2007.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 18

Case-based learning on theme: “Certain types of acute purulent diseases”

Plan of lesson Test to determine the initial level of student’s knowledge (individually) Test to determine the initial level of student’s knowledge (in group) Discuss about clinical case Give whole answer about diagnosis & treatment of patient Test based on clinical case Pass practical skills Conclusions of less 0 n Feed back

History of Case-based learning (CBL&PBL) was first implemented at Mc. Master University in Hamilton, Canada, in the late 1960 s. It can also be argued that CBL(PBL) is the formalisation of a process that has underpinned clinical teaching for many years.
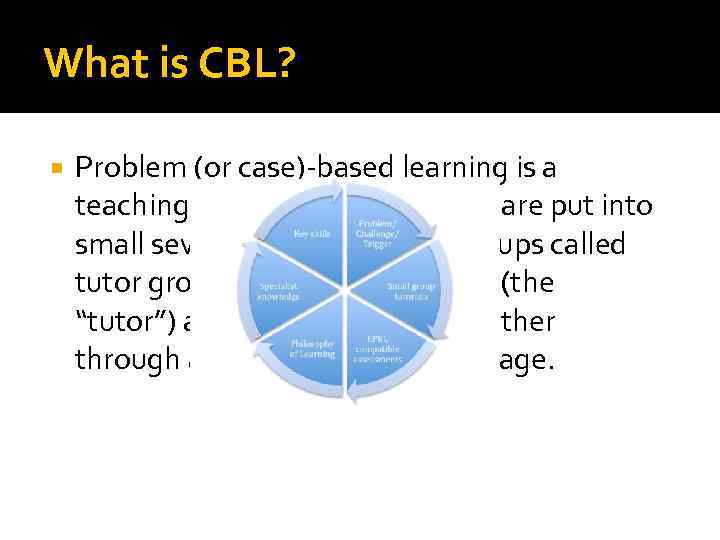
What is CBL? Problem (or case)-based learning is a teaching style in which students are put into small seven-to-eight-person groups called tutor groups with one instructor (the “tutor”) and work their way together through a clinical case page by page.
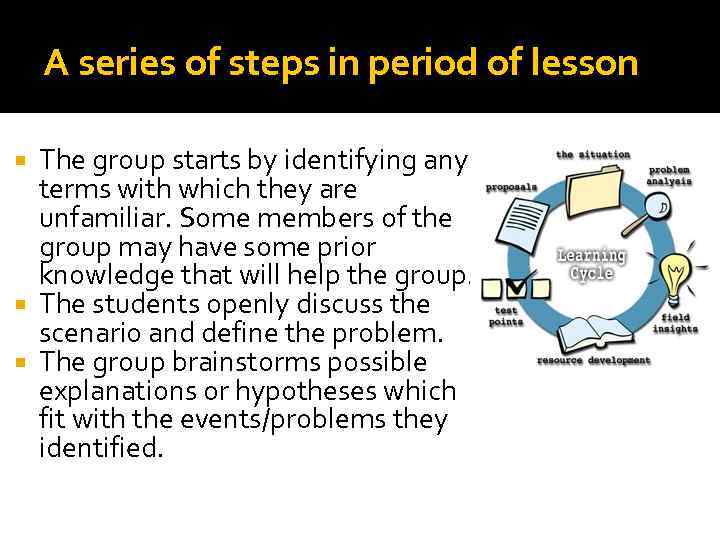
A series of steps in period of lesson The group starts by identifying any terms with which they are unfamiliar. Some members of the group may have some prior knowledge that will help the group. The students openly discuss the scenario and define the problem. The group brainstorms possible explanations or hypotheses which fit with the events/problems they identified.

Some provisional explanations/conclusions are reached that would reasonably explain the essence of the case. The students formulate their learning objectives – those aspects which the group have determined need further study. Working independently (or in pairs) the students use the resources available to them to achieve the learning objectives. The group meets again a few days later to pool the information they have gained from private study and discuss the case in the light of this new knowledge.

First part of lesson begins on test to determine the initial level of student’s knowledge (individually) Time: 10 min.

Second part of lesson begins on test to determine the initial level of student’s knowledge (in group) Time: 10 min.

