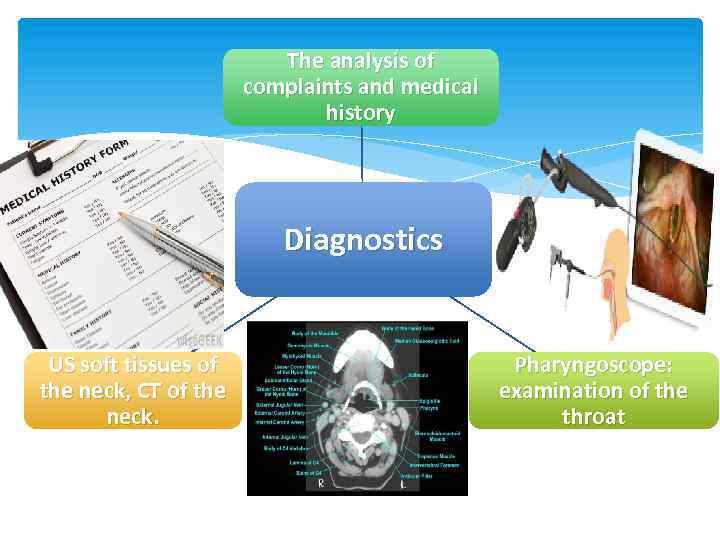 The analysis of complaints and medical history Diagnostics US soft tissues of the neck, CT of the neck. Pharyngoscope: examination of the throat
The analysis of complaints and medical history Diagnostics US soft tissues of the neck, CT of the neck. Pharyngoscope: examination of the throat
 Treatment: Penicillin or clindamycin Incision and drainage of an abscess, if the patient does not respond to therapy in the first 12 to 24 hours Giving oral antibiotics immediately at a fever for 24 hours and dysphagia improved
Treatment: Penicillin or clindamycin Incision and drainage of an abscess, if the patient does not respond to therapy in the first 12 to 24 hours Giving oral antibiotics immediately at a fever for 24 hours and dysphagia improved
 Prognosis: q Good q Recurrent peritonsillar abscesses are rare q Treatment with IV antibiotics generations can often prevent suppuration
Prognosis: q Good q Recurrent peritonsillar abscesses are rare q Treatment with IV antibiotics generations can often prevent suppuration
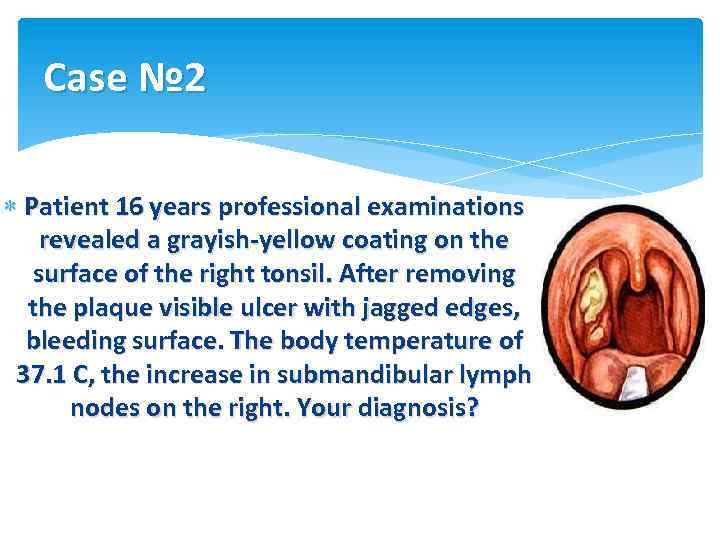 Case № 2 Patient 16 years professional examinations revealed a grayish-yellow coating on the surface of the right tonsil. After removing the plaque visible ulcer with jagged edges, bleeding surface. The body temperature of 37. 1 C, the increase in submandibular lymph nodes on the right. Your diagnosis?
Case № 2 Patient 16 years professional examinations revealed a grayish-yellow coating on the surface of the right tonsil. After removing the plaque visible ulcer with jagged edges, bleeding surface. The body temperature of 37. 1 C, the increase in submandibular lymph nodes on the right. Your diagnosis?