Clinical case The woman with the sick child of 8 has addressed in emergency aid. Child had high temperature, an indisposition and painful consolidation on a back surface of the neck, similar on waist and a hip. At survey on a surface of infiltrate purulent-nekrotic pustule was revealed.
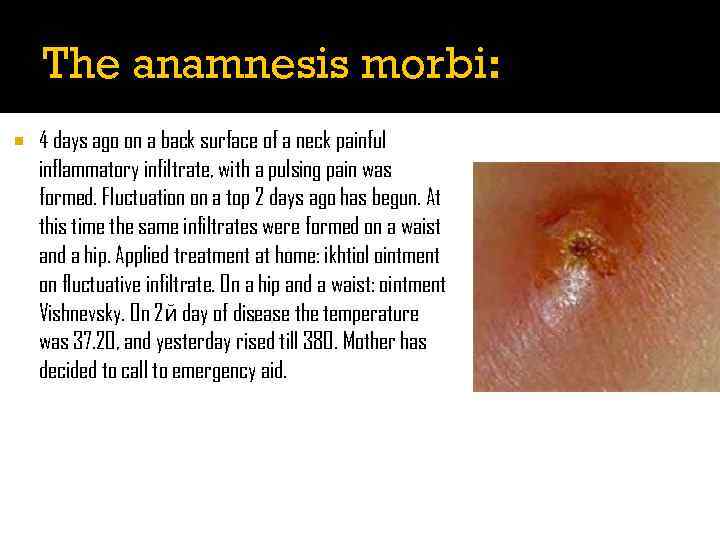
The anamnesis morbi: 4 days ago on a back surface of a neck painful inflammatory infiltrate, with a pulsing pain was formed. Fluctuation on a top 2 days ago has begun. At this time the same infiltrates were formed on a waist and a hip. Applied treatment at home: ikhtiol ointment on fluctuative infiltrate. On a hip and a waist: ointment Vishnevsky. On 2 й day of disease the temperature was 37. 20, and yesterday rised till 380. Mother has decided to call to emergency aid.

The anamnesis vitae: From childbirth passed by natural way, length at a birth 55 sm, weight 3, 5 kg. Child suffers a food allergy on sweet and a citrus since a birth. And he often caught a cold. The heredity is not burdened. Mother works as the bookkeeper in a private firm. The father works as the chief of credit department in bank.
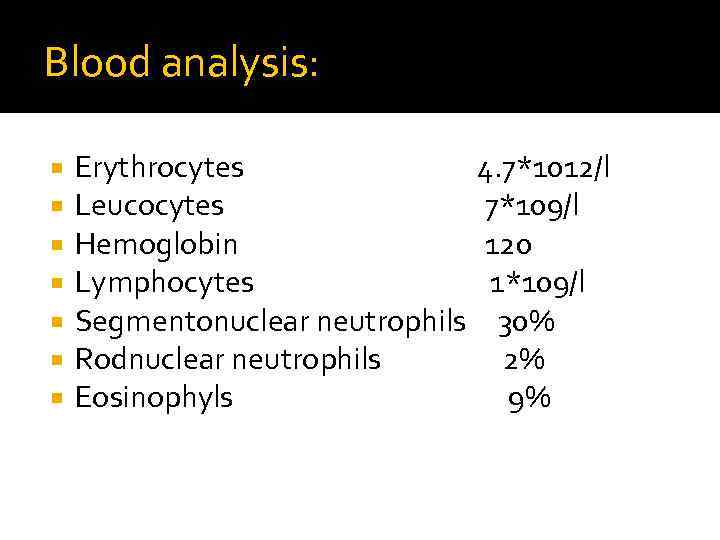
Blood analysis: Erythrocytes Leucocytes Hemoglobin Lymphocytes Segmentonuclear neutrophils Rodnuclear neutrophils Eosinophyls 4. 7*1012/l 7*109/l 120 1*109/l 30% 2% 9%

Biochemical analysis Glucose 3. 8 mmol/l Bilirubin 4. 0 mmol/l Kreatinin 32 mkmol/l Vit B 12 150 pg/ml Ca 1. 5 mmol/l Phosphorus 1. 5 mmol/l

The urine analysis Color – pale yellow Urine transparency- transparent Relative density-1015 Ph 5. 0 Leucocytes- 2 in sight Proteins – absent Glucose- absent

Questions for you. . 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. What acute purulent diseases do you know? Describe general clinical picture at acute purulent diseases? What etiology of this diseases? What differences between furuncul and carbuncul? What is phlegmon? What is gidradenit, lymphadenit, differentiation? What is erysipelas? Call and describe all complications of acute purulent diseases Conservative treatment of acute purulent diseases Surgical treatment of acute purulent diseases

Fundamentals of purulent-septic surgery. Suppurative disease of the skin and cellular spaces. Practical skills. ü ü ü The student should be able to determine the stage of development of boils and carbuncles. To be able to differentiate between diseases such as carbuncle, furunculosis. To be able to clinical and laboratory criteria the diagnosis, to distinguish phlegmon and abscess. To be able to make a diagnostic algorithm for suppurative diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Make a plan of treatment, to determine the method of anesthesia and the nature of the surgical treatment of patients with purulent diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The student should be able to interpret the patient's blood with a purulent pathology of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.

Final tests (individually) Time: 10 min.
Feed back Thank you for attention!!!
2007.pptx