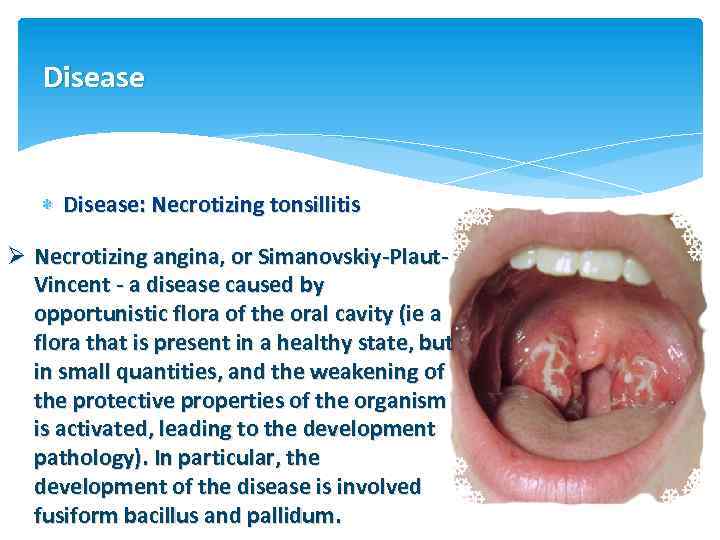 Disease Disease: Necrotizing tonsillitis Ø Necrotizing angina, or Simanovskiy-Plaut. Vincent - a disease caused by opportunistic flora of the oral cavity (ie a flora that is present in a healthy state, but in small quantities, and the weakening of the protective properties of the organism is activated, leading to the development pathology). In particular, the development of the disease is involved fusiform bacillus and pallidum.
Disease Disease: Necrotizing tonsillitis Ø Necrotizing angina, or Simanovskiy-Plaut. Vincent - a disease caused by opportunistic flora of the oral cavity (ie a flora that is present in a healthy state, but in small quantities, and the weakening of the protective properties of the organism is activated, leading to the development pathology). In particular, the development of the disease is involved fusiform bacillus and pallidum.
 Clinical signs and symptoms Awkwardness when swallowing Pain syndrome The body temperature often remains normal Pathological process involves only one side Visualized film whitish-yellowish-gray
Clinical signs and symptoms Awkwardness when swallowing Pain syndrome The body temperature often remains normal Pathological process involves only one side Visualized film whitish-yellowish-gray
 Differential diagnosis : Diphtheria throat Tonsil tumor Syphilis, tuberculosis
Differential diagnosis : Diphtheria throat Tonsil tumor Syphilis, tuberculosis
 What research is needed to confirm the diagnosis? v. Detection at the smear microscopy spindle rods and spirochetes buccal; v. When pharyngoscope on the free surface of the tonsils visible film of gray or yellowishwhite, like a spot of stearic candles, round, soft consistency, sometimes extending to the front shackle
What research is needed to confirm the diagnosis? v. Detection at the smear microscopy spindle rods and spirochetes buccal; v. When pharyngoscope on the free surface of the tonsils visible film of gray or yellowishwhite, like a spot of stearic candles, round, soft consistency, sometimes extending to the front shackle
 Treatment: • Light diet • Rinsing the throat bismuth-containing mixtures garamitsinom, calendula, a wide range of physiotherapy, parenteral preparations of bismuth • Prescribe antibiotic therapy and bracing
Treatment: • Light diet • Rinsing the throat bismuth-containing mixtures garamitsinom, calendula, a wide range of physiotherapy, parenteral preparations of bismuth • Prescribe antibiotic therapy and bracing
 Case № 3 Children 5 years of bad breath nose, often suffer from respiratory diseases, several times suffered angina, sleeps poorly, cries in his sleep, says bedwetting. Determined: pale skin, half-open mouth. When viewed from flatness of nasolabial folds. Your diagnosis?
Case № 3 Children 5 years of bad breath nose, often suffer from respiratory diseases, several times suffered angina, sleeps poorly, cries in his sleep, says bedwetting. Determined: pale skin, half-open mouth. When viewed from flatness of nasolabial folds. Your diagnosis?
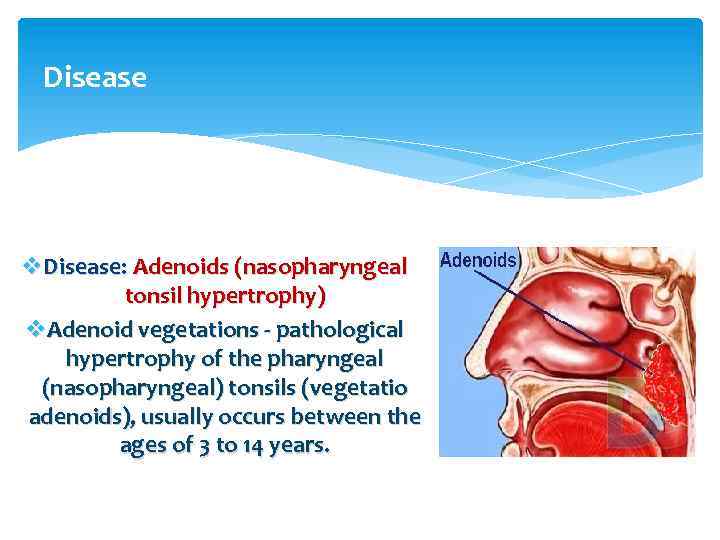 Disease v. Disease: Adenoids (nasopharyngeal tonsil hypertrophy) v. Adenoid vegetations - pathological hypertrophy of the pharyngeal (nasopharyngeal) tonsils (vegetatio adenoids), usually occurs between the ages of 3 to 14 years.
Disease v. Disease: Adenoids (nasopharyngeal tonsil hypertrophy) v. Adenoid vegetations - pathological hypertrophy of the pharyngeal (nasopharyngeal) tonsils (vegetatio adenoids), usually occurs between the ages of 3 to 14 years.
 There are three degrees of hypertrophy of nasopharyngeal tonsil I degree - adenoids cover 1/3 opener II degree - hypertrophic tonsils closed 2/3 opener III degree - choanae closed completely
There are three degrees of hypertrophy of nasopharyngeal tonsil I degree - adenoids cover 1/3 opener II degree - hypertrophic tonsils closed 2/3 opener III degree - choanae closed completely
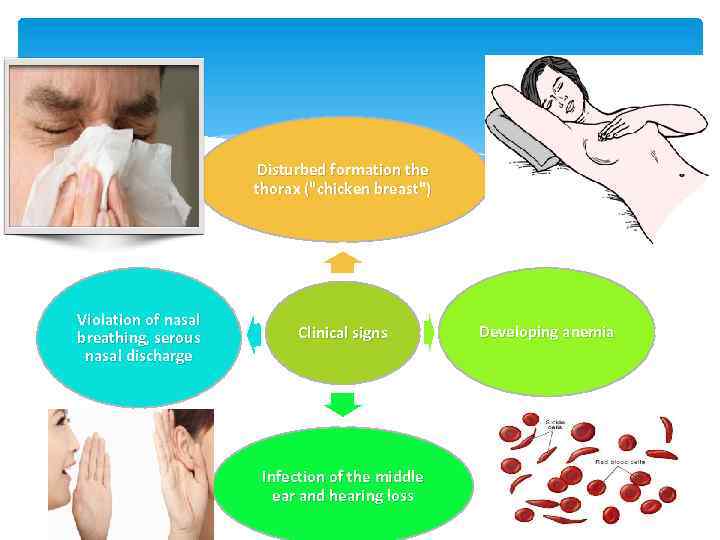 Disturbed formation the thorax ("chicken breast") Violation of nasal breathing, serous nasal discharge Clinical signs Infection of the middle ear and hearing loss Developing anemia
Disturbed formation the thorax ("chicken breast") Violation of nasal breathing, serous nasal discharge Clinical signs Infection of the middle ear and hearing loss Developing anemia
 Differential diagnosis : Angiofibroma of the nasopharynx Encephalocele Antrohoanalnym polyp
Differential diagnosis : Angiofibroma of the nasopharynx Encephalocele Antrohoanalnym polyp
 Treatment: v. Surgical treatment - adenotomy The operation is performed annular knife - adenotomy Beckman applicative under anesthesia. Spatula pressed tongue to the bottom of the mouth, adenotom introduced into the nasopharynx to the middle line and move up to the dome of the nasopharynx at the back edge of the opener. When pressing the dome adenotomy nasopharynx and adenoid tissue opener enters the ring tool. After this short and quick movement knife adenotomy shifted downwards on the back of the nose and throat, while adenoids are cut off at the base and released into the oral cavity or left hanging on a thin strip of tissue from which they were removed with forceps.
Treatment: v. Surgical treatment - adenotomy The operation is performed annular knife - adenotomy Beckman applicative under anesthesia. Spatula pressed tongue to the bottom of the mouth, adenotom introduced into the nasopharynx to the middle line and move up to the dome of the nasopharynx at the back edge of the opener. When pressing the dome adenotomy nasopharynx and adenoid tissue opener enters the ring tool. After this short and quick movement knife adenotomy shifted downwards on the back of the nose and throat, while adenoids are cut off at the base and released into the oral cavity or left hanging on a thin strip of tissue from which they were removed with forceps.



